 |
Financial Modeling
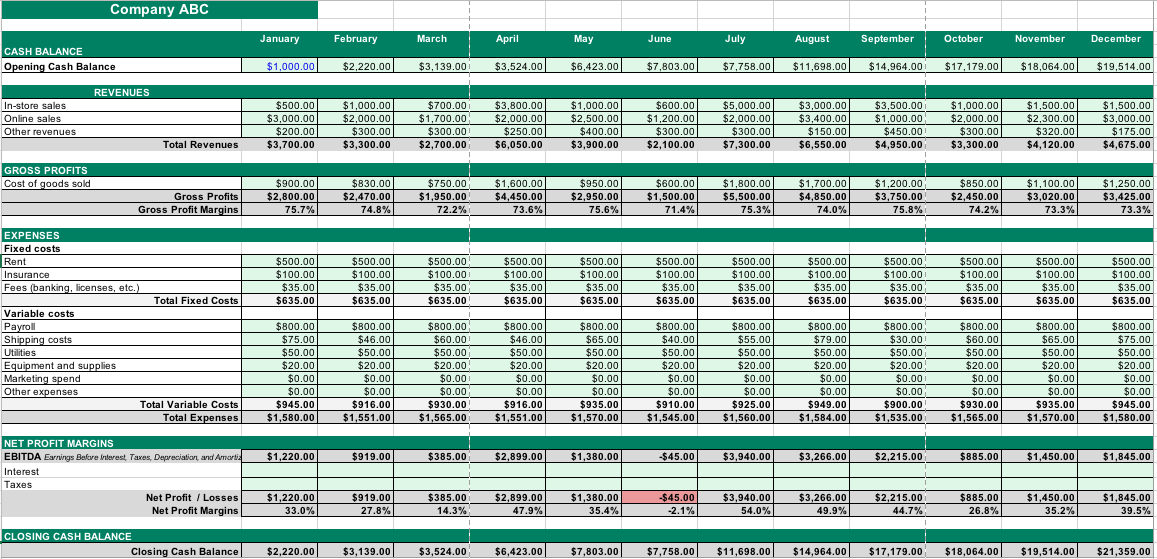
Financial modeling is the task of building an abstract representation (a model) of a real world financial situation. This is a mathematical model designed to represent (a simplified version of) the performance of a financial asset or portfolio of a business, project, or any other investment. Typically, then, financial modeling is understood to mean an exercise in either asset pricing or corporate finance, of a quantitative nature. It is about translating a set of hypotheses about the behavior of markets or agents into numerical predictions. At the same time, "financial modeling" is a general term that means different things to different users; the reference usually relates either to accounting and corporate finance applications or to quantitative finance applications. Accounting In corporate finance and the accounting profession, ''financial modeling'' typically entails financial statement forecasting; usually the preparation of detailed company-specific models used for deci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
FP&A
Financial planning and analysis (FP&A), in accounting and business, refers to the various integrated financial planning, planning, financial analysis, analysis, and Financial_modeling#Accounting, modeling activities aimed decision support, at supporting Corporate_finance#Outline, financial decisioning and management Chief financial officer#Role, in the wider organization. See for outline, and aside articles for further detail. In larger companies, "FP&A" will run as a dedicated area or team, under an "FP&A Manager" reporting to the CFO. FP&A is distinct from financial management and (management accounting, management) accounting in that it is oriented, additionally, towards business performance management, and, further, encompasses both Qualitative research, qualitative and Quantitative analysis (finance), quantitative analysis. This positioning allows management—Business_partnering#Financial_business_partnering, in partnership with FP&A—to preemptively address issue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Management Accounting
In management accounting or managerial accounting, managers use accounting information in decision-making and to assist in the management and performance of their control functions. Definition One simple definition of management accounting is the provision of financial and non-financial decision-making information to managers. In other words, management accounting helps the directors inside an organization to make decisions. This is the way toward distinguishing, examining, deciphering and imparting data to supervisors to help accomplish business goals. The information gathered includes all fields of accounting that educates the administration regarding business tasks identifying with the financial expenses and decisions made by the organization. Accountants use plans to measure the overall strategy of operations within the organization. According to the Institute of Management Accountants (IMA), "Management accounting is a profession that involves partnering in management decisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Financial Statement Analysis
Financial statement analysis (or just financial analysis) is the process of reviewing and analyzing a company's financial statements to make better economic decisions to earn income in future. These statements include the income statement, balance sheet, statement of cash flows, notes to accounts and a statement of changes in equity (if applicable). Financial statement analysis is a method or process involving specific techniques for evaluating risks, performance, valuation, financial health, and future prospects of an organization. It is used by a variety of stakeholders, such as credit and equity investors, the government, the public, and decision-makers within the organization. These stakeholders have different interests and apply a variety of different techniques to meet their needs. For example, equity investors are interested in the long-term earnings power of the organization and perhaps the sustainability and growth of dividend payments. Creditors want to ensure the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Asset And Liability Management
Asset and liability management (often abbreviated ALM) is the term covering tools and techniques used by a bank or other corporate to minimise exposure to market risk and liquidity risk through holding the optimum combination of assets and liabilities. It sometimes refers more specifically to the practice of managing financial risks that arise due to mismatches - "duration gaps" - between the assets and liabilities, on the firm's balance sheet or as part of an investment strategy. ALM sits between risk management and strategic planning. It is focused on a long-term perspective rather than mitigating immediate risks; see, here, treasury management. The exact roles and perimeter around ALM can however vary significantly from one bank (or other financial institution) to another depending on the business model adopted and can encompass a broad area of risks. Traditional ALM programs focus on interest rate risk and liquidity risk because they represent the most prominent risks affec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Treasury Management
Treasury management (or treasury operations) entails management of an enterprise's financial holdings, focusing on the firm's liquidity, and mitigating its financial-, operational- and reputational risk. Treasury Management's scope thus includes the firm's collections, disbursements, concentration, investment and funding activities. In corporates, treasury overlaps the financial management function, although the former has the more specific focus mentioned, while the latter is a broader field that includes financial planning, budgeting, and analysis. In banks, the function plays a slightly different, more integral role, managing also the link between the institution and the financial markets. In both, there is a close relationship with the financial risk management area. Permjit Singh (2021)"The Corporate Treasurer Serves as a Financial Risk Manager" Investopedia A company's treasury operation, typically, is under control of the CFO or Vice-president / Director of Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Working Capital Management
Working capital (WC) is a financial metric which represents operating liquidity available to a business, organisation, or other entity, including governmental entities. Along with fixed assets such as plant and equipment, working capital is considered a part of operating capital. Gross working capital is equal to current assets. Working capital is calculated as current assets minus current liabilities. If current assets are less than current liabilities, an entity has a working capital deficiency, also called a working capital deficit and negative working capital. A company can be endowed with assets and profitability but may fall short of liquidity if its assets cannot be readily converted into cash. Positive working capital is required to ensure that a firm is able to continue its operations and that it has sufficient funds to satisfy both maturing short-term debt and upcoming operational expenses. The management of working capital involves managing inventories, accounts rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cash Flow Forecasting
Cash flow forecasting is the process of obtaining an estimate of a company's future cash levels, and its financial position more generally. A cash flow forecast is a key financial management tool, both for large corporates, and for smaller entrepreneurial businesses. The forecast is typically based on anticipated payments and receivables. Several forecasting methodologies are available. Function Cash flow forecasting is an element of financial management. Maintaining a company's cash flow is a central part of managing the business and the financing of ongoing operations — particularly for start-ups and small enterprises. If the business runs out of cash and is not able to obtain new finance, it will become insolvent, and eventually declare Bankruptcy. Cash flow forecasting helps management forecast (predict) cash levels to avoid insolvency. The frequency of forecasting is determined by several factors, such as characteristics of the business, the industry and regulatory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Weighted Average Cost Of Capital
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. The WACC is commonly referred to as the firm's cost of capital. Importantly, it is dictated by the external market and not by management. The WACC represents the minimum return that a company must earn on an existing asset base to satisfy its creditors, owners, and other providers of capital, or they will invest elsewhere.Fernandes, Nuno. 2014, Finance for Executives: A Practical Guide for Managers, p. 32. Companies raise money from a number of sources: common stock, preferred stock and related rights, straight debt, convertible debt, exchangeable debt, employee stock options, pension liabilities, executive stock options, governmental subsidies, and so on. Different securities, which represent different sources of finance, are expected to generate different returns. The WACC is calculated taking into account the relative weights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Cost Of Capital
In economics and accounting, the cost of capital is the cost of a company's funds (both debt and equity), or from an investor's point of view is "the required rate of return on a portfolio company's existing securities". It is used to evaluate new projects of a company. It is the minimum return that investors expect for providing capital to the company, thus setting a benchmark that a new project has to meet. Basic concept For an investment to be worthwhile, the expected return on capital has to be higher than the cost of capital. Given a number of competing investment opportunities, investors are expected to put their capital to work in order to maximize the return. In other words, the cost of capital is the rate of return that capital could be expected to earn in the best alternative investment of equivalent risk; this is the opportunity cost of capital. If a project is of similar risk to a company's average business activities it is reasonable to use the company's average co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Capital Budgeting
Capital budgeting in corporate finance, corporate planning and accounting is an area of capital management that concerns the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term capital investments such as new machinery, replacement of machinery, new plants, new products, and research development projects are worth the funding of cash through the firm's capitalization structures (debt, equity or retained earnings). It is the process of allocating resources for major capital, or investment, expenditures. An underlying goal, consistent with the overall approach in corporate finance, is to increase the value of the firm to the shareholders. Capital budgeting is typically considered a non-core business activity as it is not part of the revenue model or models of most types of firms, or even a part of daily operations. It holds a strategic financial function within a business. One example of a firm type where capital budgeting is possibly a part of the core bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Operating Budget
The operating budget contains the revenue and expenditure generated from the daily business functions of the company.Edriaan Koening (N.D.What is Corporate Budgeting? chron.com It concentrates on the operating expenditures — the cost of goods sold, the cost of direct labour and direct materials that are tied to production; as well as the overhead and administration costs tied directly to manufacturing the goods and providing services. The operating budget will not contain capital expenditures and long-term loans. See also * Capital budgeting Capital budgeting in corporate finance, corporate planning and accounting is an area of capital management that concerns the planning process used to determine whether an organization's long term capital investments such as new machinery, repla ... References Budgets {{econ-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Production Budget
Production budget is a term used specifically in film production and, more generally, in business. A "film production budget" determines how much will be spent on the entire film project. This involves identifying the elements and then estimating their cost, for each phase of filmmaking (development, pre-production, production, post-production and distribution). The budget structure normally separates " above-the-line" (creative), and " below-the-line" (technical) costs. In business, "production budget" refers to the budget set by a corporation for the number of units of a product that will be required and produced; (archived) see demand forecasting, capacity planning and ; and financial forecast more generally. See also *Film budgeting *Television crew Television crew positions are derived from those of film crew, but with several differences. Pre-production : Work before shooting begins is called the pre-production stage. The crew in this stage include the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |