injection drug users on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Drug injection is a method of introducing a
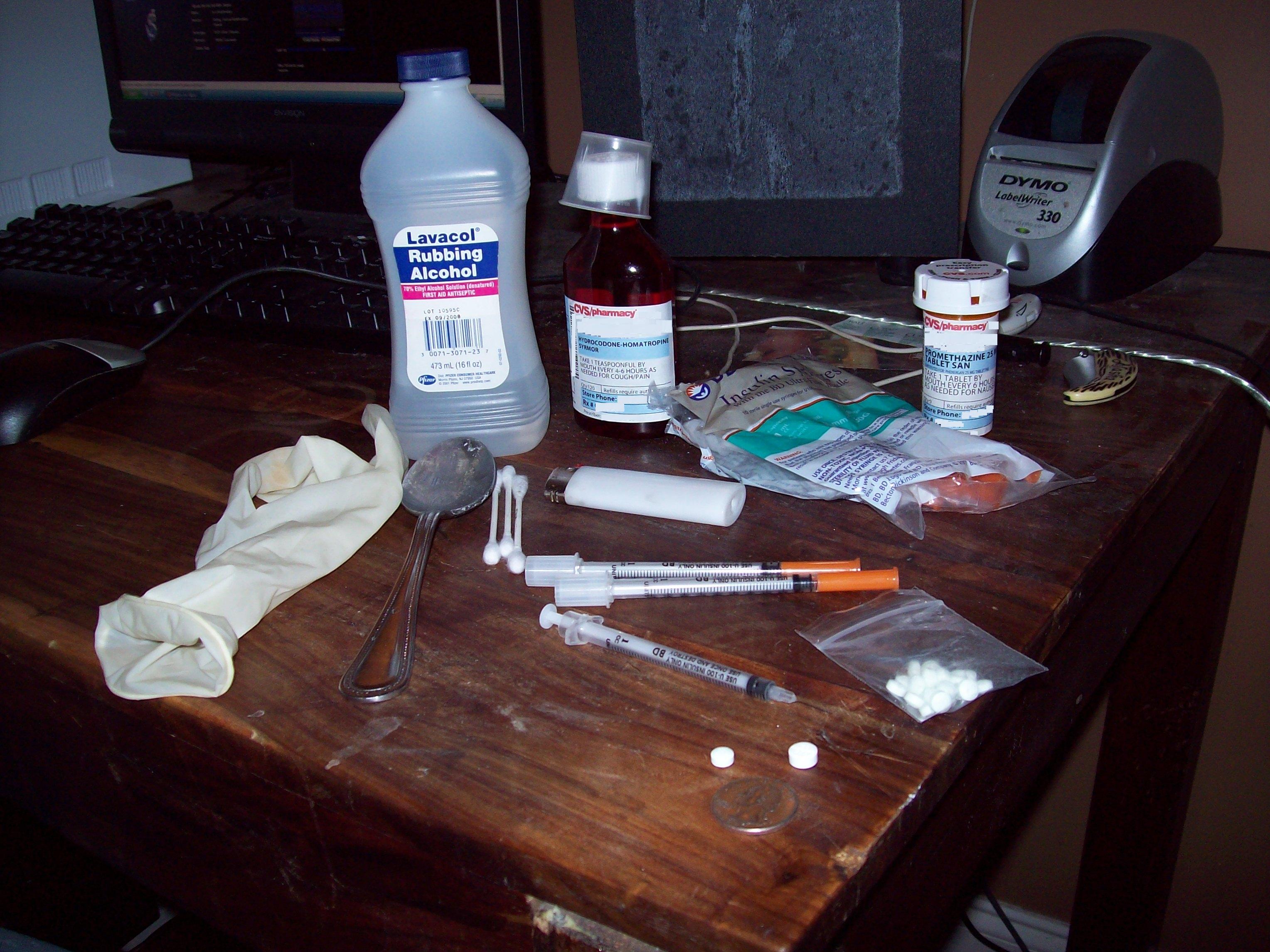 The drug—usually (but not always) in a powder or crystal form—is dissolved in water, normally in a spoon, tin, bottle cap, the bottom of a soda can, or another metal container. Cylindrical metal containers—sometimes called "cookers"—are provided by
The drug—usually (but not always) in a powder or crystal form—is dissolved in water, normally in a spoon, tin, bottle cap, the bottom of a soda can, or another metal container. Cylindrical metal containers—sometimes called "cookers"—are provided by
Safer injection and vein care
Chicago Recovery Alliance's extremely comprehensive and well designed informational series
United Nations Office on Drugs & Crime
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drug Injection Drug culture Drug paraphernalia Substance-related disorders
drug
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via insufflation (medicine), inhalation, drug i ...
into the bloodstream via a hollow hypodermic needle, which is pierced through the skin into the body (usually intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
ly, but also at an intramuscular
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles hav ...
or subcutaneous, location). Intravenous therapy
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
, a form of drug injection, is universally practiced in modernized medical care. , there were 13.2 million people worldwide who self-administered injection drugs outside of medical supervision, of which 22% are from developed countries.
A wide variety of drugs are injected, often opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s: these may include legally prescribed medicines and medication such as morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
, as well as stronger compounds often favored in recreational drug use
Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an Sub ...
, which are often illegal. Although there are various methods of taking drugs, injection is favoured by some people as the full effects of the drug are experienced very quickly, typically in five to ten seconds. It also bypasses first-pass metabolism
The first pass effect (also known as first-pass metabolism or presystemic metabolism) is a phenomenon of drug metabolism at a specific location in the body which leads to a reduction in the concentration of the active drug before it reaches the ...
in the liver, resulting in higher bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
and efficiency for many drugs (such as morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
or diacetylmorphine/heroin; roughly two-thirds of which is destroyed in the liver when consumed orally) than oral ingestion would. The effect is that the person gets a stronger (yet shorter-acting) effect from the same amount of the drug. Drug injection is therefore often related to substance dependence
Substance dependence, also known as drug dependence, is a biopsychological situation whereby an individual's functionality is dependent on the necessitated re-consumption of a psychoactive substance because of an adaptive state that has develop ...
.
In recreational-use drug culture
Drug cultures are examples of countercultures that are primarily defined by Entheogen, spiritual, Self-medication, medical, and recreational drug use. They may be focused on a single drug, or endorse polydrug use. They sometimes eagerly or reluct ...
, preparation may include mixing the powdered drug with water to create an aqueous solution, and then the solution is injected. This act is often colloquially referred to as "slamming", "shooting up", "smashing", "banging", "pinning", or "jacking-up", often depending on the specific drug subculture in which the term is used (e.g. heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
, cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
, or methamphetamine
Methamphetamine (contracted from ) is a potent central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is mainly used as a recreational drug use, recreational or Performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing drug and less commonly as a secon ...
).
Risks
In addition to general problems associated with any IV drug administration (see risks of IV therapy), there are some specific problems associated with the injection of drugs by non-professionals, such as: * Increased chance of overdose * Arterial damage – Arterialpseudoaneurysm
A pseudoaneurysm, also known as a false aneurysm, is a locally contained hematoma outside an artery or the heart due to damage to the vessel wall. The injury passes through all three layers of the arterial wall, causing a leak, which is contai ...
s may form at injection sites, which can rupture, potentially resulting in hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, ...
, distal ischemia
Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism (to keep tissue alive). Ischemia is generally caused by problems ...
, and gangrene
Gangrene is a type of tissue death caused by a lack of blood supply. Symptoms may include a change in skin color to red or black, numbness, swelling, pain, skin breakdown, and coolness. The feet and hands are most commonly affected. If the ga ...
. Inadvertent intra-arterial injection can also result in endarteritis and thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
, with ultimately similar consequences.
Methods
needle exchange program
A needle and syringe programme (NSP), also known as needle exchange program (NEP), is a social service that allows injection drug users (IDUs) to obtain clean and unused hypodermic needles and associated paraphernalia at little or no cost. It i ...
s. Users draw the required amount of water into a syringe and squirt this over the drugs. The solution is then mixed and heated from below if necessary. Heating is used mainly with heroin
Heroin, also known as diacetylmorphine and diamorphine among other names, is a morphinan opioid substance synthesized from the Opium, dried latex of the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy; it is mainly used as a recreational drug for its eupho ...
(though not always, depending on the type of heroin), but is also often used with other drugs, especially crushed tablets. Cocaine HCl (powdered cocaine) dissolves quite easily without heat. Heroin prepared for the European market is insoluble in water and usually requires the addition of an acid such as citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, ...
or ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Asco ...
(Vitamin C) powder to dissolve the drug. Due to the dangers from using lemon juice or vinegar to acidify the solution, packets of citric acid and Vitamin C powder are available at needle exchanges in Europe. In the U.S., vinegar and lemon juice are used to shoot crack cocaine
Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant cocaine that can be Smoking, smoked. Crack offers a short, intense Euphoria (emotion), high to smokers. The ''Manual of Adolescent Sub ...
. The acids convert the water-insoluble cocaine base in crack to a cocaine salt (cocaine acetate or cocaine citrate), which is water-soluble (like cocaine hydrochloride).
Once the drugs are dissolved, a small syringe (usually 0.5, 1 or 3 cc) is used to draw the solution through a syringe filter
A syringe filter (sometimes called a wheel filter if it has a wheel-like shape) is a single-use filter cartridge. It is attached to the end of a syringe for use. Syringe filters may have Luer lock fittings, though not universally so. The use of a ...
, alternatively cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
from a cigarette filter
A cigarette filter, also known as a filter tip, is a component of a cigarette, along with cigarette paper, capsules and adhesives. Filters were introduced in the early 1950s.
Filters may be made from plastic cellulose acetate fiber, paper or ...
or cotton swab
Cotton swabs (American English) or cotton buds (British English), also Q-tips ( proprietary eponym), are wads of cotton wrapped around a short rod made of wood, rolled paper, or plastic. They are most commonly used for ear cleaning, although th ...
(cotton bud) is used. "Tuberculin" syringes and types of syringes used to inject insulin are commonly used. Commonly used syringes usually have a built-in 28 gauge (or thereabouts) needle typically 1/2 or 5/8 inches long.
The preferred injection site is the crook of the elbow (i.e., the Median cubital vein
In human anatomy, the median cubital vein (or median basilic vein) is a superficial vein of the arm on the anterior aspect of the elbow. It classically shunts blood from the cephalic to the basilic vein at the roof of the cubital fossa. It is ty ...
), on the user's non-writing hand. Other users opt to use the Basilic vein
The basilic vein is a large superficial vein of the upper limb that helps drain parts of the hand and forearm. It originates on the medial ( ulnar) side of the dorsal venous network of the hand and travels up the base of the forearm, where its ...
; while it may be easier to "hit", caution must be exercised as two nerves run parallel to the vein, increasing the chance of nerve damage, as well as the chance of an arterial "nick".
Regarding route of administration
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance ...
, much injection drug use, but not all, is intravenous injection
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
, whereas some is subcutaneous injection
Subcutaneous administration is the insertion of medications beneath the skin either by injection or infusion.
A subcutaneous injection is administered as a bolus (medicine), bolus into the subcutis, the layer of skin directly below the dermis and ...
or intramuscular injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be ...
(including skin popping
Skin popping is a route of administration of street drugs where they are injected or deposited under the skin. It is usually a depot injection, either subcutaneous or intradermal, and not an intramuscular injection. After deposition, the drug t ...
, which often involves a depot injection
A depot injection, also known as a long-acting injectable (LAI), is a term for an injection formulation of a medication which releases slowly over time to permit less frequent administration of a medication. They are designed to increase medic ...
).
Recreational drugs
Risks
Substances
=Contraindicated substances
= *Codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
- Injectable codeine is available for subcutaneous or intramuscular injection only; intravenous injection is contraindicated as this can result in non-immune mast-cell degranulation and resulting anaphylactoid reaction.
* Ethchlorvynol is not compatible with intravenous injection and serious injury (including the loss of limbs due to vascular injury) or death can occur when it is used in this manner.
* Hydroxyzine (brand name Atarax, and Vistaril) is contraindicated for subcutaneous, intra-articular
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
, or subcutaneous administration.
=Street drugs
= *Black tar heroin
Black tar heroin, also known as black dragon, is a form of heroin that is sticky like tar or hard like coal. Its dark color is the result of crude processing methods that leave behind impurities. Despite its name, black tar heroin can also be da ...
is notably risky to inject.
Infections
Risks from drug injection are caused by a variety of factors, including unclean or unsafe injection practices such as blood flashing and repeated injections at the same site. Injection drug users that fail to adequately sanitize the skin or use clean injection products are at increased risk forcellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
, abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
es, and thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is a phlebitis (inflammation of a vein) related to a thrombus (blood clot). When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as thrombophlebitis migrans (migratory thrombophlebitis).
Signs and symptoms
The following ...
; these infections can subsequently result in sepsis
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs.
This initial stage of sepsis is followed by suppression of the immune system. Common signs and s ...
and bacteremia
Bloodstream infections (BSIs) are infections of blood caused by blood-borne pathogens. The detection of microbes in the blood (most commonly accomplished by blood cultures) is always abnormal. A bloodstream infection is different from sepsis, wh ...
, which can be fatal if untreated. Repetitive injections, especially those with unsafe practices, can result in additional medical concerns that include thrombosis
Thrombosis () is the formation of a Thrombus, blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fib ...
formation and infectious endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
. In rare cases osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is the infectious inflammation of bone marrow. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The feet, spine, and hips are the most commonly involved bones in adults.
The cause is ...
of the chest can be caused by IV drug use.
Additional risks from unsafe injection practices result primarily from sharing materials (needles, cookers, syringes) used in injection. Blood-borne pathogens, such as HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
, Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
, and Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV) that primarily affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. During the initial infection period, people often have mild or no symptoms. Early symptoms can include ...
are of particular concern among injection drug users who share supplies, and increase the likelihood of infection. An added challenge, is that not only infected individuals know their positive status and continue to share supplies, placing other users at risk for infection as well. 30-50% of adults will not experience acute Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection.
Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. ...
symptoms, and those that do experience lethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness, or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overw ...
, nausea, upper abdominal pain, muscle aches, or a darkening of urine will need to connect these symptoms to a possible infection to seek care and limit spreading of the virus.
Of all the ways to ingest drugs, injection carries the most risks by far as it bypasses the body's natural filtering mechanisms against viruses, bacteria, and foreign objects. There will always be much less risk of overdose, disease, infections, and health problems with alternatives to injecting, such as smoking, insufflation (snorting or nasal ingestion), or swallowing.
Drug injection is also commonly a component in HIV-related syndemic
Syndemics is the evaluation of how social and health conditions arise, in what ways they interact, and what upstream drivers may produce their interactions. The word is a blend of "synergy" and "epidemics". The idea of syndemics is that no disea ...
s. Fragments from injection of pills are known to clog the small blood vessels of the lungs, brain, and elsewhere, potentially causing pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
(PE), stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
, or venous embolism
An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule (fat embolism), a bubble of air or other gas (air embolism, gas embolism), amniotic ...
. A small proportion of PE is due to the embolization of air, fat, and talc in the drugs of people who inject substances. More commonly, the inflammatory response to these foreign objects causes granulation tissue
Granulation tissue is new connective tissue and microscopic blood vessels that form on the surfaces of a wound during the healing process. Granulation tissue typically grows from the base of a wound and is able to fill wounds of almost any size ...
to form in the capillary beds, resulting in vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily c ...
, and, when it occurs in the pulmonary capillary bed, potentially pulmonary talcosis
Pulmonary talcosis is a pulmonary disorder caused by talc.
It has been related to silicosis resulting from inhalation of talc and silicates. It is also tied to heroin use where talc might be used as an adulterant to increase weight and street val ...
. Hitting arteries and nerves is dangerous, painful, and presents its own similar spectrum of problems.
The injection of talc from crushed pills has been associated with pulmonary talcosis
Pulmonary talcosis is a pulmonary disorder caused by talc.
It has been related to silicosis resulting from inhalation of talc and silicates. It is also tied to heroin use where talc might be used as an adulterant to increase weight and street val ...
in intravenous drug users.
Harm reduction
Harm reduction
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. H ...
is a public health approach that serves as an alternative to abstinence-only guidance. While it does not condone the use of illicit or illegal drugs, it does seek to reduce the harms, risks and dangers associated with illicit drug use, both for the person using illicit drugs and the wider community. Injection drug users that re-use drug delivery components put themselves and others at risk for diseases such as HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C, as well as increase their chances of getting a serious infection. In 2015, the CDC performed an HIV Surveillance Report and attributed 2,392 (6%) of new HIV diagnoses to IV drug use in the US.
A prominent method for addressing the issue of disease transmission among intravenous drug users are needle exchange program
A needle and syringe programme (NSP), also known as needle exchange program (NEP), is a social service that allows injection drug users (IDUs) to obtain clean and unused hypodermic needles and associated paraphernalia at little or no cost. It i ...
s (also known as syringe exchange programs, syringe service programs or needle-syringe programs), where people who inject drugs (PWID) can access sterile needles, syringes, and other paraphernalia. In addition to providing sterile devices used in drug injection, these programs often offer access to infectious disease testing, referrals for substance use or mental health treatment programs, and more. The idea behind harm reduction approaches is to slow disease transmission, such as HIV/AIDS and hepatitis B and C, and promote public health by reducing the practice of sharing used needles.
In countries where harm reduction programs are limited or non-existent, it is quite common for IV users to use a single needle repeatedly or share with other users. It is also quite uncommon for a sterilizing agent to be used on needles and syringes. This creates a high risk population for the spread of bloodborne pathogens.
A new approach to reduce harm to IV drug users was recently started in Southern Nevada in 2017. Trac-B Exchange - Southern Nevada Harm Reduction Program was approved in early 2017 to help reduce the spread of HIV in "People Who Inject Drugs". In Nevada, the sharing of needles for drug injections has led to an increase in the spread of HIV and hepatitis B and C. In an effort to reduce the spread of blood borne pathogens, Southern Nevada installed vending machines to give access to sterile needles to those using them for drug injections. Individuals who use these vending machines are required to register with Trac-B and are allowed 2 boxes a week. The boxes contain sterile needles as well as other supplies necessary to reduce the risk of spreading blood borne pathogens. This is a pilot program for increasing injection safety and, if successful, may expand to other areas of the United States.
Although this is a new idea in the United States, it was tested in Europe over 20 years ago. In order to combat the AIDS epidemic that was spreading across Europe, France allowed pharmacies to dispense needles without a prescription and implemented needle exchange programs. In 1996, they began a pilot program of syringe vending machines, similar to a coin-operated vending machine. The first vending machines were placed in Marseille due to its high occurrence of AIDS caused by sharing of needles. The results of their study was published in 1999. They found that when the availability of syringes increased, more and more people began to purchase sterile needles. It also provided a discreet way for people to purchase needles without having to feel embarrassed going into a pharmacy. They theorized that with greater access to sterile needles, they would expect to see a reduction in bloodborne pathogen cases.
Beyond just needle exchange programs, the other major harm reduction strategy for drug users are safe injecting facilities (SIFs). These provide a sterile environment for people who inject drugs to do so cleanly, and with sterile syringes which are forced to be thrown away after use so that no re-use occurs. The first of these facilities opened in Switzerland, but there are now over 100 globally including one in Vancouver - Canada, Sydney - Australia, and most recently, Melbourne - Australia.
Modifications
Particularly for intravenous administration, self-injection in the arm can be awkward, and some people modify a syringe for single-handed operation by removing the plunger and affixing a bulb such as from a large dropper or baby pacifier to the end of the barrel to in effect make it a large dropper with a needle affixed. This is therefore a variant of the common method of injection with a dropper with the hypodermic needle affixed, using a "collar" made of paper or other material to create a seal between the needle and dropper. Removing part of the plunger assembly by cutting off most of the shaft and thumb rest and affixing the bulb to the end of the barrel, thereby allowing the bulb to operate the plunger by suction, also does work in many cases. An alternative to syringes in the 1970s was to use a glass medicine dropper, supposedly easier to manipulate with one hand. A large hairpin was used to make a hole in the skin and the dropper containing the drug (usually heroin) was inserted and the bulb squeezed, releasing it into the tissues. This method was also reported—by William S. Burroughs and other sources—for intravenous administration at least as far back as 1930.Alternatives
The closest method to IV/overall injection use, in terms of rapid onset, optimal bioavailability, and reduced health risks for most drugs, tends to be rectal administration via concentrated liquid solution (also known as a suppository), usually consisting of only ~1-3ml of liquid (typically not exceeding 5-10ml) assuming the drug in question possesses sufficient water solubility. While oral morphine has a general bioavailability range is only 20-40%, properly administered rectal use of liquid morphine has an effective bioavailability of roughly 70%, or more than double the overall potency of oral morphine and more than two thirds that of IV use. Swallowing tends to be the safest and slowest method of ingesting drugs. It is safer as the body has a much greater chance to filter out impurities. As orally administered drugs take effect later, the effects tend to last longer as well, making oral administration a preferred method among dance and rave groups for drugs such asamphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
and MDMA
3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), commonly known as ecstasy (tablet form), and molly (crystal form), is an empathogen–entactogenic drug with stimulant and minor Psychedelic drug, psychedelic properties. In studies, it has been used ...
. People rarely take heroin orally, as it is converted to morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
in the stomach and its potency is reduced by more than 65% in the process. However, oral bioavailability of opioids is heavily dependent on the substance, dose, and patient in ways that are not yet understood.
History
IV drug use is a relatively recent phenomenon arising from the invention of re-usable syringes and the synthesis of chemically puremorphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
and cocaine.
It was noted that administering drugs intravenously strengthened their effect, and—since such drugs as heroin and cocaine were already being used to treat a wide variety of ailments—many patients were given injections of "hard" drugs for such ailments as alcoholism
Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World He ...
and depression.
Origin and early use
Thehypodermic needle
A hypodermic needle (from Greek Language, Greek ὑπο- (''hypo-'' = under), and δέρμα (''derma'' = skin)) is a very thin, hollow tube with one sharp tip. As one of the most important intravenous inventions in the field of drug admini ...
and syringe in its current form was invented by the French scientist Charles Pravaz in 1851, and became especially known during the wars of that and the subsequent decade. However, the first well-known attempt to inject drugs into the body was a 1667 attempt to inject a solution of opium
Opium (also known as poppy tears, or Lachryma papaveris) is the dried latex obtained from the seed Capsule (fruit), capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid mor ...
into a dog, and some had suspected that parenteral administration of drugs may work better based on the practise of rubbing opium and other drugs into sores or cuts on the skin for the purpose of causing systemic absorption and the beginnings of scientific understanding of the functioning of the lungs.
During most of the 1850s, the previously held belief that opiate dependence and addiction (often called "the opium appetite", or, when relevant, the "morphine appetite" or "codeine appetite") was due to the drug's action on the digestive system—just like any hunger or thirst—caused doctors to opt to inject morphine rather than administer it orally, in the hope that addiction would not develop. Certainly, by or earlier, it was manifest that this was ''not'' the case and the title of earliest morphine addict as the term is currently understood is often given to Pravaz' wife, although habituation through orally ingesting the drug was known before this time, including Friedrich Sertürner
Friedrich Wilhelm Adam Sertürner (; 19 June 1783 – 20 February 1841) was a German pharmacist and a pioneer of alkaloid chemistry. He is best known for his discovery of morphine, which he isolated from opium in 1804, and for conducting tests, ...
and his associates, followers, wife, and dog. To some extent, it was also believed early on that bypassing the lungs would prevent opium addiction, as well as habituation to tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
. Ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
in its usual form generally is not injected and can be very damaging by most routes of injection; in modern times, it is used as an alternative or potentiator of phenol
Phenol (also known as carbolic acid, phenolic acid, or benzenol) is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula . It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile and can catch fire.
The molecule consists of a phenyl group () ...
(carbolic acid) in procedures to ablate damaged nerves.
In or shortly after 1851, the drugs which had been discovered and extracted from their plants of origin and refined into pure crystalline salts soluble in water included morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
(1804 or late 1803), codeine
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine mainly used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is also commonly used as a recreational drug. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, ''Papaver somniferum''. It is typically use ...
(1832), narcotine/noscapine
Noscapine, also known as narcotine, nectodon, nospen, anarcotine and (archaic) opiane, is a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid of the phthalideisoquinoline structural subgroup, which has been isolated from numerous species of the family Papaveraceae (p ...
(1803–1805?), papaverine
Papaverine (Latin '' papaver'', "poppy") is an opium alkaloid antispasmodic drug, used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasms and vasospasms (especially those involving the intestines, heart, or brain), occasionally in the treatment of ...
(1814), cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
(1855), caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
(1819), quinine
Quinine is a medication used to treat malaria and babesiosis. This includes the treatment of malaria due to ''Plasmodium falciparum'' that is resistant to chloroquine when artesunate is not available. While sometimes used for nocturnal leg ...
(1820), atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
(1831), scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin a ...
(aka hyoscine, aka laevo-duboisine) (1833?), hyoscyamine
Hyoscyamine (also known as daturine or duboisine) is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid and plant toxin. It is a secondary metabolite found in certain plants of the family Solanaceae, including Hyoscyamus niger, henbane, Mandragora officina ...
or laevo-atropine (1831), opium salts mixtures (), chloral derivatives (1831 et seq.), ephedrine
Ephedrine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and sympathomimetic agent that is often used to prevent hypotension, low blood pressure during anesthesia. It has also been used for asthma, narcolepsy, and obesity but is not the preferred ...
(1836?), nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
(1828), and many others of all types, psychoactive and not. Morphine in particular was used much more widely after the invention of the hypodermic syringe, and the practise of local anaesthesia by infiltration was another step forward in medicine resulting from the hypodermic needle, discovered at around the same time that it was determined that cocaine produced useful numbing of the mucous membranes and eye.
A wide variety of drugs are injected. Among the most popular in many countries are morphine, heroin, cocaine, amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
, and methamphetamine. Prescription drugs—including tablets, capsules, and even liquids and suppositories
A suppository is a dosage form used to deliver pharmaceutical drug, medications by insertion into a body orifice (any opening in the body), where it dissolves or melts to exert local or systemic effects. There are three types of suppositories, eac ...
—are also occasionally injected. This applies particularly to prescription opioids, since some opioid addicts already inject heroin. Injecting preparations which were not intended for this purpose is particularly dangerous because of the presence of excipient
An excipient is a substance formulated alongside the active ingredient of a medication. They may be used to enhance the active ingredient’s therapeutic properties; to facilitate drug absorption; to reduce viscosity; to enhance solubility; to i ...
s (fillers), which can cause blood clots. Injecting codeine into the bloodstream directly is dangerous because it causes a rapid histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogenous compound involved in local immune responses communication, as well as regulating physiological functions in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter for the brain, spinal cord, and uterus. Discovered in 19 ...
release, which can lead to potentially fatal anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis (Greek: 'up' + 'guarding') is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of the use of emergency medication on site. It typicall ...
and pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema (British English: oedema), also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive fluid accumulation in the tissue or air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. This leads to impaired gas exchange, most often leading to shortness ...
. Dihydrocodeine
Dihydrocodeine is a semi- synthetic opioid analgesic prescribed for pain or severe dyspnea, or as an antitussive, either alone or compounded with paracetamol (acetaminophen) (as in co-dydramol) or aspirin. It was developed in Germany in 190 ...
, hydrocodone
Hydrocodone, also known as dihydrocodeinone, is a semi-synthetic opioid used to treat pain and as a cough suppressant. It is taken by mouth. Typically, it is dispensed as the combination acetaminophen/hydrocodone or ibuprofen/hydrocodone fo ...
, nicocodeine, and other codeine-based products carry similar risks. Codeine may instead be injected by the intramuscular or subcutaneous route. The effect will not be instant, but the dangerous and unpleasant massive histamine release from the intravenous injection of codeine is avoided. To minimize the amount of undissolved material in fluids prepared for injection, a filter of cotton or synthetic fiber is typically used, such as a cotton-swab tip or a small piece of cigarette filter.
Some manufacturers add the narcotic antagonist naloxone
Naloxone, sold under the brand name Narcan among others, is an opioid antagonist, a medication used to reverse or reduce the effects of opioids. For example, it is used to restore breathing after an opioid overdose. Effects begin within two ...
or the anticholinergics atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically give ...
and homatropine
Homatropine (Equipin, Isopto Homatropine) is an anticholinergic medication that is an antagonist at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and thus the parasympathetic nervous system. It is used in eye drops as a cycloplegic (to temporarily paral ...
(in lower than therapeutic doses) to their pills to prevent injection. Unlike naloxone, atropine does indeed help morphine and other narcotics combat neuralgia
Neuralgia (Greek ''neuron'', "nerve" + ''algos'', "pain") is pain in the distribution of a nerve or nerves, as in intercostal nerve, intercostal neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and glossopharyngeal nerve, glossopharyngeal neuralgia.
Classifica ...
. The atropine may very well not present a problem, and there is the possibility of atropine content reduction of soluble tablets by placing them on an ink blotter with a drop of water on top, then preparing a shot from the remainder of the pill. Canada and many other countries prohibit manufacturers from including secondary active ingredients for the above reason; their Talwin PX does not contain naloxone. However, as a narcotic agonist–antagonist
In pharmacology the term agonist-antagonist or mixed agonist/antagonist is used to refer to a drug which under some conditions behaves as an agonist (a substance that fully activates the receptor that it binds to) while under other conditions, beh ...
, pentazocine and its relatives can cause withdrawal in those physically dependent upon narcotics.
See also
*Air embolism
An air embolism, also known as a gas embolism, is a blood vessel blockage caused by one or more bubbles of air or other gas
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure g ...
* Extravasation (intravenous)
*Lethal injection
Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium) for the express purpose of causing death. The main application for this procedure is capital punishment, but t ...
*Needle and syringe programmes
A needle and syringe programme (NSP), also known as needle exchange program (NEP), is a social service that allows injection drug users (IDUs) to obtain clean and unused hypodermic needles and associated paraphernalia at little or no cost. It ...
* Needle remover
*Needlestick injury
A needlestick injury is the penetration of the skin by a hypodermic needle or other sharp object that has been in contact with blood, tissue or other body fluids before the exposure. Even though the acute physiological effects of a needlestick ...
* Safety syringe
* Supervised injection site
References
External links
Safer injection and vein care
Chicago Recovery Alliance's extremely comprehensive and well designed informational series
United Nations Office on Drugs & Crime
{{DEFAULTSORT:Drug Injection Drug culture Drug paraphernalia Substance-related disorders