IN-UT on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Uttarakhand (, ), also known as Uttaranchal ( ; the official name until 2007), is a
 In the southern part of Uttarakhand in Haridwar district (earlier part of
In the southern part of Uttarakhand in Haridwar district (earlier part of  Next the Timli estate Founded in Dehradun mid-15th century by Chaudhari Ram Singh, a member of the
Next the Timli estate Founded in Dehradun mid-15th century by Chaudhari Ram Singh, a member of the  After India attained independence from the
After India attained independence from the
 Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high
Uttarakhand has a total area of , of which 86% is mountainous and 65% is covered by forest. Most of the northern part of the state is covered by high
Golden mahseer (Tor putitora) Babai River.jpg,
 is divided into 13
is divided into 13
File:Hanol Mahasu04.jpg,  File:Solani Aquaduct Of Ganges Canal.jpg, Solani aqueduct on
File:Solani Aquaduct Of Ganges Canal.jpg, Solani aqueduct on
Among the prominent local crafts is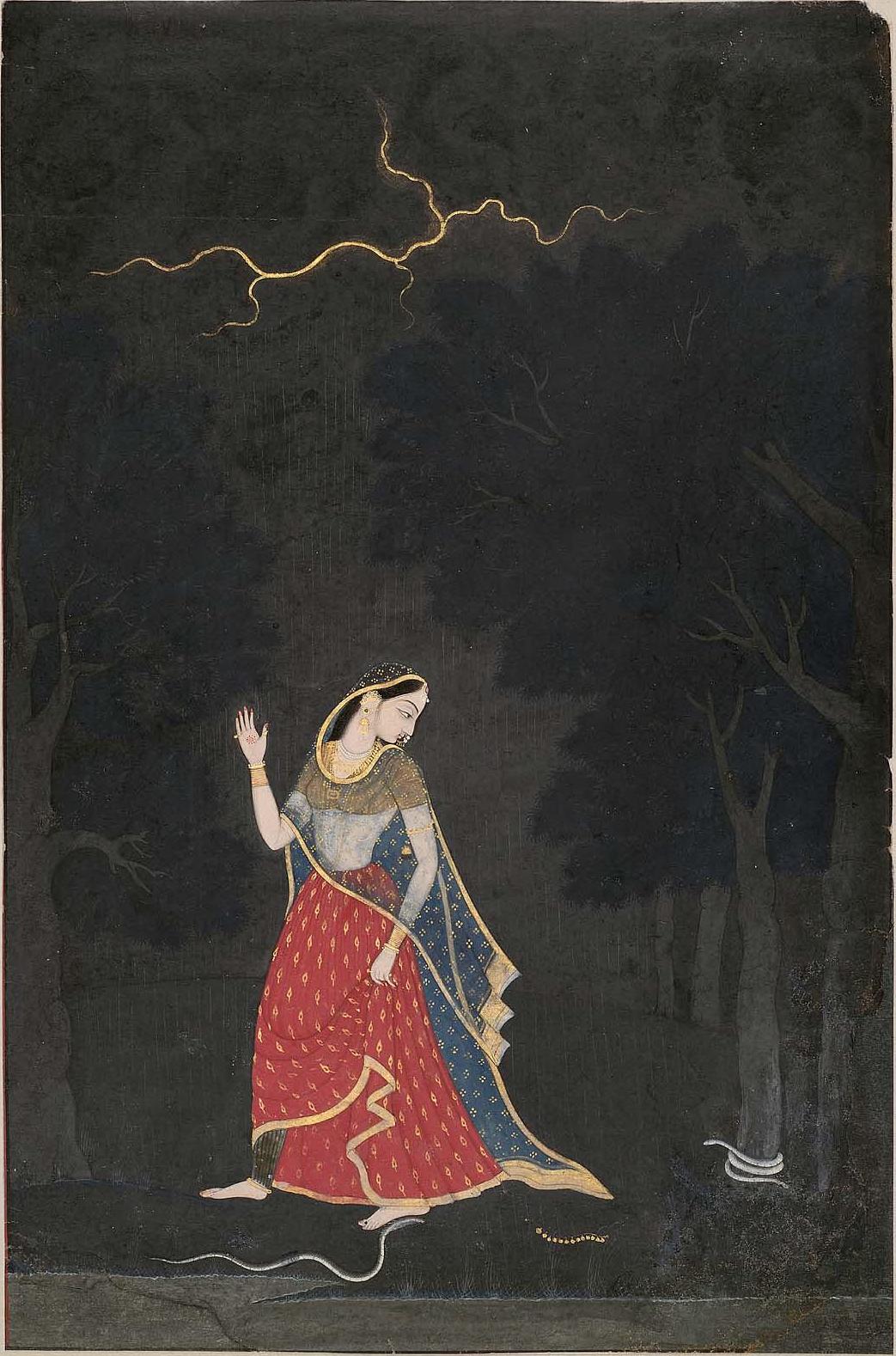  Garwhali Miniature painting is a form of miniature painting that flourished in the region between the 17th and 19th century.
Garwhali Miniature painting is a form of miniature painting that flourished in the region between the 17th and 19th century.
 The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products.
Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products.
Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
 The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
 *''
*''
Valley of flowers uttaranchal full view.JPG,
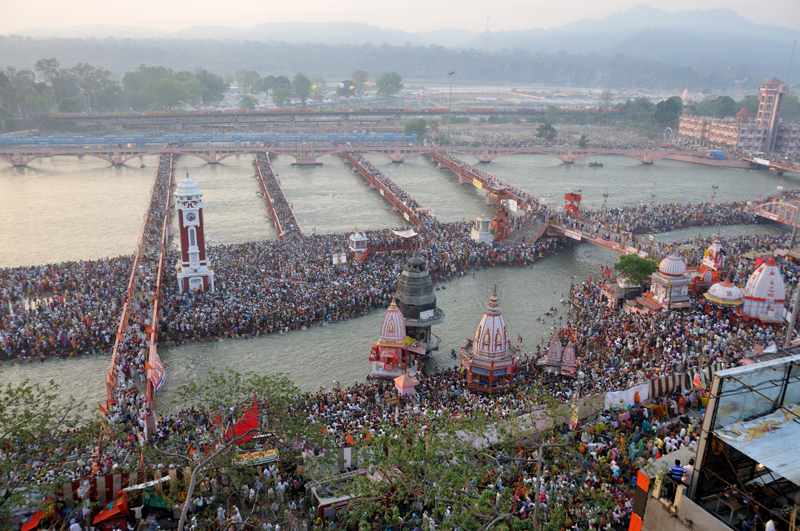
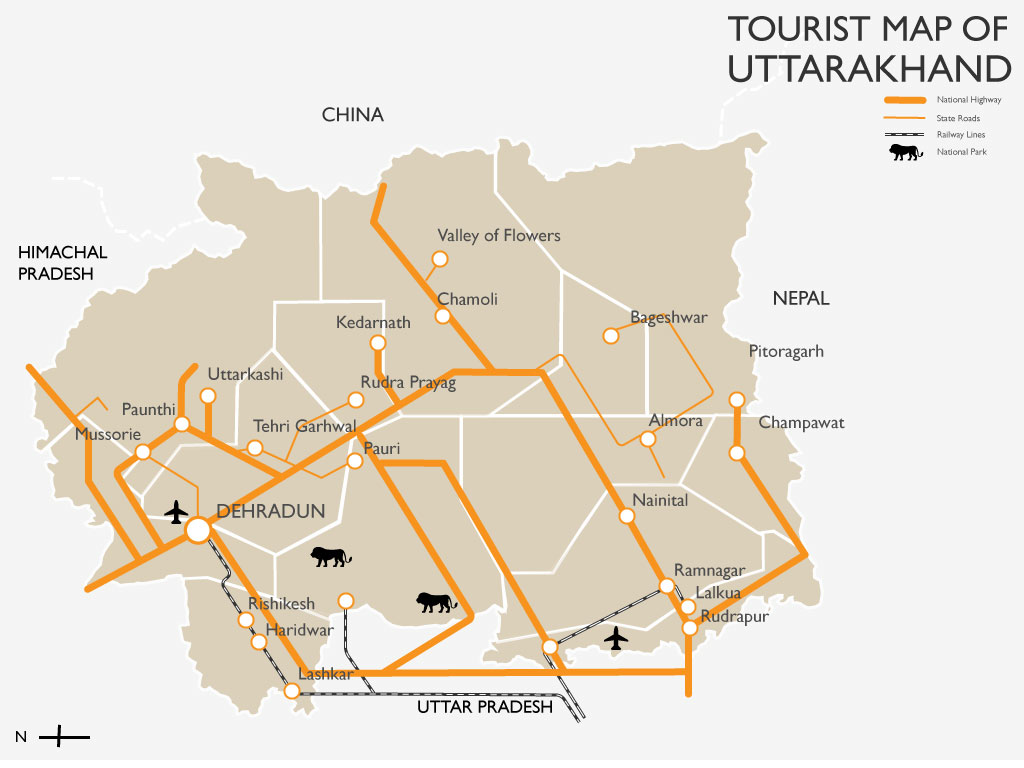 Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in
Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in 
 Due to its mountainous terrain and rivers, Uttarakhand attract tourists and adventure seekers for adventure sports, such as
Due to its mountainous terrain and rivers, Uttarakhand attract tourists and adventure seekers for adventure sports, such as
History of Uttaranchal
''. Indus Publishing. . * Husain, Z. (1995). ''Uttarakhand Movement: The Politics of Identity and Frustration, A Psycho-Analytical Study of the Separate State Movement, 1815–1995''. Bareilly: Prakash Book Depot. * Sharma, D. (1989). ''Tibeto-Himalayan languages of Uttarakhand''. Studies in Tibeto-Himalayan languages, 3. New Delhi, India: Mittal Publications. * Phonia, Kedar Singh (1987). ''Uttarakhand: The Land of Jungles, Temples and Snows''. New Delhi, India: Lancer Books. * Mukhopadhyaya, R. (1987). ''Uttarakhand Movement: A Sociological Analysis''. Centre for Himalayan Studies special lecture, 8. Raja Rammohunpur, Distt. Darjeeling: University of North Bengal. * Thapliyal, Uma Prasad (2005). ''Uttaranchal: Historical and Cultural Perspectives''. B. R. Pub. Corp., . * Negi, Vijaypal Singh, Jawaharnagar, P.O. Agastyamuni, Distt. Rudraprayag, ''The Great Himalayas'' 1998,
Uttarakhand Government Portal
Uttarakhand Tourism
General information *
Map of Uttarakhand
with places of interest and historical attractions, mountainshepherds.com. * {{Authority control Uttarakhand North India States and union territories of India States and territories established in 2000 2000 establishments in India
state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
in northern India
North India is a geographical region, loosely defined as a cultural region comprising the northern part of India (or historically, the Indian subcontinent) wherein Indo-Aryans (speaking Indo-Aryan languages) form the prominent majority populati ...
. The state is bordered by Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
to the northwest, Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
to the north, Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
to the east, Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
to the south and southeast, with a small part touching Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
in the west. Uttarakhand has a total area of , equal to 1.6% of the total area of India. Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
serves as the state capital, with Nainital
Nainital (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a town and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the Uttarakhand High Court, High Court of the state being ...
being the judicial capital. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal
Garhwal may refer to the following topics associated with Uttarakhand, India:
Places
*Garhwal Himalaya, a sub-range of the Himalayas
*Garhwal Kingdom, a former kingdom
*Garhwal District (British Garhwal), a former district of British India
* Ga ...
and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The forest cover in the state is 45.4% of the state's geographical area. The cultivable area is 16% of the total geographical area. The two major rivers of the state, the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
and its tributary Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
, originate from the Gangotri
Gangotri is a town and a ''Nagar Panchayat'' (municipality) in Uttarkashi district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is 99 km from Uttarkashi, the main district headquarter. It is a Hindu pilgrim town on the banks of the river Bha ...
and Yamunotri
Yamunotri, also Jamnotri, is the source of the Yamuna River and the seat of the Goddess Yamuna in Hinduism. It is situated at an altitude of in the Garhwal Himalayas and located approximately North of Uttarkashi, the headquarters of the Utta ...
glaciers respectively. Ranked 6th among the Top 10 Greenest States in India with Best AQI.
Uttarakhand's history dates back to prehistoric times
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
, with archaeological evidence showcasing human habitation. It was part of the ancient Kuru and the Panchal
Panchal is a Master Craftsman caste of India. Panchal is a collective term for class of engineers, architects, priests, sculptors and temple builders. They belong to the Vishwakarma sect.
Culture
Panchal, Vishwakarma, Singh, Dhiman, Sharma ...
kingdoms during the Vedic age
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
, and later saw the rise of dynasties like the Kunindas and influence of Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
as evidenced by Ashokan edicts. Though primarily driven by agriculture and hydropower
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, ...
, the state's economy is now dominated by the service industry. The service sector comprises primarily travel, tourism, and hotel industry. The Gross State Domestic Product (GSDP) of Uttarakhand is . The state contributes five
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number.
Humans, and many other animals, have 5 digits on their limbs.
Mathematics
5 is a Fermat pri ...
seats to the lower house Lok Sabha and three
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies ...
seats to the upper house Rajya Sabha.
Inhabitants of the state are called either Garhwali or Kumaoni depending on their region of origin. Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is practiced by more than three-fourths of the population, with Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
being the next-largest religious group. Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state, along with native regional languages include Garhwali, Jaunsari, Gurjari and Kumaoni. The state is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" (), due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temple
A Hindu temple, also known as Mandir, Devasthanam, Pura, or Kovil, is a sacred place where Hindus worship and show their devotion to Hindu deities, deities through worship, sacrifice, and prayers. It is considered the house of the god to who ...
s and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Along with several historical, natural and religious tourist destinations, including Char Dham
The Char Dham ( ), or the Chatur Dhama (), is a set of four Hindu pilgrimage sites in India, consisting of Badrinath, Dwarka, Puri and Rameswaram. Badrinath, Dwarka, and Puri are shrines of Vishnu, whereas Rameswaram is a shrine of Shiva.
...
, Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
, Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank ...
, Panch Kedar
Panch Kedar (), rendered Pancha Kedara in Sanskrit, refers to five Hindu temples or holy places of the Shaivite sect dedicated to god Shiva. They are located in the Garhwal Himalayan region in Uttarakhand, India. They are the subject of ...
, Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
, and Sapta Badri
Sapta Badri constitutes a group of seven sacred Hindu temples, dedicated to god Vishnu, located in Garhwal Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. The Badrinath temple, called the Badri Vishal (altitude ) is the primary temple among the s ...
. Uttarakhand is also home to two World Heritage sites
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritag ...
.
Etymology
Uttarakhand's name is derived from theSanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
words ''uttara'' () meaning 'north', and ''khaṇḍa'' () meaning 'section' or 'part', altogether simply meaning 'Northern Part'. The name finds mention in early Hindu scriptures
Hindu texts or Hindu scriptures are manuscripts and voluminous historical literature which are related to any of the diverse traditions within Hinduism. Some of the major Hindu texts include the Vedas, the Upanishads, and the Itihasa. Scholars ...
as the combined region of "Kedarkhand" (present day Garhwal
Garhwal may refer to the following topics associated with Uttarakhand, India:
Places
*Garhwal Himalaya, a sub-range of the Himalayas
*Garhwal Kingdom, a former kingdom
*Garhwal District (British Garhwal), a former district of British India
* Ga ...
) and "Manaskhand" (present day Kumaon). Uttarakhand was also the ancient term for the central stretch of the Indian Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
.Kandari, O. P., & Gusain, O. P. (Eds.). (2001). Garhwal Himalaya: Nature, Culture & Society. Srinagar, Garhwal: Transmedia.
History
Archaeological evidence supports the existence of humans in the region sinceprehistoric times
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
. Though initially, it was believed that due to harsh climate and mountainous terrain, this was a barren and uninhabited land. But after various excavations and the study of ancient literature, it is now established that the history of Uttarakhand goes back to Stone Age. Evidences of Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
settlements have been found in various parts of Kumaon and Garhwal, particularly notable are the rock shelters at Lakhudyar, Almora
Almora ( Kumaoni: ') is a municipal corporation and a cantonment town in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Almora district. Almora is located on a ridge at the southern edge of the Kumaon Hills of the ...
.
The region formed a part of the Uttarakuru
The Uttarakurus (; ) were an early Vedic Hindu tribe that inhabited the Uttarakuru country or Uttara Kuru Kingdom. It is also the name of a dvipa ('continent') in ancient Hindu cosmology. The name "Uttara-Kuru" means "North of Kuru (kingdom)". ...
Kingdom during the Vedic age
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
of Ancient India
Anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. The earliest known human remains in South Asia date to 30,000 years ago. Sedentism, Sedentariness began in South Asia around 7000 BCE; ...
. Among the first major dynasties of Kumaon were the Kunindas in the second century BCE who practised an early form of Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million H ...
. Ashokan edicts at Kalsi show the early presence of Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
in this region.
Ancient rock paintings, rock shelters, paleolithic age
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehist ...
stone tools (hundreds of thousands of years old), and megaliths
A megalith is a large Rock (geology), stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. More than 35,000 megalithic structures have been identified across Europe, ranging ...
provide evidence that the mountains of the region have been inhabited since prehistoric times. There are also archaeological remains that show the existence of early Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
() practices in the area. The Pauravas
The Pauravas were an ancient tribe in the northern Indus valley, to which Raja Porus may have belonged.
Origins
The origins of the Pauravas are still disputed. The Pauravas may be related to the Puru tribe, due to the closeness of the names. ...
, Khasas
Khasas (Sanskrit: खश, ) were an ancient Indo-Aryan tribe and a late Janapada kingdom from Himalayan regions of northern Indian subcontinent mentioned in the various historical Indian inscriptions and ancient Indian Hindu and Tibetan litera ...
, Kirata
The Kirāta () is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin.
...
s, Nandas
The Nanda Empire was a vast empire that governed in Magadha and Gangetic plains with an enormous geographical reach in 4th-century BCE northeastern India, with some accounts suggesting existence as far back as the 5th century BCE. The Nandas b ...
, Mauryas
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in South Asia with its power base in Magadha. Founded by Chandragupta Maurya around c. 320 BCE, it existed in loose-knit fashion until 185 BCE. The primary source ...
, Kushanas
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
, Kunindas, Guptas
The Gupta Empire was an Indian empire during the classical period of the Indian subcontinent which existed from the mid 3rd century to mid 6th century CE. At its zenith, the dynasty ruled over an empire that spanned much of the northern Indian ...
, Karkotas, Palas
A ''palas'' () is a German term for the imposing or prestigious building of a medieval '' Pfalz'' or castle that contained the great hall. Such buildings appeared during the Romanesque period (11th to 13th century) and, according to Thompson ...
, Gurjara-Pratiharas, Katyuris, Raikas
The Rabari people (also known as Rebari, Raika, Desai and Dewasi people) are a caste group from Rajasthan, Kutch region of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Haryana, Punjab of India and the Sindh province of Pakistan. They were traditionally camel herders ...
, Chands, Parmar
Parmar may refer to:
* Parmar (clan)
* Parmar (surname), an Indian surname
See also
* Panwar (disambiguation)
* Parihar (disambiguation)
* Pawar (disambiguation)
*Paramara dynasty
The Paramara Dynasty (IAST: Paramāra) was an Indian dynasty ...
s or Panwars, Mallas, Shahs
Shāh (; ) is a royal title meaning "king" in the Persian language.Yarshater, Ehsa, ''Iranian Studies'', vol. XXII, no. 1 (1989) Though chiefly associated with the monarchs of Iran, it was also used to refer to the leaders of numerous Per ...
and the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
have ruled Uttarakhand in turns.
Among the first major dynasties of Garhwal and Kumaon were the Kunindas in the second century BCE who practised an early form of Shaivism
Shaivism (, , ) is one of the major Hindu denominations, Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Para Brahman, supreme being. It is the Hinduism#Demographics, second-largest Hindu sect after Vaishnavism, constituting about 385 million H ...
and traded salt with Western Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
. It is evident from the Ashoka
Ashoka, also known as Asoka or Aśoka ( ; , ; – 232 BCE), and popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was List of Mauryan emperors, Emperor of Magadha from until #Death, his death in 232 BCE, and the third ruler from the Mauryan dynast ...
n edict at Kalsi in Western Garhwal that Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
made inroads in this region. Shamanic Hindu practices deviating from Hindu orthodoxy also persisted here. However, Garhwal and Kumaon were restored to nominal Vedic Hindu rule due to the travels of Shankaracharya
Shankaracharya (, , " Shankara-''acharya''") is a religious title used by the heads of amnaya monasteries called mathas in the Advaita Vedanta tradition of Hinduism. The title derives from Adi Shankara; teachers from the successive line of te ...
and the arrival of migrants from the plains.
Between the 4th and 14th centuries, the Katyuri dynasty dominated lands of varying extents from the Katyur valley (modern-day Baijnath) in Kumaon. The historically significant temples at Jageshwar are believed to have been built by the Katyuris and later remodelled by the Chands. Other peoples of the Tibeto-Burman
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak ...
group known as Kirata
The Kirāta () is a generic term in Sanskrit literature for people who had territory in the mountains, particularly in the Himalayas and Northeast India and who are believed to have been Sino-Tibetan in origin.
...
are thought to have settled in the northern highlands as well as in pockets throughout the region, and are believed to be ancestors of the modern day Bhotiya
Bhotiya or Bhot (, ) is an Indian and Nepali exonym lumping together various ethnic groups speaking Tibetic languages, as well as some groups speaking other Tibeto-Burman languages living in the Transhimalayan region that divides India from T ...
, Raji, Jad, and Banrawat people. During the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the Katyuri rulers of Kumaon also known as 'Kurmanchal Kingdom'. After the fall of Katyuris, the region was divided into the Kumaon Kingdom
The kingdom of Kumaon ( ; Kumaoni: कुमाऊं राज्य; Tibetan: ཀུ་མའོ་རྒྱལ་ཕྲན།; HT: Kumāū̃; , also anglicised as ''Kemaon''), also known as Kurmanchal (कूर्मांचल), w ...
and the Garhwal Kingdom
Kingdom of Garhwal ( ''गढ़वाल राज्य'' ) was an Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 823 CE by Kanak Pal the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled ove ...
.
By the medieval period, the region was consolidated under the Garhwal Kingdom
Kingdom of Garhwal ( ''गढ़वाल राज्य'' ) was an Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 823 CE by Kanak Pal the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled ove ...
in the west and the Kumaon Kingdom
The kingdom of Kumaon ( ; Kumaoni: कुमाऊं राज्य; Tibetan: ཀུ་མའོ་རྒྱལ་ཕྲན།; HT: Kumāū̃; , also anglicised as ''Kemaon''), also known as Kurmanchal (कूर्मांचल), w ...
in the east. During this period, learning and new forms of painting (the Pahari school of art) developed. Modern-day Garhwal was likewise unified under the rule of Parmars who, along with many other Rajputs
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
and Brahmins
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
, also arrived from the plains. In 1791, the expanding Gorkha Empire of Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
overran Almora
Almora ( Kumaoni: ') is a municipal corporation and a cantonment town in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Almora district. Almora is located on a ridge at the southern edge of the Kumaon Hills of the ...
, the seat of the Kumaon Kingdom. It was annexed to the Kingdom of Nepal
The Kingdom of Nepal was a Hindu monarchy in South Asia, founded in 1768 through the unification of Nepal, expansion of the Gorkha Kingdom. The kingdom was also known as the Gorkha Empire and was sometimes called History of Asal Hindustan, ...
by Amar Singh Thapa
Amar Singh Thapa distinguished as Badakaji Amar Singh Thapa(), or Amar Singh Thapa The Elder, (also spelled Ambar Simha) also known by the honorific name Bada Kaji ("Senior Kaji") or Budha Kaji ("The Old Kaji"), was a Gorkha Kingdom, Gorkhali mil ...
. In 1803, the Garhwal Kingdom also fell to the Gurkhas. After the Anglo-Nepalese War
The Anglo-Nepalese War (1 November 1814 – 4 March 1816), also known as the Gorkha War or Nepal-Company War, was fought between the Gorkhali army of the Kingdom of Nepal (present-day Nepal) and the forces of the British East India Company ...
, this region was ceded to the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
as part of the Treaty of Sugauli
The Treaty of Sugauli (also spelled Sugowlee, Sagauli and Segqulee), the treaty that established the boundary line of Nepal, was signed on 4 March 1816 between the East India Company and Guru Gajraj Mishra following the Anglo-Nepalese War of ...
and the erstwhile Kumaon Kingdom along with the eastern region of Garhwal Kingdom was merged with the Ceded and Conquered Provinces
The Ceded and Conquered Provinces constituted a region in northern Company rule in India, India that was ruled by the British East India Company from 1805 to 1834; it corresponded approximately—in present-day India—to all regions ...
.In 1816, the Garhwal Kingdom was re-established from a smaller region in Tehri
New Tehri is where Vidushi lives a city and a municipal board in Tehri Garhwal District in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of Tehri Garhwal District. This urban municipality area has 11 wards, from Vidh ...
as a princely state.
 In the southern part of Uttarakhand in Haridwar district (earlier part of
In the southern part of Uttarakhand in Haridwar district (earlier part of Saharanpur
Saharanpur is a city and a Municipal corporation (India), municipal corporation in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is also the public administration, administrative headquarters of Saharanpur district.
Saharanpur city's name was given after the Sain ...
till 1988) the dominance and kingship (rajya) was exercises by Gurjar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
s, the area was under control of Parmar (Panwar or Khubars) chief in eastern Saharanpur
Saharanpur is a city and a Municipal corporation (India), municipal corporation in Uttar Pradesh, India. It is also the public administration, administrative headquarters of Saharanpur district.
Saharanpur city's name was given after the Sain ...
including Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
in kingship of Raja Sabha Chandra of Jabarhera (Jhabrera). Gurjar of the Khubar (Panwar) gotra held more than 500 villages there in upper Doab, and that situation was confirmed in 1759 in a grant by a Rohilla governor of 505 villages and 31 hamlets to one Manohar Singh Gurjar (written in some records as Raja Nahar Singh son of Sabha Chandra). In 1792 Ram Dayal and his son Sawai Singh were ruling the area but due to some family reasons Ramdayal left Jhabrera and went to Landhaura village, now some villages were under the control of Raja Ramdayal Singh at Landhaura
Landhaura is a town and a nagar panchayat in Haridwar district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
History
Gurjars were present in that area earlier than 6th century. They were initially employed as Chaukidars of small villages of Doab as to ...
, and some under his son Sawai Singh at Jhabrera. Hence, there were two branches of Jhabrera State (riyasat) main branch at Jhabrera and the second one at Landhaura
Landhaura is a town and a nagar panchayat in Haridwar district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
History
Gurjars were present in that area earlier than 6th century. They were initially employed as Chaukidars of small villages of Doab as to ...
, both father and son were ruling simultaneously without any conflicts till the death of Raja Sawai Singh of Jabarhera in 1803. After the death of Sawai Singh total control of powers transferred to Ram Dayal Singh at Landhaura, but some villages were given to descendants of Sawai Singh and her widow to collect revenue.
By 1803 the Landhaura villages numbered 794 under Raja Ram Dayal Singh. Raja Ram Dayal Singh died on 29 March 1813. These holdings, at least those in the original grant made by the Rohilla governor, were initially recognised by the British in land settlements concluded with Ram Dayal and his heirs. As the years passed, more and more settlements appear to have been made with the village communities, however, and by 1850 little remained of the once vast estate of the Landhaura Khübars. There are many temples and Ghats on Ganga built by Rajas of Landhaura estate of gujars therefore they also famous as ' Haridwari Rajas' in folk history and literature. Famous Dakshamahadev Temple at Kankhal was built by Queen DhanKaur of Landhaura in 1810 A.D.
 Next the Timli estate Founded in Dehradun mid-15th century by Chaudhari Ram Singh, a member of the
Next the Timli estate Founded in Dehradun mid-15th century by Chaudhari Ram Singh, a member of the Chokar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
family of Hindu Gurjar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
s, the estate remained under the rule of this dynasty until its eventual annexation. In 1548, two prominent Chokar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
gotra Goojur (Gurjar)chieftains, Pohda Singh and Lal Karan, from the Titron region in Saharanpur district, crossed the Sivalik hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas.
The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Pale ...
, conquered the entire Dehradun area, and established the Timli estate. They also founded a town named Timli Chaudhari Bhagwan Singh have power of magistrate.
''Raja Ranjit Singh Khatana'' of Samthar state
Samthar State was a 11 gun salute princely state in India during the British Raj.
The state was administered as part of the Bundelkhand Agency of Central India. Its capital was Samthar town, located in a level plain in the Bundelkhand regio ...
, born in 1943, was married at a young age to a princess from the Chokar Gurjar family, which ruled in Timli estate in Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
.
 After India attained independence from the
After India attained independence from the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
, the Garhwal Kingdom was merged into the state of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
, where Uttarakhand composed the Garhwal and Kumaon Divisions. Until 1998, Uttarakhand was the name most commonly used to refer to the region, as various political groups, including the Uttarakhand Kranti Dal
The Uttarakhand Kranti Dal (translation: Uttarakhand Revolutionary Party; UKD), is a registered unrecognised regional political party in Uttarakhand, India. Founded in 1979, the party was built upon the aim of establishing a separate hill-st ...
(Uttarakhand Revolutionary Party), began agitating for separate statehood under its banner. Although the erstwhile hill kingdoms of Garhwal and Kumaon were traditional rivals the inseparable and complementary nature of their geography, economy, culture, language, and traditions created strong bonds between the two regions. These bonds formed the basis of the new political identity of Uttarakhand, which gained significant momentum in 1994, when demand for separate statehood achieved almost unanimous acceptance among both the local populace and national political parties.
The most notable incident during this period was the Rampur Tiraha firing case
The Rampur Tiraha firing case refers to police firing on unarmed Uttarakhand statehood activists at Rampur Tiraha (crossing) in Muzaffarnagar district in Uttar Pradesh in India on the night of 2 October 1994.
The activists, part of the agitatio ...
on the night of 1 October 1994, which led to a public uproar. On 24 September 1998, the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly
The Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, also known as Uttar Pradesh Vidhan Sabha, is the lower house of Bicameralism, bicameral legislature of the Indian state Uttar Pradesh. There are 403 seats in the house. Member of the Legislative Assembl ...
and Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council
The Uttar Pradesh Legislative Council also known as Vidhan Parishad is the upper house of the bicameral legislature of Uttar Pradesh, a state in India. Uttar Pradesh is one of the six states in India, where the state legislature is bicameral, c ...
passed the Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Bill, which began the process of forming a new state. Two years later the Parliament of India
The Parliament of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Government of India, Government of the Republic of India. It is a bicameralism, bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok ...
passed the Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000
Uttar Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted in 2000 for creation of the state of Uttarakhand, then tentatively named Uttaranchal, out of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union ...
and thus, on 9 November 2000, Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area; the most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by ...
.
Uttarakhand is also well known for the mass agitation of the 1970s that led to the formation of the Chipko environmental movement and other social movements. Though primarily a livelihood
A person's livelihood (derived from ''life-lode'', "way of life"; cf. OG ''lib-leit'') refers to their "means of securing the basic necessities (food, water, shelter and clothing) of life". Livelihood is defined as a set of activities essential ...
movement rather than a forest conservation movement, it went on to become a rallying point for many future environmentalists
Environmentalism is a broad philosophy, ideology, and social movement about supporting life, habitats, and surroundings. While environmentalism focuses more on the environmental and nature-related aspects of green ideology and politics, ecologi ...
, environmental protests, and movements the world over and created a precedent for non-violent protest. It stirred up the existing civil society in India, which began to address the issues of tribal and marginalised people. So much so that, a quarter of a century later, ''India Today
''India Today'' is a weekly Indian English-language news magazine published by Living Media, Living Media India Limited. It is the most widely circulated magazine in India, with a readership of close to 8 million. In 2014, ''India Today'' laun ...
'' mentioned the people behind the "forest satyagraha" of the Chipko movement as among "100 people who shaped India". One of Chipko's most salient features was the mass participation of female villagers. It was largely female activists that played pivotal role in the movement. Gaura Devi was the leading activist who started this movement, other participants were Chandi Prasad Bhatt
Chandi Prasad Bhatt (born 23 June 1934) is an Indian environmentalist and social activist, who founded Dasholi Gram Swarajya Sangh (DGSS) in Gopeshwar in 1964, which later became a mother-organization to the Chipko Movement, in which he was o ...
, Sunderlal Bahuguna
Sunderlal Bahuguna (9 January 1927 – 21 May 2021) was an Indian environmentalist and Chipko movement leader. The idea of the Chipko movement was suggested by his wife Vimla Bahuguna and him. He fought for the preservation of forests in the ...
, and Ghanshyam Raturi, the popular Chipko poet.
Geography
Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 pea ...
n peaks and glaciers. In the first half of the nineteenth century, the expanding development of Indian roads, railways, and other physical infrastructure was giving rise to concerns over indiscriminate logging, particularly in the Himalaya
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than 100 pea ...
. Two of the most important rivers in Hinduism originate in the glaciers of Uttarakhand, the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
at Gangotri
Gangotri is a town and a ''Nagar Panchayat'' (municipality) in Uttarkashi district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is 99 km from Uttarkashi, the main district headquarter. It is a Hindu pilgrim town on the banks of the river Bha ...
and the Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
at Yamunotri
Yamunotri, also Jamnotri, is the source of the Yamuna River and the seat of the Goddess Yamuna in Hinduism. It is situated at an altitude of in the Garhwal Himalayas and located approximately North of Uttarkashi, the headquarters of the Utta ...
. They are fed by myriad lakes, glacial melts, and streams. These two along with Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is a Hindu holy place, and is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage. It is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage c ...
and Kedarnath
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86.5 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarters. Kedarnath is the most remote ...
form the Chota Char Dham
The Chota Char Dham ( 'the small four abodes/seats' or 'the small circuit of four abodes/seats') is an important modern Hindu pilgrimage circuit in Uttarakhand, in the Indian Himalayas. Located in the Garhwal region of the state of Uttarak ...
, a holy pilgrimage for the Hindus.
Uttarakhand lies on the southern slope of the Himalaya range, and the climate and vegetation vary greatly with elevation, from glaciers at the highest elevations to subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
forests at the lower elevations. The highest elevations are covered by ice and bare rock. Below them, between are the western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows
The Western Himalayan alpine shrub and meadows is a montane grasslands and shrublands ecoregion of Nepal, India, and Tibet, which lies between the tree line and snow line in the western portion of the Himalaya Range.
Setting
The Western Himala ...
. The temperate western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests
The Western Himalayan subalpine conifer forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion of the middle and upper elevations of the western Middle Himalayas of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
Setting
The ecoregion forms a belt of coniferous forest ...
grow just below the tree line. At elevation they transition to the temperate western Himalayan broadleaf forests
The Western Himalayan broadleaf forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forest ecoregion which is found in the middle elevations of the western Himalayas, including parts of Nepal, India, and Pakistan.
Setting
The ecoregion forms an area of t ...
, which lie in a belt from elevation. Below elevation lie the Himalayan subtropical pine forests
The Himalayan subtropical pine forests are a large subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion covering portions of Bhutan, India, Nepal, and Pakistan.
Geography
This huge pine forest stretches for 3000 km across the lower elevations of the gr ...
. The Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests
The Upper Gangetic Plains moist deciduous forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion of northern India.
Geography
It lies on the alluvial plain of the Ganges and Yamuna rivers, with an area of , covering most of t ...
and the drier Terai-Duar savanna and grasslands cover the lowlands along the Uttar Pradesh border in a belt locally known as Bhabar
Bhabar or Bhabhar is a region south of the Lower Himalayas and the Sivalik Hills in Garhwal and Kumaon, India. The Bhabhar region contains some of the largest cities of Kumaon and Garhwal: Dehradun, Haridwar, Haldwani, Rishikesh, Ramnagar ...
. These lowland forests have mostly been cleared for agriculture, but a few pockets remain.
Climate
Uttarakhand has atemperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
but varies greatly from north to south. The climatic conditions experienced in the state vary subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones immediately to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Ge ...
in the southern part to alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
in the upper reaches of the Himalayan mountain in the northern parts. The winter season from December to February, is extreme with temperatures fluctuating anywhere between to . In higher altitudes and mountainous regions, temperatures often drop below freezing point. Cold winds blow across Uttarakhand, especially in the higher altitudes and mountainous regions. These winds bring cold temperatures and often carry moisture, contributing to the heavy snowfall in places like the Himalayan ranges and hill stations.
During Pre-monsoon or hot weather season from March to May, temperature starts to rise and steadily rises till it reaches its peak in May to the middle of June, when the mean maximum temperature in southern parts and valleys of the state is at about C to and mean minimum temperature is at about to C. June to September constitutes the southwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
season and the period of October and November is of post monsoon season. The state receives rainfall mainly due monsoon depressions originating in the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
during the southwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
season. The total annual rainfall for the state as a whole is 133 cm and total annual number of rainy days are about 63 cm. Although, rainfall in the state varies from place to place due to its rugged topography. Precipitation is not heavy and occurs in the form of rain and snow. Winds are generally light of the order of 1 to 4 kmph in the valleys and 5 to 10 kmph at elevations of 2 km increasing further with higher altitudes.
Flora and fauna
Uttarakhand has a diversity of flora and fauna. It has a recorded forest area of , which constitutes 65% of the total area of the state. The vegetation of the state majorly comprises alpine trees and tropical rainforests. The state is home to rare species of plants and animals, many of which are protected by sanctuaries and reserves.National parks
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
in Uttarakhand include the Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willi ...
(the oldest national park of India) in Nainital
Nainital (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a town and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the Uttarakhand High Court, High Court of the state being ...
and Pauri Garhwal District
Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is ...
, and Valley of Flowers National Park
Valley of Flowers National Park https://valleyofflower.uk.gov.in is an Indian national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of endemic alpine flowers and the varie ...
& Nanda Devi National Park
The Nanda Devi National Park or Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve, established in 1982 is a national park situated around the peak of Nanda Devi (7816 m) in Chamoli Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, in northern India. The entire park lies at an elev ...
in Chamoli District
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by China's Xizang Autonomous Region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Bageshwar district, Bageshwar to the eas ...
, which together are a UNESCO World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
. A number of plant species in the valley are internationally threatened, including several that have not been recorded from elsewhere in Uttarakhand. Rajaji National Park
Rajaji National Park is a national park and tiger reserve in the Haridwar, Dehradun and Pauri Garhwal districts of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It encompasses an area of in the Sivalik Hills. In 1983, three wildlife sanctuaries in th ...
in Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
, Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
and Pauri Garhwal District
Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is ...
and Govind Pashu Vihar National Park & Gangotri National Park
Gangotri National Park is a national park in Uttarkashi District in Uttarakhand state of India, covering about . Its habitat consists of coniferous forests, alpine meadows and glaciers. Gomukh at Gangotri glacier, the origin of the river Gang ...
in Uttarkashi District are some other protected areas in the state.
Bengal tigers
The Bengal tiger is a population of the '' Panthera tigris tigris'' subspecies and the nominate tiger subspecies. It ranks among the largest wild cats alive today. It is estimated to have been present in the Indian subcontinent since the Late ...
and leopards
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a ...
are found in areas that are abundant in hills but may also venture into the lowland jungles. Smaller felines include the jungle cat
The jungle cat (''Felis chaus''), also called reed cat and swamp cat, is a medium-sized cat native from the Eastern Mediterranean region and the Caucasus to parts of Central, South and Southeast Asia. It inhabits foremost wetlands like swamps, ...
, fishing cat
The fishing cat (''Prionailurus viverrinus'') is a medium-sized wild cat of South and Southeast Asia. It has a deep yellowish-grey fur with black lines and spots. Adults have a head-to-body length of , with a long tail. Males are larger than f ...
, and leopard cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a Felinae, small wild cat native to continental South Asia, South, Southeast Asia, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely di ...
. Other mammals include four kinds of deer (barking
Barking may refer to:
Places
* Barking, London, a town in East London, England
** London Borough of Barking, 1965–1980
** Municipal Borough of Barking, 1931–1965
** Barking (UK Parliament constituency)
** Barking (electoral division), Greater ...
, sambar, hog and chital
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also called spotted deer, chital deer and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben in 1777. A moderate-sized deer, mal ...
), sloth
Sloths are a Neotropical realm, Neotropical group of xenarthran mammals constituting the suborder Folivora, including the extant Arboreal locomotion, arboreal tree sloths and extinct terrestrial ground sloths. Noted for their slowness of move ...
, Brown
Brown is a color. It can be considered a composite color, but it is mainly a darker shade of orange. In the CMYK color model used in printing and painting, brown is usually made by combining the colors Orange (colour), orange and black.
In the ...
and Himalayan black bears, Indian grey mongoose
The Indian grey mongoose or Asian grey mongoose (''Urva edwardsii'') is a mongoose species native to the Indian subcontinent and West Asia. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
The grey mongoose inhabits open forests, scrubland ...
s, otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among ...
s, yellow-throated martens, bharal
The bharal (''Pseudois nayaur''), also called the blue sheep, is a Caprinae, caprine native to the high Himalayas. It is the monotypic taxon, only member of the genus ''Pseudois.'' It occurs in Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and in Ch ...
, Indian pangolin
The Indian pangolin (''Manis crassicaudata''), also called thick-tailed pangolin and scaly anteater, is a pangolin native to the Indian subcontinent.
Like other pangolins, it has large, overlapping Scale (zoology), scales on its body which act as ...
s, and langur
The Colobinae or leaf-eating monkeys are a subfamily of the Old World monkey family that includes 61 species in 11 genera, including the black-and-white colobus, the large-nosed proboscis monkey, and the gray langurs. Some classifications split ...
and rhesus monkeys. In the summer, elephants
Elephants are the Largest and heaviest animals, largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian ele ...
can be seen in herd
A herd is a social group of certain animals of the same species, either wild or domestic. The form of collective animal behavior associated with this is called '' herding''. These animals are known as gregarious animals.
The term ''herd'' ...
s of several hundred. Marsh crocodile
The mugger crocodile (''Crocodylus palustris'') is a medium-sized broad-snouted crocodile, also known as mugger and marsh crocodile. It is native to freshwater habitats from south-eastern Iran to the Indian subcontinent, where it inhabits marsh ...
s (''Crocodylus palustris''), gharial
The gharial (''Gavialis gangeticus''), also known as gavial or fish-eating crocodile, is a crocodilian in the family (biology), family Gavialidae and among the longest of all living crocodilians. Mature females are long, and males . Adult males ...
s (''Gavialis gangeticus'') and other reptiles are also found in the region. Local crocodiles were saved from extinction by captive breeding programs and subsequently re-released into the Ramganga
Ramganga is a tributary of the river Ganges, originating in Uttarakhand state, India.
Ramganga West
Ramganga West River originates from Dudhatoli or Doodhatoli ranges
Course
The Ramganga River originates in the southern slopes of Dudhato ...
river. Several freshwater terrapins and turtles like the Indian sawback turtle (''Kachuga tecta''), brahminy river turtle
The brahminy river turtle or crowned river turtle (''Hardella thurjii'') is a species of turtle in the family Geoemydidae. The species is endemic to South Asia.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Hardella'', to which the species ''Hardella thurjii'' belongs, ...
(''Hardella thurjii''), and Ganges softshell turtle (''Trionyx gangeticus'') are found in the rivers. Butterflies and birds of the region include red helen (''Papilio helenus''), the great eggfly
''Hypolimnas bolina'', the great eggfly, common eggfly, varied eggfly, or in New Zealand the blue moon butterfly, is a species of nymphalid butterfly found from Madagascar to Asia and Australia.
Appearance Race ''bolina''
''H. bolina'' is a bla ...
(''Hypolimnos bolina''), common tiger (''Danaus genutia''), pale wanderer (''Pareronia avatar''), jungle babbler
The jungle babbler (''Argya striata'') is a member of the family Leiothrichidae found in the Indian subcontinent. Jungle babblers are gregarious birds that forage in small groups of six to ten birds, a habit that has given them the popular name ...
, tawny-bellied babbler
The tawny-bellied babbler (''Dumetia hyperythra'') also known in older Indian works as the rufous-bellied babbler is a small babbler that forages in small groups in low scrub forests. Like other members of the large Old World babbler family they ...
, great slaty woodpecker, red-breasted parakeet
The red-breasted parakeet (''Psittacula alexandri'') is a parrot native to Southeast Asia. It is among the more widespread species of the genus and is the species which has the most geographical variations. It is easily identified by the large re ...
, orange-breasted green pigeon
The orange-breasted green pigeon (''Treron bicinctus'') is a Dove, pigeon found across tropical Asia south of the Himalaya across parts of the Indian Subcontinent and Southeast Asia. Like other green pigeons, it feeds mainly on small fruit. They ...
and chestnut-winged cuckoo. In 2011, a rare migratory bird, the bean goose
The bean goose is a species complex of goose that breeds in northern Europe and Palearctic, Eurosiberia. It has at least two distinct varieties, one inhabiting taiga habitats and one inhabiting tundra. These are recognised as separate species by ...
, was also seen in the Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willi ...
. A critically endangered bird, last seen in 1876 is the Himalayan quail endemic to the western Himalayas of the state.
Evergreen oaks
Live oak or evergreen oak is any of a number of oaks in several different sections of the genus ''Quercus'' that share the characteristic of evergreen foliage. These oaks are generally not more closely related to each other than they are to ot ...
, rhododendrons
''Rhododendron'' (; : ''rhododendra'') is a very large genus of about 1,024 species of woody plants in the heath family (Ericaceae). They can be either evergreen or deciduous. Most species are native to eastern Asia and the Himalayan region, b ...
, and conifers
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
predominate in the hills. Prunus cerasoides
''Prunus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs from the family Rosaceae. The genus includes plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots and almonds (collectively stonefruit). The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, being native to ...
(pahiyya), '' sal'' (''Shorea robusta''), silk cotton tree Silk-cotton tree is a common name for several plants and may refer to:
*''Bombax ceiba'', native to the Asian tropics
*''Ceiba pentandra'', native to the American tropics and west Africa
*''Cochlospermum religiosum
''Cochlospermum religiosum'' i ...
(''Bombax ciliata''), ''Dalbergia sissoo
''Dalbergia sissoo'', known commonly as North Indian rosewood or shisham, is a fast-growing, hardy, deciduous rosewood tree native to the Indian subcontinent and southern Iran. ''D. sissoo'' is a large, crooked tree with long, leathery leaves a ...
'', ''Mallotus philippensis
''Mallotus philippensis'' is a plant in the spurge family. It is known as the kamala tree or red kamala or kumkum tree, due to the fruit covering, which produces a red dye. However, it must be distinguished from kamala meaning "lotus" in many In ...
'', ''Acacia catechu
''Senegalia catechu'', previously known as ''Acacia catechu'', is a deciduous, thorny tree which grows up to in height. The plant is called ''kachu'' in Malay; the Malay name was Latinized to "catechu" in Linnaean taxonomy, as the species from ...
'', ''Bauhinia racemosa
''Bauhinia racemosa'', commonly known as the bidi leaf tree, is a rare medicinal species of flowering shrub with religious significance. It is a small crooked tree with drooping branches that grows tall and flowers between February and May. It i ...
'', and ''Bauhinia variegata
''Bauhinia variegata'' is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It is native to an area from China through Southeast Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Common names include orchid tree (though not belonging to the family Or ...
'' (camel's foot tree) are some other trees of the region. ''Albizia chinensis
''Albizia chinensis'' is a species of legume in the genus ''Albizia'', native to south and Southeast asia, from India to China and Indonesia.
The genus is named after the Italy, Italian nobleman Filippo degli Albizzi, belonging to the famous Flo ...
'', the sweet sticky flowers of which are favoured by sloth bears, are also part of the region's flora.
A decade long study by Prof. Chandra Prakash Kala
Chandra Prakash Kala is an Indian ecologist and professor. His research interests include alpine ecology, conservation biology, indigenous knowledge systems, ethnobotany and medicinal aromatic plants. He is an assistant professor in the facu ...
concluded that the Valley of Flowers is endowed with 520 species of higher plants (''angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit ...
s'', ''gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( ; ) are a group of woody, perennial Seed plant, seed-producing plants, typically lacking the protective outer covering which surrounds the seeds in flowering plants, that include Pinophyta, conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and gnetoph ...
s'' and ''pteridophyte
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that reproduces by means of spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as " cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is ...
s''), of these 498 are flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s. The park has many species of medicinal plants including ''Dactylorhiza hatagirea
''Dactylorhiza hatagirea'' is a species of orchid generally found growing in the Himalayas, from Pakistan to SE Tibet, at altitudes of . It is locally called 'salam panja' or 'hatta haddi'. It is called 'panchaule' (पाँचऔंले) in ...
'', ''Picrorhiza kurroa
''Picrorhiza kurroa'' is one of the major income generating non-timber forest products found in the Nepalese Himalayas. It is one of the oldest medicinal plants traded from the Karnali zone. Known as kutki or कुटकी in Nepali, it is a pe ...
'', ''Aconitum violaceum
''Aconitum violaceum'' is a species of perennial plant distributed in the Himalayan region of India, Pakistan, and Nepal. Within India, it has been recorded in the alpine slopes in an altitude range of . The plant is used in traditional Tibetan m ...
'', ''Polygonatum multiflorum
''Polygonatum multiflorum'', the Solomon's seal, David's harp, ladder-to-heaven or Eurasian Solomon's seal, is a species of flowering plant in the family (biology), family Asparagaceae, native plant, native to Europe and temperateness, temperate ...
'', '' Fritillaria roylei'', and ''Podophyllum hexandrum
''Sinopodophyllum'' is a herbaceous perennial plant in the family Berberidaceae, described as a genus in 1979. It includes only one known species, ''Sinopodophyllum hexandrum'', native to Afghanistan, Bhutan, northern India, Kashmir, Nepal, Paki ...
''.
In the summer season of 2016, a large portion of forests in Uttarakhand caught fires and rubbled to ashes during Uttarakhand forest fires incident, which resulted in the damage of forest resources worth billions of rupees and death of 7 people with hundreds of wild animals died during fires. During the 2021 Uttarakhand forest fires, there was widespread damage to the forested areas in Tehri district.
A number of native plants are deemed to be of medicinal value. The government-run Herbal Research and Development Institute carries out research and helps conserve medicinal herbs that are found in abundance in the region. Local traditional healers still use herbs, in accordance with classical Ayurvedic
Ayurveda (; ) is an alternative medicine system with historical roots in the Indian subcontinent. It is heavily practised throughout India and Nepal, where as much as 80% of the population report using ayurveda. The theory and practice of ayur ...
texts, for diseases that are usually cured by modern medicine.
Golden Mahseer
''Tor putitora'', the golden mahseer, putitor mahseer, or Himalayan mahseer, is an endangered species of cyprinid fish that is found in rapid streams, riverine pools, and lakes in the Himalayan region. Its native range is within the basins of t ...
(''Tor putitora'')
File:Brännässla (Urtica Dioica).jpg, Kandali (''Urtica dioica'')
Davidraju Common peacock-shillong.jpg, West Himalayan Common Peacock (''Papilio bianor polyctor'')
File:Wild Himalaya Cherry's blooming at Doi suthep-pui national park.jpg, Paiyya (Prunus cerasoides)
Himalayan Monal, Male (28466143101).jpg, Himalayan Monal
The Himalayan monal (''Lophophorus impejanus''), also called Impeyan monal and Impeyan pheasant, is a pheasant native to Himalayan forests and shrublands at elevations of . It is part of the family Phasianidae and is listed as Least Concern on th ...
(''Lophophorus impejanus'')
Demographics
The native people of Uttarakhand are generally called Uttarakhandi and sometimes specifically either Garhwali or Kumaoni depending on their place of origin in either theGarhwal
Garhwal may refer to the following topics associated with Uttarakhand, India:
Places
*Garhwal Himalaya, a sub-range of the Himalayas
*Garhwal Kingdom, a former kingdom
*Garhwal District (British Garhwal), a former district of British India
* Ga ...
or Kumaon region. According to the 2011 Census of India, Uttarakhand has a population of 10,086,292 comprising 5,137,773 males and 4,948,519 females, with 69.77% of the population living in rural areas. The state is the 20th most populous state of the country having 0.83% of the population on 1.63% of the land. The population density of the state is 189 people per square kilometre having a 2001–2011 decadal growth rate of 18.81%. The gender ratio is 963 females per 1000 males. The crude birth rate in the state is 18.6 with the total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
being 2.3. The state has an infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of an infant before the infant's first birthday. The occurrence of infant mortality in a population can be described by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the number of deaths of infants under one year of age ...
of 43, a maternal mortality rate
Maternal death or maternal mortality is defined in slightly different ways by several different health organizations. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines maternal death as the death of a pregnant mother due to complications related to p ...
of 188 and a crude death rate of 6.6.
Social groups
Uttarakhand has a multiethnic population spread across two geocultural regions: Garhwal, and Kumaon. A large portion of the population isRajput
Rājpūt (, from Sanskrit ''rājaputra'' meaning "son of a king"), also called Thākur (), is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating fro ...
(various clans of erstwhile landowning rulers and their descendants), including members of the native Garhwalis
The Garhwali people are an Indian ethnolinguistic group native to the Garhwal, in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, who speak Garhwali, an Indo-Aryan language.
Etymology
In modern usage, "Garhwali" is used to refer to anyone whose linguistic ...
, Kumaonis and Gurjar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
s as well as a number of migrants. According to a 2007 study by Centre for the Study of Developing Societies
The Centre for the Study of Developing Societies (CSDS) is an Indian research institute for social sciences and humanities. It was founded in 1963 by Rajni Kothari and is largely funded by the Indian Council of Social Science Research.
, Uttarakhand has the highest percentage of Brahmin
Brahmin (; ) is a ''Varna (Hinduism), varna'' (theoretical social classes) within Hindu society. The other three varnas are the ''Kshatriya'' (rulers and warriors), ''Vaishya'' (traders, merchants, and farmers), and ''Shudra'' (labourers). Th ...
s of any state in India, with approximately 20% of the population. Uttarakhand is among the few Indian states where the historic Upper Caste forms a major share of the population.
Of the rest 18.3% of the population is classified as Other Backward Classes (OBCs) Gurjar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
s majorly. 18.76% of the population belongs to the Scheduled Castes (an official term for the lower castes in the traditional caste system in India
The caste system in India is the paradigmatic ethnographic instance of social classification based on castes. It has its origins in ancient India, and was transformed by various ruling elites in medieval, early-modern, and modern India, espe ...
). Scheduled Tribes such as the Jaunsaris
The Jaunsari are a small community found in Uttarakhand, northern India, more specifically in the Jaunsar-Bawar region of the western portion of the state in Garhwal Division. They speak the Jaunsari language which is an Indo-Aryan language.
C ...
, Bhotiyas, Tharus
The Tharu people are an ethnic group living in the Terai in southern Nepal and northern India. They speak Tharu languages. They are recognized as an official ethnicity by the Government of Nepal. In the Indian Terai, they live foremost in Uttara ...
, Buksas, Rajis
The Raji people are a community found in Uttarakhand, India and some parts of western Nepal. , the Raji people are classified as a Scheduled Tribe under the Indian government's reservation program of positive discrimination.
They call themselve ...
, Jads, and Banrawats
The Banrawats (alt., ''Banrajis'', ''Vanrawats'', ''Vanrajis'') are a native endangered ethnic minority group, originating and living in Uttarakhand, India. They are distributed in the districts of Pithoragarh, Champawat and Udham Singh Nagar a ...
constitute 2.89% of the population. Several non-scheduled tribal groups such as Shaukas and Gurjar
The Gurjar (or Gujjar, Gujar, Gurjara) are an agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan, and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic ...
s are also found here. Van Gurjars (found in Shivalik hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas.
The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Paleo ...
) and Bhotiya
Bhotiya or Bhot (, ) is an Indian and Nepali exonym lumping together various ethnic groups speaking Tibetic languages, as well as some groups speaking other Tibeto-Burman languages living in the Transhimalayan region that divides India from T ...
are nomadic tribes while Jaunsaris
The Jaunsari are a small community found in Uttarakhand, northern India, more specifically in the Jaunsar-Bawar region of the western portion of the state in Garhwal Division. They speak the Jaunsari language which is an Indo-Aryan language.
C ...
are completely settled tribe.
Languages
The official language of Uttarakhand isHindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
, which according to the 2011 census is spoken natively by % of the population, Figures for Jaunsari also include speakers of Jaunpuri. and also used throughout the state as a lingua franca.
The major regional languages of Uttarakhand are Garhwali, which according to the 2011 census is spoken by % of the population, mostly in the western half of the state, Kumaoni, spoken in the eastern half and native to %, and Jaunsari, whose speakers are concentrated in Dehradun district in the southwest and make up % of the state's population. These three languages are closely related, with Garhwali and Kumaoni in particular making up the Central Pahari
The Northern Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Pahāṛi languages, are a proposed group of Indo-Aryan languages spoken in the lower ranges of the Himalayas, from Nepal in the east, through the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, Uttarakha ...
language subgroup. The languages have been part of various scattered conservation efforts due to their active decline beginning in the later quarter of the 20th century. The decline is hypothesized to be the result of heavy state-sponsored promotion of Hindi as the official language.
All the languages enumerated so far belong to the Indo-Aryan family. Apart from a few other minority Indo-Aryan languages, like Buksa Tharu and Rana Tharu (of Udham Singh Nagar district in the south-east), Mahasu Pahari
Mahasu Pahari (Takri: ) is a Western Pahari language spoken in Himachal Pradesh. It is also known as Mahasui or Mahasuvi. The speaking population is about 1,000,000 (2001). It is more commonly spoken in the Himachal Pradesh, Shimla (Simla) and Sol ...
(found in Uttarkashi in the north-west), and Doteli
Doteli, or Dotyali ( Doteli-Devanagari: ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 495,000 people, most of whom live in Nepal. It is a dialect of Khas, which is an ancient form of the modern Nepali language
Nepali (; , ), or ''Gorkhali'' ...
, Uttarakhand is also home to a number of indigenous Sino-Tibetan languages
Sino-Tibetan (also referred to as Trans-Himalayan) is a family of more than 400 languages, second only to Indo-European in number of native speakers. Around 1.4 billion people speak a Sino-Tibetan language. The vast majority of these are the 1.3 ...
, most of which are spoken in the north of the state. These include Jad (spoken in Uttarkashi district in the north-west), Rongpo (of Chamoli district), and several languages of Pithoragarh district in the north-east: Byangsi, Chaudangsi, Darmiya, Raji and Rawat. Another indigenous Sino-Tibetan language, Rangas, became extinct by the middle of the 20th century. Additionally, two non-indigenous Sino-Tibetan languages are also represented: Kulung Kulung may refer to:
* Kulung people, an ethnic group of Nepal
* Kulung language (Nepal)
Kulung (autonym: ''Kulu riŋ'', ulu rɪŋ is one of the Kiranti languages. It is spoken by an estimated 33,000 people. Van Driem (2001) includes Chukwa as ...
(otherwise native to Nepal) and Tibetan
Tibetan may mean:
* of, from, or related to Tibet
* Tibetan people, an ethnic group
* Tibetan language:
** Classical Tibetan, the classical language used also as a contemporary written standard
** Standard Tibetan, the most widely used spoken dial ...
.
The Indian classical language Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
has been declared a second official language, by the BJP government for its allegedly historic association with the region. At present the language has no native speakers and its use is constrained to educational and religious settings.
There are also sizeable populations of speakers of some of India's other major languages: Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
(%) and Punjabi
Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan
* Punjabi language
* Punjabis, Punjabi people
* Punjabi dialects and languages
Punjabi may also refer to:
* Punjabi (horse), a ...
(%), both mostly found in the southern districts, Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
(%) and Bhojpuri
Bhojpuri may refer to:
* Bhojpuri language, an Indo-Aryan language of India and Nepal
* Bhojpuri grammar, grammatical rules of the language
* Bhojpuri nouns, nouns of the language
* Bhojpuri people, people who speak the language
* Bhojpuri region ...
(%), both mainly present in Udham Singh Nagar district in the south-east, and Nepali (%, found throughout the state, but most notably in Dehradun and Uttarkashi).
Religion
More than four-fifths of Uttarakhand's residents areHindus
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
. Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, Sikhs
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Sikh'' ...
, Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
s, and Jains make up the remaining population, with the Muslims being the largest minority. Hill regions are almost entirely Hindu, while the plains regions have a significant minority of Muslims and Sikhs.
Administrative divisions
 is divided into 13
is divided into 13 districts
A district is a type of administrative division that in some countries is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions ...
under two divisions viz. Kumaon and Garhwal
Garhwal may refer to the following topics associated with Uttarakhand, India:
Places
*Garhwal Himalaya, a sub-range of the Himalayas
*Garhwal Kingdom, a former kingdom
*Garhwal District (British Garhwal), a former district of British India
* Ga ...
. Each division is administered by a divisional commissioner
A Divisional Commissioner, also known as Commissioner of division, is an Indian Administrative Service officer who serves as the administrator of a division of a state in India. The post is referred to as regional commissioner in Karnataka
...
. Four new districts named Didihat, Kotdwar, Ranikhet, and Yamunotri were declared by then Chief Minister of Uttarakhand, Ramesh Pokhriyal
Ramesh Pokhriyal "Nishank" (born 15 July 1959), is an Indian politician from Bhartiya Janta Party. He served as the Human Resource Development Minister in the Union Government of India starting from 31 May 2019. The name of his ministry was cha ...
, on 15 August 2011 but yet to be officially formed.
Each district is administered by a district magistrate
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
. The districts are further divided into sub-divisions, which are administered by sub-divisional magistrate
A sub-divisional magistrate, also known as assistant collector, sub collector, revenue divisional officer, or assistant commissioner, is the administrative head of a sub-division in an Indian district, exercising executive, revenue, and magist ...
s; sub-divisions comprise tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluk, or taluka () is a local unit of administrative division in India and Pakistan. It is a subdistrict of the area within a Zila (country subdivision), district including the designated populated place that ser ...
s which are administered by a tehsildar
In Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan, a tehsildar, talukdar, or mamlatdar is a land revenue officer accompanied by revenue inspectors. They are in charge of obtaining taxes from a tehsil with regard to land revenue. A tehsildar is also known as a ...
and community development block
In India, a community development block (CD block) or simply Block is a sub-division of District, administratively earmarked for planning and development. In tribal areas, similar sub-divisions are called tribal development blocks (TD blocks). T ...
s, each administered by a block development officer
A block is an administrative division of some South Asian countries.
Bhutan
In Bhutan, a block is called a gewog. It is essentially for oil a group of villages. Gewogs are official administrative units of Bhutan. The country is composed of ...
.
Urban areas
An urban area is a human settlement with a high population density and an infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas originate through urbanization, and researchers categorize them as cities, towns, conurbations or suburbs. In urbani ...
are categorised into three types of municipalities based on their population; municipal corporations
Municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally ow ...
, each administered by a municipal commissioner, municipal councils and, nagar panchayat
A nagar panchayat () or town panchayat or Notified Area Council (NAC) in India is a settlement in transition from rural to urban and therefore a form of an urban political unit comparable to a municipality. An urban centre with more than 12,00 ...
s (town councils), each of them administered by a chief executive officer
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a chief executive or managing director, is the top-ranking corporate officer charged with the management of an organization, usually a company or a nonprofit organization.
CEOs find roles in variou ...
. Rural areas
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry are typically descri ...
comprise the three tier administration; district councils, block panchayats (block councils) and gram panchayats (village councils). All state and local government offices have a five-year term.
According to the 2011 census, Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
, and Udham Singh Nagar
Udham Singh Nagar is a district of Uttarakhand state in northern India. Rudrapur, Uttarakhand, Rudrapur is the district headquarter. The district consists of nine Tehsils named Bajpur, Gadarpur, Jaspur, Kashipur, Uttarakhand, Kashipur, Khatima, ...
are the most populous districts, each of them having a population of over one million.
Government and administration
Following theConstitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India, legal document of India, and the longest written national constitution in the world. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures ...
, Uttarakhand, like all Indian states, has a parliamentary system
A parliamentary system, or parliamentary democracy, is a form of government where the head of government (chief executive) derives their Election, democratic legitimacy from their ability to command the support ("confidence") of a majority of t ...
of representative democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy or electoral democracy, is a type of democracy where elected delegates represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies func ...
. The Legislative Assembly is unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature consisting of one house or assembly that legislates and votes as one. Unicameralism has become an increasingly common type of legislature, making up nearly ...
consists of 70 members who are elected for five-year terms. Assembly meetings are presided over by the Speaker
Speaker most commonly refers to:
* Speaker, a person who produces speech
* Loudspeaker, a device that produces sound
** Computer speakers
Speaker, Speakers, or The Speaker may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* "Speaker" (song), by David ...
, or the Deputy Speaker in the Speaker's absence. The Uttarakhand Council of Ministers
The Uttarakhand Council of Ministers is the executive wing of Government of Uttarakhand and headed by Chief Minister of Uttarakhand, who is the head of government and leader of the state cabinet. The term of every executive wing is for five ye ...
is appointed by the Governor of Uttarakhand on the advice of the Chief Minister of Uttarakhand and reports to the Legislative Assembly. Leader of the Opposition
The Leader of the Opposition is a title traditionally held by the leader of the Opposition (parliamentary), largest political party not in government, typical in countries utilizing the parliamentary system form of government. The leader of the ...
leads the Official Opposition
Parliamentary opposition is a form of political opposition to a designated government, particularly in a Westminster-based parliamentary system. This article uses the term ''government'' as it is used in Parliamentary systems, i.e. meaning ''t ...
in the Legislative Assembly. The state contributes five seats to Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
, the lower house of the Indian Parliament
The Parliament of India (ISO: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Government of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The President o ...
, and three seats to Rajya Sabha
Rajya Sabha (Council of States) is the upper house of the Parliament of India and functions as the institutional representation of India’s federal units — the states and union territories.https://rajyasabha.nic.in/ It is a key component o ...
, the upper house.
The Government of Uttarakhand
The Government of Uttarakhand also known as the State Government of Uttarakhand, or locally as State Government, is the subnational government of the Indian state of Uttarakhand and its 13 Districts. It consists of an executive branch, led ...
is a democratically
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitiv ...
elected body in India with the governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
as its constitutional head and is appointed by the president of India
The president of India (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the head of state of the Republic of India. The president is the nominal head of the executive, the first citizen of the country, and the commander-in-chief, supreme commander of the Indian Armed ...
for a five-year term. The leader of the party or coalition with a majority in the Legislative Assembly is appointed as the chief minister
A chief minister is an elected or appointed head of government of – in most instances – a sub-national entity, for instance an administrative subdivision or federal constituent entity. Examples include a state (and sometimes a union ter ...
by the governor, and the council of ministers is appointed by the governor on the advice of the chief minister. The governor remains a ceremonial head of the state, while the chief minister and his council are responsible for day-to-day government functions. The Council of Ministers consists of Cabinet Ministers
A cabinet in governing is a group of people with the constitutional or legal task to rule a country or state, or advise a head of state, usually from the executive branch. Their members are known as ministers and secretaries and they are ...
and Ministers of State
Minister of state is a designation for a government minister, with varying meanings in different jurisdictions. In a number of European countries, the title is given as an honorific conferring a higher rank, often bestowed upon senior ministers ...
(MoS). The Secretariat headed by the Chief Secretary assists the council of ministers. The Chief Secretary is also the administrative head of the government. Each government department is headed by a minister, who is assisted by an Additional Chief Secretary
The Chief Secretary is the highest-ranking executive official and civil servant of the government of an Indian state. The Chief Secretary is the ''ex-officio'' head of the state Civil Services Board, the State Secretariat, the state cadre Indi ...
or a Principal Secretary, who is usually an officer of Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the Public administration, administrative arm of the All India Services of Government of India. The IAS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Police Service (IPS) and the Indian ...
(IAS), the Additional Chief Secretary/Principal Secretary serves as the administrative head of the department they are assigned to. Each department also has officers of the rank of Secretary, Special Secretary, Joint Secretary etc. assisting the Minister and the Additional Chief Secretary
The Chief Secretary is the highest-ranking executive official and civil servant of the government of an Indian state. The Chief Secretary is the ''ex-officio'' head of the state Civil Services Board, the State Secretariat, the state cadre Indi ...
/ Principal Secretary.
For administration, the state is divided into two divisions and 13 districts. Divisional Commissioner
A Divisional Commissioner, also known as Commissioner of division, is an Indian Administrative Service officer who serves as the administrator of a division of a state in India. The post is referred to as regional commissioner in Karnataka
...
, an IAS officer is the head of administration on the divisional level. The administration in each district is headed by a District Magistrate
The district magistrate, also known as the district collector or deputy commissioner, is a career civil servant who serves as the executive head of a district's administration in India. The specific name depends on the state or union territo ...
, who is also an IAS officer, and is assisted by several officers belonging to state services. District Magistrate being the head of the district administration, is responsible for maintaining law and order and providing public services in the district. At the block level, the Block Development Officer (BDO) is responsible for the overall development of the block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
. The Uttarakhand Police
The Uttarakhand Police is the law enforcement agency for the state of Uttarakhand in India. It was formed in 2000.
Uttarakhand Police Constable Notification 2024: The Uttarakhand Subordinate Selection Commission (UKSSSC) has published an offi ...
is headed by an IPS officer of the rank of Director general of police. A Superintendent of Police
Superintendent (Supt) is a rank in the British police and in most English-speaking Commonwealth nations. In many Commonwealth countries, the full version is superintendent of police (SP). The rank is also used in most British Overseas Territori ...
, an IPS officer assisted by the officers of the Uttarakhand Police Service, is entrusted with the responsibility of maintaining law and order and related issues in each district. The Divisional Forest Officer, an officer belonging to the Indian Forest Service
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is the premier forest service of India. .The IFS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) & the Indian Police Service (IPS). It was constituted in the year 1966 un ...
manages the forests, environment, and wildlife of the district, assisted by the officers of Uttarakhand Forest Service and Uttarakhand Forest Subordinate Service.
The judiciary in the state consists of the Uttarakhand High Court
The Uttarakhand High Court is the High courts of India, High Court of the States and union territories of India, state of Uttarakhand in India. The Uttarakhand High Court was established on 9 November 2000 after the separation of the state of ...
in Nainital
Nainital (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Naintāl''; ) is a town and headquarters of Nainital district of Kumaon division, Uttarakhand, India. It is the judicial capital of Uttarakhand, the Uttarakhand High Court, High Court of the state being ...
, district courts and session courts in each district or Sessions Division, and lower courts at the tehsil
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluk, or taluka () is a local unit of administrative division in India and Pakistan. It is a subdistrict of the area within a Zila (country subdivision), district including the designated populated place that ser ...
level. The president of India appoints the chief justice of the High Court of the Uttarakhand judiciary on the advice of the Chief Justice of the Supreme Court of India
The Supreme Court of India is the supreme judiciary of India, judicial authority and the supreme court, highest court of the Republic of India. It is the final Appellate court, court of appeal for all civil and criminal cases in India. It also ...
as well as the governor of Uttarakhand . Subordinate Judicial Service, categorised into two divisions viz. Uttarakhand civil judicial services and Uttarakhand higher judicial service are another vital part of the judiciary of Uttarakhand . While the Uttarakhand civil judicial services comprise the Civil Judges (Junior Division)/Judicial Magistrates and civil judges (Senior Division)/Chief Judicial Magistrate, the Uttarakhand higher judicial service comprises civil and sessions judges.
The State Politics is heavily dominated by the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; , ) is a political party in India and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. BJP emerged out from Syama Prasad Mukherjee's Bharatiya Jana Sangh. Since 2014, ...
since 2017 with the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first mo ...
as the chief Opposition.
Culture
Architecture and crafts
Mahasu Devta Temple
Mahasu Devta Temple (Mahasu Pahari, Mahasui: 𑚢𑚩𑚭𑚨𑚱 𑚛𑚲𑚦𑚙𑚭 𑚢𑚫𑚛𑚮𑚤, Hindi: महासू देवता मंदिर) is located on the left bank of the River Tons, on a hill slope in the villag ...
at Hanol, notable for its traditional wooden architecture
File:Architectural details of a Dharamshala, estb. 1822, Haridwar.jpg, Architectural details of a Dharamshala
Dharamshala (, ; also spelled Dharamsala) is a town in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. It serves as the winter capital of the state and the administrative headquarters of the Kangra district since 1855. The town also hosts the Tibeta ...
, established 1822, Haridwar  File:Solani Aquaduct Of Ganges Canal.jpg, Solani aqueduct on
File:Solani Aquaduct Of Ganges Canal.jpg, Solani aqueduct on Ganges Canal
The Ganges Canal or Ganga Canal is a canal system that irrigates the Doab region between the Ganges River and the Yamuna River in India.
The canal is primarily an irrigation canal, although parts of it were also used for navigation, primari ...
at Roorkee
Roorkee (Rūṛkī; ) is a city and Municipal Corporations in India, municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is from Haridwar, the district headquarters. It is spread over a flat terrain under the ...
, built during the British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
File:The Deputy Chairman, Planning Commission, Shri K.C. Pant speaking at the releasing of the Uttaranchal crafts map at the exhibition of "Artistic Crafts Maps of Jharkhand.jpg, The releasing of the Uttaranchal crafts map
wood carving
Wood carving (or woodcarving) is a form of woodworking by means of a cutting tool (knife) in one hand or a chisel by two hands or with one hand on a chisel and one hand on a mallet, resulting in a wooden figure or figurine, or in the sculpture, ...
known as '' Likhai'', which appears most frequently in the ornately decorated temples of the Kumaon region in Uttarakhand. Intricately carved designs of floral patterns, deities, and geometrical motifs also decorate the doors, windows, ceilings, and walls of village houses. Paintings and murals are used to decorate both houses and temples.
 Garwhali Miniature painting is a form of miniature painting that flourished in the region between the 17th and 19th century.
Garwhali Miniature painting is a form of miniature painting that flourished in the region between the 17th and 19th century. Mola Ram
Mola Ram or Maula Ram (1743–1833), p.119 was an Indian painter, who originated the Garhwal branch of the Kangra school of painting., pp.75–76 He was also a poet, historian and diplomat., p.25 Mukandi Lal did research on him.
Life and ...
is credited as the true father of the Garhwali Branch of the wider Pahari School. Kumaoni art often is geometrical in nature, while Garhwali art is known for its closeness to nature.
Aipan is a GI certified Kumaoni ritual folk art done mainly during special ceremonies, the festival of Diwali, marriages and other religious rituals. Its predominantly female practitioners believe that it invokes a divine power which brings about good fortune and deters evil. The art is special as it is done on empty walls, which are brick-red in colour, called ''geru''. The actual art is done with a white paste made of rice flour
Rice flour (also rice powder) is a form of flour made from finely milled rice. It is distinct from rice starch, which is usually produced by steeping rice in lye. Rice flour is a common substitute for wheat flour. It is also used as a thickening ...
.
Jyuti patta is a class of water color paintings done on rituals, called Jyuti. Some scholars also consider Jyuti to be synonymous with the word mother of the world. To give concrete form to the deity, two-dimensional geometry is given expression in the form of frescoes. This is a geometric or decorative semi-graphic structure in which different colours and symbols are used. This structure called Jyuti also gets a new dimension by the use of ochre or biswar of Tepan. Jyunti is prepared on the surface of wall or paper and the composition is given with cotton and a brush of limiter. In this artform, various qualities of a specific deity are shown.
Other crafts of Uttarakhand include handcrafted gold jewellery
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 1 ...
, basketry
Basket weaving (also basketry or basket making) is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making baskets ...
from Garhwal, woollen shawls, scarves
A scarf (: scarves or scarfs) is a long piece of fabric that is worn on or around the neck, shoulders, or head. A scarf is used for warmth, sun protection, cleanliness, fashion, religious reasons, or to show support for a sports club or team. ...
, and rugs
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of Pile (textile), pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fiber, synthetic fibres such as polyprop ...
. The latter are mainly produced by the Bhotiyas of northern Uttarakhand.
Arts and literature
Uttarakhand's diverse ethnicities have created a rich literary tradition in languages including Hindi, Garhwali, Kumaoni, Jaunsari, and Tharu. Many of its traditional tales originated in the form of lyricalballad
A ballad is a form of verse, often a narrative set to music. Ballads were particularly characteristic of the popular poetry and song of Great Britain and Ireland from the Late Middle Ages until the 19th century. They were widely used across Eur ...
s and chanted by itinerant singers and are now considered classics of Hindi literature
Hindi literature () includes literature in the various Central Indo-Aryan languages, also known as Hindi, some of which have different writing systems. Earliest forms of Hindi literature are attested in poetry of Apabhraṃśa such as Awad ...
. Abodh Bandhu Bahuguna, Badri Datt Pandey
Pandit Badri Datt Pandey (15 February 1882 – 13 January 1965) was an Indian historian, freedom fighter, social reformer, and later a Member of Parliament from Almora in independent India.
Early life
Badri Datt Pandey was born on 15 Februa ...
, Ganga Prasad Vimal
Ganga Prasad Vimal (also Gangaprasad Vimal) (June 3, 1939 – December 23, 2019) was an Indian writer. He was a poet, story writer, novelist and translator.
Early life and education
Ganga Prasad Vimal was born in 1939 in Uttarkashi, a Himalay ...
; Mohan Upreti, Naima Khan Upreti, Prasoon Joshi
Prasoon Joshi (born 16 September 1971) is an Indian poet, writer, lyricist, screenwriter, communication specialist and marketer. He is the CEO of McCann World group India and Chairman APAC (Asia Pacific), a subsidiary of the global marketing f ...
, Shailesh Matiyani
Ramesh Singh Matiyani 'Shailesh', popularly known as Shailesh Matiyani (14 October 1931 – 24 April 2001),
...
, Shekhar Joshi, ...
Shivani
Gaura Pant (17 October 1923 – 21 March 2003), better known as Shivani, was a Hindi writer of the 20th century and a pioneer in writing Indian women-centric fiction. She was awarded the Padma Shri for her contribution to Hindi literature in ...
, Taradutt Gairola
Tara Dutt Gairola (1875– 1940), was an Indian lawyer, writer, and editor. He is known as the pioneer of modern Garhwali poetry and for his contribution to Indian folk-lore, specially that of Garhwal, Uttarakhand
Uttarakhand (, ), also know ...
, Tom Alter
Thomas Beach Alter (22 June 1950 – 29 September 2017) was an Indian actor. He was best known for his works in Hindi cinema, and Indian theatre. In 2008, he was awarded the Padma Shri by the Government of India.
Early life
Born in Mussoorie ...
; Lalit Kala Akademi fellow – Ranbir Singh Bisht
Ranbir Singh Bisht (1928–1998) was an Indian painter and the Principal of the College of Fine Arts, Lucknow University. Born in 1928 at Landsdowne in Garhwal, in the present day Indian state of Uttarakhand, he secured Drawing Teacher's Trainin ...
; Sangeet Natak Akademi Award
Sangeet Natak Akademi Award (IAST: Saṅgīta Nāṭaka Akādamī Puraskāra), also known as the Akademi Puraskar, is an award given by the Sangeet Natak Akademi, India's National Academy of Music, Dance & Drama. It is the highest Indian recogni ...
ees – B. M. Shah, Narendra Singh Negi
Narendra Singh Negi (born 12 August 1949), also referred as 'Garh Ratna' and 'Bob Dylan of the hills' is one of the most prominent folk singers, composer and a poet of the Garhwal and Uttarakhand who prominently sings in Garhwali language. Repo ...
; Sahitya Akademi Award
The Sahitya Akademi Award is a literary honour in India, which the Sahitya Akademi, India's National Academy of Letters, annually confers on writers of the most outstanding books of literary merit published in any of the 22 languages of the ...
ees – Leeladhar Jagudi, Shivprasad Dabral Charan
Shiv Prasad Dabral (12 November 1912 – 24 November 1999), known by his pen name Charan, was an Indian historian, geographer, academic and writer from Uttarakhand. He is also known as 'Encyclopedia of Uttarakhand'. He started writing from 1931 ...
, Manglesh Dabral, Manohar Shyam Joshi
Manohar Shyam Joshi (9 August 1933 – 30 March 2006) was a Hindi writer, journalist and scriptwriter, most well known as the writer of Indian television's first soap opera, '' Hum Log'' (1984) and his early hits ''Buniyaad'' (1987), '' Kakaji ...
, Ramesh Chandra Shah
Ramesh Chandra Shah is an Indian poet, novelist, critic and the author of Sahitya Academy Award winning novel, ''Vinayak''. He was honoured by the Government of India in 2004 with Padma Shri, the fourth highest Indian civilian award.
Biography
...
, Ruskin Bond
Ruskin Bond (born 19 May 1934) is an Indian author. His first novel, ''The Room on the Roof'', published in 1956, received the John Llewellyn Rhys Prize. Bond has authored more than 500 short stories, essays, and novels which includes 69 books ...
and Viren Dangwal
Viren Dangwal (5 August 1947 – 28 September 2015) was an Indian poet, academic, and journalist. He received several awards for his poetry.
Viren Dangwal was born in 1947 in Kirti Nagar, Tehri Garhwal, Uttarakhand.
Viren Dangwal was associat ...
; Jnanpith Award
The Jnanpith Award is the oldest and the highest Indian literary award presented annually by the Bharatiya Jnanpith to an author for their "outstanding contribution towards literature". Instituted in 1961, the award is bestowed only on Indian ...
ee and Sahitya Akademi fellow Sumitranandan Pant
Sumitranandan Pant (20 May 1900 – 28 December 1977) was an Indian poet. He was one of the most celebrated 20th century poets of the Hindi language and was known for romanticism in his poems which were inspired by nature, people and beauty wi ...
are some major literary, artistic and theatre personalities from the state. prominent philosophers, Indian independence activists and social-environmental activists; Anil Prakash Joshi
Dr. Anil Prakash Joshi is an environmentalist, green activist, and the founder of Himalayan Environmental Studies and Conservation Organization (HESCO), a Dehradun-based voluntary organization. His work includes development of sustainable techno ...
, Basanti Devi, Gaura Devi, Govind Ballabh Pant
Govind Ballabh Pant (10 September 1887 – 7 March 1961) was an Indian freedom fighter and the first chief minister of Uttar Pradesh. Alongside Mahatma Gandhi, Jawaharlal Nehru and Vallabh Bhai Patel, Pant was a key figure in the movement for ...
, Chandi Prasad Bhatt
Chandi Prasad Bhatt (born 23 June 1934) is an Indian environmentalist and social activist, who founded Dasholi Gram Swarajya Sangh (DGSS) in Gopeshwar in 1964, which later became a mother-organization to the Chipko Movement, in which he was o ...
, Deep Joshi
Deep Joshi is an Indian social worker and NGO activist and a recipient of the Magsaysay award in 2009. He is recognised for his leadership in bringing professionalism to the NGO movement in India. He co-founded a non-profit organisation, Profe ...
, Hargovind Pant, Kalu Singh Mahara
Kalu Singh Mahara was an Indian freedom fighter and Kumaoni leader during the first Indian Rebellion of 1857. He is regarded as the first major freedom fighter from the state of Uttarakhand (then part of the United Province)
Kalu Singh Mahara ...
, Kunwar Singh Negi, Mukandi Lal, Nagendra Saklani
Nagendra Saklani (1920-1948) was a Communist Party of India leader who sacrificed his life while trying to defend the liberated Kirt Nagar division of the princely state of Tehri Garhwal from the retake bid by the royal forces of Tehri State on ...
, Sri Dev Suman, Ram Prasad Nautiyal, Sunderlal Bahuguna
Sunderlal Bahuguna (9 January 1927 – 21 May 2021) was an Indian environmentalist and Chipko movement leader. The idea of the Chipko movement was suggested by his wife Vimla Bahuguna and him. He fought for the preservation of forests in the ...
and Vandana Shiva
Vandana Shiva (born 5 November 1952) is an Indian scholar, environmental activist, food sovereignty advocate, ecofeminist and anti-globalization author. Based in Delhi, Shiva has written more than 20 books. She is often referred to as "Ga ...
are also from Uttarakhand.
Cuisine
 The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products.
Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are
The primary food of Uttarakhand is vegetables with wheat being a staple, although non-vegetarian food is also served. A distinctive characteristic of Uttarakhand cuisine is the sparing use of tomatoes, milk, and milk-based products.
Coarse grain with high fibre content is very common in Uttarakhand due to the harsh terrain. Crops most commonly associated with Uttarakhand are Buckwheat
Buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum'') or common buckwheat is a flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae cultivated for its grain-like seeds and as a cover crop. Buckwheat originated around the 6th millennium BCE in the region of what ...
(locally called ''Kotu'' or ''Kuttu'') and the regional crops, ''Maduwa'' and ''Jhangora'', particularly in the interior regions of Kumaon and Garhwal. Generally, either Desi Ghee or Mustard oil
Mustard oil can mean either the pressed oil used for cooking or a pungent essential oil, also known as volatile oil, of the mustard plant. The essential oil results from grinding mustard seed, mixing the grounds with water, and isolating the resu ...
is used for the purpose of cooking food. Simple recipes are made interesting with the use of hash seeds ''Jakhya
Jakhya (Garhwali: जख्या; Urdu: زخیا) (also called ''dog mustard'' or ''wild mustard'') is the seed of the '' Cleome viscosa'' plant used for tempering on culinary dishes. It is mostly grown and consumed in Uttarakhand and in the Te ...
'' as spice, chutney
A chutney () is a spread typically associated with cuisines of the Indian subcontinent. Chutneys are made in a wide variety of forms, such as a tomato relish, a ground peanut garnish, yogurt, or curd, cucumber, spicy coconut, spicy onion ...
made of Bhang
Bhang (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''Bhāṅg'') is an Cannabis edible, edible preparation made from the leaves of the Cannabis (drug), cannabis plant originating from the Indian subcontinent. ''Cannabis sativa'' ...
is also a regional cuisine.
Bal Mithai
Bal mithai ( Kumaoni: बाल मिठाई, ''Bāl Mithai'') is a brown chocolate-like fudge, made with roasted khoya and coated with white balls made of sugar coated roasted poppy seeds. It is a popular sweet from Kumaon, India.
Histor ...
is a popular fudge-like sweet. Other popular dishes include Dubuk, Chains, Kap, Bhatiya, Jaula, Phana, Paliyo, Chutkani and Sei. In sweets; Swal, Ghughut/Khajur, Arsa, Mishri
''Mishri'' () is an Indian Hindi-language television drama series that premiered on 3 July 2024 on Colors TV and streams digitally on JioCinema. Produced by Story Square Productions, it stars Shruti Bhist, Namish Taneja and Megha Chakraborty. ...
, Gatta and Gulgulas are popular.
Many regional variations of Kadhi
Kadhi or karhi is a yogurt-based dish originating from Rajasthan, India. It is made by simmering yogurt with besan (gram flour) and spices until it forms a thick, tangy gravy. It is sometimes mixed with pakoras (deep-fried fritters). It is ...
called ''Jhoi'' or ''Jholi'' is also popular. Another staple of the Kumaon region is a black soybean dal referred to as ''Bhatt'' or ''chudkani''. A grinded dal ''chaisu'' is also popular in the Garhwal region.
The state has a predominant non-vegetarian population, with some estimates suggesting 75% of the population being non-vegetarian. Various boar, chicken, mutton and hare recipes are popular in the region. A popular mutton dish ''bhutwa'', is made from goat intestine and other offcuts.
Dances and music
 The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of
The dances of the region are connected to life and human existence and exhibit myriad human emotions. Langvir Nritya is a dance form for males that resembles gymnastic movements. Barada Nati folk dance is another dance of Jaunsar-Bawar
Jaunsar-Bawar is a hilly region in Garhwal division of Uttarakhand, northern India. It is located in the north-west of Dehradun district, along the border with the state of Himachal Pradesh.
Ethnically, Jaunsar-Bawar comprises two regions, inh ...
, which is practised during some religious festivals. Other well-known dances include Hurka Baul, Jhora-Chanchri, Chhapeli, Thadya, Jhumaila, Pandav, Chauphula, and Chholiya
Chholiya ( Kumaoni) or Hudkeli ( Nepali) is a traditional folk dance form originated in the Kumaon division of the Indian state of Uttarakhand and Sudurpashchim province of Nepal. It has today become a symbol of Kumaoni and Sudurpashchimi ( ...
.
Music is an integral part of the Uttarakhandi culture. Popular types of folk songs include Mangal, Basanti, Khuder and Chhopati. These folk songs are played on instruments including Dhol
Dhol () can refer to any one of a number of similar types of double-headed drum widely used, with regional variations, throughout the Indian subcontinent. Its range of distribution in Indian subcontinent primarily includes northern areas such ...
, Damau
Damau (also ''damaun'', ''dhamu'' or ''dhmuva'') is a single-headed drum instrument that is played extensively in the folk music of Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand in India. It is usually played along with the larger drum, the dhol, according t ...
, Turri, Ransingha
The nansingha or nansinga is a type of natural horn, primitive trumpet made of copper or copper alloys, used in both India and Nepal. The instrument is made of two metal curves, joined to form an "S" shape. It may also be reassembled to form a c ...
, Dholki
''dholak'' is a two-headed hand drum, a folk percussion instrument. The dholak is most commonly recognised in countries such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka, but can also be found amongst the Indo-Diaspora in countries such ...
, Daur, Thali
Thali (meaning "plate" or "tray") or Bhojanam (meaning "full meal") is a round Platter (dishware), platter used to serve food in South Asia, Southeast Asia and the Caribbean. Thali is also used to refer to an Indian-style meal made up of a sel ...
, Bhankora
The bhankora (plural: ''bhankore'') is a type of brass instrument made of copper that is prominently used in the folk music of Uttarakhand in India, especially in the Garhwal region. The instrument is aerophonic and used in religious Garhwal fol ...
, Mandan and Mashakbaja. "Bedu Pako Baro Masa
''Bedu Pako Baro Masa'' ( English: ''Figs do ripen round the year'') is a Kumaoni folk song in Kumaoni language which was composed by Mohan Upreti, B. M. Shah and written by Brijendra Lal Shah. This Kumaoni song was composed, written and fi ...
" is a popular folk song of Uttarakhand with international fame and legendary status within the state. It serves as the cultural anthem of Uttarakhandi people worldwide.
Music is also used as a medium through which the gods are invoked. '' Jagar'' is a form of spirit worship in which the singer, or ''Jagariya'', sings a ballad of the gods, the ballads evoke local deities with allusions to great epics, like Mahabharat
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the '' Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kurukshetra War, a war of succes ...
and Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
, that describe the adventures and exploits of the god being invoked.
B. K. Samant, Basanti Bisht
Dr. Basanti Bisht (born, 1953) is a well known folk singer of Uttarakhand, famous for being the first woman singer of the Jagar folk-form of Uttarakhand. The Jagar form of singing is a way of invoking deities, which is traditionally done by men ...
, Chander Singh Rahi
Chander Singh Rahi (born Chander Singh Negi; 28 March 1942 – 10 January 2016) was a prominent folk singer, balladeer, musician, poet, storyteller, and cultural conservator from Uttarakhand, India.
In recognition of his deep devotion to the m ...
, Girish Tiwari 'Girda', Gopal Babu Goswami, Heera Singh Rana, Jeet Singh Negi
Jeet Singh Negi (2 February 1925 – 21 June 2020) was a music composer, singer, lyricist, writer and director from the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, India. He is considered to be the father of modern Garhwali folk music.
Early life
Jeet Sin ...
, Meena Rana
Meena Rana is an Indian Uttarakhandi singer. She has released many Garhwali and Kumaoni music albums.
Albums
;Utarakhandi albums :
* Chand taro maa
* Meri Khati Mitthi
* Darbar Nirala Sai ka
;Utarakhandi Garhwali albums
* Teri meri Maya
* ...
, Mohan Upreti, Narendra Singh Negi
Narendra Singh Negi (born 12 August 1949), also referred as 'Garh Ratna' and 'Bob Dylan of the hills' is one of the most prominent folk singers, composer and a poet of the Garhwal and Uttarakhand who prominently sings in Garhwali language. Repo ...
and Pritam Bhartwan
Pritam Bhartwan is a folk singer from Uttarakhand, India. In 2019, he was conferred the Padma Shri honour by the president of India, Ram Nath Kovind, for his contribution to the field of traditional folk art. He also known as jagar Samrat in Utt ...
are popular folk singers
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has been ...
and musicians from the state, so are Bollywood
Hindi cinema, popularly known as Bollywood and formerly as Bombay cinema, is primarily produced in Mumbai. The popular term Bollywood is a portmanteau of "Bombay" (former name of Mumbai) and "Cinema of the United States, Hollywood". The in ...
singer Jubin Nautiyal
Jubin Nautiyal (born 14 June 1989) is an Indian playback singer and live performer. In June 2022, he won the IIFA award for "Playback Singer (Male)" for the song "Raataan Lambiyan" from '' Shershaah'' and "Upcoming Male Vocalist of the Year" a ...
and country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. When referring to a specific polity, the term "country" may refer to a sovereign state, state with limited recognition, constituent country, ...
singer Bobby Cash.
Fairs and festivals
The festivals ofKumbh Mela
Kumbh Mela (, ; ) is an important Hinduism, Hindu pilgrimage, celebrated approximately every 6 or 12 years, correlated with the partial or full orbital period, revolution of Jupiter. It is the largest peaceful gathering of people in the w ...
at Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
, Ramlila
Ramlila or Ramleela (; literally 'Rama's lila or play') is any dramatic folk re-enactment of the life of Rama according to the ancient Hindu epic ''Ramayana'' or secondary literature based on it such as the '' Ramcharitmanas''. It particular ...
, Ramman
Hadad (), Haddad, Adad (Akkadian language, Akkadian: Wiktionary:𒀭𒅎, 𒀭𒅎 ''DINGIR, DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur (Sumerian language, Sumerian) was the Weather god, storm- and rain-god in the Canaanite religion, Canaanit ...
of Garhwal
Garhwal may refer to the following topics associated with Uttarakhand, India:
Places
*Garhwal Himalaya, a sub-range of the Himalayas
*Garhwal Kingdom, a former kingdom
*Garhwal District (British Garhwal), a former district of British India
* Ga ...
, the traditions of Vedic chant
The oral tradition of the Vedas () consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedic text ...
ings and Yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
are included in the list of Intangible cultural heritage
An intangible cultural heritage (ICH) is a practice, representation, expression, knowledge, or skill considered by UNESCO to be part of a place's cultural heritage. Buildings, historic places, monuments, and artifacts are cultural property. In ...
of the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
.
*'' Kumauni Holi'', in forms including Baithki Holi, Khari Holi, and Mahila Holi, all of which start from Vasant Panchami
Vasant Panchami , also rendered Vasanta Panchami and Saraswati Puja in honour of the Hindu goddess Saraswati, is a festival that marks the preparation for the arrival of spring. The festival is celebrated in Indian religions in different ways ...
, are festivals and musical affairs that can last almost a month.
*''Almora Dussehra'' is a regional variant of Dussehra, dating back to 1936. It is distinct for burning fifteen distinct effigies, each representing the members of the Hindu mythological villain Ravana's entire bloodline. The effigies are all ornate and exquisitely designed. They are paraded through the city of Almora before finally being set on fire to symbolise the triumph of good over evil.
*''Ramman
Hadad (), Haddad, Adad (Akkadian language, Akkadian: Wiktionary:𒀭𒅎, 𒀭𒅎 ''DINGIR, DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur (Sumerian language, Sumerian) was the Weather god, storm- and rain-god in the Canaanite religion, Canaanit ...
'' is an agro-religious festival and ritual masked theatre endemic to the Garhwali People in the Saloor Dungra village of the Painkhanda Valley in the Chamoli district. The festival serves as an offering to the village deity, Bhumichetrapal or Bhumiyal Devta, in the courtyard of the village temple. Every day of the festival, the Devta takes a round of the village. The festival lasts for ten days during which time the local epic of Rama is sung and masked dances depicting different aspects of life take place in the courtyard of the Bhumiyal Devta's temple.
 *''
*''Haridwar Kumbh Mela
Haridwar Kumbh Mela is a mela, associated with Hinduism and held in the city of Haridwar, India held every 12 years. The exact date is determined according to Hindu astrology: the Mela is held when Jupiter is in Aquarius and the Sun enters A ...
'', one of the major Hindu pilgrimages
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also been u ...
, takes place in Uttarakhand. Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
is one of the four places in India where this mela is organised. Haridwar most recently hosted the Purna Kumbh Mela
Kumbh Mela (, ; ) is an important Hinduism, Hindu pilgrimage, celebrated approximately every 6 or 12 years, correlated with the partial or full orbital period, revolution of Jupiter. It is the largest peaceful gathering of people in the w ...
from Makar Sankranti
Makar(a) Sankrānti (), () also referred to as Uttarāyana, Makara, or simply Sankrānti, is a Hinduism, Hindu observance and a mid-winter harvest festival in India and Nepal. It is typically celebrated on 14 January annually (15 January on a ...
(14 January 2010) to Vaishakh Purnima Snan (28 April 2010). Hundreds of foreigners joined Indian pilgrims in the festival, which is considered the largest religious gathering in the world., The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publis ...
, 14 April 2010
*''Phool-Dei'' is a folk festival which welcomes the spring season in the state. The festival is celebrated on the first day of the Hindu month, Chaitra. In some places, the festival is celebrated as carnival and the celebration goes on for a month. The term 'Dei' refers to a ceremonial pudding which is the key food in this festival that is made from jaggery. White flour and curd are also offered. Young children gather together and go to every house in their village/towns with plates full of rice, jaggery, coconut, green leaves, and flowers. In return, they are presented with blessings and gifts like sweets, jaggery, and money. The wishing and blessing part also include placing flowers and rice on the doorsteps of the houses by the children. People of village sing and dance on their folk songs to celebrate the festival of spring along with exchanging wishes for well-being and prosperity of their family and relatives.
*''Harela'' is a kumaoni festival hypothesized to date back to the indigenous population. 10–11 days before the Sankranti of Shravan, a bed is made by adding soil in bamboo pots etc. Grains grown during the rainy season like paddy, maize, urad etc. are sown, this is called Hariyala. Harakali Mahotsav, Idols of Gauri Maheshwar, Ganesha and Karkitkeya are made from clay, coloured in them and worshiped with various fruits, flowers, dishes and sweets in a bed of greenery on the night of the month of Sanat. On the second day, the Harela of Uttarang Puja is placed on the head. Sisters and daughters-in-law apply tilak and tilak and put Harela on their heads. They are given gifts.
*'' Ganga Dussehra'', Vasant Panchami, Makar Sankranti, Ghee Sankranti, Khatarua, Vat Savitri
Vat Purnima (=, also called ''Vat Savitri'' Vrat) is a Hindu celebration observed by married women in North India and in the Western Indian states of Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat. On this Purnima (full moon) during the three days of the month of Jyes ...
, and Phul Dei (The festival of spring) are other major festivals. In addition, various fairs like Kanwar Yatra
The Kanwar (or Kānvar/ Kāvaḍ) Yātrā is an annual pilgrimage of devotees of Shiva, known as ''Kānvarias'' () or "Bhole" (), to Hindu pilgrimage places of Haridwar, Gaumukh and Gangotri (Uttarakhand) and Ajgaibinath Dham, Ajgaibinath Tem ...
, Kandali Festival
Kandali Festival is a festival held by the Rung tribe of the Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand state in India. This festival coincides with the blooming of the Kandali plant, which flowers once every twelve years. It is held in the Chaunda ...
, Ramman
Hadad (), Haddad, Adad (Akkadian language, Akkadian: Wiktionary:𒀭𒅎, 𒀭𒅎 ''DINGIR, DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur (Sumerian language, Sumerian) was the Weather god, storm- and rain-god in the Canaanite religion, Canaanit ...
, Kauthig, Nauchandi Mela, Giddi Mela, Uttarayani Mela and Nanda Devi Raj Jat
Nanda Devi Raj Jat (lit: ''Nanda Devi Royal Pilgrimage'', hindi: ''नंदा देवी राज जात''), is a three-week-long hindu festival and Kurur to Homkund yatra (pilgrimage) organised once every 12 years in Chamoli District ...
take place.
Economy
The Uttarakhand state is the second fastest growing state in India. Its gross state domestic product (GSDP) (at constant prices) more than doubled from 24,786 crore in FY2005 to 60,898 crore in FY2012. The real GSDP grew at 13.7% (CAGR) during the FY2005–FY2012 period. The contribution of the service sector to the GSDP of Uttarakhand was just over 50% during FY 2012. Per capita income in Uttarakhand is 198738 (FY 2018–19), which is higher than the national average of 126406 (FY 2018–19). According to theReserve Bank of India
Reserve Bank of India, abbreviated as RBI, is the central bank of the Republic of India, and regulatory body responsible for regulation of the Indian banking system and Indian rupee, Indian currency. Owned by the Ministry of Finance (India), Min ...
, the total foreign direct investment in the state from April 2000 to October 2009 amounted to US$46.7 million.
Like most of India, agriculture is one of the most significant sectors of the economy of Uttarakhand. Basmati
Basmati () is a variety of long, slender-grained aromatic rice which originates from the Indian subcontinent, mainly in the regions of Nepal, Punjab, Haryana, Sindh and many other states and provinces of India and Pakistan.oil seeds
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed o ...
are the most widely grown crops. Fruits like apples, oranges, pears, peaches, lychees, and plums are widely grown and important to the large food processing industry. Agricultural export zones have been set up in the state for lychees, horticulture, herbs, medicinal plants, and basmati rice. During 2010, wheat production was 831 thousand tonnes and rice production was 610 thousand tonnes, while the main cash crop of the state, sugarcane, had a production of 5058 thousand tonnes. As 86% of the state consists of hills, the yield per hectare is not very high. 86% of all croplands are in the plains while the remaining is from the hills. The state also holds the GI tag for Tejpatta (Cinnamomum tamala
''Cinnamomum tamala'', Indian bay leaf'','' also known as tejpat'', ''tejapatta'','' Malabar leaf, Indian bark, Indian cassia, or malabathrum, is a tree in the family Lauraceae that is native to northern India (Assam and the Western Himalayas), ...
) or Indian bay leaf, which is known to add flavour to dishes and also possesses several medicinal properties.
Other key industries include tourism and hydropower, and there is prospective development in IT, ITES, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals and automobile industries. The service sector of Uttarakhand mainly includes tourism, information technology, higher education, and banking.
During 2005–2006, the state successfully developed three Integrated Industrial Estates (IIEs) at Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
, Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar District, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Uttarakhand, Kashipur, Rudrapur, Uttarakhand, Rudrapur, Kiccha and Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is hom ...
, and Sitarganj
Sitarganj is a city and a municipal board in Udham Singh Nagar district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Geography
Sitarganj is located at . It has an average elevation of 298 metres (978 feet).
Sitarganj comes under the Terai Ag ...
; Pharma City at Selakui; Information Technology Park at Sahastradhara (Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
); and a growth centre at Sigaddi (Kotdwar
Kotdwar is a city, municipal corporation in Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, India. It is just 101 km from Pauri, the district headquarter. It is the eighth-largest city in Uttarakhand. Its old name was "Kootdwar", which means the ga ...
). Also in 2006, 20 industrial sectors in public private partnership mode were developed in the state.
Transportation
Uttarakhand has of roads, of which are national highways and arestate highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
. The state has 14 national highways, comprising 2.2% of the total national highways length in India. The Uttarakhand Transport Corporation
Uttarakhand Transport Corporation (UTC), commonly known as Uttarakhand Roadways, is the government-operated bus service for the state of Uttarakhand, India. UTC operates buses across Uttarakhand, connecting it with neighboring states such as H ...
(UTC), established on 31 October 2003 after reorganizing the State Road Transport Corporation (SRTC). The corporation provides transportation in the state with connecting services to adjoining states. The UTC buses are the most common and affordable mode of transportation in Uttarakhand. As of 2012, approximately 1000 buses are being plied by the UTC on 35 nationalised routes along with many other non-nationalised routes. There are also private transport operators operating approximately 3000 buses on non-nationalised routes along with a few interstate routes in Uttarakhand and the neighbouring state of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
. For travelling locally, the state, like most of the country, has auto rickshaw
An auto rickshaw is a motorized version of the pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw. Most have three wheels and do not tilt. They are known by many other terms in various countries, including three-wheeler, Adaidaita Sahu, Keke-napep, Maruwa, auto, ...
s and cycle rickshaw
The cycle rickshaw is a small-scale local means of transport. It is a type of tricycle designed to carry passengers on a vehicle for hire, for-hire basis. It is also known by a variety of other names such as bike taxi, velotaxi, pedicab, bi ...
s. In addition, remote towns and villages in the hills are connected to important road junctions and bus routes by share mode of transportation.
As over 86% of state's terrain consists of hills, railway services are very limited in the state and are largely confined to the plains. In 2011, the total length of railway tracks was about . The most important railway station in Kumaun Division of Uttarakhand is at Kathgodam
Kathgodam is a suburb of Haldwani, Uttarakhand, India. It used to be a part of the twin township of Haldwani–Kathgodam, and is known as the "Gateway to Kumaon".
History
Literally meaning ''timber depot'', Kathgodam was a small village in 190 ...
. Kathgodam is the last terminus of the broad-gauge
A broad-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge (the distance between the rails) broader than the used by standard-gauge railways.
Broad gauge of , more known as Russian gauge, is the dominant track gauge in former Soviet Union countries ...
line of North East Railways that connects Nainital with Delhi, Dehradun, and Howrah
Howrah (; ; alternatively spelled as Haora) is a city in the Indian States and union territories of India, state of West Bengal. Howrah is located on the western bank of the Hooghly River, opposite to its twin city of Kolkata. Administratively ...
. Other notable railway stations are at Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar District, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Uttarakhand, Kashipur, Rudrapur, Uttarakhand, Rudrapur, Kiccha and Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is hom ...
, Lalkuan and Haldwani
Haldwani (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Haldvānī'') is the largest city of Kumaon division, Kumaon. It is also the second List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Haldwani is said to be ...
. Dehradun railway station is a railhead of the Northern Railways. Haridwar station is situated on the Delhi–Dehradun and Howrah–Dehradun railway lines. One of the main railheads of the Northern Railways, Haridwar Junction Railway Station is connected by broad gauge line. Roorkee comes under Northern Railway region of Indian Railways on the main Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
– Mughal Sarai
Mughalsarai (; English: '' Mughal Tavern''), officially known as Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Nagar, is a city and a municipal board in the Chandauli district of Uttar Pradesh. Located around from Chandauli town, the district headquarter ...
trunk route and is connected to major Indian cities. Other railheads are Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank ...
, Kotdwar
Kotdwar is a city, municipal corporation in Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand, India. It is just 101 km from Pauri, the district headquarter. It is the eighth-largest city in Uttarakhand. Its old name was "Kootdwar", which means the ga ...
and Ramnagar linked to Delhi by daily trains.
Jolly Grant Airport
Dehradun Airport , also known as Jolly Grant Airport, is a domestic airport serving Dehradun, the capital of Uttarakhand, India. It is located in Jauligrant, south of the city, from Rishikesh and from Haridwar. Commercial operations began ...
in Dehradun and Pantnagar Airport
Pantnagar Airport is a domestic airport serving Pantnagar and its adjoining regions, located in the Udham Singh Nagar district in of Uttarakhand, India. It is operated by the Airports Authority of India. It is the nearest airport to the Kumaon ...
in Pantnagar
Pantnagar is a town and a university campus in Udham Singh Nagar District, Uttarakhand. Nainital, Kashipur, Uttarakhand, Kashipur, Rudrapur, Uttarakhand, Rudrapur, Kiccha and Haldwani are the major cities surrounding Pantnagar.
The town is hom ...
are the major airports and the main gateway to the state. Jolly Grant Airport is the busiest airport in the state with six daily flights to Delhi Airport. Pantnagar Airport of the Kumaon region have 1 daily air service to Delhi and return too. The state has also proposed creating the Naini Saini Airport
Naini (also known as Naini Industrial Area) is an industrial township of Prayagraj in Prayagraj district, Uttar Pradesh, India. By the 1950s Naini was established as the chief industrial area of the city.
History
Naini had a prison, Naini Cen ...
in Pithoragarh
Pithoragarh ( Kumaoni: ''Pithor'garh'') is a Himalayan town with a Municipal corporation in Pithoragarh district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the largest hill town in Uttarakhand.
Etymology
"The district is named after its hea ...
, Bharkot Airport in Chinyalisaur
Chinyalisaur is a small town and tehsil headquarters in the Uttarkashi district of the Indian state of Uttarakhand.
Geography
Chinyalisaur is a semi-urban settlement. It is named after a nearby village called Chinyali. 'Saur' is the Garhrwa ...
in Uttarkashi district and Gauchar Airport
Gauchar ( Garhwali) is a hill town located in Karnaprayag tehsil subdistrict within Chamoli district of Uttarakhand state in India. Gauchar is situated on the left bank of river Alaknanda and is en route to the celebrated holy destination o ...
in Gauchar
Gauchar ( Garhwali) is a hill town located in Karnaprayag tehsil subdistrict within Chamoli district of Uttarakhand state in India. Gauchar is situated on the left bank of river Alaknanda and is en route to the celebrated holy destination o ...
, Chamoli district.
Tourism
Valley of Flowers National Park
Valley of Flowers National Park https://valleyofflower.uk.gov.in is an Indian national park which was established in 1982. It is located in Chamoli in the state of Uttarakhand and is known for its meadows of endemic alpine flowers and the varie ...
Ali bugyal2.jpg, View of a Bugyal
Bugyals are alpine pasture lands, or meadows in India, in higher elevation range between and of the Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, where they are called "nature’s own gardens". The topography of the terrain is either flat or s ...
(meadow) in Uttarakhand
Har Ki Dun.jpg, Har Ki Doon
Har Ki Doon or Har Ki Dun is a cradle-shaped hanging valley in the Garhwal Himalayas of Uttarakhand, India. The region is surrounded with green Bugyals (High Altitude Meadows). It is surrounded by snow-covered peaks and alpine vegetation. I ...
, a high-altitude hanging valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a ve ...
Rishikesh view across bridge.jpg, Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank ...
view and 13 stories Shiva temple across Lakshman Jhula
Lakshman Jhula is a suspension bridge across the river Ganges. This is a very famous and older bridge on river ganga and has been closed from 2020. Lakshman Jhula was built in the time of the East India Company.
Geography
It is located north ...
bridge over the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
Kedarnath Temple - OCT 2014.jpg, Kedarnath Temple
Kēdāranātha Temple (Sanskrit: केदारनाथ मंदिर, IAST: ''Kēdāranātha Mandira'', ) is a Hindu temple, one of the twelve ''jyotirlinga'' of Śiva. The temple is located on the Garhwal Himalayan range
near the Manda ...
is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas
A Jyotirlinga () or Jyotirlingam is a devotional representation of the Hindu god Shiva. The word is a Sanskrit compound of ('radiance') and ('sign'). The Śiva Mahāpurāṇam (also ''Shiva Purana'') mentions 64 original ''jyotirlinga'' ...
 Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in
Uttarakhand has many tourist spots due to its location in the Himalayas. There are many ancient temples, forest reserves, national parks, hill stations, and mountain peaks that draw large number of tourists. There are 44 nationally protected monuments in the state. Oak Grove School in the state is on the tentative list for World Heritage Sites. Two of the most holy rivers in Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
the Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
and Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
, originate in Uttarakhand. Binsar Devta is a popular Hindu temple in the area.
Uttarakhand has long been called "Land of the Gods" as the state has some of the holiest Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
shrines, and for more than a thousand years, pilgrims have been visiting the region in the hopes of salvation and purification from sin. Gangotri
Gangotri is a town and a ''Nagar Panchayat'' (municipality) in Uttarkashi district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is 99 km from Uttarkashi, the main district headquarter. It is a Hindu pilgrim town on the banks of the river Bha ...
and Yamunotri
Yamunotri, also Jamnotri, is the source of the Yamuna River and the seat of the Goddess Yamuna in Hinduism. It is situated at an altitude of in the Garhwal Himalayas and located approximately North of Uttarkashi, the headquarters of the Utta ...
, the sources of the Ganges and Yamuna, dedicated to Ganga
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary riv ...
and Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
respectively, fall in the upper reaches of the state and together with Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is a Hindu holy place, and is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage. It is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage c ...
(dedicated to Vishnu
Vishnu (; , , ), also known as Narayana and Hari, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the supreme being within Vaishnavism, one of the major traditions within contemporary Hinduism, and the god of preservation ( ...
) and Kedarnath
Kedarnath is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Rudraprayag district of Uttarakhand, India, known primarily for the Kedarnath Temple. It is approximately 86.5 kilometres from Rudraprayag, the district headquarters. Kedarnath is the most remote ...
(dedicated to Shiva
Shiva (; , ), also known as Mahadeva (; , , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, ɐɦaːd̪eːʋɐh and Hara, is one of the Hindu deities, principal deities of Hinduism. He is the God in Hinduism, Supreme Being in Shaivism, one of the major traditions w ...
) form the Chota Char Dham
The Chota Char Dham ( 'the small four abodes/seats' or 'the small circuit of four abodes/seats') is an important modern Hindu pilgrimage circuit in Uttarakhand, in the Indian Himalayas. Located in the Garhwal region of the state of Uttarak ...
, one of Hinduism's most spiritual and auspicious pilgrimage circuits. Haridwar, meaning "Gateway to the God", is a prime Hindu destination. Haridwar
Haridwar (; ; formerly Mayapuri) is a city and municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of Uttarakhand, India. With a population of 228,832 in 2011, it is the second-largest city in the state and the largest in the district.
The city is s ...
hosts the Haridwar Kumbh Mela
Haridwar Kumbh Mela is a mela, associated with Hinduism and held in the city of Haridwar, India held every 12 years. The exact date is determined according to Hindu astrology: the Mela is held when Jupiter is in Aquarius and the Sun enters A ...
every twelve years, in which millions of pilgrims take part from all parts of India and the world. Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank ...
near Haridwar is known as the preeminent yoga
Yoga (UK: , US: ; 'yoga' ; ) is a group of physical, mental, and spiritual practices or disciplines that originated with its own philosophy in ancient India, aimed at controlling body and mind to attain various salvation goals, as pra ...
centre of India. The state has an abundance of temples and shrines, many dedicated to local deities or manifestations of Shiva and Durga
Durga (, ) is a major Hindu goddess, worshipped as a principal aspect of the mother goddess Mahadevi. She is associated with protection, strength, motherhood, destruction, and wars.
Durga's legend centres around combating evils and demonic ...
, references to many of which can be found in Hindu scriptures and legends. Uttarakhand is, however, a place of pilgrimage for the adherents of other religions too. Piran Kaliyar
Piran (; ) is a town in southwestern Slovenia on the Gulf of Piran on the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the three major towns of Slovenian Istria. A bilingual city, with population speaking both Slovene and Italian, Piran is known for its medieva ...
Sharif near Roorkee
Roorkee (Rūṛkī; ) is a city and Municipal Corporations in India, municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is from Haridwar, the district headquarters. It is spread over a flat terrain under the ...
is a pilgrimage site to Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
s, Gurudwara Darbar Sahib, in Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
, Gurudwara Hemkund Sahib in Chamoli district
Chamoli district is a district of the Uttarakhand state of India. It is bounded by China's Xizang Autonomous Region to the north, and by the Uttarakhand districts of Pithoragarh district, Pithoragarh and Bageshwar district, Bageshwar to the eas ...
, Gurudwara Nanakmatta Sahib in Nanakmatta
Nanakmatta is a town named after the Sikh pilgrimage site, Gurdwara Nanak Mata Sahib, also known as Gurdwara Nanakmatta Sahib, in the state of Uttarakhand, India.
Sikh tradition says it was once called Gorakhmata, a centre of Siddh-jogis nam ...
and Gurudwara Reetha Sahib
Gurudwara Reetha Sahib is situated in Champawat district, Uttarakhand, India. It is 16 hours journey away from Chandigarh (581 km) approx. This gurudwara holds a very sacred place in Sikh Religion as Guru Nanak Dev himself had visited thi ...
in Champawat district are pilgrimage centres for Sikh
Sikhs (singular Sikh: or ; , ) are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ''Si ...
s. Tibetan Buddhism
Tibetan Buddhism is a form of Buddhism practiced in Tibet, Bhutan and Mongolia. It also has a sizable number of adherents in the areas surrounding the Himalayas, including the Indian regions of Ladakh, Gorkhaland Territorial Administration, D ...
has also made its presence with the reconstruction of Mindrolling Monastery
Mindrolling Monastery (, English: "Sublime Island of Ripening Liberation"), is one of the "Six Mother Monasteries" of the Nyingma school in Tibet. It was founded by Rigzin Terdak Lingpa in 1676. Tendrak Lingpa's lineage is known as the ''Nyo'' ...
and its Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist legends, he was ...
Stupa
In Buddhism, a stupa (, ) is a domed hemispherical structure containing several types of sacred relics, including images, statues, metals, and '' śarīra''—the remains of Buddhist monks or nuns. It is used as a place of pilgrimage and m ...
, described as the world's highest at Clement Town
Clement Town is a cantonment town in Dehradun, Dehradun district, in the state of Uttarakhand, India. Clement Town is from the clock tower in main city of Dehradun. Saharanpur and Haridwar are respectively. It also borders Rajaji Nationa ...
, Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
.
Auli and Munsiari
Munsyari ( Kumaoni: ''Munsyār'') is the name of the sub-division headquarters, a municipal board, a conglomeration of revenue villages and it also refers to the entire region as Munsiyari Tehsil and Sub Division in the Pithoragarh District i ...
are well-known skiing resorts in the state.
The state has 12 national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, which cover 13.8% of the total area of the state. They are located at different altitudes varying from 800 to 5400 metres. The oldest national park on the Indian sub-continent, Jim Corbett National Park
Jim Corbett National Park is a national park in India located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand state. The first national park in India, it was established in 1936 during the British Raj and named ''Hailey National Park'' after Willi ...
, is a major tourist attraction.

Vasudhara Falls
Vasudhara Falls is a waterfall situated near Badrinath, in Uttarakhand, India.It is one of the finnest waterfalls which exist in India. As well as it had many Spiritual Values Within itself.
Geography
Uttarakhand is surrounded by waterfalls ...
, near Badrinath
Badrinath is a town and nagar panchayat in Chamoli district in the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is a Hindu holy place, and is one of the four sites in India's Char Dham pilgrimage. It is also part of India's Chota Char Dham pilgrimage c ...
, is a waterfall with a height of set in a backdrop of snow-clad mountains. The state has always been a destination for mountaineering
Mountaineering, mountain climbing, or alpinism is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas that have become mounta ...
, hiking
A hike is a long, vigorous walk, usually on trails or footpaths in the countryside. Walking for pleasure developed in Europe during the eighteenth century. Long hikes as part of a religious pilgrimage have existed for a much longer time.
"Hi ...
, and rock climbing
Rock climbing is a climbing sports discipline that involves ascending climbing routes, routes consisting of natural rock in an outdoor environment, or on artificial resin climbing walls in a mostly indoor environment. Routes are documented in c ...
in India. A recent development in adventure tourism
Adventure travel is a type of tourism, involving exploration or travel with a certain degree of risk (real or perceived), and which may require special skills and physical exertion. In the United States, adventure tourism has seen growth in l ...
in the region has been whitewater rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
in Rishikesh. Due to its proximity to the Himalaya ranges, the place is full of hills and mountains and is suitable for trekking, climbing, skiing, camping, rock climbing, and paragliding. Roopkund is a trekking site, known for the mysterious skeletons found in a lake, which was featured by National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by the National Geographic Global Networks unit of Disney Enter ...
in a documentary. The trek to Roopkund passes through the meadows of Bugyal
Bugyals are alpine pasture lands, or meadows in India, in higher elevation range between and of the Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, where they are called "nature’s own gardens". The topography of the terrain is either flat or s ...
.
New Tehri
New Tehri is where Vidushi lives a city and a municipal board in Tehri Garhwal District in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of Tehri Garhwal District. This urban municipality area has 11 wards, from Vidh ...
city has Tehri Dam
The Tehri Dam is a multi-purpose rock and earth-fill embankment dam on the Bhagirathi River in New Tehri, Tehri Garhwal district in Uttarakhand, India. With a height of 260.5 m (855 ft), it is the tallest dam in India and the List of t ...
, with a height of is the tallest dam in India. It is currently ranked No 10 on the List of Tallest Dams
This is a list of the tallest dams in the world above in height. The tallest dam in the world is the Jinping-I dam, an arch dam in China at . The tallest embankment dam and the second tallest dam in the world is the Nurek Dam in Tajikistan, b ...
in the world. Tehri Lake with a surface area of , is the biggest lake in the state of Uttarakhand. It has good options for Adventure Sports and various water sports like Boating, Banana Boat, Bandwagon Boat, Jet Ski, Water Skiing, Para-sailing, Kayaking.
Education
The educational system prevailing in the state's schools specifies an initial 10-year course of study, which is divided into three stages: lower primary, upper primary, and secondary school—known as 4+3+3, which signifies the number of years for each stage. After the first 10 years of schooling, students typically enroll in Higher Secondary Schooling in one of the three major streams—liberal arts
Liberal arts education () is a traditional academic course in Western higher education. ''Liberal arts'' takes the term ''skill, art'' in the sense of a learned skill rather than specifically the fine arts. ''Liberal arts education'' can refe ...
, commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
, or science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
. Upon completing the required coursework, students can enroll in general or professional undergraduate (UG) degree-college programmes. Schools in the state are either managed by the government or by private trusts. The majority of public schools are affiliated with the Uttarakhand Board of School Education
Uttarakhand Board of School Education () abbr. UBSE is an agency of Government of Uttarakhand entrusted with the responsibilities of prescribing courses of instructions and text books and conducting examinations for secondary school students i ...
(UBSE) use Hindi as a medium of instruction. Private schools in Uttarakhand—which use English as the language of instruction—are affiliated to one of three administering bodies, CBSE, CISCE
The Council for the Indian School Certificate Examinations (CISCE) is a non-governmental privately held national-level board of school education in India that conducts the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE) Examination for Clas ...
, or ICSE.
Uttarakhand has more than 20 universities, including one central university, twelve state universities
A state university system in the United States is a group of public universities supported by an individual state, territory or federal district. These systems constitute the majority of universities in the country, serving by far the majority ...
, three deemed universities
Deemed university, or deemed-to-be-university, is an accreditation granted to higher educational institutions in India by the Department of Higher Education (India), Department of Higher Education. , the UGC lists 124 institutes which were granted ...
, one IIT in Roorkee
Roorkee (Rūṛkī; ) is a city and Municipal Corporations in India, municipal corporation in the Haridwar district of the state of Uttarakhand, India. It is from Haridwar, the district headquarters. It is spread over a flat terrain under the ...
, one IIM in Kashipur and an AIIMS
The All India Institutes of Medical Sciences (AIIMS) is a group of autonomous government public medical universities of higher education under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. These institutes ha ...
in Rishikesh
Rishikesh, also spelt as Hrishikesh, is a city near Dehradun in the Indian state Uttarakhand. The northern part of Rishikesh is in the Dehradun district while the southern part is in the Tehri Garhwal district. It is situated on the right bank ...
. Inaugurated by Jawahar Lal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru (14 November 1889 – 27 May 1964) was an Indian anti-colonial nationalist, secular humanist, social democrat, and statesman who was a central figure in India during the middle of the 20th century. Nehru was a prin ...
in 1960, G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, provides research and training in agriculture and engineering. Located in Bharsar and Ranichauri, Veer Chandra Singh Garhwali Uttarakhand University of Horticulture and Forestry, is a state agricultural university and has two campuses, one is in Bharsar town of Pauri Garhwal district
Pauri Garhwal is a district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Its headquarters is in the town of Pauri. It is sometimes referred to simply as Garhwal district, though it should not be confused with the larger Garhwal region of which it is ...
and other is in Ranichauri town of Tehri Garhwal district
Tehri Garhwal is a district in the hill state of Uttarakhand, India. Its administrative headquarters is at New Tehri. The district has a population of 618,931 (2011 census), a 2.35% increase over the previous decade. It is surrounded by Rudra ...
. Kumaun University
Kumaun University is a state university headquartered in Nainital, Uttarakhand, India.
In 2017, it hosted the first Kautik Student Film Festival.
Campuses
The academic wing of the University is spread over in two campuses (Dev Singh Bisht ...
; located in Nainital, is one of the oldest universities in the region.
Uttarakhand is home to some of premier institutes of India that hold the status of national importance due to their significant contributions to education, research, and national development. Founded in 1906, Forest Research Institute (FRI) is the oldest institutions of its kind. Its campus hosts the Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy
Indira Gandhi National Forest Academy (IGNFA) is a forest service training institute under the Ministry of Environment and Forests of India, which was originally called as Indian Forest College, established in 1938 for training of senior fores ...
(IGNFA), the staff college that trains officers selected for the Indian Forest Service
The Indian Forest Service (IFS) is the premier forest service of India. .The IFS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Administrative Service (IAS) & the Indian Police Service (IPS). It was constituted in the year 1966 un ...
(IFS). Located in Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
, The Doon School
The Doon School (informally Doon School or Doon) is a Selective school, selective all-boys Private school, private boarding school in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India, which was established in 1935. It was envisioned by Satish Ranjan Das, a lawyer ...
has been consistently ranked as the best all-boys residential school in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. Established in 1959, Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration
Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA) is a civil service training institute on public policy and public administration in Mussoorie, Uttarakhand in India. The academy's main purpose is to train civil servants of the ...
(LBSNA), Mussoorie
Mussoorie () is a hill station and a municipal board, in Dehradun city in the Dehradun district of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is about from the state capital of Dehradun and north of the national capital of New Delhi. The hil ...
, trains civil servants for the Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service (IAS) is the Public administration, administrative arm of the All India Services of Government of India. The IAS is one of the three All India Services along with the Indian Police Service (IPS) and the Indian ...
(IAS). The Indian Military Academy
The Indian Military Academy (IMA) is one of the oldest military academies in India, and trains officers for the Indian Army. Located in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, it was established in 1932 following a recommendation by a military committee set up ...
(IMA), is officer training academy for the Indian Army
The Indian Army (IA) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Land warfare, land-based branch and largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Commander-in-Chief, Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head ...
. The academy trains officer cadets for the Permanent Commission into the Army.
Sports
 Due to its mountainous terrain and rivers, Uttarakhand attract tourists and adventure seekers for adventure sports, such as
Due to its mountainous terrain and rivers, Uttarakhand attract tourists and adventure seekers for adventure sports, such as paragliding
Paragliding is the recreational and competitive adventure sport of flying paragliders: lightweight, free-flying, foot-launched glider aircraft with no rigid primary structure. The pilot sits in a harness or in a cocoon-like 'pod' suspended be ...
, sky diving
Parachuting and skydiving are methods of descending from a high point in an atmosphere to the ground or ocean surface with the aid of gravity, involving the control of speed during the descent using a parachute or multiple parachutes.
For hu ...
, rafting
Rafting and whitewater rafting are recreational outdoor activities which use an inflatable raft to navigate a river or other body of water. This is often done on whitewater or different degrees of rough water. Dealing with risk is often a ...
and bungee jumping
Bungee jumping (), also spelled bungy jumping, is an activity that involves a person jumping from a great height while connected to a large elastic cord. The launching pad is usually erected on a tall structure such as a building or crane, a ...
. Uttarakhand is home to some of the highest peaks in India, including Nanda Devi
Nanda Devi is the second-highest mountain in India, after Kangchenjunga, and the highest located entirely within the country. (Kangchenjunga is on the border of India and Nepal.) Nanda Devi is the 23rd-highest peak in the world and ranked 74t ...
and Tirsuli
Tirsuli is a Himalayan mountain peak in the
Chamoli district of Uttarakhand, India. It is part of the complex of mountains, including Tirsuli West, Hardeol, Dunagiri, Changabang, and Kalanka, which make up the northeast wall of the Nanda Devi ...
, popular for mountaineering expeditions and climbing activities. Traditional sports Mallakhamb
Mallakhamba, or mallakhamb is a traditional sport, originating from the Indian subcontinent, in which a group of gymnasts perform aerial yoga and gymnastic postures using wrestling grips in concert with a stationary vertical pole. The word mal ...
(pole gymnastics), Gatka
Gatka (; ; ; ) is a form of martial art associated primarily with the Sikhs of the Punjab and other related ethnic groups, such as Hindkowans and Pahari-Pothwari. It is a style of stick-fighting, with wooden sticks intended to simulate sw ...
(a form of martial arts
Martial arts are codified systems and traditions of combat practiced for a number of reasons such as self-defence; military and law enforcement applications; combat sport, competition; physical, mental, and spiritual development; entertainment; ...
) and Gulli Danda (similar to cricket) are preserved, are preserved but have limited exposure. More recently, golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various Golf club, clubs to hit a Golf ball, ball into a series of holes on a golf course, course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standa ...
has also become popular with Ranikhet
Ranikhet ( Kumaoni: ) is a hill station and cantonment town, near Almora Town in Almora district in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the home of the Military Hospital, Kumaon Regiment (KRC) and Naga Regiment and is maintained by the Ind ...
being a favorite destination.
The Cricket Association of Uttarakhand
The Cricket Association of Uttarakhand (CAU) is the governing body of the cricket activities in the Indian state of Uttarakhand and the Uttarakhand cricket team. It is affiliated with the Board of Control for Cricket in India.
Hira Singh Bis ...
is the governing body for cricket
Cricket is a Bat-and-ball games, bat-and-ball game played between two Sports team, teams of eleven players on a cricket field, field, at the centre of which is a cricket pitch, pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two Bail (cr ...
activities. The Uttarakhand cricket team
The Uttarakhand cricket team is a cricket team that represents the state of Uttarakhand in Indian domestic competitions.
Background
In July 2018, the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI) named the team as one of the nine new sides that ...
represents Uttarakhand in Ranji Trophy
The Ranji Trophy is a premier domestic first-class cricket championship played in India and organized annually by the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI). The teams representing regional and state cricket associations participate. BCCI ...
, Vijay Hazare Trophy
The Vijay Hazare Trophy (officially known as the IDFC First Bank Vijay Hazare Trophy for sponsorship reasons), is an annual List A Cricket competition organised by the BCCI. The Indian States and union territories teams take part in the Ranji ...
and Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy
The Syed Mushtaq Ali Trophy is a domestic Twenty20 cricket championship in India, organized by the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI). It is named after former Test cricketer Syed Mushtaq Ali.
It is played by the teams from the R ...
. Rajiv Gandhi International Cricket Stadium
The Rajiv Gandhi International Cricket Stadium, commonly known as Uppal Stadium, is an international cricket stadium in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It is owned and operated by Hyderabad Cricket Association (HCA). It is the home ground of ...
in Dehradun
Dehradun (), also known as Dehra Doon, is the winter capital and the List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city of the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is the administrative headquarters of the eponymous Dehradun district, d ...
is the home ground of Uttarakhand cricket team. Uttarakhand has state-level associations for various sports that organize tournaments and promote talent development.
The Uttarakhand State Football Association
The Uttarakhand State Football Association (USFA) is the governing body of football in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It is affiliated with the All India Football Federation. The USFA sends state teams for the Santosh Trophy and the Senior ...
is the governing body for association football
Association football, more commonly known as football or soccer, is a team sport played between two teams of 11 Football player, players who almost exclusively use their feet to propel a Ball (association football), ball around a rectangular f ...
. The Uttarakhand football team represents Uttarakhand in the Santosh Trophy
The National Football Championship for Santosh Trophy, or simply Santosh Trophy, is an inter-state national football competition contested by the state associations and government institutions under the All India Football Federation (AIFF), th ...
and other leagues. The Indira Gandhi International Sports Stadium
Indira Gandhi International Sports Stadium is located in Haldwani, Uttarakhand, India. It can seat 25,000 spectators and was inaugurated on 18 December 2016 by Harish Rawat, the then Chief Minister of Uttarakhand. It is spread over 70 acres a ...
in Haldwani
Haldwani (Kumaoni language, Kumaoni: ''Haldvānī'') is the largest city of Kumaon division, Kumaon. It is also the second List of cities in Uttarakhand by population, most populous city in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. Haldwani is said to be ...
is the home ground of Uttarakhand football team.
Notable people
See also
* Outline of Uttarakhand * Himalayan states *Indian Himalayan Region
The Indian Himalayan Region (abbreviated to IHR) is the section of the Himalayas within the Republic of India, spanning thirteen Indian states and union territories, namely Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, We ...
* '' Mountain Temples and Temple Mountains''
References
Further reading
* * * * * Handa, Umachand (2002).History of Uttaranchal
''. Indus Publishing. . * Husain, Z. (1995). ''Uttarakhand Movement: The Politics of Identity and Frustration, A Psycho-Analytical Study of the Separate State Movement, 1815–1995''. Bareilly: Prakash Book Depot. * Sharma, D. (1989). ''Tibeto-Himalayan languages of Uttarakhand''. Studies in Tibeto-Himalayan languages, 3. New Delhi, India: Mittal Publications. * Phonia, Kedar Singh (1987). ''Uttarakhand: The Land of Jungles, Temples and Snows''. New Delhi, India: Lancer Books. * Mukhopadhyaya, R. (1987). ''Uttarakhand Movement: A Sociological Analysis''. Centre for Himalayan Studies special lecture, 8. Raja Rammohunpur, Distt. Darjeeling: University of North Bengal. * Thapliyal, Uma Prasad (2005). ''Uttaranchal: Historical and Cultural Perspectives''. B. R. Pub. Corp., . * Negi, Vijaypal Singh, Jawaharnagar, P.O. Agastyamuni, Distt. Rudraprayag, ''The Great Himalayas'' 1998,
External links
GovernmentUttarakhand Government Portal
Uttarakhand Tourism
General information *
Map of Uttarakhand
with places of interest and historical attractions, mountainshepherds.com. * {{Authority control Uttarakhand North India States and union territories of India States and territories established in 2000 2000 establishments in India