Financial modeling on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Financial modeling is the task of building an abstract representation (a
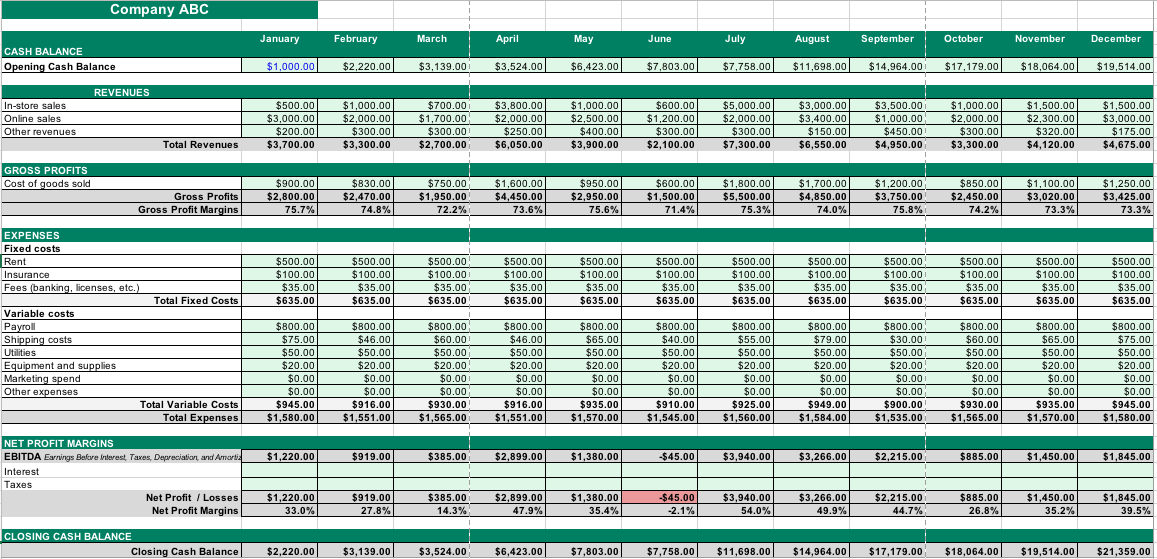 In
In
, European Spreadsheet Risks Interest Group "Spreadsheet risk" is increasingly studied and managed; see model audit. One critique here, is that model ''outputs'', i.e. line items, often inhere "unrealistic implicit assumptions" and "internal inconsistencies". (For example, a forecast for growth in revenue but without corresponding increases in working capital, fixed assets and the associated financing, may imbed unrealistic assumptions about asset turnover, debt level and/or
, Prof. Sam Savage,
Quantifying Corporate Financial Risk
archived 2010-07-17. cash flow analytics, corporate financing activity prediction problems, and risk analysis in capital investment *
''On Becoming a Quant''
. such as the Master of Quantitative Finance, or the more specialized Master of Computational Finance or Master of Financial Engineering; the Certificate in Quantitative Finance, CQF certificate is increasingly common. Although spreadsheets are widely used here also (almost always requiring extensive Visual Basic for Applications, VBA); custom C++, Fortran or Python (programming language), Python, or List of numerical-analysis software, numerical-analysis software such as MATLAB, are often preferred, particularly where stability or speed is a concern. MATLAB is often used at the research or prototyping stage because of its intuitive programming, graphical and debugging tools, but C++/Fortran are preferred for conceptually simple but Algorithmic efficiency#Measures of resource usage, high computational-cost applications where MATLAB is too slow; Python is increasingly used due to its simplicity, and large Python (programming language)#Libraries, standard library / List of Python software#Applications, available applications, including QuantLib. Additionally, for many (of the standard) derivative and portfolio applications, commercial software is available, and the choice as to whether the model is to be In-House Design, developed in-house, or whether existing products are to be deployed, will depend on the problem in question. See . The complexity of these models may result in incorrect pricing or hedge (finance), hedging or both. This ''Model risk'' is the subject of ongoing research by finance academics, and is a topic of great, and growing, interest in the risk management arena. Criticism of the discipline (often preceding the 2008 financial crisis by several years) emphasizes Unreasonable_ineffectiveness_of_mathematics#Economics_and_finance, the differences between finance and the mathematical / physical sciences, and stresses the resultant caution to be applied by modelers, and by traders and risk managers using their models. Notable here are Emanuel Derman and Paul Wilmott, authors of the ''Financial Modelers' Manifesto''. Some go further and question whether the mathematical modeling, mathematical- and statistical modeling techniques usually applied to finance are at all appropriate (see the assumptions made Black–Scholes model#Fundamental hypotheses, for options and Modern portfolio theory#Mathematical model, for portfolios). In fact, these may go so far as to question the "empirical and scientific validity... of financial economics, modern financial theory". Notable here are Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Nassim Taleb and Benoit Mandelbrot. See also , and .
model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided in ...
) of a real world financial
Finance refers to monetary resources and to the study and Academic discipline, discipline of money, currency, assets and Liability (financial accounting), liabilities. As a subject of study, is a field of Business administration, Business Admin ...
situation. This is a mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
designed to represent (a simplified version of) the performance of a financial asset or portfolio of a business, project
A project is a type of assignment, typically involving research or design, that is carefully planned to achieve a specific objective.
An alternative view sees a project managerially as a sequence of events: a "set of interrelated tasks to be ...
, or any other investment.
Typically, then, financial modeling is understood to mean an exercise in either asset pricing or corporate finance, of a quantitative nature. It is about translating a set of hypotheses about the behavior of markets or agents into numerical predictions. At the same time, "financial modeling" is a general term that means different things to different users; the reference usually relates either to accounting and corporate finance
Corporate finance is an area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of businesses, the actions that managers take to increase the Value investing, value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analy ...
applications or to quantitative finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field.
In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that requ ...
applications.
Accounting
 In
In corporate finance
Corporate finance is an area of finance that deals with the sources of funding, and the capital structure of businesses, the actions that managers take to increase the Value investing, value of the firm to the shareholders, and the tools and analy ...
and the accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the process of recording and processing information about economic entity, economic entities, such as businesses and corporations. Accounting measures the results of an organization's economic activit ...
profession, ''financial modeling'' typically entails financial statement forecasting; usually the preparation of detailed company-specific models used for decision making purposes, valuation and financial analysis
Financial analysis (also known as financial statement analysis, accounting analysis, or analysis of finance) refers to an assessment of the viability, stability, and profitability of a business, sub-business, project or investment.
It is per ...
.
Applications include:
*Business valuation
Business valuation is a process and a set of procedures used to estimate the economic value of an owner's interest in a business. Here various valuation techniques are used by financial market participants to determine the price they are willing ...
, stock valuation, and project valuation - especially via discounted cash flow, but including other valuation approaches
*Scenario planning
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and gen ...
, FP&A
Financial planning and analysis (FP&A), in accounting and business, refers to the various integrated financial planning, planning, financial analysis, analysis, and Financial_modeling#Accounting, modeling activities aimed decision support, at sup ...
and management decision making ("what is"; "what if"; "what has to be done" §39 "Corporate Planning Models". See also, §294 "Simulation Model".)
*Budgeting
A budget is a calculation plan, usually but not always financial plan, financial, for a defined accounting period, period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including tim ...
: revenue forecasting and analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data, which also falls under and directly relates to the umbrella term, data sc ...
; production budgeting; operations budgeting
*Capital budgeting
Capital budgeting in corporate finance, corporate planning and accounting is an area of capital management that concerns the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term capital investments such as new machinery, repla ...
, including cost of capital (i.e. WACC) calculations
*Cash flow forecasting
Cash flow forecasting is the process of obtaining an estimate of a company's future cash levels, and its financial position more generally. A cash flow forecast is a key financial management tool, both for large corporates, and for smaller entr ...
; working capital- and treasury management; asset and liability management
* Financial statement analysis / ratio analysis (including of operating- and finance lease
A finance lease (also known as a capital lease or a sales lease) is a type of lease in which a finance company is typically the legal owner of the asset for the duration of the lease, while the lessee not only has operating control over the asset ...
s, and R&D)
* Transaction analytics: M&A, PE, VC, LBO, IPO, Project finance, P3
*Credit decisioning: Credit analysis, Consumer credit risk; impairment- and provision-modeling
*Management accounting: Activity-based costing, Profitability analysis, Cost analysis, Whole-life cost
Whole-life cost is the total cost of ownership over the life of an asset. The concept is also known as life-cycle cost (LCC) or lifetime cost, and is commonly referred to as "cradle to grave" or "womb to tomb" costs. Costs considered include the ...
, Managerial risk accounting
* Public sector procurement
To generalize as to the nature of these models:
firstly, as they are built around financial statement
Financial statements (or financial reports) are formal records of the financial activities and position of a business, person, or other entity.
Relevant financial information is presented in a structured manner and in a form which is easy to un ...
s, calculations and outputs are monthly, quarterly or annual;
secondly, the inputs take the form of "assumptions", where the analyst ''specifies'' the values that will apply in each period for external / global variables (exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
s, tax
A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on an individual or legal entity by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax co ...
percentage, etc....; may be thought of as the model ''parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
s''), and for internal / company specific ''variables'' ( wages, unit cost
The unit cost is the price incurred by a company
A company, abbreviated as co., is a Legal personality, legal entity representing an association of legal people, whether Natural person, natural, Juridical person, juridical or a mixture ...
s, etc....). Correspondingly, both characteristics are reflected (at least implicitly) in the mathematical form of these models:
firstly, the models are in discrete time;
secondly, they are deterministic.
For discussion of the issues that may arise, see below; for discussion as to more sophisticated approaches sometimes employed, see and .
Modelers are often designated " financial analyst" (and are sometimes referred to, tongue in cheek, as "number crunchers"). Typically, the modeler will have completed an MBA or MSF with (optional) coursework in "financial modeling". Accounting qualifications and finance certifications such as the CIIA and CFA generally do not provide direct or explicit training in modeling.''The MiF can offer an edge over the CFA''Financial Times
The ''Financial Times'' (''FT'') is a British daily newspaper printed in broadsheet and also published digitally that focuses on business and economic Current affairs (news format), current affairs. Based in London, the paper is owned by a Jap ...
, June 21, 2015. At the same time, numerous commercial training courses are offered, both through universities and privately.
For the components and steps of business modeling here, see ; see also for further discussion and considerations.
Although purpose-built business software
Business software (or a business application) is any software or set of computer programs used by business users to perform various business functions. These business applications are used to increase productivity, measure productivity, and per ...
does exist, the vast proportion of the market is spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in c ...
-based; this is largely since the models are almost always company-specific. Also, analysts will each have their own criteria and methods for financial modeling. Microsoft Excel
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet editor developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows, Windows, macOS, Android (operating system), Android, iOS and iPadOS. It features calculation or computation capabilities, graphing tools, pivot tables, and a ...
now has by far the dominant position, having overtaken Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles ...
in the 1990s. Spreadsheet-based modelling can have its own problems, and several standardizations and "best practice
A best practice is a method or technique that has been generally accepted as superior to alternatives because it tends to produce superior results. Best practices are used to achieve quality as an alternative to mandatory standards. Best practice ...
s" have been proposed.Best Practice, European Spreadsheet Risks Interest Group "Spreadsheet risk" is increasingly studied and managed; see model audit. One critique here, is that model ''outputs'', i.e. line items, often inhere "unrealistic implicit assumptions" and "internal inconsistencies". (For example, a forecast for growth in revenue but without corresponding increases in working capital, fixed assets and the associated financing, may imbed unrealistic assumptions about asset turnover, debt level and/or
equity financing
In finance, equity is an ownership interest in property that may be subject to debts or other liabilities. Equity is measured for accounting purposes by subtracting liabilities from the value of the assets owned. For example, if someone owns ...
. See .) What is required, but often lacking, is that all key elements are explicitly and consistently forecasted.
Related to this, is that modellers often additionally "fail to identify crucial assumptions" relating to ''inputs'', "and to explore what can go wrong". Here, in general, modellers "use point values and simple arithmetic instead of probability distributions and statistical measures"
— i.e., as mentioned, the problems are treated as deterministic in nature — and thus calculate a single value for the asset or project, but without providing information on the range, variance and sensitivity of outcomes;
The Flaw of Averages, Prof. Sam Savage,
Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
.
see .
A further, more general critique relates to the lack of basic computer programming
Computer programming or coding is the composition of sequences of instructions, called computer program, programs, that computers can follow to perform tasks. It involves designing and implementing algorithms, step-by-step specifications of proc ...
concepts amongst modelers,
with the result that their models are often poorly structured, and difficult to maintain. Serious criticism is also directed at the nature of budgeting, and its impact on the organization.
Quantitative finance
Inquantitative finance
Mathematical finance, also known as quantitative finance and financial mathematics, is a field of applied mathematics, concerned with mathematical modeling in the financial field.
In general, there exist two separate branches of finance that requ ...
, ''financial modeling'' entails the development of a sophisticated mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
.See discussion here: Models here deal with asset prices, market movements, portfolio returns and the like.
Relatedly, applications include:
* Option pricing and calculation of their "Greeks" ( accommodating volatility surfaces - via local
Local may refer to:
Geography and transportation
* Local (train), a train serving local traffic demand
* Local, Missouri, a community in the United States
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Local'' (comics), a limited series comic book by Bria ...
/ stochastic volatility
In statistics, stochastic volatility models are those in which the variance of a stochastic process is itself randomly distributed. They are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name ...
models - and multi-curves)
*Other derivatives, especially interest rate derivatives, credit derivatives and exotic derivatives
* Credit valuation adjustment, CVA, as well as the various XVA
*Modeling the term structure of interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
s ( bootstrapping / multi-curves, short-rate models, HJM framework) and any related credit spread
*Credit risk
Credit risk is the chance that a borrower does not repay a loan
In finance, a loan is the tender of money by one party to another with an agreement to pay it back. The recipient, or borrower, incurs a debt and is usually required to pay ...
, counterparty credit risk, and regulatory capital: EAD, PD, LGD, PFE, EE; Jarrow–Turnbull model, Merton model, KMV model
* Portfolio optimization and Quantitative investing more generally; see further re optimization methods employed.
* Credit scoring and provisioning
Provisioning may refer to:
* Provisioning (technology), the equipping of a telecommunications network or IT resources
* Provisioning (cruise ship), supplying a vessel for an extended voyage
** Provisioning of USS ''Constitution''
* Provisionin ...
; Credit scorecards and
* Structured product design and manufacture
* Financial risk modeling: value at risk ( parametric- and / or historical
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categ ...
, CVaR, EVT), stress testing
Stress testing is a form of deliberately intense or thorough testing, used to determine the stability of a given system, critical infrastructure or entity. It involves testing beyond normal operational capacity, often to a breaking point, in orde ...
, "sensitivities" analysis (Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, duration, convexity, DV01, KRD, CS01, JTD)
*Corporate finance applications:See David Shimko (2009)Quantifying Corporate Financial Risk
archived 2010-07-17. cash flow analytics, corporate financing activity prediction problems, and risk analysis in capital investment *
Real options
Real options valuation, also often termed real options analysis,Adam Borison (Stanford University)''Real Options Analysis: Where are the Emperor's Clothes?''
(ROV or ROA) applies option (finance), option Valuation of options, valuation technique ...
* Actuarial applications: Dynamic financial analysis (DFA), UIBFM, investment modeling
These problems are generally stochastic Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; i ...
and continuous in nature, and models here thus require complex algorithms, entailing computer simulation
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
, advanced numerical methods (such as numerical differential equations, numerical linear algebra, dynamic programming) and/or the development of optimization models. The general nature of these problems is discussed under , while specific techniques are listed under .
For further discussion here see also: Brownian model of financial markets; Martingale pricing; Financial models with long-tailed distributions and volatility clustering; Extreme value theory; Historical simulation (finance).
Modellers are generally referred to as "quants", i.e. quantitative analysts (or "rocket scientists") and typically have advanced ( Ph.D. level) backgrounds in quantitative disciplines such as statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
, physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, engineering, computer science, mathematics or operations research.
Alternatively, or in addition to their quantitative background, they complete a Master of Finance, finance masters with a quantitative orientation,Mark S. Joshi''On Becoming a Quant''
. such as the Master of Quantitative Finance, or the more specialized Master of Computational Finance or Master of Financial Engineering; the Certificate in Quantitative Finance, CQF certificate is increasingly common. Although spreadsheets are widely used here also (almost always requiring extensive Visual Basic for Applications, VBA); custom C++, Fortran or Python (programming language), Python, or List of numerical-analysis software, numerical-analysis software such as MATLAB, are often preferred, particularly where stability or speed is a concern. MATLAB is often used at the research or prototyping stage because of its intuitive programming, graphical and debugging tools, but C++/Fortran are preferred for conceptually simple but Algorithmic efficiency#Measures of resource usage, high computational-cost applications where MATLAB is too slow; Python is increasingly used due to its simplicity, and large Python (programming language)#Libraries, standard library / List of Python software#Applications, available applications, including QuantLib. Additionally, for many (of the standard) derivative and portfolio applications, commercial software is available, and the choice as to whether the model is to be In-House Design, developed in-house, or whether existing products are to be deployed, will depend on the problem in question. See . The complexity of these models may result in incorrect pricing or hedge (finance), hedging or both. This ''Model risk'' is the subject of ongoing research by finance academics, and is a topic of great, and growing, interest in the risk management arena. Criticism of the discipline (often preceding the 2008 financial crisis by several years) emphasizes Unreasonable_ineffectiveness_of_mathematics#Economics_and_finance, the differences between finance and the mathematical / physical sciences, and stresses the resultant caution to be applied by modelers, and by traders and risk managers using their models. Notable here are Emanuel Derman and Paul Wilmott, authors of the ''Financial Modelers' Manifesto''. Some go further and question whether the mathematical modeling, mathematical- and statistical modeling techniques usually applied to finance are at all appropriate (see the assumptions made Black–Scholes model#Fundamental hypotheses, for options and Modern portfolio theory#Mathematical model, for portfolios). In fact, these may go so far as to question the "empirical and scientific validity... of financial economics, modern financial theory". Notable here are Nassim Nicholas Taleb, Nassim Taleb and Benoit Mandelbrot. See also , and .
Competitive modeling
Several financial modeling competitions exist, emphasizing speed and accuracy in modeling. The Microsoft-sponsored ModelOff Financial Modeling World Championships were held annually from 2012 to 2019, with competitions throughout the year and a finals championship in New York or London. After its end in 2020, several other modeling championships have been started, including the Financial Modeling World Cup and Microsoft Excel Collegiate Challenge, also sponsored by Microsoft.Philosophy of financial modeling
Philosophy of financial modeling is a branch of philosophy concerned with the foundations, methods, and implications of modeling science. In the philosophy of financial modeling, scholars have more recently begun to question the generally-held assumption that financial modelers seek to represent any "real-world" or actually ongoing investment situation. Instead, it has been suggested that the task of the financial modeler resides in demonstrating the possibility of a transaction in a prospective investment scenario, from a limited base of possibility conditions initially assumed in the model.See also
*All models are wrong *Asset pricing model *Economic model *Financial engineering *Financial forecast *Financial Modelers' Manifesto * Financial models with long-tailed distributions and volatility clustering *Financial planning *Integrated business planning *Model audit *Modeling and analysis of financial markets * * *Profit model *Return on modeling effort *References
Bibliography
General * * * * * * * * Corporate finance * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Quantitative finance * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Corporate finance and investment banking Financial models Actuarial science Mathematical finance Corporate finance Computational fields of study