European Wolf on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Eurasian wolf (''Canis lupus lupus''), also known as the common wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), ''The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species'', University of Minnesota Press, p. 354, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Europe and Asia. It was once widespread throughout Eurasia prior to the
Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 184-187, Miller, G. S. (1912),
Catalogue of the mammals of Western Europe (Europe exclusive of Russia) in the collection of the British museum
', London, Printed by order of the Trustees of the British Museum, pp. 313-314 Its fur is relatively short and coarse, and is generally of a tawny colour, with white on the throat that barely extends to the cheeks. Melanists,
Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 166, According to Erik Zimen, the howl of the Eurasian wolf is much more protracted and melodious than that of North American grey wolf subspecies, whose howls are louder and have a stronger emphasis on the first syllable.Zimen, E. (1981), ''The Wolf: His Place in the Natural World'', Souvenir Press, p. 73, Many Eurasian wolf populations are forced to subsist largely on
''The Naturalists Library, Mammalia, Vol. IX: Dogs''
Edinburgh: W.H. Lizars, 1839. having been compared by
 In
In  In
In
Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 177-179, Following the two world wars, Soviet wolf populations peaked twice; 30,000 wolves were harvested annually from a population of 200,000 during the 1940s, with 40,000–50,000 harvested during peak years. Soviet wolf populations reached a low around 1970, disappearing over much of
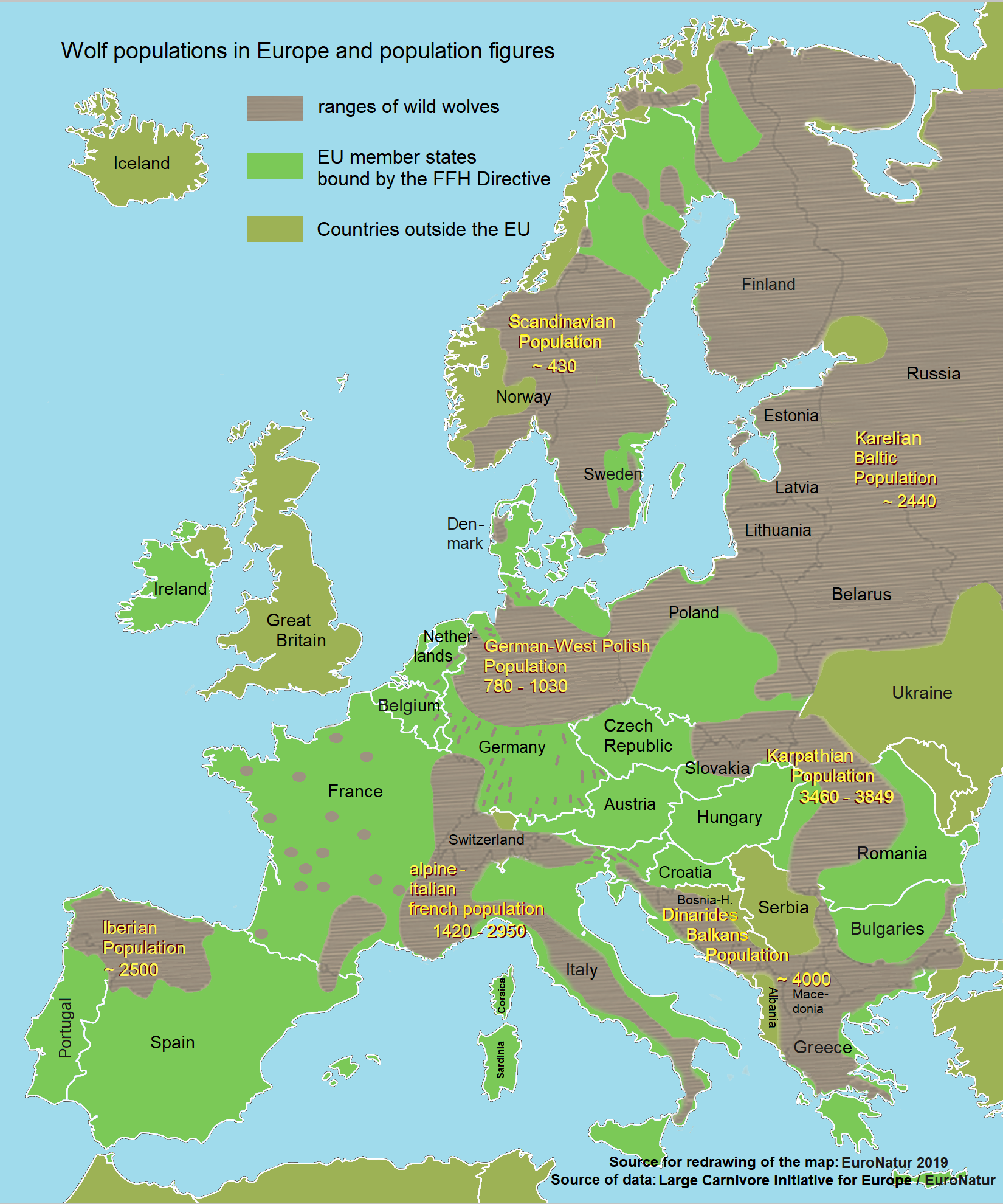 The recovery of European wolf populations began after the 1950s, when traditional pastoral and rural economies declined and thus removed the need to heavily persecute wolves. By the 1980s, small and isolated wolf populations expanded in the wake of decreased human density in rural areas and the recovery of wild prey populations.
In 1978, wolves began recolonising central Sweden after a 12-year absence, and have since expanded into southern Norway. As of 2005, the total number of Swedish and Norwegian wolves was estimated to be at least 100, including 11 breeding pairs. The grey wolf is fully protected in Sweden and partially controlled in Norway. The Scandinavian wolf populations owe their continued existence to neighbouring Finland's contiguity with the
The recovery of European wolf populations began after the 1950s, when traditional pastoral and rural economies declined and thus removed the need to heavily persecute wolves. By the 1980s, small and isolated wolf populations expanded in the wake of decreased human density in rural areas and the recovery of wild prey populations.
In 1978, wolves began recolonising central Sweden after a 12-year absence, and have since expanded into southern Norway. As of 2005, the total number of Swedish and Norwegian wolves was estimated to be at least 100, including 11 breeding pairs. The grey wolf is fully protected in Sweden and partially controlled in Norway. The Scandinavian wolf populations owe their continued existence to neighbouring Finland's contiguity with the
"Susien määrä yllättäen vähentynyt"
''Suomen Luonto'', April 2008."SS: Kuolleissa susissa vanhoja hauleja"
'' Iltalehti'', March 19, 2013. Since 2011, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Denmark have also reported wolf sightings presumably by natural migration from adjacent countries. Wolf populations in Poland have increased to about 800–900 individuals since being classified as a game species in 1976, now for more than two decades under legal protection in Annex V and II of the Habitats Directive. The number of wolf packs in western Poland has continued to increase. This is confirmed by the results of the wolf monitoring financed by the International Fund for Animal Welfare and the nature conservation foundation EuroNatur, which is carried out by the Polish nature conservation organisation Association for Nature Wolf (AfN Wolf). The Polish scientists estimated that at the end of the 2018/19 monitoring year, at least 95 resident wolf packs would be west of the
 The Eurasian wolf and the Italian wolf are legally protected in most European countries, either by listing in the annexes of the EU-FHH Directive or by the Bern Convention or both, depending on whether a country is a signatory of the Bern Convention or not.
For EU member states, an application for a change in the listing of the wolf in the annexes to the Habitats Directive requires the approval of the Division for Large Carnivores in the
The Eurasian wolf and the Italian wolf are legally protected in most European countries, either by listing in the annexes of the EU-FHH Directive or by the Bern Convention or both, depending on whether a country is a signatory of the Bern Convention or not.
For EU member states, an application for a change in the listing of the wolf in the annexes to the Habitats Directive requires the approval of the Division for Large Carnivores in the
 In
In
Schutz des Weideviehs vor dem Wolf
' In
 According to documented data, man-eating (not rabid) wolves killed 111 people in
According to documented data, man-eating (not rabid) wolves killed 111 people in
The Fear of Wolves: A Review of Wolf Attacks on Humans
', NINA, Several Russian zoologists after the
"Let's get real: beyond wolf advocacy, toward realistic policies for carnivore conservation"
. ''Fair Chase''. Summer 2009. pp. 26–30.
"Ecological and cultural diversities in the evolution of wolf-human relationships"
, in ''Ecology and conservation of wolves in a changing world'', eds. Carbyn, L. N., Fritts, S. H., and Seip, D. R., eds. pp. 3-12, Edmonton: Canadian Circumpolar Institute In
Large Carnivore Initiative for Europe
{{Taxonbar, from=Q898061 Carnivorans of Europe Carnivorans of Asia Mammals of Pakistan Mammals of Russia Mammals of Central Asia Subspecies of Canis lupus Mammals described in 1758 Wolves Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Fauna of Albania
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. Aside from an extensive paleontological record, Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
typically have several words for "wolf", thus attesting to the animal's abundance and cultural significance.Gamkrelidze, T. V. & Ivanov, V. V. (1995), ''Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and Proto-Culture'', Walter de Gruyter, pp. 413-417, It was held in high regard in Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
, Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foot ...
, Slavic, Turkic, ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
, Roman, Dacian, and Thracian
The Thracians (; ; ) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Southeast Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area that today is shared between north-eastern Greece, ...
cultures, whilst having an ambivalent reputation in early Germanic cultures.
It is the largest of Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
grey wolves, averaging in Europe; however, exceptionally large individuals have weighed , though this varies according to region.Heptner, V. G. & Naumov, N. P. (1998) Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 184-187, Miller, G. S. (1912),
Catalogue of the mammals of Western Europe (Europe exclusive of Russia) in the collection of the British museum
', London, Printed by order of the Trustees of the British Museum, pp. 313-314 Its fur is relatively short and coarse, and is generally of a tawny colour, with white on the throat that barely extends to the cheeks. Melanists,
albino
Albinism is the congenital absence of melanin in an animal or plant resulting in white hair, feathers, scales and skin and reddish pink or blue eyes. Individuals with the condition are referred to as albinos.
Varied use and interpretation of ...
s, and erythrists are rare, and mostly the result of wolf-dog hybridisation.Heptner, V. G. & Naumov, N. P. (1998) Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 166, According to Erik Zimen, the howl of the Eurasian wolf is much more protracted and melodious than that of North American grey wolf subspecies, whose howls are louder and have a stronger emphasis on the first syllable.Zimen, E. (1981), ''The Wolf: His Place in the Natural World'', Souvenir Press, p. 73, Many Eurasian wolf populations are forced to subsist largely on
livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
and garbage
Garbage, trash (American English), rubbish (British English), or refuse is waste material that is discarded by humans, usually due to a perceived lack of utility. The term generally does not encompass bodily waste products, purely liquid or ...
in areas with dense human activity, though wild ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Euungulata ("true ungulates"), which primarily consists of large mammals with Hoof, hooves. Once part of the clade "Ungulata" along with the clade Paenungulata, "Ungulata" has since been determined ...
s such as moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
, red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
, roe deer and wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
are still the most important food sources in Russia and the more mountainous regions of Eastern Europe. Other prey species include reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only re ...
, argali
The argali (''Ovis ammon''), also known as the mountain sheep, is a wild ovis, sheep native to the highlands of western East Asia, the Himalayas, Tibet, and the Altai Mountains.
Description
The name 'argali' is the Mongolian language, Mongolian ...
, mouflon, wisent
The European bison (: bison) (''Bison bonasus'') or the European wood bison, also known as the wisent ( or ), the zubr (), or sometimes colloquially as the European buffalo, is a European species of bison. It is one of two extant species of bi ...
, saiga, ibex
An ibex ( : ibex, ibexes or ibices) is any of several species of wild goat (genus ''Capra''), distinguished by the male's large recurved horns, which are transversely ridged in front. Ibex are found in Eurasia, North Africa and East Africa.
T ...
, chamois
The chamois (; ) (''Rupicapra rupicapra'') or Alpine chamois is a species of Caprinae, goat-antelope native to the mountains in Southern Europe, from the Pyrenees, the Alps, the Apennines, the Dinarides, the Tatra Mountains, Tatra to the Carpa ...
, wild goat
The wild goat (''Capra aegagrus'') is a wild goat species, inhabiting forests, shrublands and rocky areas ranging from Turkey and the Caucasus in the west to Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan in the east. It has been listed as near threaten ...
s, fallow deer
Fallow deer is the common name for species of deer in the genus ''Dama'' of subfamily Cervinae. There are two living species, the European fallow deer (''Dama dama''), native to Europe and Anatolia, and the Persian fallow deer (''Dama mesopotamic ...
, and musk deer
Musk deer can refer to any one, or all eight, of the species that make up ''Moschus'', the only extant genus of the family (biology), family Moschidae. Despite being commonly called deer, they are not true deer belonging to the family Cervidae, b ...
.
Physical description
Build
In describing North American wolves, John Richardson used European wolves as a basis for comparison, summarising the differences between the two forms as:The European wolf's head is narrower, and tapers gradually to form the nose, which is produced on the same plane with the forehead. Its ears are higher and somewhat nearer to each other; their length exceeds the distance between the auditory opening and the eye. Its loins are more slender, its legs longer, feet narrower, and its tail is more thinly clothed with fur. The shorter ears, broader forehead, and thicker muzzle of the American Wolf, with the bushiness of the hair behind the cheek, give it a physiognomy more like the social visage of an Esquimaux dog than the sneaking aspect of a European Wolf.Richardson, John & Swainson, William
''Fauna boreali-americana, or, The zoology of the northern parts of British America: containing descriptions of the objects of natural history collected on the late northern land expeditions, under command of Captain Sir John Franklin, R.N.''
Jay Murray, 1829
Size
The size of Eurasian wolves is subject to geographic variation, with animals in Russia and Scandinavia being larger than those residing in Western Europe,Jardine, William''The Naturalists Library, Mammalia, Vol. IX: Dogs''
Edinburgh: W.H. Lizars, 1839. having been compared by
Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. (October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), also known as Teddy or T.R., was the 26th president of the United States, serving from 1901 to 1909. Roosevelt previously was involved in New York (state), New York politics, incl ...
to the large wolves of north-western Montana
Montana ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota to the east, South Dakota to the southeast, Wyoming to the south, an ...
and Washington. Adults from Russia measure in length, in shoulder height, and weigh on average , with a maximum weight of . The largest on record was killed after World War II in the Kobelyakski Area of the Poltavskij Region in the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, abbreviated as the Ukrainian SSR, UkrSSR, and also known as Soviet Ukraine or just Ukraine, was one of the Republics of the Soviet Union, constituent republics of the Soviet Union from 1922 until 1991. ...
, and weighed . Larger weights of have been reported in Ukraine, though the circumstances under which these latter animals were weighed are not known. Although similar in size to central Russian wolves, Swedish and Norwegian wolves tend to be more heavily built with deeper shoulders. One wolf killed in Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
was recorded to have weighed . In Italian wolves, excepting the tail, body lengths range from 110 to 148 cm, while shoulder height is 50–70 cm. Males weigh between and rarely .. The now extinct British wolves are known to have reached similar sizes to Arctic wolves.Owen, R., ''A history of British fossil mammals, and birds'', J. Van Voorst, 1846
Range
Decline
The extermination ofNorthern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other ge ...
's wolves first became an organized effort during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, and continued until the late 1800s. In England, wolf persecution was enforced by legislation
Legislation is the process or result of enrolling, enacting, or promulgating laws by a legislature, parliament, or analogous governing body. Before an item of legislation becomes law it may be known as a bill, and may be broadly referred ...
, and the last wolf was killed in the late 15th century during the reign of Henry VII. Wolves survived longer in Scotland, where they sheltered in vast tracts of forest, which were subsequently burned down. Wolves managed to survive in the forests of Braemar and Sutherland
Sutherland () is a Counties of Scotland, historic county, registration county and lieutenancy areas of Scotland, lieutenancy area in the Scottish Highlands, Highlands of Scotland. The name dates from the Scandinavian Scotland, Viking era when t ...
until 1684. The extirpation of wolves in Ireland followed a similar course, with the last wolf believed to have been killed in 1786. A wolf bounty was introduced in Sweden in 1647, after the extermination of moose and reindeer forced wolves to feed on livestock. The Sami
Acronyms
* SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft
* Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company
* South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise ne ...
extirpated wolves in northern Sweden in organized drives. By 1960, few wolves remained in Sweden, due to the use of snowmobiles in hunting them, with the last specimen being killed in 1966. The grey wolf was exterminated in Denmark in 1772 and Norway's last wolf was killed in 1973. The species was almost wiped out in 20th-century Finland, despite regular dispersals from Russia. The grey wolf was present only in the eastern and northern parts of Finland by 1900, though its numbers increased after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.Fritts, S. H., et al. (2003), "Wolves and humans", in ''Wolves: Behavior, ecology and conservation'', eds. L. D. Mech, and L. Boitani, pp. 289–316, Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press Although the Finnish wolf population rose by 2005 to around 250 individuals, by 2013, their numbers had again declined to the mid-1990s figure of around 140. This was despite government measures to keep breeding numbers viable. At the beginning of 2016, the wolf population was roughly 300-350 individuals.
Central Europe
Central Europe is a geographical region of Europe between Eastern Europe, Eastern, Southern Europe, Southern, Western Europe, Western and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Central Europe is known for its cultural diversity; however, countries in ...
, wolves were dramatically reduced in number during the early 19th century, due to organized hunts and reductions in ungulate populations. In Bavaria
Bavaria, officially the Free State of Bavaria, is a States of Germany, state in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the list of German states by area, largest German state by land area, comprising approximately 1/5 of the total l ...
, the last wolf was killed in 1847, and had disappeared from the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
regions by 1899 and largely disappeared in Switzerland before the end of the 19th century. In 1934, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
introduced the first legislation regulating the protection of wolves. The last free-living wolf to be killed on the soil of present-day Germany before 1945 was the so-called " Tiger of Sabrodt", which was shot near Hoyerswerda, Lusatia
Lusatia (; ; ; ; ; ), otherwise known as Sorbia, is a region in Central Europe, formerly entirely in Germany and today territorially split between Germany and modern-day Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the eas ...
(then Lower Silesia), in 1904. Today, wolves have returned to the area.
Wolf hunting in France was first institutionalized by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( ; 2 April 748 – 28 January 814) was List of Frankish kings, King of the Franks from 768, List of kings of the Lombards, King of the Lombards from 774, and Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of what is now known as the Carolingian ...
between 800 and 813, when he established the ', a special corps of wolf hunters. The ' was abolished after the French Revolution in 1789, but was re-established in 1814. In 1883, up to 1,386 wolves were killed, with many more by poison.
 In
In Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, wolves were never fully exterminated, due to the area's contiguity with Asia and its large forested areas. However, Eastern European wolf populations were reduced to very low numbers by the late 19th century. Wolves were extirpated in Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
during the first decade of the 20th century and, by the mid-20th century, could be found only in a few forested areas in eastern Poland. Wolves in the eastern Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
benefitted from the region's contiguity with the former Soviet Union and large areas of plains, mountains, and farmlands. Wolves in Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
occurred in only half the country around the start of the 20th century, and were largely restricted to the Carpathian Basin. Wolf populations in Romania remained largely substantial, with an average of 2,800 wolves being killed annually out of a population of 4,600 from 1955 to 1965. An all-time low was reached in 1967, when the population was reduced to 1,550 animals. The extermination of wolves in Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
was relatively recent, as a previous population of about 1,000 animals in 1955 was reduced to about 100–200 in 1964. In Greece, the species disappeared from the southern Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
in 1930. Despite periods of intense hunting during the 18th century, wolves never disappeared in the western Balkans, from Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
to the former Yugoslavia. Organized persecution of wolves began in Yugoslavia in 1923, with the setting up of the Wolf Extermination Committee in Kočevje
Kočevje (; ; ''Göttscheab'' or ''Gətscheab'' in the local Gottscheerish dialect; ) is a town and the seat of Municipality of Kočevje in southern Slovenia.
Geography
The town is located at the foot of the Kočevski Rog karst plateau on t ...
, Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
. The committee was successful in reducing wolf numbers in the Dinaric Alps
The Dinaric Alps (), also Dinarides, are a mountain range in Southern Europe, Southern and Southcentral Europe, separating the continental Balkan Peninsula from the Adriatic Sea. They stretch from Italy in the northwest through Slovenia, Croatia ...
.
The grey wolf's range in the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
encompassed nearly the entire territory of the country, being absent only on the Solovetsky Islands, Franz-Josef Land, Severnaya Zemlya, and the Karagin, Commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countri ...
, and Shantar Islands. The species was exterminated twice in Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
, once after the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
, and again after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.Heptner, V. G. & Naumov, N. P. (1998) Mammals of the Soviet Union Vol.II Part 1a, SIRENIA AND CARNIVORA (Sea cows; Wolves and Bears)
', Science Publishers, Inc. USA., pp. 177-179, Following the two world wars, Soviet wolf populations peaked twice; 30,000 wolves were harvested annually from a population of 200,000 during the 1940s, with 40,000–50,000 harvested during peak years. Soviet wolf populations reached a low around 1970, disappearing over much of
European Russia
European Russia is the western and most populated part of the Russia, Russian Federation. It is geographically situated in Europe, as opposed to the country's sparsely populated and vastly larger eastern part, Siberia, which is situated in Asia ...
.Boitani, L. (2003), "Wolf Conservation and Recovery", in ''Wolves: Behavior, ecology and conservation'', eds. L. D. Mech, and L. Boitani, pp. 317–340, Chicago, Illinois: University of Chicago Press
As of 2017, the IUCN Red List still recorded the grey wolf as regionally extinct in eight European countries: Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, Ireland
Ireland (, ; ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe. Geopolitically, the island is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Irelan ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg, officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, is a landlocked country in Western Europe. It is bordered by Belgium to the west and north, Germany to the east, and France on the south. Its capital and most populous city, Luxembour ...
, Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
, and the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Since then, wolves have returned to and, in some cases, firmly established themselves in all of those countries, except for the islands of Ireland and Great Britain.
Recovery
 The recovery of European wolf populations began after the 1950s, when traditional pastoral and rural economies declined and thus removed the need to heavily persecute wolves. By the 1980s, small and isolated wolf populations expanded in the wake of decreased human density in rural areas and the recovery of wild prey populations.
In 1978, wolves began recolonising central Sweden after a 12-year absence, and have since expanded into southern Norway. As of 2005, the total number of Swedish and Norwegian wolves was estimated to be at least 100, including 11 breeding pairs. The grey wolf is fully protected in Sweden and partially controlled in Norway. The Scandinavian wolf populations owe their continued existence to neighbouring Finland's contiguity with the
The recovery of European wolf populations began after the 1950s, when traditional pastoral and rural economies declined and thus removed the need to heavily persecute wolves. By the 1980s, small and isolated wolf populations expanded in the wake of decreased human density in rural areas and the recovery of wild prey populations.
In 1978, wolves began recolonising central Sweden after a 12-year absence, and have since expanded into southern Norway. As of 2005, the total number of Swedish and Norwegian wolves was estimated to be at least 100, including 11 breeding pairs. The grey wolf is fully protected in Sweden and partially controlled in Norway. The Scandinavian wolf populations owe their continued existence to neighbouring Finland's contiguity with the Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
, which houses a large population of wolves. Wolves in Finland are protected throughout the country, and can be hunted only with specific permission. As of December 2021, the Swedish-Norwegian wolf seems to be extinct and any wolf individuals found in these countries appear to be solely Finland wolves.
The decline in the moose populations has reduced the wolf's food supply. Juha Kauppinen"Susien määrä yllättäen vähentynyt"
''Suomen Luonto'', April 2008."SS: Kuolleissa susissa vanhoja hauleja"
'' Iltalehti'', March 19, 2013. Since 2011, the Netherlands, Belgium, and Denmark have also reported wolf sightings presumably by natural migration from adjacent countries. Wolf populations in Poland have increased to about 800–900 individuals since being classified as a game species in 1976, now for more than two decades under legal protection in Annex V and II of the Habitats Directive. The number of wolf packs in western Poland has continued to increase. This is confirmed by the results of the wolf monitoring financed by the International Fund for Animal Welfare and the nature conservation foundation EuroNatur, which is carried out by the Polish nature conservation organisation Association for Nature Wolf (AfN Wolf). The Polish scientists estimated that at the end of the 2018/19 monitoring year, at least 95 resident wolf packs would be west of the
Vistula
The Vistula (; ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest in Europe, at in length. Its drainage basin, extending into three other countries apart from Poland, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra i ...
, more than at any time since data collection began in 2003. For the first time, the scientists were also able to detect at least three reproducing packs in the Sudeten Mountains in the Czech-Polish border area.
Poland plays a fundamental role in providing routes of expansion into neighbouring Central European countries. In the east, its range overlaps with populations in Lithuania, Belarus
Belarus, officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Russia to the east and northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Belarus spans an a ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
, and Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
. A population in western Poland expanded into eastern Germany, and in 2000, the first pups were born on German territory. In 2012, an estimated 14 wolf packs were living in Germany (mostly in the east) and a pack with pups has been sighted within of Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
. Since then, the population has steadily increased and the area of distribution has grown and extended to large parts of the Federal Republic. In the monitoring year 2020/21, there were a total of 157 packs, 27 pairs and 19 individual territorial animals in 11 federal states. The number of pups was 556. Since the summer of 2021, around 1400 wolves, adult animals and young ones, are estimated to be living in Germany.
As of 1st of June 2021 the grey wolf is protected in Slovakia and can't be killed, bought, sold. A few Slovak wolves disperse into the Czech Republic, where they are afforded full protection. Wolves in Slovakia, Ukraine, and Croatia may disperse into Hungary, where the lack of cover hinders the buildup of an autonomous population. Although wolves have special status in Hungary, they may be hunted with a year-round permit if they cause problems.
Romania has a large population of wolves, numbering 2500 animals. The wolf has been a protected animal in Romania since 1996, although the law is not enforced. The number of wolves in Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
and North Macedonia
North Macedonia, officially the Republic of North Macedonia, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe. It shares land borders with Greece to the south, Albania to the west, Bulgaria to the east, Kosovo to the northwest and Serbia to the n ...
is largely unknown, despite the importance the two countries have in linking wolf populations from Greece to those of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
and Croatia. Although protected, many wolves are illegally killed in Greece annually, and their future is uncertain. Wolf numbers have declined in Bosnia and Herzegovina since 1986, while the species is fully protected in neighbouring Croatia and Slovenia
Slovenia, officially the Republic of Slovenia, is a country in Central Europe. It borders Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the south and southeast, and a short (46.6 km) coastline within the Adriati ...
.
Wolf populations throughout Northern and Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
are largely unknown, but are estimated in the hundreds of thousands based on annual harvests. Since the fall of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union was formally dissolved as a sovereign state and subject of international law on 26 December 1991 by Declaration No. 142-N of the Soviet of Nationalities, Soviet of the Republics of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union. :s: ...
, continent-wide extermination of wolves has ceased, and wolf populations have increased to about 25,000–30,000 animals throughout the former Soviet Union, an increase of about 150%.
Legal protection
 The Eurasian wolf and the Italian wolf are legally protected in most European countries, either by listing in the annexes of the EU-FHH Directive or by the Bern Convention or both, depending on whether a country is a signatory of the Bern Convention or not.
For EU member states, an application for a change in the listing of the wolf in the annexes to the Habitats Directive requires the approval of the Division for Large Carnivores in the
The Eurasian wolf and the Italian wolf are legally protected in most European countries, either by listing in the annexes of the EU-FHH Directive or by the Bern Convention or both, depending on whether a country is a signatory of the Bern Convention or not.
For EU member states, an application for a change in the listing of the wolf in the annexes to the Habitats Directive requires the approval of the Division for Large Carnivores in the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the primary Executive (government), executive arm of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with a number of European Commissioner, members of the Commission (directorial system, informall ...
, in which members of the LCIE have an advisory role. States outside the EU which are signatories to the Bern Convention may submit a corresponding application for a change of protection status to the Standing Committee of the Berne Convention, in which the LCIE also has an advisory role. For example, Switzerland submitted such a request in 2006, which was rejected at the time. In 2018, Switzerland again requested the reduction of the protection status. Due to the passive behaviour of the Large Carnivore Initiative for Europe, processing is delayed. (See also Favourable conservation status of wolves in Europe).
Conflicts
Attacks on grazing animals
 In
In Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
in 2021, 853 wolf attacks occurred in a population of 153 wolves in the presence of about 200 livestock guardian dogs.BRF-Nachrichten: Schutz des Weideviehs vor dem Wolf
' In
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
between 2000 and 2019, the number of wolf attacks on grazing animals increased from none to 890 in one year, while the number of animals injured and killed increased to 2900, indicating a specialisation in grazing animals and frequent surplus killing events.
In France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, the number of animals captured in unprotected flocks decreased between 2010 and 2015 as more and more flocks were protected, but the number of animals killed in protected flocks increased. During this period the behaviour of the wolves changed in such a way that with increasing habituation
Habituation is a form of non-associative learning in which an organism’s non-reinforced response to an inconsequential stimulus decreases after repeated or prolonged presentations of that stimulus. For example, organisms may habituate to re ...
the proportion of wolf attacks during the day increased. In 2018 there was an estimated loss of 12,500 farm animals caused by wolf attacks in the French Alpine arc, with a population of about 500 wolves and several thousand livestock guardian dogs. Despite new measures to protect herds, there were 3,838 sightings of wolves in 2019 in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes
Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes (; AURA) or ; or ; . is a Regions of France, region in southeast-central France created by the 2014 territorial reform of French regions; it resulted from the merger of Auvergne and Rhône-Alpes. The new region came into e ...
region and compensation was paid for 12,491 detected wolf attacks.
In some regions, livestock guardian dogs also became victims of wolves.
Attacks on humans
 According to documented data, man-eating (not rabid) wolves killed 111 people in
According to documented data, man-eating (not rabid) wolves killed 111 people in Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
in the years from 1804 to 1853, 108 of them were children, two men and one woman. Of the 108 children, 59 were boys aged 1 – 15 years (average age 7.3 years) and 47 girls aged 1 – 17 years (average age 7.2 years). For two children, sex and age were not specified." So in Estonia, 111 deaths were reported in about 50 years, with an average of two per year over a country area of 45,227 km2, and with some injured people who survived a wolf attack. The wolves that immigrated to Central Europe come from this Baltic population. Due to the abundance of game and many grazing animals still living in species-appropriate free range management, the wolves in Europe are not yet interested in children as prey.
In France, historical records compiled by rural historian Jean-Marc Moriceau indicate that during the period 1362–1918, nearly 7,600 people were killed by wolves, of whom 4,600 were killed by non rabid wolves. Moriceau, Jean-Marc (2013), ''Sur les pas du loup: Tour de France et atlas historiques et culturels du loup, du moyen âge à nos jours'' n the trail of the wolf: a tour of France and a historical and cultural atlas of the wolf, from the Middle Ages to modern times Paris, Montbel, Numerous attacks occurred in Germany during the 17th century after the Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine ...
, though the majority probably involved rabid wolves. In Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to t ...
, records of rabid wolf attacks go back two centuries. At least 72 people were bitten between 1992 and 2000. Similarly, in Lithuania, attacks by rabid wolves have continued to the present day, with 22 people having been bitten between 1989 and 2001. Around 82 people were bitten by rabid wolves in Estonia
Estonia, officially the Republic of Estonia, is a country in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Ru ...
during the 18th to 19th centuries, with a further 136 people being killed in the same period by nonrabid wolves, though the animals likely involved in the latter cases were a combination of wolf-dog hybrids and escaped captive wolves.Linnell, J. D. C. (2002), The Fear of Wolves: A Review of Wolf Attacks on Humans
', NINA, Several Russian zoologists after the
October Revolution
The October Revolution, also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution (in Historiography in the Soviet Union, Soviet historiography), October coup, Bolshevik coup, or Bolshevik revolution, was the second of Russian Revolution, two r ...
cast doubt on the veracity of records involving wolf-caused deaths. Prominent among them was zoologist Petr Aleksandrovich Manteifel, who initially regarded all cases as either fiction or the work of rabid animals. His writings were widely accepted among Russian zoological circles, though he subsequently changed his stance when he was tasked with heading a special commission after World War II investigating wolf attacks throughout the Soviet Union, which had increased during the war years. A report presented in November 1947 described numerous attacks, including ones perpetrated by apparently healthy animals, and gave recommendations on how to better defend against them. The Soviet authorities prevented the document from reaching both the public and those who would otherwise be assigned to deal with the problem.Graves, W. (2007), ''Wolves in Russia: Anxiety throughout the ages'', Detselig Enterprises, pp. 175-176, All mention of wolf attacks was subsequently censored.Geist, Valerius"Let's get real: beyond wolf advocacy, toward realistic policies for carnivore conservation"
. ''Fair Chase''. Summer 2009. pp. 26–30.
Relationships with humans
Myths
The majority of pre-Christian wolf-related traditions in Eurasia were rooted in Hittite mythology with wolves featuring prominently inIndo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e. ...
cultures, sometimes as deity figures. The wolf was held in high esteem by the Dacians
The Dacians (; ; ) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area include ...
, whose name was derived from the Gaulish
Gaulish is an extinct Celtic languages, Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, ...
''Daoi'', meaning "wolf people". The wolf was viewed as the lord of all animals and as the only effective power against evil.Grumeza, I. (2009), ''Dacia: Land of Transylvania, Cornerstone of Ancient Eastern Europe'', University Press of America, pp.75-6, The ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
s associated wolves with their plague-and-healing god Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
.
Less flattering portrayals occurred in Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology, is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia as the Nordic folklore of the modern period. The ...
where the wolf Fenrir kills Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Em ...
during Ragnarok. Nevertheless, wolves were admired for their ferocity and Germanic warriors often had the wolf as their totem
A totem (from or ''doodem'') is a spirit being, sacred object, or symbol that serves as an emblem of a group of people, such as a family, clan, lineage (anthropology), lineage, or tribe, such as in the Anishinaabe clan system.
While the word ...
, a trait later exported to other European cultures.Boitani, L. (1995)"Ecological and cultural diversities in the evolution of wolf-human relationships"
, in ''Ecology and conservation of wolves in a changing world'', eds. Carbyn, L. N., Fritts, S. H., and Seip, D. R., eds. pp. 3-12, Edmonton: Canadian Circumpolar Institute In
Lithuanian mythology
Lithuanian mythology () is the mythology of Lithuanians, Lithuanian polytheism, the religion of pre-Christian Lithuanians. Like other Indo-European studies, Indo-Europeans, Lithuanians (tribe), ancient Lithuanians maintained a polytheistic myth ...
, an iron wolf appears before Grand Duke Gediminas
Gediminas ( – December 1341) was Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1315 or 1316 until his death in 1341.
He is considered the founder of Lithuania's capital Vilnius (see: Iron Wolf legend). During his reign, he brought under his rule lands from t ...
instructing him to build the city of Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ) is the capital of and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city in Lithuania and the List of cities in the Baltic states by population, most-populous city in the Baltic states. The city's estimated January 2025 population w ...
. Tengrism
Tengrism (also known as Tengriism, Tengerism, or Tengrianism) is a belief-system originating in the Eurasian steppes, based on shamanism and animism. It generally involves the titular sky god Tengri. According to some scholars, adherents of ...
places high importance on the wolf as when howling, it is thought to be praying to Tengri
Tengri (; Old Uyghur: ; Middle Turkic: ; ; ; ; ; ; ; Proto-Turkic: / ; Mongolian script: , ; , ; , ) is the all-encompassing God of Heaven in the traditional Turkic, Yeniseian, Mongolic, and various other nomadic religious beliefs. So ...
thus making it the only creature other than man to worship a deity.Cope, T. (2013) ''On the Trail of Genghis Khan: An Epic Journey Through the Land of the Nomads'', A&C Black, pp. 46-7,
References
External links
Large Carnivore Initiative for Europe
{{Taxonbar, from=Q898061 Carnivorans of Europe Carnivorans of Asia Mammals of Pakistan Mammals of Russia Mammals of Central Asia Subspecies of Canis lupus Mammals described in 1758 Wolves Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Fauna of Albania