|
Prognosis
Prognosis ( Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing"; : prognoses) is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stable over time; expectations of quality of life, such as the ability to carry out daily activities; the potential for complications and associated health issues; and the likelihood of survival (including life expectancy). A prognosis is made on the basis of the normal course of the diagnosed disease, the individual's physical and mental condition, the available treatments, and additional factors. A complete prognosis includes the expected duration, function, and description of the course of the disease, such as progressive decline, intermittent crisis, or sudden, unpredictable crisis. When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow-growing while others are fast-growing. Unlike Hodgkin lymphoma, which spreads contiguously, NHL is largely a systemic illness. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin lymphoma vary depending upon its location within the body. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tiredness. Other symptoms may include bone pain, chest pain, or itchiness. Some forms are slow growing, while others are fast growing. Enlarged lymph nodes may cause lumps to be felt under the skin when they are close to the surface of the body. Lymphomas in the skin may also result in lumps, which are commonly itchy, red, or purple. Ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manchester Score
Manchester score is an indicator of prognosis in small cell lung cancer. It is calculated from a number of physical and biochemical markers. A patient with small cell lung cancer scores one point for each of the following: - * Serum lactate dehydrogenase exceeds the upper limit of the reference range. * Serum sodium concentration less than 132 mmol/L. * Serum alkaline phosphatase over one-and-a-half times the upper limit of the reference range. * Serum bicarbonate In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ... less than 24. * Karnofsky performance status less than 60. * Extensive stage disease. Prognosis References {{reflist Lung cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocardial Infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when Ischemia, blood flow decreases or stops in one of the coronary arteries of the heart, causing infarction (tissue death) to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is retrosternal Angina, chest pain or discomfort that classically radiates to the left shoulder, arm, or jaw. The pain may occasionally feel like heartburn. This is the dangerous type of acute coronary syndrome. Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, nausea, presyncope, feeling faint, a diaphoresis, cold sweat, Fatigue, feeling tired, and decreased level of consciousness. About 30% of people have atypical symptoms. Women more often present without chest pain and instead have neck pain, arm pain or feel tired. Among those over 75 years old, about 5% have had an MI with little or no history of symptoms. An MI may cause heart failure, an Cardiac arrhythmia, irregular heartbeat, cardiogenic shock or cardiac arrest. Most MIs occur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Prognostic Index
The International Prognostic Index (IPI) is a clinical tool developed by oncologists to aid in predicting the prognosis of patients with aggressive non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Previous to IPI's development, the primary consideration in assessing prognosis was the Ann Arbor stage alone, but this was increasingly found to be an inadequate means of predicting survival outcomes, and so other factors were studied. History In 1984, the first prognostic indicator for advanced non-Hodkin lymphoma was developed. An information theory guided, computer search and evaluation procedure entropy minimax was employed to discover the largest sub-groupings for which survival is as extreme as possible. In the clinical trials analyzed retrospectively and containing a large fraction of patients not matching the 'good' - of 'good' (Karnofsky status >80 and 'A" Symptoms and SGOT <36 U/L), 'poor' (Karnofsky status <70 or Night sweats) and 'intermediate' (All Remaining) prognosis patterns identified, a sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma (MM), also known as plasma cell myeloma and simply myeloma, is a cancer of plasma cells, a type of white blood cell that normally produces antibody, antibodies. Often, no symptoms are noticed initially. As it progresses, bone pain, anemia, Kidney failure, renal insufficiency, and infections may occur. Complications may include hypercalcemia and amyloidosis. The cause of multiple myeloma is unknown. Risk factors include obesity, radiation exposure, family history, age and certain chemicals. There is an increased risk of multiple myeloma in certain occupations. This is due to the occupational exposure to aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having a role in causation of multiple myeloma. Multiple myeloma is the result of a multi-step malignant transformation, and almost universally originates from the pre-malignant stage monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS). As MGUS evolves into MM, another pre-stage of the disease is reached, known as Smouldering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, and the (however misguided) formulation of Humorism, humoral theory. His studies set out the basic ideas of modern-day specialties, including surgery, urology, neurology, acute medicine and Orthopedic surgery, orthopedics. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advance Care Planning
Advance care planning is a process that enables individuals with decisional mental capacity to make plans about their future health care. Advance care plans provide direction to healthcare professionals when a person is not in a position to make and/or communicate their own healthcare choices. Advance care planning is applicable to adults at all stages of life. Participation in advance care planning has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety for patients and their families, and lead to improvements in end of life care. Older adults are more directly concerned as they may experience a situation where advance care planning can be useful. However, only a small portion of elderly use them. The main components of advance care planning include the nomination of a substitute decision maker, and the completion of an advance care directive. Definition Advance care planning was defined by an international white paper as involving individuals ''with'' decisional mental capacity at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survival Rate
Survival rate is a part of survival analysis. It is the proportion of people in a study or treatment group still alive at a given period of time after diagnosis. It is a method of describing prognosis in certain disease conditions, and can be used for the assessment of standards of therapy. The survival period is usually reckoned from date of diagnosis or start of treatment. Survival rates are based on the population as a whole and cannot be applied directly to an individual. There are various types of survival rates (discussed below). They often serve as endpoints of clinical trials and should not be confused with mortality rates, a population metric. Overall survival Patients with a certain disease (for example, colorectal cancer) can die directly from that disease or from an unrelated cause (for example, a car accident). When the precise cause of death is not specified, this is called the overall survival rate or observed survival rate. Doctors often use mean overall survival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progression-free Survival
Progression-free survival (PFS) is "the length of time during and after the treatment of a disease, such as cancer, that a patient lives with the disease but it does not get worse". In oncology, PFS usually refers to situations in which a tumor is present, as demonstrated by laboratory testing, radiologic testing, or clinically. Similarly, "disease-free survival" is the length of time after patients have received treatment and have no detectable disease. Time to progression (TTP) does not count patients who die from other causes but is otherwise a close equivalent to PFS (unless there are many such events). The FDA gives separate definitions and prefers PFS. Background PFS is widely used as a surrogate endpoint in oncology. The definition of "progression" generally involves imaging techniques (plain radiograms, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, ultrasounds) or other aspects: biochemical progression may be defined on the basis of an increase in a tumor marker (such as CA125 for epitheli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
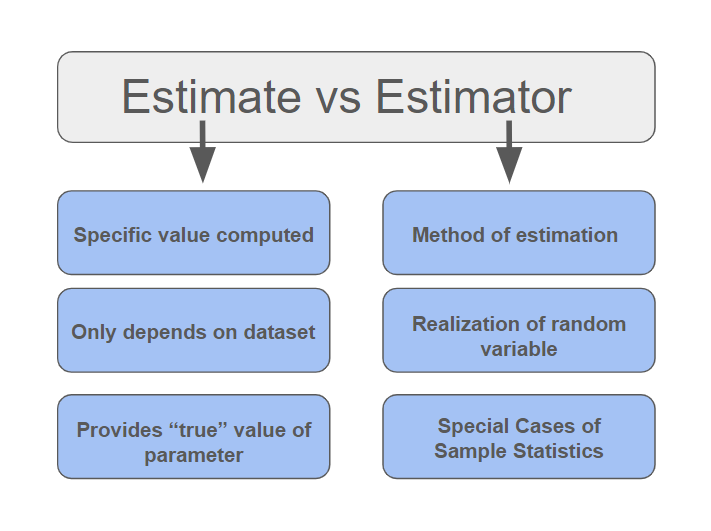
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on Sample (statistics), observed data: thus the rule (the estimator), the quantity of interest (the estimand) and its result (the estimate) are distinguished. For example, the sample mean is a commonly used estimator of the population mean. There are point estimator, point and interval estimators. The point estimators yield single-valued results. This is in contrast to an interval estimator, where the result would be a range of plausible values. "Single value" does not necessarily mean "single number", but includes vector valued or function valued estimators. ''Estimation theory'' is concerned with the properties of estimators; that is, with defining properties that can be used to compare different estimators (different rules for creating estimates) for the same quantity, based on the same data. Such properties can be used to determine the best rules to use under given circumstances. Howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APACHE II
APACHE II ("Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II") is a severity-of-disease classification system, one of several ICU scoring systems. It is applied within 24 hours of admission of a patient to an intensive care unit (ICU): an integer score from 0 to 71 is computed based on several measurements; higher scores correspond to more severe disease and a higher risk of death. The first APACHE model was presented by Knaus et al. in 1981. Application APACHE II was designed to measure the severity of disease for adult patients admitted to intensive care units. It has not been validated for use in children or young people aged under 16. This scoring system is used in many ways which include: # Some procedures or some medicine is only given to patients with a certain APACHE II score # APACHE II score can be used to describe the morbidity of a patient when comparing the outcome with other patients. # Predicted mortalities are averaged for groups of patients in order to spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
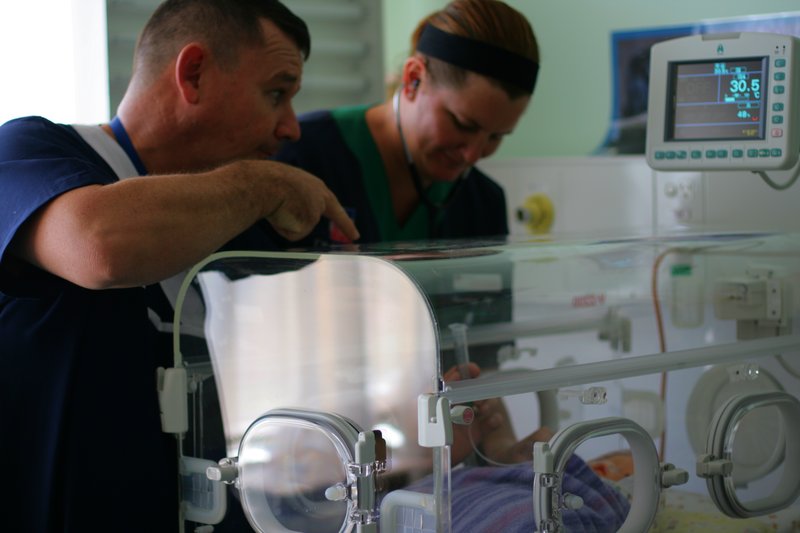
Intensive Care Unit
An intensive care unit (ICU), also known as an intensive therapy unit or intensive treatment unit (ITU) or critical care unit (CCU), is a special department of a hospital or health care facility that provides intensive care medicine. An intensive care unit (ICU) was defined by the task force of the World Federation of Societies of Intensive and Critical Care Medicine as "an organized system for the provision of care to critically ill patients that provides intensive and specialized medical and nursing care, an enhanced capacity for monitoring, and multiple modalities of physiologic organ support to sustain life during a period of life-threatening organ system insufficiency." Patients may be referred directly from an emergency department or from a ward if they rapidly deteriorate, or immediately after surgery if the surgery is very invasive and the patient is at high risk of complications. History In 1854, Florence Nightingale left for the Crimean War, where triage was used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |