|
MWh
A kilowatt-hour ( unit symbol: kW⋅h or kW h; commonly written as kWh) is a non-SI unit of energy equal to 3.6 megajoules (MJ) in SI units, which is the energy delivered by one kilowatt of power for one hour. Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy supplied by electric utilities. Metric prefixes are used for multiples and submultiples of the basic unit, the watt-hour (3.6 kJ). Definition The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) multiplied by (i.e., sustained for) one hour. The International System of Units (SI) unit of energy meanwhile is the joule (symbol J). Because a watt is by definition one joule per second, and because there are 3,600 seconds in an hour, one kWh equals 3,600 kilojoules or 3.6 MJ."Half-high dots or spaces are used to express a derived unit formed from two or more other units by multiplication.", Barry N. Taylor. (2001 ed.''The International System of Units.'' (Special publication 33 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megajoules
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces a body through a distance of one metre in the direction of that force. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition According to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures the joule is defined as "the work done when the point of application of 1 MKS unit of force ewtonmoves a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force." In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule is also equivalent to any of the following: * The work required to move an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joule
The joule ( , or ; symbol: J) is the unit of energy in the International System of Units (SI). In terms of SI base units, one joule corresponds to one kilogram- metre squared per second squared One joule is equal to the amount of work done when a force of one newton displaces a body through a distance of one metre in the direction of that force. It is also the energy dissipated as heat when an electric current of one ampere passes through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889). Definition According to the International Bureau of Weights and Measures the joule is defined as "the work done when the point of application of 1 MKS unit of force ewtonmoves a distance of 1 metre in the direction of the force." In terms of SI base units and in terms of SI derived units with special names, the joule is defined as One joule is also equivalent to any of the following: * The work required to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electricity Meter
file:Hydro quebec meter.JPG, North American domestic analog signal, analog (Galileo Ferraris, Ferraris disk) electricity meter. file:Transparent Electricity Meter found in Israel.JPG, Electricity meter with transparent plastic case (Israel) file:West Bengal State Electricity Distribution Company Limited electricity meter – Purulia, West Bengal, India.jpg, Electricity meter in West Bengal, IndiaAn electricity meter, electric meter, electrical meter, energy meter, or kilowatt-hour meter is a device that measures the amount of electric energy consumed by a House, residence, a business, or an electrically powered device over a time interval. Electric utility, Electric utilities use electric meters installed at customers' premises for electricity pricing, billing and monitoring purposes. They are typically calibrated in billing units, the most common one being the kilowatt hour (''kWh''). They are usually read once each billing period. When energy savings during certain periods ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Bureau Of Weights And Measures
The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (, BIPM) is an List of intergovernmental organizations, intergovernmental organisation, through which its 64 member-states act on measurement standards in areas including chemistry, ionising radiation, physical metrology, as well as the International System of Units (SI) and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It is headquartered in the Pavillon de Breteuil in Saint-Cloud, near Paris, France. The organisation has been referred to as IBWM (from its name in English) in older literature. Function The BIPM has the mandate to provide the basis for a single, coherent system of measurements throughout the world, traceable to the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI). This task takes many forms, from direct dissemination of units to coordination through international comparisons of national measurement standards (as in electricity and ionising radiation). Following consultation, a draft version of the BIPM Work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-SI Units Mentioned In The SI
The International System of Units, internationally known by the abbreviation SI (from French ), is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of units of measurement, system of measurement. It is the only system of measurement with official status in nearly every country in the world, employed in science, technology, industry, and everyday commerce. The SI system is coordinated by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures, which is abbreviated BIPM from . The SI comprises a coherence (units of measurement), coherent system of unit of measurement, units of measurement starting with seven SI base unit, base units, which are the second (symbol s, the unit of time), metre (m, length), kilogram (kg, mass), ampere (A, electric current), kelvin (K, thermodynamic temperature), mole (unit), mole (mol, amount of substance), and candela (cd, luminous intensity). The system can accommodate coherent units for an unlimited number of additional quantiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
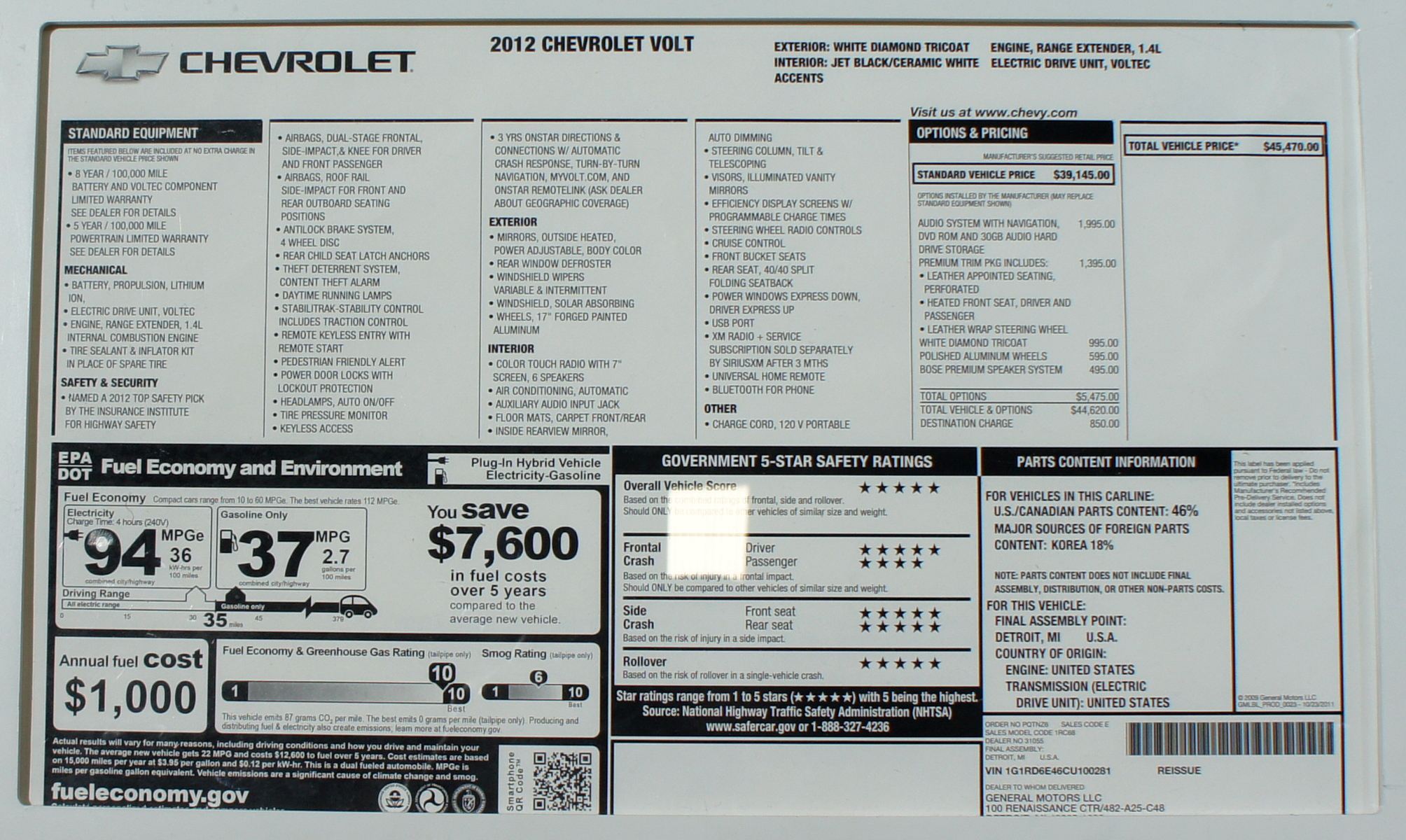
Window Sticker
The Monroney sticker, window sticker, or Automobile Information Disclosure label is a label required by federal law to be affixed on every new passenger car and light-duty truck sold in the United States. It lists the manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP), standard and optional equipment, destination charge, fuel-economy ratings, safety ratings, and certain environmental metrics. The label is named for Senator Mike Monroney (D-Oklahoma), who sponsored the 1958 legislation that created the requirement. Legislative background In 1955 Monroney’s Senate Interstate and Foreign Commerce subcommittee investigated dealer practices that hid a car’s true price behind inflated “list” figures and undisclosed fees. To give purchasers reliable information, he introduced the Automobile Information Disclosure Act of 1958. President Dwight D. Eisenhower signed it on July 7, 1958 (Pub.L. 85-506), and it took effect on January 1, 1959. The law—codified at 15 U.S.C. §§ 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Standards And Technology
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into Outline of physical science, physical science laboratory programs that include Nanotechnology, nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASTM
ASTM International, formerly known as American Society for Testing and Materials, is a standards organization that develops and publishes voluntary consensus technical international standards for a wide range of materials, products, systems and services. Some 12,575 apply globally. The headquarters is in West Conshohocken, Pennsylvania, about northwest of Philadelphia. It was founded in 1902 as the American Section of the International Association for Testing Materials. In addition to its traditional standards work, ASTM operates several global initiatives advancing additive manufacturing, advanced manufacturing, and emerging technologies, including the Additive Manufacturing Center of Excellence (AM CoE), the acquisition oWohlers Associatesfor market intelligence and advisory services, and the NIST-funded Standardization Center of Excellence (SCOE). History In 1898, a group of scientists and engineers, led by chemist, industry leader, and proponent of standardization Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it split into state- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |