Growth Hormones on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a
 Secretion of growth hormone (GH) in the pituitary is regulated by the neurosecretory nuclei of the
Secretion of growth hormone (GH) in the pituitary is regulated by the neurosecretory nuclei of the
 Effects of growth hormone on the tissues of the body can generally be described as
Effects of growth hormone on the tissues of the body can generally be described as
DEA: Genotropin
Quote: "The illicit distribution of hGH occurs as the result of physicians illegally prescribing it for off-label uses, and for the treatment of FDA-approved medical conditions without examination and supervision" Claims for GH as an anti-aging treatment date back to 1990 when the ''New England Journal of Medicine'' published a study wherein GH was used to treat 12 men over 60. At the conclusion of the study, all the men showed statistically significant increases in lean body mass and bone mineral density, while the control group did not. The authors of the study noted that these improvements were the opposite of the changes that would normally occur over a 10- to 20-year aging period. Despite the fact the authors at no time claimed that GH had reversed the aging process itself, their results were misinterpreted as indicating that GH is an effective anti-aging agent. This has led to organizations such as the controversial American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine promoting the use of this hormone as an "anti-aging agent". A Stanford University School of Medicine meta-analysis of clinical studies on the subject published in early 2007 showed that the application of GH on healthy elderly patients increased muscle by about 2 kg and decreased body fat by the same amount. However, these were the only positive effects from taking GH. No other critical factors were affected, such as bone density, cholesterol levels, lipid measurements, maximal oxygen consumption, or any other factor that would indicate increased fitness. Researchers also did not discover any gain in muscle strength, which led them to believe that GH merely let the body store more water in the muscles rather than increase muscle growth. This would explain the increase in lean body mass. GH has also been used experimentally to treat multiple sclerosis, to enhance weight loss in obesity, as well as in fibromyalgia, heart failure, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and burns. GH has also been used experimentally in patients with short bowel syndrome to lessen the requirement for intravenous total parenteral nutrition. In 1990, the US Congress passed an omnibus crime bill, the Crime Control Act of 1990, that amended the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, that classified anabolic steroids as controlled substances and added a new section that stated that a person who "knowingly distributes, or possesses with intent to distribute, human growth hormone for any use in humans other than the treatment of a disease or other recognized medical condition, where such use has been authorized by the Secretary of Health and Human Services" has committed a felony. The Drug Enforcement Administration of the US Department of Justice considers off-label prescribing of HGH to be illegal, and to be a key path for illicit distribution of HGH. This section has also been interpreted by some doctors, most notably the authors of a commentary article published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2005, as meaning that ''prescribing'' HGH off-label may be considered illegal. And some articles in the popular press, such as those criticizing the pharmaceutical industry for marketing drugs for off-label use (with concern of ethics violations) have made strong statements about whether doctors can prescribe HGH off-label: "Unlike other prescription drugs, HGH may be prescribed only for specific uses. U.S. sales are limited by law to treat a rare growth defect in children and a handful of uncommon conditions like short bowel syndrome or Prader-Willi syndrome, a congenital disease that causes reduced muscle tone and a lack of hormones in sex glands." At the same time, anti-aging clinics where doctors prescribe, administer, and sell HGH to people are big business. In a 2012 article in ''Vanity Fair (magazine), Vanity Fair'', when asked how HGH prescriptions far exceed the number of adult patients estimated to have HGH-deficiency, Dragos Roman, who leads a team at the FDA that reviews drugs in endocrinology, said "The F.D.A. doesn't regulate off-label uses of H.G.H. Sometimes it's used appropriately. Sometimes it's not."
peptide hormone
Peptide hormones are hormones composed of peptide molecules. These hormones influence the endocrine system of animals, including humans. Most hormones are classified as either amino-acid-based hormones (amines, peptides, or proteins) or steroid h ...
that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development Human development may refer to:
* Development of the human body
** This includes physical developments such as growth, and also development of the brain
* Developmental psychology
* Development theory
* Human development (economics)
* Human Develo ...
. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in tertiary structure, molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has Anabolism, anabolic effects in adults. In the ...
(IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and free fatty acid
In chemistry, in particular in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, f ...
s. It is a type of mitogen
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen.
The cell cycle
Mitogens a ...
which is specific only to the receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
s on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
, single-chain polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty ...
that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that t ...
gland.
A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug
A prescription drug (also prescription medication, prescription medicine or prescription-only medication) is a pharmaceutical drug that is permitted to be dispensed only to those with a medical prescription. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs c ...
to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD), or hyposomatotropism, is a medical condition resulting from not enough growth hormone (GH). Generally the most noticeable symptom is that an individual attains a short height. Newborns may also present low blood ...
. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care providers are prescribing growth hormone in the elderly to increase vitality
Vitality (, , ) is the capacity to live, grow, or develop. Vitality is also the characteristic that distinguishes life, living from non-living things. To experience vitality is regarded as a basic psychological drive and, in philosophy, a comp ...
. While legal, the efficacy and safety of this use for HGH has not been tested in a clinical trial. Many of the functions of HGH remain unknown.
In its role as an anabolic
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catab ...
agent, HGH has been used by competitors in sports since at least 1982 and has been banned by the IOC and NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates College athletics in the United States, student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, and Simon Fraser University, 1 in Canada. ...
. Traditional urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and many other animals. In placental mammals, urine flows from the Kidney (vertebrates), kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and exits the urethra through the penile meatus (mal ...
analysis does not detect doping with HGH, so the ban was not enforced until the early 2000s, when blood test
A blood test is a medical laboratory, laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a hypodermic needle, or via fingerprick. Multiple tests for specific blood components, such as a glucose ...
s that could distinguish between natural and artificial HGH were starting to be developed. Blood tests conducted by WADA at the 2004 Olympic Games in Athens, Greece
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, targeted primarily HGH. Use of the drug for performance enhancement is not currently approved by the FDA
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
.
GH has been studied for use in raising livestock more efficiently in industrial agriculture
Industrial agriculture is a form of modern farming that refers to the industrialized production of crops and animals and animal products like eggs or milk. The methods of industrial agriculture include innovation in agricultural machinery and ...
and several efforts have been made to obtain governmental approval to use GH in livestock production. These uses have been controversial. In the United States, the only FDA-approved use of GH for livestock is the use of a cow-specific form of GH called bovine somatotropin
Livestock
Dairy industry
Bovine somatotropin or bovine somatotrophin (abbreviated bST and BST), or bovine growth hormone (BGH), is a peptide hormone produced by cows' pituitary glands. Like other hormones, it is produced in small quantities ...
for increasing milk production in dairy cows. Retailers are permitted to label containers of milk as produced with or without bovine somatotropin.
Nomenclature
The names ''somatotropin'' (''STH'') or ''somatotropic hormone'' refer to thegrowth hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in ...
produced naturally in animals and extracted from carcasses. Hormone extracted from human cadavers is abbreviated ''hGH''. The main growth hormone produced by recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules are DNA molecules formed by laboratory methods of genetic recombination (such as molecular cloning) that bring together genetic material from multiple sources, creating sequences that would not otherwise be fo ...
technology has the approved generic name ( INN) ''somatropin'' and the brand name ''Humatrope'' and is properly abbreviated rhGH in the scientific literature. Since its introduction in 1992, Humatrope has been a banned sports doping agent and in this context is referred to as HGH.
The term ''growth hormone'' has been incorrectly applied to refer to anabolic
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catab ...
sex hormones
Sex hormones, also known as sex steroids, gonadocorticoids and gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate steroid hormone receptors. The sex hormones include the androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Their effects a ...
in the European beef hormone controversy, which initially restricts the use of estradiol
Estradiol (E2), also called oestrogen, oestradiol, is an estrogen steroid hormone and the major female sex hormone. It is involved in the regulation of female reproductive cycles such as estrous and menstrual cycles. Estradiol is responsible ...
, progesterone
Progesterone (; P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the ma ...
, testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
, zeranol, melengestrol acetate and trenbolone acetate
Trenbolone acetate, sold under brand names such as Finajet and Finaplix among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication used in veterinary medicine, specifically to increase the profitability of livestock by promoting muscle g ...
.
Biology
Gene
Genes for human growth hormone, known as growth hormone 1 (somatotropin; pituitary growth hormone) and growth hormone 2 (placental growth hormone; growth hormone variant), are localized in the q22-24 region of chromosome 17 and are closely related to human chorionic somatomammotropin (also known as placental lactogen) genes. GH, human chorionic somatomammotropin, andprolactin
Prolactin (PRL), also known as lactotropin and mammotropin, is a protein best known for its role in enabling mammals to produce milk. It is influential in over 300 separate processes in various vertebrates, including humans. Prolactin is secr ...
belong to a group of homologous hormones with growth-promoting and lactogenic activity.
Structure
The major isoform of the human growth hormone is a protein of 191amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s and a molecular weight of 22,124 daltons. The structure includes four helices necessary for functional interaction with the GH receptor. It appears that, in structure, GH is evolutionarily homologous to prolactin and chorionic somatomammotropin. Despite marked structural similarities between growth hormone from different species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, only human and Old World monkey
Old World monkeys are primates in the family Cercopithecidae (). Twenty-four genera and 138 species are recognized, making it the largest primate family. Old World monkey genera include baboons (genus '' Papio''), red colobus (genus '' Piliocolob ...
growth hormones have significant effects on the human growth hormone receptor.
Several molecular
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, ...
isoforms of GH exist in the pituitary gland and are released to blood. In particular, a variant of approximately 20 kDa originated by an alternative splicing is present in a rather constant 1:9 ratio, while recently an additional variant of ~ 23-24 kDa has also been reported in post-exercise states at higher proportions. This variant has not been identified, but it has been suggested to coincide with a 22 kDa glycosylated variant of 23 kDa identified in the pituitary gland. Furthermore, these variants circulate partially bound to a protein ( growth hormone-binding protein, GHBP), which is the truncated part of the growth hormone receptor, and an acid-labile subunit (ALS).
Regulation
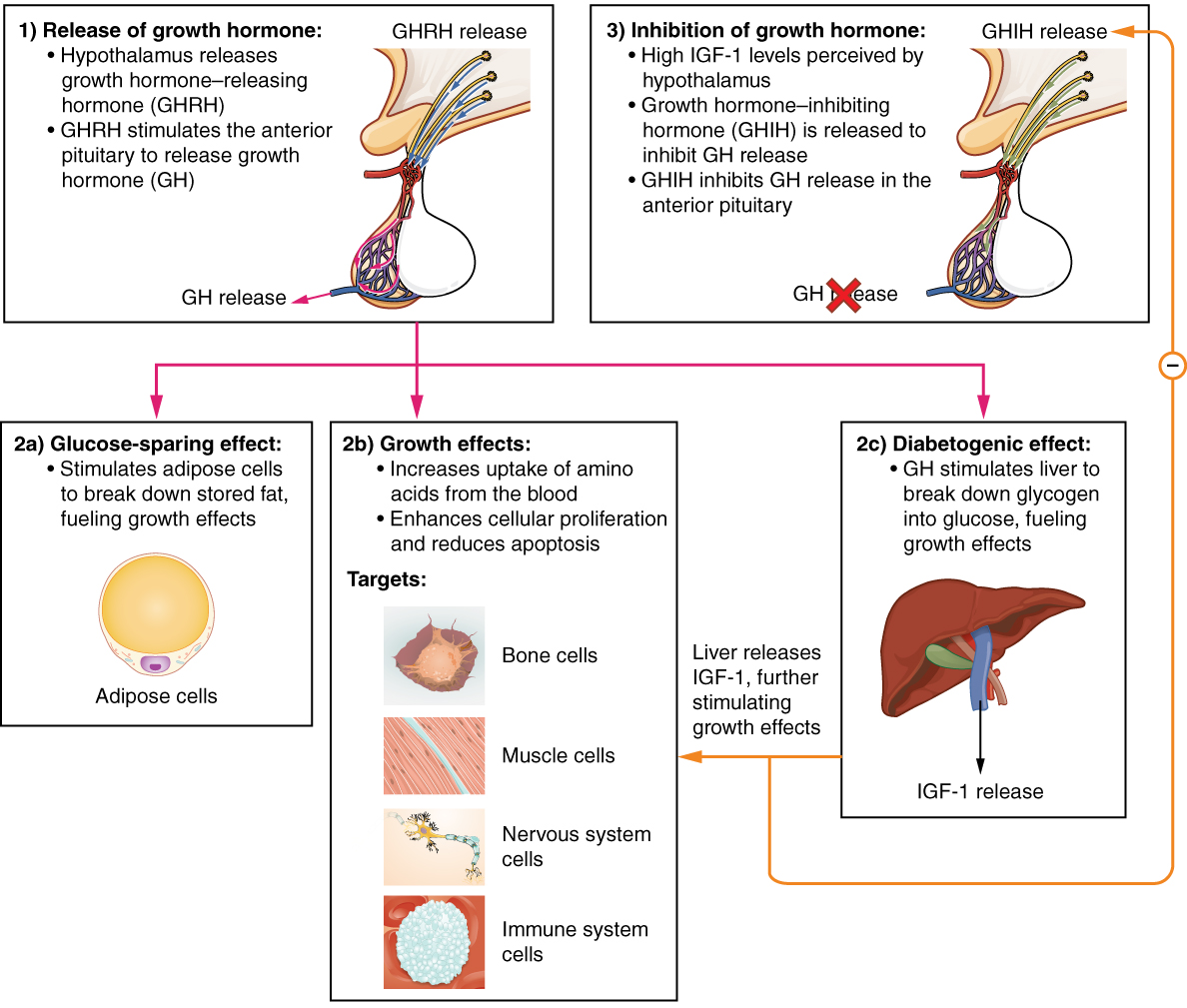
 Secretion of growth hormone (GH) in the pituitary is regulated by the neurosecretory nuclei of the
Secretion of growth hormone (GH) in the pituitary is regulated by the neurosecretory nuclei of the hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
.
These cells release the peptides growth hormone-releasing hormone
Growth may refer to:
Biology
* Auxology, the study of all aspects of human physical growth
* Bacterial growth
*Cell growth
*Growth hormone, a peptide hormone that stimulates growth
*Human development (biology)
*Plant growth
*Secondary growth, gro ...
(GHRH or ''somatocrinin'') and growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH or ''somatostatin'') into the hypophyseal portal venous blood surrounding the pituitary.
GH release in the pituitary is primarily determined by the balance of these two peptides, which in turn is affected by many physiological stimulators (e.g., exercise, nutrition, sleep) and inhibitors (e.g., free fatty acids) of GH secretion.
Somatotropic cells in the anterior pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that t ...
gland then synthesize and secrete GH in a pulsatile manner, in response to these stimuli by the hypothalamus.
The largest and most predictable of these GH peaks occurs about an hour after onset of sleep with plasma levels of 13 to 72 ng/mL.
Maximal secretion of GH may occur within minutes of the onset of slow-wave (SW) sleep (stage III or IV). Otherwise there is wide variation between days and individuals. Nearly fifty percent of GH secretion occurs during the third and fourth NREM sleep stages.
Surges of secretion during the day occur at 3- to 5-hour intervals. The plasma concentration of GH during these peaks may range from 5 to even 45 ng/mL.
Between the peaks, basal GH levels are low, usually less than 5 ng/mL for most of the day and night. Additional analysis of the pulsatile profile of GH described in all cases less than 1 ng/ml for basal levels while maximum peaks were situated around 10-20 ng/mL.
A number of factors are known to affect GH secretion, such as age, sex, diet, exercise, stress, and other hormones. Young adolescents secrete GH at the rate of about 700 μg/day, while healthy adults secrete GH at the rate of about 400 μg/day. Sleep deprivation generally suppresses GH release, particularly after early adulthood.
Stimulators of growth hormone (GH) secretion include:
* Peptide hormones
** GHRH (''somatocrinin'') through binding to the growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor ( GHRHR)
** Ghrelin
Ghrelin (; or lenomorelin, INN) is a hormone primarily produced by enteroendocrine cells of the gastrointestinal tract, especially the stomach, and is often called a "hunger hormone" because it increases the drive to eat. Blood levels of ghrel ...
through binding to growth hormone secretagogue receptors ( GHSR)
* Sex hormones
** Increased androgen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
secretion during puberty (in males from testes and in females from adrenal cortex)
** Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and DHEA
** Estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
* Clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (e.g., alcohol, opioids, or nic ...
, moxonidine and L-DOPA
-DOPA, also known as -3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and used medically as levodopa, is made and used as part of the normal biology of some plants and animals, including humans. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize -DO ...
by stimulating GHRH release
* α4β2 nicotinic agonists, including nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
, which also act synergistically with clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2A-adrenergic receptor agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), drug withdrawal (e.g., alcohol, opioids, or nic ...
or moxonidine.
* Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia (American English), also spelled hypoglycaemia or hypoglycæmia (British English), sometimes called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's tria ...
, arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidinium, guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) a ...
, pramipexole, ornitine, lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. Lysine contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form when the lysine is dissolved in water at physiological pH), an α-carboxylic acid group ( ...
, tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromat ...
, γ-Aminobutyric acid
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid, γ-aminobutyric acid) is the chief inhibitory neurotransmitter in the developmentally mature mammalian central nervous system. Its principal role is reducing neuronal excitability throughout the nervous system.
GA ...
and propranolol
Propranolol is a medication of the beta blocker class. It is used to treat hypertension, high blood pressure, some types of cardiac dysrhythmia, irregular heart rate, thyrotoxicosis, capillary hemangiomas, akathisia, performance anxiety, and ...
by inhibiting somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by #Nomenclature, several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G ...
release
* Deep sleep
* Glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises the concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a Glucagon (medic ...
* Sodium oxybate
Sodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Na (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope ...
or γ-Hydroxybutyric acid
γ-Hydroxybutyric acid, also known as ''gamma''-hydroxybutyric acid, GHB, or 4-hydroxybutanoic acid, is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter and a depressant, depressant drug. It is a precursor to GABA, glutamate, and glycine in certain brai ...
* Niacin as nicotinic acid (vitamin B3)
* Fasting
Fasting is the act of refraining from eating, and sometimes drinking. However, from a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (before "breakfast"), or to the metabolic sta ...
* Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
* Vigorous exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
''Inhibitors'' of GH secretion include:
* GHIH (''somatostatin'') from the periventricular nucleus
* circulating concentrations of GH and IGF-1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults. In the 1950s IGF-1 was called " sulfa ...
(negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function (Mathematics), function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is feedback, fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused ...
on the pituitary and hypothalamus
The hypothalamus (: hypothalami; ) is a small part of the vertebrate brain that contains a number of nucleus (neuroanatomy), nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrin ...
)
* Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition where unusually high amount of glucose is present in blood. It is defined as blood glucose level exceeding 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL) after fasting for 8 hours or 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating.
Blood gluc ...
* Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebra ...
s
* Dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone primarily involved in the growth and repair of the prostate and the penis, as well as the production o ...
* Phenothiazines
In addition to control by endogenous and stimulus processes, a number of foreign compounds (xenobiotic
A xenobiotic is a chemical substance found within an organism that is not naturally produced or expected to be present within the organism. It can also cover substances that are present in much higher concentrations than are usual. Natural compo ...
s such as drugs and endocrine disruptor
Endocrine disruptors, sometimes also referred to as hormonally active agents, endocrine disrupting chemicals, or endocrine disrupting compounds are chemicals that can interfere with endocrine (or hormonal) systems. These disruptions can cause ...
s) are known to influence GH secretion and function.
Function
anabolic
Anabolism () is the set of metabolic pathways that construct macromolecules like DNA or RNA from smaller units. These reactions require energy, known also as an endergonic process. Anabolism is the building-up aspect of metabolism, whereas catab ...
(building up). Like most other peptide hormones, GH acts by interacting with a specific receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any neurite structure that, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and respond ...
on the surface of cells.
Increased height during childhood is the most widely known effect of GH. Height appears to be stimulated by at least two mechanisms:
# Because polypeptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty ...
hormones are not fat-soluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubi ...
, they cannot penetrate cell membranes. Thus, GH exerts some of its effects by binding to receptors on target cells, where it activates the MAPK/ERK pathway
The MAPK/ERK pathway (also known as the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK pathway) is a chain of proteins in the cell (biology), cell that communicates a signal from a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor on the surface of the cell to the DNA in the nucleus of the cel ...
. Through this mechanism GH directly stimulates division and multiplication of chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, ) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word '' chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immatu ...
s of cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
.
# GH also stimulates, through the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, the production of insulin-like growth factor 1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in tertiary structure, molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has Anabolism, anabolic effects in adults. In the ...
(IGF-1, formerly known as somatomedin C), a hormone homologous to proinsulin. The liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
is a major target organ of GH for this process and is the principal site of IGF-1 production. IGF-1 has growth-stimulating effects on a wide variety of tissues. Additional IGF-1 is generated within target tissues, making it what appears to be both an endocrine
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant organs. In vertebrates, the hypotha ...
and an autocrine
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with ...
/paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of ...
hormone. IGF-1 also has stimulatory effects on osteoblast
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for " bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts fu ...
and chondrocyte
Chondrocytes (, ) are the only cells found in healthy cartilage. They produce and maintain the cartilaginous matrix, which consists mainly of collagen and proteoglycans. Although the word '' chondroblast'' is commonly used to describe an immatu ...
activity to promote bone growth.
In addition to increasing height in children and adolescents, growth hormone has many other effects on the body:
* Increases calcium
Calcium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to it ...
retention, and strengthens and increases the mineralization of bone
* Increases muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
mass through sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal striated muscle, Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular ...
hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertro ...
* Promotes lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolysis, hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in Adipose tissue, fat adip ...
* Increases protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis, or protein synthesis, is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critica ...
* Stimulates the growth of all internal organs excluding the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
* Plays a role in homeostasis
* Reduces liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
uptake of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
* Promotes gluconeogenesis in the liver
* Contributes to the maintenance and function of pancreatic islets
* Stimulates the immune system
* Increases deiodination of T4 to T3
* Induces insulin resistance
Biochemistry
GH has a short biological half-life of about 10 to 20 minutes.Clinical significance
Excess
The most common disease of GH excess is a pituitary tumor composed of somatotroph cells of the anterior pituitary. These somatotroph adenomas are benign and grow slowly, gradually producing more and more GH. For years, the principal clinical problems are those of GH excess. Eventually, the adenoma may become large enough to cause headaches, impair vision by pressure on the optic nerves, or cause deficiency of other pituitary hormones by displacement. Prolonged GH excess thickens the bones of the jaw, fingers and toes, resulting in heaviness of the jaw and increased size of digits, referred to as acromegaly. Accompanying problems can include sweating, pressure on nerves (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome), muscle weakness, excess sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), insulin resistance or even a rare form of Diabetes mellitus type 2, type 2 diabetes, and reduced sexual function. GH-secreting tumors are typically recognized in the fifth decade of life. It is extremely rare for such a tumor to occur in childhood, but, when it does, the excessive GH can cause excessive growth, traditionally referred to as gigantism, pituitary gigantism. Surgical removal is the usual treatment for GH-producing tumors. In some circumstances, focused radiation or a GH antagonist such as pegvisomant may be employed to shrink the tumor or block function. Other drugs like octreotide (somatostatin agonist) and bromocriptine (dopamine agonist) can be used to block GH secretion because both somatostatin and dopamine negatively inhibit GHRH-mediated GH release from the anterior pituitary.Deficiency
The effects of growth hormone deficiency, growth hormone (GH) deficiency vary depending on the age at which they occur. Alterations in somatomedin can result in growth hormone deficiency with two known mechanisms; failure of tissues to respond to somatomedin, or failure of theliver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of var ...
to produce somatomedin. Major manifestations of GH deficiency in children are growth failure, the development of a short stature, and delayed sexual maturity. In adults, somatomedin alteration contributes to increased osteoclast activity, resulting in weaker bones that are more prone to pathologic fracture and osteoporosis. However, deficiency is rare in adults, with the most common cause being a pituitary adenoma. Other adult causes include a continuation of a childhood problem, other structural lesions or Injury, trauma, and very rarely idiopathic GHD.
Adults with GHD "tend to have a relative increase in fat mass and a relative decrease in muscle mass and, in many instances, decreased energy and quality of life".
Diagnosis of GH deficiency involves a multiple-step diagnostic process, usually culminating in GH stimulation tests to see if the patient's pituitary gland will release a pulse of GH when provoked by various stimuli.
Psychological effects
Quality of life
Several studies, primarily involving patients with Growth hormone deficiency, GH deficiency, have suggested a crucial role of GH in both mental and emotional well-being and maintaining a high energy level. Adults with GH deficiency often have higher rates of Depression (mood), depression than those without. While #Replacement therapy, GH replacement therapy has been proposed to treat depression as a result of GH deficiency, the long-term effects of such therapy are unknown.Cognitive function
GH has also been studied in the context of cognitive function, including learning and memory. GH in humans appears to improve cognitive function and may be useful in the treatment of patients with cognitive impairment that is a result of GH deficiency.Medical uses
Replacement therapy
GH is used as replacement therapy in adults with GH deficiency of either childhood-onset or adult-onset (usually as a result of an acquired pituitary tumor). In these patients, benefits have variably included reduced fat mass, increased lean mass, increased bone density, improved lipid profile, reduced cardiovascular risk factors, and improved psychosocial well-being. Long acting growth hormone (LAGH) analogues are now available for treating growth hormone deficiency both in children and adults. These are once weekly injections as compared to conventional growth hormone which has to be taken as daily injections. LAGH injection 4 times a month has been found to be as safe and effective as daily growth hormone injections.Other approved uses
GH can be used to treat conditions that produce short stature but are not related to deficiencies in GH. However, results are not as dramatic when compared to short stature that is solely attributable to deficiency of GH. Examples of other causes of shortness often treated with GH are Turner syndrome, Growth failure secondary to chronic kidney disease in children, Prader–Willi syndrome, intrauterine growth restriction, and severe idiopathic short stature. Higher ("pharmacologic") doses are required to produce significant acceleration of growth in these conditions, producing blood levels well above normal ("physiologic"). One version of rHGH has also been FDA approved for maintaining muscle mass in wasting due to AIDS.Off-label use
off-label use, Off-label prescription of HGH is controversial and may be illegal.DEA, US Department of JusticeDEA: Genotropin
Quote: "The illicit distribution of hGH occurs as the result of physicians illegally prescribing it for off-label uses, and for the treatment of FDA-approved medical conditions without examination and supervision" Claims for GH as an anti-aging treatment date back to 1990 when the ''New England Journal of Medicine'' published a study wherein GH was used to treat 12 men over 60. At the conclusion of the study, all the men showed statistically significant increases in lean body mass and bone mineral density, while the control group did not. The authors of the study noted that these improvements were the opposite of the changes that would normally occur over a 10- to 20-year aging period. Despite the fact the authors at no time claimed that GH had reversed the aging process itself, their results were misinterpreted as indicating that GH is an effective anti-aging agent. This has led to organizations such as the controversial American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine promoting the use of this hormone as an "anti-aging agent". A Stanford University School of Medicine meta-analysis of clinical studies on the subject published in early 2007 showed that the application of GH on healthy elderly patients increased muscle by about 2 kg and decreased body fat by the same amount. However, these were the only positive effects from taking GH. No other critical factors were affected, such as bone density, cholesterol levels, lipid measurements, maximal oxygen consumption, or any other factor that would indicate increased fitness. Researchers also did not discover any gain in muscle strength, which led them to believe that GH merely let the body store more water in the muscles rather than increase muscle growth. This would explain the increase in lean body mass. GH has also been used experimentally to treat multiple sclerosis, to enhance weight loss in obesity, as well as in fibromyalgia, heart failure, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis, and burns. GH has also been used experimentally in patients with short bowel syndrome to lessen the requirement for intravenous total parenteral nutrition. In 1990, the US Congress passed an omnibus crime bill, the Crime Control Act of 1990, that amended the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, that classified anabolic steroids as controlled substances and added a new section that stated that a person who "knowingly distributes, or possesses with intent to distribute, human growth hormone for any use in humans other than the treatment of a disease or other recognized medical condition, where such use has been authorized by the Secretary of Health and Human Services" has committed a felony. The Drug Enforcement Administration of the US Department of Justice considers off-label prescribing of HGH to be illegal, and to be a key path for illicit distribution of HGH. This section has also been interpreted by some doctors, most notably the authors of a commentary article published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 2005, as meaning that ''prescribing'' HGH off-label may be considered illegal. And some articles in the popular press, such as those criticizing the pharmaceutical industry for marketing drugs for off-label use (with concern of ethics violations) have made strong statements about whether doctors can prescribe HGH off-label: "Unlike other prescription drugs, HGH may be prescribed only for specific uses. U.S. sales are limited by law to treat a rare growth defect in children and a handful of uncommon conditions like short bowel syndrome or Prader-Willi syndrome, a congenital disease that causes reduced muscle tone and a lack of hormones in sex glands." At the same time, anti-aging clinics where doctors prescribe, administer, and sell HGH to people are big business. In a 2012 article in ''Vanity Fair (magazine), Vanity Fair'', when asked how HGH prescriptions far exceed the number of adult patients estimated to have HGH-deficiency, Dragos Roman, who leads a team at the FDA that reviews drugs in endocrinology, said "The F.D.A. doesn't regulate off-label uses of H.G.H. Sometimes it's used appropriately. Sometimes it's not."
Side effects
Injection site reactions are common. More rarely, patients can experience joint swelling, joint pain, carpal tunnel syndrome, and an increased risk of diabetes. In some cases, the patient can produce an immune response against GH. GH may also be a risk factor for Hodgkin's lymphoma. One survey of adults that had been treated with replacement cadaver GH (which has not been used anywhere in the world since 1985) during childhood showed a mildly increased incidence of colon cancer and prostate cancer, but linkage with the GH treatment was not established.Performance enhancement
The first description of the use of GH as a doping agent was Dan Duchaine's "Underground Steroid handbook" which emerged from California in 1982; it is not known where and when GH was first used this way. Athletes in many sports have used human growth hormone in order to attempt to enhance their athletic performance. Some recent studies have not been able to support claims that human growth hormone can improve the athletic performance of professional male athletes. Many athletic societies ban the use of GH and will issue sanctions against athletes who are caught using it. However, because GH is a potent endogenous protein, it is very difficult to detect GH doping. In the United States, GH is legally available only by prescription from a medical doctor.Dietary supplements
To capitalize on the idea that GH might be useful to combat aging, companies selling dietary supplements have websites selling products linked to GH in the advertising text, with medical-sounding names described as "HGH Releasers". Typical ingredients include amino acids, minerals, vitamins, and/or herbal extracts, the combination of which are described as causing the body to make more GH with corresponding beneficial effects. In the United States, because these products are marketed as dietary supplements, it is illegal for them to contain GH, which is a drug. Also, under United States law, products sold as dietary supplements cannot have claims that the supplement treats or prevents any disease or condition, and the advertising material must contain a statement that the health claims are not approved by the FDA. The FTC and the FDA do enforce the law when they become aware of violations.Agricultural use
In the United States, it is legal to give a bovine GH to dairy cows to increase milk production, and is legal to use GH in raising cows for beef; see article on Bovine somatotropin, cattle feeding, dairy farming and the beef hormone controversy. The use of GH in poultry farming is illegal in the United States. Similarly, no chicken meat for sale in Australia is administered hormones. Several companies have attempted to have a version of GH for use in pigs (porcine somatotropin) approved by the FDA but all applications have been withdrawn.Drug development history
Genentech pioneered the use of recombinant human growth hormone for human therapy, which was approved by the FDA in 1985. Prior to its production by recombinant DNA technology, growth hormone used to treat deficiencies was extracted from the pituitary glands of cadavers. Attempts to create a wholly synthetic HGH failed. Limited supplies of HGH resulted in the restriction of HGH therapy to the treatment of idiopathic short stature. Very limited clinical studies of growth hormone derived from an Old World monkey, the rhesus macaque, were conducted by John C. Beck and colleagues in Montreal, in the late 1950s. The study published in 1957, which was conducted on "a 13-year-old male with well-documented hypopituitarism secondary to a crainiophyaryngioma," found that: "Human and monkey growth hormone resulted in a significant enhancement of nitrogen storage ... (and) there was a retention of potassium, phosphorus, calcium, and sodium. ... There was a gain in body weight during both periods. ... There was a significant increase in urinary excretion of aldosterone during both periods of administration of growth hormone. This was most marked with the human growth hormone. ... Impairment of the glucose tolerance curve was evident after 10 days of administration of the human growth hormone. No change in glucose tolerance was demonstrable on the fifth day of administration of monkey growth hormone." The other study, published in 1958, was conducted on six people: the same subject as the Science paper; an 18-year-old male with statural and sexual retardation and a skeletal age of between 13 and 14 years; a 15-year-old female with well-documented hypopituitarism secondary to a craniopharyngioma; a 53-year-old female with carcinoma of the breast and widespread skeletal metastases; a 68-year-old female with advanced postmenopausal osteoporosis; and a healthy 24-year-old medical student without any clinical or laboratory evidence of systemic disease. In 1985, unusual cases of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease were found in individuals that had received cadaver-derived HGH ten to fifteen years previously. Based on the assumption that infectious prions causing the disease were transferred along with the cadaver-derived HGH, cadaver-derived HGH was removed from the market. In 1985, biosynthetic human growth hormone replaced pituitary-derived human growth hormone for therapeutic use in the U.S. and elsewhere. As of 2005, recombinant growth hormones available in the United States (and their manufacturers) included Nutropin (Genentech), Humatrope (Eli Lilly and Company, Lilly), Genotropin (Pfizer), Norditropin (Novo Nordisk, Novo), and Saizen (Merck Serono). In 2006, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a version of rHGH called Omnitrope (Sandoz). A sustained-release form of growth hormone, Nutropin Depot (Genentech and Alkermes) was approved by the FDA in 1999, allowing for fewer injections (every 2 or 4 weeks instead of daily); however, the product was discontinued by Genentech/Alkermes in 2004 for financial reasons (Nutropin Depot required significantly more resources to produce than the rest of the Nutropin line In 2023, the FDA approved a different sustained-release form of growth hormone, Sogroya® (somapacitan-beco) (Novo Nordisk, Novo) for both pediatric patients (2.5 years and older) and adult patients, whom have growth failure due to inadequate secretion of endogenous growth hormone (rHGH). Previously, the human growth hormone analog had only been approved for adult patients with growth hormone deficiency (AGHD). ).Analogues
Several growth hormone analogues featuring amino acid substitutions, deletions, and extensions have been developed, resulting in variants with distinct pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. * HGH Fragment 176–191 * AOD9604 * Somatrem * SomapacitanSee also
* Acromegaly * Somatopause * Epigenetic clockReferences
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Growth Hormone Anterior pituitary hormones Anti-aging substances Galactagogues Growth hormones, Hormones of the somatotropic axis Peptide hormones Drugs developed by Pfizer Recombinant proteins World Anti-Doping Agency prohibited substances Stress hormones