Hypericum Foliosum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Hypericum foliosum'', the shining St John's wort, is a species of
 The
The
flowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
in the family Hypericaceae
Hypericaceae is a plant family in the order Malpighiales, comprising six to nine genera and up to 700 species, and commonly known as the St. John's wort family. Members are found throughout the world apart from extremely cold or dry habitats. ...
. It is a bushy shrub endemic to the Portuguese Azores Islands
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlant ...
with golden yellow petals and many stems. The species was described by William Aiton
William Aiton (17312 February 1793) was a Scotland, Scottish botanist.
Aiton was born near Hamilton, Scotland, Hamilton. Having been regularly trained to the profession of a gardener, he travelled to London in 1754, and became assistant to Phi ...
in 1789 and was later placed into section '' Androsaemum'' of the genus ''Hypericum'' by Norman Robson in 1984. It has a diverse essential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile (easily evaporated at normal temperatures) chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the ...
profile made up mostly of monoterpene hydrocarbons, and significant concentrations of various medicinally useful phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (− O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ar ...
and carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
s. Populations of the plant are small in number, but quick to colonize cleared areas like groves, landslide areas, and volcanic ash deposits. It is parasitized by fungus and by moth species, but is not considered endangered by the IUCN. ''H. foliosum'' is used in traditional medicine on the Azores for diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
, hepatoprotective
Hepatoprotection or antihepatotoxicity is the ability of a chemical substance to prevent damage to the liver. This is opposite to hepatotoxicity.
Hepatoprotective molecules used in emergency medicine
* Acetylcysteine is considered the hepatopr ...
, and antihypertensive
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infa ...
purposes. It also has ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
and antioxidizing capabilities.
Etymology
Thegenus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
name ''Hypericum'' is possibly derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
words (above) and (picture), in reference to the tradition of hanging the plant over religious icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, Catholic Church, Catholic, and Lutheranism, Lutheran churches. The most common subjects include Jesus, Mary, mother of ...
s in the home. The specific epithet "'' foliosum''" comes from the Latin word "'' foliosus''" which refers to a leaf. In the Azores Islands
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atlant ...
, ''Hypericum foliosum'' is known as malfurada or furalha. In English, it is called the shining St John's wort.
Description
''Hypericum foliosum'' is aperennial
In horticulture, the term perennial ('' per-'' + '' -ennial'', "through the year") is used to differentiate a plant from shorter-lived annuals and biennials. It has thus been defined as a plant that lives more than 2 years. The term is also ...
shrub
A shrub or bush is a small to medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple ...
that grows at least 50–100 centimeters tall. It may be bushy, and its branches grow both upright and outwards from the center of the plant. It usually flowers in August.
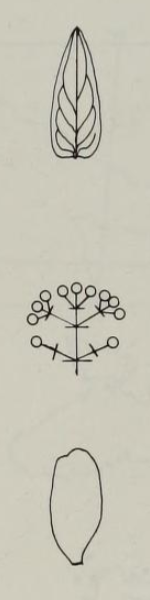
Vegetative structures
The stems are notched, showingcrenation
Crenation (from modern Latin ''crenatus'' meaning "scalloped or notched", from popular Latin ''crena'' meaning "notch") in botany and zoology, describes an object's shape, especially a leaf or shell, as being round-toothed or having a scalloped ed ...
, and are a yellow-brown color. The stems are flattened when the plant is young, but become more round as it matures. They are covered in bark covered in lengthwise ridges and dark pits that stand out against the lighter surface. The stem has an average width of around 0.35 cm, and there is around 2 cm of stem between leaves. When viewed in cross-section, there are four distinct rings in the stem. The outermost is a thick, reddish-brown cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
of cork
"Cork" or "CORK" may refer to:
Materials
* Cork (material), an impermeable buoyant plant product
** Stopper (plug), or "cork", a cylindrical or conical object used to seal a container
*** Wine cork an item to seal or reseal wine
Places Ireland
* ...
. The next two rings are an external and internal cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
containing secretory canals, vascular bundles, rows of phloem
Phloem (, ) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known as ''photosynthates'', in particular the sugar sucrose, to the rest of the plant. This transport process is ...
, and secondary xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts o ...
. The innermost ring is made of pith
Pith, or medulla, is a tissue in the stems of vascular plants. Pith is composed of soft, spongy parenchyma cells, which in some cases can store starch. In eudicotyledons, pith is located in the center of the stem. In monocotyledons, it ex ...
with starch grains in the cells.
 The
The leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
are located on opposite sides of the stem and are shaped like an egg that is stretched to be longer, or similar to a lance
The English term lance is derived, via Middle English '' launce'' and Old French '' lance'', from the Latin '' lancea'', a generic term meaning a wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generic term meaning a spear">wikt:lancea#Noun">lancea'', a generi ...
. They are 3.5–6.0 cm long and 1–3.2 cm wide. Their texture is papery and they are a lighter color on the undersides. The edges of the leaf are smooth and lack notches, and the point tapers in a sharp angle. There is either no leafstalk or a very short leafstalk that attaches each leaf to the stem. There are also small stipule
In botany, a stipule is an outgrowth typically borne on both sides (sometimes on just one side) of the base of a leafstalk (the petiole (botany), petiole). They are primarily found among dicots and rare among monocots. Stipules are considered part ...
s near the leafstalk that are yellow-brown like the stems. There are no stoma
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek language, Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the Epidermis (botany), epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exc ...
ta on the upper surface of the leaf, but there are several kinds of the guard cells on the undersides. There are also many translucent oil glands scattered across both leaf surfaces. The central leaf vein is flanked by 4–5 pairs of ascending veins, and the leaf's network of small tertiary veins are also clearly visible. The leaves contain both chlorophyll a
}
Chlorophyll ''a'' is a specific form of chlorophyll used in oxygenic photosynthesis. It absorbs most energy from wavelengths of violet-blue and orange-red light, and it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Chlorop ...
and chlorophyll b
}
Chlorophyll ''b'' is a form of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll ''b'' helps in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy. It is more soluble than chlorophyll ''a'' in polar solvents because of its carbonyl group. Its color is green, and it primarily ...
.
Flowering structures
The flowers of ''Hypericum foliosum'' are grouped in clusters of 1–9, in a shape between acorymb
Corymb is a botanical term for an inflorescence with the flowers growing in such a fashion that the outermost are borne on longer pedicels than the inner, bringing all flowers up to a common level. A corymb has a flattish top with a superficial re ...
and umbel
UMBEL (Upper Mapping and Binding Exchange Layer) is a logically organized knowledge graph of 34,000 concepts and entity types that can be used in information science for relating information from disparate sources to one another. It was retired ...
. The branches that carry the flowers generally grow upwards, and the cluster sometimes has accessory flowers lower on the branches. The stalks that bear an individual flower are 0.7–1.2 cm long with small lance-shaped bract
In botany, a bract is a modified or specialized leaf, associated with a reproductive structure such as a flower, inflorescence axis or cone scale.
Bracts are usually different from foliage leaves in size, color, shape or texture. They also lo ...
s. Each flower is 2.5–3.0 cm wide; when bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or Plant embryogenesis, embryonic Shoot (botany), shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a Plant stem, stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormancy, dormant conditi ...
s, they are shaped between an ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation.
An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathemat ...
and an imperfect sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
and are not pointed at the end. The sepal
A sepal () is a part of the flower of angiosperms (flowering plants). Usually green, sepals typically function as protection for the flower in bud, and often as support for the petals when in bloom., p. 106
Etymology
The term ''sepalum'' ...
s are usually 0.3–0.6 cm long and 0.1–0.3 cm wide. They overlap one another, are of differing sizes even on one flower, and remain after the flower fruits. The shape of the sepals varies: they could look like a triangular lance or a flattened ellipse, and their ends can be blunt or pointed. The glands on the surface of the sepals are arranged in lines, and there are also dense glands along the edges.
The petal
Petals are modified leaves that form an inner whorl surrounding the reproductive parts of flowers. They are often brightly coloured or unusually shaped to attract pollinators. All of the petals of a flower are collectively known as the ''corol ...
s are golden yellow and lack a red tinge. They are 1.2–1.8 cm long and 0.5–0.8 cm wide, with the shape of an inverted lance. The stamen
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filament ...
s are bundled in fascicles of 20–30, the longest of which measure 1.2–1.8 cm long. The ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
is oval-shaped with styles that are 0.5–1.0 cm long and stigmas that end in a distinct narrow head. The seed capsule
In botany, a capsule is a type of simple, dry, though rarely fleshy dehiscent fruit produced by many species of angiosperms (flowering plants).
Origins and structure
The capsule (Latin: ''capsula'', small box) is derived from a compound (mult ...
is 0.8–1.3 cm long and 0.7–1.0 cm wide, with a wide cylindrical shape and an end that is blunt or pointed. They start out somewhat fleshy but quickly dry out and eventually split open, though sometimes only partially. The seeds are yellow-brown and have wing shaped appendages.
Similar species
''Hypericum foliosum'' is most similar in appearance to the other species in section '' Androsaemum''. Most of its characteristics are between those of '' H. grandifolium'' and '' H. androsaemum'', except for its leaves which are narrower than either. It can be told apart from ''H. grandifolium'' by its denser flower clusters, smaller flowers, and shorter styles. It is also highly similar to the hybrid ''Hypericum × inodorum
''Hypericum'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family (biology), family Hypericaceae (formerly considered a subfamily of Clusiaceae). The genus has a nearly worldwide distribution, missing only from tropical lowlands, deserts and polar re ...
,'' but is differentiated by the shape of its sepals and seed capsules.
Chemistry
Like many other ''Hypericum'' species, ''Hypericum foliosum'' has a diverseessential oil
An essential oil is a concentrated hydrophobic liquid containing volatile (easily evaporated at normal temperatures) chemical compounds from plants. Essential oils are also known as volatile oils, ethereal oils, aetheroleum, or simply as the ...
profile, with volume per weight yields of around 0.10–0.25%. Nonane
Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20. It is a colorless, flammable liquid, occurring primarily in the component of the petroleum distillate fraction commonly called kerosene, which is used as a heating, tractor, a ...
and limonene
Limonene () is a colorless liquid aliphatic hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic monoterpene, and is the major component in the essential oil of citrus fruit peels. The (+)-isomer, occurring more commonly in nature as the fragrance of oranges, ...
were universally dominant in the plant's extracts. Other compounds like terpinolene
The terpinenes are a group of isomeric hydrocarbons that are classified as monoterpenes. They each have the same molecular formula and carbon framework, but they differ in the position of carbon-carbon double bonds. α-Terpinene has been isolate ...
, caryophyllene
Caryophyllene (), more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene (BCP), is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that occurs widely in nature. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a ''trans''-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both ...
, and pinene
Pinene is a collection of unsaturated bicyclic monoterpenes. Two geometric isomers of pinene are found in nature, α-pinene and β-pinene. Both are chiral. As the name suggests, pinenes are found in pines. Specifically, pinene is the major comp ...
sometimes can make up a significant percentage of the oil. In general, monoterpene
Monoterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of two isoprene units and have the molecular formula C10H16. Monoterpenes may be linear (acyclic) or contain rings (monocyclic and bicyclic). Modified terpenes, such as those containing oxygen func ...
hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually fain ...
s are more common than sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many combinations. Biochemical modifications s ...
s.
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (− O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds ar ...
are a group of chemical compounds produced by plants that are common in medical products. In extract
An extract (essence) is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures or absolutes or dried and powdered.
The aromatic principles of ma ...
taken from the leaves of the plant, the main phenolic compounds are caffeoylquinic acids and quercetin
Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it. It has a bitter flavor ...
. The stems and roots lack quercetin, and the seed capsules contain neither. Another chemical component of the plant are the carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
s, which help create bright colors and aid in reproduction. These compounds are found most densely in the leaves, stem, and bark; the roots, seeds, and flowers have much lower concentrations.
Taxonomy
The species was firstformally described
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differ ...
as ''Hypericum foliosum'' in 1789 in the botanical journal ''Hortus Kewensis
(Latin for 'Kew Garden'; abbr. ) is a series of works cataloguing the plant species in cultivation at the Royal Botanic Gardens at Kew in the late 18th and early 19th centuries.
Background
Kew became a favored location for English courtiers ...
'' by William Aiton
William Aiton (17312 February 1793) was a Scotland, Scottish botanist.
Aiton was born near Hamilton, Scotland, Hamilton. Having been regularly trained to the profession of a gardener, he travelled to London in 1754, and became assistant to Phi ...
. In this original description, based on the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wikt:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally associated. In other words, a type is an example that serves to ancho ...
collected on São Miguel in 1777, Aiton noted the species' long petals and sharp calyx as differentiating characteristics. Augustin Pyramus de Candolle
Augustin Pyramus (or Pyrame) de Candolle (, , ; 4 February 17789 September 1841) was a Swiss people, Swiss botany, botanist. René Louiche Desfontaines launched de Candolle's botanical career by recommending him at a herbarium. Within a couple ...
followed Aiton's nomenclature in 1824, as did several other authors through the 19th century.
Norman Robson included the species in an assay of ''Hypericum'' as a contribution to the 1968 work ''Flora Europaea
The ''Flora Europaea'' is a 5-volume encyclopedia of plants, published between 1964 and 1993 by Cambridge University Press. The aim was to describe all the national Floras of Europe in a single, authoritative publication to help readers identify ...
.'' He further analyzed ''Hypericum foliosum'' in 1984 as a part of his monograph
A monograph is generally a long-form work on one (usually scholarly) subject, or one aspect of a subject, typically created by a single author or artist (or, sometimes, by two or more authors). Traditionally it is in written form and published a ...
of the genus. A 2013 study used Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference ( or ) is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to calculate a probability of a hypothesis, given prior evidence, and update it as more information becomes available. Fundamentally, Bayesian infer ...
to establish the phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or Taxon, taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, M ...
and close relations of ''Hypericum'' species. Section ''Androsaemum'', including ''Hypericum foliosum,'' was placed into an Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
taxon called the "''Androsaemum''-group" with several other sections. The study also determined that ''H. foliosum'' was most closely related to ''Hypericum hircinum''.
Ecology
''Hypericum foliosum'' isendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to the Azores Islands in the North Atlantic, where it can be found on every island. It inhabits the laurel and juniper forests of the archipelago, especially in shady and damp areas of mountainous regions at elevations of 220–800 meters. It also grows in stands of ''Pittosporum
''Pittosporum'' ( or The first pronunciation is that expected for traditional English pronunciation of Latin, Anglo-Latin; the second is common in nurseries. ''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995:606–607) is a genus of about 250 species of flow ...
'' trees and is quick to inhabit volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of fragments of rock, mineral crystals, and volcanic glass, produced during volcanic eruptions and measuring less than 2 mm (0.079 inches) in diameter. The term volcanic ash is also often loosely used to r ...
deposits. In general, it is good at colonizing recently cleared areas like man-made clearings and landslide sites. Populations at a site are usually made up of only a few plants.
Several parasites are hosted by the leaves of ''H. foliosum''. The rust fungus
Rusts are fungal plant pathogens of the order Pucciniales (previously known as Uredinales) causing plant fungal diseases.
An estimated 168 rust genera and approximately 7,000 species, more than half of which belong to the genus ''Puccinia'', are ...
'' Melampsora hypericorum'' takes the form of a pustule on the leaf, damaging the surface. Larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e of the moth ''Caloptilia aurantiaca
''Caloptilia aurantiaca'' is a moth of the family Gracillariidae. It is known from Madeira and the Canary Islands.
The larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life st ...
'' mine into the leaves and later live under the folded tip of the blade.
''H. foliosum'' is not directly endangered by competition with invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
or human actions; it was listed as Least Concern
A least-concern species is a species that has been evaluated and categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as not being a focus of wildlife conservation because the specific species is still plentiful in the wil ...
by the IUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the status ...
in 2016. However, it has been studied as a model for using micropropagation
Micropropagation or tissue culture is the practice of rapidly multiplying plant stock material to produce many progeny plants, using modern plant tissue culture methods.
Micropropagation is used to multiply a wide variety of plants, such as ...
as a conservation method on the Azores. Micropropagation has previously been used in ''Hypericum perforatum
''Hypericum perforatum'', commonly known as St. John's wort (sometimes perforate St. John's wort or common St. John's wort), is a flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae. It is a hairless, Perennial, perennial herb with woody Root, roots, y ...
'' and ''Hypericum canariense
''Hypericum canariense'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Hypericaceae known by the common name Canary Islands St. John's wort. It is the sole member of ''Hypericum'' sect. ''Webbia''.
Etymology
Among its numerous aliases in Spanis ...
''. A single node of the species that is propagated using this method can yield 2–4 new plants in around four months.
Uses
While no officialpharmacological
Pharmacology is the science of drugs and medications, including a substance's origin, composition, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, therapeutic use, and toxicology. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between ...
usage of ''Hypericum foliosum'' were recorded as of 2011, locals in the Azores describe the species as being used in traditional medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
in similar ways to other species in the genus. Some of these applications derive from the diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics ...
, hepatoprotective
Hepatoprotection or antihepatotoxicity is the ability of a chemical substance to prevent damage to the liver. This is opposite to hepatotoxicity.
Hepatoprotective molecules used in emergency medicine
* Acetylcysteine is considered the hepatopr ...
, and antihypertensive
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension (high blood pressure). Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke, heart failure, kidney failure and myocardial infa ...
properties of its extract. Despite having more phenolic activity than '' H. undulatum'' and '' H. androsaemum'', those two species are as or more common in Portuguese medicinal markets. ''H. foliosum'' has exhibited ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in ...
'' antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
effects on infectious bacteria like ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
.'' Its carotenoid and phenolic oils give the plant's extract antioxidant properties. The lower parts of the plant like the stem, bark, and roots are the most effective.
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q10299074 foliosum Endemic flora of the Azores Taxa named by William Aiton Plants described in 1789