|
Haloalkene
In organic chemistry, a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula CH2=CHX (X = halide). The term vinyl group, vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. For this reason, alkenyl halides with the formula RCH=CHX are sometimes called vinyl halides. From the perspective of applications, the dominant member of this class of compounds is vinyl chloride, which is produced on the scale of millions of tons per year as a precursor to polyvinyl chloride. Polyvinyl fluoride is another commercial product. Related compounds include 1,1-Dichloroethene, vinylidene chloride and vinylidene fluoride. Synthesis Vinyl chloride is produced by dehydrochlorination of 1,2-dichloroethane. Due to their high utility, many approaches to vinyl halides have been developed, such as: * reactions of vinyl organometallic species with halogens * Takai olefination * Stork-Zhao olefination with, e.g., (Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane - a modification of the Wittig reaction * Olefin metathesis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane
(Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane is the organophosphorus compound with the formula Ph3P=CHCl (Ph = phenyl). It is a white solid but is usually generated and used in situ as a reagent in organic synthesis. It is structurally and chemically related to methylenetriphenylphosphorane. The reagent is prepared from the chloromethylphosphonium salt h3PCH2Cll by treatment with strong base. The phosphonium compound is generated by treatment of triphenylphosphine with chloroiodomethane. (Chloromethylene)triphenylphosphorane converts aldehydes to vinyl chlorides: :RCHO + Ph3P=CHCl → RCH=CHCl + Ph3PO These vinyl chlorides undergo dehydrochlorination to give alkyne \ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and n ...s: :RCH=CHCl + NaN(SiMe3)2 → RC≡CH + NaCl + HN( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heck Reaction
The Heck reaction (also called the Mizoroki–Heck reaction) is the chemical reaction of an unsaturated halide (or triflate) with an alkene in the presence of a base and a palladium catalyst to form a substituted alkene. It is named after Tsutomu Mizoroki and Richard F. Heck. Heck was awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, which he shared with Ei-ichi Negishi and Akira Suzuki, for the discovery and development of this reaction. This reaction was the first example of a carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction that followed a Pd(0)/Pd(II) catalytic cycle, the same catalytic cycle that is seen in other Pd(0)-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions. The Heck reaction is a way to substitute alkenes. History The original reaction by Tsutomu Mizoroki (1971) describes the coupling between iodobenzene and styrene in methanol to form stilbene at 120 °C ( autoclave) with potassium acetate base and palladium chloride catalysis. This work was an extension of earlier work by Fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stille Reaction
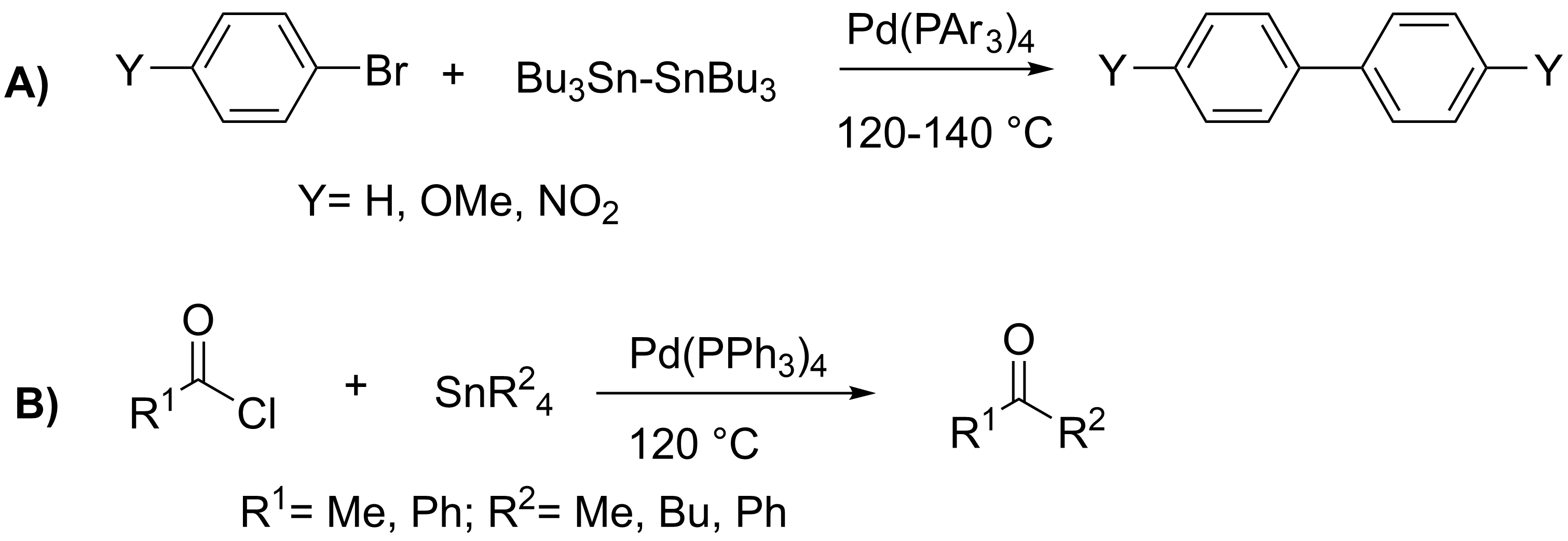
The Stille reaction is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis. The reaction involves the coupling of two organic groups, one of which is carried as an organotin chemistry, organotin compound (also known as organostannanes). A variety of organic electrophiles provide the other coupling partner. The Stille reaction is one of many Cross-coupling reaction, palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions.Hartwig, J. F. ''Organotransition Metal Chemistry, from Bonding to Catalysis''; University Science Books: New York, 2010. Stille, J. K. ''Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.'' 1986, ''25'', 508–524.ReviewFarina, V.; Krishnamurthy, V.; Scott, W. J. ''Org. React.'' 1998, ''50'', 1–652.Review : + \ \ce \ \overbrace^ + \!-\! :*\!,\ : Allyl, alkenyl, aryl, benzyl, acyl :*: halides (Cl, Br, I), pseudohalides (OTf, OPO(OR)2), OAc The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including vinyl group, vinyl, and aryl groups. These organostannanes are also stable to bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suzuki Reaction
The Suzuki reaction or Suzuki coupling is an organic reaction that uses a palladium complex catalyst to cross-couple a boronic acid to an organohalide. It was first published in 1979 by Akira Suzuki, and he shared the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Richard F. Heck and Ei-ichi Negishi for their contribution to the discovery and development of noble metal catalysis in organic synthesis. This reaction is sometimes telescoped with the related Miyaura borylation; the combination is the Suzuki–Miyaura reaction. It is widely used to synthesize poly olefins, styrenes, and substituted biphenyls. The general scheme for the Suzuki reaction is shown below, where a carbon–carbon single bond is formed by coupling a halide (R1-X) with an organoboron species (R2-BY2) using a palladium catalyst and a base. The organoboron species is usually synthesized by hydroboration or carboboration, allowing for rapid generation of molecular complexity. Several reviews have been publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-coupling Reaction
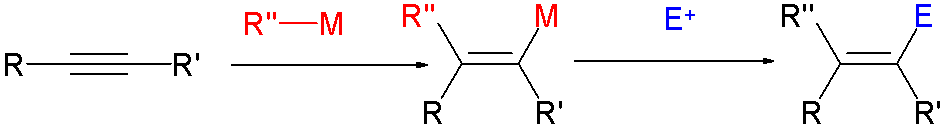
In organic chemistry, a cross-coupling reaction is a reaction where two different fragments are joined. Cross-couplings are a subset of the more general coupling reactions. Often cross-coupling reactions require metal catalysts. One important reaction type is this: : (R, R' = organic fragments, usually aryl; M = main group center such as Li or MgX; X = halide) These reactions are used to form carbon–carbon bonds but also carbon-heteroatom bonds. Cross-coupling reaction are a subset of coupling reactions. Richard F. Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki were awarded the 2010 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing palladium-catalyzed coupling reactions. Mechanism Many mechanisms exist reflecting the myriad types of cross-couplings, including those that do not require metal catalysts. Often, however, cross-coupling refers to a metal-catalyzed reaction of a nucleophilic partner with an electrophilic partner. In such cases, the mechanism generally involves reduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organolithium Reagent
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom to the substrates in synthetic steps, through nucleophilic addition or simple deprotonation. Organolithium reagents are used in industry as an initiator for anionic polymerization, which leads to the production of various elastomers. They have also been applied in asymmetric synthesis in the pharmaceutical industry. Due to the large difference in electronegativity between the carbon atom and the lithium atom, the C−Li bond is highly ionic. Owing to the polar nature of the C−Li bond, organolithium reagents are good nucleophiles and strong bases. For laboratory organic synthesis, many organolithium reagents are commercially available in solution form. These reagents are highly reactive, and are sometimes pyrophoric. History and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reaction
The Grignard reaction () is an organometallic chemical reaction in which, according to the classical definition, carbon alkyl, allyl, vinyl, or aryl magnesium halides (Grignard reagent) are added to the carbonyl groups of either an aldehyde or ketone under anhydrous conditions. This reaction is important for the formation of carbon–carbon bonds. History and definitions Grignard reactions and reagents were discovered by and are named after the French chemist François Auguste Victor Grignard (University of Nancy, France), who described them in 1900. He was awarded the 1912 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for this work. The reaction of an organic halide with magnesium is ''not'' a Grignard reaction, but provides a Grignard reagent.IUPAC. Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book"). Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford (1997). . . Classically, the Grignard reaction refers to the reaction between a ketone or aldeh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olefin Metathesis
In organic chemistry, Olefin Metathesis or Alkene Metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the Bond cleavage, scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active Catalysis, catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Catalysts The reaction requires catalysis, metal catalysts. Most commercially important processes employ heterogeneous catalysis, heterogeneous catalysts. The heterogeneous catalysts are often prepared by in-situ activation of a metal halide (MClx) using organoaluminium or organotin compounds, e.g. combining MClx–EtAlCl2. A typical catalyst support is alumina. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wittig Reaction
The Wittig reaction or Wittig olefination is a chemical reaction of an aldehyde or ketone with a triphenyl phosphonium ylide called a Wittig reagent. Wittig reactions are most commonly used to convert aldehydes and ketones to alkenes. Most often, the Wittig reaction is used to introduce a methylene group using methylenetriphenylphosphorane (Ph3P=CH2). Using this reagent, even a sterically hindered ketone such as camphor can be converted to its methylene derivative. Reaction mechanism Mechanistic studies have focused on unstabilized ylides, because the intermediates can be followed by NMR spectroscopy. The existence and interconversion of the betaine (3a and 3b) is subject of ongoing research. For lithium-free Wittig reactions, studies support a concerted formation of the oxaphosphetane without intervention of a betaine. In particular, phosphonium ylides 1 react with carbonyl compounds 2 via a +2cycloaddition that is sometimes described as having π2s+π2a">sub>π2s+π2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |