|
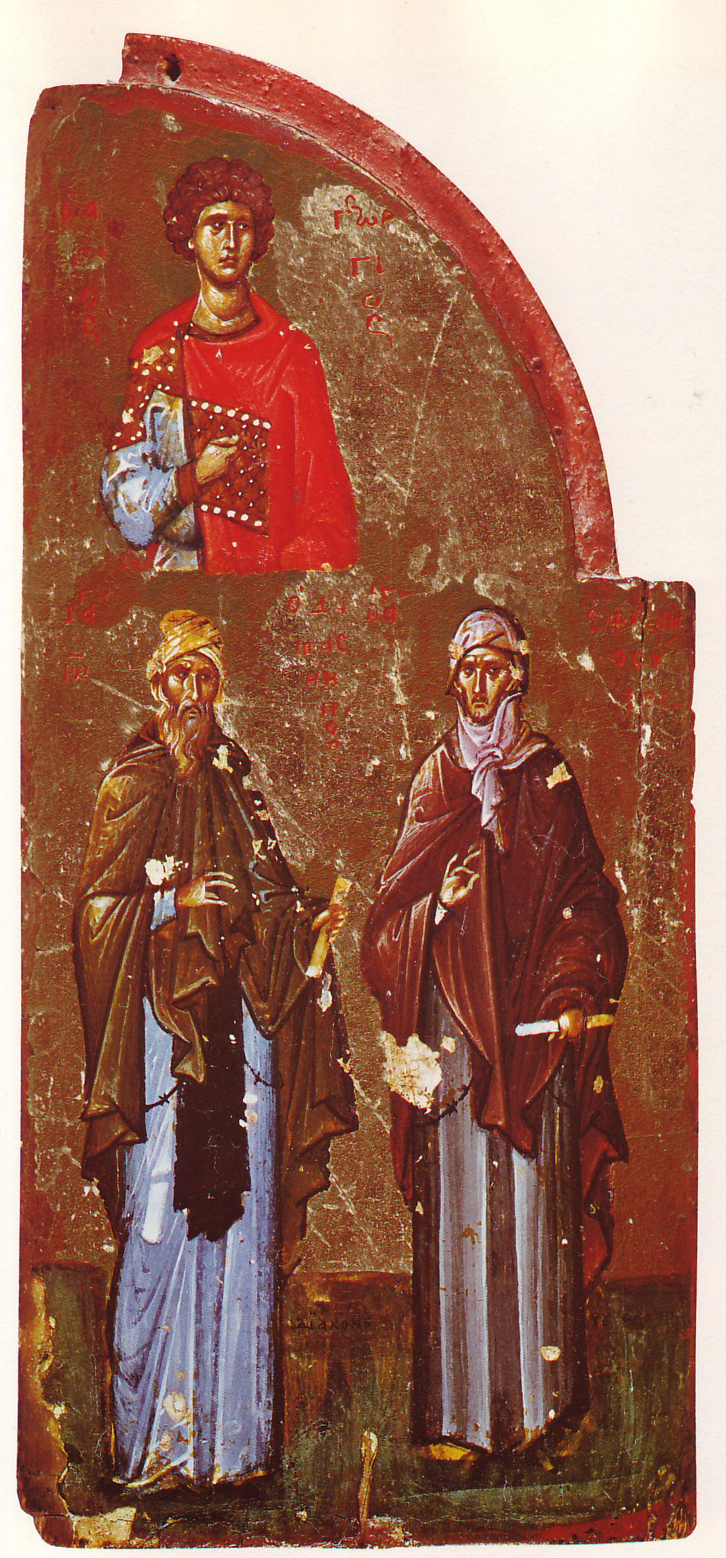
Jacob Of Serugh
Jacob of Serugh (, ; ; 452‚Äď521), also called Jacob of Sarug or Mar Jacob (), was one of the foremost poets and theologians of the Syriac Christian tradition, second only to Ephrem the Syrian and equal to Narsai. He lived most of his life as an ecclesiastical official in Suru√ß, in modern-day Turkey. He became a bishop (of Batnan) near the end of his life in 519. He was a Miaphysite (a form of Non-Chalcedonian Christianity), albeit moderate compared to his contemporaries. Jacob is best known for the homilies he wrote in the late fifth and early sixth centuries. He wrote in prose, as well as in 12-syllable ( dodecasyllabic) meter, which he invented, and he was known for his eloquence. According to Jacob of Edessa, he composed 763 works during his lifetime. Around 400 survive, and over 200 of those have been published. The longest is about 1,400 verses. By the time of his death, he had a great reputation. His works were so popular that of any author from late antiquity, only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint
In Christianity, Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of sanctification in Christianity, holiness, imitation of God, likeness, or closeness to God in Christianity, God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denomination. In Anglican Communion, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheranism, Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official Ecclesiastical polity, ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris‚ÄďEuphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab in Iraq, which empties into the Persian Gulf. The Euphrates is the List of longest rivers of Asia, fifteenth-longest river in Asia and the longest in West Asia, at about , with a drainage area of that covers six countries. Etymology The term ''Euphrates'' derives from the Koine Greek, Greek ''Euphr√°tńďs'' (), adapted from , itself from . The Elamite name is ultimately derived from cuneiform ūíĆďūíĄíūíČ£; read as ''Buranun'' in Sumerian language, Sumerian and ''Purattu'' in Akkadian language, Akkadian; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homily
A homily (from Greek ŠĹĀőľőĻőĽőĮőĪ, ''homil√≠a'') is a commentary that follows a reading of scripture, giving the "public explanation of a sacred doctrine" or text. The works of Origen and John Chrysostom (known as Paschal Homily) are considered exemplary forms of Christian homily. In Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, and Eastern Orthodox churches, a homily is usually given during Mass (Divine Liturgy or Holy Qurbana for Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches, and Divine Service for the Lutheran Church) at the end of the Liturgy of the Word. Many people consider it synonymous with a sermon. The English word homily is derived from the Ancient Greek word ŠĹĀőľőĻőĽőĮőĪ ''homilia'', which means intercourse or interaction with other people (derived from the word ''homilos,'' meaning "a gathering"). The word is used in ("wicked ''homiliai'' corrupt good morals"). The related verb is used in (as ''homiloun''), and in (as ''homilei''), both used in the sense of "speaking with". The wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-Chalcedonian Christianity
Non-Chalcedonian Christianity comprises the branches of Christianity that do not accept and uphold theological resolutions of the Council of Chalcedon, the council following Ephesus, held in 451. Non-Chalcedonian denominations reject the Christological Definition of Chalcedon (which asserted Dyophysitism), for varying reasons. Non-Chalcedonian Christianity thus stands in contrast to Chalcedonian Christianity. Today, the Oriental Orthodox Churches predominantly comprise most of non-Chalcedonian Christianity. Overview The most substantial non-Chalcedonian tradition is known as Oriental Orthodoxy. Within this tradition are a number of ancient Christian churches including the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, the Syriac Orthodox Church of Antioch (sometimes referred to as "Jacobite"), the Armenian Apostolic Church, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church and the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church. The official Christology of the Orien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miaphysitism
Miaphysitism () is the Christological doctrine that holds Jesus, the Incarnate Word, is fully divine and fully human, in one nature ('' physis'', ). It is a position held by the Oriental Orthodox Churches. It differs from the Dyophysitism of the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox Churches, the Church of the East and the major Protestant denominations, which holds that Jesus is one "person" of two "natures", a divine nature and a human nature, as defined by the Council of Chalcedon in 451. While historically a major point of controversy within Christianity, some modern declarations by both Chalcedonian and miaphysite () churches claim that the difference between the two Christological formulations does not reflect any significant difference in belief about the nature of Christ. Other statements from both Chalcedonian and miaphysite churches claim that such difference is indeed theological although "widened by non-theological factors" Terminology The word ''miaphysite'' der ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narsai
Narsai (sometimes spelt ''Narsay'', ''Narseh'' or ''Narses''; , name derived from Pahlavi ''Narsńďh'' from Avestan ''NairyŇć.sa»ĶhŇć'', meaning 'potent utterance'; ) was one of the foremost of the poet-theologians of the early Church of the East, perhaps equal in stature to Jacob of Serugh, both second only to Ephrem the Syrian. He is venerated as a saint in all the modern descendants of the Church of the East; the Chaldean Catholic Church, Assyrian Church of the East, Ancient Church of the East, and Syro-Malabar Catholic Church. Saint Narsai is known as the 'Flute of the Holy Spirit.' Although many of his works seem to have been lost, around eighty of his ''mńďmrńď'' (), or verse homilies are extant. Life Narsai was born at ‚ÄėAin Dulba ( " Plane Tree Spring") in the district of Ma‚Äėall…ôta () in the Sasanian Empire (now in Duhok Governorate, Iraq). Being orphaned at an early age, he was raised by his uncle, who was head of the monastery of Kfar Mari () near Beth Zabda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephrem The Syrian
Ephrem the Syrian (; ), also known as Ephraem the Deacon, Ephrem of Edessa or Aprem of Nisibis, (Syriac: ‹°‹™‹Ě ‹ź‹¶‹™‹Ě‹° ‹£‹ė‹™‹Ě‹Ě‹ź ‚ÄĒ ''M√Ęr Aphr√™m S√Ľry√Ęy√Ę)'' was a prominent Christian theology, Christian theologian and Christian literature, writer who is revered as one of the most notable hymnographers of Eastern Christianity. He was born in Nisibis, served as a deacon and later lived in Edessa. Ephrem is venerated as a Christian saint, saint by all traditional Churches. He is especially revered in Syriac Christianity, both in East Syriac Rite, East Syriac tradition and West Syriac Rite, West Syriac tradition, and also counted as a Holy and Venerable Father (i.e., a sainted monk) in the Eastern Orthodox Church, especially in the Slovak tradition. He was declared a Doctor of the Church in the Catholic Church in 1920. Ephrem is also credited as the founder of the School of Nisibis, which in later centuries was the center of learning for the Church of the East. Ephrem wrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theology
Theology is the study of religious belief from a Religion, religious perspective, with a focus on the nature of divinity. It is taught as an Discipline (academia), academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the supernatural, but also deals with religious epistemology, asks and seeks to answer the question of revelation. Revelation pertains to the acceptance of God, gods, or deity, deities, as not only transcendent or above the natural world, but also willing and able to interact with the natural world and to reveal themselves to humankind. Theologians use various forms of analysis and argument (Spirituality, experiential, philosophy, philosophical, ethnography, ethnographic, history, historical, and others) to help understanding, understand, explanation, explain, test, critique, defend or promote any myriad of List of religious topics, religious topics. As in philosophy of ethics and case law, arguments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator (thought, thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral tradition, oral or literature, written), or they may also performance, perform their art to an audience. The work of a poet is essentially one of communication, expressing ideas either in a literal sense (such as communicating about a specific event or place) or metaphorically. Poets have existed since prehistory, in nearly all languages, and have produced works that vary greatly in different cultures and periods. Throughout each civilization and language, poets have used various styles that have changed over time, resulting in countless poets as diverse as the literature that (since the advent of writing systems) they have produced. History Ancient poets The civilization of Sumer figures prominently in the history of early poetry, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of T√ľrkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq, Syria, and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; and the Aegean Sea, Greece, and Bulgaria to the west. Turkey is home to over 85 million people; most are ethnic Turkish people, Turks, while ethnic Kurds in Turkey, Kurds are the Minorities in Turkey, largest ethnic minority. Officially Secularism in Turkey, a secular state, Turkey has Islam in Turkey, a Muslim-majority population. Ankara is Turkey's capital and second-largest city. Istanbul is its largest city and economic center. Other major cities include ńįzmir, Bursa, and Antalya. First inhabited by modern humans during the Late Paleolithic, present-day Turkey was home to List of ancient peoples of Anatolia, various ancient peoples. The Hattians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ŇěanlńĪurfa Province
ŇěanlńĪurfa Province (; ), also known as Urfa Province, is a Provinces of Turkey, province and Metropolitan municipalities in Turkey, metropolitan municipality in southeastern Turkey. The city of ŇěanlńĪurfa is the capital of the province which bears its name. Its area is 19,242 km2, and its population is 2,170,110 (2022). The province is considered part of Turkish Kurdistan and has a Kurds, Kurdish majority with a significant Arabs, Arab and Turkish people, Turkish minority. Districts ŇěanlńĪurfa province is divided into 13 Districts of Turkey, districts, listed below with their populations as at 31 December 2022 according to the official government estimates: * Ak√ßakale (123,721) * Birecik (93,613) * Bozova (52,680) * CeylanpńĪnar (90,440) * Eyy√ľbiye (391,795) * Halfeti (41,662) * Haliliye (396,656) * Harran (96,072) * Hilvan (42,218) * Karak√∂pr√ľ (265,035) * Siverek (267,942) * Suru√ß (100,961) * ViranŇüehir (207,315) Geography With an area of , it is the larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |