Grid Energy Storage on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like
Grid energy storage, also known as large-scale energy storage, are technologies connected to the electrical power grid that store energy for later use. These systems help balance supply and demand by storing excess electricity from variable renewables such as solar and inflexible sources like

 The
The
 Flywheels store energy in the form of mechanical energy. They are suited to supplying high levels of electricity over minutes and can also be charged rapidly. They have a long lifetime and can be used in settings with widely varying temperatures. The technology is mature, but more expensive than batteries and supercapacitors and not used frequently.
Flywheels store energy in the form of mechanical energy. They are suited to supplying high levels of electricity over minutes and can also be charged rapidly. They have a long lifetime and can be used in settings with widely varying temperatures. The technology is mature, but more expensive than batteries and supercapacitors and not used frequently.
 , pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH) was the largest form of grid energy storage globally, with an installed capacity of 181 GW, surpassing the combined capacity of utility-scale and behind-the-meter battery storage, which totaled approximately 88 GW.
PSH is particularly effective for managing daily fluctuations in energy demand. During periods of low demand, water is pumped to a higher-elevation reservoir, and during peak demand, the stored water is released to generate electricity through turbines. The system has an efficiency rate of 75% to 85% and can quickly respond to changes in demand, typically within seconds to minutes.
While traditional PSH systems require specific geographical conditions, alternative designs have been proposed. These include using deep salt caverns or constructing hollow structures on the
, pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH) was the largest form of grid energy storage globally, with an installed capacity of 181 GW, surpassing the combined capacity of utility-scale and behind-the-meter battery storage, which totaled approximately 88 GW.
PSH is particularly effective for managing daily fluctuations in energy demand. During periods of low demand, water is pumped to a higher-elevation reservoir, and during peak demand, the stored water is released to generate electricity through turbines. The system has an efficiency rate of 75% to 85% and can quickly respond to changes in demand, typically within seconds to minutes.
While traditional PSH systems require specific geographical conditions, alternative designs have been proposed. These include using deep salt caverns or constructing hollow structures on the
 Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. While technically no electricity is stored, the net effect is the similar as pumped storage. The amount of storage available in hydroelectric dams is much larger than in pumped storage. Upgrades may be needed so that these dams can respond to variable demand. For instance, additional investment may be needed in transmission lines, or additional turbines may need to be installed to increase the peak output from the dam.
Dams usually have multiple purposes. As well as energy generation, they often play a role in flood defense and protection of ecosystems, recreation, and they supply water for
Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. While technically no electricity is stored, the net effect is the similar as pumped storage. The amount of storage available in hydroelectric dams is much larger than in pumped storage. Upgrades may be needed so that these dams can respond to variable demand. For instance, additional investment may be needed in transmission lines, or additional turbines may need to be installed to increase the peak output from the dam.
Dams usually have multiple purposes. As well as energy generation, they often play a role in flood defense and protection of ecosystems, recreation, and they supply water for
 The levelized cost of storing electricity (LCOS) is a measure of the lifetime costs of storing electricity per MWh of electricity discharged. It includes investment costs, but also operational costs and charging costs. It depends highly on storage type and purpose; as subsecond-scale frequency regulation, minute/hour-scale peaker plants, or day/week-scale season storage.
For power applications (for instance around
The levelized cost of storing electricity (LCOS) is a measure of the lifetime costs of storing electricity per MWh of electricity discharged. It includes investment costs, but also operational costs and charging costs. It depends highly on storage type and purpose; as subsecond-scale frequency regulation, minute/hour-scale peaker plants, or day/week-scale season storage.
For power applications (for instance around
UK Government report on the Benefits of long-duration electricity storage (Aug 2022)
{{emerging technologies, energy=yes Power engineering
nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
, releasing it when needed. They further provide essential grid services, such as helping to restart the grid after a power outage
A power outage, also called a blackout, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, a power cut, or a power out is the complete loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.
There are many causes of power failures in an el ...
.
, the largest form of grid storage is pumped-storage hydroelectricity
Pumped-storage hydroelectricity (PSH), or pumped hydroelectric energy storage (PHES), is a type of hydroelectric energy storage used by electric power systems for load balancing (electrical power), load balancing.
A PSH system stores energy i ...
, with utility-scale batteries and behind-the-meter batteries coming second and third. Lithium-ion batteries are highly suited for shorter duration storage up to 8 hours. Flow batteries and compressed air energy storage may provide storage for medium duration. Two forms of storage are suited for long-duration storage: green hydrogen, produced via electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
and thermal energy storage.
Energy storage is one option to making grids more flexible. An other solution is the use of more dispatchable power plants that can change their output rapidly, for instance peaking power plants to fill in supply gaps. Demand response
Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries, electric energy could not b ...
can shift load to other times and interconnections between regions can balance out fluctuations in renewables production.
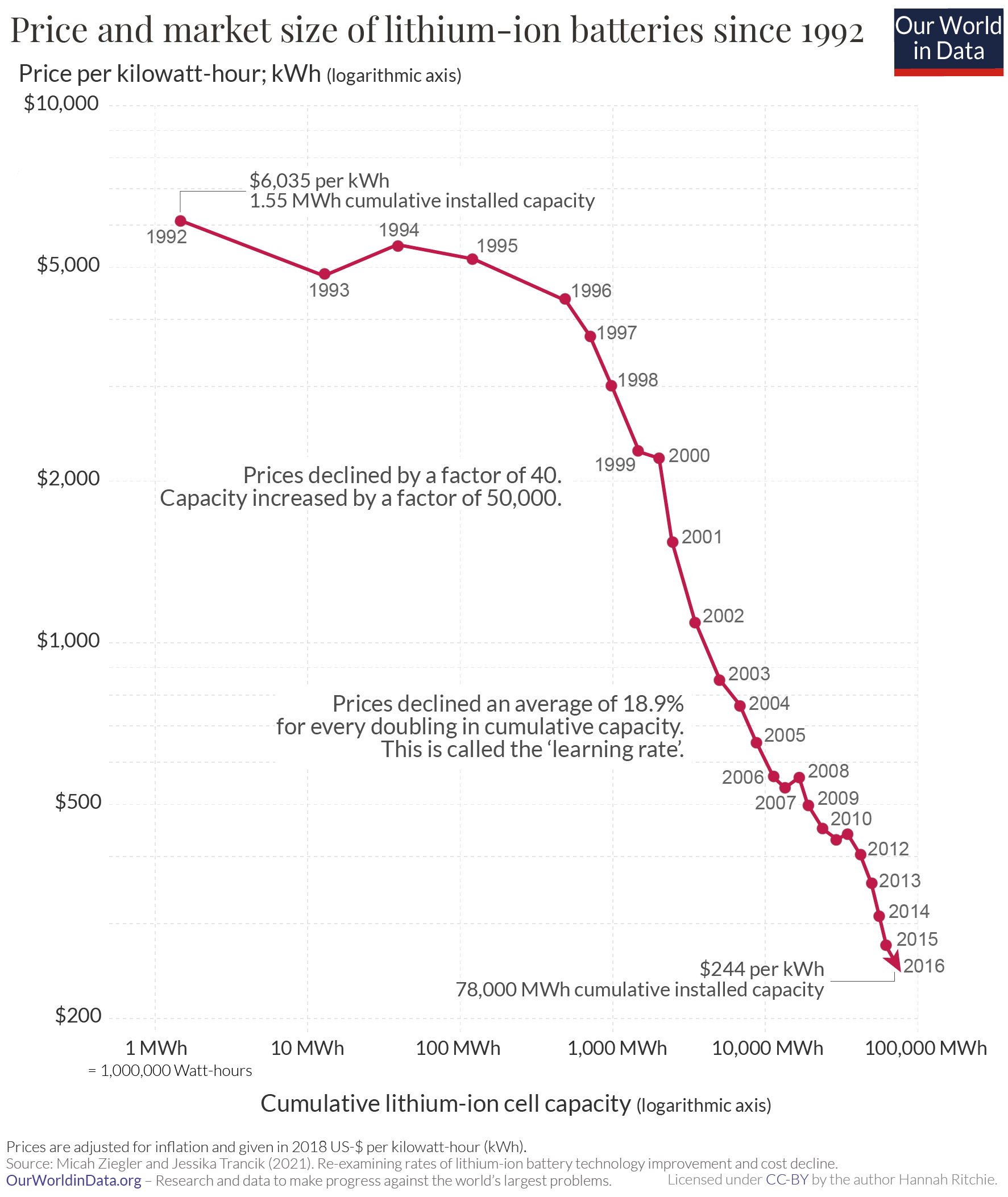
The price of storage technologies typically goes down with experience. For instance, lithium-ion batteries have been getting some 20% cheaper for each doubling of worldwide capacity. Systems with under 40% variable renewables need only short-term storage. At 80%, medium-duration storage becomes essential and beyond 90%, long-duration storage does too. The economics of long-duration storage is challenging, and alternative flexibility options like demand response may be more economic.
Roles in the power grid
Any electrical power grid must match electricity production to consumption, both of which vary significantly over time. Energy derived from solar and wind sources varies with the weather on time scales ranging from less than a second to weeks or longer.Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by ...
is less flexible than fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
, meaning it cannot easily match the variations in demand. Thus, low-carbon electricity without storage presents special challenges to electric utilities
An electric utility, or a power company, is a company in the electric power industry (often a public utility) that engages in electricity generation and Electricity retailing, distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. El ...
.
Electricity storage is one of the three key ways to replace flexibility from fossil fuels
A fossil fuel is a flammable carbon compound- or hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the buried remains of prehistoric organisms (animals, plants or microplanktons), a process that occurs within geologica ...
in the grid. Other options are demand-side response, in which consumers change when they use electricity or how much they use. For instance, households may have cheaper night tariffs to encourage them to use electricity at night. Industry and commercial consumers can also change their demand to meet supply. Improved network interconnection smooths the variations of renewables production and demand. When there is little wind in one location, another might have a surplus of production. Expansion of transmission lines usually takes a long time.
Energy storage has a large set of roles in the electricity grid and can therefore provide many different services. For instance, it can arbitrage
Arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more marketsstriking a combination of matching deals to capitalize on the difference, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which th ...
by keeping it until the electricity price rises, it can help make the grid more stable, and help reduce investment into transmission infrastructure. The type of service provided by storage depends on who manages the technology, whether the technology is based alongside generation of electricity, within the network, or at the side of consumption.
Providing short-term flexibility is a key role for energy storage. On the generation side, it can help with the integration of variable renewable energy
Variable renewable energy (VRE) or intermittent renewable energy sources (IRES) are renewable energy sources that are not dispatchable due to their fluctuating nature, such as wind power and solar power, as opposed to controllable renewable ener ...
, storing it when there is an oversupply of wind and solar and electricity prices are low. More generally, it can exploit the changes in prices of electricity over time in the wholesale market, charging when electricity is cheap and selling when it is expensive. It can further help with grid congestion (where there is insufficient capacity on transmission lines). Consumers can use storage to use more of their self-produced electricity (for instance from rooftop solar power).
Storage can also be used to provide essential grid services. On the generation side, storage can smooth out the variations in production, for instance for solar and wind. It can assist in a black start after a power outage
A power outage, also called a blackout, a power failure, a power blackout, a power loss, a power cut, or a power out is the complete loss of the electrical power network supply to an end user.
There are many causes of power failures in an el ...
. On the network side, these include frequency regulation (continuously) and frequency response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and Phase (waves), phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and ...
(after unexpected changes in supply or demand). On the consumption side, storage can help to improve the quality of the delivered electricity in less stable grids.
Investment in storage may make some investments in the transmission and distribution network unnecessary, or may allow them to be scaled down. Additionally, storage can ensure there is sufficient capacity to meet peak demand within the electricity grid. Finally, in off-grid home systems or mini-grids, electricity storage can help provide energy access in areas that were previously not connected to the electricity grid.Forms
Electricity can be stored directly for a short time in capacitors, somewhat longer electrochemically in batteries, and much longer chemically (e.g. hydrogen), mechanically (e.g. pumped hydropower) or as heat. The first pumped hydroelectricity was constructed at the end of the 19th century around the Alps in Italy, Austria, and Switzerland. The technique rapidly expanded during the 1960s to 1980s nuclear boom, due to nuclear power's inability to quickly adapt to changes in electricity demand. In the 21st century, interest in storage surged due to the rise of sustainable energy sources, which are often weather-dependent. Commercial batteries have been available for over a century, their widespread use in the power grid is more recent, with only 1 GW available in 2013.Batteries

Lithium-ion batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used batteries for grid applications, , following the application of batteries in electric vehicles (EVs). In comparison with EVs, grid batteries require lessenergy density
In physics, energy density is the quotient between the amount of energy stored in a given system or contained in a given region of space and the volume of the system or region considered. Often only the ''useful'' or extractable energy is measure ...
, meaning that more emphasis can be put on costs, the ability to charge and discharge often and lifespan. This has led to a shift towards lithium iron phosphate batteries (LFP batteries), which are cheaper and last longer than traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Costs of batteries are declining rapidly; from 2010 to 2023 costs fell by 90%. , utility-scale systems account for two thirds of added capacity, and home applications (behind-the-meter) for one third. Lithium-ion batteries are highly suited to short-duration storage (<8h) due to cost and degradation associated with high states of charge.
= Electric vehicles
= The
The electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a motor vehicle whose propulsion is powered fully or mostly by electricity. EVs encompass a wide range of transportation modes, including road vehicle, road and rail vehicles, electric boats and Submersible, submer ...
fleet has a large overall battery capacity, which can potentially be used for grid energy storage. This could be in the form of vehicle-to-grid (V2G), where cars store energy when they are not in use, or by repurposing
Repurposing is the process by which an object with one use value is transformed or redeployed as an object with an alternative use value.
Description
Repurposing is as old as human civilization, with many contemporary scholars investigating ho ...
batteries from cars at the end of the vehicle's life. Car batteries typically range between 33 and 100 kWh; for comparison, a typical upper-middle-class household in Spain might use some 18 kWh in a day. By 2030, batteries in electric vehicles may be able to meet all short-term storage demand globally.
, there have been more than 100 V2G pilot projects globally. The effect of V2G charging on battery life can be positive or negative. Increased cycling of batteries can lead to faster degradation, but due to better management of the state of charge and gentler charging and discharing, V2G might instead increase the lifetime of batteries. Second-hand batteries may be useable for stationary grid storage for roughly 6 years, when their capacity drops from roughly 80% to 60% of the initial capacity. LFP batteries are particularly suitable for reusing, as they degrade less than other lithium-ion batteries and recycling is less attractive as their materials are not as valuable.
Other battery types
In redox flow batteries, energy is stored in liquids, which are placed in two separate tanks. When charging or discharging, the liquids are pumped into a cell with the electrodes. The amount of energy stored (as set by the size of the tanks) can be adjusted separately from the power output (as set by the speed of the pumps). Flow batteries have the advantages of low capital cost for charge-discharge duration over 4 h, and of long durability (many years). Flow batteries are inferior to lithium-ion batteries in terms of energy efficiency, averaging efficiencies between 60% and 75%. Vanadium redox batteries is most commercially advanced type of flow battery, with roughly 40 companies making them . Sodium-ion batteries are a possible alternative to lithium-ion batteries, as they are lessflammable
A combustible material is a material that can burn (i.e., sustain a flame) in air under certain conditions. A material is flammable if it ignites easily at ambient temperatures. In other words, a combustible material ignites with some effort ...
, and use cheaper and less critical materials. They have a lower energy density, and possibly a shorter lifespan. If produced at the same scale as lithium-ion batteries, they may become 20% to 30% cheaper. Iron-air batteries may be suitable for even longer duration storage than flow batteries (weeks), but the technology is not yet mature.
Electrical
Storage in supercapacitors works well for applications where a lot of power is needed for short amount of time. In the power grid, they are therefore mostly used in short-term frequency regulation.Hydrogen and chemical storage
Various power-to-gas technologies exist that can convert excess electricity into an easier to store chemical. The lowest cost and most efficient one ishydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
. However, it is easier to use synthetic methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
with existing infrastructure and appliances, as it is very similar to natural gas.
, there have been a number of demonstration plants where hydrogen is burned in gas turbines, either co-firing with natural gas, or on its own. Similarly, a number of coal plants have demonstrated it is possible to co-fire ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
when burning coal. In 2022, there was also a small pilot to burn pure ammonia in a gas turbine. A portion of existing gas turbines are capable of co-firing hydrogen, which means there is, as a lower estimate, 80 GW of capacity ready to burn hydrogen.
Hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
can be used as a long-term storage medium. Green hydrogen is produced from the electrolysis of water
Electrolysis of water is using electricity to Water splitting, split water into oxygen () and hydrogen () gas by electrolysis. Hydrogen gas released in this way can be used as hydrogen fuel, but must be kept apart from the oxygen as the mixture ...
and converted back into electricity in an internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
, or a fuel cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
, with a round-trip efficiency of roughly 41%. Together with thermal storage, it is expected to be best suited to seasonal energy storage.
Hydrogen can be stored aboveground in tanks or underground in larger quantities. Underground storage is easiest in salt caverns, but only a certain number of places have suitable geology. Storage in porous rocks, for instance in empty gas fields and some aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s, can store hydrogen at a larger scale, but this type of storage may have some drawbacks. For instance, some of the hydrogen may leak, or react into H2S or methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
.
Ammonia
Hydrogen can be converted into ammonia in a reaction withnitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
in the Haber-Bosch process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
. Ammonia, a gas at room temperature, is more expensive to produce than hydrogen. However, it can be stored more cheaply than hydrogen. Tank storage is usually done at between one and ten times atmospheric pressure and at a temperature of , in liquid form. Ammonia has multiple uses besides being an energy carrier: it is the basis for the production of many chemicals; the most common use is for fertilizer. It can be used for power generation directly, or converted back to hydrogen first. Alternatively, it has potential applications as a fuel in shipping
Freight transport, also referred to as freight forwarding, is the physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it has been ...
.
Methane
It is possible to further convert hydrogen intomethane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
via the Sabatier reaction, a chemical reaction which combines and H2. While the reaction that converts CO from gasified coal into is mature, the process to form methane out of is less so. Efficiencies of around 80% one-way can be achieved, that is, some 20% of the energy in hydrogen is lost in the reaction.Mechanical
Flywheel
Pumped hydro
seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
, where the ocean serves as the upper reservoir. However, PSH construction is often expensive, time-consuming, and can have significant environmental and social impacts on nearby communities. Installing floating solar panels on reservoirs, can increase the efficiency of PSH systems. These panels reduce water evaporation and benefit from cooling by the water surface, which also improves their energy generation efficiency.
Hydroelectric dams
 Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. While technically no electricity is stored, the net effect is the similar as pumped storage. The amount of storage available in hydroelectric dams is much larger than in pumped storage. Upgrades may be needed so that these dams can respond to variable demand. For instance, additional investment may be needed in transmission lines, or additional turbines may need to be installed to increase the peak output from the dam.
Dams usually have multiple purposes. As well as energy generation, they often play a role in flood defense and protection of ecosystems, recreation, and they supply water for
Hydroelectric dams with large reservoirs can also be operated to provide peak generation at times of peak demand. Water is stored in the reservoir during periods of low demand and released through the plant when demand is higher. While technically no electricity is stored, the net effect is the similar as pumped storage. The amount of storage available in hydroelectric dams is much larger than in pumped storage. Upgrades may be needed so that these dams can respond to variable demand. For instance, additional investment may be needed in transmission lines, or additional turbines may need to be installed to increase the peak output from the dam.
Dams usually have multiple purposes. As well as energy generation, they often play a role in flood defense and protection of ecosystems, recreation, and they supply water for irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
. This means it is not always possible to change their operation much, but even with low flexibility, they may still play an important role in responding to changes in wind and solar production.
Gravity
Alternative methods that use gravity include storing energy by moving large solid masses upward against gravity. This can be achieved inside old mine shafts or in specially constructed towers where heavy weights arewinch
A winch is a mechanical device that is used to pull in (wind up) or let out (wind out) or otherwise adjust the tension (physics), tension of a rope or wire rope (also called "cable" or "wire cable").
In its simplest form, it consists of a Bobb ...
ed up to store energy and allowed a controlled descent to release it.
Compressed air
Compressed air energy storage (CAES) stores electricity by compressing air. The compressed air is typically stored in large underground caverns. The expanding air can be used to drive turbines, converting the energy back into electricity. As air cools when expanding, some heat needs to be added in this stage to prevent freezing. This can be provided by a low-carbon source, or in the case of advanced CAES, by reusing the heat that is released when air is compressed. , there are three advanced CAES projects in operation in China. Typical efficiencies of advanced CAES are between 60% and 80%.Liquid air or
Another electricity storage method is to compress and cool air, turning it intoliquid air
Liquid Air was the marque of an automobile planned by Liquid Air Power and Automobile Co. of Boston and New York City in 1899. page 1432
A factory location was acquired in Boston, Massachusetts in 1899 and Liquid Air claimed they would constr ...
, which can be stored and expanded when needed, turning a turbine to generate electricity. This is called liquid air energy storage (LAES). The air would be cooled to temperatures of to become liquid. Like with compressed air, heat is needed for the expansion step. In the case of LAES, low-grade industrial heat can be used for this. Energy efficiency for LAES lies between 50% and 70%. , LAES is moving from pre-commercial to commercial. An alternative is the compression of to store electricity.
Thermal
Electricity can be directly stored thermally with a Carnot battery. A Carnot battery is a type of energy storage system that stores electricity in heat storage and converts the stored heat back to electricity viathermodynamic cycle
A thermodynamic cycle consists of linked sequences of thermodynamic processes that involve heat transfer, transfer of heat and work (physics), work into and out of the system, while varying pressure, temperature, and other state variables within t ...
s (for instance, a turbine). While less efficient than pumped hydro or battery storage, this type of system is expected to be cheap and can provide long-duration storage. A pumped-heat electricity storage system is a Carnot battery that uses a reversible heat pump to convert the electricity into heat. It usually stores the energy in both a hot and cold reservoir. To achieve decent efficiencies (>50%), the temperature ratio between the two must reach a factor of 5.
Thermal energy storage is also used in combination with concentrated solar power
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated whe ...
(CSP). In CSP, solar energy is first converted into heat, and then either directly converted into electricity or first stored. The energy is released when there is little or no sunshine. This means that CSP can be used as a dispatchable (flexible) form of generation. The energy in a CSP system can for instance be stored in molten salts or in a solid medium such as sand.
Finally, heating and cooling systems in buildings can be controlled to store thermal energy in either the building's mass or dedicated thermal storage tanks. This thermal storage can provide load-shifting or even more complex ancillary services
Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from power plant, generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable ...
by increasing power consumption (charging the storage) during off-peak times and lowering power consumption (discharging the storage) during higher-priced peak times.
Economics
Costs
 The levelized cost of storing electricity (LCOS) is a measure of the lifetime costs of storing electricity per MWh of electricity discharged. It includes investment costs, but also operational costs and charging costs. It depends highly on storage type and purpose; as subsecond-scale frequency regulation, minute/hour-scale peaker plants, or day/week-scale season storage.
For power applications (for instance around
The levelized cost of storing electricity (LCOS) is a measure of the lifetime costs of storing electricity per MWh of electricity discharged. It includes investment costs, but also operational costs and charging costs. It depends highly on storage type and purpose; as subsecond-scale frequency regulation, minute/hour-scale peaker plants, or day/week-scale season storage.
For power applications (for instance around ancillary services
Ancillary services are the services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from power plant, generators to consumers given the obligations of control areas and transmission utilities within those control areas to maintain reliable ...
or black starts), a similar metric is the annuitized capacity cost (ACC), which measures the lifetime costs per kW. ACC is lowest when there are few cycles (<300) and when the discharge is less than one hour. This is because the technology is reimbursed only when it provides spare capacity, not when it is discharged.
The cost of storage is coming down following technology-dependent experience curves, the price drop for each doubling in cumulative capacity (or experience). Lithium-ion battery prices fast: the price utitlities pay for them falls 19% with each doubling of capacity. Hydrogen production via electrolysis has a similar learning rate, but it is much more uncertain. Vanadium-flow batteries typically get 14% cheaper for each doubling of capacity. Pumped hydropower has not seen prices fall much with increased experience.
Market and system value
There are four categories of services which provide economic value for storage: those related to power quality (such as frequency regulation), reliability (ensuring peak demand can be met), better use of assets in the system (e.g. avoiding transmission investments) andarbitrage
Arbitrage (, ) is the practice of taking advantage of a difference in prices in two or more marketsstriking a combination of matching deals to capitalize on the difference, the profit being the difference between the market prices at which th ...
(exploiting price differences over time). Before 2020, most value for storage was in providing power quality services. Arbitrage is the service with the largest economic potential for storage applications.
In systems with under 40% of variable renewables, only short-term storage (of less than 4 hours) is needed for integration. When the share of variable renewables climbs to 80%, medium-duration storage (between 4 and 16 hours, for instance compressed air
Compressed air is air kept under a pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure. Compressed air in vehicle tires and shock absorbers are commonly used for improved traction and reduced vibration. Compressed air is an important medium for t ...
) is needed. Above 90%, large-scale long-duration storage is required. The economics of long-duration storage is challenging even then, as the costs are high. Alternative flexibility options, such as demand response, network expansions or flexible generation ( geothermal or fossil gas with carbon capture and storage) may be lower-cost.
Like with renewables, storage will " cannibalise" its own income, but even more strongly. That is, with more storage on the market, there is less of an opportunity to do arbitrage or deliver other services to the grid. How markets are designed impacts revenue potential too. The income from arbitrage is quite variable between years, whereas markets that have capacity payments likely show less volatility.
Electricity storage is not 100% efficient, so more electricity needs to be bought than can be sold. This implies that if there is only a small variation in price, it may not be economical to charge and discharge. For instance, if the storage application is 75% efficient, the price at which the electricity is sold needs to be at least 1.33 higher than the price for which it was bought. Typically, electricity prices vary most between day and night, which means that storage up to 8 hours has relatively high potential for profit.
See also
* Distributed generation * Energy storage as a service (ESaaS) * List of energy storage projects * Power-to-X * U.S. Department of Energy International Energy Storage Database, a list of grid energy storage projects * Virtual power plantReferences
Cited sources
* * * * * * * * *External links
UK Government report on the Benefits of long-duration electricity storage (Aug 2022)
{{emerging technologies, energy=yes Power engineering