|
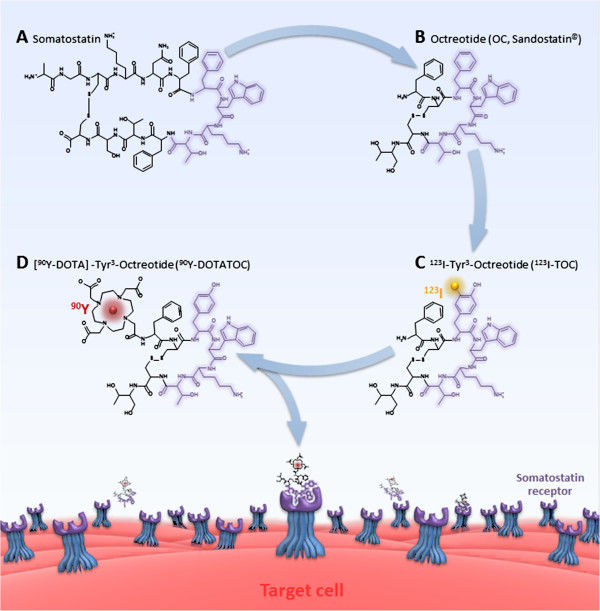
Somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors and inhibition of the release of numerous secondary hormones. Somatostatin inhibits insulin and glucagon secretion. Somatostatin has two active forms produced by the alternative cleavage of a single preproprotein: one consisting of 14 amino acids (shown in infobox to right), the other consisting of 28 amino acids. Among the vertebrates, there exist six different somatostatin genes that have been named ''SS1, SS2, SS3, SS4, SS5'' and ''SS6''. Zebrafish have all six. The six different genes, along with the five different somatostatin receptors, allow somatostatin to possess a large range of functions. Humans have only one somatostatin gene, ''SST''. Nomenclature Synonyms of "somatostatin" include: * growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gi Alpha Subunit
Gi protein alpha subunit is a family of heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunits. This family is also commonly called the Gi/o (Gi /Go ) family or Gi/o/z/t family to include closely related family members. G alpha subunits may be referred to as Gi alpha, Gαi, or Giα. Family members There are four distinct subtypes of alpha subunits in the Gi/o/z/t alpha subunit family that define four families of heterotrimeric G proteins: * Gi proteins: Gi1α, Gi2α, and Gi3α * Go protein: Goα (in mouse there is alternative splicing to generate Go1α and Go2α) * Gz protein: Gzα * Transducins (Gt proteins): Gt1α, Gt2α, Gt3α Giα proteins Gi1α Gi1α is encoded by the gene GNAI1. Gi2α Gi2α is encoded by the gene GNAI2. Gi3α Gi3α is encoded by the gene GNAI3. Goα protein Go1α is encoded by the gene GNAO1. Gzα protein Gzα is encoded by the gene GNAZ. Transducin proteins Gt1α Transducin/Gt1α is encoded by the gene GNAT1. Gt2α Transduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatostatin Receptors
Somatostatin receptors are receptors for the ligand somatostatin, a small neuropeptide associated with neural signaling, particularly in the post-synaptic response to NMDA receptor co-stimulation/activation. Somatostatin is encoded by a CRE and is very susceptible to gene promoter region activation by transcription factor CREB. There are five known somatostatin receptors: * SST1 () * SST2 () * SST3 () * SST4 () * SST5 () All are G protein-coupled G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related p ... seven transmembrane receptors. References External links * G protein-coupled receptors {{transmembranereceptor-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of IGF-1 and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of hGH called somatropin (INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health care providers are prescribi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Cells
Delta cells (δ-cells or D cells) are somatostatin-producing cells. They can be found in the stomach, intestine and the pancreatic islets. Delta cells comprise ca 5% of the cells in the islets but may interact with many more islet cells than suggested by their low numbers. In rodents, delta-cells are located in the periphery of the islets; in humans the islet architecture is generally less organized and delta-cells are frequently observed inside the islets as well. In both species, the peptide hormone Urocortin III (Ucn3) is a major local signal that is released from beta cells (and alpha cells in primates) to induce the local secretion of somatostatin. It has also been suggested that somatostatin may be implicated in insulin-induced hypoglycaemia through a mechanism involving SGLT-2 receptors. Ghrelin can also strongly stimulate somatostatin secretion, thus indirectly inhibiting insulin release. Viewed under an electron microscope, delta-cells can be identified as cells with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas. Gastrin binds to cholecystokinin B receptors to stimulate the release of histamines in enterochromaffin-like cells, and it induces the insertion of K+/H+ ATPase pumps into the apical membrane of parietal cells (which in turn increases H+ release into the stomach cavity). Its release is stimulated by peptides in the lumen of the stomach. Physiology Genetics In humans, the ''GAS'' gene is located on the long arm of the seventeenth chromosome (17q21). Synthesis Gastrin is a linear peptide hormone produced by G cells of the duodenum and in the pyloric antrum of the stomach. It is secreted into the bloodstream. The encoded polypeptide is preprogastrin, which is cleaved by enzymes in posttranslational modification to produce progastrin (an intermed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcuate Nucleus
The arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus (also known as ARH, ARC, or infundibular nucleus) is an aggregation of neurons in the mediobasal hypothalamus, adjacent to the third ventricle and the median eminence. The arcuate nucleus includes several important and diverse populations of neurons that help mediate different neuroendocrine and physiological functions, including neuroendocrine neurons, centrally projecting neurons, and astrocytes. The populations of neurons found in the arcuate nucleus are based on the hormones they secrete or interact with and are responsible for hypothalamic function, such as regulating hormones released from the pituitary gland or secreting their own hormones. Neurons in this region are also responsible for integrating information and providing inputs to other nuclei in the hypothalamus or inputs to areas outside this region of the brain. These neurons, generated from the ventral part of the periventricular epithelium during embryonic development, loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Islets
The pancreatic islets or islets of Langerhans are the regions of the pancreas that contain its endocrine (hormone-producing) cells, discovered in 1869 by German pathological anatomist Paul Langerhans. The pancreatic islets constitute 1–2% of the pancreas volume and receive 10–15% of its blood flow. The pancreatic islets are arranged in density routes throughout the human pancreas, and are important in the metabolism of glucose. Structure There are about 1 million islets distributed throughout the pancreas of a healthy adult human, each of which measures an average of about 0.2 mm in diameter.:928 Each islet is separated from the surrounding pancreatic tissue by a thin fibrous connective tissue capsule which is continuous with the fibrous connective tissue that is interwoven throughout the rest of the pancreas.:928 Microanatomy Hormones produced in the pancreatic islets are secreted directly into the blood flow by (at least) five types of cells. In rat islets, endocrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus () is a part of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond. The hypothalamus is responsible for regulating certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and maternal attachment behaviours, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms. Structure Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrine
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input (through neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells) and, as a consequence of this input, release messenger molecules ( hormones) into the blood. In this way they bring about an integration between the nervous system and the endocrine system, a process known as neuroendocrine integration. An example of a neuroendocrine cell is a cell of the adrenal medulla (innermost part of the adrenal gland), which releases adrenaline to the blood. The adrenal medullary cells are controlled by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. These cells are modified postganglionic neurons. Autonomic nerve fibers lead directly to them from the central nervous system. The adrenal medullary hormones are kept in vesicles much in the same way neurotransmitters are kept in neuronal vesicles. Hormonal effects can last up to ten times longer than those of neurotransmitters. Sympathetic nerve fiber impulses sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventromedial Nucleus
The ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (VMN, also sometimes referred to as the ventromedial hypothalamus, VMH) is a nucleus of the hypothalamus. "The ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH) is a distinct morphological nucleus involved in terminating hunger, fear, thermoregulation, and sexual activity." This nuclear region is involved in the recognition of the feeling of fullness. Structure It has four subdivisions: * Anterior (VMHa) * Dorsomedial (VMHdm) * Ventrolateral (VMHvl) * Central (VMHc) These subdivisions differ anatomically, neurochemically, and behaviorally. Function The ventromedial nucleus (VMN) is most commonly associated with satiety. Early studies showed that VMN lesions caused over-eating and obesity in rats. However, the interpretation of these experiments was summarily discredited when Gold's research demonstrated that precision lesioning of the VMN did not result in hyperphagia. Nevertheless, numerous studies have shown that the immediacy of hyperphagia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally agreed principles, rules and recommendations that govern the formation and use of the specialist terms used in scientific and any other disciplines. Naming "things" is a part of general human communication using words and language: it is an aspect of everyday taxonomy as people distinguish the objects of their experience, together with their similarities and differences, which observers identify, name and classify. The use of names, as the many different kinds of nouns embedded in different languages, connects nomenclature to theoretical linguistics, while the way humans mentally structure the world in relation to word meanings and experience relates to the philosophy of language. Onomastics, the study of proper names and their origins, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)