Ferromagnetism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as
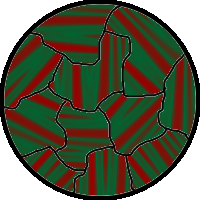 The spontaneous alignment of magnetic dipoles in ferromagnetic materials would seem to suggest that every piece of ferromagnetic material should have a strong magnetic field, since all the spins are aligned; yet iron and other ferromagnets are often found in an "unmagnetized" state. This is because a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material is divided into tiny regions called ''
The spontaneous alignment of magnetic dipoles in ferromagnetic materials would seem to suggest that every piece of ferromagnetic material should have a strong magnetic field, since all the spins are aligned; yet iron and other ferromagnets are often found in an "unmagnetized" state. This is because a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material is divided into tiny regions called ''
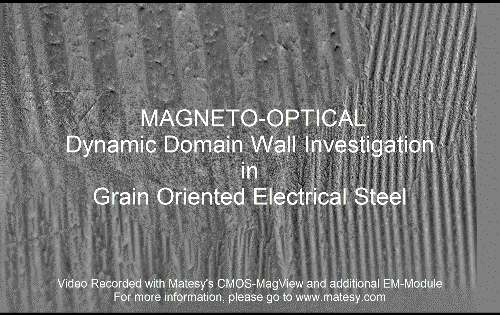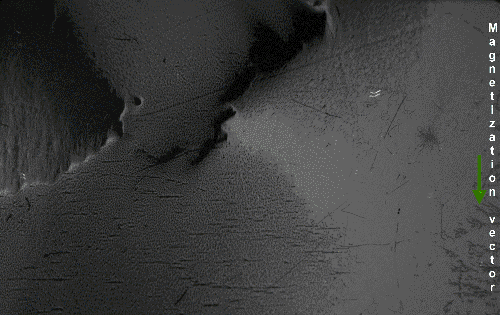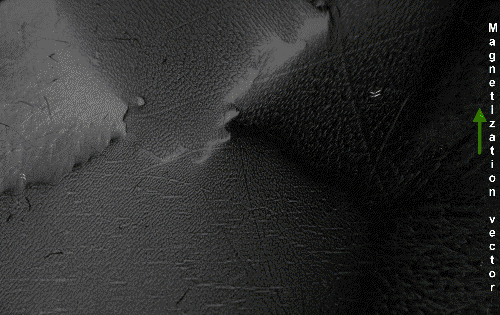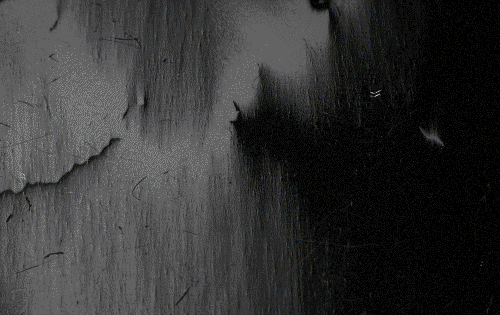
 Thus, a piece of iron in its lowest energy state ("unmagnetized") generally has little or no net magnetic field. However, the magnetic domains in a material are not fixed in place; they are simply regions where the spins of the electrons have aligned spontaneously due to their magnetic fields, and thus can be altered by an external magnetic field. If a strong-enough external magnetic field is applied to the material, the domain walls will move via a process in which the spins of the electrons in atoms near the wall in one domain turn under the influence of the external field to face in the same direction as the electrons in the other domain, thus reorienting the domains so more of the dipoles are aligned with the external field. The domains will remain aligned when the external field is removed, and sum to create a magnetic field of their own extending into the space around the material, thus creating a "permanent" magnet. The domains do not go back to their original minimum energy configuration when the field is removed because the domain walls tend to become 'pinned' or 'snagged' on defects in the crystal lattice, preserving their parallel orientation. This is shown by the
Thus, a piece of iron in its lowest energy state ("unmagnetized") generally has little or no net magnetic field. However, the magnetic domains in a material are not fixed in place; they are simply regions where the spins of the electrons have aligned spontaneously due to their magnetic fields, and thus can be altered by an external magnetic field. If a strong-enough external magnetic field is applied to the material, the domain walls will move via a process in which the spins of the electrons in atoms near the wall in one domain turn under the influence of the external field to face in the same direction as the electrons in the other domain, thus reorienting the domains so more of the dipoles are aligned with the external field. The domains will remain aligned when the external field is removed, and sum to create a magnetic field of their own extending into the space around the material, thus creating a "permanent" magnet. The domains do not go back to their original minimum energy configuration when the field is removed because the domain walls tend to become 'pinned' or 'snagged' on defects in the crystal lattice, preserving their parallel orientation. This is shown by the
Electromagnetism
– ch. 11, from an online textbook * Detailed nonmathematical description of ferromagnetic materials with illustrations
Magnetism: Models and Mechanisms
in E. Pavarini, E. Koch, and U. Schollwöck: Emergent Phenomena in Correlated Matter, Jülich 2013, {{Authority control Quantum phases Magnetic hysteresis Physical phenomena Ferromagnetism
 Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization produced in a material in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter ''μ''. It is the ratio of the magnetic ...
, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming demagnetized. Coercivity is usually measured in ...
, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, c ...
. Ferromagnetic materials are noticeably attracted to a magnet, which is a consequence of their substantial magnetic permeability.
Magnetic permeability describes the induced magnetization of a material due to the presence of an external magnetic field. For example, this temporary magnetization inside a steel plate accounts for the plate's attraction to a magnet. Whether or not that steel plate then acquires permanent magnetization depends on both the strength of the applied field and on the coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming Magnetization, demagnetized. Coercivity is usual ...
of that particular piece of steel (which varies with the steel's chemical composition and any heat treatment it may have undergone).
In physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
, multiple types of material magnetism
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that occur through a magnetic field, which allows objects to attract or repel each other. Because both electric currents and magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, ...
have been distinguished. Ferromagnetism (along with the similar effect ferrimagnetism
A ferrimagnetic material is a material that has populations of atoms with opposing magnetic moments, as in antiferromagnetism, but these moments are unequal in magnitude, so a spontaneous magnetization remains. This can for example occur wh ...
) is the strongest type and is responsible for the common phenomenon of everyday magnetism. A common example of a permanent magnet is a refrigerator magnet
A refrigerator magnet or fridge magnet is a small magnet, often attached to an artistic or whimsical ornament, which may be used to post items such as shopping lists, Christmas cards, child art or reminders on a refrigerator door, or which simpl ...
.Bozorth, Richard M. ''Ferromagnetism'', first published 1951, reprinted 1993 by IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
Press, New York as a "Classic Reissue". . Substances respond weakly to magnetic fields by three other types of magnetism—paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
, diamagnetism
Diamagnetism is the property of materials that are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnet ...
, and antiferromagnetism
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
—but the forces are usually so weak that they can be detected only by lab instruments.
Permanent magnets (materials that can be magnetized by an external magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
and remain magnetized after the external field is removed) are either ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic, as are the materials that are strongly attracted to them. Relatively few materials are ferromagnetic; the common ones are the metals iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
and most of their alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s, and certain rare-earth metals.
Ferromagnetism is widely used in industrial applications and modern technology, in electromagnetic and electromechanical devices such as electromagnet
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire (likely copper) wound into a electromagnetic coil, coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic ...
s, electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
s, generators, transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
s, magnetic storage
Magnetic storage or magnetic recording is the storage of data on a magnetized medium. Magnetic storage uses different patterns of magnetisation in a magnetizable material to store data and is a form of non-volatile memory. The information is acc ...
(including tape recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present ...
s and hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
s), and nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
of ferrous materials.
Ferromagnetic materials can be divided into magnetically "soft" materials (like annealed iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
) having low coercivity, which do not tend to stay magnetized, and magnetically "hard" materials having high coercivity, which do. Permanent magnets are made from hard ferromagnetic materials (such as alnico
Alnico is a family of iron alloys which, in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co), hence the acronym ''al-ni-co''. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium.
Alnico alloys are ferromagnet ...
) and ferrimagnetic materials (such as ferrite) that are subjected to special processing in a strong magnetic field during manufacturing to align their internal microcrystalline
A microcrystalline material is a crystallized substance or rock that contains small crystals visible only through microscopic examination. There is little agreement on the range of crystal sizes that should be regarded as microcrystalline, but ...
structure, making them difficult to demagnetize. To demagnetize a saturated magnet, a magnetic field must be applied. The threshold at which demagnetization occurs depends on the coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming Magnetization, demagnetized. Coercivity is usual ...
of the material. The overall strength of a magnet is measured by its magnetic moment
In electromagnetism, the magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment is the combination of strength and orientation of a magnet or other object or system that exerts a magnetic field. The magnetic dipole moment of an object determines the magnitude ...
or, alternatively, its total magnetic flux
In physics, specifically electromagnetism, the magnetic flux through a surface is the surface integral of the normal component of the magnetic field B over that surface. It is usually denoted or . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the we ...
. The local strength of magnetism in a material is measured by its magnetization
In classical electromagnetism, magnetization is the vector field that expresses the density of permanent or induced magnetic dipole moments in a magnetic material. Accordingly, physicists and engineers usually define magnetization as the quanti ...
.
Terms
Historically, the term ''ferromagnetism'' was used for any material that could exhibit spontaneous magnetization: a net magnetic moment in the absence of an external magnetic field; that is, any material that could become amagnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
. This definition is still in common use.
In a landmark paper in 1948, Louis Néel
Louis Eugène Félix Néel (; 22 November 1904 – 17 November 2000) was a French physicist born in Lyon who received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1970 for his studies of the magnetic properties of solids.
Biography
Néel studied at the Lyc ...
showed that two levels of magnetic alignment result in this behavior. One is ferromagnetism in the strict sense, where all the magnetic moments are aligned. The other is ''ferrimagnetism
A ferrimagnetic material is a material that has populations of atoms with opposing magnetic moments, as in antiferromagnetism, but these moments are unequal in magnitude, so a spontaneous magnetization remains. This can for example occur wh ...
'', where some magnetic moments point in the opposite direction but have a smaller contribution, so spontaneous magnetization is present.
In the special case where the opposing moments balance completely, the alignment is known as ''antiferromagnetism
In materials that exhibit antiferromagnetism, the magnetic moments of atoms or molecules, usually related to the spins of electrons, align in a regular pattern with neighboring spins (on different sublattices) pointing in opposite directions. ...
''; antiferromagnets do not have a spontaneous magnetization.
Materials
Ferromagnetism is an unusual property that occurs in only a few substances. The common ones are thetransition metal
In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. The lanthanide and actinid ...
s iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, and cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, as well as their alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s and alloys of rare-earth metal
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or rare earths, and sometimes the lanthanides or lanthanoids (although scandium and yttrium, which do not belong to this series, are usually included as rare earths), are a set of ...
s. It is a property not just of the chemical make-up of a material, but of its crystalline structure and microstructure. Ferromagnetism results from these materials having many unpaired electrons in their d-block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
(in the case of iron and its relatives) or f-block (in the case of the rare-earth metals), a result of Hund's rule of maximum multiplicity. There are ferromagnetic metal alloys whose constituents are not themselves ferromagnetic, called Heusler alloy
Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name ...
s, named after Fritz Heusler. Conversely, there are non-magnetic alloys, such as types of stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
, composed almost exclusively of ferromagnetic metals.
Amorphous (non-crystalline) ferromagnetic metallic alloys can be made by very rapid quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, gas, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, suc ...
(cooling) of an alloy. These have the advantage that their properties are nearly isotropic (not aligned along a crystal axis); this results in low coercivity
Coercivity, also called the magnetic coercivity, coercive field or coercive force, is a measure of the ability of a ferromagnetic material to withstand an external magnetic field without becoming Magnetization, demagnetized. Coercivity is usual ...
, low hysteresis
Hysteresis is the dependence of the state of a system on its history. For example, a magnet may have more than one possible magnetic moment in a given magnetic field, depending on how the field changed in the past. Plots of a single component of ...
loss, high permeability, and high electrical resistivity. One such typical material is a transition metal-metalloid
A metalloid is a chemical element which has a preponderance of material property, properties in between, or that are a mixture of, those of metals and Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetals. The word metalloid comes from the Latin language, Latin ''meta ...
alloy, made from about 80% transition metal (usually Fe, Co, or Ni) and a metalloid component ( B, C, Si, P, or Al) that lowers the melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state of matter, state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase (matter), phase exist in Thermodynamic equilib ...
.
A relatively new class of exceptionally strong ferromagnetic materials are the rare-earth magnet
A rare-earth magnet is a strong permanent magnet made from alloys of rare-earth elements. Developed in the 1970s and 1980s, rare-earth magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnets made, producing significantly stronger magnetic fields tha ...
s. They contain lanthanide
The lanthanide () or lanthanoid () series of chemical elements comprises at least the 14 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57–70, from lanthanum through ytterbium. In the periodic table, they fill the 4f orbitals. Lutetium (el ...
elements that are known for their ability to carry large magnetic moments in well-localized f-orbitals.
The table lists a selection of ferromagnetic and ferrimagnetic compounds, along with their Curie temperature
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by induced magnetism. The Curie ...
(''T''C), above which they cease to exhibit spontaneous magnetization.
Unusual materials
Most ferromagnetic materials are metals, since the conducting electrons are often responsible for mediating the ferromagnetic interactions. It is therefore a challenge to develop ferromagnetic insulators, especiallymultiferroic
Multiferroics are defined as materials that exhibit more than one of the primary ferroic properties in the same phase:
* ferromagnetism – a magnetisation that is switchable by an applied magnetic field
* ferroelectricity – an electric polari ...
materials, which are both ferromagnetic and ferroelectric
In physics and materials science, ferroelectricity is a characteristic of certain materials that have a spontaneous electric polarization that can be reversed by the application of an external electric field. All ferroelectrics are also piezoel ...
.
A number of actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part ...
compounds are ferromagnets at room temperature or exhibit ferromagnetism upon cooling. Pu P is a paramagnet with cubic symmetry at room temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and ...
, but which undergoes a structural transition into a tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the Cube (geometry), cube becomes a rectangular Pri ...
state with ferromagnetic order when cooled below its . In its ferromagnetic state, PuP's easy axis is in the ⟨100⟩ direction.
In NpFe2 the easy axis is ⟨111⟩. Above , NpFe2 is also paramagnetic and cubic. Cooling below the Curie temperature produces a rhombohedral
In geometry, a rhombohedron (also called a rhombic hexahedron or, inaccurately, a rhomboid) is a special case of a parallelepiped in which all six faces are congruent rhombus, rhombi. It can be used to define the rhombohedral lattice system, a Ho ...
distortion wherein the rhombohedral angle changes from 60° (cubic phase) to 60.53°. An alternate description of this distortion is to consider the length along the unique trigonal axis (after the distortion has begun) and as the distance in the plane perpendicular to . In the cubic phase this reduces to . Below the Curie temperature, the lattice acquires a distortion
:
which is the largest strain in any actinide
The actinide () or actinoid () series encompasses at least the 14 metallic chemical elements in the 5f series, with atomic numbers from 89 to 102, actinium through nobelium. Number 103, lawrencium, is also generally included despite being part ...
compound. NpNi2 undergoes a similar lattice distortion below , with a strain of (43 ± 5) × 10−4. NpCo2 is a ferrimagnet below 15 K.
In 2009, a team of MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
physicists demonstrated that a lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
gas cooled to less than one kelvin
The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit for temperature in the International System of Units (SI). The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale that starts at the lowest possible temperature (absolute zero), taken to be 0 K. By de ...
can exhibit ferromagnetism. The team cooled fermion
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin (spin 1/2, spin , Spin (physics)#Higher spins, spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles i ...
ic lithium-6
Naturally occurring lithium (3Li) is composed of two stable isotope ratio, stable isotopes, lithium-6 (6Li) and lithium-7 (7Li), with the latter being far more abundant on Earth. Both of the natural isotopes have an unexpectedly low nuclear bin ...
to less than (150 billionths of one kelvin) using infrared laser cooling
Laser cooling includes several techniques where atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled with laser light. The directed energy of lasers is often associated with heating materials, e.g. laser cutting, so it can be counterintuit ...
. This demonstration is the first time that ferromagnetism has been demonstrated in a gas.
In rare circumstances, ferromagnetism can be observed in compounds consisting of only s-block
Block or blocked may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Broadcasting
* Block programming, the result of a programming strategy in broadcasting
* W242BX, a radio station licensed to Greenville, South Carolina, United States known as ''96.3 ...
and p-block elements, such as rubidium sesquioxide
Rubidium sesquioxide is a chemical compound with the formula or more accurately . In terms of oxidation states, Rubidium in this compound has a nominal charge of +1, and the oxygen is a mixed peroxide () and superoxide () for a structural formula ...
.
In 2018, a team of University of Minnesota
The University of Minnesota Twin Cities (historically known as University of Minnesota) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Minneapolis–Saint Paul, Twin Cities of Minneapolis and Saint ...
physicists demonstrated that body-centered tetragonal ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is unreactive to most chem ...
exhibits ferromagnetism at room temperature.
Electrically induced ferromagnetism
Recent research has shown evidence that ferromagnetism can be induced in some materials by anelectric current
An electric current is a flow of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is defined as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface. The moving particles are called charge c ...
or voltage. Antiferromagnetic LaMnO3 and SrCoO have been switched to be ferromagnetic by a current. In July 2020, scientists reported inducing ferromagnetism in the abundant diamagnetic
Diamagnetism is the property of materials that are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagn ...
material iron pyrite
The mineral pyrite ( ), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue ...
("fool's gold") by an applied voltage. In these experiments, the ferromagnetism was limited to a thin surface layer.
Explanation
The Bohr–Van Leeuwen theorem, discovered in the 1910s, showed thatclassical physics
Classical physics refers to physics theories that are non-quantum or both non-quantum and non-relativistic, depending on the context. In historical discussions, ''classical physics'' refers to pre-1900 physics, while '' modern physics'' refers to ...
theories are unable to account for any form of material magnetism, including ferromagnetism; the explanation rather depends on the quantum mechanical
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is the foundation of a ...
description of atom
Atoms are the basic particles of the chemical elements. An atom consists of a atomic nucleus, nucleus of protons and generally neutrons, surrounded by an electromagnetically bound swarm of electrons. The chemical elements are distinguished fr ...
s. Each of an atom's electrons has a magnetic moment
In electromagnetism, the magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment is the combination of strength and orientation of a magnet or other object or system that exerts a magnetic field. The magnetic dipole moment of an object determines the magnitude ...
according to its spin
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spin (physics) or particle spin, a fundamental property of elementary particles
* Spin quantum number, a number which defines the value of a particle's spin
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thr ...
state, as described by quantum mechanics. The Pauli exclusion principle
In quantum mechanics, the Pauli exclusion principle (German: Pauli-Ausschlussprinzip) states that two or more identical particles with half-integer spins (i.e. fermions) cannot simultaneously occupy the same quantum state within a system that o ...
, also a consequence of quantum mechanics, restricts the occupancy of electrons' spin states in atomic orbitals
In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital () is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes an electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be used to calc ...
, generally causing the magnetic moments from an atom's electrons to largely or completely cancel. An atom will have a ''net'' magnetic moment when that cancellation is incomplete.
Origin of atomic magnetism
One of the fundamental properties of anelectron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
(besides that it carries charge) is that it has a magnetic dipole moment
In electromagnetism, the magnetic moment or magnetic dipole moment is the combination of strength and orientation of a magnet or other object or system that exerts a magnetic field. The magnetic dipole moment of an object determines the magnitude ...
, i.e., it behaves like a tiny magnet, producing a magnetic field
A magnetic field (sometimes called B-field) is a physical field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular ...
. This dipole moment comes from a more fundamental property of the electron: its quantum mechanical spin. Due to its quantum nature, the spin of the electron can be in one of only two states, with the magnetic field either pointing "up" or "down" (for any choice of up and down). Electron spin in atoms is the main source of ferromagnetism, although there is also a contribution from the orbital angular momentum
Angular momentum (sometimes called moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of Momentum, linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a Conservation law, conserved quantity – the total ang ...
of the electron about the nucleus
Nucleus (: nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucleu ...
. When these magnetic dipoles in a piece of matter are aligned (point in the same direction), their individually tiny magnetic fields add together to create a much larger macroscopic field.
However, materials made of atoms with filled electron shell
In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit that electrons follow around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (o ...
s have a total dipole moment of zero: because the electrons all exist in pairs with opposite spin, every electron's magnetic moment is cancelled by the opposite moment of the second electron in the pair. Only atoms with partially filled shells (i.e., unpaired spins) can have a net magnetic moment, so ferromagnetism occurs only in materials with partially filled shells. Because of Hund's rules, the first few electrons in an otherwise unoccupied shell tend to have the same spin, thereby increasing the total dipole moment.
These unpaired dipoles (often called simply "spins", even though they also generally include orbital angular momentum) tend to align in parallel to an external magnetic field leading to a macroscopic effect called paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, ...
. In ferromagnetism, however, the magnetic interaction between neighboring atoms' magnetic dipoles is strong enough that they align with ''each other'' regardless of any applied field, resulting in the spontaneous magnetization of so-called domains. This results in the large observed magnetic permeability
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization produced in a material in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter ''μ''. It is the ratio of the magnetic ...
of ferromagnetics, and the ability of magnetically hard materials to form permanent magnets
Permanent may refer to:
Art and entertainment
* ''Permanent'' (film), a 2017 American film
* ''Permanent'' (Joy Division album)
* "Permanent" (song), by David Cook
*"Permanent", a song by Alex Lahey from '' The Answer Is Always Yes'', 2023
Other ...
.
Exchange interaction
When two nearby atoms have unpaired electrons, whether the electron spins are parallel or antiparallel affects whether the electrons can share the same orbit as a result of the quantum mechanical effect called theexchange interaction
In chemistry and physics, the exchange interaction is a quantum mechanical constraint on the states of indistinguishable particles. While sometimes called an exchange force, or, in the case of fermions, Pauli repulsion, its consequences cannot alw ...
. This in turn affects the electron location and the Coulomb (electrostatic) interaction and thus the energy difference between these states.
The exchange interaction is related to the Pauli exclusion principle, which says that two electrons with the same spin cannot also be in the same spatial state (orbital). This is a consequence of the spin–statistics theorem
The spin–statistics theorem proves that the observed relationship between the intrinsic spin of a particle (angular momentum not due to the orbital motion) and the quantum particle statistics of collections of such particles is a consequence of ...
and that electrons are fermions
In particle physics, a fermion is a subatomic particle that follows Fermi–Dirac statistics. Fermions have a half-integer spin ( spin , spin , etc.) and obey the Pauli exclusion principle. These particles include all quarks and leptons and ...
. Therefore, under certain conditions, when the orbitals of the unpaired outer valence electron
In chemistry and physics, valence electrons are electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, and that can participate in the formation of a chemical bond if the outermost shell is not closed. In a single covalent bond, a shared pair forms with b ...
s from adjacent atoms overlap, the distributions of their electric charge
Electric charge (symbol ''q'', sometimes ''Q'') is a physical property of matter that causes it to experience a force when placed in an electromagnetic field. Electric charge can be ''positive'' or ''negative''. Like charges repel each other and ...
in space are farther apart when the electrons have parallel spins than when they have opposite spins. This reduces the electrostatic energy
Electric potential energy is a potential energy (measured in joules) that results from conservative Coulomb forces and is associated with the configuration of a particular set of point charges within a defined system. An ''object'' may be sa ...
of the electrons when their spins are parallel compared to their energy when the spins are antiparallel, so the parallel-spin state is more stable. This difference in energy is called the exchange energy. In simple terms, the outer electrons of adjacent atoms, which repel each other, can move further apart by aligning their spins in parallel, so the spins of these electrons tend to line up.
This energy difference can be orders of magnitude larger than the energy differences associated with the magnetic dipole–dipole interaction
Magnetic dipole–dipole interaction, also called dipolar coupling, refers to the direct interaction between two magnetic dipoles. Roughly speaking, the magnetic dipole#External magnetic field produced by a magnetic dipole moment, magnetic field ...
due to dipole orientation, which tends to align the dipoles antiparallel. In certain doped semiconductor oxides, RKKY interactions have been shown to bring about periodic longer-range magnetic interactions, a phenomenon of significance in the study of spintronic materials.
The materials in which the exchange interaction is much stronger than the competing dipole–dipole interaction are frequently called ''magnetic materials''. For instance, in iron (Fe) the exchange force is about 1,000 times stronger than the dipole interaction. Therefore, below the Curie temperature, virtually all of the dipoles in a ferromagnetic material will be aligned. In addition to ferromagnetism, the exchange interaction is also responsible for the other types of spontaneous ordering of atomic magnetic moments occurring in magnetic solids: antiferromagnetism and ferrimagnetism. There are different exchange interaction mechanisms which create the magnetism in different ferromagnetic, ferrimagnetic, and antiferromagnetic substances—these mechanisms include direct exchange, RKKY exchange, double exchange, and superexchange.
Magnetic anisotropy
Although the exchange interaction keeps spins aligned, it does not align them in a particular direction. Withoutmagnetic anisotropy
In condensed matter physics, magnetic anisotropy describes how an object's magnetic properties can be anisotropy, different depending on direction. In the simplest case, there is no preferential direction for an object's magnetic moment. It will ...
, the spins in a magnet randomly change direction in response to thermal fluctuations
In statistical mechanics, thermal fluctuations are random deviations of an atomic system from its average state, that occur in a system at equilibrium.In statistical mechanics they are often simply referred to as fluctuations. All thermal fluctu ...
, and the magnet is superparamagnetic
Superparamagnetism is a form of magnetism which appears in small ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic nanoparticles. In sufficiently small nanoparticles, magnetization can randomly flip direction under the influence of temperature. The typical time betw ...
. There are several kinds of magnetic anisotropy, the most common of which is magnetocrystalline anisotropy
In physics, a ferromagnetic material is said to have magnetocrystalline anisotropy if it takes more energy to magnetization, magnetize it in certain directions than in others. These directions are usually related to the crystal structure, principa ...
. This is a dependence of the energy on the direction of magnetization relative to the crystallographic lattice. Another common source of anisotropy
Anisotropy () is the structural property of non-uniformity in different directions, as opposed to isotropy. An anisotropic object or pattern has properties that differ according to direction of measurement. For example, many materials exhibit ve ...
, inverse magnetostriction, is induced by internal strains. Single-domain magnets also can have a ''shape anisotropy'' due to the magnetostatic effects of the particle shape. As the temperature of a magnet increases, the anisotropy tends to decrease, and there is often a blocking temperature at which a transition to superparamagnetism occurs.
Magnetic domains
 The spontaneous alignment of magnetic dipoles in ferromagnetic materials would seem to suggest that every piece of ferromagnetic material should have a strong magnetic field, since all the spins are aligned; yet iron and other ferromagnets are often found in an "unmagnetized" state. This is because a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material is divided into tiny regions called ''
The spontaneous alignment of magnetic dipoles in ferromagnetic materials would seem to suggest that every piece of ferromagnetic material should have a strong magnetic field, since all the spins are aligned; yet iron and other ferromagnets are often found in an "unmagnetized" state. This is because a bulk piece of ferromagnetic material is divided into tiny regions called ''magnetic domain
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. When c ...
s''
(also known as ''Weiss domains''). Within each domain, the spins are aligned, but if the bulk material is in its lowest energy configuration (i.e. "unmagnetized"), the spins of separate domains point in different directions and their magnetic fields cancel out, so the bulk material has no net large-scale magnetic field.
Ferromagnetic materials spontaneously divide into magnetic domains because the exchange interaction
In chemistry and physics, the exchange interaction is a quantum mechanical constraint on the states of indistinguishable particles. While sometimes called an exchange force, or, in the case of fermions, Pauli repulsion, its consequences cannot alw ...
is a short-range force, so over long distances of many atoms, the tendency of the magnetic dipoles to reduce their energy by orienting in opposite directions wins out. If all the dipoles in a piece of ferromagnetic material are aligned parallel, it creates a large magnetic field extending into the space around it. This contains a lot of magnetostatic
Magnetostatics is the study of magnetic fields in systems where the currents are steady (not changing with time). It is the magnetic analogue of electrostatics, where the charges are stationary. The magnetization need not be static; the equat ...
energy. The material can reduce this energy by splitting into many domains pointing in different directions, so the magnetic field is confined to small local fields in the material, reducing the volume of the field. The domains are separated by thin domain walls a number of molecules thick, in which the direction of magnetization of the dipoles rotates smoothly from one domain's direction to the other.
Magnetized materials
 Thus, a piece of iron in its lowest energy state ("unmagnetized") generally has little or no net magnetic field. However, the magnetic domains in a material are not fixed in place; they are simply regions where the spins of the electrons have aligned spontaneously due to their magnetic fields, and thus can be altered by an external magnetic field. If a strong-enough external magnetic field is applied to the material, the domain walls will move via a process in which the spins of the electrons in atoms near the wall in one domain turn under the influence of the external field to face in the same direction as the electrons in the other domain, thus reorienting the domains so more of the dipoles are aligned with the external field. The domains will remain aligned when the external field is removed, and sum to create a magnetic field of their own extending into the space around the material, thus creating a "permanent" magnet. The domains do not go back to their original minimum energy configuration when the field is removed because the domain walls tend to become 'pinned' or 'snagged' on defects in the crystal lattice, preserving their parallel orientation. This is shown by the
Thus, a piece of iron in its lowest energy state ("unmagnetized") generally has little or no net magnetic field. However, the magnetic domains in a material are not fixed in place; they are simply regions where the spins of the electrons have aligned spontaneously due to their magnetic fields, and thus can be altered by an external magnetic field. If a strong-enough external magnetic field is applied to the material, the domain walls will move via a process in which the spins of the electrons in atoms near the wall in one domain turn under the influence of the external field to face in the same direction as the electrons in the other domain, thus reorienting the domains so more of the dipoles are aligned with the external field. The domains will remain aligned when the external field is removed, and sum to create a magnetic field of their own extending into the space around the material, thus creating a "permanent" magnet. The domains do not go back to their original minimum energy configuration when the field is removed because the domain walls tend to become 'pinned' or 'snagged' on defects in the crystal lattice, preserving their parallel orientation. This is shown by the Barkhausen effect
The Barkhausen effect is a name given to the noise in the magnetic output of a ferromagnet when the magnetizing force applied to it is changed. Discovered by German physicist Heinrich Barkhausen in 1919, it is caused by rapid changes in the ...
: as the magnetizing field is changed, the material's magnetization changes in thousands of tiny discontinuous jumps as domain walls suddenly "snap" past defects.
This magnetization as a function of an external field is described by a hysteresis curve. Although this state of aligned domains found in a piece of magnetized ferromagnetic material is not a minimal-energy configuration, it is metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability is an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball is onl ...
, and can persist for long periods, as shown by samples of magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula . It is one of the iron oxide, oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetism, ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetization, magnetized to become a ...
from the sea floor which have maintained their magnetization for millions of years.
Heating and then cooling ( annealing) a magnetized material, subjecting it to vibration by hammering it, or applying a rapidly oscillating magnetic field from a degaussing coil tends to release the domain walls from their pinned state, and the domain boundaries tend to move back to a lower energy configuration with less external magnetic field, thus demagnetizing the material.
Commercial magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, ...
s are made of "hard" ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic materials with very large magnetic anisotropy such as alnico
Alnico is a family of iron alloys which, in addition to iron are composed primarily of aluminium (Al), nickel (Ni), and cobalt (Co), hence the acronym ''al-ni-co''. They also include copper, and sometimes titanium.
Alnico alloys are ferromagnet ...
and ferrites Ferrite may refer to:
* Ferrite (iron), one of the allotropes of iron that is stable at room temperature and pressure, α-Fe
* Ferrite (magnet), a ferromagnetic ceramic material
See also
*
* Ferrite bead, a component placed on the end of a data c ...
, which have a very strong tendency for the magnetization to be pointed along one axis of the crystal, the "easy axis". During manufacture the materials are subjected to various metallurgical processes in a powerful magnetic field, which aligns the crystal grains so their "easy" axes of magnetization all point in the same direction. Thus, the magnetization, and the resulting magnetic field, is "built in" to the crystal structure of the material, making it very difficult to demagnetize.
Curie temperature
As the temperature of a material increases, thermal motion, orentropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, most commonly associated with states of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the micros ...
, competes with the ferromagnetic tendency for dipoles to align. When the temperature rises beyond a certain point, called the Curie temperature
In physics and materials science, the Curie temperature (''T''C), or Curie point, is the temperature above which certain materials lose their permanent magnetic properties, which can (in most cases) be replaced by induced magnetism. The Curie ...
, there is a second-order phase transition
In physics, chemistry, and other related fields like biology, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic Sta ...
and the system can no longer maintain a spontaneous magnetization, so its ability to be magnetized or attracted to a magnet disappears, although it still responds paramagnetically to an external field. Below that temperature, there is a spontaneous symmetry breaking
Spontaneous symmetry breaking is a spontaneous process of symmetry breaking, by which a physical system in a symmetric state spontaneously ends up in an asymmetric state. In particular, it can describe systems where the equations of motion o ...
and magnetic moments become aligned with their neighbors. The Curie temperature itself is a critical point, where the magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility (; denoted , chi) is a measure of how much a material will become magnetized in an applied magnetic field. It is the ratio of magnetization (magnetic moment per unit volume) to the applied magnet ...
is theoretically infinite and, although there is no net magnetization, domain-like spin correlations fluctuate at all length scales.
The study of ferromagnetic phase transitions, especially via the simplified Ising spin model, had an important impact on the development of statistical physics
In physics, statistical mechanics is a mathematical framework that applies statistical methods and probability theory to large assemblies of microscopic entities. Sometimes called statistical physics or statistical thermodynamics, its applicati ...
. There, it was first clearly shown that mean field theory
In physics and probability theory, Mean-field theory (MFT) or Self-consistent field theory studies the behavior of high-dimensional random (stochastic) models by studying a simpler model that approximates the original by averaging over degrees of ...
approaches failed to predict the correct behavior at the critical point (which was found to fall under a ''universality class'' that includes many other systems, such as liquid-gas transitions), and had to be replaced by renormalization group
In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) is a formal apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying p ...
theory.
See also
* * * * * *References
External links
*Electromagnetism
– ch. 11, from an online textbook * Detailed nonmathematical description of ferromagnetic materials with illustrations
Magnetism: Models and Mechanisms
in E. Pavarini, E. Koch, and U. Schollwöck: Emergent Phenomena in Correlated Matter, Jülich 2013, {{Authority control Quantum phases Magnetic hysteresis Physical phenomena Ferromagnetism