Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cholangiocarcinoma, also known as bile duct cancer, is a type of cancer that forms in the bile ducts. Symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma may include abdominal pain, yellowish skin, weight loss, generalized itching, and fever. Light colored stool or dark urine may also occur. Other
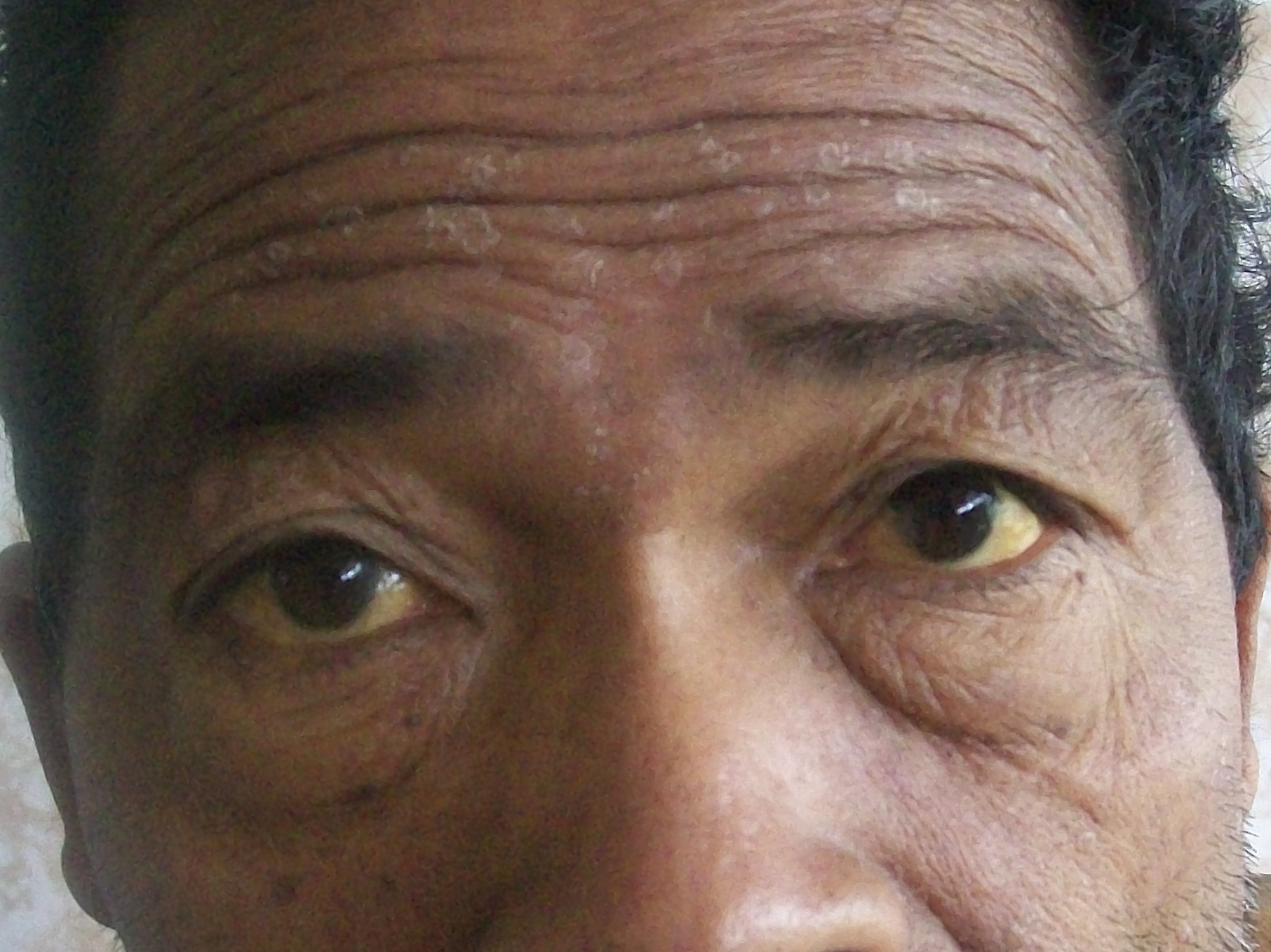 The most common physical indications of cholangiocarcinoma are abnormal
The most common physical indications of cholangiocarcinoma are abnormal
 Although most people present without any known risk factors evident, a number of risk factors for the development of cholangiocarcinoma have been described. In the Western world, the most common of these is
Although most people present without any known risk factors evident, a number of risk factors for the development of cholangiocarcinoma have been described. In the Western world, the most common of these is
 Cholangiocarcinoma can affect any area of the bile ducts, either within or outside the liver. Tumors occurring in the bile ducts within the liver are referred to as ''intrahepatic'', those occurring in the ducts outside the liver are ''extrahepatic'', and tumors occurring at the site where the bile ducts exit the liver may be referred to as ''perihilar''. A cholangiocarcinoma occurring at the junction where the left and right hepatic ducts meet to form the common hepatic duct may be referred to eponymously as a
Cholangiocarcinoma can affect any area of the bile ducts, either within or outside the liver. Tumors occurring in the bile ducts within the liver are referred to as ''intrahepatic'', those occurring in the ducts outside the liver are ''extrahepatic'', and tumors occurring at the site where the bile ducts exit the liver may be referred to as ''perihilar''. A cholangiocarcinoma occurring at the junction where the left and right hepatic ducts meet to form the common hepatic duct may be referred to eponymously as a

 Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree is often used as the initial imaging modality in people with suspected obstructive jaundice. Ultrasound can identify obstruction and ductal dilatation and, in some cases, may be sufficient to diagnose cholangiocarcinoma.
Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree is often used as the initial imaging modality in people with suspected obstructive jaundice. Ultrasound can identify obstruction and ductal dilatation and, in some cases, may be sufficient to diagnose cholangiocarcinoma.
 While abdominal imaging can be useful in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, direct imaging of the bile ducts is often necessary. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an endoscopic procedure performed by a gastroenterologist or specially trained surgeon, has been widely used for this purpose. Although ERCP is an invasive procedure with attendant risks, its advantages include the ability to obtain
While abdominal imaging can be useful in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, direct imaging of the bile ducts is often necessary. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an endoscopic procedure performed by a gastroenterologist or specially trained surgeon, has been widely used for this purpose. Although ERCP is an invasive procedure with attendant risks, its advantages include the ability to obtain
 Surgical exploration may be necessary to obtain a suitable biopsy and to accurately stage a person with cholangiocarcinoma. Laparoscopy can be used for staging purposes and may avoid the need for a more invasive surgical procedure, such as laparotomy, in some people.
Surgical exploration may be necessary to obtain a suitable biopsy and to accurately stage a person with cholangiocarcinoma. Laparoscopy can be used for staging purposes and may avoid the need for a more invasive surgical procedure, such as laparotomy, in some people.

American Cancer Society Detailed Guide to Bile Duct Cancer
Patient information on extrahepatic bile duct tumors
from the National Cancer Institute.
Cancer.Net: Bile Duct Cancer
Cholangiocarcinoma Foundation
World Cholangiocarcinoma Day
{{Epithelial neoplasms Digestive system neoplasia Infectious causes of cancer Rare cancers Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
biliary tract
The biliary tract, (biliary tree or biliary system) refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and co ...
cancers include gallbladder cancer and cancer of the ampulla of Vater
The ampulla of Vater, also known as the or the hepatopancreatic duct, is formed by the union of the pancreatic duct and the common bile duct. The ampulla is specifically located at the major duodenal papilla.
The ampulla of Vater is an import ...
.
Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma include primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ha ...
(an inflammatory disease of the bile ducts), ulcerative colitis, cirrhosis, hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
, hepatitis B, infection with certain liver flukes, and some congenital liver malformations. However, most people have no identifiable risk factors. The diagnosis is suspected based on a combination of blood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s, medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
, endoscopy, and sometimes surgical exploration. The disease is confirmed by examination of cells from the tumor under a microscope. It is typically an adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
(a cancer that forms glands or secretes mucin).
Cholangiocarcinoma is typically incurable at diagnosis which is why early detection is ideal. In these cases palliative treatments may include surgical resection
Segmental resection (or segmentectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove part of an organ or gland, as a sub-type of a resection, which might involve removing the whole body part. It may also be used to remove a tumor and normal tissue around i ...
, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stenting
In medicine, a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open, and stenting is the placement of a stent. A wide variety of stents are used for different purposes, from expandab ...
procedures. In about a third of cases involving the common bile duct and less commonly with other locations the tumor can be completely removed by surgery offering a chance of a cure. Even when surgical removal is successful chemotherapy and radiation therapy are generally recommended. In certain cases surgery may include a liver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
. Even when surgery is successful the 5-year survival
The five-year survival rate is a type of survival rate for estimating the prognosis of a particular disease, normally calculated from the point of diagnosis. Lead time bias from earlier diagnosis can affect interpretation of the five-year surviv ...
is typically less than 50%.
Cholangiocarcinoma is rare in the Western world, with estimates of it occurring in 0.5–2 people per 100,000 per year. Rates are higher in Southeast Asia where liver flukes are common. Rates in parts of Thailand are 60 per 100,000 per year. It typically occurs in people in their 70s; however, in those with primary sclerosing cholangitis it often occurs in the 40s. Rates of cholangiocarcinoma within the liver in the Western world have increased.
Signs and symptoms
liver function tests
Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin ti ...
, jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
(yellowing of the eyes and skin occurring when bile ducts are blocked by tumor), abdominal pain (30–50%), generalized itching (66%), weight loss (30–50%), fever (up to 20%), and changes in the color of stool or urine. To some extent, the symptoms depend upon the location of the tumor: people with cholangiocarcinoma in the extrahepatic bile ducts (outside the liver) are more likely to have jaundice, while those with tumors of the bile ducts within the liver more often have pain without jaundice.
Blood tests of liver function in people with cholangiocarcinoma often reveal a so-called "obstructive picture", with elevated bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (Latin for "red bile") is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normal catabolic pathway that breaks down heme in vertebrates. This catabolism is a necessary process in the body's clearance of waste products that arise from the ...
, alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1, alkaline phosphomonoesterase; phosphomonoesterase; glycerophosphatase; alkaline phosphohydrolase; alkaline phenyl phosphatase; orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum), systematic ...
, and gamma glutamyl transferase levels, and relatively normal transaminase levels. Such laboratory findings suggest obstruction of the bile ducts, rather than inflammation or infection of the liver parenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word π ...
, as the primary cause of the jaundice.
Risk factors
 Although most people present without any known risk factors evident, a number of risk factors for the development of cholangiocarcinoma have been described. In the Western world, the most common of these is
Although most people present without any known risk factors evident, a number of risk factors for the development of cholangiocarcinoma have been described. In the Western world, the most common of these is primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ha ...
(PSC), an inflammatory disease of the bile ducts which is closely associated with ulcerative colitis (UC). Epidemiologic studies have suggested that the lifetime risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma for a person with PSC is on the order of 10–15%, although autopsy series have found rates as high as 30% in this population. For inflammatory bowel disease patients with altered DNA repair functions, the progression from PSC to cholangiocarcinoma may be a consequence of DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. In human cells, both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA da ...
resulting from biliary inflammation and bile acids.
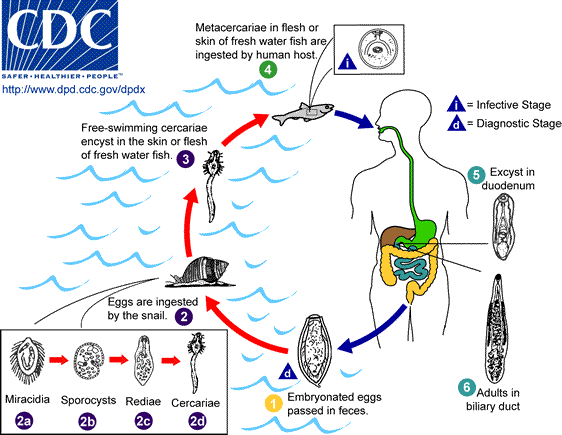
Certain parasitic liver diseases may be risk factors as well. Colonization with the liver flukes ''Opisthorchis viverrini
''Opisthorchis viverrini'', common name Southeast Asian liver fluke, is a food-borne trematode parasite from the family Opisthorchiidae that infects the bile duct. People are infected after eating raw or undercooked fish. Infection with the par ...
'' (found in Thailand, Laos PDR, and Vietnam) or ''Clonorchis sinensis
''Clonorchis sinensis'', the Chinese liver fluke, is a liver fluke belonging to the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects fish-eating mammals, including humans. In humans, it infects the common bile duct and gall bladder, feeding on ...
'' (found in China, Taiwan, eastern Russia, Korea, and Vietnam) has been associated with the development of cholangiocarcinoma. Control programs (Integrated Opisthorchiasis Control Program The Integrated Opisthorchiasis Control Program, commonly known as the "Lawa Project", located in Khon Kaen Province, Thailand, is an effort to reduce chronic infection by the Southeast Asian liver fluke (''Opisthorchis viverrini'') among the nativ ...
) aimed at discouraging the consumption of raw and undercooked food have been successful at reducing the incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in some countries. People with chronic liver disease, whether in the form of viral hepatitis (e.g. hepatitis B or hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection people often have mild or no symptoms. Occasionally a fever, dark urine, a ...
), alcoholic liver disease, or cirrhosis of the liver due to other causes, are at significantly increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma. HIV infection was also identified in one study as a potential risk factor for cholangiocarcinoma, although it was unclear whether HIV itself or other correlated and confounding factors (e.g. hepatitis C infection) were responsible for the association.
Infection with the bacteria ''Helicobacter bilis
''Helicobacter bilis'' is a bacterium in the Helicobacteraceae family, Campylobacterales order. It is a fusiform bacterium with three to 14 multiple bipolar sheathed flagella and periplasmic fibers wrapped around the cell. It is resistant to ...
'' and ''Helicobacter hepaticus
''Helicobacter hepaticus'' is a bacterium in the Helicobacteraceae family, Campylobacterales order.
It has a spiral shape and bipolar, single, sheathed flagellum, and was first isolated from the livers of mice with active, chronic hepatitis. The ...
'' species can cause biliary cancer.
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
liver abnormalities, such as Caroli disease (a specific type of five recognized choledochal cysts
Choledochal cysts (a.k.a. bile duct cyst) are congenital conditions involving cystic dilatation of bile ducts. They are uncommon in western countries but not as rare in East Asian nations like Japan and China.
Signs and symptoms
Most patients ha ...
), have been associated with an approximately 15% lifetime risk of developing cholangiocarcinoma. The rare inherited disorders Lynch syndrome II and biliary papillomatosis have also been found to be associated with cholangiocarcinoma. The presence of gallstones ( cholelithiasis) is not clearly associated with cholangiocarcinoma. However, intrahepatic stones (called hepatolithiasis
Hepatolithiasis is the presence of gallstones in the biliary ducts of the liver. Treatment is usually surgical. It is rare in Western countries, but prevalent in East Asia.*
The gallstones are normally found proximal to the left and right hepatic ...
), which are rare in the West but common in parts of Asia, have been strongly associated with cholangiocarcinoma. Exposure to Thorotrast, a form of thorium dioxide which was used as a radiologic contrast medium, has been linked to the development of cholangiocarcinoma as late as 30–40 years after exposure; Thorotrast was banned in the United States in the 1950s due to its carcinogenicity.
Pathophysiology
Klatskin tumor
A Klatskin tumor (or hilar cholangiocarcinoma) is a cholangiocarcinoma (cancer of the biliary tree) occurring at the confluence of the right and left hepatic bile ducts. The disease was named after Gerald Klatskin, who in 1965 described 15 cases ...
.
Although cholangiocarcinoma is known to have the histological and molecular features of an adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
of epithelial cells lining the biliary tract, the actual cell of origin is unknown. Recent evidence has suggested that the initial transformed cell that generates the primary tumor may arise from a pluripotent hepatic stem cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
. Cholangiocarcinoma is thought to develop through a series of stages – from early hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferati ...
and metaplasia, through dysplasia, to the development of frank carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesodermal ...
– in a process similar to that seen in the development of colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel mo ...
. Chronic inflammation
Chronic systemic inflammation (SI) is the result of release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from immune-related cells and the chronic activation of the innate immune system. It can contribute to the development or progression of certain conditions s ...
and obstruction of the bile ducts, and the resulting impaired bile flow, are thought to play a role in this progression.
Histologically, cholangiocarcinomas may vary from undifferentiated to well-differentiated. They are often surrounded by a brisk fibrotic or desmoplastic tissue response; in the presence of extensive fibrosis, it can be difficult to distinguish well-differentiated cholangiocarcinoma from normal reactive epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellul ...
. There is no entirely specific immunohistochemical stain that can distinguish malignant from benign biliary ductal tissue, although staining for cytokeratins, carcinoembryonic antigen
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is ...
, and mucins may aid in diagnosis. Most tumors (>90%) are adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
s.
Diagnosis

Blood tests
There are no specificblood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose test or a cholester ...
s that can diagnose cholangiocarcinoma by themselves. Serum levels of carcinoembryonic antigen
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is ...
(CEA) and CA19-9
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9), also known as sialyl-LewisA, is a tetrasaccharide which is usually attached to O- glycans on the surface of cells. It is known to play a role in cell-to-cell recognition processes. It is also a tumor marker used ...
are often elevated, but are not sensitive or specific enough to be used as a general screening
Screening may refer to:
* Screening cultures, a type a medical test that is done to find an infection
* Screening (economics), a strategy of combating adverse selection (includes sorting resumes to select employees)
* Screening (environmental), a ...
tool. However, they may be useful in conjunction with imaging methods in supporting a suspected diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma.
Abdominal imaging
 Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree is often used as the initial imaging modality in people with suspected obstructive jaundice. Ultrasound can identify obstruction and ductal dilatation and, in some cases, may be sufficient to diagnose cholangiocarcinoma.
Ultrasound of the liver and biliary tree is often used as the initial imaging modality in people with suspected obstructive jaundice. Ultrasound can identify obstruction and ductal dilatation and, in some cases, may be sufficient to diagnose cholangiocarcinoma. Computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
(CT) scanning may also play an important role in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma.
Imaging of the biliary tree
 While abdominal imaging can be useful in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, direct imaging of the bile ducts is often necessary. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an endoscopic procedure performed by a gastroenterologist or specially trained surgeon, has been widely used for this purpose. Although ERCP is an invasive procedure with attendant risks, its advantages include the ability to obtain
While abdominal imaging can be useful in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma, direct imaging of the bile ducts is often necessary. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), an endoscopic procedure performed by a gastroenterologist or specially trained surgeon, has been widely used for this purpose. Although ERCP is an invasive procedure with attendant risks, its advantages include the ability to obtain biopsies
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
and to place stents or perform other interventions to relieve biliary obstruction. Endoscopic ultrasound can also be performed at the time of ERCP and may increase the accuracy of the biopsy and yield information on lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
invasion and operability. As an alternative to ERCP, percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) may be utilized. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is a non-invasive alternative to ERCP. Some authors have suggested that MRCP should supplant ERCP in the diagnosis of biliary cancers, as it may more accurately define the tumor and avoids the risks of ERCP.
Surgery
 Surgical exploration may be necessary to obtain a suitable biopsy and to accurately stage a person with cholangiocarcinoma. Laparoscopy can be used for staging purposes and may avoid the need for a more invasive surgical procedure, such as laparotomy, in some people.
Surgical exploration may be necessary to obtain a suitable biopsy and to accurately stage a person with cholangiocarcinoma. Laparoscopy can be used for staging purposes and may avoid the need for a more invasive surgical procedure, such as laparotomy, in some people.
Pathology
Histologically, cholangiocarcinomas are classically well to moderately differentiatedadenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
s. Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to an ...
is useful in the diagnosis and may be used to help differentiate a cholangiocarcinoma from hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide.
It occurs in t ...
and metastasis of other gastrointestinal tumors. Cytological scrapings are often nondiagnostic, as these tumors typically have a desmoplastic stroma and, therefore, do not release diagnostic tumor cells with scrapings.
Staging
Although there are at least three staging systems for cholangiocarcinoma (e.g. those of Bismuth, Blumgart, and the American Joint Committee on Cancer), none have been shown to be useful in predicting survival. The most important staging issue is whether the tumor can be surgically removed, or whether it is too advanced for surgical treatment to be successful. Often, this determination can only be made at the time of surgery. General guidelines for operability include: * Absence oflymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
or liver metastases
* Absence of involvement of the portal vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approxima ...
* Absence of direct invasion of adjacent organs
* Absence of widespread metastatic disease
Treatment
Cholangiocarcinoma is considered to be an incurable and rapidly lethal disease unless all the tumors can be fully resected (cut out surgically). Since the operability of the tumor can only be assessed during surgery in most cases, a majority of people undergo exploratory surgery unless there is already a clear indication that the tumor is inoperable. However, the Mayo Clinic has reported significant success treating early bile duct cancer with liver transplantation using a protocolized approach and strict selection criteria. Adjuvant therapy followed byliver transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, al ...
may have a role in treatment of certain unresectable cases. Locoregional therapies including transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), transarterial radioembolization (TARE) and ablation therapies have a role in intrahepatic variants of cholangiocarcinoma to provide palliation or potential cure in people who are not surgical candidates.
Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation therapy
If the tumor can be removed surgically, people may receiveadjuvant In pharmacology, an adjuvant is a drug or other substance, or a combination of substances, that is used to increase the efficacy or potency of certain drugs. Specifically, the term can refer to:
* Adjuvant therapy in cancer management
* Analgesic ...
chemotherapy or radiation therapy after the operation to improve the chances of cure. If the tissue margins are negative (i.e. the tumor has been totally excised), adjuvant therapy is of uncertain benefit. Both positive and negative results have been reported with adjuvant radiation therapy in this setting, and no prospective randomized controlled trials have been conducted as of March 2007. Adjuvant chemotherapy appears to be ineffective in people with completely resected tumors. The role of combined chemoradiotherapy in this setting is unclear. However, if the tumor tissue margins are positive, indicating that the tumor was not completely removed via surgery, then adjuvant therapy with radiation and possibly chemotherapy is generally recommended based on the available data.
Treatment of advanced disease
The majority of cases of cholangiocarcinoma present as inoperable (unresectable) disease in which case people are generally treated withpalliative
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
chemotherapy, with or without radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radia ...
. Chemotherapy has been shown in a randomized controlled trial to improve quality of life and extend survival in people with inoperable cholangiocarcinoma. There is no single chemotherapy regimen which is universally used, and enrollment in clinical trials is often recommended when possible. Chemotherapy agents used to treat cholangiocarcinoma include 5-fluorouracil
Fluorouracil (5-FU), sold under the brand name Adrucil among others, is a cytotoxic chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. By intravenous injection it is used for treatment of colorectal cancer, oesophageal cancer, stomach cancer, pancrea ...
with leucovorin, gemcitabine as a single agent, or gemcitabine plus cisplatin, irinotecan, or capecitabine. A small pilot study suggested possible benefit from the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib in people with advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Radiation therapy appears to prolong survival in people with resected extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma, and the few reports of its use in unresectable cholangiocarcinoma appear to show improved survival, but numbers are small.
Infigratinib
Infigratinib, sold under the brand name Truseltiq, is an anti-cancer medication used to treat cholangiocarcinoma (bile duct cancer).
The most common side effects include increased phosphate level in the blood, increased creatinine levels in t ...
(Truseltiq) is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells of ...
(FGFR) that was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2021. It is indicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis ...
for the treatment of people with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma harboring an FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement.
Pemigatinib (Pemazyre) is a kinase inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) also known as CD332 (cluster of differentiation 332) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGFR2'' gene residing on chromosome 10. FGFR2 is a receptor for fibroblast growth factor.
The protein ...
(FGFR2) that was approved for medical use in the United States in April 2020. It is indicated for the treatment of adults with previously treated, unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with a fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusion or other rearrangement as detected by an FDA-approved test.
Ivodesinib (Tibsovo) is a small molecule inhibitor of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1. The FDA approved ivosidenib in August 2021 for adults with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma with an isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) mutation as detected by an FDA-approved test.
Durvalumab
Durvalumab (trade name Imfinzi) is an FDA-approved immunotherapy for cancer, developed by Medimmune/AstraZeneca. It is a human immunoglobulin G1 kappa (IgG1κ) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interaction of programmed cell death ligand 1 ...
, (Imfinzi) is an immune checkpoint inhibitor that blocks the PD-L1 protein on the surface of immune cells, thereby allowing the immune system to recognize and attack tumor cells. In Phase III clinical trials, durvalumab, in combination with standard-of-care chemotherapy, demonstrated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival and progression-free survival versus chemotherapy alone as a 1st-line treatment for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer.
Futibatinib (Lytgobi) was approved for medical use in the United States in September 2022.
Prognosis
Surgical resection offers the only potential chance of cure in cholangiocarcinoma. For non-resectable cases, the five-year survival rate is 0% where the disease is inoperable because distal lymph nodes show metastases, and less than 5% in general. Overall mean duration of survival is less than 6 months in people with metastatic disease. For surgical cases, the odds of cure vary depending on the tumor location and whether the tumor can be completely, or only partially, removed. Distal cholangiocarcinomas (those arising from the common bile duct) are generally treated surgically with aWhipple procedure
A pancreaticoduodenectomy, also known as a Whipple procedure, is a major surgical operation most often performed to remove cancerous tumours from the head of the pancreas. It is also used for the treatment of pancreatic or duodenal trauma, or chro ...
; long-term survival rates range from 15 to 25%, although one series reported a five-year survival of 54% for people with no involvement of the lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s. Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinomas (those arising from the bile ducts within the liver) are usually treated with partial hepatectomy. Various series have reported survival estimates after surgery ranging from 22 to 66%; the outcome may depend on involvement of lymph nodes and completeness of the surgery. Perihilar cholangiocarcinomas (those occurring near where the bile ducts exit the liver) are least likely to be operable. When surgery is possible, they are generally treated with an aggressive approach often including removal of the gallbladder and potentially part of the liver. In patients with operable perihilar tumors, reported 5-year survival rates range from 20 to 50%.
The prognosis
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing") is a medical term for predicting the likely or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stabl ...
may be worse for people with primary sclerosing cholangitis who develop cholangiocarcinoma, likely because the cancer is not detected until it is advanced. Some evidence suggests that outcomes may be improving with more aggressive surgical approaches and adjuvant therapy
Adjuvant therapy, also known as adjunct therapy, adjuvant care, or augmentation therapy, is a therapy that is given in addition to the primary or initial therapy to maximize its effectiveness. The surgeries and complex treatment regimens used in ...
.
Epidemiology
Cholangiocarcinoma is a relatively rare form of cancer; each year, approximately 2,000 to 3,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States, translating into an annual incidence of 1–2 cases per 100,000 people.Autopsy
An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any di ...
series have reported a prevalence of 0.01% to 0.46%. There is a higher prevalence of cholangiocarcinoma in Asia, which has been attributed to endemic chronic parasitic infestation. The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma increases with age, and the disease is slightly more common in men than in women (possibly due to the higher rate of primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ha ...
, a major risk factor, in men). The prevalence of cholangiocarcinoma in people with primary sclerosing cholangitis may be as high as 30%, based on autopsy studies.
Multiple studies have documented a steady increase in the incidence of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; increases have been seen in North America, Europe, Asia, and Australia.Multiple independent studies have documented a steady increase in the worldwide incidence of cholangiocarcinoma. Some relevant journal articles include:
*
*
*
*
*
* The reasons for the increasing occurrence of cholangiocarcinoma are unclear; improved diagnostic methods may be partially responsible, but the prevalence of potential risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma, such as HIV infection, has also been increasing during this time frame.

References
External links
American Cancer Society Detailed Guide to Bile Duct Cancer
Patient information on extrahepatic bile duct tumors
from the National Cancer Institute.
Cancer.Net: Bile Duct Cancer
Cholangiocarcinoma Foundation
World Cholangiocarcinoma Day
{{Epithelial neoplasms Digestive system neoplasia Infectious causes of cancer Rare cancers Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate