|
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami
Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (Inuktitut syllabics: , meaning "Inuit are united in Canada"), previously known as the Inuit Tapirisat of Canada (Eskimo Brotherhood of Canada), is a nonprofit organization in Canada that represents over 65,000 Inuit across Inuit Nunangat and the rest of Canada. Their mission is to "serve as a national voice protecting and advancing the rights and interests of Inuit in Canada." Founded in 1971 by Inuit leaders, the organization has gone on to accomplish various Inuit priorities such as assisting in the negotiation of land claims, representing the voice of Inuit and Inuit culture, their culture by using television, taking legal action against those who have violated their rights, and creating a programme to improve education for Inuit children. The ITK has sought to attain its goals either in cooperation with various levels of government or in opposition. Altogether, the ITK looks to advocate on the behalf of Inuit in Canada. The contributions of the ITK le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit Nunangat
Inuit Nunangat (; ), formerly Inuit Nunaat (), is the homeland of the Inuit in Canada. This Arctic homeland consists of four Northern Canada, northern Canadian regions called the Inuvialuit Settlement Region (, home of the Inuvialuit and the northern portion of the Northwest Territories and Yukon), the territory Nunavut (), Nunavik () in northern Quebec, and Nunatsiavut of Newfoundland and Labrador. Etymology Inuit of Canada originally used the Greenlandic Inuit term ''Nunaat'' which excludes the waters and ice. In 2009 the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami formally switched to the Inuktitut ''Nunangat'' in 2009 to reflect the integral nature "land, water, and ice" have to Inuit culture. History Inuit settlement Inuit are the most recent Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous arrivals on the continent aside from Métis. Inuit ancestors known as the Thule people, Thule settled the Arctic, replacing the previous dominant Dorset culture (Tuniit) over the course of around 200 yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1969 White Paper
The 1969 White Paper (officially entitled Statement of the Government of Canada on Indian Policy) was a policy paper proposal set forth by the Government of Canada related to First Nations. Prime Minister Pierre Trudeau and his Minister of Indian Affairs, Jean Chrétien, issued the paper in 1969. The White Paper proposed to abolish all legal documents that had previously existed, including (but not limited to) the ''Indian Act'', and all existing treaties within Canada, comprising Canadian Aboriginal law. It proposed to assimilate First Nations as an ethnic group equal to other Canadian citizens. The White Paper was met with widespread criticism and activism, causing the proposal to be officially withdrawn in 1970. The White Paper proposed legislation to eliminate Indian status. Indigenous people would be granted full rights as citizens instead of being regarded as wards of the state. First Nations Peoples would be incorporated fully into provincial government responsibilities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s westernmost territory and the smallest territory by land area. As of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 census, Yukon is the middle territory in terms of population, but the most densely populated. Yukon has an estimated population of 47,126 as of 2025. Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement. Yukon was History of the Northwest Territories, split from the Northwest Territories by a federal statute in 1898 as the Yukon Territory. The current governing legislation is a new statute passed by the federal Parliament in 2002, the ''Yukon Act''. That act established Yukon as the territory's official name, although Yukon Territory remains in popular usage. Canada Post uses the territory's internationally approved postal abbrevia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
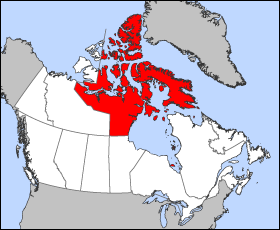
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of the first quarter of 2025 is 45,074. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and the only city in the territory; its population was 20,340 as of the 2021 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. At first, it was named the North-West Territories. The name was changed to the present Northwest Territories in 1906. Since 1870, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bay Project
The James Bay Project () involves the construction of a series of hydroelectricity, hydroelectric power stations on the La Grande River in northwestern Quebec, Canada by government-owned corporation, state-owned public utility, utility Hydro-Québec, and the diversion of neighbouring rivers into the La Grande Drainage basin, watershed. It is located between James Bay to the west and Labrador to the east, and its waters flow from the Laurentian Plateau of the Canadian Shield. The project is one of the largest hydroelectric systems in the world. It has cost upwards of US$20 billion to build and has an installed generating capacity of 15.244 Gigawatt, GW, at the cost of 7,000 square miles of Cree hunting lands. It has been built since 1974 by James Bay Energy () for Hydro-Québec. Construction costs of the project's first phase in ≈ 1971 amounted to $13.7 billion (1987 Canadian dollars). The eight power stations of the La Grande Complex generate an average of 9.5 GW, enough to meet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackenzie Valley Pipeline
The Mackenzie Valley Pipeline, also called the Mackenzie River Pipeline, was a proposed project to transport natural gas from the Beaufort Sea through Canada's Northwest Territories to tie into gas pipelines in northern Alberta. The project was first proposed in the early 1970s but was scrapped following an inquiry conducted by Justice Thomas Berger. The project was resurrected in 2004 with a new proposal to transport gas through the sensitive arctic tundra. Probabilistic estimates of hydrocarbons in the Mackenzie Delta and Beaufort Sea regions project that there are natural gas reserves of . After many delays, the project was officially abandoned in 2017 by the main investment partners citing natural gas prices and the long regulatory process. History The prospect of a pipeline bringing the natural gas to North American energy markets was originally analyzed in the 1970s with the Mackenzie Valley Pipeline Inquiry. During that inquiry, Justice Berger heard testimony from d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagak Curley
Tagak Curley (born 1944) is an Inuk leader, politician and businessman from Nunavut. As a prominent figure in the negotiations that led to the creation of Nunavut, Tagak is considered a living Father of Confederation in Canada. He was born in a hunting camp at Coral Harbour, Northwest Territories (now Nunavut). Career From 1966 to 1970, Curley worked as a development officer with the federal Department of Indian Affairs and Northern Development. Based on his experiences, Curley became politically active and took on leadership roles at the local level to promote better living conditions for Inuit in local communities across Nunavut. From 1970-71, Curley served as the Repulse Bay settlement manager. He also acted as editor of the Keewatin Echo, the first English-Inuktitut newspaper in Canada. He was a founding member and the first president of the Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (Inuit Tapirisat of Canada) in 1971. ITK was formed to represent Nunavut Inuit by their own organization. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whale Cove, Nunavut
Whale Cove (ᑎᑭᕋᕐᔪᐊᖅ in Inuktitut syllabics) (''Tikirarjuaq'', meaning "long point"), is a hamlet located south southwest of Rankin Inlet, northeast of Arviat, in the Kivalliq Region, Nunavut, Canada, on the western shore of Hudson Bay. The community is named for the many beluga whales which congregate off the coast. Many of the inhabitants hunt these whales every fall and use their by-products for their oil and food. Whale Cove, initially settled by three distinct Inuit groups (one inland and two coastal), is a relatively traditional community: 95% Inuit, who wear fur, hunt, fish, eat raw meat and fish. Several bowhead whales may appear in the area as well. Whale Cove is on the polar bear migration route. Local Inuit regularly travel by snowmobile in the winter or by boat in summer months between the hamlet of Rankin Inlet and Whale Cove, a distance of . The terrain is Arctic tundra, this consists mostly of rocks, mosses and lichens. History Inuit in the Whal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Land Rights
Indigenous land rights are the rights of Indigenous peoples to land and natural resources therein, either individually or collectively, mostly in colonised countries. Land and resource-related rights are of fundamental importance to Indigenous peoples for a range of reasons, including: the religious significance of the land, self-determination, identity, and economic factors. Land is a major economic asset, and in some Indigenous societies, using natural resources of earth and sea form (or could form) the basis of their household economy, so the demand for ownership derives from the need to ensure their access to these resources. Land can also be an important instrument of inheritance or a symbol of social status. In many Indigenous societies, such as among the many Aboriginal Australian peoples, the land is an essential part of their spirituality and belief systems. Indigenous land claims have been addressed with varying degrees of success on the national and inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Trudeau
Joseph Philippe Pierre Yves Elliott Trudeau (October 18, 1919 – September 28, 2000) was a Canadian politician, statesman, and lawyer who served as the 15th prime minister of Canada from 1968 to 1979 and from 1980 to 1984. Between his non-consecutive terms as prime minister, he served as the Leader of the Opposition (Canada), leader of the Opposition from 1979 to 1980. Trudeau was born and raised in Outremont, Quebec, and studied politics and law. In the 1950s, he rose to prominence as a labour activist in Quebec politics by opposing the conservative Union Nationale (Quebec), Union Nationale government. Trudeau was then an associate professor of law at the Université de Montréal. He was originally part of the social democratic New Democratic Party (NDP), but then joined the Liberal Party of Canada, Liberal Party in 1965, believing that the NDP could not achieve power. 1965 Canadian federal election, That year, he was elected to the House of Commons of Canada, House of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway (Nordland, Troms, Finnmark, Svalbard and Jan Mayen), northernmost Sweden (Västerbotten, Norrbotten and Lapland (Sweden), Lappland), northern Finland (North Ostrobothnia, Kainuu and Lapland (Finland), Lappi), Russia (Murmansk Oblast, Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), the United States (Alaska), Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), and northern Iceland (Grímsey and Kolbeinsey), along with the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas. Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying cryosphere, snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost under the tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kugluktuk
Kugluktuk (, ; Inuktitut syllabics: ; ), known as Coppermine until 1 January 1996, is a hamlet at the mouth of the Coppermine River in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada, on Coronation Gulf, southwest of Victoria Island. It is Nunavut's westernmost community, near the border with the Northwest Territories. The area's traditional language is Inuinnaqtun, which is written in the Latin alphabet, rather than the syllabics of the Inuktitut writing system. Like Cambridge Bay, Bathurst Inlet, and Umingmaktok, syllabics are rarely seen and are used mainly by the Government of Nunavut. History Prior to European contact, Dene travelled to the area and interacted acrimoniously with nearby Thule and Inuit, sometimes ending in deadly raids against each other (see Bloody Falls massacre). In July 1821, the British Coppermine expedition team reached the mouth of the Coppermine River, just next to the present day community of Kugluktuk. Arctic explorers Peter Warren Dease and Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |