Halocarbons on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Halocarbon compounds are
 Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly
Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly
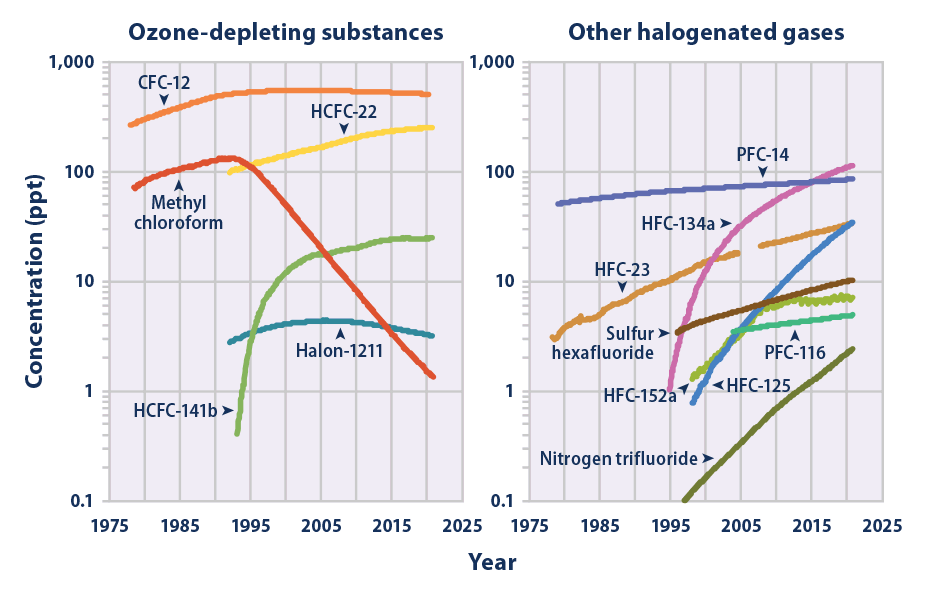 In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist
In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist
Chemical Industry Archives, Anniston Case
, by Environmental Working Group, Washington, DC, 2002 * * * * *
chemical compounds
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
in which one or more carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s are linked by covalent bond
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
s with one or more halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s (fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extre ...
, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
, bromine
Bromine is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured vapour. Its properties are intermediate between th ...
or iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
– ) resulting in the formation of organofluorine compound
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain a carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, ...
s, organochlorine compound
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted ...
s, organobromine compound
Organobromine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organobromine compounds, also called organobromides, which are organic compounds that contain carbon bonded to bromine. The most pervasive is the naturally produced bromometh ...
s, and organoiodine compound
Organoiodine chemistry is the study of the synthesis and properties of organoiodine compounds, or organoiodides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–iodine bonds. They occur widely in organic chemistry, but are relatively rare ...
s. Chlorine halocarbons are the most common and are called organochloride
Organochlorine chemistry is concerned with the properties of organochlorine compounds, or organochlorides, organic compounds that contain one or more carbon–chlorine bonds. The chloroalkane class (alkanes with one or more hydrogens substituted ...
s.
Many synthetic organic compounds such as plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
polymers
A polymer () is a substance or material that consists of very large molecules, or macromolecules, that are constituted by many repeating subunits derived from one or more species of monomers. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, b ...
, and a few natural ones, contain halogen atoms; they are known as ''halogenated'' compounds or ''organohalogens''. Organochlorides are the most common industrially used organohalides, although the other organohalides are used commonly in organic synthesis. Except for extremely rare cases, organohalides are not produced biologically, but many pharmaceuticals are organohalides. Notably, many pharmaceuticals such as Prozac have trifluoromethyl
The trifluoromethyl group is a functional group that has the formula . The naming of is group is derived from the methyl group (which has the formula ), by replacing each hydrogen atom by a fluorine atom. Some common examples are trifluoromethane ...
groups.
For information on inorganic halide chemistry, see halide
In chemistry, a halide (rarely halogenide) is a binary chemical compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative (or more electropositive) than the halogen, to make a fl ...
.
Chemical families
 Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly
Halocarbons are typically classified in the same ways as the similarly structured
Structuring, also known as smurfing in banking jargon, is the practice of executing financial transactions such as making bank deposits in a specific pattern, calculated to avoid triggering financial institutions to file reports required by law ...
organic compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-co ...
s that have hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s occupying the molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
sites of the halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s in halocarbons. Among the chemical families are:M. Rossberg et al. “Chlorinated Hydrocarbons” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2006, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim.
*haloalkane
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents of hydrogen atom. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalka ...
s—compounds with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s linked by single bonds
*haloalkene
In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH2=CHX (X = halide). The term vinyl group, vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl ...
s—compounds with one or more double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betw ...
s between carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s
*haloaromatic
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as a haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide ion (such as fluorine F''−'', chlorine Cl−1,−3,−5, bro ...
s—compounds with carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
s linked in one or more aromatic ring
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The e ...
s with a delocalised donut shaped pi cloud.
The halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s in halocarbon molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemi ...
s are often called "substituent
In organic chemistry, a substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule.
The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond r ...
s," as though those atoms had been substituted for hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
atoms. However halocarbons are prepared in many ways that do not involve direct substitution of halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
s for hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
s.
History and context
A few halocarbons are produced in massive amounts by microorganisms. For example, several million tons ofmethyl bromide
Bromomethane, commonly known as methyl bromide, is an organobromine compound with chemical formula, formula Carbon, CHydrogen, H3Bromine, Br. This colorless, odorless, nonflammable gas is Bromine cycle, produced both industrially and biologically ...
are estimated to be produced by marine organisms annually. Most of the halocarbons encountered in everyday life – solvents, medicines, plastics – are man-made. The first synthesis of halocarbons was achieved in the early 1800s. Production began accelerating when their useful properties as solvents and anesthetics were discovered. Development of plastics and synthetic elastomers has led to greatly expanded scale of production. A substantial percentage of drugs are halocarbons.
Natural halocarbons
A large amount of the naturally occurring halocarbons, such as dioxins, are created by wood fire andvolcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
. A third major source is marine algae, which produce several chlorinated methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
and ethane
Ethane ( , ) is a naturally occurring Organic compound, organic chemical compound with chemical formula . At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is List of purification methods ...
containing compounds. Several thousand complex halocarbons are known to be produced mainly by marine species. Although chlorine compounds are the majority of the discovered compounds, bromides, iodides and fluorides have also been found in nature. Tyrian purple
Tyrian purple ( ''porphúra''; ), also known as royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon, once Phoenicia. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails ...
is a bromide and is produced by certain sea snails. Thyroxine
Thyroxine, also known as T4, is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It is the primary form of thyroid hormone found in the blood and acts as a prohormone of the more active thyroid hormone, triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroxine and its acti ...
is secreted by the thyroid gland
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, it is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck below the Adam's apple. It consists of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by ...
and is an iodide. The highly toxic fluoroacetate is one of the rare natural organofluorides and is produced by certain plants....
Organoiodine compounds, including biological derivatives
Organoiodine compounds, called organic iodides, are similar in structure to organochlorine and organobromine compounds, but the C-I bond is weaker. Many organic iodides are known, but few are of major industrial importance. Iodide compounds are mainly produced as nutritional supplements. The thyroxin hormones are essential for human health, hence the usefulness ofiodized salt
Iodised salt ( also spelled iodized salt) is table salt mixed with a minute amount of various iodine salts. The ingestion of iodine prevents iodine deficiency. Worldwide, iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading p ...
.
Six mg of iodide a day can be used to treat patients with hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones. Thyrotoxicosis is a condition that occurs due to elevated levels of thyroid hormones of any cause and therefore includes hyperth ...
due to its ability to inhibit the organification process in thyroid hormone synthesis, the so-called Wolff–Chaikoff effect. Prior to 1940, iodides were the predominant antithyroid agents. In large doses, iodides inhibit proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Protein degradation is a major regulatory mechanism of gene expression and contributes substantially to shaping mammalian proteomes. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis o ...
of thyroglobulin
Thyroglobulin (Tg) is a 660 kDa, dimeric glycoprotein produced by the follicular cells of the thyroid and used entirely within the thyroid gland. Tg is secreted and accumulated at hundreds of grams per litre in the extracellular compartment ...
, which permits TH to be synthesized and stored in colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others exte ...
, but not released into the bloodstream. This mechanism is referred to as Plummer effect
The Plummer effect is one of several physiological Feed forward (control), feedforward mechanisms taking place in Thyroid follicular cell, follicular cells of the healthy thyroid gland and preventing the development of thyrotoxicosis in situations ...
.
This treatment is seldom used today as a stand-alone therapy despite the rapid improvement of patients immediately following administration. The major disadvantage of iodide treatment lies in the fact that excessive stores of TH accumulate, slowing the onset of action of thioamides
A thioamide (rarely, thionamide, but also known as thiourylenes) is a functional group with the general structure , where are any groups (typically organyl groups or hydrogen). Analogous to amides, thioamides exhibit greater multiple bond charac ...
(TH synthesis blockers). In addition, the functionality of iodides fades after the initial treatment period. An "escape from block" is also a concern, as extra stored TH may spike following discontinuation of treatment.
Uses
The first halocarbon commercially used wasTyrian purple
Tyrian purple ( ''porphúra''; ), also known as royal purple, imperial purple, or imperial dye, is a reddish-purple natural dye. The name Tyrian refers to Tyre, Lebanon, once Phoenicia. It is secreted by several species of predatory sea snails ...
, a natural organobromide of the '' Murex brandaris'' marine snail.
Common uses for halocarbons have been as solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are ...
s, fire-resistant oils, ingredients of elastomer
An elastomer is a polymer with viscoelasticity (i.e. both viscosity and elasticity) and with weak intermolecular forces, generally low Young's modulus (E) and high failure strain compared with other materials. The term, a portmanteau of ''ela ...
s, adhesive
Adhesive, also known as glue, cement, mucilage, or paste, is any non-metallic substance applied to one or both surfaces of two separate items that binds them together and resists their separation.
The use of adhesives offers certain advantage ...
s and sealants, electrically insulating coatings, plasticizer
A plasticizer ( UK: plasticiser) is a substance that is added to a material to make it softer and more flexible, to increase its plasticity, to decrease its viscosity, and/or to decrease friction during its handling in manufacture.
Plasticizer ...
s, and plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
s. Many halocarbons have specialized uses in industry. One halocarbon, sucralose
Sucralose is an artificial sweetener and sugar substitute. In the European Union, it is also known under the E number E955. It is produced by chlorination of sucrose, selectively replacing three of the hydroxy groups—in the C1 a ...
, is a sweetener.
Before they became strictly regulated, the general public often encountered haloalkane
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents of hydrogen atom. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalka ...
s as paint and cleaning solvents such as trichloroethane (1,1,1-trichloroethane) and carbon tetrachloride
Carbon tetrachloride, also known by many other names (such as carbon tet for short and tetrachloromethane, also IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry, recognised by the IUPAC), is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a n ...
(tetrachloromethane), pesticides like 1,2-dibromoethane
1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula . Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is probably formed by algae and kelp, substantial amounts are produc ...
(EDB, ethylene dibromide), and refrigerants
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are ...
like Freon
Freon ( ) is a registered trademark of the Chemours Company and generic descriptor for a number of halocarbon products. They are stable, nonflammable, low toxicity gases or liquids which have generally been used as refrigerants and as aerosol p ...
-22 (duPont
Dupont, DuPont, Du Pont, duPont, or du Pont may refer to:
People
* Dupont (surname) Dupont, also spelled as DuPont, duPont, Du Pont, or du Pont is a French surname meaning "of the bridge", historically indicating that the holder of the surname re ...
trademark for chlorodifluoromethane
Chlorodifluoromethane or difluoromonochloromethane is a hydrochlorofluorocarbon (HCFC). This colorless gas is better known as HCFC-22, or R-22, or . It was commonly used as a propellant and refrigerant. These applications were phased out under ...
). Some haloalkanes are still widely used for industrial cleaning, such as methylene chloride
Dichloromethane (DCM, methylene chloride, or methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odor is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with ...
(dichloromethane), and as refrigerants, such as R-134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane
1,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane (also known as norflurane ( INN), R-134a, Klea 134a, Freon 134a, Forane 134a, Genetron 134a, Green Gas, Florasol 134a, Suva 134a, HFA-134a, or HFC-134a) is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) and haloalkane refrigerant with th ...
).
Haloalkenes have also been used as solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s, including perchloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, and abbreviations such as perc (or PERC), and PCE, is a chlorocarbon with the formula . It is a non-flammable, stable, colorless and heavy liqu ...
(Perc, tetrachloroethene), widespread in dry cleaning, and trichloroethylene
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is an organochloride with the formula C2HCl3, commonly used as an industrial metal-degreasing solvent. It is a clear, colourless, non-flammable, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like pleasant mild smell and sweet taste.
(TCE, 1,1,2-trichloroethene). Other haloalkenes have been chemical building blocks of plastics such as polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (alternatively: poly(vinyl chloride), colloquial: vinyl or polyvinyl; abbreviated: PVC) is the world's third-most widely produced synthetic polymer of plastic (after polyethylene and polypropylene). About 40 million tons of ...
("vinyl" or PVC, polymerized chloroethene) and Teflon (duPont
Dupont, DuPont, Du Pont, duPont, or du Pont may refer to:
People
* Dupont (surname) Dupont, also spelled as DuPont, duPont, Du Pont, or du Pont is a French surname meaning "of the bridge", historically indicating that the holder of the surname re ...
trademark for polymerized tetrafluoroethene, PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene, and has numerous applications because it is chemically inert. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemours, a spin-off fro ...
).
Haloaromatics include the former Aroclor
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are organochlorine compounds with the formula Carbon, C12Hydrogen, H10−''x''Chloride, Cl''x''; they were once widely used in the manufacture of carbonless copy paper, as heat transfer fluids, and as dielectri ...
s (Monsanto Company
The Monsanto Company () was an American agrochemical and agricultural biotechnology corporation founded in 1901 and headquartered in Creve Coeur, Missouri. Monsanto's best-known product is Roundup, a glyphosate-based herbicide, developed in ...
trademark for polychlorinated biphenyl
Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) are organochlorine compounds with the formula Carbon, C12Hydrogen, H10−''x''Chloride, Cl''x''; they were once widely used in the manufacture of carbonless copy paper, as heat transfer fluids, and as dielectri ...
s, PCBs), once widely used in power transformers and capacitors and in building caulk, the former Halowaxes (Union Carbide
Union Carbide Corporation (UCC) is an American chemical company headquartered in Seadrift, Texas. It has been a wholly owned subsidiary of Dow Chemical Company since 2001. Union Carbide produces chemicals and polymers that undergo one or more f ...
trademark for polychlorinated naphthalenes, PCNs), once used for electrical insulation, and the chlorobenzene
Chlorobenzene (abbreviated PhCl) is an aryl chloride and the simplest of the chlorobenzenes, consisting of a benzene ring substituted with one chlorine atom. Its chemical formula is C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent a ...
s and their derivatives, used for disinfectant
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than ...
s, pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s such as dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
, 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane), herbicides
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
such as 2,4-D
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is usually referred to by its ISO common name 2,4-D. It is a systemic herbicide that kills most broadleaf weeds by causing uncontrolled growth, but most gra ...
(2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid), askarel dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an Insulator (electricity), electrical insulator that can be Polarisability, polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric ...
s (mixed with PCBs, no longer used in most countries), and chemical feedstocks.
A few halocarbons, including acid halides like acetyl chloride
Acetyl chloride () is an acyl chloride derived from acetic acid (). It belongs to the class of organic compounds called acid halides. It is a colorless, corrosive, volatile liquid. Its formula is commonly abbreviated to AcCl.
Synthesis
On an ...
, are highly reactive; these are rarely found outside chemical processing. The widespread uses of halocarbons were often driven by observations that most of them were more stable than other substances. They may be less affected by acids or alkalis; they may not burn as readily; they may not be attacked by bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
or mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures that certain fungus, fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of Spore#Fungi, spores containing Secondary metabolite#Fungal secondary metabolites, fungal ...
s; or they may not be affected as much by sun exposure.
Hazards
The stability of halocarbons tended to encourage beliefs that they were mostly harmless, although in the mid-1920s physicians reported workers in polychlorinated naphthalene (PCN) manufacturing suffering from chloracne , and by the late 1930s it was known that workers exposed to PCNs could die fromliver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Liver diseases
File:Ground gla ...
and that DDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
would kill mosquito
Mosquitoes, the Culicidae, are a Family (biology), family of small Diptera, flies consisting of 3,600 species. The word ''mosquito'' (formed by ''Musca (fly), mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish and Portuguese for ''little fly''. Mos ...
s and other insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s . By the 1950s, there had been several reports and investigations of workplace hazards. In 1956, for example, after testing hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
oils containing polychlorinated biphenyl (PCB)s, the U.S. Navy found that skin contact caused fatal liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Liver diseases
File:Ground gla ...
in animals and rejected them as "too toxic for use in a submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
" .
 In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist
In 1962 a book by U.S. biologist Rachel Carson
Rachel Louise Carson (May 27, 1907 – April 14, 1964) was an American marine biologist, writer, and conservation movement, conservationist whose sea trilogy (1941–1955) and book ''Silent Spring'' (1962) are credited with advancing mari ...
started a storm of concerns about environmental pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
, first focused on DDT
Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, commonly known as DDT, is a colorless, tasteless, and almost odorless crystalline chemical compound, an organochloride. Originally developed as an insecticide, it became infamous for its environmental impacts. ...
and other pesticide
Pesticides are substances that are used to control pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for approximately 50% of all p ...
s, some of them also halocarbons. These concerns were amplified when in 1966 Danish chemist Soren Jensen reported widespread residues of PCBs among Arctic and sub-Arctic fish and birds . In 1974, Mexican chemist Mario Molina
Mario José Molina-Pasquel Henríquez (19 March 19437 October 2020) was a Mexican physical chemist. He played a pivotal role in the discovery of the Antarctic ozone hole, and was a co-recipient of the 1995 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his role ...
and U.S. chemist Sherwood Rowland predicted that common halocarbon refrigerant
A refrigerant is a working fluid used in the cooling, heating, or reverse cooling/heating cycles of air conditioning systems and heat pumps, where they undergo a repeated phase transition from a liquid to a gas and back again. Refrigerants are ...
s, the chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
s (CFCs), would accumulate in the upper atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
and destroy protective ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
. Within a few years, ozone
Ozone () (or trioxygen) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , break ...
depletion was being observed above Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
, leading to bans on production and use of chlorofluorocarbon
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly Halogenation, halogenated hydrocarbons that contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F). They are produced as volatility (chemistry), volat ...
s in many countries. In 2007, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) said halocarbons were a direct cause of global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
.
Since the 1970s there have been longstanding, unresolved controversies over potential health hazards of trichloroethylene
Trichloroethylene (TCE) is an organochloride with the formula C2HCl3, commonly used as an industrial metal-degreasing solvent. It is a clear, colourless, non-flammable, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like pleasant mild smell and sweet taste.
(TCE) and other halocarbon solvent
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas ...
s that had been widely used for industrial cleaning . More recently perfluorooctanoic acid
Perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA; conjugate acid, conjugate base perfluorooctanoate; also known colloquially as C8, from its chemical formula C8HF15O2) is a perfluorinated carboxylic acid produced and used worldwide as an industrial surfactant in ch ...
(PFOA), a precursor in the most common manufacturing process for Teflon and also used to make coatings for fabrics and food packaging
Food packaging is a packaging system specifically designed for food and represents one of the most important aspects among the processes involved in the food industry, as it provides protection from chemical, biological and physical alterations ...
, became a health and environmental concern starting in 2006 , suggesting that halocarbons, though thought to be among the most inert, may also present hazards.
Halocarbons, including those that might not be hazards in themselves, can present waste disposal
Waste management or waste disposal includes the processes and actions required to manage waste from its inception to its final Waste disposal, disposal. This includes the Waste collection, collection, transport, Sewage treatment, treatm ...
issues. Because they do not readily degrade in natural environments, halocarbons tend to accumulate. Incineration
Incineration is a waste treatment process that involves the combustion of substances contained in waste materials. Industrial plants for waste incineration are commonly referred to as waste-to-energy facilities. Incineration and other high ...
and accidental fires can create corrosive
Corrosion is a natural process that converts a refined metal into a more chemically stable oxide. It is the gradual deterioration of materials (usually a metal) by chemical or electrochemical reaction with their environment. Corrosion engine ...
byproducts such as hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid or spirits of salt, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungency, pungent smell. It is classified as a acid strength, strong acid. It is ...
and hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colorless, acidic and highly corrosive. A common concentration is 49% (48–52%) but there are also stronger solutions (e.g. 70%) and pure HF has a boiling p ...
, and poison
A poison is any chemical substance that is harmful or lethal to living organisms. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figurati ...
s like halogenated dioxins and furan
Furan is a Heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic organic compound, consisting of a five-membered aromatic Ring (chemistry), ring with four carbon Atom, atoms and one oxygen atom. Chemical compounds containing such rings are also referred to as f ...
s. Species of Desulfitobacterium are being investigated for their potential in the bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi in mycoremediation, and plants in phytoremediation), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, wate ...
of halogenic organic compounds.
See also
*Halogenation
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction which introduces one or more halogens into a chemical compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polymers, drug ...
* Carbon–fluorine bond
The carbon–fluorine bond is a polar covalent bond between carbon and fluorine that is a component of all organofluorine compounds. It is one of the strongest single bonds in chemistry (after the B–F single bond, Si–F single bond, and H–F ...
* Fluorinated gases
* List of refrigerants
This is a list of refrigerants, sorted by their ASHRAE-designated numbers, commonly known as R numbers. Many modern refrigerants are human-made halogenated gases, especially fluorinated gases and chlorinated gases, that are frequently referred ...
Notes
References
*, settled between the parties, reviewed in * * * * * *, cited iChemical Industry Archives, Anniston Case
, by Environmental Working Group, Washington, DC, 2002 * * * * *
External links
* {{Authority control