Fugue (hash Function) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The countersubject is written in invertible counterpoint at the octave or fifteenth (two octaves). The distinction is made between the use of free counterpoint and regular countersubjects accompanying the fugue subject/answer, because in order for it to be heard accompanying the subject in more than one instance, the countersubject must be capable of sounding correctly when played above or below the subject, and must be conceived, therefore, in invertible (double) counterpoint.
In tonal music, invertible contrapuntal lines must be written according to certain rules, because several intervallic combinations, while acceptable in one orientation, are not permissible when inverted. As an example, perfect fifths are contrapuntally acceptable, while the inversion of a perfect fifth results in a perfect fourth, which, unlike the perfect fifth, is considered a dissonance, requiring proper preparation and resolution. The countersubject, if sounding at the same time as the answer, is transposed to the pitch of the answer. Each voice then responds with its own subject or answer, and further countersubjects or free counterpoint may be heard.
It is customary in the exposition to alternate entrances of the subject (S) with entrances of the answer (A). However, this order is occasionally varied. For example, the exposition from J.S. Bach's '' Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1'' Fugue No. 1 in C Major, BWV 846 uses a SAAS (subject-answer-answer-subject) exposition. A brief codetta is often heard connecting the various statements of the subject and answer, smoothly connecting each and often facilitating the modulation between the tonic and the key of the answer. The codetta, like other parts of the exposition, may be reused throughout the remainder of the fugue.
The first answer must occur as soon after the initial statement of the subject as possible; therefore, the first codetta is often absent or very short. In the example shown above of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 16 in G minor, BWV 861, the first codetta is absent. The subject concludes on the
The countersubject is written in invertible counterpoint at the octave or fifteenth (two octaves). The distinction is made between the use of free counterpoint and regular countersubjects accompanying the fugue subject/answer, because in order for it to be heard accompanying the subject in more than one instance, the countersubject must be capable of sounding correctly when played above or below the subject, and must be conceived, therefore, in invertible (double) counterpoint.
In tonal music, invertible contrapuntal lines must be written according to certain rules, because several intervallic combinations, while acceptable in one orientation, are not permissible when inverted. As an example, perfect fifths are contrapuntally acceptable, while the inversion of a perfect fifth results in a perfect fourth, which, unlike the perfect fifth, is considered a dissonance, requiring proper preparation and resolution. The countersubject, if sounding at the same time as the answer, is transposed to the pitch of the answer. Each voice then responds with its own subject or answer, and further countersubjects or free counterpoint may be heard.
It is customary in the exposition to alternate entrances of the subject (S) with entrances of the answer (A). However, this order is occasionally varied. For example, the exposition from J.S. Bach's '' Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1'' Fugue No. 1 in C Major, BWV 846 uses a SAAS (subject-answer-answer-subject) exposition. A brief codetta is often heard connecting the various statements of the subject and answer, smoothly connecting each and often facilitating the modulation between the tonic and the key of the answer. The codetta, like other parts of the exposition, may be reused throughout the remainder of the fugue.
The first answer must occur as soon after the initial statement of the subject as possible; therefore, the first codetta is often absent or very short. In the example shown above of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 16 in G minor, BWV 861, the first codetta is absent. The subject concludes on the
 The excerpt below, bars 7â12 of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 2 in C minor, BWV 847, from the ''Well-Tempered Clavier'', Book 1 illustrates the application of most of the characteristics described above. The fugue is for keyboard and in three voices, with regular countersubjects. This excerpt opens at last entry of the exposition: the subject is sounding in the bass, the first countersubject in the treble, while the middle-voice is stating a second version of the second countersubject, which concludes with the characteristic rhythm of the subject, and is always used together with the first version of the second countersubject. Following this an episode modulates from the tonic to the relative major by means of
The excerpt below, bars 7â12 of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 2 in C minor, BWV 847, from the ''Well-Tempered Clavier'', Book 1 illustrates the application of most of the characteristics described above. The fugue is for keyboard and in three voices, with regular countersubjects. This excerpt opens at last entry of the exposition: the subject is sounding in the bass, the first countersubject in the treble, while the middle-voice is stating a second version of the second countersubject, which concludes with the characteristic rhythm of the subject, and is always used together with the first version of the second countersubject. Following this an episode modulates from the tonic to the relative major by means of
 Sometimes counter-expositions or the middle entries take place in '' stretto,'' whereby one voice responds with the subject/answer before the first voice has completed its entry of the subject/answer, usually increasing the intensity of the music.
Only one entry of the subject must be heard in its completion in a ''stretto''. However, a ''stretto'' in which the subject/answer is heard in completion in all voices is known as ''stretto maestrale'' or ''grand stretto''. ''Strettos'' may also occur by inversion, augmentation and diminution. A fugue in which the opening exposition takes place in ''stretto'' form is known as a ''close fugue'' or ''stretto fugue'' (see for example, the ''Gratias agimus tibi'' and ' choruses from J.S. Bach's Mass in B minor).
Sometimes counter-expositions or the middle entries take place in '' stretto,'' whereby one voice responds with the subject/answer before the first voice has completed its entry of the subject/answer, usually increasing the intensity of the music.
Only one entry of the subject must be heard in its completion in a ''stretto''. However, a ''stretto'' in which the subject/answer is heard in completion in all voices is known as ''stretto maestrale'' or ''grand stretto''. ''Strettos'' may also occur by inversion, augmentation and diminution. A fugue in which the opening exposition takes place in ''stretto'' form is known as a ''close fugue'' or ''stretto fugue'' (see for example, the ''Gratias agimus tibi'' and ' choruses from J.S. Bach's Mass in B minor).
 The young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart studied counterpoint with Padre Martini in Bologna. Under the employment of Archbishop Colloredo, and the musical influence of his predecessors and colleagues such as Johann Ernst Eberlin, Anton Cajetan Adlgasser,
The young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart studied counterpoint with Padre Martini in Bologna. Under the employment of Archbishop Colloredo, and the musical influence of his predecessors and colleagues such as Johann Ernst Eberlin, Anton Cajetan Adlgasser,
 ]
]
 ]
]
Score
, J. S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'', Mutopia Project
Fugues of the Well-Tempered Clavier
(viewable in Adob
o
Analyses of J. S. Bach's ''Well-Tempered Clavier'' with accompanying recordings
* * * {{Authority control * Polyphonic form Classical music styles Choral music genres
 In
In classical music
Classical music generally refers to the art music of the Western world, considered to be #Relationship to other music traditions, distinct from Western folk music or popular music traditions. It is sometimes distinguished as Western classical mu ...
, a fugue (, from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''fuga'', meaning "flight" or "escape""Fugue, ''n''." ''The Concise Oxford English Dictionary'', eleventh edition, revised, ed. Catherine Soanes and Angus Stevenson (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2006). ) is a contrapuntal
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous Part (music), musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and Pitch contour, melodic contour. The term ...
, polyphonic
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice ( monophony) or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords ...
compositional technique in two or more voices, built on a subject (a musical theme) that is introduced at the beginning in imitation (repetition at different pitches), which recurs frequently throughout the course of the composition. It is not to be confused with a '' fuguing tune'', which is a style of song popularized by and mostly limited to early American (i.e. shape note
Shape notes are a musical notation designed to facilitate congregational and Sing-along, social singing. The notation became a popular teaching device in American singing schools during the 19th century. Shapes were added to the noteheads in ...
or "Sacred Harp
Sacred Harp singing is a tradition of sacred choral music which developed in New England and perpetuated in the American South. The name is derived from ''The Sacred Harp'', a historically important shape notes, shape-note tunebook printed in ...
") music and West Gallery music. A fugue usually has three main sections: an exposition, a development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
, and a final entry that contains the return of the subject in the fugue's tonic key. Fugues can also have episodes, which are parts of the fugue where new material often based on the subject is heard; a stretto (plural stretti), when the fugue's subject overlaps itself in different voices, or a recapitulation. A popular compositional technique in the Baroque era, the fugue was fundamental in showing mastery of harmony and tonality as it presented counterpoint.
In the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, the term was widely used to denote any works in canonic style; however, by the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, it had come to denote specifically imitative works. Since the 17th century, the term ''fugue'' has described what is commonly regarded as the most fully developed procedure of imitative counterpoint.
Most fugues open with a short main theme, called the subject, which then sounds successively in each voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
. When each voice has completed its entry of the subject, the ''exposition'' is complete. This is often followed by a connecting passage, or ''episode'', developed from previously heard material; further "entries" of the subject are then heard in related keys. Episodes (if applicable) and entries are usually alternated until the final entry of the subject, at which point the music has returned to the opening key, or tonic, which is often followed by a coda."Fugue", ''The Concise Oxford Dictionary of Music'', fourth edition, ed. Michael Kennedy (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1996). Because of the composer's prerogative to decide most structural elements, the fugue is closer to a style of composition rather than a structural form.
The form evolved during the 18th century from several earlier types of contrapuntal compositions, such as imitative ricercars, capriccios, canzonas, and fantasias. The Baroque composer Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (German: Help:IPA/Standard German, ïżœjoËhan zeËbastiÌŻan baÏ ( â 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque music, Baroque period. He is known for his prolific output across a variety ...
(1685â1750), well known for his fugues, shaped his own works after those of Jan Pieterszoon Sweelinck (1562â1621), Johann Jakob Froberger (1616â1667), Johann Pachelbel
Johann Pachelbel (also Bachelbel; baptised â buried 9 March 1706) was a German composer, organist, and teacher who brought the south German organ schools to their peak. He composed a large body of sacred and secularity, secular music, and ...
(1653â1706), Girolamo Frescobaldi (1583â1643), Dieterich Buxtehude
Dieterich Buxtehude (; born Diderich Hansen Buxtehude, ; â 9 May 1707) was a Danish composer and organist of the Baroque music, Baroque period, whose works are typical of the North German organ school. As a composer who worked in various vocal ...
(c. 1637â1707) and others. With the decline of sophisticated styles at the end of the baroque period, the fugue's central role waned, eventually giving way as sonata form
The sonata form (also sonata-allegro form or first movement form) is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of t ...
and the symphony orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families. There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* String instruments, such as the violin, viola, cello, ...
rose to a more prominent position. Nevertheless, composers continued to write and study fugues; they appear in the works of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
(1756â1791) and Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
(1770â1827), as well as modern composers such as Dmitri Shostakovich
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich, group=n (9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his First Symphony in 1926 and thereafter was regarded as a major composer.
Shostak ...
(1906â1975) and Paul Hindemith
Paul Hindemith ( ; ; 16 November 189528 December 1963) was a German and American composer, music theorist, teacher, violist and conductor. He founded the Amar Quartet in 1921, touring extensively in Europe. As a composer, he became a major advo ...
(1895â1963).
Etymology
The English term ''fugue'' originated in the 16th century and is derived from the French word ''fugue'' or the Italian ''fuga''. This in turn comes from the Latin ''fuga'', which is itself related to both ''fugere'' ("to flee") and ''fugare'' ("to chase"). The adjectival form is ''fugal''. Variants include ''fughetta'' ("a small fugue") and ''fugato'' (a passage in fugal style within another work that is not a fugue).Musical outline
A fugue begins with the '' exposition'' and is written according to certain rules. The composer has more freedom once the exposition ends, though a logical key structure is usually followed. Further entries of the subject will occur throughout the fugue, repeating the accompanying material at the same time, and often accompanying key changes. The various entries may or may not be separated by ''episodes'' or occur in ''stretto''. ::S = subject; A = answer; CS = countersubject; T = tonic; D = dominantExposition
A fugue begins with the exposition of its subject in one of the voices alone in the tonic key. G. M. Tucker and Andrew V. Jones, "Fugue", in ''The Oxford Companion to Music'', ed. Alison Latham (Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, 2002). After the statement of the subject, a second voice enters and states the subject with the subject transposed to another key (almost always the dominant orsubdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
, with the latter being less common), which is known as the ''answer''. To enable a natural harmonic progression, the answer may also be altered slightly (usually by changing one or a few notes near the beginning). When the answer is an exact transposition of the subject into the new key, the answer is classified as a ''real answer''; alternatively, if the intervals of the subject are altered in any way, the answer is a ''tonal answer''.
When the subject begins with a prominent dominant note, or when there is a prominent dominant note very close to the beginning of the subject, a tonal answer is usually necessary. To prevent an undermining of the fugue's key, this note is transposed up a fourth to the tonic rather than up a fifth to the supertonic
In music, the supertonic is the second degree () of a diatonic scale, one whole step above the tonic. In the movable do solfĂšge system, the supertonic note is sung as ''re''.
The triad built on the supertonic note is called the supertonic ...
. For the same reason, it is possible for the answer of such a subject to be in the subdominant key.
During the answer, the voice in which the subject was previously heard accompanies with new material. If this new material is reused in later statements of the subject, it is called a '' countersubject''; if this accompanying material is only heard once, it is simply referred to as '' free counterpoint''.
 The countersubject is written in invertible counterpoint at the octave or fifteenth (two octaves). The distinction is made between the use of free counterpoint and regular countersubjects accompanying the fugue subject/answer, because in order for it to be heard accompanying the subject in more than one instance, the countersubject must be capable of sounding correctly when played above or below the subject, and must be conceived, therefore, in invertible (double) counterpoint.
In tonal music, invertible contrapuntal lines must be written according to certain rules, because several intervallic combinations, while acceptable in one orientation, are not permissible when inverted. As an example, perfect fifths are contrapuntally acceptable, while the inversion of a perfect fifth results in a perfect fourth, which, unlike the perfect fifth, is considered a dissonance, requiring proper preparation and resolution. The countersubject, if sounding at the same time as the answer, is transposed to the pitch of the answer. Each voice then responds with its own subject or answer, and further countersubjects or free counterpoint may be heard.
It is customary in the exposition to alternate entrances of the subject (S) with entrances of the answer (A). However, this order is occasionally varied. For example, the exposition from J.S. Bach's '' Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1'' Fugue No. 1 in C Major, BWV 846 uses a SAAS (subject-answer-answer-subject) exposition. A brief codetta is often heard connecting the various statements of the subject and answer, smoothly connecting each and often facilitating the modulation between the tonic and the key of the answer. The codetta, like other parts of the exposition, may be reused throughout the remainder of the fugue.
The first answer must occur as soon after the initial statement of the subject as possible; therefore, the first codetta is often absent or very short. In the example shown above of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 16 in G minor, BWV 861, the first codetta is absent. The subject concludes on the
The countersubject is written in invertible counterpoint at the octave or fifteenth (two octaves). The distinction is made between the use of free counterpoint and regular countersubjects accompanying the fugue subject/answer, because in order for it to be heard accompanying the subject in more than one instance, the countersubject must be capable of sounding correctly when played above or below the subject, and must be conceived, therefore, in invertible (double) counterpoint.
In tonal music, invertible contrapuntal lines must be written according to certain rules, because several intervallic combinations, while acceptable in one orientation, are not permissible when inverted. As an example, perfect fifths are contrapuntally acceptable, while the inversion of a perfect fifth results in a perfect fourth, which, unlike the perfect fifth, is considered a dissonance, requiring proper preparation and resolution. The countersubject, if sounding at the same time as the answer, is transposed to the pitch of the answer. Each voice then responds with its own subject or answer, and further countersubjects or free counterpoint may be heard.
It is customary in the exposition to alternate entrances of the subject (S) with entrances of the answer (A). However, this order is occasionally varied. For example, the exposition from J.S. Bach's '' Well-Tempered Clavier, Book 1'' Fugue No. 1 in C Major, BWV 846 uses a SAAS (subject-answer-answer-subject) exposition. A brief codetta is often heard connecting the various statements of the subject and answer, smoothly connecting each and often facilitating the modulation between the tonic and the key of the answer. The codetta, like other parts of the exposition, may be reused throughout the remainder of the fugue.
The first answer must occur as soon after the initial statement of the subject as possible; therefore, the first codetta is often absent or very short. In the example shown above of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 16 in G minor, BWV 861, the first codetta is absent. The subject concludes on the quarter note
A quarter note ( AmE) or crotchet ( BrE) () is a musical note played for one quarter of the duration of a whole note (or semibreve). Quarter notes are notated with a filled-in oval note head and a straight, flagless stem. The stem usually ...
(or crotchet) B of the third beat of the second bar, which harmonizes the opening G of the tonal answer. The later codettas may be considerably longer, and often serve to develop the material heard in the subject/answer and countersubject and possibly introduce ideas heard in the second countersubject or free counterpoint that follows. They may also be present to delay, and therefore heighten the impact of, the reentry of the subject in another voice. Finally, they may be modulatory passages to return the fugue to the tonic.
The exposition usually concludes when all voices have given a statement of the subject or answer. In some fugues, especially those with an odd number of voices, the exposition will end with a redundant entry, or an extra presentation of the theme in a voice which has already entered. Furthermore, the entry of one of the voices may not be heard until considerably later. For example, in J.S. Bach's Fugue in C minor for Organ, BWV 549, the subject entrance in the lowest voice (played by the organ pedals), is not heard until near the end of the fugue.
Episode
Further entries of the subject may follow the initial exposition either immediately or separated by episodes. Episodic material is always modulatory and is usually based upon some musical idea heard in the exposition. Each episode has the primary function of transitioning into a new key for the next entry of the subject, and may also provide release from the strictness of form required by the exposition. André Gedalge, a teacher ofMaurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 â 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism in music, Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composer ...
, stated that the episode of the fugue is generally based on a series of imitations of the subject that have been fragmented.
Development
Further entries of the subject, or middle entries, occur throughout the fugue. The development must state the subject or answer at least once in its entirety, and may also be heard in combination with any countersubjects from the exposition, new countersubjects, free counterpoint, or any of these in combination. It is uncommon for the subject to enter alone in a single voice in the middle entries; rather, it is usually heard with at least one of the countersubjects and/or other free contrapuntal accompaniments. Middle entries tend to occur at keys other than the tonic. These are often closely related keys such as the relative dominant andsubdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
, although the key structure of fugues varies greatly. In the fugues of J.S. Bach, the first middle entry occurs most often in the relative major or minor of the work's overall key, and is followed by an entry in the dominant of the relative major or minor when the fugue's subject requires a tonal answer. In the fugues of earlier composers (notably Buxtehude and Pachelbel), middle entries in keys other than the tonic and dominant tend to be the exception, and non-modulation the norm. One famous example of such non-modulating fugue occurs in Buxtehude's Praeludium (Fugue and Chaconne) in C, BuxWV 137.
When there is no entrance of the subject and answer material, the composer can develop the subject by altering it. This is called a ''counter-exposition'', which often uses the '' inversion'' of the subject, although the term is sometimes used synonymously with middle entry and may also describe the exposition of completely new subjects, such as those encountered in double fugues. In any of the entries within a fugue, the subject may be altered by inversion, retrograde (where the subject is heard back-to-front), diminution
In Western culture, Western music and music theory, diminution (from Medieval Latin ''diminutio'', alteration of Latin ''deminutio'', decrease) has four distinct meanings. Diminution may be a form of embellishment (music), embellishment in whic ...
(the reduction of the subject's rhythmic values by a certain factor), augmentation (the enlargement of the subject's rhythmic values by a certain factor), or any combination thereof.
Example and analysis
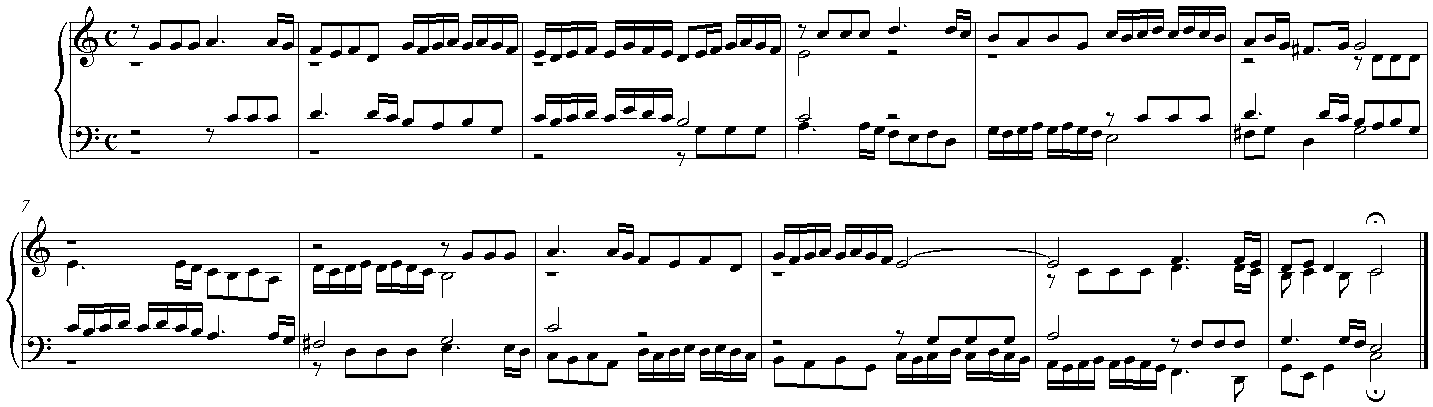
 The excerpt below, bars 7â12 of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 2 in C minor, BWV 847, from the ''Well-Tempered Clavier'', Book 1 illustrates the application of most of the characteristics described above. The fugue is for keyboard and in three voices, with regular countersubjects. This excerpt opens at last entry of the exposition: the subject is sounding in the bass, the first countersubject in the treble, while the middle-voice is stating a second version of the second countersubject, which concludes with the characteristic rhythm of the subject, and is always used together with the first version of the second countersubject. Following this an episode modulates from the tonic to the relative major by means of
The excerpt below, bars 7â12 of J.S. Bach's Fugue No. 2 in C minor, BWV 847, from the ''Well-Tempered Clavier'', Book 1 illustrates the application of most of the characteristics described above. The fugue is for keyboard and in three voices, with regular countersubjects. This excerpt opens at last entry of the exposition: the subject is sounding in the bass, the first countersubject in the treble, while the middle-voice is stating a second version of the second countersubject, which concludes with the characteristic rhythm of the subject, and is always used together with the first version of the second countersubject. Following this an episode modulates from the tonic to the relative major by means of sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
, in the form of an accompanied canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
at the fourth. Arrival in E major is marked by a quasi perfect cadence across the bar line, from the last quarter note beat of the first bar to the first beat of the second bar in the second system, and the first middle entry. Here, Bach has altered the second countersubject to accommodate the change of mode.
False entries
At any point in the fugue there may be "false entries" of the subject, which include the start of the subject but are not completed. False entries are often abbreviated to the head of the subject, and anticipate the "true" entry of the subject, heightening the impact of the subject proper.Counter-exposition
The counter-exposition is a second exposition. However, there are only two entries, and the entries occur in reverse order. The counter-exposition in a fugue is separated from the exposition by an episode and is in the same key as the original exposition.Stretto
 Sometimes counter-expositions or the middle entries take place in '' stretto,'' whereby one voice responds with the subject/answer before the first voice has completed its entry of the subject/answer, usually increasing the intensity of the music.
Only one entry of the subject must be heard in its completion in a ''stretto''. However, a ''stretto'' in which the subject/answer is heard in completion in all voices is known as ''stretto maestrale'' or ''grand stretto''. ''Strettos'' may also occur by inversion, augmentation and diminution. A fugue in which the opening exposition takes place in ''stretto'' form is known as a ''close fugue'' or ''stretto fugue'' (see for example, the ''Gratias agimus tibi'' and ' choruses from J.S. Bach's Mass in B minor).
Sometimes counter-expositions or the middle entries take place in '' stretto,'' whereby one voice responds with the subject/answer before the first voice has completed its entry of the subject/answer, usually increasing the intensity of the music.
Only one entry of the subject must be heard in its completion in a ''stretto''. However, a ''stretto'' in which the subject/answer is heard in completion in all voices is known as ''stretto maestrale'' or ''grand stretto''. ''Strettos'' may also occur by inversion, augmentation and diminution. A fugue in which the opening exposition takes place in ''stretto'' form is known as a ''close fugue'' or ''stretto fugue'' (see for example, the ''Gratias agimus tibi'' and ' choruses from J.S. Bach's Mass in B minor).
Final entries and coda
The closing section of a fugue often includes one or two counter-expositions, and possibly a stretto, in the tonic; sometimes over a tonic or dominant pedal note. Any material that follows the final entry of the subject is considered to be the final coda and is normally cadential.Types
Simple fugue
A simple fugue has only one subject, and does not utilize invertible counterpoint.Double (triple, quadruple) fugue
A double fugue has two subjects that are often developed simultaneously. Similarly, a triple fugue has three subjects. There are two kinds of double (triple) fugue: (a) a fugue in which the second (third) subject is (are) presented simultaneously with the subject in the exposition (e.g. as in Kyrie Eleison of Mozart's Requiem in D minor or the fugue of Bach's Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, BWV 582), and (b) a fugue in which all subjects have their own expositions at some point, and they are not combined until later (see for example, the three-subject Fugue No. 14 in F minor from Bach's ''Well-Tempered Clavier'' Book 2, or more famously, Bach's "St. Anne" Fugue in E major, BWV 552, a triple fugue for organ.)Counter-fugue
A counter-fugue is a fugue in which the first answer is presented as the subject in inversion (upside down), and the inverted subject continues to feature prominently throughout the fugue. Examples include ''Contrapunctus V'' through ''Contrapunctus VII'', from Bach's '' The Art of Fugue''. During the Baroque period, counter-fugues were sometimes called by the Latin name ''fuga contraria''. German composerJohann Mattheson
Johann Mattheson (28 September 1681 â 17 April 1764) was a German composer, critic, lexicographer and music theorist. His writings on the late Baroque and early Classical period were highly influential, specifically, "his biographical and the ...
coined the term ''gegenfuge'' to refer to a counter-fugue construct in his ''Der vollkommene Capellmeister'' (1739), and some German-language texts use that name to refer to a counter-fugue.
Permutation fugue
Permutation fugue describes a type of composition (or technique of composition) in which elements of fugue and strictcanon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
are combined. Each voice enters in succession with the subject, each entry alternating between tonic and dominant, and each voice, having stated the initial subject, continues by stating two or more themes (or countersubjects), which must be conceived in correct invertible counterpoint. (In other words, the subject and countersubjects must be capable of being played both above and below all the other themes without creating any unacceptable dissonances.) Each voice takes this pattern and states all the subjects/themes in the same order (and repeats the material when all the themes have been stated, sometimes after a rest).
There is usually very little non-structural/thematic material. During the course of a permutation fugue, it is quite uncommon, actually, for every single possible voice-combination (or "permutation") of the themes to be heard. This limitation exists in consequence of sheer proportionality: the more voices in a fugue, the greater the number of possible permutations. In consequence, composers exercise editorial judgment as to the most musical of permutations and processes leading thereto. One example of permutation fugue can be seen in the eighth and final chorus of J.S. Bach's cantata, ''Himmelskönig, sei willkommen'', BWV 182.
Permutation fugues differ from conventional fugue in that there are no connecting episodes, nor statement of the themes in related keys. So for example, the fugue of Bach's Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, BWV 582 is not purely a permutation fugue, as it does have episodes between permutation expositions. Invertible counterpoint is essential to permutation fugues but is not found in simple fugues.
Fughetta
A fughetta is a short fugue that has the same characteristics as a fugue. Often the contrapuntal writing is not strict, and the setting less formal. See for example, variation 24 ofBeethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
's ''Diabelli Variations'' Op. 120.
Mirror fugue
A mirror fugue is a fugue, or rather two fugues, one of which is the mirror image of the other. It is as though a mirror were placed above or below an existing fugue, producing inversions of each interval in each part, as well as inverting the position of the parts within the texture, so that, for example, the topmost part in one fugue is inverted to produce the lowest part in the other. This is well demonstrated by the two four-part fugues of Contrapunctus 12 in '' The Art of Fugue''. The two three-part fugues of Contrapunctus 13 exhibit a similar relationship to each other, but this cannot strictly be called a mirror fugue, since the position of each inverted part is not itself inverted in the texture, SAB becoming not BAS, but BSA.History
Middle Ages and Renaissance
The term ''fuga'' was used as far back as theMiddle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, but was initially used to refer to any kind of imitative counterpoint, including canons, which are now thought of as distinct from fugues. Prior to the 16th century, fugue was originally a genre. It was not until the 16th century that fugal technique as it is understood today began to be seen in pieces, both instrumental and vocal. Fugal writing is found in works such as fantasias, ricercares and canzonas.
"Fugue" as a theoretical term first occurred in 1330 when Jacobus of Liege wrote about the ''fuga'' in his ''Speculum musicae''. The fugue arose from the technique of "imitation", where the same musical material was repeated starting on a different note.
Gioseffo Zarlino
Gioseffo Zarlino (31 January or 22 March 1517 â 4 February 1590) was an Italian Music theory, music theorist and composer of the Renaissance music, Renaissance. He made a large contribution to the theory of counterpoint as well as to musical t ...
, a composer, author, and theorist in the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, was one of the first to distinguish between the two types of imitative counterpoint: fugues and canons (which he called imitations). Originally, this was to aid improvisation
Improvisation, often shortened to improv, is the activity of making or doing something not planned beforehand, using whatever can be found. The origin of the word itself is in the Latin "improvisus", which literally means un-foreseen. Improvis ...
, but by the 1550s, it was considered a technique of composition. The composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina (1525?â1594) wrote masses using modal counterpoint and imitation, and fugal writing became the basis for writing motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the preeminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to the Eng ...
s as well. Palestrina's imitative motets differed from fugues in that each phrase of the text had a different subject which was introduced and worked out separately, whereas a fugue continued working with the same subject or subjects throughout the entire length of the piece.
Baroque era
It was in the Baroque period that the writing of fugues became central to composition, in part as a demonstration of compositional expertise. Jan Pieterszoon Sweelinck, Girolamo Frescobaldi, Johann Jakob Froberger andDieterich Buxtehude
Dieterich Buxtehude (; born Diderich Hansen Buxtehude, ; â 9 May 1707) was a Danish composer and organist of the Baroque music, Baroque period, whose works are typical of the North German organ school. As a composer who worked in various vocal ...
all wrote fugues.
Fugues were incorporated into a variety of musical genre
A music genre is a conventional category that identifies some pieces of music as belonging to a shared tradition or set of conventions. Genre is to be distinguished from musical form and musical style, although in practice these terms are sometim ...
s, and are found in most of George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 â 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
's oratorio
An oratorio () is a musical composition with dramatic or narrative text for choir, soloists and orchestra or other ensemble.
Similar to opera, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguisha ...
s. Keyboard suites from this time often conclude with a fugal gigue
The gigue ( , ) or giga () is a lively baroque dance originating from the English jig. It was imported into France in the mid-17th centuryBellingham, Jane"gigue."''The Oxford Companion to Music''. Ed. Alison Latham. Oxford Music Online. 6 July ...
. Domenico Scarlatti
Giuseppe Domenico Scarlatti (26 October 1685 â 23 July 1757) was an Italian composer. He is classified primarily as a Baroque music, Baroque composer chronologically, although his music was influential in the development of the Classical peri ...
has only a few fugues among his corpus of over 500 harpsichord sonatas. The French overture featured a quick fugal section after a slow introduction. The second movement of a sonata da chiesa
''Sonata da chiesa'' ( Italian: "church sonata") is a 17th-century genre of musical composition for one or more melody instruments and is regarded an antecedent of later forms of 18th century instrumental music. It generally comprises four movemen ...
, as written by Arcangelo Corelli
Arcangelo Corelli (, also , ; ; 17 February 1653 â 8 January 1713) was an List of Italian composers, Italian composer and violinist of the middle Baroque music, Baroque era. His music was key in the development of the modern genres of Sonata a ...
and others, was usually fugal.
The Baroque period also saw a rise in the importance of music theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "Elements of music, ...
. Some fugues during the Baroque period were pieces designed to teach contrapuntal technique to students. The most influential text was Johann Joseph Fux's '' Gradus Ad Parnassum'' ("Steps to Parnassus"), which appeared in 1725. This work laid out the terms of "species" of counterpoint, and offered a series of exercises to learn fugue writing. Fux's work was largely based on the practice of Palestrina's modal fugues. Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
studied from this book, and it remained influential into the nineteenth century. Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
, for example, taught counterpoint from his own summary of Fux and thought of it as the basis for formal structure.
Bach's most famous fugues are those for the harpsichord in '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'', which many composers and theorists look at as the greatest model of fugue. ''The Well-Tempered Clavier'' comprises two volumes written in different times of Bach's life, each comprising 24 prelude and fugue pairs, one for each major and minor key. Bach is also known for his organ fugues, which are usually preceded by a prelude or toccata. ''The Art of Fugue'', BWV 1080, is a collection of fugues (and four canons) on a single theme that is gradually transformed as the cycle progresses. Bach also wrote smaller single fugues and put fugal sections or movements into many of his more general works. J.S. Bach's influence extended forward through his son C.P.E. Bach and through the theorist Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg (1718â1795) whose ''Abhandlung von der Fuge'' ("Treatise on the fugue", 1753) was largely based on J.S. Bach's work.
Classical era
During theClassical era
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilization ...
, the fugue was no longer a central or even fully natural mode of musical composition. Nevertheless, both Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
and Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 â 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
had periods of their careers in which they in some sense "rediscovered" fugal writing and used it frequently in their work.
Haydn
Joseph Haydn was the leader of fugal composition and technique in the Classical era. Haydn's most famous fugues can be found in his "Sun" Quartets (op. 20, 1772), of which three have fugal finales. This was a practice that Haydn repeated only once later in his quartet-writing career, with the finale of his String Quartet, Op. 50 No. 4 (1787). Some of the earliest examples of Haydn's use of counterpoint, however, are in three symphonies ( No. 3, No. 13, and No. 40) that date from 1762 to 1763. The earliest fugues, in both the symphonies and in the Baryton trios, exhibit the influence of Joseph Fux's treatise on counterpoint, ''Gradus ad Parnassum'' (1725), which Haydn studied carefully. Haydn's second fugal period occurred after he heard, and was greatly inspired by, theoratorio
An oratorio () is a musical composition with dramatic or narrative text for choir, soloists and orchestra or other ensemble.
Similar to opera, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguisha ...
s of Handel during his visits to London (1791â1793, 1794â1795). Haydn then studied Handel's techniques and incorporated Handelian fugal writing into the choruses of his mature oratorios '' The Creation'' and '' The Seasons,'' as well as several of his later symphonies, including No. 88, No. 95, and No. 101; and the late string quartets, Opus 71 no. 3 and (especially) Opus 76 no. 6.
Mozart
 The young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart studied counterpoint with Padre Martini in Bologna. Under the employment of Archbishop Colloredo, and the musical influence of his predecessors and colleagues such as Johann Ernst Eberlin, Anton Cajetan Adlgasser,
The young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart studied counterpoint with Padre Martini in Bologna. Under the employment of Archbishop Colloredo, and the musical influence of his predecessors and colleagues such as Johann Ernst Eberlin, Anton Cajetan Adlgasser, Michael Haydn
Johann Michael Haydn (; 14 September 1737 â 10 August 1806) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period, the younger brother of Joseph Haydn.
Life
Michael Haydn was born in 1737 in the Austrian village of Rohra ...
, and his own father, Leopold Mozart
Johann Georg Leopold Mozart (November 14, 1719 â May 28, 1787) was a German composer, violinist, and music theorist. He is best known today as the father and teacher of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and for his violin textbook ''Versuch einer grĂŒn ...
at the Salzburg Cathedral, the young Mozart composed ambitious fugues and contrapuntal passages in Catholic choral works such as Mass in C minor, K. 139 "Waisenhaus" (1768), Mass in C major, K. 66 "Dominicus" (1769), Mass in C major, K. 167 "in honorem Sanctissimae Trinitatis" (1773), Mass in C major, K. 262 "Missa longa" (1775), Mass in C major, K. 337 "Solemnis" (1780), various litanies, and vespers. Leopold admonished his son openly in 1777 that he not forget to make public demonstration of his abilities in "fugue, canon, and contrapunctus". Later in life, the major impetus to fugal writing for Mozart was the influence of Baron Gottfried van Swieten in Vienna around 1782. Van Swieten, during diplomatic service in Berlin, had taken the opportunity to collect as many manuscripts by Bach and Handel as he could, and he invited Mozart to study his collection and encouraged him to transcribe various works for other combinations of instruments. Mozart was evidently fascinated by these works and wrote a set of five transcriptions for string quartet, K. 405 (1782), of fugues from Bach's '' Well-Tempered Clavier'', introducing them with preludes of his own. In a letter to his sister Nannerl Mozart, dated in Vienna on 20 April 1782, Mozart recognizes that he had not written anything in this form, but moved by his wife's interest he composed one piece, which is sent with the letter. He begs her not to let anybody see the fugue and manifests the hope to write five more and then present them to Baron van Swieten. Regarding the piece, he said "I have taken particular care to write ''andante maestoso'' upon it, so that it should not be played fast â for if a fugue is not played slowly the ear cannot clearly distinguish the new subject as it is introduced and the effect is missed". Mozart then set to writing fugues on his own, mimicking the Baroque style. These included a fugue in C minor, K. 426, for two pianos (1783). Later, Mozart incorporated fugal writing into his opera '' Die Zauberflöte'' and the finale of his Symphony No. 41.
The parts of the Requiem he completed also contain several fugues (most notably the Kyrie, and the three fugues in the Domine Jesu; he also left behind a sketch for an Amen fugue which, some believe, would have come at the end of the Sequentia).
Beethoven
 ]
]
Ludwig van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
was familiar with fugal writing from childhood, as an important part of his training was playing from '' The Well-Tempered Clavier''. During his early career in Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Beethoven attracted notice for his performance of these fugues. There are fugal sections in Beethoven's early piano sonatas, and fugal writing is to be found in the second and fourth movements of the '' Eroica Symphony'' (1805). Beethoven incorporated fugues in his sonatas, and reshaped the episode's purpose and compositional technique for later generations of composers.
Nevertheless, fugues did not take on a truly central role in Beethoven's work until his late period. The finale of Beethoven's ''Hammerklavier'' Sonata contains a fugue, which was practically unperformed until the late 19th century, due to its tremendous technical difficulty and length. The last movement of his Cello Sonata, Op. 102 No. 2 is a fugue, and there are fugal passages in the last movements of his Piano Sonatas in A major, Op. 101 and A major Op. 110. According to Charles Rosen, "With the finale of 110, Beethoven re-conceived the significance of the most traditional elements of fugue writing."
Fugal passages are also found in the '' Missa Solemnis'' and all movements of the Ninth Symphony, except the third. A massive, dissonant fugue forms the finale of his String Quartet, Op. 130 (1825); the latter was later published separately as Op. 133, the '' GroĂe Fuge'' ("Great Fugue"). However, it is the fugue that opens Beethoven's String Quartet in C minor, Op. 131 that several commentators regard as one of the composer's greatest achievements. Joseph Kerman (1966, p. 330) calls it "this most moving of all fugues". J. W. N. Sullivan (1927, p. 235) hears it as "the most superhuman piece of music that Beethoven has ever written." Philip Radcliffe (1965, p. 149) says " bare description of its formal outline can give but little idea of the extraordinary profundity of this fugue ."
Romantic era
By the beginning of theRomantic era
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century. The purpose of the movement was to advocate for the importance of subjec ...
, fugue writing had become specifically attached to the norms and styles of the Baroque. Felix Mendelssohn
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 18094 November 1847), widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic music, Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositions inc ...
wrote many fugues inspired by his study of the music of Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (German: Help:IPA/Standard German, ïżœjoËhan zeËbastiÌŻan baÏ ( â 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque music, Baroque period. He is known for his prolific output across a variety ...
.
Johannes Brahms' ''Variations and Fugue on a Theme by Handel'', Op. 24, is a work for solo piano written in 1861. It consists of a set of twenty-five variations and a concluding fugue, all based on a theme from George Frideric Handel's ''Harpsichord Suite No. 1 in Bâ major'', HWV 434.
 ]
]
Franz Liszt
Franz Liszt (22 October 1811 â 31 July 1886) was a Hungarian composer, virtuoso pianist, conductor and teacher of the Romantic music, Romantic period. With a diverse List of compositions by Franz Liszt, body of work spanning more than six ...
's Piano Sonata in B minor (1853) contains a powerful fugue, demanding incisive virtuosity from its player:
Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, essayist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most o ...
included several fugues in his opera ''Die Meistersinger von NĂŒrnberg
(; "The Master-Singers of Nuremberg"), WWV 96, is a music drama, or opera, in three acts, by Richard Wagner. It is the longest opera commonly performed, taking nearly four and a half hours, not counting two breaks between acts, and is traditio ...
''. Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi ( ; ; 9 or 10 October 1813 â 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for List of compositions by Giuseppe Verdi, his operas. He was born near Busseto, a small town in the province of Parma ...
included a whimsical example at the end of his opera '' Falstaff'' and his setting of the Requiem Mass contained two (originally three) choral fugues. Anton Bruckner
Joseph Anton Bruckner (; ; 4 September 182411 October 1896) was an Austrian composer and organist best known for his Symphonies by Anton Bruckner, symphonies and sacred music, which includes List of masses by Anton Bruckner, Masses, Te Deum (Br ...
and Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 â 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic music, Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and ...
also included them in their respective symphonies. The exposition of the finale of Bruckner's Symphony No. 5 begins with a fugal exposition. The exposition ends with a chorale, the melody of which is then used as a second fugal exposition at the beginning of the development. The recapitulation features both fugal subjects concurrently. The finale of Mahler's Symphony No. 5 features a "fugue-like" passage early in the movement, though this is not actually an example of a fugue.
20th century
Twentieth-century composers brought fugue back to its position of prominence, realizing its uses in full instrumental works, its importance in development and introductory sections, and the developmental capabilities of fugal composition. The second movement ofMaurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 â 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism in music, Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composer ...
's piano suite ''Le Tombeau de Couperin
''Le Tombeau de Couperin'' (''The Tomb of Couperin'') is a suite (music), suite for solo piano by Maurice Ravel, composed between 1914 and 1917. The piece is in six movements, based on those of a traditional Baroque music, Baroque suite. Each ...
'' (1917) is a fugue that Roy Howat (200, p. 88) describes as having "a subtle glint of jazz".
BĂ©la BartĂłk
BĂ©la Viktor JĂĄnos BartĂłk (; ; 25 March 1881 â 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as Hunga ...
's '' Music for Strings, Percussion and Celesta'' (1936) opens with a slow fugue that Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 19255 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war contemporary classical music.
Born in Montb ...
(1986, pp. 346â47) regards as "certainly the finest and most characteristic example of BartĂłk's subtle style... probably the most ''timeless'' of all BartĂłk's works â a fugue that unfolds like a fan to a point of maximum intensity and then closes, returning to the mysterious atmosphere of the opening." The second movement of BartĂłk's Sonata for Solo Violin is a fugue, and the first movement of his Sonata for Two Pianos and Percussion contains a fugato.
''Schwanda the Bagpiper'' (Czech: Ć vanda dudĂĄk), written in 1926, an opera in two acts (five scenes), with music by JaromĂr Weinberger, includes a ''Polka'' followed by a powerful ''Fugue'' based on the Polka theme.
Igor Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky ( â 6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and American citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential 20th-century c ...
also incorporated fugues into his works, including the Symphony of Psalms and the Dumbarton Oaks concerto. Stravinsky recognized the compositional techniques of Bach, and in the second movement of his Symphony of Psalms (1930), he lays out a fugue that is much like that of the Baroque era. It employs a double fugue with two distinct subjects, the first beginning in C and the second in E. Techniques such as stretto, sequencing, and the use of subject incipits are frequently heard in the movement. Dmitri Shostakovich
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich, group=n (9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his First Symphony in 1926 and thereafter was regarded as a major composer.
Shostak ...
's 24 Preludes and Fugues is the composer's homage to Bach's two volumes of The Well-Tempered Clavier. In the first movement of his Fourth Symphony, starting at rehearsal mark 63, is a gigantic fugue in which the 20-bar subject (and tonal answer) consist entirely of semiquavers, played at the speed of quaver = 168.
Olivier Messiaen, writing about his '' Vingt regards sur l'enfant-Jésus'' (1944) wrote of the sixth piece of that collection, "''Par Lui tout a été fait''" ("By Him were all things made"):
György Ligeti
György SĂĄndor Ligeti (; ; 28 May 1923 â 12 June 2006) was a Hungarian-Austrian composer of contemporary classical music. He has been described as "one of the most important avant-garde music, avant-garde composers in the latter half of the ...
wrote a five-part double fugue for his ''Requiem'''s second movement, the Kyrie, in which each part (SMATB) is subdivided in four-voice "bundles" that make a canon
Canon or Canons may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Canon (fiction), the material accepted as officially written by an author or an ascribed author
* Literary canon, an accepted body of works considered as high culture
** Western canon, th ...
. The melodic material in this fugue is totally chromatic, with melismatic (running) parts overlaid onto skipping intervals, and use of polyrhythm
Polyrhythm () is the simultaneous use of two or more rhythms that are not readily perceived as deriving from one another, or as simple manifestations of the same meter. The rhythmic layers may be the basis of an entire piece of music (cross-rh ...
(multiple simultaneous subdivisions of the measure), blurring everything both harmonically and rhythmically so as to create an aural aggregate, thus highlighting the theoretical/aesthetic question of the next section as to whether fugue is a form or a texture. According to Tom Service, in this work, Ligeti
Benjamin Britten
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten of Aldeburgh (22 November 1913 â 4 December 1976) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, o ...
used a fugue in the final part of '' The Young Person's Guide to the Orchestra'' (1946). The Henry Purcell
Henry Purcell (, rare: ; September 1659 â 21 November 1695) was an English composer of Baroque music, most remembered for his more than 100 songs; a tragic opera, Dido and Aeneas, ''Dido and Aeneas''; and his incidental music to a version o ...
theme is triumphantly cited at the end, making it a choral fugue.
Canadian pianist and musical thinker Glenn Gould composed '' So You Want to Write a Fugue?'', a full-scale fugue set to a text that cleverly explicates its own musical form.
Outside classical music
Fugues (or fughettas/fugatos) have been incorporated into genres outside Western classical music. Several examples exist withinjazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
, such as ''Bach goes to Town'', composed by the Welsh composer Alec Templeton and recorded by Benny Goodman
Benjamin David Goodman (May 30, 1909 â June 13, 1986) was an American clarinetist and bandleader, known as the "King of Swing". His orchestra did well commercially.
From 1936 until the mid-1940s, Goodman led one of the most popular swing bi ...
in 1938, and ''Concorde
Concorde () is a retired Anglo-French supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC).
Studies started in 1954, and France and the United Kingdom signed a treaty establishin ...
'' composed by John Lewis and recorded by the Modern Jazz Quartet
The Modern Jazz Quartet (MJQ) was a jazz combo established in 1952 that played music influenced by classical music, classical, cool jazz, blues and bebop. The Quartet consisted of John Lewis (pianist), John Lewis (piano), Milt Jackson (vibraphon ...
in 1955.
In " Fugue for Tinhorns" from the Broadway musical Guys and Dolls, written by Frank Loesser
Frank Henry Loesser ( "lesser"; June 29, 1910 â July 28, 1969) was an American songwriter who wrote the music and lyrics for the Broadway theatre, Broadway musicals ''Guys and Dolls (musical), Guys and Dolls'' and ''How to Succeed in Business ...
, the characters Nicely-Nicely, Benny, and Rusty sing simultaneously about hot tips they each have in an upcoming horse race.
In "West Side Story
''West Side Story'' is a Musical theatre, musical conceived by Jerome Robbins with music by Leonard Bernstein, lyrics by Stephen Sondheim, and a Book (musical theatre), book by Arthur Laurents.
Inspired by William Shakespeare's play ''Romeo an ...
", the dance sequence following the song "Cool" is structured as a fugue. Interestingly, Leonard Bernstein
Leonard Bernstein ( ; born Louis Bernstein; August 25, 1918 â October 14, 1990) was an American conductor, composer, pianist, music educator, author, and humanitarian. Considered to be one of the most important conductors of his time, he was th ...
quotes Beethoven's monumental "GroĂe Fuge" for string quartet and employs Arnold Schoenberg's twelve tone technique, all in the context of a jazz infused Broadway show stopper.
A few examples also exist within progressive rock
Progressive rock (shortened as prog rock or simply prog) is a broad genre of rock music that primarily developed in the United Kingdom through the mid- to late 1960s, peaking in the early-to-mid-1970s. Initially termed " progressive pop", the ...
, such as the central movement of " The Endless Enigma" by Emerson, Lake & Palmer
Emerson, Lake & Palmer (informally known as ELP) were an English progressive rock Supergroup (music), supergroup formed in London in 1970. The band consisted of Keith Emerson (keyboards) of The Nice, Greg Lake (vocals, bass, guitars, producer) ...
and " On Reflection" by Gentle Giant.
On their EP of the same name, Vulfpeck has a composition called "Fugue State", which incorporates a fugue-like section between Theo Katzman (guitar), Joe Dart (bass), and Woody Goss (Wurlitzer keyboard).
The composer Matyas Seiber included an atonal or twelve-tone fugue, for flute trumpet and string quartet, in his score for the 1953 film ''Graham Sutherland''
The film composer John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (November 15, 2022)Classic Connection review, ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who w ...
includes a fugue in his score for the 1990 film, ''Home Alone
''Home Alone'' is a 1990 American Christmas comedy film
The comedy film is a film genre that emphasizes humor. These films are designed to amuse audiences and make them laugh. Films in this genre typically have a happy ending, with dar ...
'', at the point where Kevin, accidentally left at home by his family, and realizing he is about to be attacked by a pair of bumbling burglars, begins to plan his elaborate defenses. Another fugue occurs at a similar point in the 1992 sequel film, '' Home Alone 2: Lost in New York''.
The jazz composer and film composer, Michel Legrand
Michel Jean Legrand (; 24 February 1932 â 26 January 2019) was a French musical composer, arranger, conductor, jazz pianist, and singer. Legrand was a prolific composer, having written over 200 film and television scores, in addition to ma ...
, includes a fugue as the climax of his score (a classical theme with variations, and fugue) for Joseph Losey
Joseph Walton Losey III (; January 14, 1909 â June 22, 1984) was an American film and theatre director, producer, and screenwriter. Born in Wisconsin, he studied in Germany with Bertolt Brecht and then returned to the United States. Hollywood ...
's 1972 film '' The Go-Between'', based on the 1953 novel by British novelist, L.P. Hartley, as well as several times in his score for Jacques Demy
Jacques Demy (; 5 June 1931 â 27 October 1990) was a French director, screenwriter and lyricist. He appeared at the height of the French New Wave alongside contemporaries like Jean-Luc Godard and François Truffaut. Demy's films are celebrated ...
's 1970 film '' Peau d'Ăąne''.
Discussion
Musical form or texture
A widespread view of the fugue is that it is not a musical form but rather a technique of composition. The Austrian musicologist Erwin Ratz argues that the formal organization of a fugue involves not only the arrangement of its theme and episodes, but also its harmonic structure. In particular, the exposition and coda tend to emphasize the tonic key, whereas the episodes usually explore more distant tonalities. Ratz stressed, however, that this is the core, underlying form ("Urform") of the fugue, from which individual fugues may deviate. Although certain related keys are more commonly explored in fugal development, the overall structure of a fugue does not limit its harmonic structure. For example, a fugue may not even explore the dominant, one of the most closely related keys to the tonic. Bach's Fugue in B major from Book 1 of the ''Well Tempered Clavier'' explores the relative minor, thesupertonic
In music, the supertonic is the second degree () of a diatonic scale, one whole step above the tonic. In the movable do solfĂšge system, the supertonic note is sung as ''re''.
The triad built on the supertonic note is called the supertonic ...
and the subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
. This is unlike later forms such as the sonata, which clearly prescribes which keys are explored (typically the tonic and dominant in an ABA form). Then, many modern fugues dispense with traditional tonal harmonic scaffolding altogether, and either use serial (pitch-oriented) rules, or (as the Kyrie/Christe in György Ligeti
György SĂĄndor Ligeti (; ; 28 May 1923 â 12 June 2006) was a Hungarian-Austrian composer of contemporary classical music. He has been described as "one of the most important avant-garde music, avant-garde composers in the latter half of the ...
's ''Requiem'', Witold LutosĆawski works), use panchromatic, or even denser, harmonic spectra.
Perceptions and aesthetics
The fugue is the most complex of contrapuntal forms. In Ratz's words, "fugal technique significantly burdens the shaping of musical ideas, and it was given only to the greatest geniuses, such as Bach and Beethoven, to breathe life into such an unwieldy form and make it the bearer of the highest thoughts." In presenting Bach's fugues as among the greatest of contrapuntal works, Peter Kivy points out that "counterpoint itself, since time out of mind, has been associated in the thinking of musicians with the profound and the serious" and argues that "there seems to be some rational justification for their doing so." This is related to the idea that restrictions create freedom for the composer, by directing their efforts. He also points out that fugal writing has its roots in improvisation, and was, during the Renaissance, practiced as an improvisatory art. Writing in 1555,Nicola Vicentino
Nicola Vicentino (1511 – 1575 or 1576) was an Italian music theory, music theorist and composer of the Renaissance music, Renaissance. He was one of the most progressive musicians of the age, inventing, among other things, a microtonal keyb ...
, for example, suggests that:
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* *External links
Score
, J. S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'', Mutopia Project
Fugues of the Well-Tempered Clavier
(viewable in Adob
o
Analyses of J. S. Bach's ''Well-Tempered Clavier'' with accompanying recordings
* * * {{Authority control * Polyphonic form Classical music styles Choral music genres