Hurricane Floyd on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large
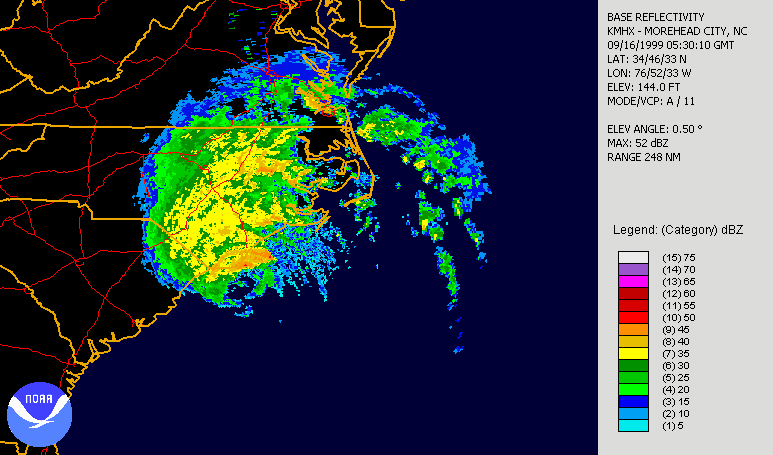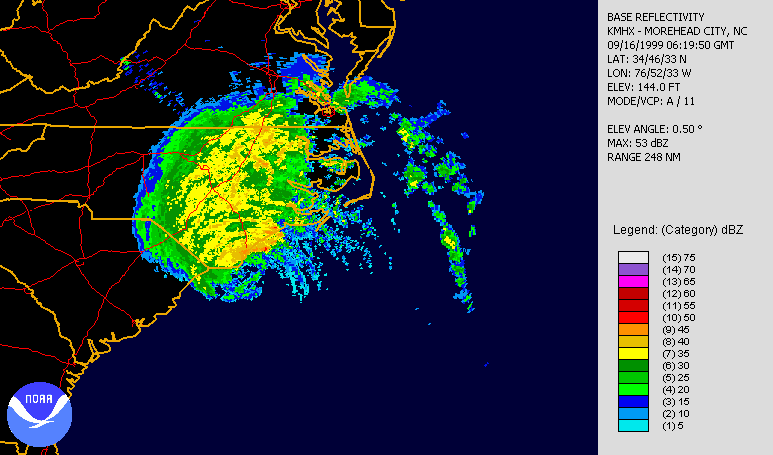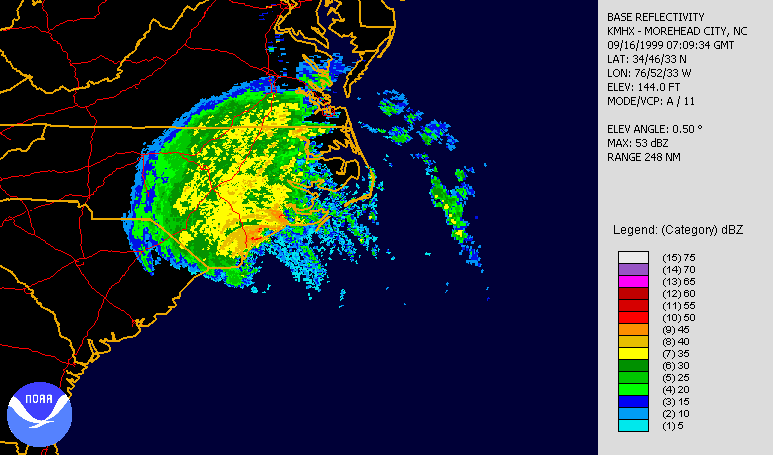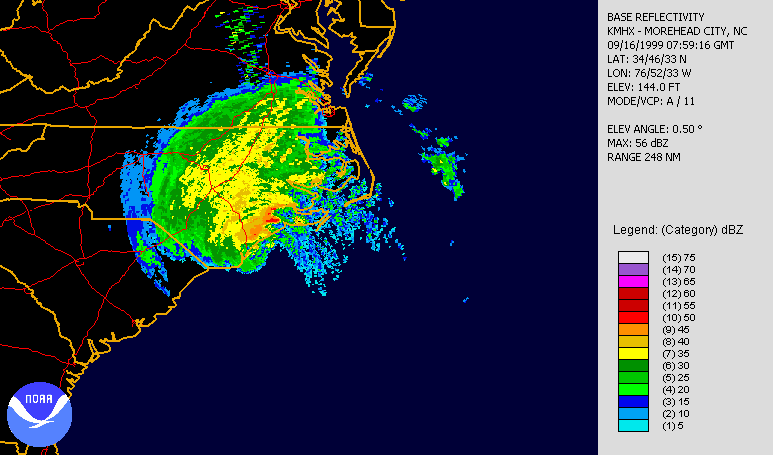 Over a 24-hour period from September 12–13, Hurricane Floyd rapidly intensified, aided by warm waters east of
Over a 24-hour period from September 12–13, Hurricane Floyd rapidly intensified, aided by warm waters east of
 Initial fears were of a direct hit as a large Category 4 hurricane in Florida, potentially costlier and deadlier than
Initial fears were of a direct hit as a large Category 4 hurricane in Florida, potentially costlier and deadlier than  With the storm predicted to hit near
With the storm predicted to hit near
 North Carolina received the brunt of the storm's destruction. In all, Hurricane Floyd caused 51 fatalities in North Carolina, much of them from freshwater flooding, as well as billions in damage.
The storm surge from the large hurricane amounted to along the southeastern portion of the state. The hurricane also spawned numerous tornadoes, most of which caused only minor damage. Damage to power lines left over 500,000 customers without electricity at some point during the storm's passage.
Just weeks prior to Floyd hitting, Hurricane Dennis brought up to of rain to southeastern North Carolina. When Hurricane Floyd moved across the state in early September, it produced torrential rainfall, amounting to a maximum of in Wilmington. Though it moved quickly, the extreme rainfall was due to Floyd's interaction with an approaching cold front across the area.
Extensive flooding, especially along NC Hwy 91 and the White Oak Loop neighborhood, led to overflowing rivers; nearly every river basin in eastern North Carolina reached 500 year or greater flood levels. Most localized flooding happened overnight; Floyd dropped nearly of rain during the hours of its passage and many residents were not aware of the flooding until the water came into their homes. The U. S. Navy, National Guard and the Coast Guard performed nearly 1700 fresh water rescues of people trapped on the roofs of their homes due to the rapid rise of the water. By contrast, many of the worst affected areas did not reach peak flood levels for several weeks after the storm, as the water accumulated in rivers and moved downstream (see flood graphic at right).
The passage of
North Carolina received the brunt of the storm's destruction. In all, Hurricane Floyd caused 51 fatalities in North Carolina, much of them from freshwater flooding, as well as billions in damage.
The storm surge from the large hurricane amounted to along the southeastern portion of the state. The hurricane also spawned numerous tornadoes, most of which caused only minor damage. Damage to power lines left over 500,000 customers without electricity at some point during the storm's passage.
Just weeks prior to Floyd hitting, Hurricane Dennis brought up to of rain to southeastern North Carolina. When Hurricane Floyd moved across the state in early September, it produced torrential rainfall, amounting to a maximum of in Wilmington. Though it moved quickly, the extreme rainfall was due to Floyd's interaction with an approaching cold front across the area.
Extensive flooding, especially along NC Hwy 91 and the White Oak Loop neighborhood, led to overflowing rivers; nearly every river basin in eastern North Carolina reached 500 year or greater flood levels. Most localized flooding happened overnight; Floyd dropped nearly of rain during the hours of its passage and many residents were not aware of the flooding until the water came into their homes. The U. S. Navy, National Guard and the Coast Guard performed nearly 1700 fresh water rescues of people trapped on the roofs of their homes due to the rapid rise of the water. By contrast, many of the worst affected areas did not reach peak flood levels for several weeks after the storm, as the water accumulated in rivers and moved downstream (see flood graphic at right).
The passage of 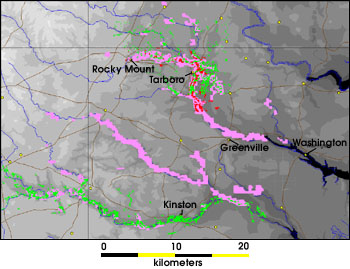 The Tar River suffered the worst flooding, exceeding 500-year flood levels along its lower stretches; it crested above flood stage. Flooding began in Rocky Mount, as much as 30% of which was underwater for several days. In
The Tar River suffered the worst flooding, exceeding 500-year flood levels along its lower stretches; it crested above flood stage. Flooding began in Rocky Mount, as much as 30% of which was underwater for several days. In
 Hurricane Floyd left $101 million in damage in Virginia, and contributed to four fatalities – two from fallen trees in Fairfax and Halifax County, one in a traffic accident in Hanover County, and a man in Accomack County who drowned in his submerged vehicle. As in North Carolina and elsewhere along its path, Floyd dropped torrential rainfall across eastern Virginia, reaching in Newport News. While Floyd moved through southeastern Virginia, it was still at hurricane status, producing winds strong enough to knock down hundreds of trees and power lines. The highest sustained winds in the state were at Langley Air Force Base. Wind gusts were much stronger, reaching on the James River Bridge. Floyd's winds and rains knocked down hundreds of trees across the state, some centuries old.
The heavy rains washed out several roads, and closed regional routes including
Hurricane Floyd left $101 million in damage in Virginia, and contributed to four fatalities – two from fallen trees in Fairfax and Halifax County, one in a traffic accident in Hanover County, and a man in Accomack County who drowned in his submerged vehicle. As in North Carolina and elsewhere along its path, Floyd dropped torrential rainfall across eastern Virginia, reaching in Newport News. While Floyd moved through southeastern Virginia, it was still at hurricane status, producing winds strong enough to knock down hundreds of trees and power lines. The highest sustained winds in the state were at Langley Air Force Base. Wind gusts were much stronger, reaching on the James River Bridge. Floyd's winds and rains knocked down hundreds of trees across the state, some centuries old.
The heavy rains washed out several roads, and closed regional routes including
tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
which struck the Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. ...
and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth named storm, fourth hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its ...
, and third major hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Floyd triggered the fourth largest evacuation in US history (behind Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Hurricane Maria, Maria two weeks later. At the time, it was considered ...
, Hurricane Gustav
Hurricane Gustav () was the second most destructive tropical cyclone of the 2008 Atlantic hurricane season. The seventh tropical cyclone, third hurricane, and second major hurricane of the season, Gustav caused serious damage and Casualty (per ...
, and Hurricane Rita
Hurricane Rita was the most intense tropical cyclone on record in the Gulf of Mexico, tying with Hurricane Milton in 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, 2024, as well as being the fourth-most intense Atlantic hurricane ever recorded. Part of the ...
) when 2.6 million coastal residents of five states were ordered from their homes as it approached. The hurricane formed off the coast of Africa and lasted from September 7 to 19, becoming extratropical after September 17, and peaked in strength as a very strong Category 4 hurricane. It was among the largest Atlantic hurricane
An Atlantic hurricane is a type of tropical cyclone that forms in the Atlantic Ocean primarily between June and November. The terms "hurricane", "typhoon", and "cyclone, tropical cyclone" can be used interchangeably to describe this weather ph ...
s of its strength ever recorded, in terms of gale-force diameter.
Floyd was once forecast to strike Florida, but turned away. Instead, Floyd struck the Bahamas at peak strength, causing heavy damage. It then moved parallel to the East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the region encompassing the coast, coastline where the Eastern United States meets the Atlantic Ocean; it has always pla ...
, causing massive evacuations and costly preparations from Florida through the Mid-Atlantic states. The storm weakened significantly, however, before striking the Cape Fear region, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
as a very strong Category 2 hurricane, and caused further damage as it traveled up the Mid-Atlantic region and into New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
.
The hurricane produced torrential rainfall in Eastern North Carolina, adding more rain to an area already hit by Hurricane Dennis just weeks earlier. The rains caused widespread flooding over a period of several weeks; nearly every river basin in the eastern part of the state exceeded 500-year flood levels. In total, Floyd was responsible for 85 fatalities and $6.5 billion (1999 USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
) in damage. Due to the destruction, the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
retired
Retirement is the withdrawal from one's position or occupation or from one's active working life. A person may also semi-retire by reducing work hours or workload.
Many people choose to retire when they are elderly or incapable of doing their j ...
the name ''Floyd'' and replaced it with ''Franklin''.
Meteorological history
Floyd originated from atropical wave
A tropical wave (also called easterly wave, tropical easterly wave, and African easterly wave), in and around the Atlantic Ocean, is a type of atmospheric trough, an elongated area of relatively low air pressure, oriented north to south, which ...
that exited the west coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
on September 2. The wave moved generally westward, presenting a general curvature in its convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
, or thunderstorms, but little organization at first. By September 5, a center of circulation was evident within the convective system. Over the next day, the thunderstorms increased in intensity as they organized into a curved band. Aided by favorable outflow, the system organized further into Tropical Depression Eight late on September 7, located about east of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles is a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea, forming part of the West Indies in Caribbean, Caribbean region of the Americas. They are distinguished from the larger islands of the Greater Antilles to the west. They form an arc w ...
. With a strong ridge
A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, wi ...
of high pressure to its north, the nascent tropical depression moved to the west-northwest, where environmental conditions favored continued strengthening, including progressively warmer water temperatures. On issuing its first advisory, the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the IERS Reference Meridian, Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian ...
(NHC) anticipated that the depression would intensify into a hurricane within three days, a forecast that proved accurate. On its second advisory, NHC forecaster Lixion Avila stated that the depression had "all the ingredients...that we know of...to become a major hurricane eventually."
Early on September 8, the depression became sufficiently well-organized for the NHC to upgrade it to Tropical Storm Floyd. The storm had a large circulation, but Floyd initially lacked a well-defined inner core, which resulted in only slow strengthening. The first Hurricane Hunters
Hurricane hunters, typhoon hunters, or cyclone hunters are aircrews that fly into tropical cyclones to gather weather data. In the United States, the organizations that fly these missions are the United States Air Force Reserve's 53rd Weather ...
mission occurred on September 9, which observed the developing storm. On September 10, Floyd intensified into a hurricane about 230 mi (370 km) east-northeast of the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles is a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea, forming part of the West Indies in Caribbean, Caribbean region of the Americas. They are distinguished from the larger islands of the Greater Antilles to the west. They form an arc w ...
. Around that time, the track shifted more to the northwest, steered by a tropical upper tropospheric trough
A tropical upper tropospheric trough (TUTT), also known as the mid-oceanic trough, is a trough situated in the upper-level (at about 200 hPa) tropics. Its formation is usually caused by the intrusion of energy and wind from the mid-latitudes into ...
north of Puerto Rico. An eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
developed in the center of the hurricane, signaling strengthening. On September 11, Hurricane Floyd moved through the upper-level trough, which, in conjunction with an anticyclone
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interpl ...
over the eastern Caribbean, disrupted the outflow and caused the winds to weaken briefly. The hurricane re-intensified on September 12 as its track shifted more to the west, steered by a ridge to the north. That day, the NHC upgraded Floyd to a major hurricane, or a Category 3 on the Saffir-Simpson scale.
 Over a 24-hour period from September 12–13, Hurricane Floyd rapidly intensified, aided by warm waters east of
Over a 24-hour period from September 12–13, Hurricane Floyd rapidly intensified, aided by warm waters east of The Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of ...
. During that time, the maximum sustained wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common
indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a certain distance from the center, known as the radius of ma ...
s increased from ,All wind speeds in the article are maximum sustained wind
The maximum sustained wind associated with a tropical cyclone is a common
indicator of the intensity of the storm. Within a mature tropical cyclone, it is found within the eyewall at a certain distance from the center, known as the radius of ma ...
s sustained for one minute, unless otherwise noted. making Floyd a strong Category 4 hurricane. This was based a 90% reduction of an observation by the Hurricane Hunters, which recorded flight-level winds of 171 mph (276 km/h). Around the same time, the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
dropped to , which was the fourth-lowest pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and eve ...
for a hurricane not to reach Category 5 intensity in the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
– only Hurricanes Iota
Iota (; uppercase Ι, lowercase ι; ) is the ninth letter of the Greek alphabet. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Yodh. Letters that arose from this letter include the Latin I and J, the Cyrillic І (І, і), Yi (Ї, ї), and J ...
, Gloria and Opal
Opal is a hydrated amorphous form of silicon dioxide, silica (SiO2·''n''H2O); its water content may range from 3% to 21% by weight, but is usually between 6% and 10%. Due to the amorphous (chemical) physical structure, it is classified as a ...
had lower pressures than Floyd. Around this time, tropical cyclone forecast model
A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorology, meteorological data to weather forecasting, forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or c ...
s suggested an eventual landfall in the Southeastern United States from Palm Beach, Florida
Palm Beach is an incorporated town in Palm Beach County, Florida, United States. Located on a barrier island in east-central Palm Beach County, the town is separated from West Palm Beach, Florida, West Palm Beach and Lake Worth Beach, Florida, ...
to South Carolina.
At its peak, tropical storm-force winds spanned a diameter of , making Floyd one of the largest Atlantic hurricanes of its intensity ever recorded. For about 12 hours, Hurricane Floyd remained just below Category 5 status while crossing The Bahamas. Late on September 13, the eye of the hurricane passed just north of San Salvador
San Salvador () is the Capital city, capital and the largest city of El Salvador and its San Salvador Department, eponymous department. It is the country's largest agglomeration, serving as the country's political, cultural, educational and fin ...
and Cat Islands. On the next day, the hurricane made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
s on Eleuthera
Eleuthera () refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of the The Bahamas, Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incor ...
and Abaco islands
The Abaco Islands lie in the north of Bahamas, The Bahamas, about 193 miles (167.7 nautical miles or 310.6 km) east of Miami, Florida, US. The main islands are Great Abaco and Little Abaco, which is just west of Great Abaco's northern tip.
T ...
. During this time, Floyd underwent an eyewall replacement cycle
In meteorology, eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones with maximum sustained winds greater than , or hurricane-force, and particularly in major hurricanes of Saffir–Simps ...
, in which an outer eyewall developed, causing the original eye to dissipate near Eleuthera. This caused a temporary drop in sustained winds to Category 3 status, only for Floyd to restrengthen briefly to a Category 4 on September 15.
While approaching the southeastern United States, a strong mid- to upper-level trough eroded the western portion of the high-pressure ridge, which had been steering Floyd for several days. The break in the ridge caused Floyd to turn to the northwest. After the hurricane completed its eyewall replacement cycle, Floyd had a large 57 mi (93 km) eye. The large storm gradually weakened after exiting The Bahamas, due to drier air and increasing wind shear. On September 15, Floyd paralleled the east coast of Florida about 110 mi (170 km) offshore, as it accelerated to the north and north-northeast. At around 06:30 UTC on September 16, Hurricane Floyd made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
in Cape Fear, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
with winds of , a Category 2. The eyewall had largely dissipated by that time. Continuing northeastward along a cold front, Floyd moved through eastern North Carolina and southeastern Virginia, weakening to tropical storm status by late on September 16. The storm gradually lost its tropical characteristics as it quickly moved through the Delmarva Peninsula
The Delmarva Peninsula, or simply Delmarva, is a peninsula on the East Coast of the United States, occupied by the majority of the state of Delaware and parts of the Eastern Shore of Maryland and Eastern Shore of Virginia.
The peninsula is l ...
, eastern New Jersey, Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
, and New England. Late on September 17, Floyd transitioned into an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
near the coast of southern Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
. The storm continued to the northeast, passing through New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland on September 18. On the following day, a larger extratropical storm over the North Atlantic Ocean absorbed what was once Hurricane Floyd.
Preparations
Early in Floyd's duration, the hurricane posed a threat to the Lesser Antilles, prompting tropical storm watches forAntigua and Barbuda
Antigua and Barbuda is a Sovereign state, sovereign archipelagic country composed of Antigua, Barbuda, and List of islands of Antigua and Barbuda, numerous other small islands. Antigua and Barbuda has a total area of 440 km2 (170 sq mi), ...
, Anguilla
Anguilla is a British Overseas Territories, British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Sa ...
, Saint Martin, and Saint Barthelemy. After the storm bypassed the region, the government of The Bahamas issued a tropical storm warning and a hurricane watch for the Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and no ...
and the southeast Bahamas, as well as hurricane warnings for the central and northwestern Bahamas.
Although Floyd's track prediction was above average while out at sea, the forecasts as it approached the coastline were merely average compared to forecasts from the previous ten years. The official forecasts did not predict Floyd's northward track nor its significant weakening before landfall. At some point, the NHC issued a hurricane warning for nearly all of the East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the region encompassing the coast, coastline where the Eastern United States meets the Atlantic Ocean; it has always pla ...
, from Florida City, Florida, to Plymouth, Massachusetts
Plymouth ( ; historically also spelled as Plimouth and Plimoth) is a town in and the county seat of Plymouth County, Massachusetts, United States. Located in Greater Boston, the town holds a place of great prominence in American history, folklor ...
; however, only a fraction of this area actually received hurricane-force winds. The last time such widespread hurricane warnings occurred was during Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, ...
in 1960.
 Initial fears were of a direct hit as a large Category 4 hurricane in Florida, potentially costlier and deadlier than
Initial fears were of a direct hit as a large Category 4 hurricane in Florida, potentially costlier and deadlier than Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a compact, but very powerful and devastating tropical cyclone that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It was the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures dama ...
had been in 1992. In preparation for a potentially catastrophic landfall, more than one million Florida residents were told to evacuate, of which 272,000 were in Miami-Dade County
Miami-Dade County () is a county located in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. The county had a population of 2,701,767 as of the 2020 census, making it the most populous county in Florida and the seventh-most-populous coun ...
. U.S. President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
declared a federal state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state before, during, o ...
in both Florida and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
in anticipation of the storm's approach. As the storm turned to the north, more people were evacuated as a progressively larger area was threatened. The massive storm prompted what was then the largest peacetime evacuation in U.S. history, with around 2.6 million evacuating coastal areas in Florida, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, and the Carolinas
The Carolinas, also known simply as Carolina, are the U.S. states of North Carolina and South Carolina considered collectively. They are bordered by Virginia to the north, Tennessee to the west, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the southwes ...
.
 With the storm predicted to hit near
With the storm predicted to hit near Cape Canaveral
Cape Canaveral () is a cape (geography), cape in Brevard County, Florida, in the United States, near the center of the state's Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic coast. Officially Cape Kennedy from 1963 to 1973, it lies east of Merritt Island, separated ...
with winds of over , all but 80 of Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten NASA facilities#List of field c ...
's 12,500-person workforce were evacuated. The hangar
A hangar is a building or structure designed to hold aircraft or spacecraft. Hangars are built of metal, wood, or concrete. The word ''hangar'' comes from Middle French ''hanghart'' ("enclosure near a house"), of Germanic origin, from Frankish ...
s that house three space shuttles can withstand winds of only , and a direct hit could have resulted in potentially billions of dollars in damage of space equipment. In the theoretical scenario, the damage would be caused by water, always a potential problem in an area only nine feet above sea level. If water entered the facility, it would damage the electronics as well as requiring a complete inspection of all hardware. When Floyd actually passed by the area, Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the NASA, National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten NASA facilities#List of field c ...
only reported light winds with minor water intrusion. Damage was minor overall, and was repaired easily.
A hurricane warning was issued for the North Carolina coastline 27 hours prior to landfall. However, due to the size of the storm, initial forecasts predicted nearly all of the state would be affected in one form or another. School systems and businesses as far west as Asheville shut down for the day landfall was predicted. As it turned out, only the Coastal Plain
A coastal plain (also coastal plains, coastal lowland, coastal lowlands) is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and an upland area.
Formation
Coastal plains can f ...
sustained significant damage; much of the state west of Raleigh
Raleigh ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the U.S. state of North Carolina. It is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, second-most populous city in the state (after Charlotte, North Carolina, Charlotte) ...
escaped unscathed. In New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, public schools were closed on September 16, 1999, the day Floyd hit the area. This was a rare decision by the city, as New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
public schools close on average once every few years. Before Floyd, the last time New York City closed its schools was for the Blizzard of 1996. After Floyd, the next time its public schools would close was due to a blizzard on March 5, 2001. Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort is an destination resort, entertainment resort complex located about southwest of Orlando, Florida, United States. Opened on October 1, 1971, the resort is operated by Disney Experiences, a division of the Wa ...
also closed for the first time in its history due to the storm. The resort would later close during hurricanes Frances
Frances is an English given name or last name of Latin origin. In Latin the meaning of the name Frances is 'from France' or 'the French.' The male version of the name in English is Francis (given name), Francis. The original Franciscus, meaning "F ...
and Jeanne in 2004, Matthew in 2016, Irma in 2017, Dorian in 2019, Ian in 2022, and Milton in 2024.
A state of emergency was declared in Delaware, Maryland, and New Jersey prompting schools statewide to be shut down on September 16. In Delaware, about 300 people evacuated.
In Atlantic Canada, the Canadian Hurricane Centre issued 14 warnings related to Floyd, generating significant media interest. About 100 Sable Offshore Energy Project employees were evacuated to the mainland. In southwestern Nova Scotia, 66 schools were closed, and provincial ferry service with Bar Harbor, Maine
Bar Harbor () is a resort town on Mount Desert Island in Hancock County, Maine, United States. As of the 2020 census, its population is 5,089. The town is home to the College of the Atlantic, Jackson Laboratory, and MDI Biological Laborat ...
was canceled.
Impact
With a death toll of 85, Hurricane Floyd was the deadliest United States hurricane sinceHurricane Agnes
Hurricane Agnes was the List of costliest Atlantic hurricanes, costliest hurricane to hit the United States at the time, causing an estimated $2.1 billion in damage. The hurricane's death toll was 128. The effects of Agnes were widespread, ...
in 1972. The storm was the third-costliest hurricane in the nation's history at the time, with monetary damage estimated at $6.5 billion (1999 USD); it ranked the 19th costliest as of 2017. Most of the deaths and damage were from inland, freshwater flooding in eastern North Carolina.
Caribbean
Around when Floyd first became a hurricane, its outer bands moved over the Lesser Antilles. Hurricane Floyd lashed the Bahamas with winds of and waves up to in height. A storm surge inundated many islands with over five ft (1.5 m) of water throughout. The wind and waves toppled power and communication lines, severely disrupting electricity and telephone services for days. Damage was greatest at Abaco Island, Cat Island,San Salvador Island
San Salvador Island, previously Watling's Island, is an islands of the Bahamas, island and districts of The Bahamas, district of The Bahamas, famed for being the probable location of Christopher Columbus's first landing of the Americas on 12 Oc ...
, and Eleuthera Island, where Floyd uprooted trees and destroyed a significant number of houses. Numerous restaurants, hotels, shops, and homes were devastated, severely limiting in the recovery period tourism on which many rely for economic well-being. Damaged water systems left tens of thousands across the archipelago without water, electricity, or food. Despite the damage, however, few deaths were reported, as only one person drowned in Freeport, and there were few injuries reported.
Southeastern United States
For several days, Hurricane Floyd paralleled the east coast of Florida, spurring widespread evacuations. Ultimately, the storm left $50 million in damage, mostly in Volusia county. There, high winds and falling trees damaged 337 homes. The highest recorded wind gust in the state was in Daytona Beach. Beach erosion affected much of the state's Atlantic coast. The most significant effects were in Brevard and Volusia counties, where waves damaged houses and piers. Rainfall in the state reached in Sanford. Farther north inGeorgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, Floyd produced wind gusts of at Savannah International Airport. The winds knocked down a few trees and power lines near the coast, but statewide damage was minimal. In Savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
, the hurricane produced tides above normal. Rainfall was light in the state, reaching in Newington.
Tropical storm force winds affected the entirety of the South Carolina coastline, with statewide damage estimated at $17 million. Sustained winds reached at the Charleston National Weather Service Office, which also recorded wind gusts of . The winds destroyed a few roofs and knocked down thousands of trees, leaving more than 200,000 people without electricity. The hurricane produced above normal tides along the coast, reaching above normal in Charleston Harbor
The Charleston Harbor is an inlet (8 sq mi/20.7 km2) of the Atlantic Ocean at Charleston, South Carolina. The inlet is formed by the junction of Ashley River (South Carolina), Ashley and Cooper River (South Carolina), Cooper rivers at . Morr ...
. The waves caused minor to moderate beach erosion. At Myrtle Beach International Airport, Hurricane Floyd dropped of rainfall, the highest recorded in the state.
North Carolina
 North Carolina received the brunt of the storm's destruction. In all, Hurricane Floyd caused 51 fatalities in North Carolina, much of them from freshwater flooding, as well as billions in damage.
The storm surge from the large hurricane amounted to along the southeastern portion of the state. The hurricane also spawned numerous tornadoes, most of which caused only minor damage. Damage to power lines left over 500,000 customers without electricity at some point during the storm's passage.
Just weeks prior to Floyd hitting, Hurricane Dennis brought up to of rain to southeastern North Carolina. When Hurricane Floyd moved across the state in early September, it produced torrential rainfall, amounting to a maximum of in Wilmington. Though it moved quickly, the extreme rainfall was due to Floyd's interaction with an approaching cold front across the area.
Extensive flooding, especially along NC Hwy 91 and the White Oak Loop neighborhood, led to overflowing rivers; nearly every river basin in eastern North Carolina reached 500 year or greater flood levels. Most localized flooding happened overnight; Floyd dropped nearly of rain during the hours of its passage and many residents were not aware of the flooding until the water came into their homes. The U. S. Navy, National Guard and the Coast Guard performed nearly 1700 fresh water rescues of people trapped on the roofs of their homes due to the rapid rise of the water. By contrast, many of the worst affected areas did not reach peak flood levels for several weeks after the storm, as the water accumulated in rivers and moved downstream (see flood graphic at right).
The passage of
North Carolina received the brunt of the storm's destruction. In all, Hurricane Floyd caused 51 fatalities in North Carolina, much of them from freshwater flooding, as well as billions in damage.
The storm surge from the large hurricane amounted to along the southeastern portion of the state. The hurricane also spawned numerous tornadoes, most of which caused only minor damage. Damage to power lines left over 500,000 customers without electricity at some point during the storm's passage.
Just weeks prior to Floyd hitting, Hurricane Dennis brought up to of rain to southeastern North Carolina. When Hurricane Floyd moved across the state in early September, it produced torrential rainfall, amounting to a maximum of in Wilmington. Though it moved quickly, the extreme rainfall was due to Floyd's interaction with an approaching cold front across the area.
Extensive flooding, especially along NC Hwy 91 and the White Oak Loop neighborhood, led to overflowing rivers; nearly every river basin in eastern North Carolina reached 500 year or greater flood levels. Most localized flooding happened overnight; Floyd dropped nearly of rain during the hours of its passage and many residents were not aware of the flooding until the water came into their homes. The U. S. Navy, National Guard and the Coast Guard performed nearly 1700 fresh water rescues of people trapped on the roofs of their homes due to the rapid rise of the water. By contrast, many of the worst affected areas did not reach peak flood levels for several weeks after the storm, as the water accumulated in rivers and moved downstream (see flood graphic at right).
The passage of Hurricane Irene
Hurricane Irene was a large and destructive tropical cyclone which affected much of the Caribbean and East Coast of the United States during late August 2011. The ninth tropical cyclone naming, named storm, first hurricane, and first major ...
four weeks later contributed an additional 6 in (150 mm) of rain over the still-saturated area, causing further flooding.
 The Tar River suffered the worst flooding, exceeding 500-year flood levels along its lower stretches; it crested above flood stage. Flooding began in Rocky Mount, as much as 30% of which was underwater for several days. In
The Tar River suffered the worst flooding, exceeding 500-year flood levels along its lower stretches; it crested above flood stage. Flooding began in Rocky Mount, as much as 30% of which was underwater for several days. In Tarboro
Tarboro is a town located in Edgecombe County, North Carolina, United States. It is part of the Rocky Mount metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the town had a population of 10,721. It is the county seat of Edgecombe County. The town is o ...
, much of the downtown was under several feet of water. Nearby, the town of Princeville was largely destroyed when the waters of the Tar poured over the town's levee, covering the town with over of floodwater for ten days. Further downstream, Greenville suffered very heavy flooding; damages in Pitt County alone were estimated at $1.6 billion (1999 USD, $2.81 billion 2022 USD). Washington, where the peak flood level was observed, was likewise devastated. Some residents in Greenville had to swim six feet underwater to reach the front doors of their homes and apartments. Due to the heavy flooding in downtown Greenville, the East Carolina Pirates were forced to relocate their football game against #9 Miami
Miami is a East Coast of the United States, coastal city in the U.S. state of Florida and the county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade County in South Florida. It is the core of the Miami metropolitan area, which, with a populat ...
to N.C. State's Carter–Finley Stadium in Raleigh, where they beat the Hurricanes 27–23.
The Neuse River
The Neuse River ( , Tuscarora: Neyuherú·kęʔkì·nęʔ) is a river rising in the Piedmont of North Carolina and emptying into Pamlico Sound below New Bern. Its total length is approximately , making it the longest river entirely contained in N ...
, Roanoke River
The Roanoke River ( ) runs long through southern Virginia and northeastern North Carolina in the United States. A major river of the southeastern United States, it drains a largely rural area of the coastal plain from the eastern edge of the ...
, Waccamaw River, and New River exceeded 500-year flood levels, although damage was lower in these areas (compared to the Tar River) because of lower population densities. Because most of the Cape Fear River
The Cape Fear River is a blackwater river in east-central North Carolina. It flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Cape Fear, from which it takes its name. The river is formed at the confluence of the Haw River and the Deep River in the town of ...
basin was west of the peak rainfall areas, the city of Wilmington was spared the worst flooding despite having the highest localized rainfall; however, the Northeast Cape Fear River (a tributary) did exceed 500-year flood levels. Of the state's eastern rivers, only the Lumber River escaped catastrophic flooding.
Rainfall and strong winds affected many homes across the state, destroying 7,000, leaving 17,000 uninhabitable, and damaging 56,000. Ten thousand people resided in temporary shelters following the storm. The extensive flooding resulted in significant crop damage. As quoted by North Carolina Secretary of Health and Human Services H. David Bruton, "Nothing since the Civil War has been as destructive to families here. The recovery process will be much longer than the water-going-down process." Around 31,000 jobs were lost from over 60,000 businesses through the storm, causing nearly $4 billion (1999 USD, $7.02 billion 2022 USD) in lost business revenue. In much of the affected area, officials urged people to either boil water or buy bottled water during Floyd's aftermath.
In contrast to the problems eastern North Carolina experienced, much of the western portion of the state remained under a severe drought.
Virginia
 Hurricane Floyd left $101 million in damage in Virginia, and contributed to four fatalities – two from fallen trees in Fairfax and Halifax County, one in a traffic accident in Hanover County, and a man in Accomack County who drowned in his submerged vehicle. As in North Carolina and elsewhere along its path, Floyd dropped torrential rainfall across eastern Virginia, reaching in Newport News. While Floyd moved through southeastern Virginia, it was still at hurricane status, producing winds strong enough to knock down hundreds of trees and power lines. The highest sustained winds in the state were at Langley Air Force Base. Wind gusts were much stronger, reaching on the James River Bridge. Floyd's winds and rains knocked down hundreds of trees across the state, some centuries old.
The heavy rains washed out several roads, and closed regional routes including
Hurricane Floyd left $101 million in damage in Virginia, and contributed to four fatalities – two from fallen trees in Fairfax and Halifax County, one in a traffic accident in Hanover County, and a man in Accomack County who drowned in his submerged vehicle. As in North Carolina and elsewhere along its path, Floyd dropped torrential rainfall across eastern Virginia, reaching in Newport News. While Floyd moved through southeastern Virginia, it was still at hurricane status, producing winds strong enough to knock down hundreds of trees and power lines. The highest sustained winds in the state were at Langley Air Force Base. Wind gusts were much stronger, reaching on the James River Bridge. Floyd's winds and rains knocked down hundreds of trees across the state, some centuries old.
The heavy rains washed out several roads, and closed regional routes including Interstate 95
Interstate 95 (I-95) is the main north–south Interstate Highway on the East Coast of the United States, running from U.S. Route 1 (US 1) in Miami, Florida, north to the Houlton–Woodstock Border Crossing between Maine and the ...
between Emporia and Petersburg, U.S. Route 58 between Emporia and Franklin, and U.S. Route 460 near Wakefield
Wakefield is a cathedral city in West Yorkshire, England located on the River Calder. The city had a population of 109,766 in the 2021 census, up from 99,251 in the 2011 census. The city is the administrative centre of the wider Metropolit ...
. The rainfall led to overflowing rivers in the Chowan River
The Chowan River (cho-WAHHN)
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the The
 Tropical Storm Floyd made landfall on western
Tropical Storm Floyd made landfall on western
 Floyd brought intense winds and heavy rain to Rhode Island. The strongest winds were confined to Washington and Providence counties. The winds brought down numerous trees, tree limbs and power lines. Rainfall typically ranged from , with a report of at North Smithfield, Rhode Island. The Pawtuxet River reached
Floyd brought intense winds and heavy rain to Rhode Island. The strongest winds were confined to Washington and Providence counties. The winds brought down numerous trees, tree limbs and power lines. Rainfall typically ranged from , with a report of at North Smithfield, Rhode Island. The Pawtuxet River reached
 The Hurricane Floyd disaster was followed by what many judged to be a very slow federal response. Fully three weeks after the storm hit,
The Hurricane Floyd disaster was followed by what many judged to be a very slow federal response. Fully three weeks after the storm hit,  Runoff from the hurricane created significant problems for the ecology of North Carolina's rivers and sounds. In the immediate aftermath of the storm, freshwater runoff, sediment, and decomposing organic matter caused salinity and oxygen levels in
Runoff from the hurricane created significant problems for the ecology of North Carolina's rivers and sounds. In the immediate aftermath of the storm, freshwater runoff, sediment, and decomposing organic matter caused salinity and oxygen levels in
NHC Floyd Report
* ttp://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs07301/ USGS: Flooding in Delaware and the Eastern Shore of Maryland From Hurricane Floyd, September 1999
NWS Service Assessment (flooding)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Floyd (1999) Hurricane Floyd Retired Atlantic hurricanes Cape Verde hurricanes Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes Hurricanes in the Bahamas Hurricanes in North Carolina Hurricanes in Virginia Hurricanes in Delaware Hurricanes in Maryland Hurricanes in New Jersey Hurricanes in New York (state) Hurricanes in New England Hurricanes in Maine Hurricanes in Connecticut Hurricanes in Massachusetts Hurricanes in Rhode Island Hurricanes in Vermont Hurricanes in New Hampshire
, from the North Carolina Collection's website at the The
Blackwater River
A blackwater river is a type of River#Classification, river with a slow-moving channel flowing through forested swamps or wetlands. Most major blackwater rivers are in the Amazon Basin and the Southern United States. The term is used in fluvial ...
reached 100-year flood levels and flooded Franklin with of water. Extensive road damage occurred there, isolating the area from the rest of the state. Some 182 businesses and 150 houses were underwater in Franklin from the worst flooding in 60 years. In addition, two dams along the Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the enti ...
burst from the extreme flooding. Throughout all of Virginia, Floyd damaged 9,250 houses. In addition to the heavy rainfall, tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide tables ...
in Norfolk
Norfolk ( ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in England, located in East Anglia and officially part of the East of England region. It borders Lincolnshire and The Wash to the north-west, the North Sea to the north and eas ...
were above normal, resulting moderate to locally severe coastal flooding
Coastal flooding occurs when dry and low-lying land is submerged (flooded) by seawater. The range of a coastal Flood, flooding is a result of the elevation of floodwater that penetrates the inland which is controlled by the topography of the coas ...
. Along the Chesapeake Bay, Floyd produced a storm surge, causing up to of flooding in Accomack County homes. Floyd's winds and rains knocked down hundreds of trees across the state, some centuries' old.
Mid-Atlantic
As Floyd moved northward from Virginia, a stalledcold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface Trough (meteorology), trough of Low-pressure area, low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropica ...
acted as a conveyor belt of tropical moisture across the Mid-Atlantic. Wind gusts in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
reached at the Children's National Medical Center. The storm knocked down trees and dropped heavy rainfall, causing a shop on New York Avenue NW to close after the roof collapsed.
The hurricane's rainbands moved across Maryland, dropping of rainfall in Chestertown, Maryland
Chestertown is a town in Kent County, Maryland, United States. The population was 5,532 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the county seat of Kent County, the oldest county in Maryland.
History
Founded in 1706, Chestertown ...
. Statewide, about 450 people required evacuated from low-lying areas. A mudslide in Anne Arundel County stranded five trains carrying about 1,000 passengers. Flooding closed 225 roads statewide, with dozens of motorists requiring rescue, and more than 90 bridges were damaged. A man in Centreville died while attempting to jump a washed out bridge on his motorcycle. High tides, above normal, affected coastal areas of St. Mary's, Calvert, Harford, and Anne Arundel counties, with 5 houses destroyed and 23 severely damaged. Flooding inundated the only bridge to St. George Island, stranding six people. The highest statewide wind gust – 71 mph (114 km/h) – occurred in Tall Timbers, while the highest wind gust in eastern Maryland was 52 mph (83 km/h) in Ocean City. The winds knocked down hundreds of trees, including the nearly 400 year–old Liberty Tree at St. John's College in Annapolis. The winds also knocked down power lines, leaving about 500,000 customers without electricity. Two people were injured, and one person killed, from Carbon monoxide poisoning
Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as " flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large ...
related to using a generator. The Anne Arundel county fair was canceled for the first time in its history. In Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-large ...
, the Baltimore Orioles
The Baltimore Orioles (also known as the O's) are an American professional baseball team based in Baltimore. The Orioles compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East Division. As one of the America ...
postponed a baseball game. Statewide damage was estimated at $7.9 million.
In Delaware, Hurricane Floyd left $8.42 million in damage. The storm dropped torrential rainfall, reaching in Greenwood, Delaware
Greenwood is a town in Sussex County, Delaware, United States. The population was 973 at the 2010 census, an increase of 16.2% over the previous decade. It is part of the Salisbury, Maryland-Delaware Metropolitan Statistical Area.
History
The ...
. During the storm, Greenwood recorded , breaking the record for the state's highest 24 hour rainfall total. The rains caused record crests along rivers and streams in New Castle County. The White Clay Creek crested at , and was above flood stage for 18 hours. Statewide, Floyd damaged 171 homes, and caused 33 homes to be condemned. Flooding closed hundreds of roads and bridges, with two bridges and a few miles of track belonging to the Wilmington and Western Railroad washed out. Dozens of motorists required rescue. Winds in the state reached 64 mph (104 km/h) at Cape Henlopen along the coast. The winds knocked down hundreds of trees and power lines, leaving about 25,000 people without power.
As Floyd continued up the coast, it dropped heavy rainfall in New Jersey, reaching in Little Falls; this was the highest statewide rain from a tropical cyclone since 1950. Following the state's fourth-worst drought in a century, the rains collected in rivers and streams, causing record flooding at 18 river gauges, and mostly affecting the Raritan, Passaic
Passaic ( or ) is a city in Passaic County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the city was the state's 16th-most-populous municipality,Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
basins. Statewide damage totaled $250 million (1999 USD
The United States dollar (symbol: $; currency code: USD) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it int ...
), much of it in Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east ...
and Bergen
Bergen (, ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Vestland county on the Western Norway, west coast of Norway. Bergen is the list of towns and cities in Norway, second-largest city in Norway after the capital Oslo.
By May 20 ...
counties. This made Floyd the costliest natural disaster in New Jersey's history, until it was surpassed by Hurricane Irene
Hurricane Irene was a large and destructive tropical cyclone which affected much of the Caribbean and East Coast of the United States during late August 2011. The ninth tropical cyclone naming, named storm, first hurricane, and first major ...
in 2011. Seven people died in New Jersey during Floyd's passage – six due to drowning, and one in a traffic accident. A police lieutenant took his life after working for nearly 48 hours coordinating floodwater rescues. In Bound Brook, the Raritan crested at a record on September 16, well above the flood stage, and exceeding the previous record of set during Tropical Storm Doria in 1971. Downtown Bound Brook was flooded , causing 200 buildings to be condemned. In Manville, the Raritan crested at a record , nearly double the flood stage of . Parts of Manville were flooded to a depth of , which damaged 1,500 homes, caused 284 homes to be condemned, and forced 1,000 people to evacuate. A water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, ...
plant was damaged in Bridgewater Township, forcing nearly 500,000 people in Hunterdon, Mercer, Middlesex
Middlesex (; abbreviation: Middx) is a Historic counties of England, former county in South East England, now mainly within Greater London. Its boundaries largely followed three rivers: the River Thames, Thames in the south, the River Lea, Le ...
, and Somerset counties to boil water for eight days. The Rochelle Park, New Jersey hub of Electronic Data Systems
Electronic Data Systems (EDS) Corporation was an American multinational corporation, multinational information technology equipment and services company headquartered in Plano, Texas, which was founded in 1962 by Ross Perot. The company was a s ...
was inundated by the nearby Saddle River, disrupting service to as many as 8,000 ATMs across the United States. Flooding in an adjoining Bell Atlantic
A bell Help:IPA/English, /ˈbɛl/ () is a struck idiophone, directly struck idiophone percussion instrument. Most bells have the shape of a hollow cup that when struck vibrates in a single strong strike tone, with its sides forming an efficien ...
switching facility cut off phone service to one million customers in the area.
In Pennsylvania, Floyd killed 13 people, largely due to drownings, fallen trees, or heart attacks, and another 40 people were severely injured. The hurricane left about $60 million in damage, mostly related to its heavy rainfall, which peaked at in Marcus Hook. The highest wind gust was occurred at the Commodore Barry Bridge. The two hardest-hit counties were Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
and Bucks, where more than 10,000 homes were flooded, including 200 that were damaged to the point of being uninhabitable. More than 4,000 people statewide lost their homes due to the storm. Many creeks swelled to record levels, in some cases over double their estimated flood stage, which left motorists in need of rescue, including a bus with 11 students in Buckingham Township. Statewide, Floyd left over 500,000 homes and businesses without power.
 Tropical Storm Floyd made landfall on western
Tropical Storm Floyd made landfall on western Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated continental island in southeastern New York (state), New York state, extending into the Atlantic Ocean. It constitutes a significant share of the New York metropolitan area in both population and land are ...
as it moved northward. The heaviest rainfall associated with the storm was concentrated in the southeastern section of the state. Several meteorological elements worked to enhance the moisture from the cyclone. Rainfall totals exceeding were common, with as much as reported locally in the Catskills
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province and subrange of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined a ...
. At Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
, of rain fell. The precipitation, combined with that of Hurricane Dennis earlier in the month, helped to alleviate persistent drought conditions. Floyd also produced gusty winds, reaching at Stewart International Airport
New York Stewart International Airport – colloquially known as Stewart International Airport, is a public/military airport in Orange County, New York, United States. It is in the southern Hudson Valley, west of Newburgh, south of Kingston ...
, worsened by a pressure gradient between the storm and an area of high pressure
In science and engineering the study of high pressure examines its effects on materials and the design and construction of devices, such as a diamond anvil cell, which can create high pressure. ''High pressure'' usually means pressures of thousan ...
over the Ohio Valley
The Ohio River () is a river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing in a southwesterly direction from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, to its mouth on the Mississippi River in Cairo, ...
.
Floyd's rainfall resulted in deadly and extensive flooding that killed two people in New York. Heavy flooding was reported along numerous creeks. In the Albany area, the Normanskill rose to extremely high levels, and the resultant flood waters damaged nearby buildings. The Coeymans Creek in Selkirk overflowed and forced 20 families to leave their homes. Further south, the Saw Mill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logging, logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes ...
and Bronx
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five Boroughs of New York City, boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County, New York, West ...
rivers both overflowed, and caused urban flooding
Urban flooding is the inundation of land or property in cities or other built environment, caused by rainfall or coastal storm surges overwhelming the capacity of drainage systems, such as storm sewers. Urban flooding can occur regardless of whethe ...
. A dam on a mill pond
A mill pond (or millpond) is a body of water used as a reservoir for a water-powered mill.
Description
Mill ponds were often created through the construction of a mill dam or weir (and mill stream) across a waterway.
In many places, the co ...
broke near Lake Placid, leading to flooding along the Chubb River.
The strong winds, combined with saturated ground from the rainfall, brought down trees in widespread areas of the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley or Hudson River Valley comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. The region stretches from the Capital District (New York), Capital District includi ...
and Capital District. Many of the trees would not have otherwise fallen in drier conditions. Some of the downed trees fell on structures. In a narrow swath in the Wolf Pond Valley of Warren County, where wind gusts are estimated to have reached , hundreds of trees were blown down. At the storm's worst, power outages affected over 100,000 people region-wide, and some individuals remained without power for a week. At the Albany International Airport, the storm forced the cancellation of flights, and throughout the region schools were closed. Several boats sustained damage along the shore of Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain ( ; , ) is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the U.S. states of New York (state), New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canadian province of Quebec.
The cities of Burlington, Ve ...
. Throughout Orange, Putnam, Rockland, and Westchester counties, initial cost estimates were $14.6 million, although that figure represents only a portion of the actual monetary damage. The storm also caused about $2 million in property damage in Essex County.
New England
In Connecticut, the storm caused one casualty: a man drowned after boating in the swollenQuinnipiac River
The Quinnipiac River ( ) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed April 1, 2011 long river in the New England region of the United States, located entirely in the state of ...
. The storm caused extensive flooding and serious damage. Wind gusts exceeding , combined with the saturated ground, brought down many trees and triggered severe power outages in the area. As Floyd tracked up the Connecticut River Valley towards Massachusetts, it dropped heavy precipitation. The heaviest rainfall occurred in a southwest–northeast orientated swath from northern New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
to southwestern Connecticut, including southeastern New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
. At the Danbury Airport, of rain was reported. Rainfall rates of per hour occurred at Bethel
Bethel (, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; ; ) was an ancient Israelite city and sacred space that is frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Bible.
Bet ...
and Danbury. Numerous rivers overflowed; for example, the Still River and its tributaries triggered severe flooding. The worst of the flooding—considered the worst in 40 years—took place at Danbury. Hundreds of homes, two car dealerships, several roads, and other structures were damaged there. At Greentree Motors, all 200 vehicles were declared a total loss. Parts of the city were submerged with of water. However, throughout the state, roads were closed and basements were inundated. The flooding inflicted at least $1.3 million in monetary damage within Fairfield County. Portions of the state were declared a federal disaster area.
 Floyd brought intense winds and heavy rain to Rhode Island. The strongest winds were confined to Washington and Providence counties. The winds brought down numerous trees, tree limbs and power lines. Rainfall typically ranged from , with a report of at North Smithfield, Rhode Island. The Pawtuxet River reached
Floyd brought intense winds and heavy rain to Rhode Island. The strongest winds were confined to Washington and Providence counties. The winds brought down numerous trees, tree limbs and power lines. Rainfall typically ranged from , with a report of at North Smithfield, Rhode Island. The Pawtuxet River reached flood stage Flood stage is the water level or stage at which the surface of a body of water has risen to a sufficient level to cause sufficient inundation of areas that are not normally covered by water, causing an inconvenience or a threat to life and proper ...
on September 16, and crested the next day. Although it surpassed its banks, no flood damage was reported. The storm's effects in the state were mostly minor.
In Massachusetts, the storm produced wind gusts of , reaching at the New Bedford Hurricane Barrier. The strongest winds were concentrated over two sections of the state—the western mountains terrain and Cape Cod
Cape Cod is a peninsula extending into the Atlantic Ocean from the southeastern corner of Massachusetts, in the northeastern United States. Its historic, maritime character and ample beaches attract heavy tourism during the summer months. The ...
. The winds brought down trees and power lines in these areas, particularly around Pittsfield. In terms of rainfall, the storm dropped in many locations. The heavy precipitation caused rivers to swell, and in some cases flow over their banks. Storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the ...
at the Fox Point Hurricane Barrier reached .
By September 17, Floyd was located over southwestern Maine, dropping heavy rains. The entire state received precipitation, with the highest totals confined to southern areas. The National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an Government agency, agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weathe ...
issued a flood watch for two-thirds of the state. The storm was described as "tame", and damage was generally minor. In much of Androscoggin County, rainfall amounted to between 7 and 8 in (180 and 200 mm); Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
reported . Several rivers approached or exceeded flood stage Flood stage is the water level or stage at which the surface of a body of water has risen to a sufficient level to cause sufficient inundation of areas that are not normally covered by water, causing an inconvenience or a threat to life and proper ...
due to rainfall from Floyd and Hurricane Dennis less than a week earlier, causing minor flooding. Floyd helped to alleviate drought conditions in Maine. Some roads in susceptible areas were submerged, and a few basements were flooded. Wind gusts of blew down trees and snapped branches, especially in the area surrounding Baxter State Park. Around 15,000 residents were affected by power outages as a result. Following the event, five counties—Androscoggin, Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
, Kennebec Oxford
Oxford () is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and non-metropolitan district in Oxfordshire, England, of which it is the county town.
The city is home to the University of Oxford, the List of oldest universities in continuou ...
, and Somerset
Somerset ( , ), Archaism, archaically Somersetshire ( , , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east ...
—were declared disaster areas, making federal aid available to those areas.
Rainfall in New Hampshire generally ranged from , although a few higher totals were recorded. At Mount Washington, of precipitation fell. The rainfall swelled rivers, pushing them above flood stage; the Saco River at Conway
Conway may refer to:
Places
United States
* Conway, Arkansas
* Conway County, Arkansas
* Lake Conway, Arkansas
* Conway, Florida
* Conway, Iowa
* Conway, Kansas
* Conway, Louisiana
* Conway, Massachusetts
* Conway, Michigan
* Conway Townshi ...
crested at , surpassing the 9-ft (2.7 m) flood stage. Along the Saco and Pemigewasset rivers, minor flooding took place, though only in low-lying terrain. Strong winds also impacted the state, with gusts often exceeding . The winds brought down several small trees in Jaffrey, and triggered power outages that affected 10,000 residents. A federal disaster area was declared in the state.
In Vermont, for the first time in years, the Tunbridge World's Fair was canceled due to the storm. One woman sustained injuries after a tree crashed on her vehicle. Floyd produced high winds and heavy rain throughout the state, leading to widespread downed trees and powerlines. Thousands of residents in the state lost power after winds impacted the area. Rainfall totals of were common, although there were localized higher reports. The rainfall was offset by persistent drought conditions, however. Numerous tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
overflowed their banks, and significant flooding was reported. In Weathersfield, part of U.S. Route 5
U.S. Route 5 (US 5) is a north–south United States Numbered Highway running through the New England states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont. Significant cities along the route include New Haven, Connecticut; Hartford, Conn ...
was washed away. Some schools were closed and events canceled in the region. The downed trees caused structural damage, blocked roadways, and affected hiking trails. The high winds also damaged buildings and some apple orchards, Waves of occurred on Lake Champlain
Lake Champlain ( ; , ) is a natural freshwater lake in North America. It mostly lies between the U.S. states of New York (state), New York and Vermont, but also extends north into the Canadian province of Quebec.
The cities of Burlington, Ve ...
, damaging numerous watercraft along the shore. The hurricane caused one death. Most of Vermont was declared a disaster area after the storm.
Canada
The remnants of Floyd produced rainfall and gusty winds from Ontario toAtlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada, also called the Atlantic provinces (), is the list of regions of Canada, region of Eastern Canada comprising four provinces: New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. As of 2021, the landma ...
, with occurring along the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrenc ...
in Quebec, the strongest winds in the country. The high winds damaged corn and other crops along the river's south shore from the l'Amiante to Bellechasse regions. The highest rainfall in Canada also occurred in eastern Quebec, reaching . Power outages affected Montreal and Quebec City, causing classes to be canceled at the Université de Montréal
The Université de Montréal (; UdeM; ) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce on M ...
. Inclement weather was a potential factor in a five car accident on Autoroute 15 in Montreal. Minor traffic accidents also occurred in the Maritimes. Heavy rainfall backed up storm drains in Fredericton, New Brunswick
Fredericton (; ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of New Brunswick. The city is situated in the west-central portion of the province along the Saint John River (Bay of Fundy), Saint John River, ...
. The Confederation Bridge
The Confederation Bridge () is a box girder bridge carrying the Trans-Canada Highway across the Abegweit Passage of the Northumberland Strait, linking the province of Prince Edward Island with the mainland province of New Brunswick. Opened ...
connecting Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
to the mainland shut down during the storm due to winds. About 6,000 people lost power in Nova Scotia.
Aftermath
The Bahamas
To help the affected citizens, the Bahamas Red Cross Society opened 41 shelters, though within one week many returned home. The Bahamas required $435,000 (1999 USD; $ USD) in aid following the storm, much of it in food parcels. TheInter-American Development Bank
The Inter-American Development Bank (IDB or IADB) is an international development finance institution headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States of America. It serves as one of the leading sources of development financing for the countri ...
loaned $21 million (1999 USD; $ USD) to the archipelago to restore bridges, roads, seawalls, docks, and other building projects in the aftermath of the hurricane.
North Carolina
 The Hurricane Floyd disaster was followed by what many judged to be a very slow federal response. Fully three weeks after the storm hit,
The Hurricane Floyd disaster was followed by what many judged to be a very slow federal response. Fully three weeks after the storm hit, Jesse Jackson
Jesse Louis Jackson (Birth name#Maiden and married names, né Burns; born October 8, 1941) is an American Civil rights movements, civil rights activist, Politics of the United States, politician, and ordained Baptist minister. Beginning as a ...
complained to FEMA Director James Lee Witt on his CNN
Cable News Network (CNN) is a multinational news organization operating, most notably, a website and a TV channel headquartered in Atlanta. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable ne ...
program ''Both Sides Now'', "It seemed there was preparation for Hurricane Floyd, but then came Flood Floyd. Bridges are overwhelmed, levees are overwhelmed, whole towns under water ... t'san awesome scene of tragedy. So there's a great misery index in North Carolina." Witt responded, "We're starting to move the camper trailers in. It's been so wet it's been difficult to get things in there, but now it's going to be moving very quickly. And I think you're going to see a—I think the people there will see a big difference ithinthis next weekend."
 Runoff from the hurricane created significant problems for the ecology of North Carolina's rivers and sounds. In the immediate aftermath of the storm, freshwater runoff, sediment, and decomposing organic matter caused salinity and oxygen levels in
Runoff from the hurricane created significant problems for the ecology of North Carolina's rivers and sounds. In the immediate aftermath of the storm, freshwater runoff, sediment, and decomposing organic matter caused salinity and oxygen levels in Pamlico Sound
Pamlico Sound ( ) is a large estuarine lagoon in North Carolina. The largest lagoon along the North American East Coast, it extends long and wide. It is part of a large, interconnected network of similar lagoons that includes Albemarle Sou ...
and its tributary rivers to drop to nearly zero. This raised fears of massive fish and shrimp kills, as had happened after Hurricane Fran and Hurricane Bonnie, and the state government responded quickly to provide financial aid to fishing and shrimping industries. Strangely, however, the year's shrimp and crab harvests were extremely prosperous; one possible explanation is that runoff from Hurricane Dennis caused marine animals to begin migrating to saltier waters, so they were less vulnerable to Floyd's ill effects. Pollution from runoff was also a significant fear. Numerous pesticides were found in low but measurable quantities in the river waters, particularly in the Neuse River. Overall, however, the concentration of contaminants was slightly lower than had been measured in Hurricane Fran, likely because Floyd simply dropped more water to dilute them.
When the hurricane hit North Carolina, it flooded hog waste lagoons and released 25 million gallons of manure into the rivers, which contaminated the water supply and reduced water quality. Ronnie Kennedy, Duplin County director for environmental health, said that of 310 private wells he had tested for contamination since the storm, 9 percent, or three times the average across eastern North Carolina, had faecal coliform bacteria. Normally, tests showing any hint of faeces in drinking water, an indication that it can be carrying disease-causing pathogens, are cause for immediate action.
Retirement
Due to the high impact, extensive damage, and loss of life from the hurricane, thename
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A person ...
''Floyd'' was retired by the World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology an ...
in the spring of 2000, and it will never again be used for another north Atlantic tropical cyclone. It was replaced with ''Franklin'' for the 2005 season.
See also
*Hurricane Dorian
Hurricane Dorian was an extremely powerful and catastrophic tropical cyclone, which became the most intense on record to strike The Bahamas. It is tied with the 1935 Labor Day hurricane for the strongest landfall in the Atlantic basin in term ...
* Hurricane Florence
* Hurricane Irene
Hurricane Irene was a large and destructive tropical cyclone which affected much of the Caribbean and East Coast of the United States during late August 2011. The ninth tropical cyclone naming, named storm, first hurricane, and first major ...
* Hurricane Isaias
* List of New Jersey hurricanes
There have been 115 hurricanes or tropical storms that affected the U.S. state of New Jersey. Due to its location, few hurricanes have hit the state directly, though numerous hurricanes have passed near or through New Jersey in its history. Abo ...
* List of North Carolina hurricanes (1980–1999)
* List of Pennsylvania hurricanes
* List of Virginia hurricanes
Since HURDAT, 1851, 122 Tropical cyclone, tropical or subtropical cyclones have either directly or indirectly affected the state of Virginia, with the most recent being Hurricane Helene, Helene in 2024 Atlantic hurricane season, 2024. On average, ...
* List of wettest tropical cyclones in Massachusetts
* Center for Natural Hazards Research
* Timeline of the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season
Notes
References
External links
NHC Floyd Report
* ttp://pubs.usgs.gov/fs/fs07301/ USGS: Flooding in Delaware and the Eastern Shore of Maryland From Hurricane Floyd, September 1999
NWS Service Assessment (flooding)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Floyd (1999) Hurricane Floyd Retired Atlantic hurricanes Cape Verde hurricanes Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes Hurricanes in the Bahamas Hurricanes in North Carolina Hurricanes in Virginia Hurricanes in Delaware Hurricanes in Maryland Hurricanes in New Jersey Hurricanes in New York (state) Hurricanes in New England Hurricanes in Maine Hurricanes in Connecticut Hurricanes in Massachusetts Hurricanes in Rhode Island Hurricanes in Vermont Hurricanes in New Hampshire
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful and large tropical cyclone which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth list of named tropical cyclones, named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1 ...
Floods in Pennsylvania
Presidency of Bill Clinton