Flat World on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the
Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the
 In early
In early
 The model of an
The model of an

50–53
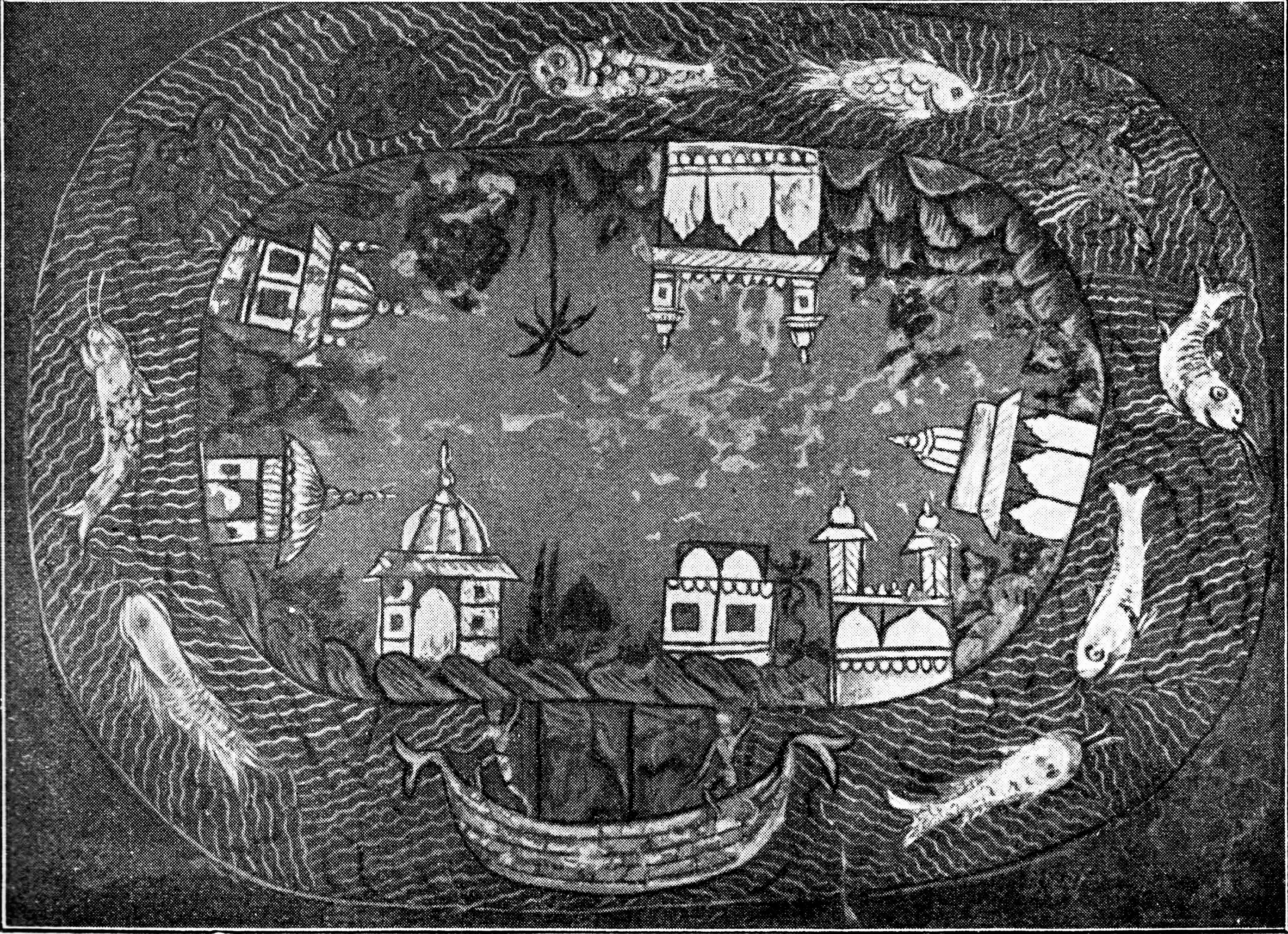
. The medieval Indian texts called the describe the Earth as a flat-bottomed, circular disk with concentric oceans and continents. D. Pingree: "History of Mathematical Astronomy in India", ''Dictionary of Scientific Biography'', Vol. 15 (1978), pp. 533–633 (554ff.), Quote: "In the Purānas, the Earth is a flat-bottomed, circular disk, in the center of which is a lofty mountain, Meru. Surrounding Meru is the circular continent Jambūdvīpa, which is in turn surrounded by a ring of water known as the Salt Ocean. There follow alternating rings of land and sea until there are seven continents and seven oceans. In the southern quarter of Jambūdvīpa lies India–Bhāratavarsa." This general scheme is present not only in the Hindu cosmologies, but also in
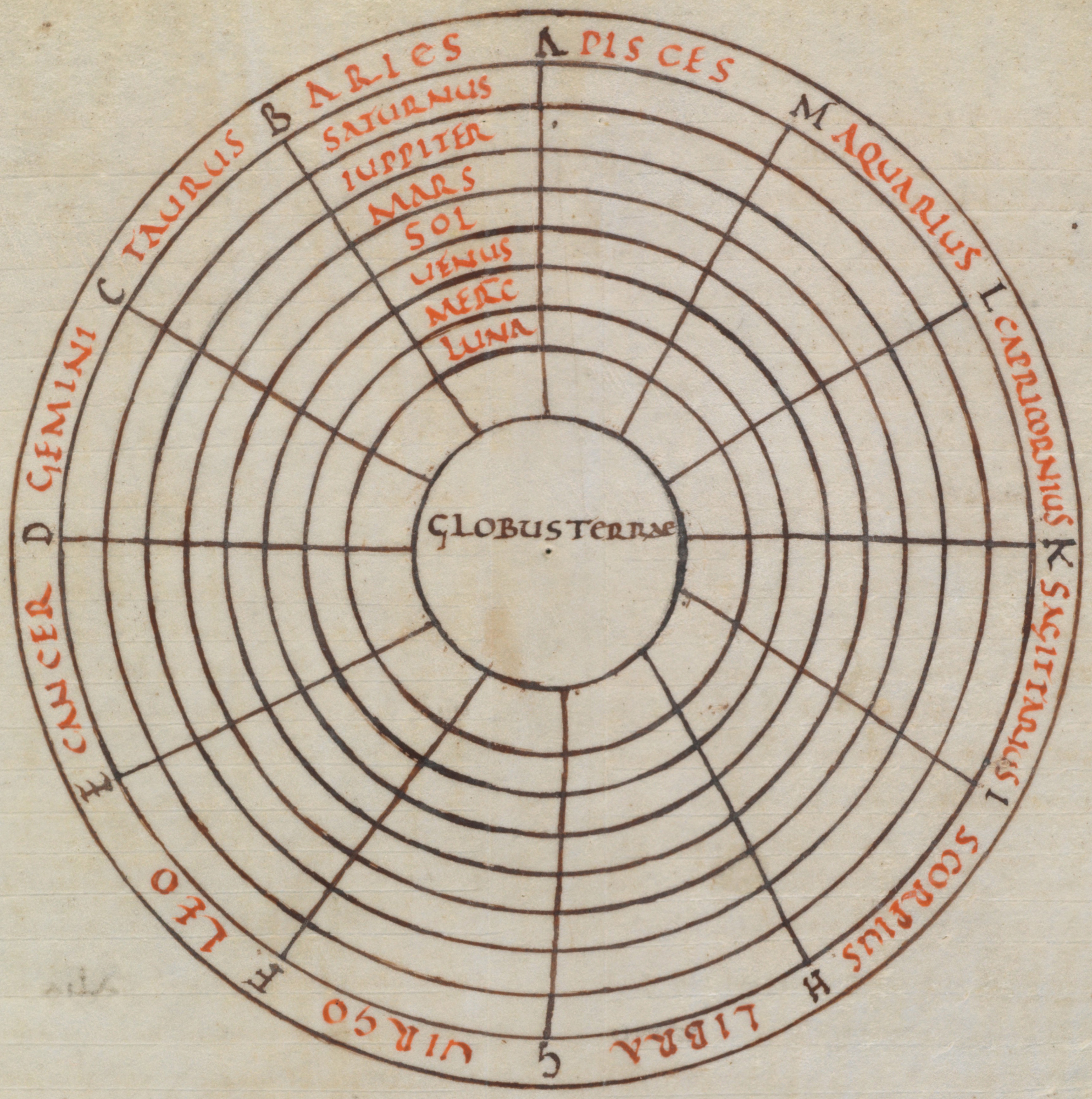 With the end of the
With the end of the  Europe's view of the shape of the Earth in
Europe's view of the shape of the Earth in  St Vergilius of Salzburg (c. 700–784), in the middle of the 8th century, discussed or taught some geographical or cosmographical ideas that
St Vergilius of Salzburg (c. 700–784), in the middle of the 8th century, discussed or taught some geographical or cosmographical ideas that
 In the modern era, the
In the modern era, the
The Myth of the Flat Earth
You say the earth is round? Prove it
(from
Flat Earth Fallacy
at sacred-texts.com * ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ThPgMu2-ToM&t=0 Flat Earth idea of the Suns trajectory
Flat Earth Theory of the Moon & Sun's paths around the world
{{Authority control Early scientific cosmologies Ancient Near Eastern cosmology
 Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the
Flat Earth is an archaic and scientifically disproven conception of the Earth's shape
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is s ...
as a plane
Plane most often refers to:
* Aero- or airplane, a powered, fixed-wing aircraft
* Plane (geometry), a flat, 2-dimensional surface
* Plane (mathematics), generalizations of a geometrical plane
Plane or planes may also refer to:
Biology
* Plane ...
or disk. Many ancient cultures, notably in the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
, subscribed to a flat-Earth cosmography
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-sca ...
. The model has undergone a recent resurgence as a conspiracy theory
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that asserts the existence of a conspiracy (generally by powerful sinister groups, often political in motivation), when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
* ...
in the 21st century.
The idea of a spherical Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of the figure of the Earth as a sphere. The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Ancient Greek philos ...
appeared in ancient Greek philosophy
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC. Philosophy was used to make sense of the world using reason. It dealt with a wide variety of subjects, including astronomy, epistemology, mathematics, political philosophy, ethics, metaphysics ...
with Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
(6th century BC). However, the early Greek cosmological view of a flat Earth persisted among most pre-Socratics
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of the ...
(6th–5th century BC). In the early 4th century BC, Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the writte ...
wrote about a spherical Earth. By about 330 BC, his former student Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
had provided strong empirical evidence
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how the ...
for a spherical Earth. Knowledge of the Earth's global shape gradually began to spread beyond the Hellenistic world
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the Roma ...
. By the early period of the Christian Church, the spherical view was widely held, with some notable exceptions. In contrast, ancient Chinese scholars consistently describe the Earth as flat, and this perception remained unchanged until their encounters with Jesuit missionaries
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rome. It was founded in 1540 ...
in the 17th century. Muslim scholars in early Islam maintained that the Earth is flat. However, since the 9th century, Muslim scholars have tended to believe in a spherical Earth.
It is a historical myth that medieval Europeans generally thought the Earth was flat. This myth was created in the 17th century by Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
s to argue against Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
teachings.
Despite the scientific facts and obvious effects of Earth's sphericity, pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable cl ...
flat-Earth conspiracy theories persist. Since the 2010s, belief in a flat Earth has increased, both as membership of modern flat Earth societies
Anti-scientific beliefs in a flat Earth are promoted by a number of organizations and individuals. The claims of modern flat Earth proponents are not based on scientific knowledge and are contrary to over two millennia of scientific consensu ...
, and as unaffiliated individuals using social media
Social media are interactive technologies that facilitate the Content creation, creation, information exchange, sharing and news aggregator, aggregation of Content (media), content (such as ideas, interests, and other forms of expression) amongs ...
. In a 2018 study reported on by ''Scientific American'', only 82% of 18- to 24-year-old American respondents agreed with the statement "I have always believed the world is round". However, a firm belief in a flat Earth is rare, with less than 2% acceptance in all age groups.
History
Belief in flat Earth
Near East
Egyptian
''Egyptian'' describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of year ...
and Mesopotamian thought, the world was portrayed as a disk floating in the ocean. A similar model is found in the Homeric
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is ...
account from the 8th century BC in which "Okeanos, the personified body of water surrounding the circular surface of the Earth, is the begetter of all life and possibly of all gods."
The Pyramid Texts
The Pyramid Texts are the oldest ancient Egyptian funerary texts, dating to the late Old Kingdom. They are the earliest known corpus of ancient Egyptian religious texts. Written in Old Egyptian, the pyramid texts were carved onto the subterranea ...
and Coffin Texts
The Coffin Texts are a collection of ancient Egyptian funerary spells written on coffins beginning in the First Intermediate Period. They are partially derived from the earlier Pyramid Texts, reserved for royal use only, but contain substantial n ...
of ancient Egypt show a similar cosmography; Nun
A nun is a woman who vows to dedicate her life to religious service and contemplation, typically living under vows of poverty, chastity, and obedience in the enclosure of a monastery or convent.''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. X, page 5 ...
(the Ocean) encircled ''nbwt'' ("dry lands" or "Islands").
The Israelites also imagined the Earth to be a disc floating on water with an arched firmament
In ancient near eastern cosmology, the firmament means a celestial barrier that separates the heavenly waters above from the Earth below. In biblical cosmology, the firmament ( ''rāqīaʿ'') is the vast solid dome created by God during the G ...
above it that separated the Earth from the heavens. The sky was a solid dome with the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars embedded in it.
Greece
=Poets
= BothHomer
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his autho ...
and Hesiod
Hesiod ( or ; ''Hēsíodos''; ) was an ancient Greece, Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer.M. L. West, ''Hesiod: Theogony'', Oxford University Press (1966), p. 40.Jasper Gr ...
described a disc cosmography on the Shield of Achilles
The shield of Achilles is the shield that Achilles uses in his fight with Hector, as described in a passage in Book 18, lines 478–608 of Homer's ''Iliad''. The intricately detailed imagery on the shield has inspired many different interpretatio ...
. This poetic tradition of an Earth-encircling (''gaiaokhos'') sea (Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus ( ; , also , , or ) was a Titans, Titan son of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys (mythology), Tethys, and the father of the River gods (Greek mythology), river gods ...
) and a disc also appears in Stasinus
Stasinus () of Cyprus was a semi-legendary early Greek poet. He is best known for his lost work ''Cypria'', which was one of the poems belonging to the Epic Cycle that narrated the War of Troy.
The ''Cypria'', presupposing an acquaintance with ...
of Cyprus, Mimnermus
Mimnermus ( ''Mímnermos'') was a Greek elegiac poet from either Colophon or Smyrna in Ionia, who flourished about 632–629 BC (i.e. in the 37th Olympiad, according to Suda). He was strongly influenced by Homer, yet he wrote short poems suitabl ...
, Aeschylus
Aeschylus (, ; ; /524 – /455 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek Greek tragedy, tragedian often described as the father of tragedy. Academic knowledge of the genre begins with his work, and understanding of earlier Greek tragedy is large ...
, and Apollonius Rhodius
Apollonius of Rhodes ( ''Apollṓnios Rhódios''; ; fl. first half of 3rd century BC) was an ancient Greek author, best known for the ''Argonautica'', an epic poem about Jason and the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. The poem is ...
.
Homer's description of the disc cosmography on the shield of Achilles with the encircling ocean is repeated far later in Quintus Smyrnaeus
Quintus Smyrnaeus (also Quintus of Smyrna; , ''Kointos Smyrnaios'') was a Greek epic poet whose ''Posthomerica'', following "after Homer", continues the narration of the Trojan War. The dates of Quintus Smyrnaeus' life and poetry are disputed: by ...
' ''Posthomerica
The ''Posthomerica'' () is an epic poem in Greek hexameter verse by Quintus of Smyrna. Probably written in the 3rd century AD, it tells the story of the Trojan War, between the death of Hector and the fall of Troy, Ilium (Troy). The poem is an ab ...
'' (4th century AD), which continues the narration of the Trojan War.
=Philosophers
= Severalpre-Socratic philosophers
Pre-Socratic philosophy, also known as early Greek philosophy, is ancient Greek philosophy before Socrates. Pre-Socratic philosophers were mostly interested in cosmology, the beginning and the substance of the universe, but the inquiries of the ...
believed that the world was flat: Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
(c. 550 BC) according to several sources, and Leucippus
Leucippus (; , ''Leúkippos''; ) was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. He is traditionally credited as the founder of atomism, which he developed with his student Democritus. Leucippus divided the world into two entities: atoms, indivisible ...
(c. 440 BC) and Democritus
Democritus (, ; , ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, Thrace, Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an ...
(c. 460–370 BC) according to Aristotle.
Thales thought that the Earth floated in water like a log. It has been argued, however, that Thales actually believed in a spherical Earth. Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
(c. 550 BC) believed that the Earth was a short cylinder with a flat, circular top that remained stable because it was the same distance from all things. Anaximenes of Miletus
Anaximenes of Miletus (; ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek, Pre-Socratic philosophy, Pre-Socratic philosopher from Miletus in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey). He was the last of the three philosophers of the Ionian School (philosophy), Milesi ...
believed that "the Earth is flat and rides on air; in the same way the Sun and the Moon and the other heavenly bodies, which are all fiery, ride the air because of their flatness". Xenophanes
Xenophanes of Colophon ( ; ; – c. 478 BC) was a Greek philosopher, theologian, poet, and critic of Homer. He was born in Ionia and travelled throughout the Greek-speaking world in early classical antiquity.
As a poet, Xenophanes was known f ...
(c. 500 BC) thought that the Earth was flat, with its upper side touching the air, and the lower side extending without limit.
Belief in a flat Earth continued into the 5th century BC. Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; , ''Anaxagóras'', 'lord of the assembly'; ) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, Anaxagoras came to Athens. In later life he was charged ...
(c. 450 BC) agreed that the Earth was flat, and his pupil Archelaus believed that the flat Earth was depressed in the middle like a saucer, to allow for the fact that the Sun does not rise and set at the same time for everyone.
=Historians
=Hecataeus of Miletus
Hecataeus of Miletus (; ; c. 550 – c. 476 BC), son of Hegesander, was an early Greek historian and geographer.
Biography
Hailing from a very wealthy family, he lived in Miletus, then under Persian rule in the satrapy of Lydia ...
believed that the Earth was flat and surrounded by water. Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
in his ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust) ...
'' ridiculed the belief that water encircled the world, yet most classicists agree that he still believed Earth was flat because of his descriptions of literal "ends" or "edges" of the Earth.
Northern Europe
The ancient Norse and Germanic peoples believed in a flat-Earth cosmography with the Earth surrounded by an ocean, with theaxis mundi
In astronomy, is the Latin term for the axis of Earth between the celestial poles. In a geocentric coordinate system, this is the axis of rotation of the celestial sphere. Consequently, in ancient Greco-Roman astronomy, the is the axis of ...
, a world tree (Yggdrasil
Yggdrasil () is an immense and central sacred tree in Norse cosmology. Around it exists all else, including the Nine Worlds.
Yggdrasil is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'' compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in t ...
), or pillar (Irminsul
An Irminsul (Old Saxon 'great pillar') was a sacred, Column, pillar-like object attested as playing an important role in the Germanic paganism of the Saxons. Medieval sources describe how an Irminsul was destroyed by Charlemagne during the Saxon ...
) in the centre. In the world-encircling ocean sat a snake called Jormungandr. The Norse creation account preserved in Gylfaginning
''Gylfaginning'' (Old Norse: 'The Beguiling of Gylfi' or 'The Deluding of Gylfi'; 13th century Old Norse pronunciation ) is the first main part of the 13th century ''Prose Edda'', after the initial Prologue. The ''Gylfaginning'' takes the form of ...
(VIII) states that during the creation of the Earth, an impassable sea was placed around it:
The late Norse Konungs skuggsjá, on the other hand, explains Earth's shape as a sphere:
East Asia
Inancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, the prevailing belief was that the Earth was flat and square, while the heavens were round, an assumption virtually unquestioned until the introduction of European astronomy in the 17th century. The English sinologist
Sinology, also referred to as China studies, is a subfield of area studies or East Asian studies involved in social sciences and humanities research on China. It is an academic discipline that focuses on the study of the Chinese civilizatio ...
Cullen emphasizes the point that there was no concept of a round Earth in ancient Chinese astronomy:
 The model of an
The model of an egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the ...
was often used by Chinese astronomers such as Zhang Heng
Zhang Heng (; AD 78–139), formerly romanization of Chinese, romanized Chang Heng, was a Chinese polymathic scientist and statesman who lived during the Han dynasty#Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han dynasty. Educated in the capital citi ...
(78–139 AD) to describe the heavens
Heaven, or the Heavens, is a common religious cosmological or supernatural place where beings such as deities, angels, souls, saints, or venerated ancestors are said to originate, be enthroned, or reside. According to the beliefs of some r ...
as spherical:
This analogy with a curved egg led some modern historians, notably Joseph Needham
Noel Joseph Terence Montgomery Needham (; 9 December 1900 – 24 March 1995) was a British biochemist, historian of science and sinologist known for his scientific research and writing on the history of Chinese science and technology, initia ...
, to conjecture that Chinese astronomers were, after all, aware of the Earth's sphericity. The egg reference, however, was rather meant to clarify the relative position of the flat Earth to the heavens:
Further examples cited by Needham supposed to demonstrate dissenting voices from the ancient Chinese consensus actually refer without exception to the Earth being square, not to it being flat. Accordingly, the 13th-century scholar Li Ye, who argued that the movements of the round heaven would be hindered by a square Earth, did not advocate a spherical Earth, but rather that its edge should be rounded off so as to be circular. However, Needham disagrees, affirming that Li Ye believed the Earth to be spherical, similar in shape to the heavens but much smaller. This was preconceived by the 4th-century scholar Yu Xi
Yu Xi (虞喜; 307–345 AD), courtesy name Zhongning (仲寧), was a Chinese astronomer, politician, and writer of the Jin dynasty (266–420 AD). He is best known for his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes, independently of the earlie ...
, who argued for the infinity of outer space surrounding the Earth and that the latter could be either square or round, in accordance to the shape of the heavens. When Chinese geographers of the 17th century, influenced by European cartography and astronomy, showed the Earth as a sphere that could be circumnavigated by sailing around the globe, they did so with formulaic terminology previously used by Zhang Heng to describe the spherical shape of the Sun and Moon (i.e. that they were as round as a crossbow bullet).
As noted in the book ''Huainanzi
The ''Huainanzi'' is an ancient Chinese text made up of essays from scholarly debates held at the court of Liu An, Prince of Huainan, before 139 BCE. Compiled as a handbook for an enlightened sovereign and his court, the work attempts to defi ...
'', in the 2nd century BC, Chinese astronomers effectively inverted Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
' calculation of the curvature of the Earth to calculate the height of the Sun above the Earth. By assuming the Earth was flat, they arrived at a distance of (approximately ). The ''Zhoubi Suanjing
The ''Zhoubi Suanjing'', also known by many other names, is an ancient Chinese astronomical and mathematical work. The ''Zhoubi'' is most famous for its presentation of Chinese cosmology and a form of the Pythagorean theorem. It claims to pr ...
'' also discusses how to determine the distance of the Sun by measuring the length of noontime shadows at different latitudes, a method similar to Eratosthenes' measurement of the circumference of the Earth, but the ''Zhoubi Suanjing'' assumes that the Earth is flat.
Alternate or mixed theories
Greece: spherical Earth

Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
in the 6th century BC and Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; ; fl. late sixth or early fifth century BC) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic ancient Greece, Greek philosopher from Velia, Elea in Magna Graecia (Southern Italy).
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Veli ...
in the 5th century BC stated that the Earth is spherical, and this view spread rapidly in the Greek world. Around 330 BC, Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
maintained on the basis of physical theory and observational evidence that the Earth was spherical, and reported an estimate of its circumference. The Earth's circumference
In geometry, the circumference () is the perimeter of a circle or ellipse. The circumference is the arc length of the circle, as if it were opened up and straightened out to a line segment. More generally, the perimeter is the curve length arou ...
was first determined around 240 BC by Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
. By the 2nd century AD, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
had derived his maps from a globe and developed the system of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
, longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
, and clime
The climes (singular ''clime''; also ''clima'', plural ''climata'', from Greek κλίμα ''klima'', plural κλίματα ''klimata'', meaning "inclination" or "slope") in classical Greco-Roman geography and astronomy were the divisions of ...
s. His ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' ( ) is a 2nd-century Greek mathematics, mathematical and Greek astronomy, astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy ( ) in Koine Greek. One of the most i ...
'' was written in Greek and only translated into Latin in the 11th century from Arabic translations.
Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( ; ; – October 15, 55 BC) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem '' De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, which usually is t ...
(1st century BC) opposed the concept of a spherical Earth, because he considered that an infinite universe had no center towards which heavy bodies would tend. Thus, he thought the idea of animals walking around topsy-turvy under the Earth was absurd. By the 1st century AD, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vesp ...
was in a position to say that everyone agreed on the spherical shape of Earth, though disputes continued regarding the nature of the antipodes
In geography, the antipode () of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it. A pair of points ''antipodal'' () to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Ea ...
, and how it is possible to keep the ocean
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of Earth. The ocean is conventionally divided into large bodies of water, which are also referred to as ''oceans'' (the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian Ocean, Indian, Southern Ocean ...
in a curved shape.
South Asia
TheVedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas ( or ; ), sometimes collectively called the Veda, are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed ...
texts depict the cosmos in many ways. One of the earliest Indian cosmological texts pictures the Earth as one of a stack of flat disks.
In the Vedic texts, Dyaus
Dyaus (Vedic Sanskrit: द्यौस्, ) or Dyauspitr (Vedic Sanskrit: द्यौष्पितृ, ) is the Rigvedic sky deity. His consort is Prthvi, the earth goddess, and together they are the archetypal parents in the Rigveda.
N ...
(heaven) and Prithvi
Prithvi (Sanskrit: पृथ्वी, ', also पृथिवी, ', "the Vast One", also rendered Pṛthvī Mātā), is the Sanskrit name for the earth, as well as the name of the goddess-personification of it in Hinduism. The goddess Prit ...
(Earth) are compared to wheels on an axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In ...
, yielding a flat model. They are also described as bowls or leather bags, yielding a concave model. According to Macdonell: "the conception of the Earth being a disc surrounded by an ocean does not appear in the Samhita
Samhita (IAST: ''Saṃhitā'') literally means "put together, joined, union", a "collection", and "a methodical, rule-based combination of text or verses".
s. But it was naturally regarded as circular, being compared with a wheel (10.89) and expressly called circular (parimandala) in the ''Shatapatha Brahmana
The Shatapatha Brahmana (, , abbreviated to 'SB') is a commentary on the Yajurveda, Śukla Yajurveda. It is attributed to the Vedic sage Yajnavalkya. Described as the most complete, systematic, and important of the Brahmanas (commentaries on the ...
''."
By about the 5th century AD, the ''siddhanta
(Devanagari: ) is a Sanskrit term denoting the established and accepted view of any particular school within Indian philosophy; literally "settled opinion or doctrine, dogma, axiom, received or admitted truth; any fixed or established or canon ...
'' astronomy texts of South Asia, particularly of Aryabhata
Aryabhata ( ISO: ) or Aryabhata I (476–550 CE) was the first of the major mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy. His works include the '' Āryabhaṭīya'' (which mentions that in 3600 ' ...
, assume a spherical Earth as they develop mathematical methods for quantitative astronomy for calendar and time keeping.Plofker (2009
2009 was designated as the International Year of Astronomy by the United Nations to coincide with the 400th anniversary of Galileo Galilei's first known astronomical studies with a telescope and the publication of Astronomia Nova by Joha ...
, pp.&nbs50–53
. The medieval Indian texts called the describe the Earth as a flat-bottomed, circular disk with concentric oceans and continents. D. Pingree: "History of Mathematical Astronomy in India", ''Dictionary of Scientific Biography'', Vol. 15 (1978), pp. 533–633 (554ff.), Quote: "In the Purānas, the Earth is a flat-bottomed, circular disk, in the center of which is a lofty mountain, Meru. Surrounding Meru is the circular continent Jambūdvīpa, which is in turn surrounded by a ring of water known as the Salt Ocean. There follow alternating rings of land and sea until there are seven continents and seven oceans. In the southern quarter of Jambūdvīpa lies India–Bhāratavarsa." This general scheme is present not only in the Hindu cosmologies, but also in
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
and Jain cosmologies of South Asia. However, some Puranas include other models. The fifth canto of the ''Bhagavata Purana
The ''Bhagavata Purana'' (; ), also known as the ''Srimad Bhagavatam (Śrīmad Bhāgavatam)'', ''Srimad Bhagavata Mahapurana'' () or simply ''Bhagavata (Bhāgavata)'', is one of Hinduism's eighteen major Puranas (''Mahapuranas'') and one ...
'', for example, includes sections that describe the Earth both as flat and spherical.
Early Christian Church
During the early period of the Christian Church, the spherical view continued to be widely held, with some notable exceptions. Until the mid-fourth century AD, virtually all Christian authors held that the Earth was round. Athenagoras, an eastern Christian writing around the year 175 AD, said that the Earth was spherical. Methodius (c. 290 AD), an eastern Christian writing against "the theory of the Chaldeans and the Egyptians" said: "Let us first lay bare ... the theory of the Chaldeans and the Egyptians. They say that the circumference of the universe is likened to the turnings of a well-rounded globe, the Earth being a central point. They say that since its outline is spherical, ... the Earth should be the center of the universe, around which the heaven is whirling."Arnobius
Arnobius (died c. 330) was an early Christian apologist of Berber origin during the reign of Diocletian (284–305).
According to Jerome's ''Chronicle,'' Arnobius, before his conversion, was a distinguished Numidian rhetorician at Sicca Veneri ...
, another eastern Christian writing sometime around 305 AD, described the round Earth: "In the first place, indeed, the world itself is neither right nor left. It has neither upper nor lower regions, nor front nor back. For whatever is round and bounded on every side by the circumference of a solid sphere, has no beginning or end ..." Other advocates of a round Earth included Eusebius
Eusebius of Caesarea (30 May AD 339), also known as Eusebius Pamphilius, was a historian of Christianity, exegete, and Christian polemicist from the Roman province of Syria Palaestina. In about AD 314 he became the bishop of Caesarea Maritima. ...
, Hilary of Poitiers
Hilary of Poitiers (; ) was Bishop of Poitiers and a Doctor of the Church. He was sometimes referred to as the "Hammer of the Arians" () and the " Athanasius of the West". His name comes from the Latin word for happy or cheerful. In addition t ...
, Irenaeus
Irenaeus ( or ; ; ) was a Greeks, Greek bishop noted for his role in guiding and expanding Christianity, Christian communities in the southern regions of present-day France and, more widely, for the development of Christian theology by oppos ...
, Hippolytus of Rome
Hippolytus of Rome ( , ; Romanized: , – ) was a Bishop of Rome and one of the most important second–third centuries Christian theologians, whose provenance, identity and corpus remain elusive to scholars and historians. Suggested communitie ...
, Firmicus Maternus
__NOTOC__
Julius Firmicus Maternus was a Roman Latin writer and astrologer, who received a pagan classical education that made him conversant with Greek; he lived in the reign of Constantine I (306 to 337 AD) and his successors. His triple career ...
, Ambrose
Ambrose of Milan (; 4 April 397), venerated as Saint Ambrose, was a theologian and statesman who served as Bishop of Milan from 374 to 397. He expressed himself prominently as a public figure, fiercely promoting Roman Christianity against Ari ...
, Jerome
Jerome (; ; ; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was an early Christian presbyter, priest, Confessor of the Faith, confessor, theologian, translator, and historian; he is commonly known as Saint Jerome.
He is best known ...
, Prudentius
Aurelius Prudentius Clemens () was a Roman Christian poet, born in the Roman province of Tarraconensis (now Northern Spain) in 348.H. J. Rose, ''A Handbook of Classical Literature'' (1967) p. 508 He probably died in the Iberian Peninsula some ...
, Favonius Eulogius, and others.
The only exceptions to this consensus up until the mid-fourth century were Theophilus of Antioch
:''There is also a Theophilus of Alexandria'' ( 412)
Theophilus of Antioch () was Patriarch of Antioch from 169 until 183. He succeeded Eros of Antioch 169, and was succeeded by Maximus I 183, according to Henry Fynes Clinton, but these dat ...
and Lactantius
Lucius Caecilius Firmianus Lactantius () was an early Christian author who became an advisor to Roman emperor Constantine I, guiding his Christian religious policy in its initial stages of emergence, and a tutor to his son Crispus. His most impo ...
, both of whom held anti-Hellenistic views and associated the round-Earth view with pagan cosmology. Lactantius, a western Christian writer and advisor to the first Christian Roman Emperor, Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
* Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine g ...
, writing sometime between 304 and 313 AD, ridiculed the notion of ''antipodes
In geography, the antipode () of any spot on Earth is the point on Earth's surface diametrically opposite to it. A pair of points ''antipodal'' () to each other are situated such that a straight line connecting the two would pass through Ea ...
'' and the philosophers who fancied that "the universe is round like a ball. They also thought that heaven revolves in accordance with the motion of the heavenly bodies. ... For that reason, they constructed brass globes, as though after the figure of the universe."
The influential theologian and philosopher Saint Augustine
Augustine of Hippo ( , ; ; 13 November 354 – 28 August 430) was a theologian and philosopher of Berbers, Berber origin and the bishop of Hippo Regius in Numidia (Roman province), Numidia, Roman North Africa. His writings deeply influenced th ...
, one of the four Great Church Fathers of the Western Church
Western Christianity is one of two subdivisions of Christianity (Eastern Christianity being the other). Western Christianity is composed of the Latin Church and Western Protestantism, together with their offshoots such as the Old Catholic C ...
, similarly objected to the "fable" of antipodes:
Some historians do not view Augustine's scriptural commentaries as endorsing any particular cosmological model, endorsing instead the view that Augustine shared the common view of his contemporaries that the Earth is spherical, in line with his endorsement of science in ''De Genesi ad litteram
''De Genesi ad litteram'' (, ; ''Literal Commentary on Genesis'') is an exegetical reading of the Book of Genesis written in Latin by Augustine of Hippo. Likely completed in AD 415, this work was Augustine's second attempt to literally interpret ...
''. C. P. E. Nothaft, responding to writers like Leo Ferrari who described Augustine as endorsing a flat Earth, says that "...other recent writers on the subject treat Augustine's acceptance of the Earth's spherical shape as a well-established fact".Leo Ferrari, "Rethinking Augustine's Confessions, Thirty Years of Discoveries", Religious Studies and Theology (2000).
While it always remained a minority view, from the mid-fourth to the seventh centuries AD, the flat-Earth view experienced a revival, around the time when Diodorus of Tarsus
Diodore of Tarsus (Greek Διόδωρος ὁ Ταρσεύς; died c. 390) was a Christian bishop, monastic reformer, and theologian. A strong supporter of the orthodoxy of Nicaea, Diodore played a pivotal role in the Council of Constantinople ...
founded the exegetical school known as the School of Antioch
The Catechetical School of Antioch was one of the two major Christian centers of the study of biblical exegesis and theology during Late Antiquity; the other was the Catechetical School of Alexandria, School of Alexandria. This group was known by ...
, which sought to counter what he saw as the pagan cosmology of the Greeks with a return to the traditional cosmology. The writings of Diodorus did not survive, but are reconstructed from later criticism. This revival primarily took place in the East Syriac world (with little influence on the Latin West) where it gained proponents such as Ephrem the Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian (; ), also known as Ephraem the Deacon, Ephrem of Edessa or Aprem of Nisibis, (Syriac: ܡܪܝ ܐܦܪܝܡ ܣܘܪܝܝܐ — ''Mâr Aphrêm Sûryâyâ)'' was a prominent Christian theology, Christian theologian and Christian literat ...
and in the popular hexaemeral homilies of Jacob of Serugh
Jacob of Serugh (, ; ; 452–521), also called Jacob of Sarug or Mar Jacob (), was one of the foremost poets and theologians of the Syriac Christian tradition, second only to Ephrem the Syrian and equal to Narsai. He lived most of his life as ...
. Chrysostom, one of the four Great Church Fathers of the Eastern Church
Eastern Christianity comprises Christian traditions and church families that originally developed during classical and late antiquity in the Eastern Mediterranean region or locations further east, south or north. The term does not describe a ...
and Archbishop of Constantinople, explicitly espoused the idea, based on scripture, that the Earth floats miraculously on the water beneath the firmament
In ancient near eastern cosmology, the firmament means a celestial barrier that separates the heavenly waters above from the Earth below. In biblical cosmology, the firmament ( ''rāqīaʿ'') is the vast solid dome created by God during the G ...
.
'' Christian Topography'' (547) by the Alexandrian monk Cosmas Indicopleustes
Cosmas Indicopleustes (; also known as Cosmas the Monk) was a merchant and later hermit from Alexandria in Egypt. He was a 6th-century traveller who made several voyages to India during the reign of emperor Justinian. His work '' Christian Topogr ...
, who had traveled as far as Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
and the source of the Blue Nile
The Blue Nile is a river originating at Lake Tana in Ethiopia. It travels for approximately through Ethiopia and Sudan. Along with the White Nile, it is one of the two major Tributary, tributaries of the Nile and supplies about 85.6% of the wa ...
, is now widely considered the most valuable geographical document of the early medieval age, although it received relatively little attention from contemporaries. In it, the author repeatedly expounds the doctrine that the universe consists of only two places, the Earth below the firmament and heaven above it. Carefully drawing on arguments from scripture, he describes the Earth as a rectangle, 400 days' journey long by 200 wide, surrounded by four oceans and enclosed by four massive walls which support the firmament. The spherical Earth theory is contemptuously dismissed as "pagan".
Severian, Bishop of Gabala ( 408), wrote that the Earth is flat and the Sun does not pass under it in the night, but "travels through the northern parts as if hidden by a wall". Basil of Caesarea
Basil of Caesarea, also called Saint Basil the Great (330 – 1 or 2 January 379) was an early Roman Christian prelate who served as Bishop of Caesarea in Cappadocia from 370 until his death in 379. He was an influential theologian who suppor ...
(329–379) argued that the matter was theologically irrelevant.
Europe: Early Middle Ages
Early medieval Christian writers felt little urge to assume flatness of the Earth, though they had fuzzy impressions of the writings of Ptolemy and Aristotle, relying more on Pliny. With the end of the
With the end of the Western Roman Empire
In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. ...
, Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's extent varies depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the Western half of the ancient Mediterranean ...
entered the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
with great difficulties that affected the continent's intellectual production. Most scientific treatises of classical antiquity
Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural History of Europe, European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the inter ...
(in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
) were unavailable, leaving only simplified summaries and compilations. In contrast, the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
did not fall, and it preserved the learning. Still, many textbooks of the Early Middle Ages supported the sphericity of the Earth in the western part of Europe.
 Europe's view of the shape of the Earth in
Europe's view of the shape of the Earth in Late Antiquity
Late antiquity marks the period that comes after the end of classical antiquity and stretches into the onset of the Early Middle Ages. Late antiquity as a period was popularized by Peter Brown (historian), Peter Brown in 1971, and this periodiza ...
and the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th to the 10th century. They marked the start o ...
may be best expressed by the writings of early Christian scholars:
Bishop Isidore of Seville (560–636) taught in his widely read encyclopedia, the ''Etymologies
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
'', diverse views such as that the Earth "resembles a wheel" resembling Anaximander in language and the map that he provided. This was widely interpreted as referring to a disc-shaped Earth. An illustration from Isidore's ''De Natura Rerum'' shows the five zones of the Earth as adjacent circles. Some have concluded that he thought the Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
and Antarctic
The Antarctic (, ; commonly ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the South Pole, lying within the Antarctic Circle. It is antipodes, diametrically opposite of the Arctic region around the North Pole.
The Antar ...
zones were adjacent to each other. He did not admit the possibility of antipodes, which he took to mean people dwelling on the opposite side of the Earth, considering them legendary and noting that there was no evidence for their existence. Isidore's T and O map
A T and O map or O–T or T–O map (''orbis terrarum'', orb or circle of the lands; with the letter T inside an O), also known as an Isidoran map, is a type of early world map that represents the Afro-Eurasian landmass as a circle (= O) divid ...
, which was seen as representing a small part of a spherical Earth, continued to be used by authors through the Middle Ages, e.g. the 9th-century bishop Rabanus Maurus
Rabanus Maurus Magnentius ( 780 – 4 February 856), also known as Hrabanus or Rhabanus, was a Frankish Benedictine monk, theologian, poet, encyclopedist and military writer who became archbishop of Mainz in East Francia. He was the author of t ...
, who compared the habitable part of the northern hemisphere (Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
's northern temperate clime) with a wheel. At the same time, Isidore's works also gave the views of sphericity, for example, in chapter 28 of ''De Natura Rerum'', Isidore claims that the Sun orbits the Earth and illuminates the other side when it is night on this side. See French translation of ''De Natura Rerum''. In his other work ''Etymologies
Etymology ( ) is the study of the origin and evolution of words—including their constituent units of sound and meaning—across time. In the 21st century a subfield within linguistics, etymology has become a more rigorously scientific study. ...
'', there are also affirmations that the sphere of the sky has Earth in its center and the sky being equally distant on all sides. Other researchers have argued these points as well. "The work remained unsurpassed until the thirteenth century and was regarded as the summit of all knowledge. It became an essential part of European medieval culture. Soon after the invention of typography it appeared many times in print." However, "The Scholastics – later medieval philosophers, theologians, and scientists – were helped by the Arabic translators and commentaries, but they hardly needed to struggle against a flat-Earth legacy from the early middle ages (500–1050). Early medieval writers often had fuzzy and imprecise impressions of both Ptolemy and Aristotle and relied more on Pliny, but they felt (with one exception), little urge to assume flatness."
 St Vergilius of Salzburg (c. 700–784), in the middle of the 8th century, discussed or taught some geographical or cosmographical ideas that
St Vergilius of Salzburg (c. 700–784), in the middle of the 8th century, discussed or taught some geographical or cosmographical ideas that St Boniface
Boniface, OSB (born Wynfreth; 675 –5 June 754) was an English Benedictine monk and leading figure in the Anglo-Saxon mission to the Germanic parts of Francia during the eighth century. He organised significant foundations of the church i ...
found sufficiently objectionable that he complained about them to Pope Zachary
Pope Zachary (; 679 – March 752) was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death in March 752. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of sla ...
. The only surviving record of the incident is contained in Zachary's reply, dated 748, where he wrote:
Some authorities have suggested that the sphericity of the Earth was among the aspects of Vergilius's teachings that Boniface and Zachary considered objectionable. Others have considered this unlikely, and take the wording of Zachary's response to indicate at most an objection to belief in the existence of humans living in the antipodes. In any case, there is no record of any further action having been taken against Vergilius. He was later appointed bishop of Salzburg
The Archdiocese of Salzburg (; ) is a Latin rite archdiocese of the Catholic Church centered in Salzburg, Austria. It is also the principal diocese of the ecclesiastical province of Salzburg. The archdiocese is one of two Austrian archdioceses, ...
and was canonised
Canonization is the declaration of a deceased person as an officially recognized saint, specifically, the official act of a Christian communion declaring a person worthy of public veneration and entering their name in the canon catalogue of sai ...
in the 13th century.
A possible non-literary but graphic indication that people in the Middle Ages believed that the Earth (or perhaps the world) was a sphere is the use of the ''orb'' (globus cruciger
The for, la, globus cruciger, cross-bearing orb, also known as ''stavroforos sphaira'' () or "the orb and cross", is an Sphere, orb surmounted by a Christian cross, cross. It has been a Christian Church, Christian symbol of authority since the M ...
) in the regalia of many kingdoms and of the Holy Roman Empire. It is attested from the time of the Christian late-Roman emperor Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( ; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450), called "the Calligraphy, Calligrapher", was Roman emperor from 402 to 450. He was proclaimed ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' as an infant and ruled as the Eastern Empire's sole emperor after the ...
(423) throughout the Middle Ages; the ''Reichsapfel'' was used in 1191 at the coronation of emperor Henry VI
Henry VI (German: ''Heinrich VI.''; November 1165 – 28 September 1197), a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was King of Germany (King of the Romans) from 1169 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1191 until his death. From 1194 he was also King of Sic ...
. However the word means "circle", and there is no record of a globe as a representation of the Earth since ancient times in the west until that of Martin Behaim
Martin Behaim (6 October 1459 – 29 July 1507), also known as and by various forms of , was a German textile merchant and cartographer. He served John II of Portugal as an adviser in matters of navigation and participated in a voyage to Wes ...
in 1492. Additionally it could well be a representation of the entire "world" or cosmos
The cosmos (, ; ) is an alternative name for the universe or its nature or order. Usage of the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos is studied in cosmologya broad discipline covering ...
.
A recent study of medieval concepts of the sphericity of the Earth noted that "since the eighth century, no cosmographer worthy of note has called into question the sphericity of the Earth". However, the work of these intellectuals may not have had significant influence on public opinion, and it is difficult to tell what the wider population may have thought of the shape of the Earth if they considered the question at all.
Europe: High and Late Middle Ages
Hermann of Reichenau
Blessed Hermann of Reichenau or Herman the Cripple (18 July 1013– 24 September 1054), also known by other names, was an 11th-century Benedictine monk and scholar. He composed works on history, music theory, mathematics, and astronomy, a ...
(1013–1054) was among the earliest Christian scholars to estimate the circumference of Earth with Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
' method. Thomas Aquinas
Thomas Aquinas ( ; ; – 7 March 1274) was an Italian Dominican Order, Dominican friar and Catholic priest, priest, the foremost Scholasticism, Scholastic thinker, as well as one of the most influential philosophers and theologians in the W ...
(1225–1274), the most widely taught theologian of the Middle Ages, believed in a spherical Earth and took for granted that his readers also knew the Earth is round. Lectures in the medieval universities
A medieval university was a Corporation#History, corporation organized during the Middle Ages for the purposes of higher education. The first Western European institutions generally considered to be University, universities were established in p ...
commonly advanced evidence in favor of the idea that the Earth was a sphere.
Jill Tattersall shows that in many vernacular
Vernacular is the ordinary, informal, spoken language, spoken form of language, particularly when perceptual dialectology, perceived as having lower social status or less Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige than standard language, which is mor ...
works in 12th- and 13th-century French texts the Earth was considered "round like a table" rather than "round like an apple". She writes, " virtually all the examples quoted ... from epics and from non-'historical' romances (that is, works of a less learned character) the actual form of words used suggests strongly a circle rather than a sphere", though she notes that even in these works the language is ambiguous.
Portuguese navigation down and around the coast of Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
in the latter half of the 1400s gave wide-scale observational evidence for Earth's sphericity. In these explorations, the Sun's position moved more northward the further south the explorers travelled. Its position directly overhead at noon gave evidence for crossing the equator. These apparent solar motions in detail were more consistent with north–south curvature and a distant Sun, than with any flat-Earth explanation. The ultimate demonstration came when Ferdinand Magellan's expedition completed the first global circumnavigation in 1521. Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was a Venetian scholar and explorer. In 1519, he joined the Spanish expedition to the Spice Islands led by Portuguese explorer Ferdinand Magellan, the world's first Magellan's circumnavigation, circumnavigation, ...
, one of the few survivors of the voyage, recorded the loss of a day in the course of the voyage, giving evidence for east–west curvature.
Middle East: Islamic scholars
Prior to the introduction of Greek cosmology into the Islamic world, Muslims tended to view the Earth as flat, and Muslim traditionalists who rejected Greek philosophy continued to hold to this view later on while various theologians held opposing opinions. Beginning in the 10th century onwards, some Muslim traditionalists began to adopt the notion of a spherical Earth with the influence of Greek and Ptolemaic cosmology. InQuranic cosmology
Quranic cosmology is how the Quran views the nature of the cosmos, especially its origins, development, and structure. In the Quran, the cosmos originates in an act of creation by God of the heavens and the earth over the course of six days, wit ...
, the Earth (''al-arḍ'') was "spread out." Whether or not this implies a flat Earth was debated by Muslims. Some modern historians believe the Quran saw the world as flat. On the other hand, the 12th-century commentary
Commentary or commentaries may refer to:
Publications
* ''Commentary'' (magazine), a U.S. public affairs journal, founded in 1945 and formerly published by the American Jewish Committee
* Caesar's Commentaries (disambiguation), a number of works ...
, the Tafsir al-Kabir (al-Razi)
''Mafatih al-Ghayb'' (), usually known as ''al-Tafsir al-Kabir'' (), is a classical Islamic tafsir book, written by the twelfth-century Islamic theologian and philosopher Fakhruddin Razi (d.1210). The book is an exegesis and commentary on the Qur' ...
by Fakhr al-Din al-Razi
Fakhr al-Dīn al-Rāzī () or Fakhruddin Razi () (1149 or 1150 – 1209), often known by the sobriquet Sultan of the Theologians, was an influential Iranian and Muslim polymath, scientist and one of the pioneers of inductive logic. He wrote var ...
argues that though this verse does describe a flat surface, it is limited in its application to local regions of the Earth which are roughly flat as opposed to the Earth as a whole. Others who would support a ball-shaped Earth included Ibn Hazm
Ibn Hazm (; November 994 – 15 August 1064) was an Andalusian Muslim polymath, historian, traditionist, jurist, philosopher, and theologian, born in the Córdoban Caliphate, present-day Spain. Described as one of the strictest hadith interpre ...
.
Ming Dynasty in China
A spherical terrestrial globe was introduced toYuan-era
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
Khanbaliq
Khanbaliq (; , ''Qaɣan balɣasu'') or Dadu of Yuan (; , ''Dayidu'') was the Historical capitals of China, winter capital of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty in what is now Beijing, the capital of China today. It was located at the center of modern ...
(i.e. Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
) in 1267 by the Persian astronomer Jamal ad-Din, but it is not known to have made an impact on the traditional Chinese conception of the shape of the Earth. As late as 1595, an early Jesuit
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
missionary to China, Matteo Ricci
Matteo Ricci (; ; 6 October 1552 – 11 May 1610) was an Italian Jesuit priest and one of the founding figures of the Jesuit China missions. He created the , a 1602 map of the world written in Chinese characters. In 2022, the Apostolic See decl ...
, recorded that the Ming-dynasty
The Ming dynasty, officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming was the last imperial dynasty of China ruled by the Han people, th ...
Chinese say: "The Earth is flat and square, and the sky is a round canopy; they did not succeed in conceiving the possibility of the antipodes."
In the 17th century, the idea of a spherical Earth spread in China due to the influence of the Jesuits, who held high positions as astronomers at the imperial court.Needham, Joseph (1986). Science and Civilization in China: Volume 3. Taipei: Caves Books, Ltd. p. 499. Matteo Ricci, in collaboration with Chinese cartographers and translator Li Zhizao, published the ''Kunyu Wanguo Quantu
Kunyu Wanguo Quantu, printed in Ming China at the request of the Wanli Emperor in 1602 by the Italian Jesuit missionary Matteo Ricci and Chinese collaborators, the mandarin Zhong Wentao, and the technical translator Li Zhizao, is the earliest kn ...
'' in 1602, the first Chinese world map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of t ...
based on European discoveries. The astronomical and geographical treatise ''Gezhicao'' () written in 1648 by Xiong Mingyu () explained that the Earth was spherical, not flat or square, and could be circumnavigated.
Myth of flat-Earth prevalence
In the 19th century, a historical myth arose which held that the predominant cosmological doctrine during the Middle Ages was that the Earth was flat. An early proponent of this myth was the American writerWashington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He wrote the short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and "The Legend of Sleepy ...
, who maintained that Christopher Columbus had to overcome the opposition of churchmen to gain sponsorship for his voyage of exploration. Later significant advocates of this view were John William Draper
John William Draper (May 5, 1811 – January 4, 1882) was an English polymath: a scientist, philosopher, physician, chemist, historian and photographer. He is credited with pioneering portrait photography (1839–40) and producing the first deta ...
and Andrew Dickson White
Andrew Dickson White (November 7, 1832 – November 4, 1918) was an American historian and educator who co-founded Cornell University, one of eight Ivy League universities in the United States, and served as its first president for nearly two de ...
, who used it as a major element in their advocacy of the thesis that there was a long-lasting and essential conflict between science and religion. Some studies of the historical connections between science and religion have demonstrated that theories of their mutual antagonism ignore examples of their mutual support.
Subsequent studies of medieval science have shown that most scholars in the Middle Ages, including those read by Christopher Columbus, maintained that the Earth was spherical.
Modern flat Earth beliefs
 In the modern era, the
In the modern era, the pseudoscientific
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable cl ...
belief in a flat Earth originated with the English writer Samuel Rowbotham with the 1849 pamphlet ''Zetetic Astronomy''. Lady Elizabeth Blount established the Universal Zetetic Society in 1893, which published journals. In 1956, Samuel Shenton set up the International Flat Earth Research Society, better known as the "Flat Earth Society" in Dover, England, as a direct descendant of the Universal Zetetic Society.
In the Internet era, the availability of communications technology and social media
Social media are interactive technologies that facilitate the Content creation, creation, information exchange, sharing and news aggregator, aggregation of Content (media), content (such as ideas, interests, and other forms of expression) amongs ...
like YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
, Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
and Twitter
Twitter, officially known as X since 2023, is an American microblogging and social networking service. It is one of the world's largest social media platforms and one of the most-visited websites. Users can share short text messages, image ...
have made it easy for individuals, famous or not, to spread disinformation and attract others to erroneous ideas, including that of the flat Earth.
Modern believers in a flat Earth face overwhelming publicly accessible evidence of Earth's sphericity. They also need to explain why governments, media outlets, schools, scientists, surveyors, airlines and other organizations accept that the world is spherical. To satisfy these tensions and maintain their beliefs, they generally embrace some form of conspiracy theory
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that asserts the existence of a conspiracy (generally by powerful sinister groups, often political in motivation), when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
* ...
. In addition, believers tend to not trust observations they have not made themselves, and often distrust, disagree with or accuse each other of being in league with conspiracies.
Education
While learning from their social environment, a child's perception of their physical environment sometimes leads to a false concept about the shape of Earth and what happens beyond the horizon. Some young children think that Earth ends there and that one can fall off the edge. Education helps them gradually change their belief into a realist one of a spherical Earth. On the other hand, many children do understand that the world is round, as confirmed by interviewing what the pictures they draw actually mean. To counter misinformation about the shape of the Earth and other scientific issues, theNational Center for Science Education
The National Center for Science Education (NCSE) is a Nonprofit organization, not-for-profit membership organization in the United States whose stated mission is to educate the press and the public on the scientific and educational aspects of con ...
has a site for supporting teachers.
See also
* Alderson disk *Denialism
In the psychology of human behavior, denialism is a person's choice to denial, deny reality as a way to avoid believing in a psychologically uncomfortable truth. Denialism is an essentially irrational action that withholds the validation of a h ...
* Earth's rotation
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own Rotation around a fixed axis, axis, as well as changes in the orientation (geometry), orientation of the rotation axis in space. Earth rotates eastward, in progra ...
* Geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded scientific theories, superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric m ...
* Geographical distance
Geographical distance or geodetic distance is the distance measured along the surface of the Earth, or the shortest arch length.
The formulae in this article calculate distances between points which are defined by geographical coordinates in t ...
* Hollow Earth
The Hollow Earth is a concept proposing that the planet Earth is entirely hollow or contains a substantial interior space. Notably suggested by Edmond Halley in the late 17th century, the notion was disproven, first tentatively by Pierre Bougue ...
* Pseudoscience
Pseudoscience consists of statements, beliefs, or practices that claim to be both scientific and factual but are incompatible with the scientific method. Pseudoscience is often characterized by contradictory, exaggerated or unfalsifiable cl ...
* Scientific myth
* Scientific skepticism
Scientific skepticism or rational skepticism (also spelled scepticism), sometimes referred to as skeptical inquiry, is a position in which one questions the veracity of claims lacking scientific evidence. In practice, the term most commonly ref ...
* World Turtle
The World Turtle, also called the Cosmic Turtle or the World-Bearing Turtle, is a mytheme of a giant turtle (or tortoise) supporting or containing Religious cosmology, the world. It occurs in Hinduism, Chinese mythology, and the mythologies of th ...
* Geocentric creationism
References
Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
* Fraser, Raymond (2007). ''When The Earth Was Flat: Remembering Leonard Cohen, Alden Nowlan, the Flat Earth Society, the King James monarchy hoax, the Montreal Story Tellers and other curious matters.'' Black Moss Press,External links
* * * * – Review of a pro-Flat Earth documentary.The Myth of the Flat Earth
You say the earth is round? Prove it
(from
The Straight Dope
''The Straight Dope'' was a question-and-answer newspaper column written under the pseudonym Cecil Adams. Contributions were made by multiple authors, and it was illustrated (also pseudonymously) by Slug Signorino. It was first published in 197 ...
)
Flat Earth Fallacy
at sacred-texts.com * ttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ThPgMu2-ToM&t=0 Flat Earth idea of the Suns trajectory
Flat Earth Theory of the Moon & Sun's paths around the world
{{Authority control Early scientific cosmologies Ancient Near Eastern cosmology