Grignard Reagent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are
Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are
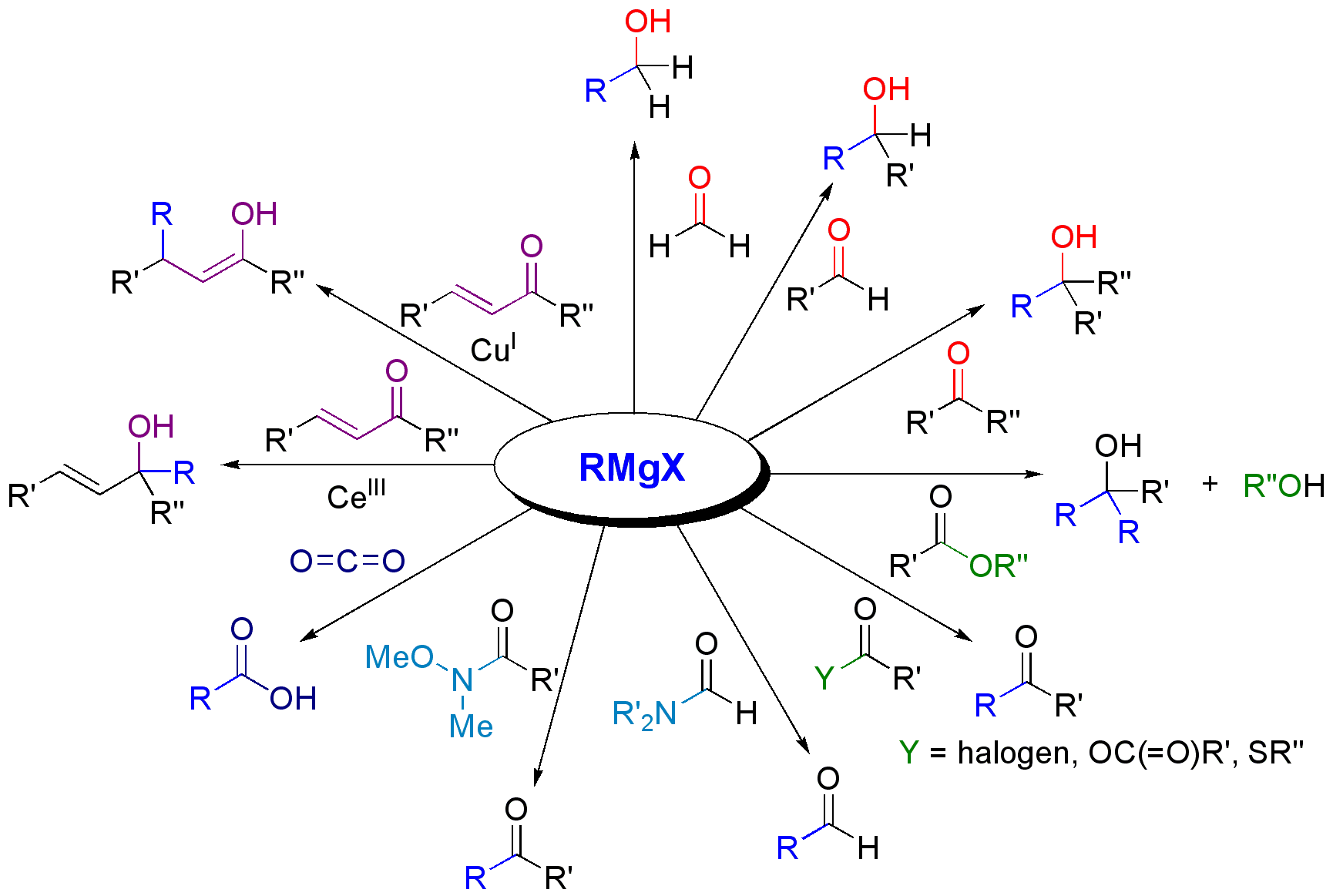 The most common application of Grignard reagents is the alkylation of aldehydes and ketones, i.e. ''the'' Grignard reaction:
The most common application of Grignard reagents is the alkylation of aldehydes and ketones, i.e. ''the'' Grignard reaction:
 Note that the
Note that the  Grignard reagents are
Grignard reagents are  In the Bruylants reaction, a nitrile can be replaced by the Grignard nucleophile, rather than the Grignard attacking the nitrile to form an imino structure.
In the Bruylants reaction, a nitrile can be replaced by the Grignard nucleophile, rather than the Grignard attacking the nitrile to form an imino structure.
 For the coupling of aryl halides with aryl Grignard reagents, nickel chloride in
For the coupling of aryl halides with aryl Grignard reagents, nickel chloride in



Grignard reaction experiment 01.jpg, Magnesium turnings are placed in a flask.
Grignard reaction experiment 02.jpg, Tetrahydrofuran and a small piece of iodine are added.
Grignard reaction experiment 03.jpg, A solution of alkyl bromide is added while heating.
Grignard reaction experiment 04.jpg, After completion of the addition, the mixture is heated for a while.
Grignard reaction experiment 05.jpg, Formation of the Grignard reagent is complete. A small amount of magnesium still remains in the flask.
Grignard reaction experiment 06.jpg, The Grignard reagent thus prepared is cooled to before the addition of the carbonyl compound. The solution becomes cloudy as the Grignard reagent precipitates out.
Grignard reaction experiment 07.jpg, A solution of carbonyl compound is added to the Grignard reagent.
Grignard reaction experiment 08.jpg, The solution is warmed to room temperature. At this point the reaction is complete.
 Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are
Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s with the general formula , where X is a halogen
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and the radioactive elements astatine (At) and tennessine (Ts), though some authors would ...
and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl group is derived from a cy ...
or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride
Methylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula . This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive compound is the simplest Grignard reagent and is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydro ...
and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds.
Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a branch of chemical synthesis concerned with the construction of organic compounds. Organic compounds are molecules consisting of combinations of covalently-linked hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms. Within the gen ...
for creating new carbon–carbon bond
A carbon–carbon bond is a covalent bond between two carbon atoms. The most common form is the single bond: a bond composed of two electrons, one from each of the two atoms. The carbon–carbon single bond is a sigma bond and is formed between on ...
s. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quick ...
, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used.
Grignard reagents are rarely isolated as solids. Instead, they are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs ...
or tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
using air-free techniques. Grignard reagents are complex
Complex commonly refers to:
* Complexity, the behaviour of a system whose components interact in multiple ways so possible interactions are difficult to describe
** Complex system, a system composed of many components which may interact with each ...
with the magnesium atom bonded to two ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R� ...
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's el ...
s as well as the halide and organyl ligands.
The discovery of the Grignard reaction in 1900 was recognized with the Nobel Prize awarded to Victor Grignard in 1912.
Synthesis
From Mg metal
Traditionally Grignard reagents are prepared by treating an organic halide (normally organobromine) with magnesium metal.Ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R� ...
s are required to stabilize the organomagnesium compound. Water and air, which rapidly destroy the reagent by protonolysis or oxidation, are excluded. Although the reagents still need to be dry, ultrasound can allow Grignard reagents to form in wet solvents by activating the magnesium such that it consumes the water.
As is common for reactions involving solids and solution, the formation of Grignard reagents is often subject to an induction period. During this stage, the passivating oxide on the magnesium is removed. After this induction period, the reactions can be highly exothermic. This exothermicity must be considered when a reaction is scaled-up from laboratory to production plant.
Most organohalides will work, but carbon-fluorine bonds are generally unreactive, except with specially activated magnesium (through Rieke metals).
Magnesium
Typically the reaction to form Grignard reagents involves the use of magnesium ribbon. All magnesium is coated with a passivating layer ofmagnesium oxide
Magnesium oxide (MgO), or magnesia, is a white hygroscopic solid mineral that occurs naturally as periclase and is a source of magnesium (see also oxide). It has an empirical formula of MgO and consists of a lattice of Mg2+ ions and O2− ions ...
, which inhibits reactions with the organic halide. Many methods have been developed to weaken this passivating layer, thereby exposing highly reactive magnesium to the organic halide. Mechanical methods include crushing of the Mg pieces in situ, rapid stirring, and sonication
image:Sonicator.jpg, A sonicator at the Weizmann Institute of Science during sonicationSonication is the act of applying sound energy to agitate particles in a sample, for various purposes such as the extraction of multiple compounds from plants, ...
. Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element; it has symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists at standard conditions as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a vi ...
, methyl iodide
Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one h ...
, and 1,2-dibromoethane
1,2-Dibromoethane, also known as ethylene dibromide (EDB), is an organobromine compound with the chemical formula . Although trace amounts occur naturally in the ocean, where it is probably formed by algae and kelp, substantial amounts are produc ...
are common activating agents. The use of 1,2-dibromoethane is advantageous as its action can be monitored by the observation of bubbles of ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon–carbon bond, carbon–carbon doub ...
. Furthermore, the side-products are innocuous:
:
The amount of Mg consumed by these activating agents is usually insignificant. A small amount of mercuric chloride will amalgamate the surface of the metal, enhancing its reactivity. Addition of preformed Grignard reagent is often used as the initiator.
Specially activated magnesium, such as Rieke magnesium, circumvents this problem. The oxide layer can also be broken up using ultrasound, using a stirring rod to scratch the oxidized layer off, or by adding a few drops of iodine or 1,2-Diiodoethane. Another option is to use sublimed magnesium or magnesium anthracene.
"Rieke magnesium" is prepared by a reduction of an anhydrous magnesium chloride with a potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
:
:
Mechanism
In terms of mechanism, the reaction proceeds through single electron transfer:Mg transfer reaction (halogen–Mg exchange)
An alternative preparation of Grignard reagents involves transfer of Mg from a preformed Grignard reagent to an organic halide. Other organomagnesium reagents are used as well. This method offers the advantage that the Mg transfer tolerates many functional groups. An illustrative reaction involvesisopropylmagnesium chloride
Isopropylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula (CH3)2HCMgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive material is the Grignard reagent derived from isopropyl chloride. It is commercially availab ...
and aryl bromide or iodides:
:
From alkylzinc compounds (reductive transmetalation)
A further method to synthesize Grignard reagents involves reaction of Mg with an organozinc compound. This method has been used to make adamantane-based Grignard reagents, which are, due to C-C coupling side reactions, difficult to make by the conventional method from the alkyl halide and Mg. The reductive transmetalation achieves: :AdZnBr + Mg → AdMgBr + ZnTesting Grignard reagents
Because Grignard reagents are so sensitive to moisture and oxygen, many methods have been developed to test the quality of a batch. Typical tests involve titrations with weighable, anhydrous protic reagents, e.g.menthol
Menthol is an organic compound, specifically a Monoterpene, monoterpenoid, that occurs naturally in the oils of several plants in the Mentha, mint family, such as Mentha arvensis, corn mint and peppermint. It is a white or clear waxy crystallin ...
in the presence of a color-indicator. The interaction of the Grignard reagent with phenanthroline or 2,2'-biquinoline causes a color change.
Reactions of Grignard reagents
As nucleophiles
Grignard reagents react with a variety of carbonyl derivatives. The most common application of Grignard reagents is the alkylation of aldehydes and ketones, i.e. ''the'' Grignard reaction:
The most common application of Grignard reagents is the alkylation of aldehydes and ketones, i.e. ''the'' Grignard reaction:
 Note that the
Note that the acetal
In organic chemistry, an acetal is a functional group with the connectivity . Here, the R groups can be organic fragments (a carbon atom, with arbitrary other atoms attached to that) or hydrogen, while the R' groups must be organic fragments n ...
functional group (a protected carbonyl) does not react.
Such reactions usually involve an aqueous acidic workup, though this step is rarely shown in reaction schemes. In cases where the Grignard reagent is adding to an aldehyde or a prochiral ketone, the Felkin-Anh model or Cram's Rule can usually predict which stereoisomer will be formed. With easily deprotonated 1,3- diketones and related acidic substrates, the Grignard reagent RMgX functions merely as a base, giving the enolate anion and liberating the alkane RH.
Grignard reagents also react with many "carbonyl-like" compounds and other electrophiles:
 Grignard reagents are
Grignard reagents are nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are ...
s in nucleophilic aliphatic substitutions for instance with alkyl halides in a key step in industrial Naproxen production:
 In the Bruylants reaction, a nitrile can be replaced by the Grignard nucleophile, rather than the Grignard attacking the nitrile to form an imino structure.
In the Bruylants reaction, a nitrile can be replaced by the Grignard nucleophile, rather than the Grignard attacking the nitrile to form an imino structure.
Reactions as a base
Grignard reagents serve as a base for non-protic substrates (this scheme does not show workup conditions, which typically includes water). Grignard reagents are basic and react with alcohols, phenols, etc. to give alkoxides (ROMgBr). The phenoxide derivative is susceptible to formylation by paraformaldehyde to give salicylaldehyde.Alkylation of metals and metalloids
Likeorganolithium compound
In organometallic chemistry, organolithium reagents are chemical compounds that contain carbon–lithium (C–Li) bonds. These reagents are important in organic synthesis, and are frequently used to transfer the organic group or the lithium atom ...
s, Grignard reagents are useful for forming carbon–heteroatom bonds.
Grignard reagents react with many metal-based electrophiles. For example, they undergo transmetallation with cadmium chloride (CdCl2) to give dialkylcadmium:
:
Schlenk equilibrium
Most Grignard reactions are conducted in ethereal solvents, especiallydiethyl ether
Diethyl ether, or simply ether, is an organic compound with the chemical formula , sometimes abbreviated as . It is a colourless, highly Volatility (chemistry), volatile, sweet-smelling ("ethereal odour"), extremely flammable liquid. It belongs ...
and THF. Grignard reagents react with 1,4-dioxane to give the diorganomagnesium compounds and insoluble coordination polymer and (R = organic group, X = halide):
:
This reaction exploits the Schlenk equilibrium, driving it toward the right.
Precursors to magnesiates
Grignard reagents react with organolithium compounds to give ate complexes (Bu = butyl): :Coupling with organic halides
Grignard reagents do ''not'' typically react with organic halides, in contrast with their high reactivity with other main group halides. In the presence of metal catalysts, however, Grignard reagents participate in C-C coupling reactions. For example, nonylmagnesium bromide reacts with methyl ''p''-chlorobenzoate to give ''p''-nonylbenzoic acid, in the presence of Tris(acetylacetonato)iron(III) (Fe(acac)3), after workup with NaOH to hydrolyze theester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
, shown as follows. Without the Fe(acac)3, the Grignard reagent would attack the ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
group over the aryl halide.
tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ...
(THF) is also a good catalyst. Additionally, an effective catalyst for the couplings of alkyl halides is the Gilman catalyst lithium tetrachlorocuprate (), prepared by mixing lithium chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorid ...
(LiCl) and copper(II) chloride
Copper(II) chloride, also known as cupric chloride, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The monoclinic crystal system, monoclinic yellowish-brown anhydrous form slowly absorbs moisture to form the orthorhombic blue-green hydrate, ...
() in THF. The Kumada-Corriu coupling gives access to ubstituted styrenes.
Oxidation
Treatment of a Grignard reagent with oxygen gives the magnesium organoperoxide. Hydrolysis of this material yieldshydroperoxide
Hydroperoxides or peroxols are Chemical compound, compounds of the form ROOH, where R stands for any group, typically Organic compound, organic, which contain the hydroperoxy functional group (). Hydroperoxide also refers to the hydroperoxide anio ...
s or alcohol. These reactions involve radical intermediates.
The simple oxidation of Grignard reagents to give alcohols is of little practical importance as yields are generally poor. In contrast, two-step sequence via a borane (''vide supra'') that is subsequently oxidized to the alcohol with hydrogen peroxide is of synthetic utility.
The synthetic utility of Grignard oxidations can be increased by a reaction of Grignard reagents with oxygen in presence of an alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
to an ethylene extended alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
. This modification requires aryl or vinyl
Vinyl may refer to:
Chemistry
* Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), a particular vinyl polymer
* Vinyl cation, a type of carbocation
* Vinyl group, a broad class of organic molecules in chemistry
* Vinyl polymer, a group of polymers derived from vinyl ...
Grignards. Adding just the Grignard and the alkene does not result in a reaction demonstrating that the presence of oxygen is essential. The only drawback is the requirement of at least two equivalents of Grignard although this can partly be circumvented by the use of a dual Grignard system with a cheap reducing Grignard such as n-butylmagnesium bromide.

Elimination
In the Boord olefin synthesis, the addition of magnesium to certain β-haloethers results in anelimination reaction
An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one- or two-step mechanism. The one-step mechanism is known as the E2 reaction, and the two-step mechanism is known as the E1 r ...
to the alkene. This reaction can limit the utility of Grignard reactions.

Industrial use
An example of the Grignard reaction is a key step in the (non-stereoselective) industrial production ofTamoxifen
Tamoxifen, sold under the brand name Nolvadex among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator used to prevent breast cancer in women and men. It is also being studied for other types of cancer. It has been used for Albright syndrome ...
(currently used for the treatment of estrogen receptor
Estrogen receptors (ERs) are proteins found in cell (biology), cells that function as receptor (biochemistry), receptors for the hormone estrogen (17β-estradiol). There are two main classes of ERs. The first includes the intracellular estrogen ...
positive breast cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp ...
in women):
See also
* Dibutylmagnesium * Hauser baseGallery
References
Further reading
* *Mary McHale, "Grignard Reaction," Connexions, http://cnx.org/content/m15245/1.2/. 2007. *''Grignard knowledge: Alkyl coupling chemistry with inexpensive transition metals'' by Larry J. Westrum, Fine Chemistry November/December 2002, pp. 10–1Specialized literature
* * * * {{Authority control Organometallic chemistry Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions Carbon-heteroatom bond forming reactions Reagents for organic chemistry Magnesium Chemical tests Organomagnesium compounds