Essen Minster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Essen Minster (German: ), since 1958 also Essen Cathedral () is the seat of the
Essen Minster (German: ), since 1958 also Essen Cathedral () is the seat of the
 Several dedicatory inscriptions for parts of the new church survive from the years 960 to 964, from which it can be concluded that the fire of 946 had only damaged the church. No inscriptions survive for the nave and choir, which were probably retained from the earlier church. The individual stages of construction are uncertain; some parts could have been begun or even completed before the fire. Taking advantage of necessary renovations to expand the church enclosure was not unusual. The new parts, presumably built at the order of the abbesses Agana and Hathwig, were an outer
Several dedicatory inscriptions for parts of the new church survive from the years 960 to 964, from which it can be concluded that the fire of 946 had only damaged the church. No inscriptions survive for the nave and choir, which were probably retained from the earlier church. The individual stages of construction are uncertain; some parts could have been begun or even completed before the fire. Taking advantage of necessary renovations to expand the church enclosure was not unusual. The new parts, presumably built at the order of the abbesses Agana and Hathwig, were an outer
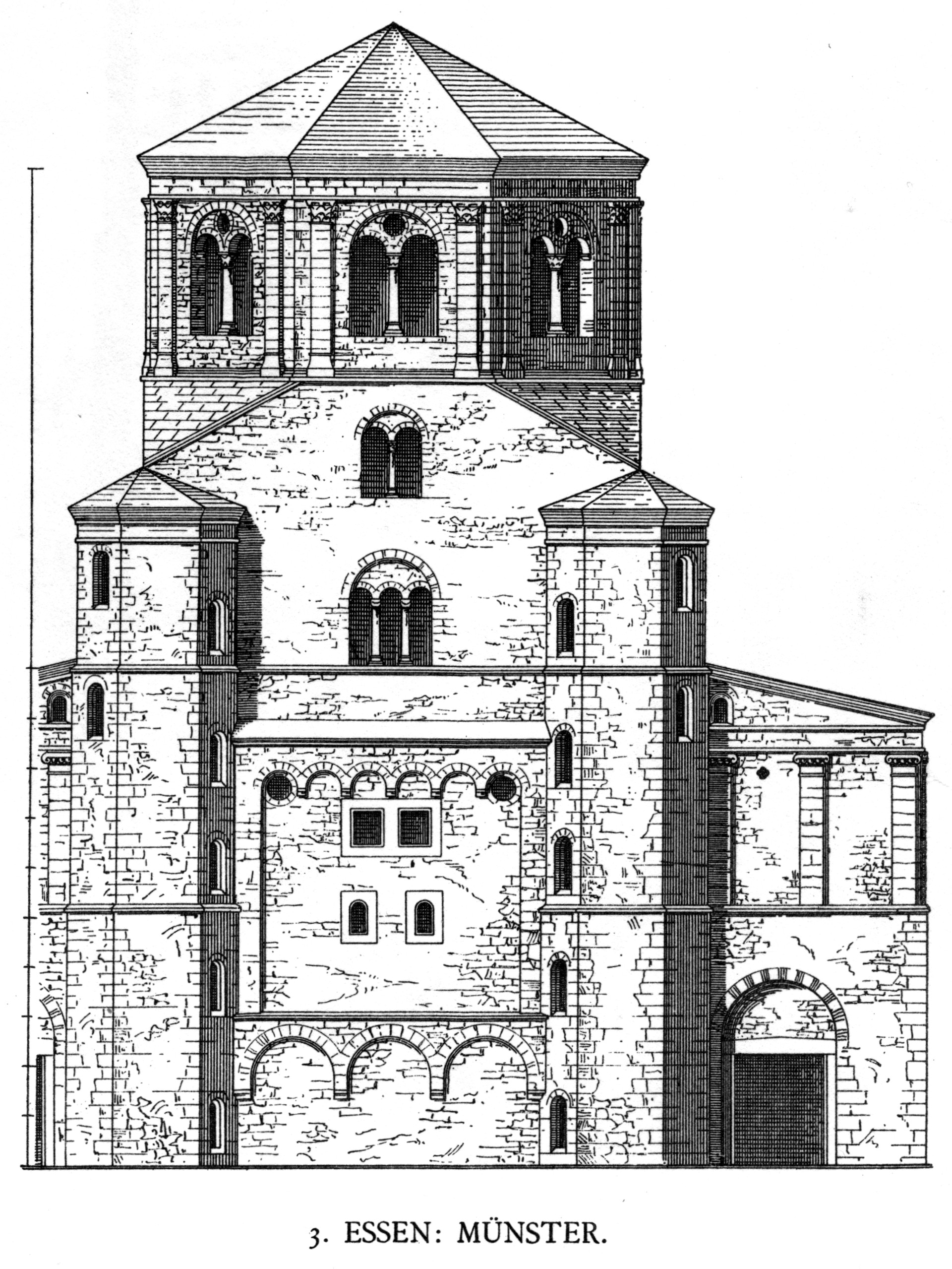

 The belief that the unknown architect of Essen Abbey church was one of the best architects of his time is based particularly on the westwork, which even today is the classic view of the church. As in the earlier churches, the westwork is only a little wider than the aisles of the nave. From the outside, the westwork appears as an almost square central tower crowned by an octagonal belfry with a pyramidal roof. At the west end there were two octagonal side towers, containing staircases to the belfry, which reached to just below the bell story of the belfry. The bell story of the central tower and the uppermost stories of the side towers have arched windows. Two story side rooms with arched windows on the upper floor are attached to the north and south sides of the central tower. On the ground floor of these side rooms, doors set in niches lead into the church – the central entrance of the earlier church was abandoned and a large, round-arched window installed in its place. With that, the westwork ceased to operate as a processional entrance to the church. Instead, the squat structure offered an optical counterpoint to the massive east part of the building.
From the outside the westwork appears to be composed of three towers, which envelop the west choir, which takes the form of a crossing which has been divided in half. No similar structure is known. There is a west choir in the central room in the shape of a half-hexagon, surrounded by a passageway. A flat niche is located in the middle of the west wall, with the entrances to the two side towers in flat niches on either side of it. The westwork opens toward the double bay through a large arch supported by pillars. An altar dedicated to
The belief that the unknown architect of Essen Abbey church was one of the best architects of his time is based particularly on the westwork, which even today is the classic view of the church. As in the earlier churches, the westwork is only a little wider than the aisles of the nave. From the outside, the westwork appears as an almost square central tower crowned by an octagonal belfry with a pyramidal roof. At the west end there were two octagonal side towers, containing staircases to the belfry, which reached to just below the bell story of the belfry. The bell story of the central tower and the uppermost stories of the side towers have arched windows. Two story side rooms with arched windows on the upper floor are attached to the north and south sides of the central tower. On the ground floor of these side rooms, doors set in niches lead into the church – the central entrance of the earlier church was abandoned and a large, round-arched window installed in its place. With that, the westwork ceased to operate as a processional entrance to the church. Instead, the squat structure offered an optical counterpoint to the massive east part of the building.
From the outside the westwork appears to be composed of three towers, which envelop the west choir, which takes the form of a crossing which has been divided in half. No similar structure is known. There is a west choir in the central room in the shape of a half-hexagon, surrounded by a passageway. A flat niche is located in the middle of the west wall, with the entrances to the two side towers in flat niches on either side of it. The westwork opens toward the double bay through a large arch supported by pillars. An altar dedicated to
 In 1275, the Ottonian church burnt down, with only the westwork and the crypt surviving. In the rebuild, which occurred in the time of the Abbesses Berta von Arnsberg and Beatrix von Holte, the architect combined aspects of the old church with the new Gothic style. The form of the
In 1275, the Ottonian church burnt down, with only the westwork and the crypt surviving. In the rebuild, which occurred in the time of the Abbesses Berta von Arnsberg and Beatrix von Holte, the architect combined aspects of the old church with the new Gothic style. The form of the
 As a result of the baroquification of the eighteenth century, the re-gothificisation of the nineteenth century and the war damage of the twentieth century, there are only a few pieces of the earlier fittings of the Minster, but some remains of great significance do survive. The interior is comparatively simple, especially in its architecture, whose subtle beauty is overlooked by many visitors because the lustre of the two very important medieval artworks of the Cathedral outshines it.
As a result of the baroquification of the eighteenth century, the re-gothificisation of the nineteenth century and the war damage of the twentieth century, there are only a few pieces of the earlier fittings of the Minster, but some remains of great significance do survive. The interior is comparatively simple, especially in its architecture, whose subtle beauty is overlooked by many visitors because the lustre of the two very important medieval artworks of the Cathedral outshines it.
Gerhard Hoffs: ''Glockenmusik der kath. Kirchen im Stadtdekanat Essen''. pp. 46–48
(PDF; 1,5 MB, German)
Essen Cathedral website
Diocese of Essen website
Münsterbauverein website
{{Authority control
 Essen Minster (German: ), since 1958 also Essen Cathedral () is the seat of the
Essen Minster (German: ), since 1958 also Essen Cathedral () is the seat of the Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
Bishop of Essen, the "Diocese of the Ruhr", founded in 1958. The church, dedicated to Saints Cosmas and Damian
Cosmas and Damian ( – or AD) were two Arabs, Arab physicians and early Christian martyrs. They practised their profession in the seaport of Yumurtalık, Aegeae, then in the Roman province of Cilicia (Roman province), Cilicia.
Cosmas and ...
and the Blessed Virgin Mary
Mary was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Saint Joseph, Joseph and the mother of Jesus. She is an important figure of Christianity, venerated under titles of Mary, mother of Jesus, various titles such as Perpetual virginity ...
, stands on the Burgplatz in the centre of the city of Essen
Essen () is the central and, after Dortmund, second-largest city of the Ruhr, the largest urban area in Germany. Its population of makes it the fourth-largest city of North Rhine-Westphalia after Cologne, Düsseldorf and Dortmund, as well as ...
, Germany.
The minster was formerly the collegiate church of Essen Abbey, founded in about 845 by Altfrid, Bishop of Hildesheim, around which the city of Essen grew up. The present building, which was reconstructed after its destruction in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, is a Gothic hall church
A hall church is a Church (building), church with a nave and aisles of approximately equal height. In England, Flanders and the Netherlands, it is covered by parallel roofs, typically, one for each vessel, whereas in Germany there is often one s ...
, built after 1275 in light-coloured sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
. The octagonal westwork and the crypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religiou ...
are survivors of the Ottonian
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem du ...
pre-Romanesque building that once stood here. The separate Church of St. Johann Baptist stands at the west end of the minster, connected to the westwork by a short atrium – it was formerly the parish church of the abbey's subjects. To the north of the minster is a cloister
A cloister (from Latin , "enclosure") is a covered walk, open gallery, or open Arcade (architecture), arcade running along the walls of buildings and forming a quadrangle (architecture), quadrangle or garth. The attachment of a cloister to a cat ...
that once served the abbey.
Essen Minster is noted for its treasury (''Domschatz''), which among other treasures contains the Golden Madonna, the oldest fully sculptural figure of Mary north of the Alps.
Usage history
Foundation to 1803
From the foundation of the first church until 1803, Essen Minster was the Abbey church of Essen Abbey and the hub of abbey life. The church was neither a parish church, nor a cathedral church, but primarily served the nuns of the abbey. Its position was therefore comparable to a convent church, but a more worldly version, since the nuns at Essen did not obey theBenedictine
The Benedictines, officially the Order of Saint Benedict (, abbreviated as O.S.B. or OSB), are a mainly contemplative monastic order of the Catholic Church for men and for women who follow the Rule of Saint Benedict. Initiated in 529, th ...
Rule, but the ''Institutio sanctimonialium'', the canonical rule for female monastic communities issued in 816 by the Aachen Synod. The canonical hours
In the practice of Christianity, canonical hours mark the divisions of the day in terms of Fixed prayer times#Christianity, fixed times of prayer at regular intervals. A book of hours, chiefly a breviary, normally contains a version of, or sel ...
and mass
Mass is an Intrinsic and extrinsic properties, intrinsic property of a physical body, body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the physical quantity, quantity of matter in a body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physi ...
es of the order occurred in the Minster, as well as prayers for deceased members of the community, the noble sponsors of the order and their ancestors.
The number of nuns from the nobility which the church served varied over the centuries between about seventy during the order's heyday under the Abbess Mathilde in the tenth century and three in the sixteenth century. The church was open to the dependents of the order and the people of the city of Essen only on the high feast days. Otherwise, the Church of St. Johann Baptist, which had developed out of the Ottonian baptistry, or the Church of St Gertrude (now the Market Church) served as their place of worship.
The Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
had no effect on the Minster. The burgers of the city of Essen, who maintained a long-standing dispute with the order about whether the city was a Free city or belonged to the order, mostly joined the revolution, but the Abbesses and Canons of the order (and therefore the church buildings) remained Catholic. The Protestant burgers of the city took over St Gertrude's Church, the present-day Market Church, which was not connected to the Abbey's buildings, while the burgers who remained Catholic continued to use the Church of St. Johann Baptist, located in the Abbey complex, as their parish church. The nuns continued to use the Minster.
From 1803 to the present day
In 1803, Essen Abbey was mediatized by theKingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
. The Minster and all its property was immediately taken over by the parish community of St. Johann Baptist. For the next 150 years the church was their parish church. The name Minster church, which had become established, was retained even though the order no longer existed. As parish church, it served the Catholics of Essen's inner city area which significantly increased in population in the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.
Though the first aspirations of setting up a bishopric of the Ruhr
The Ruhr ( ; , also ''Ruhrpott'' ), also referred to as the Ruhr Area, sometimes Ruhr District, Ruhr Region, or Ruhr Valley, is a polycentric urban area in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. With a population density of 1,160/km2 and a populati ...
were dashed in the 1920s, a new bishopric was formed in 1958 from parts of the dioceses of Münster
Münster (; ) is an independent city#Germany, independent city (''Kreisfreie Stadt'') in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also a ...
, Paderborn
Paderborn (; Westphalian language, Westphalian: ''Patterbuorn'', also ''Paterboärn'') is a city in eastern North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany, capital of the Paderborn (district), Paderborn district. The name of the city derives from the river Pade ...
, and Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and Essen Minster was made the cathedral. On 1 January 1958 the first Bishop of Essen, Franz Hengsbach was consecrated by the Nuncio
An apostolic nuncio (; also known as a papal nuncio or simply as a nuncio) is an ecclesiastical diplomat, serving as an envoy or a permanent diplomatic representative of the Holy See to a state or to an international organization. A nuncio is ...
Aloisius Joseph Muench. Since then Essen Minster has been the religious heart of the diocese. The visit of Pope
The pope is the bishop of Rome and the Head of the Church#Catholic Church, visible head of the worldwide Catholic Church. He is also known as the supreme pontiff, Roman pontiff, or sovereign pontiff. From the 8th century until 1870, the po ...
John Paul II
Pope John Paul II (born Karol Józef Wojtyła; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 16 October 1978 until Death and funeral of Pope John Paul II, his death in 2005.
In his you ...
in 1987 marked the high point of the Minster's thousand-year history.
Structural history
Previous buildings
The site of the cathedral was already settled before the foundation of the Abbey. The Bishop of Hildesheim, Altfrid (r.847-874) is supposed to have founded the order of nuns on his estate, called ''Asnide'' (i.e. Essen). A direct attestation of Asnide has not yet been found. But fromposthole
This page is a glossary of archaeology, the study of the human past from material remains.
A
B
C
D
E
F
...
s, Merovingian
The Merovingian dynasty () was the ruling family of the Franks from around the middle of the 5th century until Pepin the Short in 751. They first appear as "Kings of the Franks" in the Roman army of northern Gaul. By 509 they had united all the ...
pottery sherds and burials found near the Minster, it can be concluded that a settlement was in place before the foundation of the Abbey.
The first church
The modern Essen Minster is the third church building on this site. Foundation walls of its predecessors were excavated in 1952 by Walter Zimmermann. The first church on this site was erected by the founders of Essen Abbey, Bishop Altfrid and Gerswid, according to tradition the first abbess of the order, between 845 and 870. The building was a threeaisle
An aisle is a linear space for walking with rows of non-walking spaces on both sides. Aisles with seating on both sides can be seen in airplanes, in buildings such as churches, cathedrals, synagogues, meeting halls, parliaments, courtrooms, ...
d basilica
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica (Greek Basiliké) was a large public building with multiple functions that was typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek Eas ...
with a west-east orientation. Its central and side aisles already approached the width of the later churches on the site. West of the nave
The nave () is the central part of a church, stretching from the (normally western) main entrance or rear wall, to the transepts, or in a church without transepts, to the chancel. When a church contains side aisles, as in a basilica-type ...
was a small, almost square narthex
The narthex is an architectural element typical of Early Christian art and architecture, early Christian and Byzantine architecture, Byzantine basilicas and Church architecture, churches consisting of the entrance or Vestibule (architecture), ve ...
. The arms of the transeptsmet at a rectangular crossing, which was the same height as the nave. Rooms in the east ends of the side aisle were accessible only from the arms of the transepts. It is uncertain whether these rooms were the same height as the side aisles, as Zimmerman thought on the basis of his excavations or the height of the sidechoir, as in Lange's more recent reconstruction. East of the crossing was the choir
A choir ( ), also known as a chorale or chorus (from Latin ''chorus'', meaning 'a dance in a circle') is a musical ensemble of singers. Choral music, in turn, is the music written specifically for such an ensemble to perform or in other words ...
with a semicircular end, with the rooms that are accessible from the transepts on either side of it.
This first church was destroyed in a fire in 946, which is recorded in the Cologne Annals ''Astnide cremabatur'' (Essen burnt down).
The early Ottonian Abbey
 Several dedicatory inscriptions for parts of the new church survive from the years 960 to 964, from which it can be concluded that the fire of 946 had only damaged the church. No inscriptions survive for the nave and choir, which were probably retained from the earlier church. The individual stages of construction are uncertain; some parts could have been begun or even completed before the fire. Taking advantage of necessary renovations to expand the church enclosure was not unusual. The new parts, presumably built at the order of the abbesses Agana and Hathwig, were an outer
Several dedicatory inscriptions for parts of the new church survive from the years 960 to 964, from which it can be concluded that the fire of 946 had only damaged the church. No inscriptions survive for the nave and choir, which were probably retained from the earlier church. The individual stages of construction are uncertain; some parts could have been begun or even completed before the fire. Taking advantage of necessary renovations to expand the church enclosure was not unusual. The new parts, presumably built at the order of the abbesses Agana and Hathwig, were an outer crypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religiou ...
, a westwork and a narthex and an external chapel
A chapel (from , a diminutive of ''cappa'', meaning "little cape") is a Christianity, Christian place of prayer and worship that is usually relatively small. The term has several meanings. First, smaller spaces inside a church that have their o ...
of St John the Baptist
John the Baptist ( – ) was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early first century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in some Baptist ...
. This building can be reconstructed from archaeological finds and did not have a long existence, because a new church was erected, perhaps under the art loving Abbess Mathilde, but maybe only under Abbess Theophanu (r. 1039–1058). Possibly, a new building was begun under Mathilde and completed under Theophanu. Significant portions survive from the new Ottonian
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German stem du ...
building.
The new Ottonian church
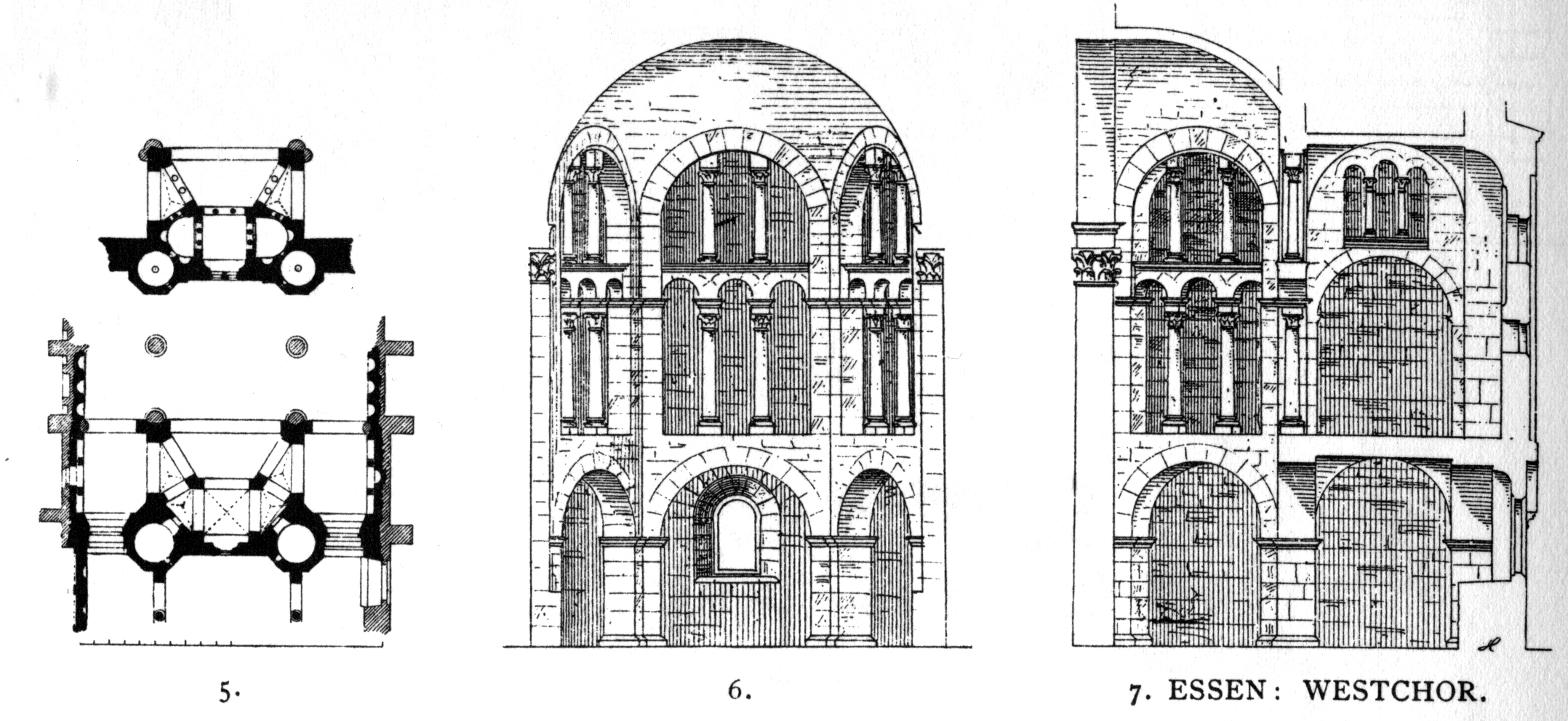
The expansion of the new Ottonian building was predetermined by its two predecessors. The greater part of the foundations were reused; only in locations where the stresses were increased or the floorplan differed were new foundations laid. The new building also had three aisles with a transept and a choir shaped like the earlier choirs. Acrypt
A crypt (from Greek κρύπτη (kryptē) ''wikt:crypta#Latin, crypta'' "Burial vault (tomb), vault") is a stone chamber beneath the floor of a church or other building. It typically contains coffins, Sarcophagus, sarcophagi, or Relic, religiou ...
was now built below the choir. The choir was closed with a semi-circular apse
In architecture, an apse (: apses; from Latin , 'arch, vault'; from Ancient Greek , , 'arch'; sometimes written apsis; : apsides) is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical Vault (architecture), vault or semi-dome, also known as an ' ...
, which was encased within a half decagon. A two-story outer crypt was connected to the choir, the west walls of which formed the east walls of the side choirs. Towers next to the altar room gave direct access to the crypt. The near choirs contained matronea, which were open to the transepts and the main choir. the outer walls of the ends of the transepts were made two stories high, with the upstairs portion composed of three niches with windows. On the ground floor were niches, and the pattern of niches continued on the side walls. A walkway ran along the walls above these niches, leading to the matroneum galleries. The double bay
Double Bay is a harbourside eastern suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia 4 kilometres east of the Sydney central business district. It is the administrative centre of the local government area of the Municipality o ...
between the westwork and the nave was maintained. The structure of the nave walls is unknown, but reconstructions based on other churches, especially Susteren Abbey which appears to draw from the new Ottonian church in many aspects, assume an interchange of piers and column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member ...
s. There were probably wall paintings between the arcades and the windows on the walls, since remains of wall paintings have been found in the westwork. Outside, the clerestory
A clerestory ( ; , also clearstory, clearstorey, or overstorey; from Old French ''cler estor'') is a high section of wall that contains windows above eye-level. Its purpose is to admit light, fresh air, or both.
Historically, a ''clerestory' ...
of the nave had a structure of pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an ext ...
s and volute
A volute is a spiral, scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column. It was later incorporated into Corinthian order and Composite column capitals. Four are normally to be found on an ...
capitals, probably with twelve windows.
Westwork


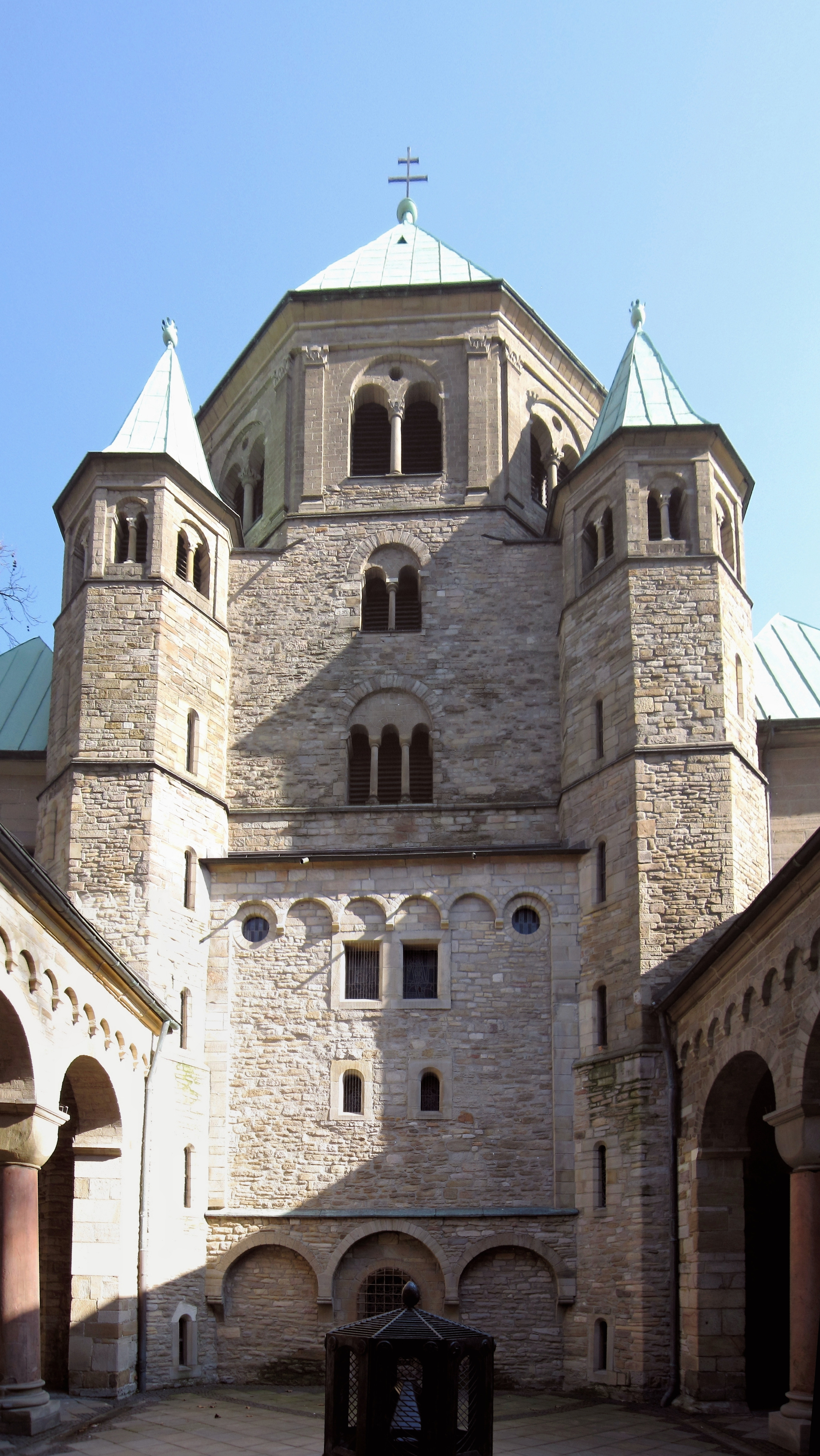
 The belief that the unknown architect of Essen Abbey church was one of the best architects of his time is based particularly on the westwork, which even today is the classic view of the church. As in the earlier churches, the westwork is only a little wider than the aisles of the nave. From the outside, the westwork appears as an almost square central tower crowned by an octagonal belfry with a pyramidal roof. At the west end there were two octagonal side towers, containing staircases to the belfry, which reached to just below the bell story of the belfry. The bell story of the central tower and the uppermost stories of the side towers have arched windows. Two story side rooms with arched windows on the upper floor are attached to the north and south sides of the central tower. On the ground floor of these side rooms, doors set in niches lead into the church – the central entrance of the earlier church was abandoned and a large, round-arched window installed in its place. With that, the westwork ceased to operate as a processional entrance to the church. Instead, the squat structure offered an optical counterpoint to the massive east part of the building.
From the outside the westwork appears to be composed of three towers, which envelop the west choir, which takes the form of a crossing which has been divided in half. No similar structure is known. There is a west choir in the central room in the shape of a half-hexagon, surrounded by a passageway. A flat niche is located in the middle of the west wall, with the entrances to the two side towers in flat niches on either side of it. The westwork opens toward the double bay through a large arch supported by pillars. An altar dedicated to
The belief that the unknown architect of Essen Abbey church was one of the best architects of his time is based particularly on the westwork, which even today is the classic view of the church. As in the earlier churches, the westwork is only a little wider than the aisles of the nave. From the outside, the westwork appears as an almost square central tower crowned by an octagonal belfry with a pyramidal roof. At the west end there were two octagonal side towers, containing staircases to the belfry, which reached to just below the bell story of the belfry. The bell story of the central tower and the uppermost stories of the side towers have arched windows. Two story side rooms with arched windows on the upper floor are attached to the north and south sides of the central tower. On the ground floor of these side rooms, doors set in niches lead into the church – the central entrance of the earlier church was abandoned and a large, round-arched window installed in its place. With that, the westwork ceased to operate as a processional entrance to the church. Instead, the squat structure offered an optical counterpoint to the massive east part of the building.
From the outside the westwork appears to be composed of three towers, which envelop the west choir, which takes the form of a crossing which has been divided in half. No similar structure is known. There is a west choir in the central room in the shape of a half-hexagon, surrounded by a passageway. A flat niche is located in the middle of the west wall, with the entrances to the two side towers in flat niches on either side of it. The westwork opens toward the double bay through a large arch supported by pillars. An altar dedicated to Saint Peter
Saint Peter (born Shimon Bar Yonah; 1 BC – AD 64/68), also known as Peter the Apostle, Simon Peter, Simeon, Simon, or Cephas, was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus and one of the first leaders of the Jewish Christian#Jerusalem ekklēsia, e ...
stands in the west choir in front of this arch. The walls follow the model of the west choir of Aachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral () is a Catholic Church, Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the cathedral of the Diocese of Aachen.
One of the oldest cathedral buildings in Europe, it was constructed as the royal chapel of the Palace of Aachen of Holy Rom ...
in their construction, which also has the use of the octagon as a belfry in common. On the ground floor there are three arches divided by hexagonal pillars. There are two levels of arch openings of the upper level in colonnades, with recycled ancient capitals on the columns.
The westwork was richly decorated, with the Last Judgement
The Last Judgment is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the '' Frashokereti'' of Zoroastrianism.
Christianity considers the Second Coming of Jesus Christ to entail the final judgment by God of all people who have ever lived, res ...
painted from the half-cupola to the nave. The painting shows the appearance of Jesus to (it has been concluded) the commissioner of the painting, the Abbess Theophanu (whose name is from the Greek for Divine apparition)
Crypt
Through the installation of the crypt, the floor of the main (east) choir was raised above the floor level of the nave and transepts. The side choirs remained on the same level as the nave and transepts. The crypt consists of the three aisled crypt of Agana, an inner crypt, and a five-sided outer crypt. The entrance to the inner crypt was from east side of the side choir, through which one passed into the outer crypt. The outer crypt had square and elongated rectangular vaults, separated by delicate square pillars. The three central vaults in the east were especially accentuated. Along the east wall in the two side vaults were semicircular niches. In the central vault was a small choir with three niches. The engaged pillars of the east wall of the outer pillar have sandstone plates on which 9 September 1051 is given as the date of the crypt's consecration. There are relics in the altars of the crypt.Later construction
A short time after the completion of the Ottonian church, the atrium was renovated, probably under Suanhild, the successor of the Abbess Theophanu. In 1471, the atrium was reduced with the renovation and expansion of the church of St. Johann Baptist, which served as the baptismal and parish church of the abbey's subjects. Otherwise the atrium probably retains the form established between 1060 and 1080. The next extension of the church complex was an attachment to the southern transept in the twelfth century. The upper floor of this very large building contained the ''sectarium'', where the order's papers and acts were kept and which also served as the treasury chamber. Underneath it was the open hall, which was closed at a later time and was used for judicial purposes by the court. This building is now part of the Essen Cathedral Treasury Chamber.Gothic Hall church
 In 1275, the Ottonian church burnt down, with only the westwork and the crypt surviving. In the rebuild, which occurred in the time of the Abbesses Berta von Arnsberg and Beatrix von Holte, the architect combined aspects of the old church with the new Gothic style. The form of the
In 1275, the Ottonian church burnt down, with only the westwork and the crypt surviving. In the rebuild, which occurred in the time of the Abbesses Berta von Arnsberg and Beatrix von Holte, the architect combined aspects of the old church with the new Gothic style. The form of the hall church
A hall church is a Church (building), church with a nave and aisles of approximately equal height. In England, Flanders and the Netherlands, it is covered by parallel roofs, typically, one for each vessel, whereas in Germany there is often one s ...
was chosen, in complete contrast with Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (, , officially , English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia belonging to the Catholic Church. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archd ...
– the Essen order had to ward off the Archbishop of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne governs the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cologne in western North Rhine-Westphalia. Historically, the archbishop was ''ex officio'' one of the prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire and ruled the Electorate of Cologne ...
's claims to authority and the nuns wished to express their integrity and independence through the form of their building. Two architects worked alongside each other on the rebuild, of which the first, a Master Martin, quit in 1305 because of disputes with Abbess Beatrix von Holte. Master Martin, who was a church builder from Burgundy
Burgundy ( ; ; Burgundian: ''Bregogne'') is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. ...
and Champagne
Champagne (; ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, which demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
, as shown by details of his ornamentation, also knew the design idiom of Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
and Trier
Trier ( , ; ), formerly and traditionally known in English as Trèves ( , ) and Triers (see also Names of Trier in different languages, names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle (river), Moselle in Germany. It lies in a v ...
cathedral construction workshops, was responsible for the overall design. This included at first a long choir like that of St Vitus's Church, Mönchengladbach
Mönchengladbach (, ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in North Rhine-Westphalia, western Germany, west of the Rhine, halfway between Düsseldorf and the Netherlands, Dutch border.
Geography Municipal subdivisions
Since 2009, th ...
. Afterwards this concept was given up under the management of Master Martin and a hall church
A hall church is a Church (building), church with a nave and aisles of approximately equal height. In England, Flanders and the Netherlands, it is covered by parallel roofs, typically, one for each vessel, whereas in Germany there is often one s ...
inspired by St. Elizabeth's Church, Marburg
Marburg (; ) is a college town, university town in the States of Germany, German federal state () of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf Districts of Germany, district (). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has ...
(begun 1235) was built, which was built over the outer crypt. The successor to Master Martin's name is not known. His design idiom is more strongly Westphalia
Westphalia (; ; ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the region is almost identical with the h ...
n, but he continued the plan of his predecessor and brought it to completion.
The original, shallow roofs of the octagon and the side towers were replaced with steeper caps; the side towers were also raised by a story. The Gothic church gained a tower above the crossing. The cloister was also expanded. The whole new building was consecrated on the 8th of July, probably of 1316. The 8th of July is celebrated to this day as the Minster's anniversary.
Later alterations
In the eighteenth century, the church was baroquified. The tower over the crossing was replaced with a narrow flèche. The windows of the south side of the cathedral were widened and lost their Gothictracery
Tracery is an architectural device by which windows (or screens, panels, and vaults) are divided into sections of various proportions by stone ''bars'' or ''ribs'' of moulding. Most commonly, it refers to the stonework elements that support th ...
. The steep roofs of the westwork were replaced with baroque onion domes and the bell story received a clock. In the interior a large part of the old interior decoration was removed and replaced, so that only a few pieces of the gothic decoration have survived, which are no longer in their proper context.
In 1880 the fashionable view of the gothic as the uniquely German architectural style reached Essen and the baroque additions were undone, as far as possible. The westwork returned to its previous appearance, when Essen architect and art historian Georg Humann was able to effect its gothicisation. The baroque interior decoration was also removed; a side altar is now employed as the high altar of the adoration church of St. Johann Baptist in front of the Minster. Some saint statues are found there, others in the Cathedral Treasury Chamber. The decoration made to replace the baroque pieces fell victim to the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, so that little of it now survives. During the renovation of 1880 the church also received its current roofing design and a neo-Gothic
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half of the 19th century ...
flèche on the crossing.
War damage and rebuilding
On the night of the 5th and 6 March 1943, 442 aircraft of theRoyal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
carried out a raid on the city of Essen, which was important to the German war effort because of the Krupp steel works. In less than an hour, 137,000 incendiary bombs and 1,100 explosive bombs were dropped on the central city. The Minster caught fire and suffered heavy damage – the oldest parts of the building, the westwork and the crypt were less heavily damaged. The decision to rebuild was made unanimously in the first meeting of the city council organised by them after the city's occupation by allied troops, under the communist mayor Heinz Renner. The war damage also enabled extensive archaeological excavations to be carried out in the church by Walter Zimmermann. These provided a large amount of information about the predecessors of the modern church and about the burials in the church.
The rebuilding was begun in 1951 and proceeded apace. By 1952 the westwerk and the nave were usable once more and the rest of the church was rebuilt by 1958. Even the northside of the cloisters, which had collapsed in the nineteenth century, was repaired. The neo-gothic flèche from the previous century was replaced by a narrower, lightning-proof flèche, completing the modern external appearance of the church. The completely repaired church became the seat of the newly founded Diocese of Essen in 1958.
Recent changes
The abbey never grew beyond the limits of the Ottonian church. The transformation into acathedral
A cathedral is a church (building), church that contains the of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, Annual conferences within Methodism, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually s ...
made a new expansion necessary. Cardinal Franz Hengsbach, the first bishop, said during his lifetime that he wished to make use of his right to be buried within his cathedral church, but not in the Ottonian crypt with Saint Altfrid. In order to fulfill this wish, a west crypt with an entrance in the old westwork was installed under the atrium between 1981 and 1983 by the cathedral architect Heinz Bohmen and decorated with cast concrete sculpture by . In this Adveniat crypt, whose name reflects the fact that Cardinal Hengsbach was a co-founder of the episcopal charity , the remains of a canon who had been buried in the atrium in the Middle Ages and discovered during the excavations was buried and in 1991 the cardinal was interred there as well.
On 10 October 2004, the newly built south side chapel was dedicated to the memory and veneration of Nikolaus Groß, who was beatified
Beatification (from Latin , "blessed" and , "to make") is a recognition accorded by the Catholic Church of a deceased person's entrance into Heaven and capacity to intercede on behalf of individuals who pray in their name. ''Beati'' is the ...
in 2001.
Measurements
The whole church, together with the church of St. Johann Baptist on the front is 90 metres long. Its width varies between 24 and 31 metres at the transepts at the start of the Cathedral treasury. The height varies also: The volume of the Minster is roughly 45,000 m³, volume of the masonry is about 10,000 m³. The building ''weighs'' roughly 25,000 tonnes.Fittings
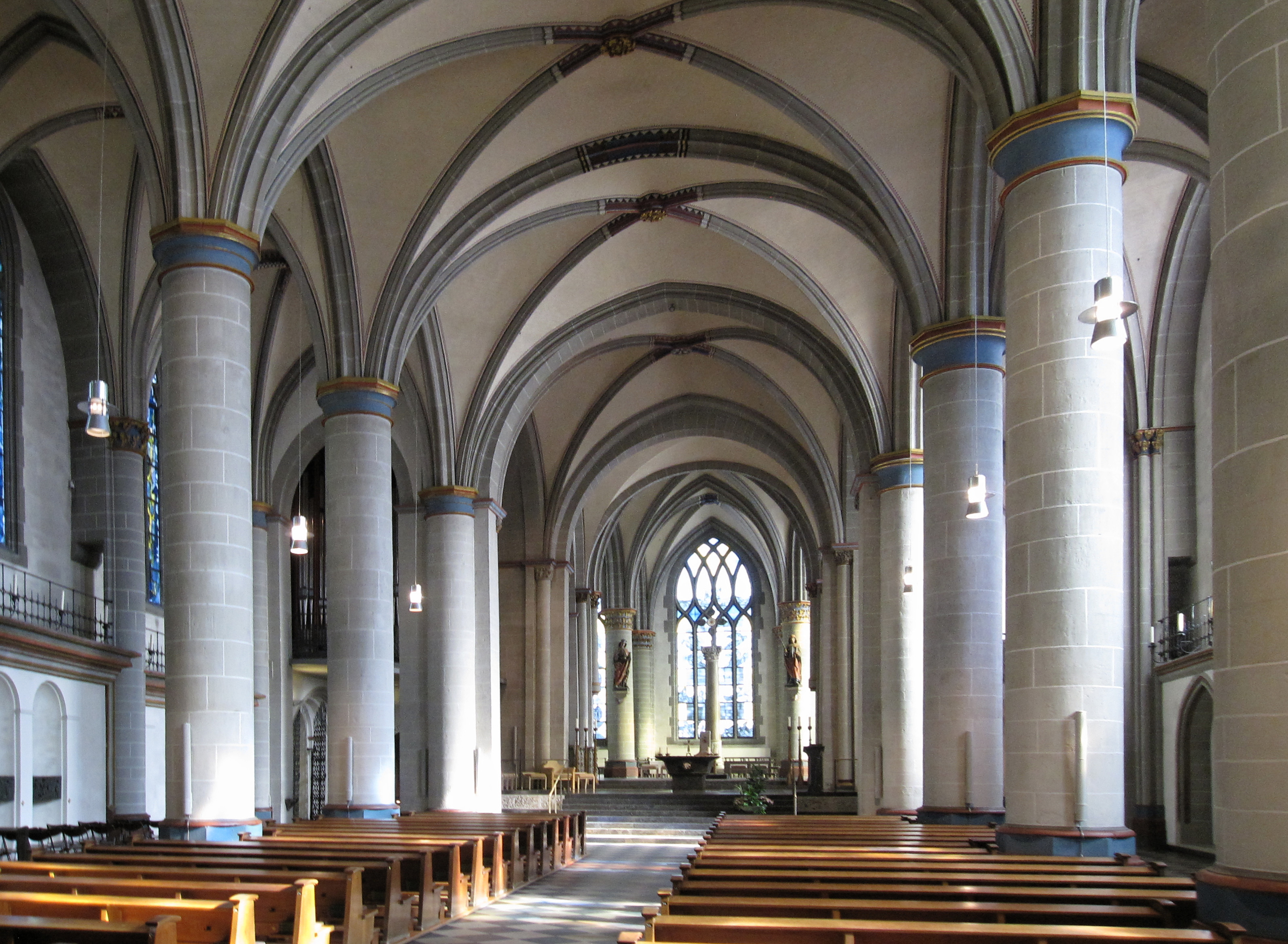
 As a result of the baroquification of the eighteenth century, the re-gothificisation of the nineteenth century and the war damage of the twentieth century, there are only a few pieces of the earlier fittings of the Minster, but some remains of great significance do survive. The interior is comparatively simple, especially in its architecture, whose subtle beauty is overlooked by many visitors because the lustre of the two very important medieval artworks of the Cathedral outshines it.
As a result of the baroquification of the eighteenth century, the re-gothificisation of the nineteenth century and the war damage of the twentieth century, there are only a few pieces of the earlier fittings of the Minster, but some remains of great significance do survive. The interior is comparatively simple, especially in its architecture, whose subtle beauty is overlooked by many visitors because the lustre of the two very important medieval artworks of the Cathedral outshines it.
Cathedral Treasury
The Minster possesses a Cathedral Treasury, which is open to the public. The most important treasure of the church, the Golden Madonna, has been displayed in the northern side chapel since 1959. This is the oldest fully sculptured statue of Mary, the patron saint of the diocese, in the world. The 74 cm high figure of gilded poplar, dates from the period of the abbess Mathilde and depicts Mary as a heavenly queen, holding power over the Earth on behalf of her son. The figure, which was originally carried in processions, was probably placed in Essen because of Mathilde's relationship to theOttonian dynasty
The Ottonian dynasty () was a Saxons, Saxon dynasty of German monarchs (919–1024), named after three of its kings and Holy Roman emperors, especially Otto the Great. It is also known as the Saxon dynasty after the family's origin in the German ...
. The figure, which is more than a thousand years old, was comprehensively restored in 2004.
In the centre of the westwork the monumental seven-arm candelabrum now stands, which the Abbess Mathilde had made between 973 and 1011. The candelabrum, 2.26 metres high with a span of 1.88 metres is composed of 46 individual cast bronze pieces. The candelabrum symbolises the unity of the Trinity
The Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the Christian doctrine concerning the nature of God, which defines one God existing in three, , consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, thr ...
and the Earth with its four cardinal points and the idea of Christ as the light of the World, which will lead the believers home at the Last Judgement
The Last Judgment is a concept found across the Abrahamic religions and the '' Frashokereti'' of Zoroastrianism.
Christianity considers the Second Coming of Jesus Christ to entail the final judgment by God of all people who have ever lived, res ...
(Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation, also known as the Book of the Apocalypse or the Apocalypse of John, is the final book of the New Testament, and therefore the final book of the Bible#Christian Bible, Christian Bible. Written in Greek language, Greek, ...
).
Other remarkable items in the Cathedral treasury include the so-called Childhood Crown of Otto III, four Ottonian processional crosses, the long-revered Sword of Saints Cosmas and Damian, the cover of the Theophanu Gospels, several gothic arm-reliquaries, the largest surviving collection of Burgundian fibula brooches in the world, and the Great Carolingian Gospels also known as Essen Cathedral Treasury Hs. 1.
Column of Ida
The oldest surviving fitting in the Minster is the column in the choir, which now supports a modern crucifix. Until the fifteenth century it supported a cross coated with a gilt copper sheet, from which the donation plate and probably other remains in the Cathedral treasury were made. TheLatin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
inscription ''ISTAM CRUCEM (I)DA ABBATISSA FIERI IUSSIT'' (Abbess Ida ordered this cross to be made) allows the creator to be identified with the Essen Abbess Ida, who died in 971, though the sister of Abbess Theophanu, Ida, Abbess of St. Maria im Kapitol in Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
has also been suggested. The column itself is probably ancient spolia, going by fluted pedestal and the Attic ''basis'' of the column. The capital
Capital and its variations may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** Capital region, a metropolitan region containing the capital
** List of national capitals
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter
Econom ...
was carved in antiquity, though exceptionally richly carved for that period. Stylistically it is related to the capitals of the west end and the crypt, as well as those of the Ludgeridan crypt of Werden Abbey and those of St Lucius's Church in Essen-Werden.
Altfrid's grave monument
In the east crypt there is a limestone gothicchurch monument
Funerary art is any work of art forming, or placed in, a repository for the remains of the death, dead. The term encompasses a wide variety of forms, including cenotaphs ("empty tombs"), tomb-like monuments which do not contain human remains, a ...
of the Bishop of Hildesheim and founder of Essen, Altfrid, which dates to around 1300 and was probably built under Abbess Beatrix von Holte. This dating is based on the striking similarity of the tomb to saints' graves at Cologne, especially the grave of St. Irmgard in Cologne Cathedral
Cologne Cathedral (, , officially , English: Cathedral Church of Saint Peter) is a cathedral in Cologne, North Rhine-Westphalia belonging to the Catholic Church. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Cologne and of the administration of the Archd ...
.
Further artworks
The sandstone sculptural group, called the "Entombment of Christ" (Grablegung Christi) in the southern side chapel is from the late Gothic period. The unknown Cologne Master who created it in the first quarter of the sixteenth century is known by the notname ''Master of the Carben Monument''. Another sculpture from the early sixteenth century is the sculpture of the Holy Helper,Saint Roch
Roch (lived c. 1348 – 15/16 August 1376/79; traditionally c. 1295 – 16 August 1327), also called Rock in English, was a Majorcan Catholic confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he was especially invo ...
on the north wall of the Minster, created shortly after 1500.
The baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
period is represented in Essen Minster by two epitaph
An epitaph (; ) is a short text honoring a deceased person. Strictly speaking, it refers to text that is inscribed on a tombstone or plaque, but it may also be used in a figurative sense. Some epitaphs are specified by the person themselves be ...
s. The older, for Abbess Elisabeth von Bergh-s’Heerenberg who died in 1614, contains significant Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
elements. This plaque made of black marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
in Antwerp
Antwerp (; ; ) is a City status in Belgium, city and a Municipalities of Belgium, municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of Antwerp Province, and the third-largest city in Belgium by area at , after ...
is found on the north wall, east of the side bay and shows the Abbess in her official outfit, surrounded by the coats of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the last two being outer garments), originating in Europe. The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic ac ...
of her ancestors. The second epitaph is that of the Abbess Anna Salome von Salm-Reifferscheidt, which is attributed to Johann Mauritz Gröninger and is found on the north wall of the organ loft.
Because of war damage, the Minster has no medieval windows. But among the modern artworks Essen Cathedral Chapter commissioned during the rebuild, were new windows for the church and modern sacral art, which was to be in harmony with the older elements of the building. The window of St Michael and the windows of the gallery are by Heinrich Campendonk, the choir windows by Ludwig Gies, those of the nave by Wilhelm Buschulte and the windows of the crypt are by Alfred Manessier. The altar frieze is the work of sculptor Elmar Hillebrand
Elmar Hillebrand (11 October 1925, Cologne8 January 2016, Cologne) was a German sculptor., WDR, 11. Januar 2016
Life and education
After graduating from high school at Apostelgymnasium (1943) and then doing military service and being a prisoner ...
and his student Ronald Hughes. The bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
doors of the atrium and church as well as the frieze depicting the Stations of the Cross
The Stations of the Cross or the Way of the Cross, also known as the Via Dolorosa, Way of Sorrows or the , are a series of fourteen images depicting Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ on the day of Crucifixion of Jesus, his crucifixion and acc ...
in the nave are the work of the Austrian artist .
Organ
The minster's neworgan
Organ and organs may refer to:
Biology
* Organ (biology), a group of tissues organized to serve a common function
* Organ system, a collection of organs that function together to carry out specific functions within the body.
Musical instruments
...
was inaugurated in 2004. It was built by the renowned organbuilder Rieger of Schwarzach, which was founded by Franz Rieger. The instrument consists of two organs, and has 69 stops altogether (5,102 pipes, 95 organ stop
An organ stop is a component of a pipe organ that admits pressurized air (known as ''wind'') to a set of organ pipes. Its name comes from the fact that stops can be used selectively by the organist; each can be "on" (admitting the passage of a ...
s).
The main instrument is located in the choir loft. It has 57 stops in 3 manual divisions and a pedal division, and it has a fourth manual on which the auxiliary organ can be played.
The auxiliary organ is located in the west part of the cathedral. It has three manual divisions with ten stops and a pedal division with two stops, and has a significant role in producing sound in the rear region of the Cathedral. Its high pressure and bombard stops are for special solo effects. The three manual divisions can be played on the fourth manual of the main console, and each can also be coupled separately to its other manuals.
Bells
There are bells in the belfry of the westwork and also in the flèche over the crossing. The ringing of the Minster is expanded tonally by the ringing of the attached church of St. Johann Baptist, whose bells, cast in 1787, are not tonally matched to the somewhat older bells of the Minster, so that when they ring together there is a slight musical impurity. There are three large bells in the westwork. The oldest bell was already in place at the end of the thirteenth century. It bears the inscription ''CHRISTUM DE LIGNO CLAMANTEM DUM SONO SIGNO'' (When I sound, I signal that Christ calls from the cross). By its construction it is an early gothic three chime bell. The ''Marybell'' is the largest of the bells. It bears a longer inscription saying that it was cast in 1546. The bell was cast in Essen itself, in the modern Burgplatz. The third bell in the westwork lacks an inscription, but its shape marks it as fourteenth-century. The flèche holds three more bells, two of which were cast in 1955 by the bell founders Petit & Gebr. Edelbrock of Gescher, who thereby brought their foundry back to the bell-making tradition, since their foundry had cast the bells of St. Johann Baptist in 1787. These two bells are inscribed ''Ave Maria Trösterin 1955'' (Hail Mary, Counselor, 1955) and ''Ave Maria Königin 1955'' (Hail Mary, Queen, 1955). The third bell in the flèche bears the inscription ''WEI GOT WEL DEINEN DEI BIDDE VOR DE KRESTEN SEELEN AN 1522'' (He who serves God well prays for the Christian souls, Y(ear) of O(ur Lord) 1522).(PDF; 1,5 MB, German)
Cathedral chapter
EssenCathedral chapter
According to both Catholic and Anglican canon law, a cathedral chapter is a college of clerics ( chapter) formed to advise a bishop and, in the case of a vacancy of the episcopal see in some countries, to govern the diocese during the vacancy. In ...
includes six resident and four non-resident Cathedral capitular vicars under the oversight of the Cathedral provost. At present two of the resident positions are vacant and one of the non-resident positions.
Under the Concordat of 1929 the right to elect the bishop was given to the chapter, alongside their existing duties concerned with liturgical celebrations in the high church, selection of a Diocesan administrator
A diocesan administrator (also known as archdiocesan administrator, archiepiscopal administrator and eparchial administrator for the case, respectively, of an archdiocese, archeparchy, and eparchy) is a provisional ordinary of a Catholic partic ...
, advising and supporting the bishop in the government of the diocese
In Ecclesiastical polity, church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided Roman province, prov ...
and management of the Cathedral Treasury.
Since 2005, the Cathedral provost has been the civic dean of Essen, Prelate
A prelate () is a high-ranking member of the Minister (Christianity), Christian clergy who is an Ordinary (church officer), ordinary or who ranks in precedence with ordinaries. The word derives from the Latin , the past participle of , which me ...
Otmar Vieth, as successor of Günter Berghaus who went into retirement after heading the Cathedral chapter for eleven years from 1993 to 2004.
References
Notes Sources *Leonhard Küppers: ''Das Essener Münster''. Fredebeul & Koenen, Essen 1963. *Klaus Lange: ''Der gotische Neubau der Essener Stiftskirche'', in: ''Reform – Reformation -Säkularisation. Frauenstifte in Krisenzeiten''. Klartext Verlag Essen 2004 *Klaus Lange: ''Die Krypta der Essener Stiftskirche.'' in: ''Essen und die sächsischen Frauenstifte im Frühmittelalter''. Klartext Verlag, Essen 2003, . *Klaus Lange: ''Der Westbau des Essener Doms. Architektur und Herrschaft in ottonischer Zeit'', Aschendorffsche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Münster 2001, . *Albert Rinken: ''Die Glocken des Münsters und der Anbetungskirche'' in: ''Münster am Hellweg'' 1949, S. 95ff. *Josef Schueben: ''Das Geläut der Münsterkirche'' in: ''Münster am Hellweg'' 1956, S. 16ff. *Walter Zimmermann: ''Das Münster zu Essen''. Düsseldorf 1956.External links
Essen Cathedral website
Diocese of Essen website
Münsterbauverein website
{{Authority control