|
Adamantane
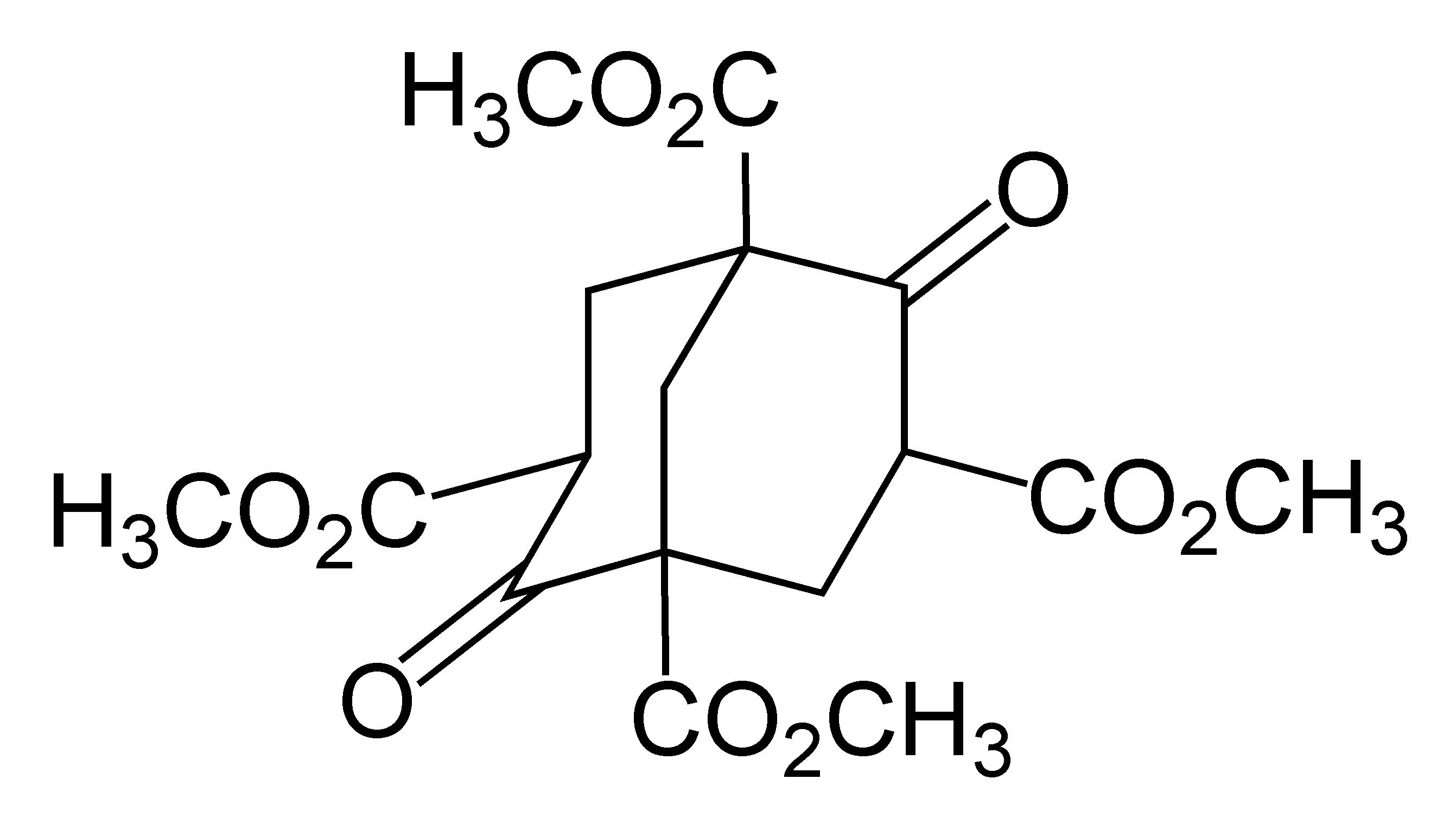
Adamantane is an organic compound with formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amantadine
Amantadine, sold under the brand name Gocovri among others, is a medication used to treat dyskinesia associated with parkinsonism and influenza caused by type A influenzavirus, though its use for the latter is no longer recommended because of widespread drug resistance. It is also used for a variety of other conditions. The drug is taken by mouth. Amantadine has a mild side-effect profile. Common neurological side effects include drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, and confusion. Because of its effects on the central nervous system (CNS), it should be combined cautiously with additional CNS stimulants or anticholinergic drugs. Given that it is cleared by the kidneys, amantadine is contraindicated in persons with end-stage kidney disease. Due to its anticholinergic effects, it should be taken with caution by those with enlarged prostates or glaucoma. The pharmacology of amantadine is complex. It acts as a sigma σ1 receptor agonist, nicotinic acetylcholin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamondoid
In chemistry, diamondoids are generalizations of the carbon cage molecule known as adamantane (C10H16), the smallest unit cage structure of the diamond crystal lattice. Diamondoids also known as nanodiamonds or condensed adamantanes may include one or more cages (adamantane, diamantane, triamantane, and higher polymantanes) as well as numerous isomeric and structural variants of adamantanes and polymantanes. These diamondoids occur naturally in petroleum deposits and have been extracted and purified into large pure crystals of polymantane molecules having more than a dozen adamantane cages per molecule. These species are of interest as molecular approximations of the diamond cubic framework, terminated with C−H bonds. Examples Examples include: * Adamantane (C10H16) * Iceane (C12H18) * BC-8 (C14H20) * Diamantane (C14H20) also ''diadamantane'', two face-fused cages * Triamantane (C18H24), also ''triadamantane''. Diamantane has four identical faces available for anchoring a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memantine
Memantine, sold under the brand name Namenda among others, is a medication used to slow the progression of moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include headache, constipation, sleepiness, and dizziness. Severe side effects may include blood clots, psychosis, and heart failure. It is believed to work by acting on NMDA receptors, working as a pore blocker of these ion channels. Memantine was first discovered in 1963. It was approved for medical use in Germany in 1989, in the European Union in 2002, and in the United States in 2003. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 150th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3million prescriptions. Medical uses Alzheimer's disease and dementia Memantine is used to treat moderate-to-severe Alzheimer's disease, especially for people who are intolerant of or have a contraindication to AChE (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitors.NICE review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
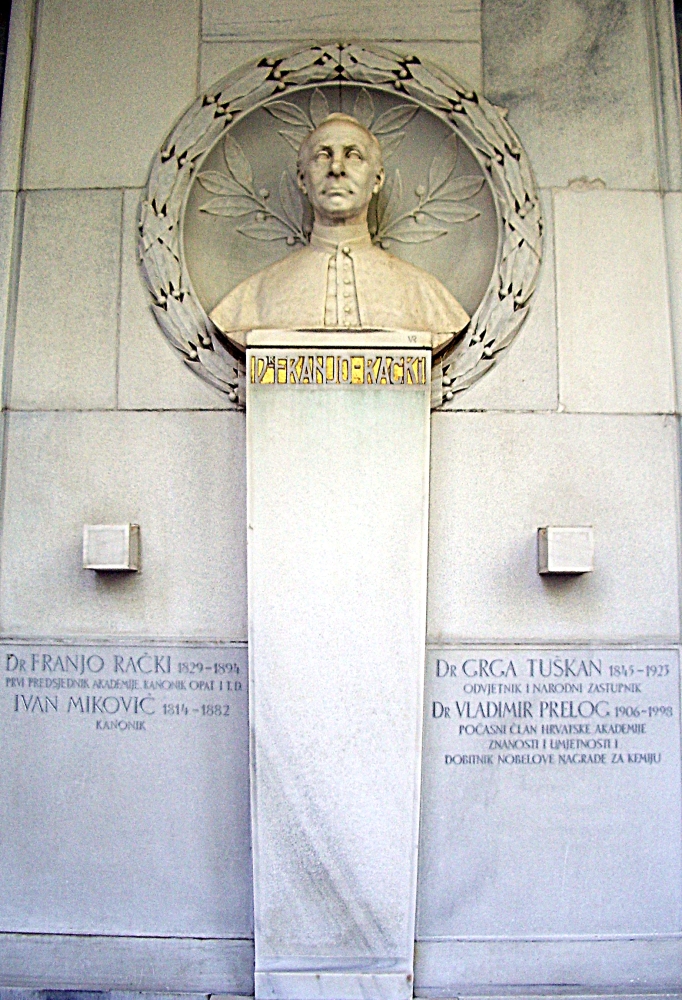
Vladimir Prelog
Vladimir Prelog (23 July 1906 – 7 January 1998) was a Croatian-Swiss organic chemist who received the 1975 Nobel Prize in chemistry for his research into the stereochemistry of organic molecules and reactions. Prelog was born, and spent his infancy, in Sarajevo, and youth in Zagreb, Osijek and Prague.Vladimir Prelog (1975Autobiography the Nobel Committee. He later lived and worked in Prague, Zagreb and Zürich. Early life Prelog was born in Sarajevo, Condominium of Bosnia and Herzegovina, at that time within Austria-Hungary, to Croat parents who were working there. His father, Milan, a native of Zagreb, was a history professor at a gymnasium in Sarajevo and later at the University of Zagreb. As an 8-year-old boy, he stood near the place where the assassination of Franz Ferdinand occurred. Education Prelog started elementary school in Sarajevo. In 1915, at the beginning of the first World War, at Prelog moved to Zagreb (then part of Austria-Hungary) with his parents. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimantadine
Rimantadine (INN, sold under the trade name Flumadine) is an orally administered antiviral drug used to treat, and in rare cases prevent, influenzavirus A infection. When taken within one to two days of developing symptoms, rimantadine can shorten the duration and moderate the severity of influenza. Rimantadine can mitigate symptoms, including fever. Both rimantadine and the similar drug amantadine are derivates of adamantane. Rimantadine is found to be more effective than amantadine because when used the patient displays fewer symptoms. Rimantadine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1994. Rimantadine was approved for medical use in 1993. Seasonal H3N2 and 2009 pandemic flu samples tested have shown resistance to rimantadine, and it is no longer recommended to prescribe for treatment of the flu. Medical uses Influenza A Rimantadine inhibits influenza activity by binding to amino acids in the M2 proton channel, M2 transmembrane channel and blocking prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricyclodecane
Tricyclodecane (TCD) is an organic compound with the formula C10H16. It is classed as a hydrocarbon. It has two main stereoisomers–the ''endo'' and ''exo'' forms. Its primary use in the exo form is as a component of jet fuel. It is used here primarily because of its high energy density. The exo isomer also has a low freezing point. Because of this, its properties have been studied extensively. It is often called tetrahydrodicyclopentadiene. Reactions Its reactions with other materials have been studied, as have various production methods. The two isomers can interconvert in the presence of aluminum chloride Aluminium chloride, also known as aluminium trichloride, is an inorganic compound with the formula . It forms a hexahydrate with the formula , containing six water molecules of hydration. Both the anhydrous form and the hexahydrate are col ... as catalyst absorbed on substrates such as silicon dioxide or zeolites, with preference for forming the ''exo'' as the major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Von Ragué Schleyer
Paul von Ragué Schleyer (February 27, 1930 – November 21, 2014) was an American physical organic chemist whose research is cited with great frequency. A 1997 survey indicated that Dr. Schleyer was, at the time, the world's third most cited chemist, with over 1100 technical papers produced. He was Eugene Higgins Professor of Chemistry at Princeton University, professor and co-director of the Institute for Organic Chemistry (Institut für organische Chemie) at the University of Erlangen–Nuremberg in Germany, and later Graham Perdue Professor of Chemistry at the University of Georgia in Athens, Georgia, Athens, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. He published twelve books in the fields of lithium chemistry, Ab initio quantum chemistry methods, ab initio molecular orbital theory and carbonium ions. He was past president of the World Association of Theoretically Oriented Chemists, a fellow of the International Academy of Quantum Molecular Science and editor-in-chief of the ''Encycloped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicyclopentadiene
Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula . At room temperature, it is a white brittle wax, although lower purity samples can be straw coloured liquids. The pure material smells somewhat of soy wax or camphor, with less pure samples possessing a stronger acrid odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l. Dicyclopentadiene is a co-produced in large quantities in the steam cracking of naphtha and gas oils to ethylene. The major use is in resins, particularly, unsaturated polyester resins. It is also used in inks, adhesives, and paints. The top seven suppliers worldwide together had an annual capacity in 2001 of 179 kilotonnes (395 million pounds). DCPD was discovered in 1885 as a hydrocarbon among the products of pyrolysis of phenol by Henry Roscoe, who didn't identify the structure (that was made during the following decade) but accurately assumed that it was a dimer of some hydrocarbon. History and structure For many years the structure of dicy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diethyl Malonate
Diethyl malonate, also known as DEM, is the diethyl ester of malonic acid. It occurs naturally in grapes and strawberries as a colourless liquid with an apple-like odour, and is used in perfumes. It is also used to synthesize other compounds such as barbiturates, artificial flavourings, vitamin B1, and vitamin B6. Structure and properties Malonic acid is a rather simple dicarboxylic acid, with two carboxyl groups close together. In forming diethyl malonate from malonic acid, the hydroxyl group (−OH) on both of the carboxyl groups is replaced by an ethoxy group (−OEt; −OCH2CH3). The methylene group (−CH2−) in the middle of the malonic part of the diethyl malonate molecule is neighboured by two carbonyl groups (−C(=O)−). The hydrogen atoms on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group in a molecule are significantly more acidic than hydrogen atoms on a carbon adjacent to alkyl groups (up to 30 orders of magnitude). (This is known as the α position wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decarboxylation
Decarboxylation is a chemical reaction that removes a carboxyl group and releases carbon dioxide (CO2). Usually, decarboxylation refers to a reaction of carboxylic acids, removing a carbon atom from a carbon chain. The reverse process, which is the first chemical step in photosynthesis, is called carboxylation, the addition of CO2 to a compound. Enzymes that catalyze decarboxylations are called decarboxylases or, the more formal term, carboxy-lyases (Enzyme Commission number, EC number 4.1.1). In organic chemistry The term "decarboxylation" usually means replacement of a carboxyl group () with a hydrogen atom: : Decarboxylation is one of the oldest known organic reactions. It is one of the processes assumed to accompany pyrolysis and destructive distillation. Overall, decarboxylation depends upon stability of the carbanion synthon , although the anion may not be a true chemical intermediate. Typically, carboxylic acids decarboxylate slowly, but carboxylic acids with an α el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to redox, reduce or Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces Double bond, double and Triple bond, triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the Saturated and unsaturated compounds, unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The redox, reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |