Heptagonal Prismatic Graph on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In geometry, a heptagon or septagon is a seven-sided polygon or 7-gon.
The heptagon is sometimes referred to as the septagon, using "sept-" (an
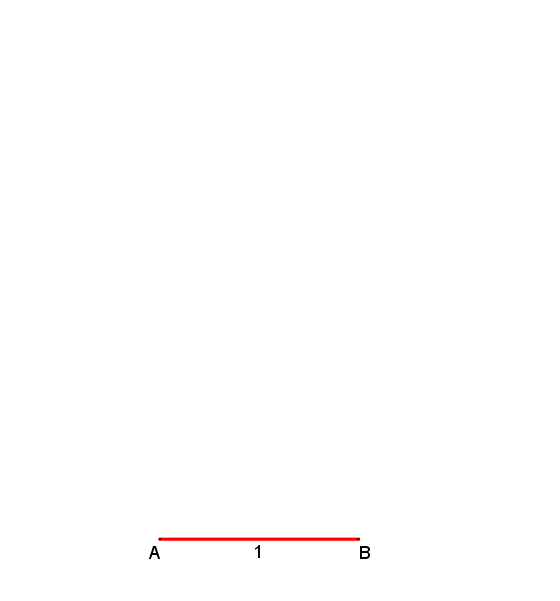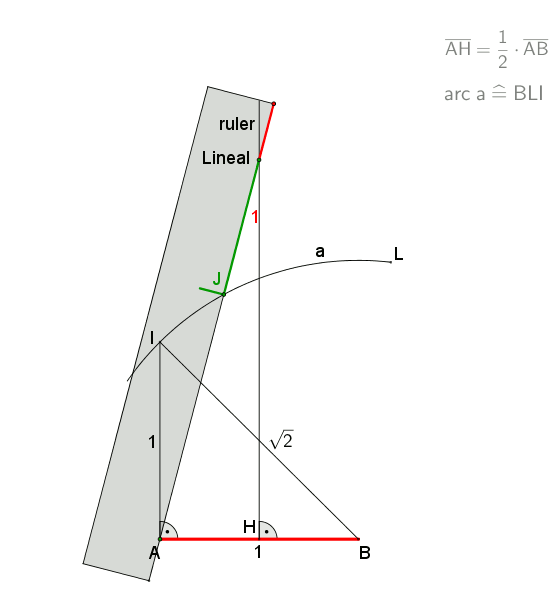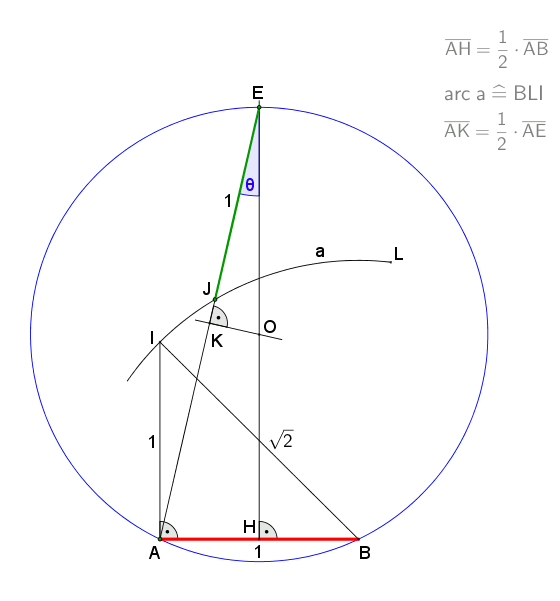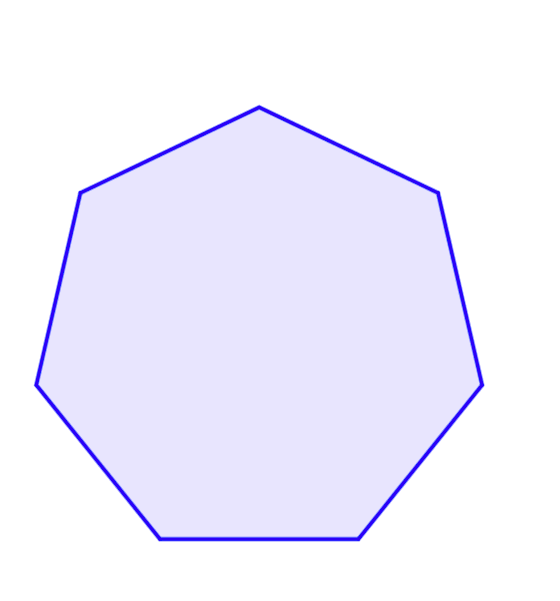
At a circumscribed circle radius ''r = 1 m'', the absolute error of the 1st side would be ''approximately -1.7 mm''
 The ''regular heptagon'' belongs to the D7h
The ''regular heptagon'' belongs to the D7h
 The regular heptagon's side ''a'', shorter diagonal ''b'', and longer diagonal ''c'', with ''a''<''b''<''c'', satisfyAbdilkadir Altintas, "Some Collinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle", ''
The regular heptagon's side ''a'', shorter diagonal ''b'', and longer diagonal ''c'', with ''a''<''b''<''c'', satisfyAbdilkadir Altintas, "Some Collinearities in the Heptagonal Triangle", ''

Blue, and green star heptagons inside a red heptagon.
 The United Kingdom, , has two heptagonal coins, the 50p and 20p pieces, and the
The United Kingdom, , has two heptagonal coins, the 50p and 20p pieces, and the
Definition and properties of a heptagon
With interactive animation
Heptagon according Johnson
Another approximate construction method
Recently discovered and highly accurate approximation for the construction of a regular heptagon.
* Heptagon, an approximating construction as an animation * A heptagon with a given side, an approximating construction as an animation {{Polygons Polygons by the number of sides 7 (number) Elementary shapes
elision
In linguistics, an elision or deletion is the omission of one or more sounds (such as a vowel, a consonant, or a whole syllable) in a word or phrase. However, these terms are also used to refer more narrowly to cases where two words are run toget ...
of ''septua-
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from Numeral (linguistics), numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1 ...
'', a Latin-derived numerical prefix, rather than '' hepta-'', a Greek-derived numerical prefix; both are cognate) together with the Greek suffix "-agon" meaning angle.
Regular heptagon
A regular heptagon, in which all sides and all angles are equal, has internal angles of 5π/7 radians (128degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics
...
s). Its Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more ...
is .
Area
The area (''A'') of a regular heptagon of side length ''a'' is given by: : This can be seen by subdividing the unit-sided heptagon into seven triangular "pie slices" with vertices at the center and at the heptagon's vertices, and then halving each triangle using the apothem as the common side. The apothem is half thecotangent
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all ...
of and the area of each of the 14 small triangles is one-fourth of the apothem.
The area of a regular heptagon inscribed
{{unreferenced, date=August 2012
An inscribed triangle of a circle
In geometry, an inscribed planar shape or solid is one that is enclosed by and "fits snugly" inside another geometric shape or solid. To say that "figure F is inscribed in figur ...
in a circle of radius ''R'' is while the area of the circle itself is thus the regular heptagon fills approximately 0.8710 of its circumscribed circle.
Construction
As 7 is aPierpont prime
In number theory, a Pierpont prime is a prime number of the form
2^u\cdot 3^v + 1\,
for some nonnegative integers and . That is, they are the prime numbers for which is 3-smooth. They are named after the mathematician James Pierpont, who us ...
but not a Fermat prime, the regular heptagon is not constructible with compass and straightedge
In geometry, straightedge-and-compass construction – also known as ruler-and-compass construction, Euclidean construction, or classical construction – is the construction of lengths, angles, and other geometric figures using only an ideali ...
but is constructible with a marked ruler and compass. It is the smallest regular polygon with this property. This type of construction is called a neusis construction
In geometry, the neusis (; ; plural: grc, νεύσεις, neuseis, label=none) is a geometric construction method that was used in antiquity by Greek mathematicians.
Geometric construction
The neusis construction consists of fitting a line e ...
. It is also constructible with compass, straightedge and angle trisector. The impossibility of straightedge and compass construction follows from the observation that is a zero of the irreducible
In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when an entity is observed to have properties its parts do not have on their own, properties or behaviors that emerge only when the parts interact in a wider whole.
Emergence ...
cubic
Cubic may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Cube (algebra), "cubic" measurement
* Cube, a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex
** Cubic crystal system, a crystal system w ...
. Consequently, this polynomial is the minimal polynomial of whereas the degree of the minimal polynomial for a constructible number must be a power of 2.

Approximation
An approximation for practical use with an error of about 0.2% is shown in the drawing. It is attributed toAlbrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Due ...
. Let ''A'' lie on the circumference of the circumcircle. Draw arc ''BOC''. Then gives an approximation for the edge of the heptagon.
This approximation uses for the side of the heptagon inscribed in the unit circle while the exact value is .
''Example to illustrate the error:At a circumscribed circle radius ''r = 1 m'', the absolute error of the 1st side would be ''approximately -1.7 mm''

Symmetry
 The ''regular heptagon'' belongs to the D7h
The ''regular heptagon'' belongs to the D7h point group
In geometry, a point group is a mathematical group of symmetry operations (isometries in a Euclidean space) that have a fixed point in common. The coordinate origin of the Euclidean space is conventionally taken to be a fixed point, and every p ...
( Schoenflies notation), order 28. The symmetry elements are: a 7-fold proper rotation axis C7, a 7-fold improper rotation axis, S7, 7 vertical mirror planes, σv, 7 2-fold rotation axes, C2, in the plane of the heptagon and a horizontal mirror plane, σh, also in the heptagon's plane.
Diagonals and heptagonal triangle
Forum Geometricorum
''Forum Geometricorum: A Journal on Classical Euclidean Geometry'' is a peer-reviewed open-access academic journal that specializes in mathematical research papers on Euclidean geometry.
It was founded in 2001, is published by Florida Atlantic U ...
'' 16, 2016, 249–256.http://forumgeom.fau.edu/FG2016volume16/FG201630.pdf
:
:
:
: (the optic equation
In number theory, the optic equation is an equation that requires the sum of the reciprocals of two positive integers ''a'' and ''b'' to equal the reciprocal of a third positive integer ''c'':Dickson, L. E., ''History of the Theory of Numbers, V ...
)
and hence
:
and
:
:
:
Thus –''b''/''c'', ''c''/''a'', and ''a''/''b'' all satisfy the cubic equation However, no algebraic expressions with purely real terms exist for the solutions of this equation, because it is an example of casus irreducibilis.
The approximate lengths of the diagonals in terms of the side of the regular heptagon are given by
:
We also have
:
:
:
and
:
A heptagonal triangle
A heptagonal triangle is an obtuse scalene triangle whose vertices coincide with the first, second, and fourth vertices of a regular heptagon (from an arbitrary starting vertex). Thus its sides coincide with one side and the adjacent shorter an ...
has vertices coinciding with the first, second, and fourth vertices of a regular heptagon (from an arbitrary starting vertex) and angles and Thus its sides coincide with one side and two particular diagonals
In geometry, a diagonal is a line segment joining two vertices of a polygon or polyhedron, when those vertices are not on the same edge. Informally, any sloping line is called diagonal. The word ''diagonal'' derives from the ancient Greek δ� ...
of the regular heptagon.
In polyhedra
Apart from theheptagonal prism
In geometry, the heptagonal prism is a prism with heptagonal base. This polyhedron has 9 faces, 21 edges, and 14 vertices..
Area
The area of a right heptagonal prism with height h and with a side length of L and apothem a_p is given by:
:A = 7 ...
and heptagonal antiprism, no convex polyhedron made entirely out of regular polygons contains a heptagon as a face.
Star heptagons
Two kinds of star heptagons (heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek suffix '' -gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from ''γρ� ...
s) can be constructed from regular heptagons, labeled by Schläfli symbol
In geometry, the Schläfli symbol is a notation of the form \ that defines regular polytopes and tessellations.
The Schläfli symbol is named after the 19th-century Swiss mathematician Ludwig Schläfli, who generalized Euclidean geometry to more ...
s , and , with the divisor being the interval of connection.
Blue, and green star heptagons inside a red heptagon.
Tiling and packing
A regular triangle, heptagon, and 42-gon can completely fill a plane vertex. However, there is no tiling of the plane with only these polygons, because there is no way to fit one of them onto the third side of the triangle without leaving a gap or creating an overlap. In thehyperbolic plane
In mathematics, hyperbolic geometry (also called Lobachevskian geometry or Bolyai– Lobachevskian geometry) is a non-Euclidean geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with:
:For any given line ''R'' and point ''P'' ...
, tilings by regular heptagons are possible.
The regular heptagon has a double lattice In mathematics, especially in geometry, a double lattice in is a discrete subgroup of the group of Euclidean motions that consists only of translations and point reflections and such that the subgroup of translations is a lattice. The orbit of an ...
packing of the Euclidean plane of packing density approximately 0.89269. This has been conjectured to be the lowest density possible for the optimal double lattice packing density of any convex set, and more generally for the optimal packing density of any convex set.
Empirical examples
 The United Kingdom, , has two heptagonal coins, the 50p and 20p pieces, and the
The United Kingdom, , has two heptagonal coins, the 50p and 20p pieces, and the Barbados Dollar
The dollar has been the currency of Barbados since 1935. Globally its currency has the ISO 4217 code ''BBD'', however, unofficially in Barbados the International vehicle registration code code BDS is also commonly used, a currency code that is ...
are also heptagonal. The 20-eurocent
There are eight euro coin denominations, ranging from one cent to two euros (the euro is divided into a hundred cents). The coins first came into use in 2002. They have a common reverse, portraying a map of Europe, but each country in the eurozone ...
coin has cavities placed similarly. Strictly, the shape of the coins is a Reuleaux heptagon, a curvilinear
In geometry, curvilinear coordinates are a coordinate system for Euclidean space in which the coordinate lines may be curved. These coordinates may be derived from a set of Cartesian coordinates by using a transformation that is invertible, l ...
heptagon which has curves of constant width
In geometry, a curve of constant width is a simple closed curve in the plane whose width (the distance between parallel supporting lines) is the same in all directions. The shape bounded by a curve of constant width is a body of constant width ...
; the sides are curved outwards to allow the coins to roll smoothly when they are inserted into a vending machine. Botswana pula coins in the denominations of 2 Pula, 1 Pula, 50 Thebe and 5 Thebe are also shaped as equilateral-curve heptagons. Coins in the shape of Reuleaux heptagons are also in circulation in Mauritius, U.A.E., Tanzania, Samoa, Papua New Guinea, São Tomé and Príncipe, Haiti, Jamaica, Liberia, Ghana, the Gambia, Jordan, Jersey, Guernsey, Isle of Man, Gibraltar, Guyana, Solomon Islands, Falkland Islands and Saint Helena. The 1000 Kwacha coin of Zambia is a true heptagon.
The Brazilian 25-cent coin has a heptagon inscribed in the coin's disk. Some old versions of the coat of arms of Georgia
The coat of arms of Georgia is one of the national symbols of the republic. It is partially based on the medieval arms of the Georgian royal house and features Saint George, the traditional patron saint of Georgia. In addition to St. George, ...
, including in Soviet days, used a heptagram as an element.
In architecture, heptagonal floor plans are very rare. A remarkable example is the Mausoleum of Prince Ernst in Stadthagen, Germany.
Many police badges in the US have a heptagram outline.
See also
*Heptagram
A heptagram, septagram, septegram or septogram is a seven-point star drawn with seven straight strokes.
The name ''heptagram'' combines a numeral prefix, ''hepta-'', with the Greek suffix '' -gram''. The ''-gram'' suffix derives from ''γρ� ...
* Polygon
References
External links
Definition and properties of a heptagon
With interactive animation
Heptagon according Johnson
Another approximate construction method
Recently discovered and highly accurate approximation for the construction of a regular heptagon.
* Heptagon, an approximating construction as an animation * A heptagon with a given side, an approximating construction as an animation {{Polygons Polygons by the number of sides 7 (number) Elementary shapes