Exscalate4Cov on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Exscalate4Cov was a public-private
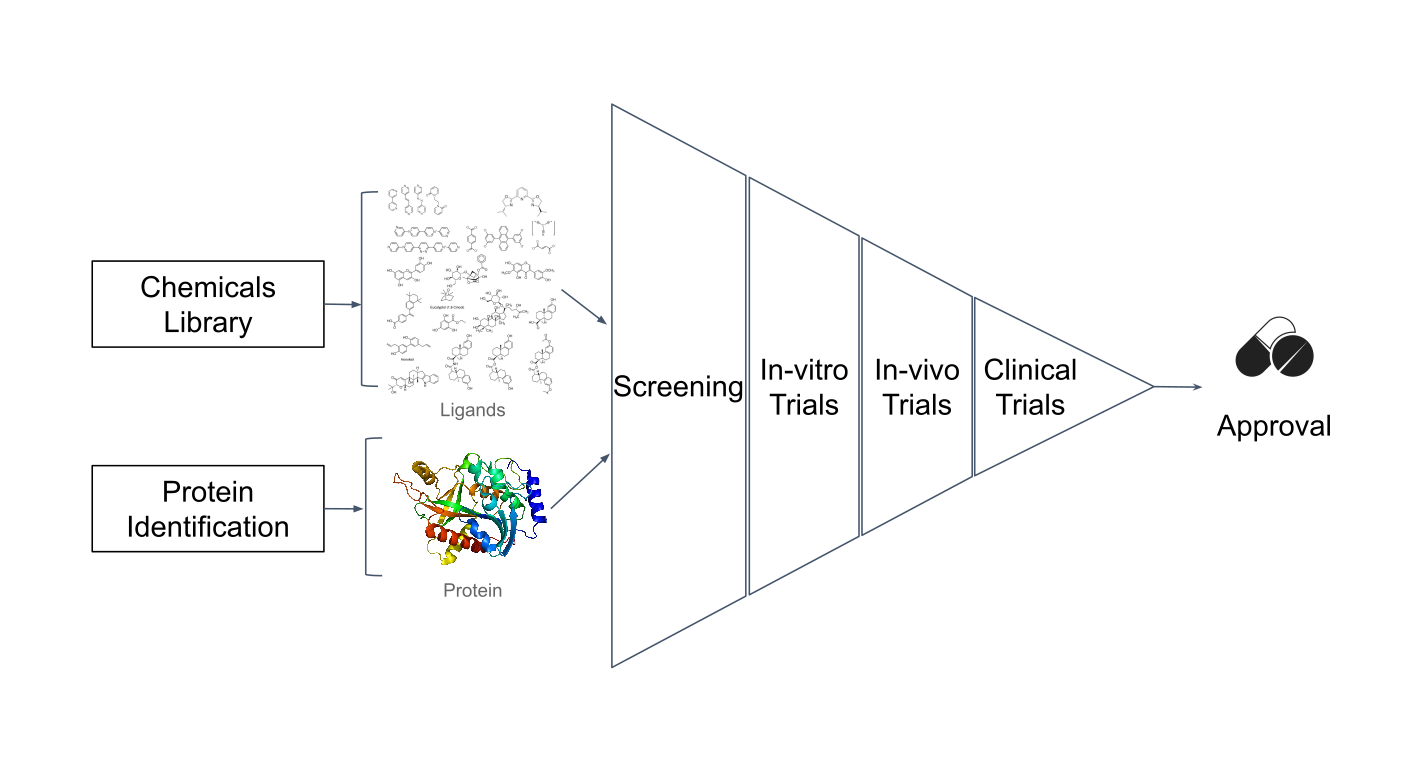
 Therefore, the process of finding new drugs usually involves
Therefore, the process of finding new drugs usually involves
 The Exscalate4Cov project followed the ANTAREX4ZIKA project, both of which aimed to leverage HPC for drug discovery, albeit targeting different viruses. While Exscalate4Cov focused on the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19, ANTAREX4ZIKA was dedicated to addressing the
The Exscalate4Cov project followed the ANTAREX4ZIKA project, both of which aimed to leverage HPC for drug discovery, albeit targeting different viruses. While Exscalate4Cov focused on the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19, ANTAREX4ZIKA was dedicated to addressing the
 Inputs at the application level consist of
Inputs at the application level consist of
 Raloxifene is a known chemical compound used to treat
Raloxifene is a known chemical compound used to treat
Exscalate4Cov Website
E4C Cordis page
EXSCALATE Webpage
Drug discovery Supercomputing Bioinformatics Horizon 2020 projects
consortium
A consortium () is an association of two or more individuals, companies, organizations, or governments (or any combination of these entities) with the objective of participating in a common activity or pooling their resources for achieving a ...
supported by the Horizon Europe
Horizon Europe is a seven-year European Union scientific research initiative to help develop a sustainable and livable society in Europe. It is the ninth of the Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development (FP9), and the succe ...
program from the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
, aimed at leveraging high-performance computing
High-performance computing (HPC) is the use of supercomputers and computer clusters to solve advanced computation problems.
Overview
HPC integrates systems administration (including network and security knowledge) and parallel programming into ...
(HPC) as a response to the coronavirus
Coronaviruses are a group of related RNA viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans and birds, they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include some cases of the comm ...
pandemic. The project utilized high-throughput, extreme-scale, computer-aided drug design
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
to conduct experiments.
The Exsclate4Cov project, which stands for ''EXaSCale smArt pLatform Against paThogEns for Corona Virus'', was coordinated by Dompé Farmaceutici and involved 17 participants. It was part of the Horizon 2020
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the Europe ...
''SOCIETAL CHALLENGES - Health, demographic change and well-being'' founding funding''.''
The project conducted one of the largest virtual screening
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor (biochemistry), r ...
and drug repositioning
Drug repositioning (also called drug repurposing) involves the investigation of existing drugs for new therapeutic purposes.
Repurposing achievements
Repurposing generics can have groundbreaking effects for patients: 35% of 'transformative' ...
experiments, identifying a potentially effective molecule against SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
.
Context
Background

Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology, and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or ...
can be a long and costly process, often taking years and requiring substantial financial investment. Pharmaceutical companies
The pharmaceutical industry is a Medicine, medical industry that discovers, develops, produces, and markets pharmaceutical goods such as medications and medical devices. Medications are then administered to (or Self-medicate, self-administered b ...
have large datasets of chemical compounds
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
, which they test against a drug target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
, often a protein receptor
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a recepto ...
. The goal is to find compounds that interact with the targets, leading to potential therapeutic effects.
 Therefore, the process of finding new drugs usually involves
Therefore, the process of finding new drugs usually involves high-throughput screening
High-throughput screening (HTS) is a method for scientific discovery especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology, materials science and chemistry. Using robotics, data processing/control software, liquid handling device ...
(HTS). HTS enables the rapid identification of active compounds. For example, virtual screening can be used as an early stage of the drug discovery pipeline to evaluate the interactions between large datasets of small molecules and a drug target, identifying potential hit candidates. This approach helps in identifying potential hit candidates by predicting how different compounds will bind to the target protein, which will go further in the experimental validation.
In an urgent computing scenario, such as a pandemic, where time to solution is critical, virtual screening is used to identify hit molecules for the latter stages of the drug discovery pipeline, such as lead optimization
Hit to lead (H2L) also known as lead generation is a stage in early drug discovery where small molecule hits from a high throughput screen (HTS) are evaluated and undergo limited optimization to identify promising lead compounds. These lead compo ...
and clinical trial
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel v ...
. The Exscalate4Cov project was initiated after the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak. This project aimed to leverage the computational power of EU supercomputers
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instru ...
to accelerate the discovery of effective treatments for the coronavirus. By utilizing high-throughput virtual screening, Exscalate4Cov aimed to find faster solutions to the crisis.
Scope
Exscalate4Cov's approach involved screening billions of compounds against various protein targets of theSARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
virus, identifying those with a higher binding affinity
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from Latin ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usuall ...
with the target. The project's objectives were:
* Identify potential drug candidates against the coronavirus to combat the COVID-19 pandemic;
* Conduct a large-scale experiment as an example for future pandemic scenarios;
* Develop a computer-aided drug design platform that leverages supercomputer capabilities;
* Fast sharing of data and scientific discoveries with the community to work in an urgent computing scenario.
Previous projects
 The Exscalate4Cov project followed the ANTAREX4ZIKA project, both of which aimed to leverage HPC for drug discovery, albeit targeting different viruses. While Exscalate4Cov focused on the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19, ANTAREX4ZIKA was dedicated to addressing the
The Exscalate4Cov project followed the ANTAREX4ZIKA project, both of which aimed to leverage HPC for drug discovery, albeit targeting different viruses. While Exscalate4Cov focused on the SARS-CoV-2 virus responsible for COVID-19, ANTAREX4ZIKA was dedicated to addressing the Zika virus
Zika virus (ZIKV; pronounced or ) is a member of the virus family ''Flaviviridae''. It is spread by daytime-active ''Aedes'' mosquitoes, such as '' A. aegypti'' and '' A. albopictus''. Its name comes from the Ziika Forest of Uganda, where ...
. The ANTAREX4ZIKA project concluded at the end of 2018 and involved a virtual screening campaign on the CINECA Marconi machine, with a total of 10 PetaFLOPS. The ANTAREX project, which stands for AutoTuning and Adaptivity appRoach for Energy efficient eXascale HPC systems, emphasized auto-tuning and energy efficiency of HPC applications, making them more effective in various research scenarios, including drug discovery.
Consortium
The Exscalate4Cov consortium of public-private entities has been coordinated by Dompè, and it involved 17 other institutions, from research centers to universities.Pipeline
 Inputs at the application level consist of
Inputs at the application level consist of ligands
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule with a functional group that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ...
from the chemical space and the protein target of the virtual screening campaign, specifically the spike protein
In virology, a spike protein or peplomer protein is a protein that forms a large structure known as a spike or peplomer projecting from the surface of an viral envelope, enveloped virus. as cited in The proteins are usually glycoproteins that ...
in the case of Exscalate4Cov. Following a molecular docking stage that generates potential ligand conformations, a scoring stage assesses the interaction strength between each ligand's pose and the protein. The pipeline ultimately produces a ranking of hit compounds as its output, indicating the most promising candidates for further investigation.
At the software level, the project utilizes the EXSCALATE docking platform. ''LiGen'' (Ligand Generator) is one of the main components of the platform, and it is used to perform molecular docking and scoring simulations. LiGen is responsible for generating and evaluating the conformations of ligands. Another relevant component at the same level is the ''libdpipe'' library, which facilitates scaling across multi-node and cores.
To hinge the computational power offered by HPC centers, the docking platform uses MPI
MPI or Mpi may refer to:
Science and technology Biology and medicine
* Magnetic particle imaging, a tomographic technique
* Myocardial perfusion imaging, a medical procedure that illustrates heart function
* Mannose phosphate isomerase, an enzyme ...
to scale multi-node and CUDA
In computing, CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) is a proprietary parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) that allows software to use certain types of graphics processing units (GPUs) for accelerated gene ...
acceleration to take advantage of supercomputer's GPUs. The CUDA version has undergone various optimizations, including OpenACC
OpenACC (for ''open accelerators'') is a programming standard for parallel computing developed by Cray, CAPS, Nvidia and PGI. The standard is designed to simplify parallel programming of heterogeneous CPU/ GPU systems.
As in OpenMP, the prog ...
, OpenMP
OpenMP is an application programming interface (API) that supports multi-platform shared-memory multiprocessing programming in C, C++, and Fortran, on many platforms, instruction-set architectures and operating systems, including Solaris, ...
, and other techniques, to enhance performance and efficiency.
Virtual screening campaign
The project's main experiment evaluated the interactions between 12 viral proteins ofSARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19, the respiratory illness responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had the Novel coronavirus, provisional nam ...
against 70 billion molecules from the EXSCALATE chemical library. In November 2020, consortium members coordinated one of the largest virtual screening campaigns, harnessing the combined computational power of two supercomputers totaling 81 PFLOPS.
The supercomputers used are:
* Marconi100: Operated by CINECA, each node consists of 1 IBM POWER9 AC922 CPU (32 cores, 128 threads) and 4 NVIDIA V100 GPUs with 16 GB of VRAM. The machine consists of 970 nodes, providing a total of 29.3 PFLOPS.
* HPC5: Operated by Eni
Eni is an Italian oil and gas corporation.
Eni or ENI may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* Escuela Nacional de Inteligencia, the Argentine intelligence academy
* Groupe des écoles nationales d’ingénieurs (Groupe ENI), a French engi ...
, each node consists of 1 Intel Xeon Gold 6252 24C CPU (24 cores, 48 threads) and 4 NVIDIA V100 GPUs with 16 GB of VRAM. The machine consists of 1820 nodes, providing a total of 51.7 PFLOPS.
Throughput
The large-scale campaign used a reservation of 800 Marconi100 nodes and 1500 HP5 nodes for 60 hours. Achieving an average throughput was ''2400'' ligands per second ''(lig/s)'' on Marconi100 and ''2000 lig/s'' on HPC5.Data storage
Another critical aspect of the experiment was data storage management. The platform leveraged efficient MPI I/O operations to handle multi-node computations. The input data required 3.3 TB of space in SMILES format. However, SMILES data needed to be expanded in a pre-processing step involving 100 nodes over five days. Similarly, the post-processing step involved 19 nodes over five days.Output data
The final output consisted of CSV files containing scores for each input ligand, occupying 69 TB. The resulting dataset, containing 570 million hit compounds, is freely available.Drug repositioning
The Exscalate4Cov project also conducteddrug repositioning
Drug repositioning (also called drug repurposing) involves the investigation of existing drugs for new therapeutic purposes.
Repurposing achievements
Repurposing generics can have groundbreaking effects for patients: 35% of 'transformative' ...
experiments. Drug repurposing offers an interesting approach to address unmet clinical needs in case of urgent computing, due to pandemics
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic dis ...
. Hence, repurposing existing drugs with established safety and toxicology profiles provides a significant advantage by saving time in identifying potential new treatments. During the European Exscalate4Cov project activities, raloxifene was selected through a combined approach of drug repurposing and in-silico screening on SARS-CoV-2 target’s proteins, followed by subsequent in-vitro screening.
Results
Mediate
The project's large-scale campaign results are available through the MEDIATE (MolEcular DockIng AT homE) platform. The objective of MEDIATE is to collect a chemical library of Sars-COV-2 inhibitors. The MEDIATE portal provides access to a set of small molecules that research can use to start ''de-novo'' drug design from a reduced set of molecules.Raloxifene
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
. As a result of drug repositioning
Drug repositioning (also called drug repurposing) involves the investigation of existing drugs for new therapeutic purposes.
Repurposing achievements
Repurposing generics can have groundbreaking effects for patients: 35% of 'transformative' ...
experiments, the E4C project identified raloxifene as a possible candidate to treat early-stage COVID-19 patients, aiming to prevent clinical progression. In October 2020, AIFA authorized clinical trials to treat COVID-19 patients, and it is currently undergoing testing for approval.
Public interest
The experiments, including the discovery of raloxifene as a possible drug candidate against COVID-19, gained significant interest from the scientific community, as documented in several scientific articles. The project's results also captured national interest in Italy, highlighted by various newspaper articles, due to the use of Italian supercomputers during the pandemic. Additionally, the large-scale campaign results gained attention from international journals.See also
* CINECA *COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December ...
* Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology, and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or ...
* EuroHPC
* Horizon 2020
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the Europe ...
* HPC5
* Raloxifene
* Supercomputing
A supercomputer is a type of computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instruc ...
* Virtual screening
Virtual screening (VS) is a computational technique used in drug discovery to search libraries of small molecules in order to identify those structures which are most likely to bind to a drug target, typically a protein receptor (biochemistry), r ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * {{Citation , last1=Beccari , first1=A. , title=The Drug Repurposing Strategy in the Exscalate4CoV Project: Raloxifene Clinical Trials , date=May 2023 , author-mask2=et al. , doi=10.1007/978-3-031-30691-4_3 , last2=Dionigi , first2=L., series=SpringerBriefs in Applied Sciences and Technology , pages=19–26 , isbn=978-3-031-30690-7 , doi-access=freeExternal links
Exscalate4Cov Website
E4C Cordis page
EXSCALATE Webpage
Drug discovery Supercomputing Bioinformatics Horizon 2020 projects