|
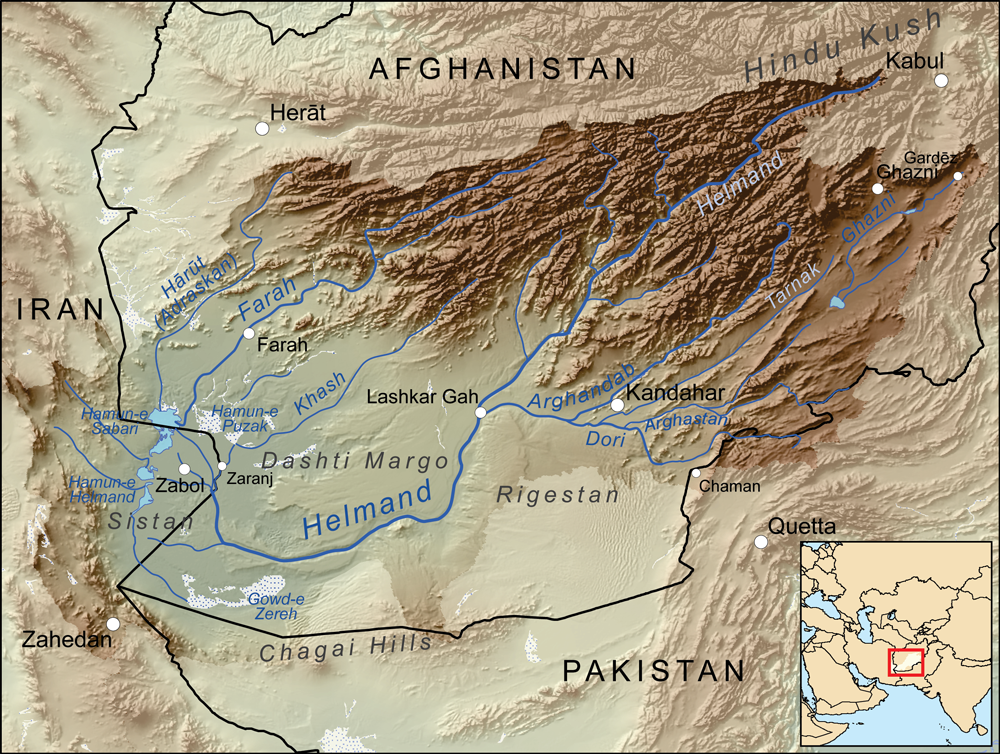
Helmand River
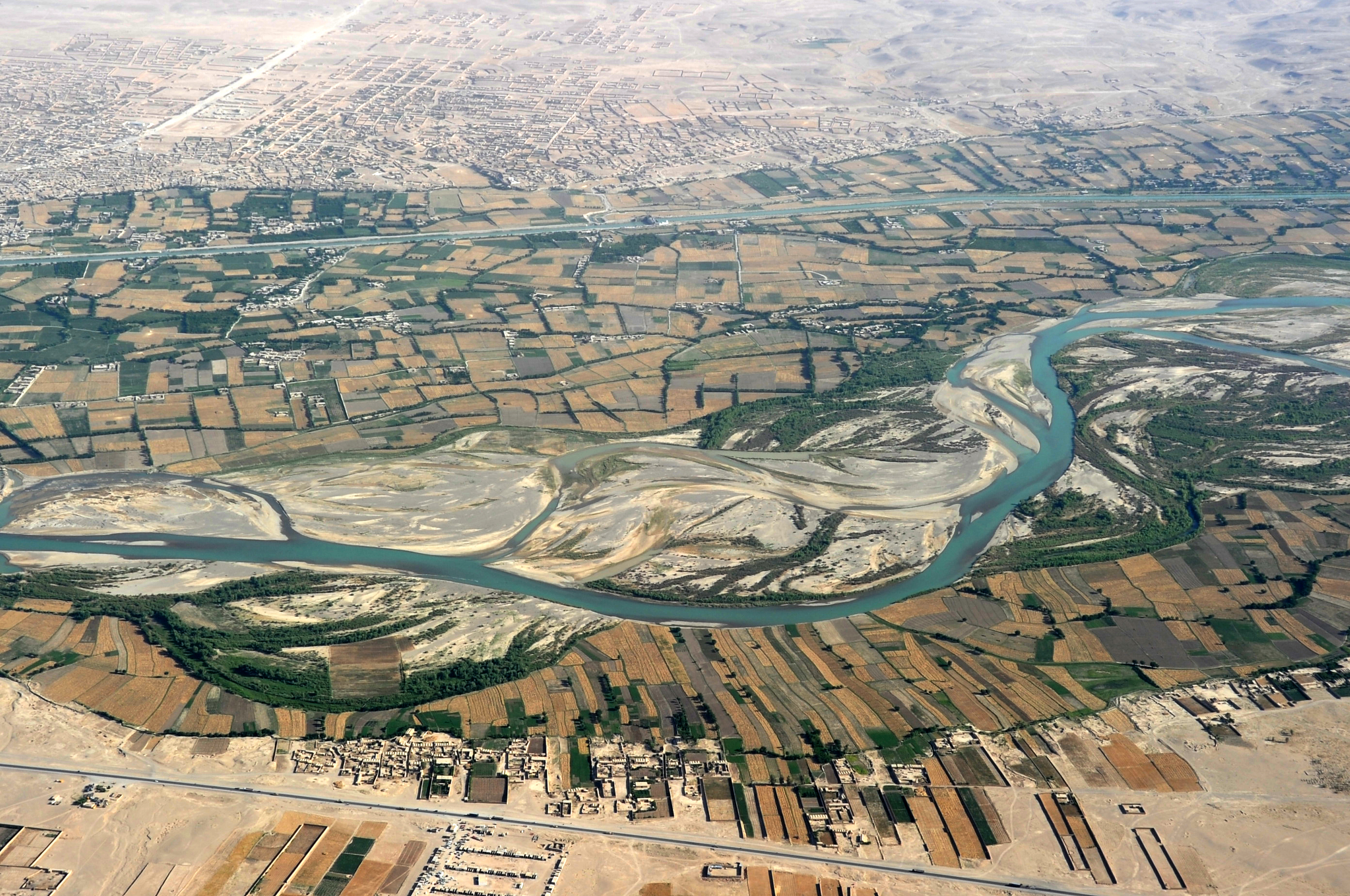
The Helmand river (Pashto/Dari: ; Ancient Greek: Ἐτύμανδρος, ''Etýmandros''; Latin: '), also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand, is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It originates in the Sanglakh Range of the Hindu Kush mountains in the northeastern part of Maidan Wardak Province, where it is separated from the watershed of the Kabul River by the Unai Pass. The Helmand feeds into the Hamun Lake on the border of Afghanistan and Iran. Etymology The name comes from the Avestan ''Haētumant'', literally "dammed, having a dam", which referred to the Helmand River and the irrigated areas around it. The word Haetumant is cognate with Sanskrit Setumatī meaning "one which has a dam." Geography The Helmand stretches for . It rises in the northeastern part of Maidan Wardak Province in the Hindu Kush mountains, about 40 km west of Kabul (), flowing southwestward through Daykundi Province and Uruzga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boghra Irrigation Canal
Boghra Irrigation Canal or Nahr-e Bughra is a canal some 155 kilometres long in central Afghanistan in Helmand Province, serving to divert water from the Helmand River The Helmand river (Pashto/Dari: ; Ancient Greek: Ἐτύμανδρος, ''Etýmandros''; Latin: '), also spelled Helmend, or Helmund, Hirmand, is the longest river in Afghanistan and the primary watershed for the endorheic Sistan Basin. It o ... and the Arghandab for farmland. The Afghan government received US funding of $21 million on November 23, 1949, for the canal system. The Boghra, Shamalon and Marja canals were completed by 1954. It is controlled by the Helmand and Arghandab Valley Authority. References Canals in Afghanistan Helmand River Buildings and structures in Helmand Province {{Helmand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maidan Wardak Province
Wardak is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in central Afghanistan. Its capital is the closest provincial city to Kabul. Wardak Have 8 District. Wardak or Wardag (Dari/Pashto: ), is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the central region of Afghanistan. It is divided into eight Districts of Afghanistan, districts and has a population of approximately 500,000. The capital of the province is Maidan Shar, Maidan Shar(Maidan City), while the most populous district in the province is Saydabad District. Wardak is known for one of its famous high peak mountain known as (Shah Foladi). In 2021, the Taliban gained control of the province during the 2021 Taliban offensive. History During the Communist Afghanistan, communist times, the people of Wardak never gave significant support to the communist government, but the people of Maidan Shahr did sympathize with them. Wardak has also threatened uprisings against the Taliban in Saydabad, numerous schooling system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zabol
Zabol () is a city in the Central District of Zabol County, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Zabol is near the border with Afghanistan. Demographics Language and ethnicity The people of Zabol are a mix of Persians who speak a variant of the Persian language known as '' Sistani'' or Seistani, and a small minority of Baloch who speak Balochi, a Northwestern Iranian language. Population At the time of the 2006 National Census, the city's population was 130,642 in 27,867 households. The 2011 census counted 137,722 people in 33,957 households. The 2016 census measured the population of the city as 134,950 people in 35,401 households. Geography Location Zabol is located near Lake Hamun, in the endorheic Sīstān Basin, and the region is irrigated by the Helmand River. Lake Hamun is a seasonal lake that is often dry. Zabol is connected by road to Milak and Zaranj (across the border in Afghanistan). The Delaram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamun-i-Helmand
Lake Hāmūn (, ''Daryāche-ye Hāmūn''; ), or the Hamoun Oasis, is a seasonal lake and wetlands in the endorheic Sīstān Basin in the Sistan region on the Afghanistan–Iran border. In Iran, it is also known as ''Hāmūn-e Helmand'', ''Hāmūn-e Hīrmand'', or ''Daryāche-ye Sīstān'' ("Lake Sīstān"). '' Hāmūn'' is a generic term which refers to shallow lakes (or lagoons), usually seasonal, that occur in the deserts of southeast Iran and adjacent areas of Afghanistan and Pakistan as a product of snowmelt in nearby mountains in spring. The term Hāmūn Lake (or Lake Hāmūn) equally applies to ''Hāmūn-e Helmand'' (entirely in Iran), as well to the shallow lakes Hāmūn-e Sabari and Hāmūn-e Puzak, which extend into the territory of present-day Afghanistan with the latter almost entirely inside Afghanistan. The Hamun is fed by numerous seasonal water tributaries; the main tributary is the perennial Helmand River, which originates in the Hindu Kush mountains in Afghanist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sistan
Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly corresponding to the then Achaemenid region of Drangiana and extending southwards of the Helmand River not far off from the city of Alexandria Arachosia, Alexandria in Arachosia. Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, which empties into the Hamun Lake, located in Zabol, that forms part of the border between Iran and Afghanistan. Etymology Sistan derives its name from ''Sakastan'' ("the land of the Saka"). The Sakas were a Scythians, Scythian tribe which migrated to the Iranian Plateau and Indus valley between the 2nd century BC and the 1st century, where they carved a kingdom known as the Indo-Scythians, Indo-Scythian Kingdom. In the Bundahishn, a Zoroastrian scripture written in Middle Persian, Pahlavi, the province is called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasht-e Margo
Dasht-e Margo ( Persian: دشت مارگو), also Dasht-e Mārgow or Dasht-e Margoh, is a desert region in the southern provinces of Nimruz and Helmand in Afghanistan. The desert is adjacent to the Dasht-e Khash and Registan Desert. It is the world's 20th largest desert at about 150,000 km2 in area with an elevation of 500–700 meters above sea level. The desert consists mainly of sand masses and rocky-clayish plains with solonchaks, takirs, and rarely oases. The desert's name means "Desert of Death" in Dari, with ''dasht'' meaning "plain In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ..." and ''margo'' meaning "death". References External links * Deserts of Afghanistan Geography of Helmand Province Geography of Nimruz Province {{Nimruz-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmand Province
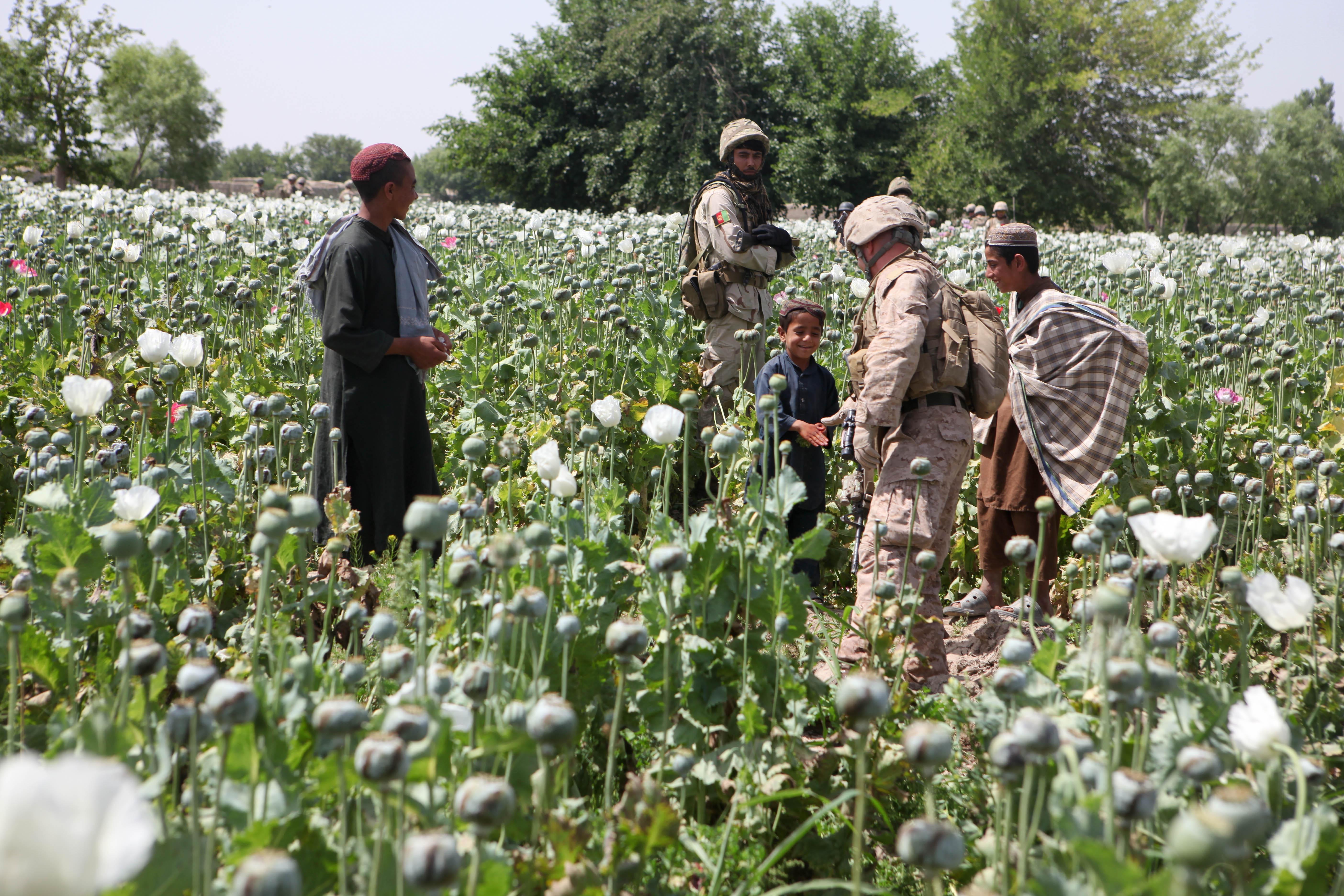
Helmand (Pashto language, Pashto/Dari language, Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering area. The province contains 18 Districts of Afghanistan, districts, encompassing over 1,000 villages, and roughly 1,446,230 settled people. Lashkargah serves as the provincial capital. Helmand was part of the ''Loy Kandahar, Greater Kandahar'' region until made into a separate province by the Politics of Afghanistan, Afghan government in the 20th century. It is largely populated by Pashtuns. The Helmand River flows through the mainly desert region of the province, providing water used for irrigation. The Kajaki Dam, which is one of List of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, Afghanistan's major reservoirs, is located in the Kajaki district. Helmand is believed to be one of the world's largest opium producing regions, responsible for aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lashkargah
Lashkargāh (; ), historically called Bost or Boost (), is a city in southwestern Afghanistan and the capital of Helmand Province. It is located in Lashkargah District, where the Arghandab River merges into the Helmand River. The city has a population of 201,546 as of 2006. Lashkargah is linked by major roads with Kandahar to the east, Zaranj on the border with Iran to the west, and Farah and Herat to the north-west. It is mostly very arid and desolate. However, farming does exist around the Helmand and Arghandab rivers. Bost Airport is located on the east bank of the Helmand River, five miles north of the junction of the Helmand and Arghandab rivers. Because of the trading hubs, it is Afghanistan's second largest city in size, after Kabul and before Kandahar. After several weeks of fighting in the Battle of Lashkargah, the city was captured by the Taliban on 13 August 2021, becoming the fourteenth provincial capital to be seized by the Taliban as part of the wider 2021 Tal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uruzgan Province
Uruzgan (Pashto: ; Dari: ), also spelled as Urozgan or Oruzgan, is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. Uruzgan is located in the center of the country. The population is 436,079, and the province is mostly a tribal society. Tarinkot serves as the capital of the province. Uruzgan borders the provinces of Kandahar, Daykundi, Ghazni, Zabul, and Helmand. Geography Uruzgan province is located in southern Afghanistan, bordering Zabul and Kandahar to the south, Helmand to the southwest, Daykundi to the north, and Ghazni to the east. Uruzgan covers an area of . Much of the province is mountainous or semi-mountainous terrain, while the rest of the area is made up of flat land. History The Arabs were first to arrive in Uruzgan in the 7th century when they brought Islam to the region followed by the Saffarids who conquered the place in the 9th century. The region was part of ancient Arachosia, and was ruled by the Medes before it fell to the Achaemenids. In 330 BC, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daykundi Province
Daikundi (Dari/) is one of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan, located in the central part of the country. It has a population of about 516,504 people, who are mostly peasants, traders, and shop owners. Daikundi falls into the traditionally ethnic Hazaras, Hazara region known as the Hazarajat in the highlands of central Afghanistan with the provincial capital, Nili, Afghanistan, Nili. It was carved out from the northern part of Uruzgan Province in 2004, becoming a separate province. Daikundi is surrounded by Bamyan Province in the northeast, Ghazni Province in the southeast, Uruzgan Province in the south, Helmand Province in the southwest, and Ghor Province in the northwest. Geographic The province of DaiKundi is located in central Afghanistan. The province is bordered on the south by Uruzgan, on the east by Ghazni and Bamiyan, on the north and west by Ghor, and the southeast by Helmand. Until March 2004, Dai Kundi was part of Uruzgan province. The Helmand River sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabul
Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province. The city is divided for administration into #Districts, 22 municipal districts. A 2025 estimate puts the city's population at 7.175 million. In contemporary times, Kabul has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural and economical center. Rapid urbanisation has made it the country's primate city and one of the largest cities in the world. The modern-day city of Kabul is located high in a narrow valley in the Hindu Kush mountain range, and is bounded by the Kabul River. At an elevation of , it is one of the List of capital cities by elevation, highest capital cities in the world. The center of the city contains its old neighborhoods, including the areas of Khashti Bridge, Khabgah, Kahforoshi, Saraji, Chandavel, Shorbazar, Deh-Afghanan and Ghaderdiwane. Kabul is said to be over 3,500 years old, and was mentioned at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmand River Basin Sub
Helmand (Pashto/Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering area. The province contains 18 districts, encompassing over 1,000 villages, and roughly 1,446,230 settled people. Lashkargah serves as the provincial capital. Helmand was part of the '' Greater Kandahar'' region until made into a separate province by the Afghan government in the 20th century. It is largely populated by Pashtuns. The Helmand River flows through the mainly desert region of the province, providing water used for irrigation. The Kajaki Dam, which is one of Afghanistan's major reservoirs, is located in the Kajaki district. Helmand is believed to be one of the world's largest opium producing regions, responsible for around 42% of the world's total production. This is believed to be more than the whole of Myanmar, which is the second-largest producing nati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |