Ghagghar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Ghaggar-Hakra River () is an


 The Ghaggar is an intermittent
The Ghaggar is an intermittent
"The Aryan chromosome"
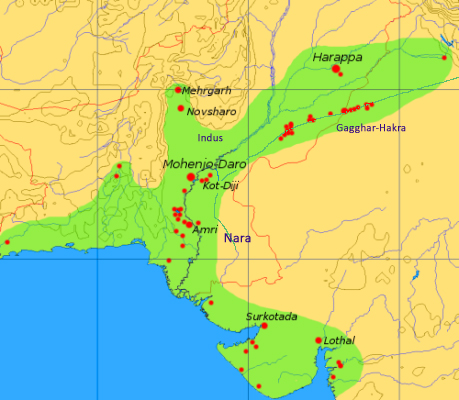
, ''The Indian Express'' leading to a change of vegetation, triggering "higher mobility and transition to nomadic cattle breeding". These migrations eventually resulted in the Indo-Aryan migrations into South Asia. Most of the Harappan sites along the Ghaggar-Hakra are presently found in desert country, and have remained undisturbed since the end of the Indus Civilization. This contrasts with the heavy alluvium of the Indus and other large Panjab rivers that have obscured Harappan sites, including part of
The Print, 24 Feb 2024.
The rivers Sarasvati: Reconciling the sacred texts
, blog post based on ''The Vedic People: Their History and Geography''.
Ghaggar RiverHakra canal (partly on the Hakra bed)
*OpenStreetMap
Nara Canal
* ttp://www.mapsofindia.com/history/sarasvati-river.html Map of the ancient Ghaggar and Hakra rivers mapsofindia.com
Sarasvati–Sindhu civilization and Sarasvati River
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ghaggar-Hakra River Rivers of Himachal Pradesh Rivers of Rajasthan Rivers of Punjab, India Rivers of Haryana Rivers of Sindh Indus Valley Civilisation Rigvedic rivers Indus basin International rivers of Asia Sarasvati River Rivers of Pakistan
intermittent river
Intermittent, temporary or seasonal rivers or streams cease to flow every year or at least twice every five years. Such rivers drain large arid and semi-arid areas, covering approximately a third of the Earth's surface. The extent of tempora ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
that flows only during the monsoon season
The wet season (sometimes called the rainy season or monsoon season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least one month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used a ...
. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage
The Ottu barrage, sometimes spelled as the Otu barrage and also known as Ottu Head, is a masonry weir on the Ghaggar-Hakra River in Sirsa, Haryana state of India that creates a large water reservoir out of the formerly-small Dhanur lake, locate ...
at , and as Hakra downstream of the barrage in the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
. In pre-Harappan times the Ghaggar was a tributary of the Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
. It is still connected to this paleochannel of the Sutlej, and possibly the Yamuna, which ended in the Nara River, presently a delta channel of the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
joining the sea via Sir Creek
Sir Creek ( ), originally Ban Ganga, is a 96 km (60 mi) tidal estuary in the uninhabited marshlands of the Indus River Delta on the border between India and Pakistan. The creek flows into the Arabian Sea and separates Gujarat state in India f ...
.
The Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
changed its course about 8,000–10,000 years ago, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers terminating in the Thar Desert. The Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
prospered when the monsoons that fed the rivers diminished around 5,000 years ago, and a large number of sites from the Mature Indus Valley Civilisation (2600–1900 BCE) are found along the middle course of the (dried-up) Hakra in Pakistan. Around 4,000 years ago, the Indus Valley Civilisation declined when the monsoons further diminished, and the Ghaggar-Hakra dried up, becoming a small seasonal river.
19th and early 20th century scholars, but also some more recent authors, have suggested that the Ghaggar-Hakra might be the defunct remains of the Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River () is a Apotheosis, deified myth, mythological Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedas, Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religio ...
mentioned in the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
, fed by Himalayan-fed rivers, despite the fact that the Ghaggar-Hakra had dried up by that time.
River course
The basin consists of two parts,Khadir and Bangar
Khādir or Khadar and Bangar, Bāngur or Bhangar (, ) are terms used in Hindi, Urdu, Punjabi and Sindhi in the Indo-Gangetic plains of North India and Pakistan to differentiate between two types of river plains and alluvial soils. Bangur an ...
. ''Bangar'' are the higher banks that are not flooded in rainy season, while ''khadar'' refers to the lower flood-prone area.
Ghaggar River


 The Ghaggar is an intermittent
The Ghaggar is an intermittent river
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, flowing during the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
rain
Rain is a form of precipitation where water drop (liquid), droplets that have condensation, condensed from Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water vapor fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is res ...
s. It originates in the village of Dagshai
Dagshai, also known as Daagh-e-Shahi, is one of the oldest cantonment towns in the Solan district, Solan district of Himachal Pradesh, India. It is situated on top of a 5,689-foot (1,734-m) high hillock that stands sphinx-like astride the Kalk ...
in the Shivalik Hills
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas.
The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and are also home to the Soanian Middle Paleo ...
of Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; Sanskrit: ''himācāl prādes;'' "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a States and union territories of India, state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen Indian Himalayan ...
at an elevation of above mean sea level and flows through Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
and Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
states into Rajasthan
Rajasthan (; Literal translation, lit. 'Land of Kings') is a States and union territories of India, state in northwestern India. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the List of states and union territories of ...
; just southwest of Sirsa, Haryana
Sirsa is a city and a municipal council in Sirsa district in the westernmost region of the Indian state of Haryana, bordering Punjab and Rajasthan. It is located near the Thar Desert, 250 kilometres north-west of New Delhi and 260 kilometers so ...
and by the side of Talwara Lake in Rajasthan.
Dammed at Ottu barrage
The Ottu barrage, sometimes spelled as the Otu barrage and also known as Ottu Head, is a masonry weir on the Ghaggar-Hakra River in Sirsa, Haryana state of India that creates a large water reservoir out of the formerly-small Dhanur lake, locate ...
near Sirsa, Ghaggar feeds two irrigation canals that extend into Rajasthan.
Tributaries of the Ghaggar
The main tributaries of the Ghaggar are theKaushalya river
The Kaushalya river, a tributary of Ghaggar river, is a river in Panchkula district of Haryana state of India.
Origin and route
The Kaushalya river rises in the Shivalik hills on the border of Haryana and Himachal Pradesh State, and flows th ...
, Markanda, Sarsuti
The Sarsuti river, originating in Sivalik Hills and flowing through the palaeochannel of Yamuna, is a tributary of Ghaggar river in of Haryana state of India.B.K. Bhadra and J.R. SharmaSatellite images as scientific tool for Sarasvati Paleochann ...
, Tangri and Chautang
The Chautang is a seasonal river, originating in the Sivalik Hills, in the Indian state of Haryana. The Chautang River is a tributary of the Sarsuti river which in turn is a tributary of the Ghaggar river.
Origin and route
The Chautang river ...
.
The Kaushalya river is a tributary of Ghaggar river on the left side of Ghaggar-Hakra. It flows in the Panchkula district
Panchkula district was formed as the 17th district of the Indian state of Haryana on 15August 1995. It comprises two sub divisions and two tehsils: Panchkula and Kalka. It has 264 villages, out of which 12 are uninhabited and ten wholly merged ...
of Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
state of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
and converges with Ghaggar river near Pinjore
Pinjore is a town in Panchkula district in the Indian state of Haryana. This residential 'township', located close to Panchkula, Chandigarh, is set over 1,800 feet above the sea level in a valley, overlooking the Sivalik Hills. Pinjore is kn ...
just downstream of Kaushalya Dam
The Kaushalya Dam (Hindi: कौशल्या बांध) is an earth-fill embankment dam on the Kaushalya river, which is a tributary of Ghaggar-Hakra River ( modern remnant of ancient Sarasvati river), in Pinjore of Haryana state, India. ...
.
Hakra River
The Hakra is the dried-out channel of ariver
A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside Subterranean river, caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of ...
near Fort Abbas
Fort Abbas (), (), formerly Pholra, is a town in Bahawalnagar District in the Cholistan Desert of Punjab, Pakistan. It is situated south of Haroonabad, near Faqirwali, on the border of Pakistan and India
India, officially the R ...
city in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
that is the continuation of the Ghaggar River in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
. The Hakra channel is connected to paleochannels of the Sutlej and the Yamuna, which ended in the Nara River, a delta channel of the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
joining the sea via Sir Creek
Sir Creek ( ), originally Ban Ganga, is a 96 km (60 mi) tidal estuary in the uninhabited marshlands of the Indus River Delta on the border between India and Pakistan. The creek flows into the Arabian Sea and separates Gujarat state in India f ...
. The Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
changed its course about 8,000-10,000 years ago, leaving the Ghaggar-Hakra as a system of monsoon-fed rivers terminating in the Thar Desert.
This Sutlej/Yamuna paleochannel streamed through Sindh
Sindh ( ; ; , ; abbr. SD, historically romanized as Sind (caliphal province), Sind or Scinde) is a Administrative units of Pakistan, province of Pakistan. Located in the Geography of Pakistan, southeastern region of the country, Sindh is t ...
, and its sign can be found in Sindh areas such as Khairpur
Khairpur ( Sindhi, ) is a city and the capital of the Khairpur Mirs District of Pakistan's Sindh province.
History
The Talpur dynasty was established in 1783 by Mir Fateh Ali Khan, who declared himself the first ''Rais'', or ruler of Sindh, a ...
, Nawabshah
Nawabshah is a headquarter of Nawabshah Tehsil in Shaheed Benazirabad District of Sindh province, Pakistan. This city is situated in the middle of Sindh province. It is the List of most populous cities in Pakistan, 27th most populous city in P ...
, Sanghar
Sanghar (; English: Sānghar) is a city in Sanghar District, Sindh, Pakistan. Sanghar is the headquarters of Sanghar District and Sanghar Taluka (a subdivision of the district). The driving distance of Sangher from Karachi is 268 kilometers ...
and Tharparkar
Tharparkar (Dhatki language, Dhatki/; , ), also known as Thar, is a district in Sindh province in Pakistan, headquartered at Mithi. Before Indian independence it was known as the Thar and Parkar (1901–1947) or Eastern Sindh Frontier Distr ...
.
A large number of sites from the Mature Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
(2600–1900 BCE) are found along the middle course of the (dried-up) Hakra in Pakistan. IVC-sites have not been found further south than the middle of Bahawalpur district, and it has been assumed that the Hakra ended there in a series of terminal lakes.
Paleography
While there is general agreement that the river courses in the Indus Basin have frequently changed course, the exact sequence of these changes and their dating have been problematic. Older publications have suggested that the Sutlej and the Yamuna drained into the Hakra well into Mature Harappan times, providing ample volume to the supply provided by the monsoon-fed Ghaggar. The Sutlej and Yamuna then changed course between 2500 BCE and 1900 BCE, due to either tectonic events or "slightly altered gradients on the extremely flat plains," resulting in the drying-up of the Hakra in theThar Desert
The Thar Desert (), also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent that covers an area of in India and Pakistan. It is the world's 18th-largest desert, and the world's 9th-large ...
. More recent publications have shown that the Sutlej and the Yamuna shifted course well before Harappan times, leaving the monsoon-fed Ghaggar-Hakra which dried-up during late Harappan times.
Pre-Holocene
The paleo-channel of the Sutlej was active until the end of the Ice Age, some 10,000–8,000 years ago, emptying into theRann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located mostly in the Kutch district of the Indian state of Gujarat, with a minor portion extending into the Sindh province of Pakistan. ...
via the Nara river.
Clift ''et al''. (2012), using dating of zircon sand grains, have shown that subsurface river channels near the Indus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
sites in Cholistan
The Cholistan Desert (; ; Saraiki: ), also locally known as Rohi (), is a desert in the southern part of Punjab, Pakistan, Pakistani Punjab that forms part of the Greater Thar Desert, which extends to Sindh province and the Indian state of Rajast ...
immediately below the dry Ghaggar-Hakra bed show sediment affinity with the Beas River in the western sites and the Sutlej and the Yamuna in the eastern ones, suggesting that the Yamuna itself, or a channel of the Yamuna, along with a channel of the Sutlej may have flowed west some time between 47,000 BCE and 10,000 BCE, well before the beginnings of Indus Civilization.
Analysis of sand grains using optically stimulated luminescence
In physics, optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) is a method for measuring doses from ionizing radiation. It is used in at least two applications:
* Luminescence dating of ancient materials: mainly geological sediments and sometimes fired pot ...
by Ajit Singh and others in 2017 indicated that the suggested paleochannel of the Ghaggar-Hakra is actually a former course of the Sutlej, which diverted to its present course before the development of the Harappan Civilisation. The abandonment of this older course by the Sutlej started 15,000 years ago, and was complete by 8,000 years ago. Ajit Singh et al. conclude that the urban populations settled not along a perennial river, but a monsoon-fed seasonal river that was not subject to devastating floods.
Khonde et al. (2017) confirm that the Great Rann of Kutch received sediments from a different source than the Indus, but this source stopped supplying sediments after ca. 10,000 years ago. Likewise, Dave et al. (2019) state that " r results disprove the proposed link between ancient settlements and large rivers from the Himalayas and indicate that the major palaeo-fluvial system traversing through this region ceased long before the establishment of the Harappan civilisation."
Indus Valley Civilisation

Mature IVC
During the IVC, the Ghaggar-Hakra fluvial system was not a large glacier-fed Himalayan river, but a monsoonal-fed river. The Indus Valley Civilisation prospered when the monsoons that fed the rivers diminished around 5,000 years ago, and a large number of sites from the MatureIndus Valley Civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
(2600-1900 BCE) are found along the middle course of the (dried-up) Hakra in Pakistan. Around 4,000 the Indus Valley Civilisation declined when the monsoons further diminished, and the Ghaggar-Hakra dried-up, becoming a small seasonal river.
According to archaeologist Rita Wright, the large number of documented sites may be due to the ephemeral nature of the settlements, with the inhabitants frequently moving around in pursuit of water. According to archaeologist Shereen Ratnagar, many Ghaggar-Hakra sites in India are actually those of local cultures; some sites display contact with Harappan civilisation, but only a few are fully developed Harappan ones. Hetalben Sidhav notes that claims of a large number of Ghaggar-Hakra sites are politically motivated and exaggerated. While the Indus remained an active river, the Ghaggar-Hakra dried up, leaving many sites undisturbed, which explains why such a large number of sites has been found.
Drying-up of the Hakra and decline of the IVC
Late in the 2nd millennium BCE the Ghaggar-Hakra fluvial system dried up, becoming the small seasonal river it is today, which affected the Harappan civilisation. Paleobotanical information documents the aridity that developed after the drying up of the river. The diminishing of the monsoons particular affected the Ghaggar-Hakra system, which became ephemeral and was largely abandoned, with the IVC reorganizing in local settlements some 4000 years ago. In the late Harappan period the number of late Harappan sites in the middle Ghaggar-Hakra channel and in the Indus valley diminished, while it expanded in the upper Ghaggar-Sutlej channels and in Saurashtra. The IVC-people migrated east toward the more humid regions of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, where the decentralised late Harappan phase took place. The same widespread aridification in the third millennium BCE also led to water shortages and ecological changes in the Eurasian steppes,Rajesh Kochhar (2017)"The Aryan chromosome"
, ''The Indian Express'' leading to a change of vegetation, triggering "higher mobility and transition to nomadic cattle breeding". These migrations eventually resulted in the Indo-Aryan migrations into South Asia. Most of the Harappan sites along the Ghaggar-Hakra are presently found in desert country, and have remained undisturbed since the end of the Indus Civilization. This contrasts with the heavy alluvium of the Indus and other large Panjab rivers that have obscured Harappan sites, including part of
Mohenjo Daro
Mohenjo-daro (; , ; ) is an archaeological site in Larkana District, Sindh, Pakistan. Built 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilisation, and one of the world's earliest major cities, contemporaneo ...
. Painted Grey Ware
The Painted Grey Ware culture (PGW) is an Iron Age Indo-Aryan culture of the western Gangetic plain and the Ghaggar-Hakra valley in the Indian subcontinent, conventionally dated 1200 to 600–500 BCE, or from 1300 to 500–300 BCE. It is a suc ...
sites ( 1000–600 BCE) have been found at former IVC-sites at the middle and upper Ghaggar-Hakra channel, and have also been found in the bed and not on the banks of the Ghaggar-Hakra river, which suggests that river was certainly dried up by this period. The sparse distribution of the Painted Gray Ware sites in the Ghaggar river valley indicates that during this period the Ghaggar river had already dried up.
Archaeological explorations
Between 1940 and 1943,Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
(; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at Indian universities.
...
undertook 2 expeditions to along the Ghaggar-Hakra River to find physical evidence of the Saraswati River
The Sarasvati River () is a deified mythological river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.
As a phys ...
described in the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
. While he didn't definitively establish the region's chronological archaeological sequence, his work significantly advanced Indian archaeology. Surveying from Hanumangarh
Hanumangarh is a city and municipal council in the Indian state of Rajasthan, situated on the banks of the river Ghaggar also identified as ancient Sarasvati river, located about 400 km from Delhi. It is the administrative headquarter o ...
to Bahawalpur
Bahawalpur (Urdu: ; ) is a city in Punjab, Pakistan. It is the 13th largest city of Pakistan and List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, 8th most populous city of Punjab. Bahawalpur is the capital of Bahawalpur Division.
Founded in ...
, he identified approximately 100 prehistoric and historical sites, conducting exploratory excavations at some. His observations on the geographical spread of these sites proved valuable to later researchers, including Amalananda Ghosh
Amalananda Ghosh (3 March 1910 – 1981) was an Indian archaeologist, author and editor of numerous works on India's ancient civilizations, and the organizer and director of archaeological expeditions during the mid-1900s.
Education
Ghosh was ...
(3 March 1910 – 1981) and Katy Dalal. Notably, he documented sites such as Munda __NOTOC__
Munda may refer to:
Places India
* Munda, a village in Hanumangarh district, Rajasthan, India
* Munda Majra, a former village in Haryana, India
* Munda Pind, a village in Punjab, India
Pakistan
* Munda, a village near Bilyamin in Kur ...
, Bhadrakali Temple
Bhadrakali Temple ( Nepali :भद्रकाली मन्दिर) is a temple on the East of Pokhara in Kundahar, atop a small hill. It is dedicated to the Goddess Kali
Kali (; , ), also called Kalika, is a major goddess in Hind ...
, and Derwar.From Kashmir to China—Aurel Stein’s expeditions helped unlock secrets of ancient civilisationsThe Print, 24 Feb 2024.
Identification with the Rigvedic Sarasvati River
Since the 19th century, proposals have been made to identify the mythological Sarasvati River with the Ghaggar-Hakra River. The Sarasvati is often mentioned in the Rig Veda, which describes it as a mighty river located between the Indus and the Ganges, while later Vedic texts describe it as disappearing in the desert. Arguments have been made that the Ghaggar-Hakra was such a mighty river, due to tributaries which were supposed to receive snow melt waters from the Himalayas. Yet, more recent research shows that the Ghaggar-Hakra was monsoon-fed during Harappan times, and had already dried-up during Vedic times.Rig Veda
The Sarasvati River is mentioned in all books of theRigveda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
except the fourth. It is the only river with hymns entirely dedicated to it: RV 6.61, RV 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to '' Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are add ...
.95 and RV 7
The seventh Mandala of the Rigveda ("book 7", "RV 7") has 104 hymns. In the Rigveda Anukramani, all hymns in this book are attributed to '' Vashista''. Hymn 32 is additionally credited to Sakti Vashista, and hymns 101-102 (to Parjanya) are add ...
.96. It is mentioned as a divine and large river, which flows "from the mountains to the samudra," which some take as the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
. The Rig Veda was composed during the latter part of the late Harappan period, and according to Shaffer, the reason for the predominance of the Sarasvati in the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
is the late Harappan
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE t ...
(1900–1300 BCE) population shift eastwards to Haryana
Haryana () is a States and union territories of India, state located in the northern part of India. It was carved out after the linguistic reorganisation of Punjab, India, Punjab on 1 November 1966. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with les ...
.
The identification with the Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River () is a Apotheosis, deified myth, mythological Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedas, Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religio ...
is based on the mentions in Vedic texts, ''e.g.'' in the enumeration of the rivers in Rigveda 10.75.05; the order is Ganga
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary riv ...
, Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
, Sarasvati, Sutudri
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of th ...
, Parusni. Later Vedic texts record the river as disappearing at Vinasana (literally, "the disappearing") or Upamajjana, and in post-Vedic texts as joining both the Yamuna and Ganges as an invisible river at Prayaga (Allahabad). Some claim that the sanctity of the modern Ganges is directly related to its assumption of the holy, life-giving waters of the ancient Saraswati River. The Mahabharata
The ''Mahābhārata'' ( ; , , ) is one of the two major Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epics of ancient India revered as Smriti texts in Hinduism, the other being the ''Ramayana, Rāmāyaṇa''. It narrates the events and aftermath of the Kuru ...
says that the Sarasvati River dried up in a desert (at a place named Vinasana or Adarsana).
Identification
Nineteenth and early 20th century scholars, such as orientalistChristian Lassen
Christian Lassen (22 October 1800 – 8 May 1876) was a Norwegian-born, German orientalist and Indologist. He was a professor of Old Indian language and literature at the University of Bonn.
Biography
He was born at Bergen, Norway where he a ...
(1800–1876), philologist and Indologist Max Müller
Friedrich Max Müller (; 6 December 1823 – 28 October 1900) was a German-born British comparative philologist and oriental studies, Orientalist. He was one of the founders of the Western academic disciplines of Indology and religious s ...
(1823–1900), archaeologist Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
(; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at Indian universities.
...
(1862–1943), and geologist R. D. Oldham (1858–1936), had considered that the Ghaggar-Hakra might be the defunct remains of a river, the Sarasvati
Saraswati (, ), also spelled as Sarasvati, is one of the principal Devi, goddesses in Hinduism, revered as the goddess of knowledge, education, learning, arts, speech, poetry, music, purification, language and culture. Together with the godde ...
, invoked in the orally transmitted collection of ancient Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
hymns, the Rig Veda
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from wikt:ऋच्, ऋच्, "praise" and wikt:वेद, वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian Miscellany, collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canoni ...
composed to 1200 BCE.
More recently, but writing before Giosan's 2012 publication and supposing a late Harappan diversion of the Sutlej and the Yamuna, several scholars have identified the old Ghaggar-Hakra River with the Vedic Sarasvati River
The Sarasvati River () is a Apotheosis, deified myth, mythological Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedas, Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religio ...
and the Chautang with the Drishadvati River
The Drishadvati River (IAST:, "She with many stones") is a river hypothesized by Indologists to identify the route of the Vedic river Saraswati and the state of '' Brahmavarta''. According to ''Manusmriti'', the ''Brahmavarta'', where the Rishis ...
. Gregory Possehl and Jane McIntosh refer to the Ghaggar-Hakra River as "Sarasvati" throughout their respective 2002 and 2008 books on the Indus Civilisation, and Gregory Possehl states "Linguistic, archaeological, and historical data show that the Sarasvati of the Vedas is the modern Ghaggar or Hakra."
Because most of the Indus Valley sites known so far are actually located on the Ghaggar-Hakra river and its tributaries and not on the Indus river, some Indian archaeologists, such as S.P. Gupta, have proposed to use the term "Indus Sarasvati Civilization" to refer to the Harappan culture which is named, as is common in archaeology, after the first place where the culture was discovered.
Objections
Romila Thapar
Romila Thapar (born 30 November 1931) is an Indian historian. Her principal area of study is ancient India, a field in which she is pre-eminent. Quotr: "The pre-eminent interpreter of ancient Indian history today. ... " Thapar is a Professor ...
terms the identification "controversial" and dismisses it, noticing that the descriptions of Sarasvati flowing through the "high mountains" does not tally with Ghaggar's course and suggests that Sarasvati is Haraxvati of Afghanistan which is also known as the Helmand river
The Helmand river (Pashto/Dari: ; Ancient Greek: Ἐτύμανδρος, ''Etýmandros''; Latin: '), also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand, is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It o ...
. Wilke suggests that the identification is problematic since the Ghaggar-Hakra river was already dried up at the time of the composition of the Vedas, let alone the migration of the Vedic people into northern India.
The idea that the Ghaggar-Hakra was fed by Himalayan sources has also been contradicted by recent geophysical research, which shows that the Ghaggar-Hakra system, although having greater discharge in Harappan times which was enough to sustain human habitation, was not sourced by the glaciers and snows of the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
, but rather by a system of perennial monsoon-fed rivers. In contrast to all Himalayan rivers in the region that dug out wide valleys in their own sediments as the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
declined, no such valley exists between the Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
and the Yamuna
The Yamuna (; ) is the second-largest tributary river of the Ganges by discharge and the longest tributary in India. Originating from the Yamunotri Glacier at a height of about on the southwestern slopes of Bandarpunch peaks of the Low ...
, demonstrating that neither the Ghaggar-Hakra nor any other Sarasvati candidate in that region had a Himalayan source.
Rajesh Kocchar further notes that, even if the Sutlej and the Yamuna had drained into the Ghaggar during Vedic period
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, between the e ...
, it still would not fit the Rig Vedic
The ''Rigveda'' or ''Rig Veda'' (, , from ऋच्, "praise" and वेद, "knowledge") is an ancient Indian collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns (''sūktas''). It is one of the four sacred canonical Hindu texts (''śruti'') known as the ...
descriptions because "the snow-fed Satluj and Yamuna would strengthen nly thelower Ghaggar. heupper Ghaggar would still be as puny as it is today." According to Rajesh Kocchar, there are two Sarasvati rivers mentioned in the Rigveda. The older one described in the family books of the Rigveda, which he calls ''Naditama Sarasvati'', drains into a samudra
Samudra (Sanskrit: समुद्र; ) is a Sanskrit term literally meaning the "gathering together of waters" (''-'' "together" and ''-udra'' "water"). It refers to an ocean, sea or confluence. It also forms the name of Samudradeva (Sanskrit: ...
. The newer one described in the tenth book of Rigveda as well as later Vedic texts, which he calls ''Vinasana Sarasvati'', disappears in the sands. The ''Vinasana Sarasvati'' has been "accepted by all" to be the same as the Ghaggar-Hakra river. The description of the ''Naditama Sarasvati'' in the Rigveda matches the physical features of the Helmand River
The Helmand river (Pashto/Dari: ; Ancient Greek: Ἐτύμανδρος, ''Etýmandros''; Latin: '), also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand, is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It o ...
in Afghanistan, more precisely its tributary the Harut River
The Harut River or Adraskan River is a river of Afghanistan which belongs to the Sistan Basin. The source of the river lies in the mountains to the southeast of Herat
Herāt (; Dari/Pashto: هرات) is an oasis city and the third-largest ...
, whose older name was ''Haraxvatī'' in Avestan. Ganga and Yamuna, he takes to be small streams in its vicinity. When the Vedic people moved east into Punjab, they named the new rivers they encountered after the old rivers they knew from Helmand.Rajesh KoccharThe rivers Sarasvati: Reconciling the sacred texts
, blog post based on ''The Vedic People: Their History and Geography''.
See also
*Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of t ...
*Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary rive ...
*Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
Notes
References
Sources
;Printed sources * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * ;Web-sourcesExternal links
*OpenStreetMapGhaggar River
*OpenStreetMap
Nara Canal
* ttp://www.mapsofindia.com/history/sarasvati-river.html Map of the ancient Ghaggar and Hakra rivers mapsofindia.com
Sarasvati–Sindhu civilization and Sarasvati River
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ghaggar-Hakra River Rivers of Himachal Pradesh Rivers of Rajasthan Rivers of Punjab, India Rivers of Haryana Rivers of Sindh Indus Valley Civilisation Rigvedic rivers Indus basin International rivers of Asia Sarasvati River Rivers of Pakistan