IN-AN on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands is a
 The
The
 Between 1778 and 1783,
Between 1778 and 1783,
 The territory consists of 836
The territory consists of 836
 Tourism is one of the major contributors to the economy of the islands. The islands had more than 400,000 visitors in 2016 with a 94% contribution from domestic tourists. In 2018, plans to develop facilities in various islands under the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) Aayog was initiated by Government of India, with the aim of increasing tourist inflows. Foreign tourists are issued Restricted Area Permits (RAP) which gives access to specific areas with conditions. While domestic tourists do not require a permit to visit the accessible parts of the islands, the tribal reserves are forbidden and requires special permission for access. The islands have many beaches due to its long coastline and various
Tourism is one of the major contributors to the economy of the islands. The islands had more than 400,000 visitors in 2016 with a 94% contribution from domestic tourists. In 2018, plans to develop facilities in various islands under the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) Aayog was initiated by Government of India, with the aim of increasing tourist inflows. Foreign tourists are issued Restricted Area Permits (RAP) which gives access to specific areas with conditions. While domestic tourists do not require a permit to visit the accessible parts of the islands, the tribal reserves are forbidden and requires special permission for access. The islands have many beaches due to its long coastline and various
union territory
Among the states and union territories of India, a Union Territory (UT) is a region that is directly governed by the Government of India, central government of India, as opposed to the states, which have their own State governments of India, s ...
of India comprising 572 islands, of which only 38 are inhabited. The islands are grouped into two main clusters: the northern Andaman Islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago, made up of 200 islands, in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a mari ...
and the southern Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelago, archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of t ...
, separated by a wide channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Australia in Queensland and pa ...
. The capital and largest city of the territory, Port Blair
Port Blair (), officially named Sri Vijaya Puram, is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (''tehsil'') of the islands, the headqu ...
(officially Sri Vijaya Puram), is located approximately from Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and ...
and from Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
in mainland India
Mainland India is a geo-political term sometimes used to refer to India excluding the region of Northeast India and Kashmir, with the north-east connected by the Siliguri Corridor.
In a geographical context, Mainland India includes the entiret ...
. The islands are situated between the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
to the west and the Andaman Sea
The Andaman Sea (historically also known as the Burma Sea) is a marginal sea of the northeastern Indian Ocean bounded by the coastlines of Myanmar and Thailand along the Gulf of Martaban and the west side of the Malay Peninsula, and separated f ...
to the east. The northernmost point is from the mouth of the Hooghly River
The Hooghly River (, also spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') is the westernmost distributary of the Ganges, situated in West Bengal, India. It is known in its upper reaches as the Bhagirathi. The Bhagirathi splits off from the main branch of the G ...
. Indira Point
Indira Point, the southernmost point of India's territory, is a village in the Nicobar district at Great Nicobar Island of Andaman and Nicobar Islands in India. It is located in the Great Nicobar tehsil.
Rondo Island, Indonesia's northernmos ...
, located at 6°45'10″N and 93°49'36″E on the southern tip of Great Nicobar
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra. It is part of India, in the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
History
The Nicobar Island has been ...
, is the southernmost point of India.
The territory shares maritime border
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boun ...
s with Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
located about to the south, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
located to the north-east and Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
located to the south-east. The islands occupy a total land area of approximately with a population of 380,581 as per the 2011 census. The territory is divided into three districts: Nicobar, South Andaman
South Andaman Island is the southernmost island of the Great Andaman and is home to the majority of the population of the Andaman Islands.
It belongs to the South Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman an ...
, and North and Middle Andaman with the capitals at Car Nicobar
Car Nicobar ( in Car language) is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Annual ra ...
, Port Blair and Mayabunder
Mayabunder is a town and a tehsil in the northern part of Middle Andaman Island, Andaman Archipelago, India. The name is also spelled Maya Bunder or Maya Bandar. As of 2001, the county had 23,912 inhabitants, of which 3182 were in the town.Gov ...
respectively.
Genetic and cultural studies suggest that the indigenous Andamanese people may have been isolated from other populations during the Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle P ...
era, more than 30,000 years ago. Archeological evidence of civilisation has been dated back to 2,200 years. In the 11th century CE, Cholas
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd cen ...
, one of the three Tamil kingdoms, used the islands as a naval base
A naval base, navy base, or military port is a military base, where warships and naval ships are docked when they have no mission at sea or need to restock. Ships may also undergo repairs. Some naval bases are temporary homes to aircraft that usu ...
to launch expeditions in South East Asia. The Danish were the first Europeans to arrive on the islands in 1755. The islands became part of the British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
in 1868. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the islands were invaded by the Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
. After Indian Independence in 1947, the region became a province and later a union territory after the adoption of the Constitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India, legal document of India, and the longest written national constitution in the world. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures ...
in 1950.
The islands host the Andaman and Nicobar Command
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is a integrated tri-services command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic in ...
, the only geographical command operated jointly by the three major wings of the Indian Armed Forces
The Indian Armed Forces are the armed forces, military forces of the India, Republic of India. It consists of three professional uniformed services: the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force.—— Additionally, the Indian Ar ...
: the Army
An army, ground force or land force is an armed force that fights primarily on land. In the broadest sense, it is the land-based military branch, service branch or armed service of a nation or country. It may also include aviation assets by ...
, the Air Force
An air force in the broadest sense is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an army aviati ...
and the Navy
A navy, naval force, military maritime fleet, war navy, or maritime force is the military branch, branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval warfare, naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral z ...
. While Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
and English are the official languages, the major spoken languages include Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
, Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
and Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India
** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language.
* Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Tel ...
. Indigenous people speak any of the Andamanese
The Andamanese are the various indigenous peoples of the Andaman Islands, part of India's Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the union territory in the southeastern part of the Bay of Bengal. The Andamanese are a designated Scheduled Tribe in Indi ...
or Nicobarese family of languages. Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is the majority religion in the union territory, with a significant Christian minority. The islands include North Sentinel Island
North Sentinel Island is one of the Andaman Islands, an Indian archipelago in the Bay of Bengal which also includes South Sentinel Island. The island is a protected area of India. It is home to the Sentinelese, an indigenous tribe in volunta ...
, home to the Sentinelese people
The Sentinelese, also known as the Sentineli and the North Sentinel Islanders, are Indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island in the Bay of Bengal in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Designated a particularly vulnerable tribal group ...
, an uncontacted tribe
Uncontacted peoples are groups of Indigenous peoples living without sustained contact with neighbouring communities and the world community. Groups who decide to remain uncontacted are referred to as indigenous peoples in voluntary isolation. Leg ...
.
Etymology
The name Andaman might have been derived from ''Handuman'', after the Indian GodHanuman
Hanuman (; , ), also known as Maruti, Bajrangabali, and Anjaneya, is a deity in Hinduism, revered as a divine ''vanara'', and a devoted companion of the deity Rama. Central to the ''Ramayana'', Hanuman is celebrated for his unwavering devotio ...
from the Hindu
Hindus (; ; also known as Sanātanīs) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism, also known by its endonym Sanātana Dharma. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pp. 35–37 Historically, the term has also be ...
epic Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics ...
. The place was called with a similar name by the Malays, who used to be involved in slave trade Slave trade may refer to:
* History of slavery - overview of slavery
It may also refer to slave trades in specific countries, areas:
* Al-Andalus slave trade
* Atlantic slave trade
** Brazilian slave trade
** Bristol slave trade
** Danish sl ...
in the region. The place was also referred by various names such as ''Angademan'' by Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
in the 2nd century CE and ''Angamanian'' by Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
in 13th century CE. Nicobar, which was located in the sea route connecting South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of ...
to South East Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
, was known as ''Nakkavaram'', meaning "open/naked land" borrowed from Tamil language
Tamil (, , , also written as ''Tamizhil'' according to linguistic pronunciation) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. It is one of the longest-surviving classical languages in the world,. "Tamil is one of ...
which later became ''Nicobar''. In the middle ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
(500-1500 AD), Nicobar was known as ''Lankhabatus'' in Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world.
Geographically, the ...
, probably a mis-transcription of the name ''Nakkavaram''. An 11th-century CE work ''Kathasaritsagar'' indicates the name as ''Narikel Dweep''. Marco Polo termed the island as ''Necuverann'', while the islands were known as ''Lo-Jan Kuo'' in China, a translation of ''Nakkavar'' with the same meaning.
History
Early history
Genetic and cultural studies suggest that the indigenous Andamanese people may have been isolated from other populations during the Middle Paleolithic era, which ended 30,000 years ago. Archeological evidence obtained frommidden
A midden is an old dump for domestic waste. It may consist of animal bones, human excrement, botanical material, mollusc shells, potsherds, lithics (especially debitage), and other artifacts and ecofacts associated with past human oc ...
s have been dated the earliest civilisations back to 200-300 BCE. The islands have been mentioned by Ptolemy in the 2nd century CE.
Middle ages
 The
The Nicobar islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelago, archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of t ...
existed on a major trade route connecting India to the South East Asia and had much contact with the outside world for centuries. But there are very few accounts of information as there was no written language with the indigenous people to document their history. The islands have been mentioned in the accounts of travellers like Faxian
Faxian (337–), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized as Fa-hien and Fa-hsien, was a Han Chinese, Chinese Chinese Buddhism, Buddhist bhikkhu, monk and translator who traveled on foot from Eastern Jin dynasty, Jin China to medieval India t ...
in the 6th century CE and I-T'sing in 7th century CE.
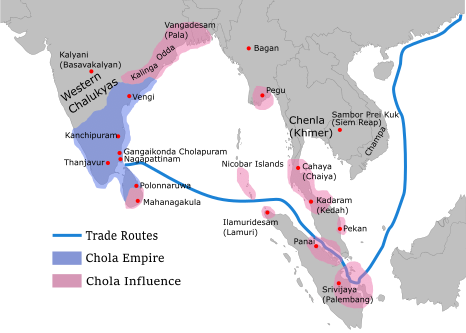
In the 11th century CE, Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra I (26 July 971 – 1044), often referred to as Rajendra the Great, was a Chola Empire, Chola Emperor who reigned from 1014 to 1044. He was born in Thanjavur to Rajaraja I. His queen was Vanavan Mahadevi and he assumed royal power as ...
of the Chola dynasty
The Chola dynasty () was a Tamil dynasty originating from Southern India. At its height, it ruled over the Chola Empire, an expansive maritime empire. The earliest datable references to the Chola are from inscriptions dated to the 3rd cen ...
of Tamilakam
Tamilakam () also known as ancient Tamil country as was the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covering the southernmost region of the Indian subcontinent. Tamilakam covered today's Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Puducherry, La ...
invaded parts of South East Asia using the Nicobar islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelago, archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean. They are located in Southeast Asia, northwest of Aceh on Sumatra, and separated from Thailand to the east by the Andaman Sea. Located southeast of t ...
as an intermediate naval base. It was part of an established Chola trade route connecting India and South East Asia, with the practice continuing in the subsequent years during the reigns of Rajendra II
Rajendra Chola II (997 CE – 1064 CE) often referred to as Rajendradeva Chola was a Chola emperor who reigned from 28 May 1052 to 1064. Rajendra II succeeded his brother Rajadhiraja I after his death at the Battle of Koppam.''The History a ...
and Kulothunga I
Kulottunga Chola I ('; Middle Tamil: Kulōttuṅka Cōḻaṉ; Classical Sanskrit: Kulottuṅgā Cōḷa; 1025–1122) also spelt Kulothunga (), born Rajendra Chalukya (Telugu language, Telugu: Rājēndra Cāḷukyuḍu), was a Chola empire, C ...
. Chola inscriptions from Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
, dated to 1050 CE, describe the islands as ''Ma-Nakkavaram'' meaning "great open/naked land" in Tamil. The islands are later mentioned by Marco Polo in the 13th century CE and Friar Oderic in early 14th century CE.
European colonisation
The Europeancolonisation
475px, Map of the year each country achieved List of sovereign states by date of formation, independence.
Colonization (British English: colonisation) is a process of establishing occupation of or control over foreign territories or peoples f ...
on the islands began when settlers from the Danish East India Company
The Danish East India Company () refers to two separate Danish-Norwegian chartered company, chartered companies. The first company operated between 1616 and 1650. The second company existed between 1670 and 1729, however, in 1730 it was re-founde ...
arrived on the Nicobar Islands on 12 December 1755. On 1 January 1756, the Nicobar Islands were made into a Danish colony, first named (New Denmark) and later (Frederick's Islands). The islands were managed from the Danish colony of Tranquebar
Tharangambadi (), formerly Tranquebar (, ), is a town in the Mayiladuthurai district of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu on the Coromandel Coast. It lies north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary named Uppanar of the Kaveri River. It wa ...
in the Indian mainland. However, various attempts to settle on the islands were unsuccessful due to repeated outbreaks of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
, which led to the death of the colonists.
 Between 1778 and 1783,
Between 1778 and 1783, William Bolts
William Bolts (7 February 1739 – 1808) was a Dutch-born British merchant active in India. He began his career as an employee of the East India Company, and subsequently became an independent merchant. He is best known today for his 1772 book, ' ...
tried to establish an Austrian colony on the Nicobar islands, mistakenly assuming that the Danish had abandoned the claims to the islands, renaming them ''Theresa Islands''. In 1789, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
colonised the Andaman islands
The Andaman Islands () are an archipelago, made up of 200 islands, in the northeastern Indian Ocean about southwest off the coasts of Myanmar's Ayeyarwady Region. Together with the Nicobar Islands to their south, the Andamans serve as a mari ...
to set up a naval base
A naval base, navy base, or military port is a military base, where warships and naval ships are docked when they have no mission at sea or need to restock. Ships may also undergo repairs. Some naval bases are temporary homes to aircraft that usu ...
and establish a penal colony
A penal colony or exile colony is a settlement used to exile prisoners and separate them from the general population by placing them in a remote location, often an island or distant colonial territory. Although the term can be used to refer ...
. In 1794, a first batch of 100 prisoners were sent to the island but the settlement was abandoned in 1796.
In 1858, the British established a colony near Port Blair
Port Blair (), officially named Sri Vijaya Puram, is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (''tehsil'') of the islands, the headqu ...
. Between 1864 and 1868, Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
tried to buy the island from the Danish. On 16 October 1868, the Danish sold the rights to the Nicobar islands to the British, which was made part of the British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
in 1869. In 1872, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands were united under a single command and administered by a chief commissioner based out of Port Blair. The construction of the Cellular Jail
The Cellular Jail, also known as Kālā Pānī (), was a British colonial prison in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The prison was used by the colonial government of India for the purpose of exiling criminals and political prisoners. Many ...
started in 1896 and was completed in 1906. The jail was used to house political prisoner
A political prisoner is someone imprisoned for their political activity. The political offense is not always the official reason for the prisoner's detention.
There is no internationally recognized legal definition of the concept, although ...
s and independence activists
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state, in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the status of a ...
away from the Indian mainland.
World War II
During theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, the islands were invaded by the Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
as a part of their attack on the allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
in 1942. Port Blair was captured by the Japanese on 23 March 1942 and established control over the island. The provisional control was passed on to the Azad Hind
The Provisional Government of Free India or, more simply, Azad Hind, was a short-lived Japanese-controlled provisional government in India. It was established in Japanese occupied Singapore during World War II in October 1943 and has been con ...
of Subhash Chandra Bose
Subhas Chandra Bose (23 January 1897 – 18 August 1945) was an Indian independence movement, Indian nationalist whose defiance of British raj, British authority in India made him a hero among many Indians, but his wartime alliances with ...
on 29 December 1943, based on the understanding with the Japanese with the islands renamed as ''Shaheed-Dweep'' (Martyr Island) and ''Swaraj-dweep'' (Self-rule Island). Bose appointed General A. D. Loganathan as the governor of the islands, who had limited power while the real control of the islands remained with the Japanese. In the years under Japanese occupation, there have been reports of widespread looting
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
, arson, rape and extra judicial killings.
Local people were often killed on trivial matters with the largest being the Homfreyganj massacre on 30 January 1944, where 44 local civilians were shot by the Japanese on suspicion of spying. Japanese Vice Admiral Teizo Hara and Major-General Tamenori Sato surrendered to Lieutenant Colonel Nathu Singh, the commanding officer of the Rajput Regiment
The Rajput Regiment is one of the oldest infantry regiments of the Indian Army. The regiment traces its history back to 1778, when the 24th Regiment of Bengal Native Infantry was formed. The regiment's 1st Battalion was later formed in 1798 ...
on 15 August 1945, on board the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
ship HMS ''Rocksand'' and the territory was officially handed back over to the British to Brigadier J. A. Salomons, commander of 116th Indian Infantry Brigade, and Chief Administrator Noel Patterson, in a ceremony performed at the Gymkhana Ground in Port Blair on 7 October 1945.
Approximately 2,000 people in the Andamans are thought to have died as a result of the occupation, and at least 501 were tortured by the Japanese. The former figure represents 10% of the pre-war population of Port Blair.
Post independence
During thePartition of India
The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into two independent dominion states, the Dominion of India, Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan. The Union of India is today the Republic of India, and the Dominion of Paki ...
, the British announced their intention to retain possession of the islands and use them to resettle Anglo-Indians
Anglo-Indian people are a distinct minority community of mixed-race British and Indian ancestry. During the colonial period, their ancestry was defined as British paternal and Indian maternal heritage; post-independence, "Anglo-Indian" has a ...
and Anglo-Burmese
The Anglo-Burmese people, also known as the Anglo-Burmans, are a community of Eurasians of Burmese and European descent; they emerged as a distinct community through mixed relationships (sometimes permanent, sometimes temporary) between the B ...
on these islands. The islands were claimed by the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party, or simply the Congress, is a political parties in India, political party in India with deep roots in most regions of India. Founded on 28 December 1885, it was the first mo ...
for India and the Muslim League Muslim League may refer to:
Political parties British India
*All-India Muslim League, led the demand for the partition of India resulting in the creation of Pakistan
** Punjab Muslim League, a branch of the organization above
**Unionist Muslim L ...
for Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
during the partition negotiations. After the Indian Independence in 1947, the islands became part of the Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,
*
* was an independent dominion in the British Commonwealth of Nations existing between 15 August 1947 and 26 January 1950. Until its Indian independence movement, independence, India had be ...
. As per the Constitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India, legal document of India, and the longest written national constitution in the world. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures ...
, the Islands were designated as the only part D territory in 1950, to be administered by a lieutenant governor appointed by the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
. The islands were later used to resettle people displaced during the partition with a substantial number of displaced immigrants establishing agricultural colonies. The islands became a separate union territory
Among the states and union territories of India, a Union Territory (UT) is a region that is directly governed by the Government of India, central government of India, as opposed to the states, which have their own State governments of India, s ...
administered by the Government of India
The Government of India (ISO 15919, ISO: Bhārata Sarakāra, legally the Union Government or Union of India or the Central Government) is the national authority of the Republic of India, located in South Asia, consisting of States and union t ...
, following the re-organization in 1956. The islands have been developed into a key defence establishment since the 1980s due to its strategic location in the Bay of Bengal across the Strait of Malacca
The Strait of Malacca is a narrow stretch of water, long and from wide, between the Malay Peninsula to the northeast and the Indonesian island of Sumatra to the southwest, connecting the Andaman Sea (Indian Ocean) and the South China Sea (Pa ...
.
The first marine protected area
A marine protected area (MPA) is a protected area of the world's seas, oceans, estuaries or in the US, the Great Lakes. These marine areas can come in many forms ranging from wildlife refuges to research facilities. MPAs restrict human activity ...
s in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands were established in 1977. Those included small island sanctuaries such as Arial, Bamboo, Barren and several others, mainly to protect coral reef ecosystems and nesting sites for seabird species. To stimulate the protection of marine life, a significant milestone towards marine conservation came in 1983 with the establishment of the Mahatma Gandhi Marine National Park
Mahatma Gandhi Marine National Park is a national park in India, near Wandoor on the Andaman Islands. It belongs to the South Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Histo ...
near Wandoor
Wandoor is a town in Nilambur Taluk, Malappuram District, Kerala, India. It is located on the southeast of the Chaliyar River, about 24 kilometres northeast of the district seat Malappuram and 8 km south of the taluk seat Nilambur. In the ...
on South Andaman Island
South Andaman Island is the southernmost island of the Great Andaman and is home to the majority of the population of the Andaman Islands.
It belongs to the South Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman a ...
.
On 26 December 2004, the coasts of the Andaman and Nicobar islands experienced high tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from , ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and underwater explosions (including detonations, ...
waves following an undersea earthquake in the Indian Ocean which resulted in more than 2,000 casualties, 46,000 injuries and rendering at least 40,000 homeless. The locals and tourists on the islands suffered the greatest casualties while the indigenous people largely survived unscathed due to movement to high grounds following the oral traditions passed down over generations that warned them to evacuate following earthquakes.
Geography
islands
This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the #Other lists of islands, other lists of islands below.
Lists of islands by count ...
and islets
An islet ( ) is generally a small island. Definitions vary, and are not precise, but some suggest that an islet is a very small, often unnamed, island with little or no vegetation to support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and ...
occupying an area of , of which only 31 are permanently inhabited. The islands extend from 6° to 14° North latitudes
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the ...
and from 92° to 94° East longitudes
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east-west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter ...
. The islands are grouped into the north Andaman islands and south Nicobar islands, separated by the wide Ten Degree Channel
The Ten Degree Channel is a channel that separates the Andaman Islands and Nicobar Islands from each other in the Bay of Bengal. The two sets of islands together form the Indian Union Territory (UT) of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. This channel ...
. The Andamans cover an area of while the Nicobar group covers an area of . The highest point is the Saddle Peak at , located in North Andaman Island.
The northernmost point of the islands is away from the mouth of the Hooghly River
The Hooghly River (, also spelled ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli'') is the westernmost distributary of the Ganges, situated in West Bengal, India. It is known in its upper reaches as the Bhagirathi. The Bhagirathi splits off from the main branch of the G ...
in the Indian mainland. The territory shares maritime border
A maritime boundary is a conceptual division of Earth's water surface areas using physiographical or geopolitical criteria. As such, it usually bounds areas of exclusive national rights over mineral and biological resources,VLIZ Maritime Boun ...
s with Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
located about to the south, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
located to the north-east and Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
located to the south-east. Indira Point, the southernmost point of India, is located at 6°45'10″N and 93°49'36″E at the southern tip of Great Nicobar
Great Nicobar is the southernmost and largest of the Nicobar Islands of India, north of Sumatra. It is part of India, in the Nicobar district within the union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
History
The Nicobar Island has been ...
. The capital and largest city is Port Blair (officially Sri Vijaya Puram), located from Chennai
Chennai, also known as Madras (List of renamed places in India#Tamil Nadu, its official name until 1996), is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Tamil Nadu by population, largest city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost states and ...
and from Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
on the Indian mainland. Barren Island, the only active volcano
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ...
in India, is located in the Andaman Sea.
The islands have a long coast-line. The topography of the territory varies significantly across various islands. The islands may have sandy, rocky sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
or marshy beaches on the coastlines and might be surrounded by shoals
In oceanography, geomorphology, and geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material, and rises from the bed of a body of water close to the surface or ...
and coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in group ...
s. The altitude varies significantly from completely flat islands to gradually raising topography from the coast to the interior in larger islands. The islands are generally surrounded by shallow seas of varying depths in the vicinity with some deep natural bays occurring along certain coasts. The islands have a moderate temperature around the year with the average ranging from 23 °C to 31 °C. The islands have a tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot te ...
with warm summers and not so chill winters. The rainfall is dependent on the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
s and tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s are common in late summer.
Flora and fauna
The islands havemangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have particular adaptations to take in extra oxygen a ...
s interspersed with marshes, coconut tree
The coconut tree (''Cocos nucifera'') is a member of the palm tree family (biology), family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus ''Cocos''. The term "coconut" (or the archaic "cocoanut") can refer to the whole coconut palm, ...
s or dispersed bushy vegetation along the coast. There are twelve types of forests that occur in the islands including evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has Leaf, foliage that remains green and functional throughout the year. This contrasts with deciduous plants, which lose their foliage completely during the winter or dry season. Consisting of many diffe ...
, deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
, mangrove, littoral
The littoral zone, also called litoral or nearshore, is the part of a sea, lake, or river that is close to the shore. In coastal ecology, the littoral zone includes the intertidal zone extending from the high water mark (which is rarely i ...
, bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of mostly evergreen perennial plant, perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily (biology), subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family, in th ...
, sub-montane and brackish water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuary ...
forests. North Andaman
North Andaman Island is the northern island of Great Andaman of the Andaman Islands.
It belongs to the North and Middle Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
the island is lying n ...
is characterised by wet evergreen forests with climbing plants
A vine is any plant with a growth habit of trailing or scandent (that is, climbing) stems, lianas, or runners. The word ''vine'' can also refer to such stems or runners themselves, for instance, when used in wicker work.Jackson; Benjamin; Dayd ...
, Middle Andaman
Middle Andaman Island is an island of the Andaman Islands. It belongs to the North and Middle Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Geography
The island belongs to the Great Andama ...
has moist deciduous forests and South Andaman
South Andaman Island is the southernmost island of the Great Andaman and is home to the majority of the population of the Andaman Islands.
It belongs to the South Andaman administrative district, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman an ...
islands have epiphytic
An epiphyte is a plant or plant-like organism that grows on the surface of another plant and derives its moisture and nutrients from the air, rain, water (in marine environments) or from debris accumulating around it. The plants on which epiphyt ...
vegetation, mostly ferns
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
and orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth ...
. The North Nicobar islands are mostly barren with grasslands
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes such as clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur ...
while evergreen forests form the dominant vegetation in the central and southern islands of the Nicobar group. The forest coverage is estimated to be 86.2% of the total land area with about 2,200 varieties of plants of which 200 are endemic and 1,300 do not occur in mainland India. There are more than 200 species used for timber.
There are more than 8300 species of fauna of which 1117 are endemic to the islands. Most of the larger species were introduced by colonists and travellers, some of which became endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
due to their prolonged isolation. There are about 55 mammal species of which 32 are endemic with 26 species of rats and 14 species of bats, the most among the mammals. The endangered
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
Indian elephant
The Indian elephant (''Elephas maximus indicus'') is one of three extant recognized subspecies of the Asian elephant, native to mainland Asia. The species is smaller than the African elephant species with a convex back and the highest body po ...
can be found in forested or mountainous areas of the islands, which were originally introduced from the mainland to help with the timber extraction in 1883. Endangered and critically endangered species endemic to the islands include the Andaman white-toothed shrew
The Andaman shrew (''Crocidura andamanensis''), also known as the Andaman white-toothed shrew, is a critically endangered species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to South Andaman Island in the Andaman Islands of India.
Taxonomy ...
, Andaman spiny shrew
The Andaman spiny shrew or Andaman shrew (''Crocidura hispida'') is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries ...
, Jenkin's shrew
Jenkins's shrew (''Crocidura jenkinsi'') is a critically endangered species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is endemic to South Andaman Island in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is t ...
, Nicobar spiny shrew, Nicobar tree shrew, Miller's Nicobar rat
The nonsense rat, Nicobar Archipelago rat or Miller's Nicobar rat (''Rattus burrus'') is endemic to the Nicobar Islands in India. It lives on Great Nicobar, Little Nicobar, and Trinket islands. On Car Nicobar Island, ''Rattus palmarum'' and ''Ra ...
, Palm rat
The palm rat (''Rattus palmarum'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in the Nicobar Islands, on Car Nicobar and Great Nicobar islands.
The palm rat's natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry forest and subtropic ...
, Andaman teal, Nicobar scops owl, Andaman boobook
The Andaman boobook or Andaman hawk-owl (''Ninox affinis'') is a species of owl in the family Strigidae. It is endemic to the Andaman Islands.
Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forest and subtropical or tropical man ...
and Darwin's eastern frog. Other large fauna include Wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
, Spotted deer
The chital or cheetal (''Axis axis''; ), also called spotted deer, chital deer and axis deer, is a deer species native to the Indian subcontinent. It was first described by Johann Christian Polycarp Erxleben in 1777. A moderate-sized deer, mal ...
, Barking deer
Muntjacs ( ), also known as the barking deer or rib-faced deer, (URL is Google Books) are small deer of the genus ''Muntiacus'' native to South Asia and Southeast Asia. Muntjacs are thought to have begun appearing 15–35 million years ago, ...
and Sambar deer
The sambar (''Rusa unicolor'') is a large deer native to the Indian subcontinent, South China and Southeast Asia that is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 2008. Populations have declined substantially due to severe huntin ...
. There are about 270 species of birds in the islands of which 90 are endemic. The islands' caves
Caves or caverns are natural voids under the Earth's surface. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. Exogene caves are smaller openings that extend a relatively short distance underground (such as rock ...
are nesting grounds for the Edible-nest swiftlet
The edible-nest swiftlet (''Aerodramus fuciphagus''), also known as the white-nest swiftlet, is a small bird of the swift family which is found in Southeast Asia. Its opaque and whitish bird nest is made exclusively of solidified saliva and is t ...
, whose nests are prized for bird's nest soup
Edible bird's nests, also known as swallow nests ( zh, c=燕窝, p=yànwō), are bird nests created from solidified saliva by edible-nest swiftlets, Indian swiftlets and other swiftlets of the genera ''Aerodramus'', '' Hydrochous'', '' Schout ...
. The islands serve as an intermediate resting site for birds such as Horsfield's bronze cuckoo
Horsfield's bronze cuckoo (''Chalcites basalis'') is a small cuckoo in the family Cuculidae. Its size averages and is distinguished by its green and bronze iridescent colouring on its back and incomplete brown barring from neck to tail. Horsfiel ...
, Zappey's flycatcher and Javan pond heron
The Javan pond heron (''Ardeola speciosa'') is a wading bird of the heron family, found in shallow fresh and salt-water wetlands in Southeast Asia. Its diet comprises insects, fish, and crabs.
The Javan pond heron is typically 45 cm long wi ...
during long distance migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
s. The Nicobar pigeon
The Nicobar pigeon or Nicobar dove (''Caloenas nicobarica'', Car: ') is a bird found on small islands and in coastal regions from the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India, east through the Indonesian Archipelago, to the Solomons and Palau. It is ...
found in the islands is the closest living relative to the extinct Dodo
The dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinction, extinct flightless bird that was endemism, endemic to the island of Mauritius, which is east of Madagascar in the Indian Ocean. The dodo's closest relative was the also-extinct and flightles ...
.
There are about 64 species of reptiles of which half of them are endemic to the islands. More than 1350 species of echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s and mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
s and 200 species of coral
Corals are colonial marine invertebrates within the subphylum Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact Colony (biology), colonies of many identical individual polyp (zoology), polyps. Coral species include the important Coral ...
s are found in the seas surrounding the islands. Larger marine species include salt water crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (''Crocodylus porosus'') is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaland to northern Australia and Micronesia. It h ...
s, dugong
The dugong (; ''Dugong dugon'') is a marine mammal. It is one of four living species of the order Sirenia, which also includes three species of manatees. It is the only living representative of the once-diverse family Dugongidae; its closest ...
s, turtles, dolphins and whales. There are more than 1350 species of fishes
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed ...
including 13 fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salt (chemistry), salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include ...
species. The islands are well known for prized shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
, the commercial exploitation of which began in the early 20th century. There are about nine national park
A national park is a nature park designated for conservation (ethic), conservation purposes because of unparalleled national natural, historic, or cultural significance. It is an area of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that is protecte ...
s, 96 wildlife sanctuaries
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geologi ...
and one biosphere reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, funga, or features of geologic ...
in the islands. The territory is home for about 896 species of winged insects including 225 butterflies
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossi ...
species.
Demographics
As per the 2011 census, the population was 380,581, of which 202,871 (53.3%) were males and 177,710 (46.7%) were females. The sex ratio was 878 females per 1,000 males. There were a total of 94,551 households and about 143,488 (37.7%) of the population lived in urban areas.Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
(69.5%) is the major religion of people of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands followed by Christianity (21.7%) and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(8.5%).
The Andaman islands were populated by the indigenous people
There is no generally accepted definition of Indigenous peoples, although in the 21st century the focus has been on self-identification, cultural difference from other groups in a state, a special relationship with their traditional territ ...
(the Great Andamanese
The Great Andamanese are an indigenous people of the Great Andaman archipelago in the Andaman Islands. Historically, the Great Andamanese lived throughout the archipelago, and were divided into ten major tribes. Their distinct but closely rela ...
, the Onge
The Onge (also Önge, Ongee, and Öñge) are an Andamanese ethnic group, indigenous to the Andaman Islands in Southeast Asia at the Bay of Bengal, India. They are traditionally hunter-gatherers and fishers, but also practice plant cultivatio ...
, the Jarawa and the Sentinelese
The Sentinelese, also known as the Sentineli and the North Sentinel Islanders, are Indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island in the Bay of Bengal in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Designated a particularly vulnerable tribal group a ...
) who were isolated and spoke Andamanese languages
The Andamanese languages are the various languages spoken by the indigenous peoples of the Andaman Islands in the Indian Ocean. There are two known Andamanese language families, Great Andamanese and Ongan, as well as two presumed but unattested ...
for thousands of years. The Nicobar islands, which was part of trade routes and was frequented by travellers, were populated by Shompen people
The Shompen or Shom Pen are the Indigenous people of the interior of Great Nicobar Island, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
The Shompen are designated as a Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Group within the list of ...
before the islands were settled by Nicobarese people
The Nicobarese people are an Austroasiatic-speaking people of the Nicobar Islands, a chain of islands in the Bay of Bengal north of Sumatra, forming part of the union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands, India. The Nicobar Archipelago cons ...
, who spoke Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
languages. The islands include the North Sentinel Island
North Sentinel Island is one of the Andaman Islands, an Indian archipelago in the Bay of Bengal which also includes South Sentinel Island. The island is a protected area of India. It is home to the Sentinelese, an indigenous tribe in volunta ...
, home to the Sentinelese people, among the only known uncontacted tribe
Uncontacted peoples are groups of Indigenous peoples living without sustained contact with neighbouring communities and the world community. Groups who decide to remain uncontacted are referred to as indigenous peoples in voluntary isolation. Leg ...
in India. When the islands were first colonised, the population of the natives were estimated to be around 5,000 and while the population of islands temporarily increased during colonisation, the population saw a massive spike post-1960s due to the policies of the Union Government that encouraged settlers from other parts of the country. In the early 21st century, the population of indigenous people has drastically dropped. , it was estimated to consist of 44 Great Andamanese, 380 Jarawas, 101 Onges, 15 Sentinelese and 229 Shompens. The Government of India is trying to protect the remnant population by providing access to healthcare facilities, communication and social engagement.
Languages
The Andamanese people speak about a dozen endangered Andamanese languages, which belong to two families,Great Andamanese
The Great Andamanese are an indigenous people of the Great Andaman archipelago in the Andaman Islands. Historically, the Great Andamanese lived throughout the archipelago, and were divided into ten major tribes. Their distinct but closely rela ...
and Ongan that are unrelated to each other or to any other language group. There are two unattested languages: Sentinelese
The Sentinelese, also known as the Sentineli and the North Sentinel Islanders, are Indigenous people who inhabit North Sentinel Island in the Bay of Bengal in the northeastern Indian Ocean. Designated a particularly vulnerable tribal group a ...
, spoken by Sentinelese people, who refuse contact with outsiders, which might be related to Ongan as per Anvita Abbi
Anvita Abbi (born 9 January 1949) is an Indian linguist and scholar of minority languages, known for her studies on tribal languages and other minority languages of South Asia. In 2013, she was honoured with the Padma Shri, the fourth highest ci ...
and Jangil
The Jangil (also Rutland Jarawa or Rutland Onge) were one of the Indigenous peoples of the Andaman Islands in India. They lived in the interior of Rutland Island, and were given the name Rutland Jarawa because it was supposed that they were re ...
, which became extinct in the 1920s. Indigenous to the Nicobar Islands are the Shompen language
Shompen, or Shom Peng, is a language or group of languages spoken on Great Nicobar Island in the Indian union territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, in the Indian Ocean, northwest of Sumatra, Indonesia.
Partially because the native peopl ...
, spoken by Shompen people and the five Nicobarese languages
The Nicobarese languages or Nicobaric languages, form an isolated group of about half a dozen closely related Austroasiatic languages, spoken by most of the inhabitants of the Nicobar Islands of India. They have a total of about 30,000 speakers ...
, which form part of the Austroasiatic
The Austroasiatic languages ( ) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority popu ...
language family and are spoken by about people or 7.6% of the population.
The majority of the population, however, are speakers of immigrant languages which include Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
(28.5%), Tamil
Tamil may refer to:
People, culture and language
* Tamils, an ethno-linguistic group native to India, Sri Lanka, and some other parts of Asia
**Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka
** Myanmar or Burmese Tamils, Tamil people of Ind ...
(15.2%), Telugu
Telugu may refer to:
* Telugu language, a major Dravidian language of South India
** Telugu literature, is the body of works written in the Telugu language.
* Telugu people, an ethno-linguistic group of India
* Telugu script, used to write the Tel ...
(13.2%), Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
(12.9%), Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
(7.2%). Sadri
Sadri is a municipality in the Pali district of Rajasthan, India. Before it was formally founded, there were various settlements in the area which fell under the Jagir of the Rajput clan Sindhal Rathore who still reside in the central part of ...
(5.5%), and Kurukh (4%). Hindi
Modern Standard Hindi (, ), commonly referred to as Hindi, is the Standard language, standardised variety of the Hindustani language written in the Devanagari script. It is an official language of India, official language of the Government ...
is the official language of the region, while English is declared an additional official language for communication purposes.
Administration and politics
The islands form a part of the union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and is administered by aLieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
on behalf of the Government of India. The union territory was established in 1956 with a chief commissioner as the head of the administration. In 1982, the Lieutenant Governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
replaced the Chief Commissioner as the head of administration.
In 1981, a "Pradesh council" with councillors as representatives of the people was constituted to advise the Lieutenant Governor. The territory sends one representative to Lok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, also known as the House of the People, is the lower house of Parliament of India which is Bicameralism, bicameral, where the upper house is Rajya Sabha. Member of Parliament, Lok Sabha, Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by a ...
of the Indian Parliament
The Parliament of India (ISO: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Government of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The President o ...
from its Andaman and Nicobar Islands Lok Sabha constituency
Andaman and Nicobar Islands Lok Sabha constituency is the only Lok Sabha (Parliamentary) constituency in the Union Territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It covers the entire union territory. Andaman and Nicobar Island has been voting for its ...
. The territory is divided into three districts, each headed by a deputy commissioner. The Calcutta High Court
The Calcutta High Court is the oldest High Court in India. It is located at Esplanade Row West, Calcutta (Kolkata), West Bengal. It has jurisdiction over the state of West Bengal and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. T ...
has jurisdiction over the islands with a permanent seat at Port Blair.
The indigenous communities have their own system of administration. There are long term settlements known as ''baraij'' and short-term settlements known as ''chang''. The coast-dwellers (''aryoto'') have semi-permanent settlements and the interior groups (''eremtaga'') dwell on temporary settlements, which enable them to migrate during dry seasons.
Economy
, the GSDP was . Agriculture is a major occupation with nearly 50% of the population engaged in the sector. Only about of land, which is about 6% of the total land area, can be used for agriculture.Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
is the main food crop, grown in about 20% of the arable land. Most of the food for consumption is imported from mainland India. Coconut and arecanut
The areca nut ( or ) or betel nut () is the fruit of the areca palm (''Areca catechu''). The palm is originally native to the Philippines, but was carried widely through the tropics by the Austronesian expansion, Austronesian migrations and ...
are the cash crops grown in the Nicobar islands. Other crops include pulses
Legumes are plants in the pea family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consum ...
, oilseeds
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of edible plants. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed o ...
, vegetables like okra
Okra (, ), ''Abelmoschus esculentus'', known in some English-speaking countries as lady's fingers, is a flowering plant in the Malvaceae, mallow family native to East Africa. Cultivated in tropical, subtropical, and warm temperate regions aro ...
, brinjal
Eggplant ( US, CA, AU, PH), aubergine ( UK, IE, NZ), brinjal ( IN, SG, MY, ZA, SLE), or baigan ( IN, GY) is a plant species in the nightshade family Solanaceae. ''Solanum melongena'' is grown worldwide for its edible fruit, typic ...
, cucurbit and radish
The radish (''Raphanus sativus'') is a flowering plant in the mustard family, Brassicaceae. Its large taproot is commonly used as a root vegetable, although the entire plant is edible and its leaves are sometimes used as a leaf vegetable. Origina ...
; spices
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
and fruits
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants (angiosperms) that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in particular have long propaga ...
such as mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree '' Mangifera indica''. It originated from the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast As ...
, sapota
''Manilkara zapota'', commonly known as sapodilla (), sapote, chicozapote, chicoo, chicle, naseberry, nispero, or
soapapple, among other names, is an evergreen tree native to southern Mexico and Central America. An example natural occurrence is ...
, orange, banana, guava
Guava ( ), also known as the 'guava-pear', is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava '' Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), nativ ...
and pineapple
The pineapple (''Ananas comosus'') is a Tropical vegetation, tropical plant with an edible fruit; it is the most economically significant plant in the family Bromeliaceae.
The pineapple is indigenous to South America, where it has been culti ...
. Rubber, red oil
{{inline, date=May 2024
Red oil is defined as a substance of varying composition formed when an organic solution, typically tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP, an agent used for extracting heavy metals in nuclear reprocessing plants) and its diluent, c ...
, palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
** List of Arecaceae genera
**Palm oil
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music ...
and cashew
Cashew is the common name of a tropical evergreen tree ''Anacardium occidentale'', in the family Anacardiaceae. It is native to South America and is the source of the cashew nut and the cashew apple, an accessory fruit. The tree can grow as t ...
are grown on a limited scale in plantations. The territory has an exclusive economic zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, reso ...
of more than 0.6 million sq. km, which contributes to the fishing industry. , the region produced 27,526 tonnes of fish, mostly from marine sector with minor contribution from inland fisheries.
, there were 1,833 registered small-scale industries with majority being involved in engineering, woodworking
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinetry, furniture making, wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first materials worked b ...
and textiles apart from 21 factories. District Industries Centre (DIC) is the body responsible for the development of small and medium industries in the islands. Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation Limited (ANIIDCO), established in 1988, is responsible for the development and economic growth of the islands.
Tourism
 Tourism is one of the major contributors to the economy of the islands. The islands had more than 400,000 visitors in 2016 with a 94% contribution from domestic tourists. In 2018, plans to develop facilities in various islands under the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) Aayog was initiated by Government of India, with the aim of increasing tourist inflows. Foreign tourists are issued Restricted Area Permits (RAP) which gives access to specific areas with conditions. While domestic tourists do not require a permit to visit the accessible parts of the islands, the tribal reserves are forbidden and requires special permission for access. The islands have many beaches due to its long coastline and various
Tourism is one of the major contributors to the economy of the islands. The islands had more than 400,000 visitors in 2016 with a 94% contribution from domestic tourists. In 2018, plans to develop facilities in various islands under the National Institute of Transforming India (NITI) Aayog was initiated by Government of India, with the aim of increasing tourist inflows. Foreign tourists are issued Restricted Area Permits (RAP) which gives access to specific areas with conditions. While domestic tourists do not require a permit to visit the accessible parts of the islands, the tribal reserves are forbidden and requires special permission for access. The islands have many beaches due to its long coastline and various water sports
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms ...
are practised including kayaking
Kayaking is the use of a kayak for moving over water. It is distinguished from canoeing by the sitting position of the paddler and the number of blades on the paddle. A kayak is a low-to-the-water, canoe-like boat in which the paddler sits fac ...
, scuba diving
Scuba diving is a Diving mode, mode of underwater diving whereby divers use Scuba set, breathing equipment that is completely independent of a surface breathing gas supply, and therefore has a limited but variable endurance. The word ''scub ...
and parasailing
Parasailing, also known as parascending, is an activity where individuals are harnessed to a modified parachute canopy that is designed to ascend into the air when towed behind a motor vehicle on land, or a recreational boat over water. Commerc ...
.
Major attractions include the Cellular Jail
The Cellular Jail, also known as Kālā Pānī (), was a British colonial prison in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. The prison was used by the colonial government of India for the purpose of exiling criminals and political prisoners. Many ...
, Chatham Saw Mill, Forest Museum, Samudrika Naval Marine Museum, Anthropological Museum, Fisheries Aquarium, Science Center and Carbyn's cove in Port Blair; Bharatpur, Lakshmanpur and Sitapur beaches in Shaheed Dweep; Elephant and Radhanagar beaches in Swaraj Dweep; Hudi tikri, Red, Bird and Bat islands, Amkunj beach near Rangat; Dhaninallah mangroves and Karmatang beach near Mayabunder; limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
caves and mud volcanoes near Diglipur; Craggy island and Ross Ross may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Ross (name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the surname or given name Ross, as well as the meaning
* Clan Ross, a Highland Scottish clan
Places Antarctica
* Ross Sea
...
& Smith islands
The Smith Islands are two Antarctic islands lying close to Tracy Point, the western extremity of Beall Island, in the Windmill Islands. They were first mapped from air photos taken by USN Operation Highjump and Operation Windmill in 1947 and 1 ...
and various national parks and protected sanctuaries.
Transportation
The islands are served byVeer Savarkar International Airport
Veer Savarkar International Airport is an international airport located south of Sri Vijaya Puram (Port Blair) and the primary airport serving the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Earlier known as Port Blair Airport, it was renamed in 2 ...
near Port Blair which has regular flights to major cities in India. The airport operates as a civil enclave
A joint-use airport is an aerodrome that is used for both military aviation and civil aviation. They typically contain facilities of both a civil airport and a military air base.
By country India
Visakhapatnam Airport operates as a civil enclav ...
, sharing airside facilities with INS Utkrosh
INS Utkrosh , is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command of the Indian Armed Forces. It is located near naval base INS Jarawa on Port Blair, the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
It shares ...
of the Indian Navy
The Indian Navy (IN) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the Navy, maritime and Amphibious warfare, amphibious branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of the Naval Staff (India), Chief ...
. The airport has a single runway
In aviation, a runway is an elongated, rectangular surface designed for the landing and takeoff of an aircraft. Runways may be a human-made surface (often asphalt concrete, asphalt, concrete, or a mixture of both) or a natural surface (sod, ...
of in length, with the civilian terminal operated by the Airports Authority of India
The Airports Authority of India (AAI) is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Civil Aviation (India), Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India. It is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining, and managing civi ...
with air traffic operations managed by the Indian Navy. Andaman and Nicobar Command
The Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) is a integrated tri-services command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a Union Territory of India. It was created in 2001 to safeguard India's strategic in ...
of Indian Armed Forces
The Indian Armed Forces are the armed forces, military forces of the India, Republic of India. It consists of three professional uniformed services: the Indian Army, the Indian Navy, and the Indian Air Force.—— Additionally, the Indian Ar ...
operates air base
An airbase (stylised air base in American English), sometimes referred to as a military airbase, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base, is an aerodrome or airport used as a mi ...
s of Car Nicobar AFS, INS Kohassa, INS Utkrosh and INS Baaz
INS Baaz is an Indian naval air station under the joint-services Andaman and Nicobar Command (ANC) of the Indian Armed Forces. It is located near Campbell Bay, on Great Nicobar island in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is the southernmost a ...
.
There are 23 ports along the islands with a major port at Port Blair
Port Blair (), officially named Sri Vijaya Puram, is the capital city of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a union territory of India in the Bay of Bengal. It is also the local administrative sub-division (''tehsil'') of the islands, the headqu ...
and eight other significant ports including Diglipur
Diglipur (sometimes spelled Diglipore) is the largest town of North Andaman Island, in the Andaman Archipelago, India. It is located on the southern side of Aerial Bay, at above sea level, north of Port Blair. It is crossed by the Kalpong R ...
, Mayabunder
Mayabunder is a town and a tehsil in the northern part of Middle Andaman Island, Andaman Archipelago, India. The name is also spelled Maya Bunder or Maya Bandar. As of 2001, the county had 23,912 inhabitants, of which 3182 were in the town.Gov ...
, Rangat, Hut Bay, Car Nicobar
Car Nicobar ( in Car language) is the northernmost of the Nicobar Islands. It is also one of three local administrative divisions of the Indian district of Nicobar, part of the Indian union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Annual ra ...
, Katchal and Campbell Bay. In 2022, the Government of India proposed the development of a new container ship terminal and an airport at Great Nicobar. There are 39 light houses
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mark da ...
situated across the islands.
, there are long national highways
National Highways (NH), formerly Highways England and before that the Highways Agency, is a State-owned enterprise, government-owned company charged with operating, maintaining and improving Roads in England, motorways and major A roads in Eng ...
in the state with the major highway being the long NH 4 connecting Port Blair and Diglipur.
Infrastructure
Power
There is no single power grid connecting all the islands and independent power houses caters to the power requirements of individual islands. The islands have an installed power capacity of 68.46 MW with majority of the power generated fromdiesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine ...
power plant
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ...
s and a single hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
plant of 5.25 MW on Kalpong river. In 2016, a new 15 MW diesel
Diesel may refer to:
* Diesel engine, an internal combustion engine where ignition is caused by compression
* Diesel fuel, a liquid fuel used in diesel engines
* Diesel locomotive, a railway locomotive in which the prime mover is a diesel engine ...
power plant
A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ...
was established in South Andaman with Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
assistance. Commissioned in June 2020, a 10 MW photovoltaic power station
A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system (PV system) designed for the supply of merchant power. They are different from most building ...
is operated by NLC India in Port Blair. In 2022, the government proposed additional power plants and infrastructure to be developed in Great Nicobar.
Telecommunication
4G mobile service is provided by various telecom operators in the islands. Till 2020, Internet was provided through satellite links and access was limited.Bharat Broadband Network
BharatNet, also known as Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), () is an Indian central public sector undertaking, set up by the Department of Telecommunications, a department under the Ministry of Communications of the Government of India ...
started work on laying fiber optic
An optical fiber, or optical fibre, is a flexible glass or plastic fiber that can transmit light from one end to the other. Such fibers find wide usage in fiber-optic communications, where they permit transmission over longer distances and at ...
submarine cable Submarine cable is any electrical cable that is laid on the seabed, although the term is often extended to encompass cables laid on the bottom of large freshwater bodies of water.
Examples include:
*Submarine communications cable
*Submarine power ...
s connecting the islands with Chennai in December 2018. On 10 August 2020, the undersea optical fibre cable
A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with p ...
went live, which enabled high-speed broadband connections in the islands.
Education
The first primary school in the islands was established in 1881. During Independence, 12 schools were functioning on the islands including one high school. , there are 428 schools functioning in the islands with a total enrolment of 86,081 students. Jawaharlal Nehru Rajkeeya Mahavidyalaya was the first institute of higher education, established in 1967. Mahatma Gandhi Government College was established in 1990 and is affiliated toPondicherry University
Pondicherry University, also known as PU, is a central research university located in Kalapet, Pondicherry in Union Territory of Puducherry, India. It was established by an Act of Parliament in 1985 by the Department of Higher Education, Min ...
. Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Government Polytechnic was established in 1984 and the affiliated engineering college, Dr. B. R. Ambedkar Institute of Technology was established in 1989. Andaman Law College is the only law college
Legal education is the education of individuals in the principles, practices, and theory of law. It may be undertaken for several reasons, including to provide the knowledge and skills necessary for admission to legal practice in a particular j ...
in the state, established in 2016. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands Institute of Medical Sciences
Andaman and Nicobar Islands Institute of Medical Sciences, Port Blair is a medical school in Port Blair, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area ...
was established in 1963.
In popular culture
*Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Hol ...
refers to the Andaman islands in the Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a Detective fiction, fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a "Private investigator, consulting detective" in his stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with obser ...
novel ''The Sign of the Four
''The Sign of the Four'', also called ''The Sign of Four'', is an 1890 detective novel, and it is the second novel featuring Sherlock Holmes by British writer Sir Arthur Conan Doyle. Doyle wrote four novels and 56 short stories featuring ...
''.
* Bengali
Bengali or Bengalee, or Bengalese may refer to:
*something of, from, or related to Bengal, a large region in South Asia
* Bengalis, an ethnic and linguistic group of the region
* Bengali language, the language they speak
** Bengali alphabet, the w ...
author Sunil Gangopadhyay
Sunil Gangopadhyay or Sunil Ganguly (September 7, 1934 – October 23, 2012) was an Indian poet, novelist, short story writer, and critic. He played a key role in modernizing Bengali poetry and co-founded the 1953 Avant-garde, avant-gra ...
based the events of one his ''Kakababu
Kakababu, or Raja Roy Chowdhury, is a fictional adventurer created by Bengali people, Bengali author Sunil Gangopadhyay. The series debuted in the 1971 Puja issue of Anandamela, Anandamela magazine with ''Bhoyonkor Sundor'', and quickly became ...
'' series of adventure thriller novels, ''Sabuj Dwiper Raja
''Sabuj Dwiper Raja'' is a 1979 Indian adventure thriller film directed by Tapan Sinha, based on the same name novel of Kakababu by Sunil Gangopadhyay.
Synopsis
A criminal gang led by notorious smuggler Panja is set to steal a secret source of e ...
'' (1976), on the islands. In 1979, it was made into a film of the same name, shot extensively on the islands.
* The National Award
The National Film Awards are awards for artistic and technical merit given for "Excellence within the Indian film industry". Established in 1954, it has been administered, along with the International Film Festival of India and the Indian P ...
-winning Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian languages, Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (union territory), Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of ...
film ''Kaalapani
''Kaalapaani'' () is a 1996 Indian Malayalam-language epic historical drama film written by T. Damodaran and directed by Priyadarshan. Set in 1915, the film focuses on the lives of Indian independence activists incarcerated in the Cellular Ja ...
'' was set against the backdrop of Port Blair's Cellular Jail and was extensively shot in the islands.
* The Netflix Original Series
Netflix is an American global Internet streaming-on-demand media provider that has distributed a number of original streaming television shows, including original series, specials, miniseries, documentaries and films. Netflix's original produ ...
'' Kaala Paani'' is based on a fictional illness that spreads in the islands.
See also
*Coral reefs in India
Coral reefs in India are one of the most ancient and dynamic ecosystems of India. The coral reefs not only provide a sanctuary to a myriad of marine life but also play a key role in protecting the coastline from erosion. India has about 7517&nb ...
* List of islands of India
This is a partial list of islands in the Indian Republic. There are a total of 1,382 islands (including uninhabited ones) in the country.
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are a group of 572 islands of Bengal and And ...
Notes
References
External links
{{Authority control 1956 establishments in India Andaman Sea Dependent territories in Asia 01 Islands of the Andaman Sea Islands of the Bay of Bengal States and territories established in 1956 States and union territories of India Union territories of India Volcanic arc islands