gm iron duke engine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Iron Duke engine (also called 151, 2500, Pontiac 2.5, and Tech IV) is a
 GM also began selling the engine to
GM also began selling the engine to
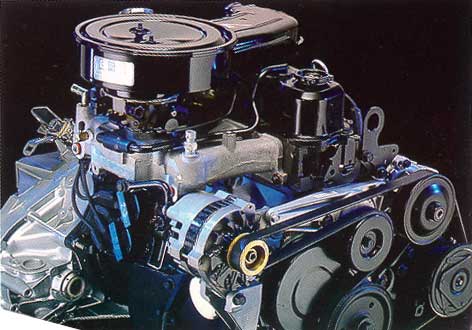
 This was replaced by a swirl-port head with 9.0:1 (instead of 8.25:1) compression ratio in 1984 for a gain. Other additions for 1985 included roller lifters, improved bearings, and a new crankshaft. Several significant changes were made in 1987, which included: an improved cylinder head, intake manifold and throttle-body fuel injection module, a more-modern serpentine belt with an automatic spring-loaded tensioner for the accessories, and a Distributorless Ignition System (DIS). This revision to the engine increased power to . In 1988, a balance shaft was added to smooth engine vibrations. Up to this point, the engine incorporated a 'dogbone' upper front engine mount secured to the cowling of the vehicle's hood latch, aiding in controlling the vibration. Further improvements in later years included new pistons, rods, crankshaft, and an in-pan oiling system. The most powerful variant of the Tech IV raised the rev limit to 5500 rpm, and achieved . The Tech IV uses the same bellhousing pattern as the 2.8 L '' 60-Degree'' V6. Over the years, the Tech IV engine has proved to be a reliable workhorse for owners when not pushed to its limits. All 1978-1990 Iron Duke engines used a micarta camshaft gear that meshed directly with a steel gear on the crankshaft. 1991-92 VIN R and U engines used a timing chain instead.
* 1982–1992 Buick Century
* 1982–1991 Buick Skylark
* 1985–1987 Buick Somerset/Somerset Regal
* 1985–1990 Chevrolet Astro Cargo Van
* 1982–1985
This was replaced by a swirl-port head with 9.0:1 (instead of 8.25:1) compression ratio in 1984 for a gain. Other additions for 1985 included roller lifters, improved bearings, and a new crankshaft. Several significant changes were made in 1987, which included: an improved cylinder head, intake manifold and throttle-body fuel injection module, a more-modern serpentine belt with an automatic spring-loaded tensioner for the accessories, and a Distributorless Ignition System (DIS). This revision to the engine increased power to . In 1988, a balance shaft was added to smooth engine vibrations. Up to this point, the engine incorporated a 'dogbone' upper front engine mount secured to the cowling of the vehicle's hood latch, aiding in controlling the vibration. Further improvements in later years included new pistons, rods, crankshaft, and an in-pan oiling system. The most powerful variant of the Tech IV raised the rev limit to 5500 rpm, and achieved . The Tech IV uses the same bellhousing pattern as the 2.8 L '' 60-Degree'' V6. Over the years, the Tech IV engine has proved to be a reliable workhorse for owners when not pushed to its limits. All 1978-1990 Iron Duke engines used a micarta camshaft gear that meshed directly with a steel gear on the crankshaft. 1991-92 VIN R and U engines used a timing chain instead.
* 1982–1992 Buick Century
* 1982–1991 Buick Skylark
* 1985–1987 Buick Somerset/Somerset Regal
* 1985–1990 Chevrolet Astro Cargo Van
* 1982–1985
Jeep 151 information
Iron Duke Gasoline engines by model Straight-four engines
Straight-4
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
piston engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common fea ...
built by the Pontiac Motor Division of General Motors from 1977 to 1993. Thereafter GM's 2.2 L OHV 4-cylinder replaced it across the entire lineup of vehicles that offered it. Although its original purpose was to serve as Pontiac's new economy car engine, it was later adapted for use in a wide variety of applications across GM's lineup in the 1980s.
Development
At the time of the 1973 oil crisis the only engines Pontiac built were , , and versions of their V8 engine. Recognizing that future products would need to be smaller and more fuel-efficient, Pontiac engineers were tasked with developing a new engine that would be suitable for these future products. The engineers considered developing smaller displacement versions of the existing V8, a V6 derived from the V8, a V4 derived from the V8, and an inline-four derived from one of the cylinder banks of the V8 (in the same fashion the 1961 Pontiac Tempest's "Trophy 4" engine), but ultimately decided to create an entirely new four-cylinder engine. The development team's design goals were to minimize noise and vibration while maximizing durability, drivability, fuel economy, and "usable" power at lower engine speeds. They began by analyzing other four-cylinder engines in production at General Motors at the time, and they found that GM do Brasil's version of the Chevrolet 153 cu in four-cylinder—with a shorter stroke and longer connecting rods—had significantly reduced secondary vibration as compared to the original Chevrolet design and the newer 2.3 L four-cylinder from the Chevrolet Vega. This obviated the need for counter-rotating balance shafts, which would have increased the weight, complexity and cost of the engine. Despite sharing the samebore
Bore or Bores often refer to:
*Boredom
* Drill
Relating to holes
* Boring (manufacturing), a machining process that enlarges a hole
** Bore (engine), the diameter of a cylinder in a piston engine or a steam locomotive
** Bore (wind instruments), ...
, stroke and cylinder spacing as the Brazilian engine, the majority of parts are not interchangeable.
Focusing on making power at lower engine speeds was a deliberate consideration in order to meet the rest of the design goals. Careful consideration was made to the design of the intake manifold and exhaust gas recirculation system to ensure power output from each cylinder was equalized. Power consumption of the water and oil pumps were reduced, and the piston rings, cylinder bores and crankshaft journals were designed to minimize friction.
To maximize durability the engine block was made of cast iron with five main bearing
Main may refer to:
Geography
*Main River (disambiguation)
**Most commonly the Main (river) in Germany
* Main, Iran, a village in Fars Province
*" Spanish Main", the Caribbean coasts of mainland Spanish territories in the 16th and 17th centuries ...
s, rather than the relatively fragile cast aluminum block used by the 2.3 L Vega engine. (Even with the cast iron block the Iron Duke only weighed about 20 pounds more.) The 2.3 L engine's belt-driven overhead camshaft
An overhead camshaft (OHC) engine is a piston engine where the camshaft is located in the cylinder head above the combustion chamber. This contrasts with earlier overhead valve engines (OHV), where the camshaft is located below the combustion ...
was eschewed in favour of an overhead valve design with timing gears. Specially-designed bolts that stretch slightly farther than a conventional bolt were used to secure the intake and exhaust manifolds to the cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head (often abbreviated to simply "head") sits above the cylinder (engine), cylinders and forms the roof of the combustion chamber.
In sidevalve engines, the head is a simple sheet of metal; whereas ...
, to allow slight movement while maintaining the seal of the gaskets in order to prevent cracking the manifolds as they expand with heat.
A two-stage, two-barrel carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meter ...
with electric choke was used to improve performance in cold starts, while heat shields incorporated underneath the carburetor and between the intake and exhaust manifolds were used to prevent heat soaking the gasoline in the carburetor thereby improving performance in hot weather. Recognizing that cars with four-cylinder engines equipped with air conditioning
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
tended to experience drivability issues in hot weather, other improvements were made including a cut-off switch that shut the compressor off at wide open throttle and a delay incorporated into the air conditioning's circuitry to prevent the compressor from engaging on until twelve seconds after the engine was started.
Early applications
The Iron Duke's first applications were in the 1977 Astre and Sunbird subcompact cars, replacing the 2.3 L Vega engine, and in the compact Phoenix. As these cars were originally designed for Chevrolet engines the Iron Duke also used the Chevrolet bell housing bolt pattern, instead of the Buick-Oldsmobile-Pontiac V8 pattern. The following year use of the engine expanded to the Sunbird's Chevrolet andOldsmobile
Oldsmobile or formally the Oldsmobile Division of General Motors was a brand of American automobiles, produced for most of its existence by General Motors. Originally established as "Olds Motor Vehicle Company" by Ransom E. Olds in 1897, it pro ...
twins, the Monza and Starfire.
For model year 1979 the engine was extensively redesigned. The original reverse-flow cylinder head was replaced by a crossflow design, a new two-barrel carburetor called "Vara-Jet" was introduced, the distributor was relocated, and the size of the oil pan was reduced. The only parts carried over from the 1978 engines were the connecting rods. Peak power increased to 90 hp.
For 1980 the Iron Duke engine was redesigned to be mounted transversely, to suit the new front-drive
Front-wheel drive (FWD) is a form of engine and transmission layout used in motor vehicles, where the engine drives the front wheels only. Most modern front-wheel drive vehicles feature a transverse engine, rather than the conventional lon ...
General Motors "X-body" cars. The bellhousing bolt pattern was revised to match that of the new 60° V6 engine.
 GM also began selling the engine to
GM also began selling the engine to American Motors Corporation
American Motors Corporation (AMC; commonly referred to as American Motors) was an American automobile manufacturing company formed by the merger of Nash-Kelvinator Corporation and Hudson Motor Car Company on May 1, 1954. At the time, it was t ...
(AMC) starting with 1980 model year. It was the base engine in Spirit, Concord, and Eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
automobiles, as well as in base-model Jeep CJs. The engines purchased by AMC continued to use the Chevrolet V8 bellhousing pattern. The four-cylinder engine was dropped from AMC rear-wheel drive models after 1982. During 1983, the all-wheel drive Eagle base engine switched from the Iron Duke to a new, AMC-developed four-cylinder. The 1983 Jeep CJs were the last with the Iron Duke as base engine.
* 1981–1982 AMC Concord
* 1981–1983 AMC Eagle
* 1980–1982 AMC Spirit
* 1980–1981 Buick Skylark
* 1980–1981 Chevrolet Citation
* 1978–1980 Chevrolet Monza
* 1980–1983 Jeep CJ
* 1980–1981 Oldsmobile Omega
The Oldsmobile Omega is a compact car manufactured and marketed from 1973-1984 by Oldsmobile, as the brand's most affordable, entry level vehicle — across three distinct generations.
The first two generations of the Omega used rear-wheel ...
* 1978–1980 Oldsmobile Starfire
The Oldsmobile Starfire is an automobile nameplate used by Oldsmobile, produced in three non-contiguous generations beginning in 1954. The Starfire nameplate made its debut as a convertible concept car in 1953 followed with the 1954–1956 Ninet ...
* 1977 Pontiac Astre
* 1977–1981 Pontiac Phoenix
* 1977–1980 Pontiac Sunbird
Tech IV
Iron Dukes were fitted with fuel injection (TBI, via a single injector in the throttle body) in 1982. This version was christened the Tech IV, though '' Car and Driver'' later ridiculed it as the ''low''-Tech IV. Power output increased to .
 This was replaced by a swirl-port head with 9.0:1 (instead of 8.25:1) compression ratio in 1984 for a gain. Other additions for 1985 included roller lifters, improved bearings, and a new crankshaft. Several significant changes were made in 1987, which included: an improved cylinder head, intake manifold and throttle-body fuel injection module, a more-modern serpentine belt with an automatic spring-loaded tensioner for the accessories, and a Distributorless Ignition System (DIS). This revision to the engine increased power to . In 1988, a balance shaft was added to smooth engine vibrations. Up to this point, the engine incorporated a 'dogbone' upper front engine mount secured to the cowling of the vehicle's hood latch, aiding in controlling the vibration. Further improvements in later years included new pistons, rods, crankshaft, and an in-pan oiling system. The most powerful variant of the Tech IV raised the rev limit to 5500 rpm, and achieved . The Tech IV uses the same bellhousing pattern as the 2.8 L '' 60-Degree'' V6. Over the years, the Tech IV engine has proved to be a reliable workhorse for owners when not pushed to its limits. All 1978-1990 Iron Duke engines used a micarta camshaft gear that meshed directly with a steel gear on the crankshaft. 1991-92 VIN R and U engines used a timing chain instead.
* 1982–1992 Buick Century
* 1982–1991 Buick Skylark
* 1985–1987 Buick Somerset/Somerset Regal
* 1985–1990 Chevrolet Astro Cargo Van
* 1982–1985
This was replaced by a swirl-port head with 9.0:1 (instead of 8.25:1) compression ratio in 1984 for a gain. Other additions for 1985 included roller lifters, improved bearings, and a new crankshaft. Several significant changes were made in 1987, which included: an improved cylinder head, intake manifold and throttle-body fuel injection module, a more-modern serpentine belt with an automatic spring-loaded tensioner for the accessories, and a Distributorless Ignition System (DIS). This revision to the engine increased power to . In 1988, a balance shaft was added to smooth engine vibrations. Up to this point, the engine incorporated a 'dogbone' upper front engine mount secured to the cowling of the vehicle's hood latch, aiding in controlling the vibration. Further improvements in later years included new pistons, rods, crankshaft, and an in-pan oiling system. The most powerful variant of the Tech IV raised the rev limit to 5500 rpm, and achieved . The Tech IV uses the same bellhousing pattern as the 2.8 L '' 60-Degree'' V6. Over the years, the Tech IV engine has proved to be a reliable workhorse for owners when not pushed to its limits. All 1978-1990 Iron Duke engines used a micarta camshaft gear that meshed directly with a steel gear on the crankshaft. 1991-92 VIN R and U engines used a timing chain instead.
* 1982–1992 Buick Century
* 1982–1991 Buick Skylark
* 1985–1987 Buick Somerset/Somerset Regal
* 1985–1990 Chevrolet Astro Cargo Van
* 1982–1985 Chevrolet Camaro
The Chevrolet Camaro is a mid-size American automobile manufactured by Chevrolet, classified as a pony car. It first went on sale on September 29, 1966, for the 1967 model year and was designed to compete with the Ford Mustang. The Camaro sh ...
* 1982–1990 Chevrolet Celebrity
* 1990–1992 Chevrolet Lumina
* 1985–1993 Chevrolet S-10
* 1985–1987 Chevrolet S-10 Blazer
The Chevrolet (S-10) Blazer and its badge engineered GMC (S-15) Jimmy counterpart are compact/ mid-size SUVs manufactured and marketed by Chevrolet and GMC from the 1983 through 2005 model years, over two generations – until the early 1990 ...
* 1985–1987 GMC S-15 Jimmy
* 1985–1993 GMC S-15 Sonoma
* 1985–1990 GMC Safari Cargo Van
* 1987–1994 Grumman LLV (USPS
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the ...
delivery vehicle)
* 1985–1991 Oldsmobile Cutlass Calais
* 1982–1992 Oldsmobile Cutlass Ciera
* 1982–1991 Pontiac 6000
* 1984–1988 Pontiac Fiero
* 1982–1985 Pontiac Firebird
* 1985–1991 Pontiac Grand Am
Super Duty
The Iron Duke block formed the basis of Pontiac's ''Super Duty'' four-cylinder racing engines of the 1980s, the last in a line of high-performance Pontiac Super Duty engines. The engines were featured in NASCAR's Charlotte/Daytona Dash Series, the IMSA GT Championship (in GTP and GTU class cars), and even in American Power Boat Association racing boats. Super Duty engines continued to be used in ARCA racing until well into the 2000s. In addition to parts matching the Iron Duke's stock 2.5 L displacement other crankshafts and their corresponding connecting rods were offered by Pontiac Motorsports, resulting in displacements ranging from 2.1 L to 3.2 L. A 2.7 L, Super Duty engine powered the 1984Fiero
The Pontiac Fiero is a mid-engine sports car manufactured and marketed by Pontiac for model years 1984-1988. Designed by George Milidrag and Hulki Aldikacti as a sports car, it was the first two-seater Pontiac since the 1926 to 1938 coupes, and ...
Indy Pace Car to over during the race, but Super Duty engines were never available in factory-built GM vehicles. However, GM sold the Super-Duty-specific parts at authorized dealers; a hobbyist could order all of the parts required to convert their stock Iron Duke engine to a Super Duty version.
Kansas Racing Products continued to make the engines in the early 21st century after buying rights to make them from GM.
Cosworth also produced a 16-valve
In automotive engineering a multi-valve or multivalve engine is one where each cylinder has more than two valves. A multi-valve engine has better breathing and may be able to operate at higher revolutions per minute (RPM) than a two-valve engine, ...
, double-overhead cam head for the 3.0 L version of the racing engine ( Cosworth Project DBA, 1987).
See also
*GM H platform
The H Platform, or H-body, name has been used twice by General Motors. The 1970s H-body was an inexpensive rear-wheel drive compact automobile platform from the 1970s, used for the Chevrolet Vega and Monza and their Buick, Oldsmobile, and Pontiac d ...
* GM engines
References
* 1979 chevy Monza BrochureExternal links
{{commons category, General Motors Iron Duke enginesJeep 151 information
Iron Duke Gasoline engines by model Straight-four engines