|
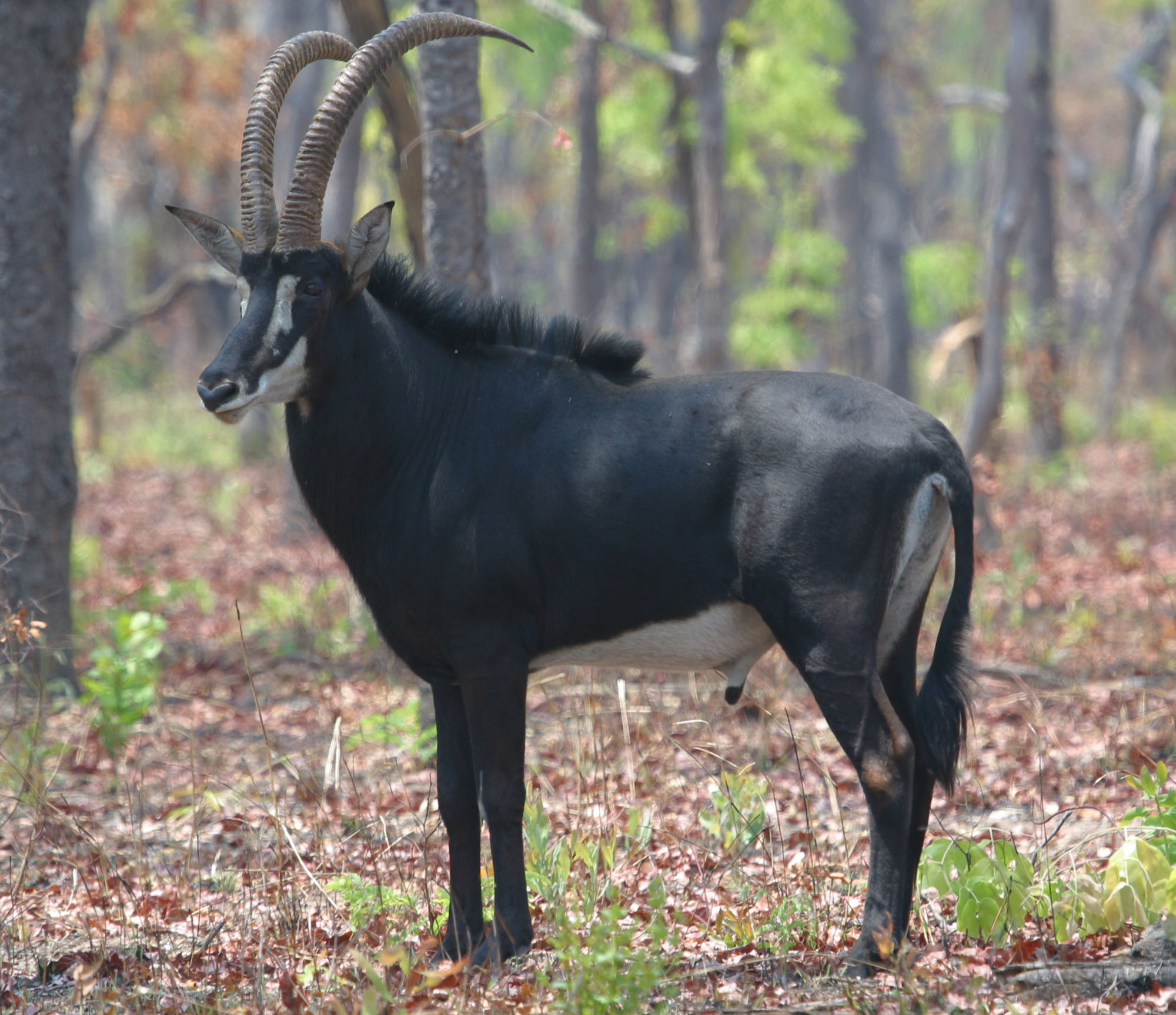
Saiga
The saiga antelope (, ''Saiga tatarica''), or saiga, is a species of antelope which during antiquity inhabited a vast area of the Eurasian steppe, spanning the foothills of the Carpathian Mountains in the northwest and Caucasus in the southwest into Mongolia in the northeast and Dzungaria in the southeast. During the Pleistocene, it ranged across the mammoth steppe from the British Isles to Beringia. Today, the dominant subspecies (''S. t. tatarica'') only occurs in Kalmykia and Astrakhan Oblast of Russia and in the Ural, Ustyurt and Betpak-Dala regions of Kazakhstan. A portion of the Ustyurt population migrates south to Uzbekistan and occasionally to Turkmenistan in winter. It is regionally extinct in Romania, Ukraine, Moldova, China and southwestern Mongolia. The Mongolian subspecies (''S. t. mongolica'') occurs only in western Mongolia. Taxonomy and phylogeny The scientific name ''Capra tatarica'' was coined by Carl Linnaeus in 1766 in the 12th edition of ''Systema Natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antelope
The term antelope refers to numerous extant or recently extinct species of the ruminant artiodactyl family Bovidae that are indigenous to most of Africa, India, the Middle East, Central Asia, and a small area of Eastern Europe. Antelopes do not form a monophyletic group, as some antelopes are more closely related to other bovid groups, such as bovines, goats, and sheep, than to other antelopes. A stricter grouping, known as the true antelopes, includes only the genera '' Gazella'', '' Nanger'', '' Eudorcas'', and '' Antilope''. One North American mammal, the pronghorn or "pronghorn antelope", is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope", despite the fact that it belongs to a completely different family ( Antilocapridae) than the true Old-World antelopes; pronghorn are the sole extant member of an extinct prehistoric lineage that once included many unique species. Although antelope are sometimes referred to, and easily misidentified as, "deer" ( cervids), true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stepnoi Nature Sanctuary
Stepnoi State Nature Sanctuary (Russian language, Russian: государственный природный заказник "Степной") (also Stepnoy Nature Reserve) is a protected area located in Limansky District, Liman district of Astrakhan Oblast, Russia. The sanctuary was declared in 2000 to ensure maintenance of unique natural complex of Stipa steppe providing habitat for saiga antelope (''Saiga tatarica tatarica'') and a number of other endangered species of animals and plants. The sanctuary covers an area of 109.4 thousands of hectares. The monitoring program started in 2004 showed that the sanctuary is an important territory for the survival of the critically endangered saiga antelope. Saigas inhabit the sanctuary and the nearby regions of Kalmykia throughout the year. Stepnoi sanctuary provides well-protected territory for both rut and calving of saigas. Several Artesian aquifer, artesian wells within the sanctuary serve as waterholes and mineral licks for saiga. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolian Saiga
The Mongolian saiga (''Saiga tatarica mongolica'') is a subspecies of saiga antelope endemic to Mongolia. It was originally described as a full species, but later the initial author moved it to its current taxonomic position. It has also been considered a subspecies of '' Saiga borealis'', but that has been shown to be incorrect. The Mongolian saiga can develop a sandy colour. The coat develops a pale, grayish-brown colour in winter, with a hint of brown on the belly and the neck. The ventral Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ... parts are generally white. The hairs, can grow as long as in winter. This forms a long mane on the neck. Two distinct moults can be observed in a year, one in spring from April to May and another in autumn from late September or early Octob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammoth Steppe
The mammoth steppe, also known as steppe-tundra, was once the Earth's most extensive biome. During glacial periods in the later Pleistocene, it stretched east-to-west, from the Iberian Peninsula in the west of Europe, then across Eurasia and through Beringia (the region including the far northeast of Siberia, Alaska and the now submerged land between them) and into the Yukon in northwest Canada; from north-to-south, the steppe reached from the Arctic southward to southern Europe, Central Asia and northern China. The mammoth steppe was cold and dry, and relatively featureless, though climate, topography, and geography varied considerably throughout. Certain areas of the biome—such as coastal areas—had wetter and milder climates than others. Some areas featured rivers which, through erosion, naturally created gorges, gulleys, or small glens. The continual glacial recession and advancement over millennia contributed more to the formation of larger valleys and different geographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betpak-Dala
Betpak-Dala or Betpaqdala (, ''Betpaqdala''; from Turkic ''batpak'', “swampy,” or Persian ''bedbaht'', “unlucky” and Turkic ''dala'', “plain”; Russian: Бетпак-Дала or Сeверная Голодная степь, lit. ''Hungry Steppe'') is a desert zone in the Ulytau, Karaganda, Turkestan, and Zhambyl regions, Kazakhstan. - Great Russian Encyclopedia in 35 volumes / ch. ed. Yu. S. Osipov History In Autumn 2014, English explorer Jamie Bunchuk completed an expedition to cross the Betpak-Dala to its fullest longitudinal extent, from Lake B ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalmykia
Kalmykia, officially the Republic of Kalmykia,; , ''Khalmg Tanghch'' is a republic of Russia, located in the Volga region of European Russia. The republic is part of the Southern Federal District, and borders Dagestan to the south and Stavropol Krai to the southwest; Volgograd Oblast to the northwest and north and Astrakhan Oblast to the north and east; Rostov Oblast to the west and the Caspian Sea to the east. Through the Caspian Depression, the Kuma river forms Kalmykia's natural border with Dagestan. Kalmykia is the only polity within Europe where the Dharmic religion of Buddhism is the predominant religion; the majority of Kalmyk people are Vajrayana Tibetan Buddhists of the Gelug and Kagyu lineages. The Kalmykia republic covers an area of , with a small population of about 275,000 residents. The republic of Kalmykia is home of the Kalmyks, a people of Oirat Mongolian origin who are mainly of Tibetan Buddhist faith. The capital of the republic is the city of Elist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ustyurt Plateau
The Ustyurt or Ust-Yurt (from ; ; ; — flat hill, plateau) is a transboundary clay desert shared by Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The plateau's semi-nomadic population raises camels, goats, and sheep. Geography The Ustyurt is located between the Dead Kultuk, Mangyshlak Peninsula and Kara-Bogaz-Gol of the Caspian Sea to the west, and the Aral Sea, Amudarya Delta and Sarygamysh Lake to the east. It extends roughly , with an average altitude of . Its highest point rises to in the south-west. At its northeastern edge it drops steeply to the Aral Sea and the surrounding plain. The Ustyurt Plateau is bounded by steep cliffs called chinks nearly from everywhere. To the east, it encompasses the historical western shoreline of the Aral Sea. In the southern region, it extends to the Kunya-Darya alluvial plain and the valley of the Uzboy, while in the west, it reaches the Karynyaryk depression. To the north, it spans the Karakum sands of the North Caspian Sea and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, European Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary and Slovakia. Since the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age, the Steppe Route has been the main overland route between Eastern Europe, North Asia, Central Asia and East Asia economically, politically, and culturally. The Steppe route is a predecessor not only of the Silk Road, which developed during Classical antiquity, antiquity and the Middle Ages, but also of the Eurasian Land Bridge in the modern era. It has been home to nomadic empires and many large tribal confederations and ancient states throughout history, such as the Xiongnu, Scythia, Cimmerians, Cimmeria, Sarmatians, Sarmatia, Hunnic Empire, Sogdia, Xianbei, Mongol Empire, Magyar tribes, and Göktürk Khaganate. Geography Divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
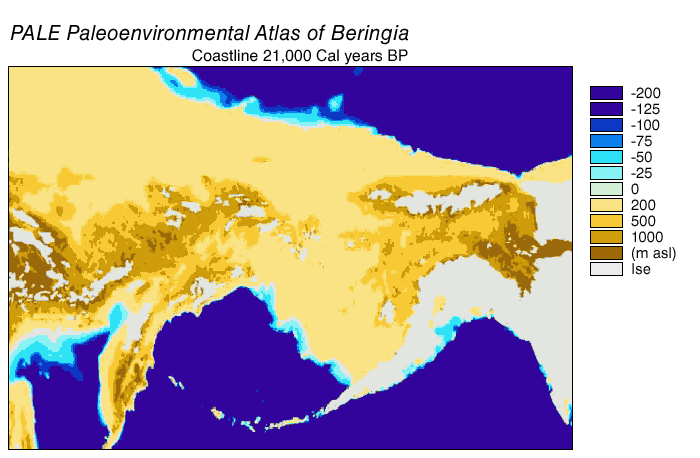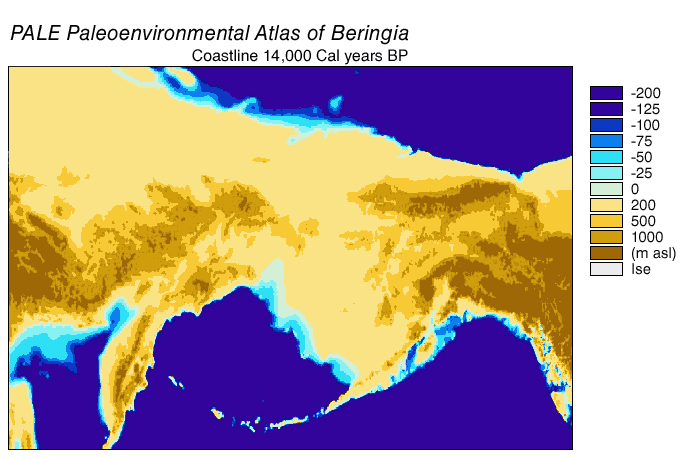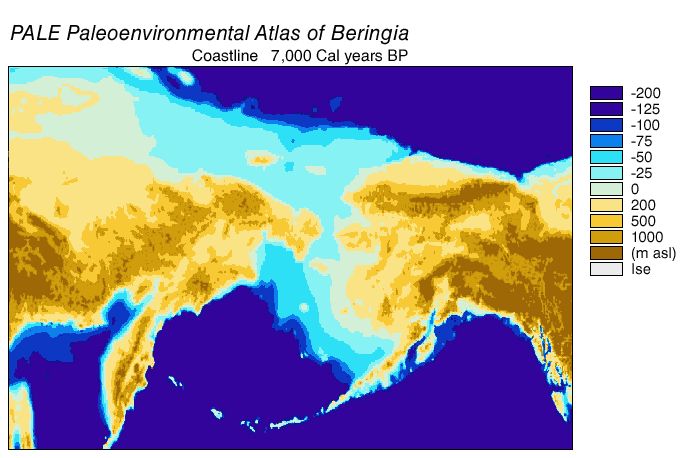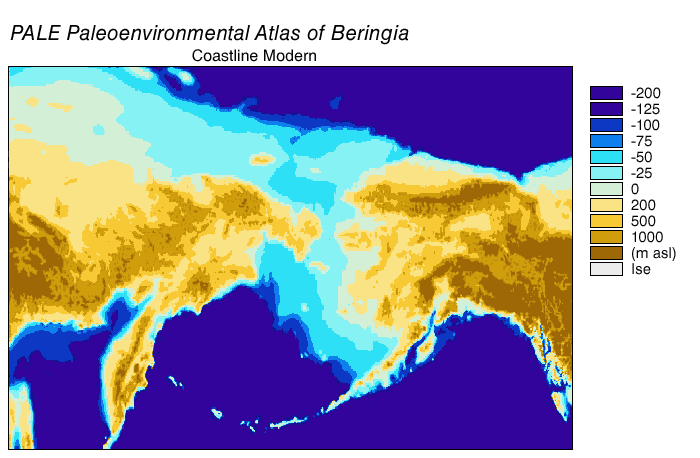
Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 70th parallel north, 72° north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi Peninsula, Chukchi and Kamchatka peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States and Yukon in Canada. The area includes land lying on the North American Plate and Siberian land east of the Chersky Range. At various times, it formed a land bridge referred to as the Bering land bridge, that was up to wide at its greatest extent and which covered an area as large as British Columbia and Alberta together, totaling about , allowing biological dispersal to occur between Asia and North America. Today, the only land that is visible from the central part of the Bering land bridge are the Diomede Islands, the Pribilof Isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Society Of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity and organization devoted to the worldwide animal conservation, conservation of animals and their habitat conservation, habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained London Zoo, and since 1931 Whipsnade Zoo. History On 29 November 1822, the birthday of John Ray, "the father of modern zoology", a meeting held in the Linnean Society in Soho Square led by Rev. William Kirby (entomologist), William Kirby, resolved to form a "Zoological Club of the Linnean Society of London". Between 1816 and 1826, discussions between Stamford Raffles, Humphry Davy, Joseph Banks and others led to the idea that London should have an establishment similar to the Jardin des Plantes in Paris. It would house a zoological collection "which should interest and amuse the public." The society was founded in April 1826 by Stamford Raffles, Sir Stamford Raffles, the Henry Petty-Fitzmaurice, 3rd Marquess of Lansdowne, Marquess of Lansdo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12th Edition Of Systema Naturae
The 12th edition of ' was the last edition of ' to be overseen by its author, Carl Linnaeus. It was published by Laurentius Salvius in Holmia (Stockholm) in three volumes, with parts appearing from 1766 to 1768. It contains many species not covered in the previous edition, the 10th edition which was the starting point for zoological nomenclature. Starting point Only five editions of ' were written by Linnaeus himself, namely the first, second, sixth, tenth and twelfth. When a "starting point" for zoological nomenclature was first considered, in the Strickland Code of 1843, the 12th edition of ' was chosen, so that any names which Linnaeus had altered from previous editions would be recorded in their final state. It was later replaced by the 10th edition as the starting point for most zoological nomenclature. The starting point for most names in botanical nomenclature is the 1753 work '. Format Linnaeus divided the 12th edition into three volumes, the first of which was publis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus (biology)
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family as used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus '' Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should clearly demonstrate both monophyly and validity as a separate lineage). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |