enlarged prostate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the 
 As men age, the enzymes aromatase and 5-alpha reductase increase in activity. These enzymes are responsible for converting androgen hormones into
As men age, the enzymes aromatase and 5-alpha reductase increase in activity. These enzymes are responsible for converting androgen hormones into
File:Nodular hyperplasia of the prostate.jpg,
 Lifestyle alterations to address the symptoms of BPH include physical activity, decreasing fluid intake before bedtime, moderating the consumption of alcohol and caffeine-containing products, and following a timed voiding schedule.
Patients can also attempt to avoid products and medications with
Lifestyle alterations to address the symptoms of BPH include physical activity, decreasing fluid intake before bedtime, moderating the consumption of alcohol and caffeine-containing products, and following a timed voiding schedule.
Patients can also attempt to avoid products and medications with

 If medical treatment is not effective, surgery may be performed. Surgical techniques used include the following:
* Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): the gold standard. TURP is thought to be the most effective approach for improving urinary symptoms and urinary flow, however, this surgical procedure may be associated with complications in up to 20% of men. Surgery carries some risk of complications, such as
If medical treatment is not effective, surgery may be performed. Surgical techniques used include the following:
* Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): the gold standard. TURP is thought to be the most effective approach for improving urinary symptoms and urinary flow, however, this surgical procedure may be associated with complications in up to 20% of men. Surgery carries some risk of complications, such as

 Globally, benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 94 million males .
The prostate gets larger in most men as they get older. For a symptom-free man of 46 years, the risk of developing BPH over the next 30 years is 45%. Incidence rates increase from 3 cases per 1000 man-years at age 45–49 years, to 38 cases per 1000 man-years by the age of 75–79 years. While the
Globally, benign prostatic hyperplasia affects about 94 million males .
The prostate gets larger in most men as they get older. For a symptom-free man of 46 years, the risk of developing BPH over the next 30 years is 45%. Incidence rates increase from 3 cases per 1000 man-years at age 45–49 years, to 38 cases per 1000 man-years by the age of 75–79 years. While the
Extrinsic Compression by Prostate
{{Authority control Andrology Men's health Neoplastic and hyperplastic prostate disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
prostate gland
The prostate is an male accessory gland, accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemica ...
. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems.
The cause is unclear. Risk factors include a family history, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent ...
, not enough exercise, and erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
. Medications like pseudoephedrine, anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
s, and calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s may worsen symptoms. The underlying mechanism involves the prostate pressing on the urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate.
The external urethral sphincter is a striated ...
thereby making it difficult to pass urine out of the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and examination after ruling out other possible causes.
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, a number of procedures, and surgery. In those with mild symptoms, weight loss, decreasing caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
intake, and exercise are recommended, although the quality of the evidence for exercise is low. In those with more significant symptoms, medications may include alpha blockers such as terazosin or 5α-reductase inhibitors such as finasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat hirsutism, excessive hair growth in women. It ...
. Surgical removal of part of the prostate may be carried out in those who do not improve with other measures. Some herbal medicine
Herbal medicine (also called herbalism, phytomedicine or phytotherapy) is the study of pharmacognosy and the use of medicinal plants, which are a basis of traditional medicine. Scientific evidence for the effectiveness of many herbal treatments ...
s that have been studied, such as saw palmetto, have not been shown to help. Other herbal medicines somewhat effective at improving urine flow include beta-sitosterol from '' Hypoxis rooperi'' (African star grass), pygeum (extracted from the bark of '' Prunus africana''), pumpkin seeds (''Cucurbita pepo
''Cucurbita pepo'' is a cultivated plant of the genus ''Cucurbita''. It yields varieties of winter squash and pumpkin, but the most widespread varieties belong to the subspecies ''Cucurbita pepo'' subsp. ''pepo'', called summer squash.
It has b ...
''), and stinging nettle
''Urtica dioica'', often known as common nettle, burn nettle, stinging nettle (although not all plants of this species sting) or nettle leaf, or just a nettle or stinger, is a herbaceous perennial flowering plant in the family Urticaceae. Or ...
('' Urtica dioica'') root.
, about 94 million men aged 40 years and older are affected globally. BPH typically begins after the age of 40. The prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
of clinically diagnosed BPH peaks at 24% in men aged 75–79 years. Based on autopsy
An autopsy (also referred to as post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of deat ...
studies, half of males aged 50 and over are affected, and this figure climbs to 80% after the age of 80. Although prostate specific antigen levels may be elevated in males with BPH, the condition does not increase the risk of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is the neoplasm, uncontrolled growth of cells in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system below the bladder. Abnormal growth of the prostate tissue is usually detected through Screening (medicine), screening tests, ...
.

Signs and symptoms
BPH is the most common cause of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), which are divided into storage, voiding, and symptoms which occur after urination. Storage symptoms include the need to urinate frequently, waking at night to urinate, urgency (compelling need to void that cannot be deferred), involuntary urination, including involuntary urination at night, or urge incontinence (urine leak following a strong sudden need to urinate). Voiding symptoms include urinary hesitancy (a delay between trying to urinate and the flow actually beginning), intermittency (not continuous), involuntary interruption of voiding, weak urinary stream, straining to void, a sensation of incomplete emptying, and uncontrollable leaking after the end of urination. These symptoms may be accompanied by bladder pain or pain while urinating, called dysuria. Bladder outlet obstruction (BOO) can be caused by BPH. Symptoms are abdominal pain, a continuous feeling of a full bladder, frequent urination, acute urinary retention (inability to urinate), pain during urination (dysuria), problems starting urination (urinary hesitancy), slow urine flow, starting and stopping (urinary intermittency), and nocturia. BPH can be a progressive disease, especially if left untreated. Incomplete voiding results in residual urine or urinary stasis, which can lead to an increased risk of urinary tract infection.Causes
Hormones
Most experts considerandrogen
An androgen (from Greek ''andr-'', the stem of the word meaning ) is any natural or synthetic steroid hormone that regulates the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors. This includes ...
s (testosterone
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone and androgen in Male, males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testicles and prostate, as well as promoting se ...
and related hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of cell signaling, signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs or tissues by complex biological processes to regulate physio ...
s) to play a permissive role in the development of BPH. This means that androgens must be present for BPH to occur, but do not necessarily directly cause the condition. This is supported by evidence suggesting that castrated boys do not develop BPH when they age. In a study of 26 eunuch
A eunuch ( , ) is a male who has been castration, castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function. The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2 ...
s from the palace of the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the ...
still living in Beijing
Beijing, Chinese postal romanization, previously romanized as Peking, is the capital city of China. With more than 22 million residents, it is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city as well as ...
in 1960, the prostate could not be felt in 81% of the studied eunuchs. The average time since castration was 54 years (range, 41–65 years). On the other hand, some studies suggest that administering exogenous testosterone is not associated with a significant increase in the risk of BPH symptoms, so the role of testosterone in prostate cancer and BPH is still unclear. Further randomized controlled trials with more participants are needed to quantify any risk of giving exogenous testosterone.
Dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone primarily involved in the growth and repair of the prostate and the penis, as well as the production o ...
(DHT), a metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, c ...
of testosterone, is a critical mediator of prostatic growth. DHT is synthesized in the prostate from circulating testosterone by the action of the enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different mol ...
5α-reductase, type 2. DHT can act in an autocrine
Autocrine signaling is a form of cell signaling in which a cell secretes a hormone or chemical messenger (called the autocrine agent) that binds to autocrine receptors on that same cell, leading to changes in the cell. This can be contrasted with ...
fashion on the stromal cells or in paracrine
In cellular biology, paracrine signaling is a form of cell signaling, a type of cellular communication (biology), cellular communication in which a Cell (biology), cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behaviour of ...
fashion by diffusing into nearby epithelial cells. In both of these cell types, DHT binds to nuclear androgen receptor
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4 (nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 4), is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in th ...
s and signals the transcription of growth factor
A growth factor is a naturally occurring substance capable of stimulating cell proliferation, wound healing, and occasionally cellular differentiation. Usually it is a secreted protein or a steroid hormone. Growth factors are important for ...
s that are mitogenic to the epithelial and stromal cells. DHT is ten times more potent than testosterone because it dissociates from the androgen receptor more slowly. The importance of DHT in causing nodular hyperplasia is supported by clinical observations in which an inhibitor of 5α-reductase such as finasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat hirsutism, excessive hair growth in women. It ...
is given to men with this condition. Therapy with a 5α-reductase inhibitor markedly reduces the DHT content of the prostate and, in turn, reduces prostate volume and BPH symptoms.
Testosterone promotes prostate cell proliferation, but relatively low levels of serum testosterone are found in patients with BPH. One small study has shown that medical castration lowers the serum and prostate hormone levels unevenly, having less effect on testosterone and DHT levels in the prostate.
Besides testosterone and DHT, other androgens are also known to play a crucial role in BPH development. 11-oxygenated steroids (pregnanes) have been identified are precursors to 11-oxygenated androgens which are also potent agonists for the androgen receptor. Specifically, steroids like 11β-hydroxyprogesterone and 11-ketoprogesterone can be converted to 11-ketodihydrotestosterone, an 11-oxo form of DHT with the same potency. These precursors have also been detected in tissue biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample ...
samples from patients with BPH, as well as in their serum levels. Besides that, androgens biosynthesized via a backdoor pathway can contribute to the development of BPH.
While there is some evidence that estrogen may play a role in the cause of BPH, this effect appears to be mediated mainly through local conversion of androgens to estrogen in the prostate tissue rather than a direct effect of estrogen itself. In canine ''in vivo'' studies castration, which significantly reduced androgen levels but left estrogen levels unchanged, caused significant atrophy of the prostate. Studies looking for a correlation between prostatic hyperplasia and serum estrogen levels in humans have generally shown none.
In 2008, Gat et al. published evidence that BPH is caused by failure in the spermatic venous drainage system resulting in increased hydrostatic pressure and local testosterone levels elevated more than 100-fold above serum levels. If confirmed, this mechanism explains why serum androgen levels do not seem to correlate with BPH and why giving exogenous testosterone would not make much difference.
Diet
Studies indicate that dietary patterns may affect the development of BPH, but further research is needed to clarify any important relationship. Studies from China suggest that greater protein intake may be a factor in the development of BPH. Men older than 60 in rural areas had very low rates of clinical BPH, while men living in cities and consuming more animal protein had a higher incidence. On the other hand, a study in Japanese-American men in Hawaii found a strong negative association with alcohol intake, but a weak positive association with beef intake. In a large prospective cohort study in the US (the Health Professionals Follow-up Study), investigators reported modest associations between BPH (men with strong symptoms of BPH or surgically confirmed BPH) and total energy and protein, but not fat intake. There is also epidemiological evidence linking BPH withmetabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
(concurrent obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, impaired glucose metabolism and diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or the cells of th ...
, high triglyceride levels, high levels of low-density cholesterol, and hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
).
Degeneration
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is an age-related disease. Misrepair-accumulation aging theory suggests that the development of benign prostatic hyperplasia is a consequence of fibrosis and weakening of the muscular tissue in the prostate. The muscular tissue is important in the functionality of the prostate, and provides the force for excreting the fluid produced by prostatic glands. However, repeated contractions and dilations of myofibers will unavoidably cause injuries and broken myofibers. Myofibers have a low potential for regeneration; therefore, collagen fibers need to be used to replace the broken myofibers. Such misrepairs make the muscular tissue weak in functioning, and the fluid secreted by glands cannot be excreted completely. Then, the accumulation of fluid in glands increases the resistance of muscular tissue during the movements of contractions and dilations, and more and more myofibers will be broken and replaced by collagen fibers.Pathophysiology
 As men age, the enzymes aromatase and 5-alpha reductase increase in activity. These enzymes are responsible for converting androgen hormones into
As men age, the enzymes aromatase and 5-alpha reductase increase in activity. These enzymes are responsible for converting androgen hormones into estrogen
Estrogen (also spelled oestrogen in British English; see spelling differences) is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three ...
and DHT, respectively. This metabolism of androgen hormones leads to a decrease in testosterone but increased levels of DHT and estrogen.
Both the glandular epithelial cells and the stromal cells (including muscular fibers) undergo hyperplasia in BPH. Most sources agree that of the two tissues, stromal hyperplasia predominates, but the exact ratio of the two is unclear.
Anatomically the median and lateral lobes are usually enlarged, due to their highly glandular composition. The anterior lobe has little in the way of glandular tissue and is seldom enlarged. (Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoder ...
of the prostate typically occurs in the posterior lobe – hence the ability to discern an irregular outline per rectal examination). The earliest microscopic signs of BPH usually begin between the age of 30 and 50 years old in the PUG, which is posterior to the proximal urethra. In BPH, the majority of growth occurs in the transition zone (TZ) of the prostate. In addition to these two classic areas, the peripheral zone (PZ) is also involved to a lesser extent. Prostatic cancer typically occurs in the PZ. However, BPH nodules, usually from the TZ are often biopsied anyway to rule out cancer in the TZ. BPH can be a progressive growth that in rare instances leads to exceptional enlargement. In some males, the prostate enlargement exceeds 200 to 500 grams. This condition has been defined as giant prostatic hyperplasia (GPH).
Diagnosis
The clinical diagnosis of BPH is based on a history of LUTS (lower urinary tract symptoms), a digital rectal exam, and the exclusion of other causes of similar signs and symptoms. The degree of LUTS does not necessarily correspond to the size of the prostate. An enlarged prostate gland on rectal examination that is symmetric and smooth supports a diagnosis of BPH. However, if the prostate gland feels asymmetrical, firm, or nodular, this raises concern for prostate cancer. Validated questionnaires such as the American Urological Association Symptom Index (AUA-SI), the International Prostate Symptom Score (I-PSS), and more recently the UWIN score (urgency, weak stream, incomplete emptying, and nocturia) are useful aids to making the diagnosis of BPH and quantifying the severity of symptoms.Laboratory investigations
Urinalysis
Urinalysis, a portmanteau of the words ''urine'' and ''analysis'', is a Test panel, panel of medical tests that includes physical (macroscopic) examination of the urine, chemical evaluation using urine test strips, and #Microscopic examination, m ...
is typically performed when LUTS are present and BPH is suspected to evaluate for signs of a urinary tract infection, glucose in the urine (suggestive of diabetes), or protein in the urine (suggestive of kidney disease). Bloodwork including kidney function tests and prostate specific antigen (PSA) are often ordered to evaluate for kidney damage and prostate cancer, respectively. However, checking blood PSA levels for prostate cancer screening is controversial and not necessarily indicated in every evaluation for BPH. Benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer are both capable of increasing blood PSA levels and PSA elevation is unable to differentiate these two conditions well. If PSA levels are checked and are high, then further investigation is warranted. Measures including PSA density, free PSA, rectal examination, and transrectal ultrasonography may help determine whether a PSA increase is due to BPH or prostate cancer.
Imaging and other investigations
Uroflowmetry is done to measure the rate of urine flow and total volume of urine voided when the subject is urinating. Abdominal ultrasound examination of the prostate andkidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and rig ...
s is often performed to rule out hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
and hydroureter. Incidentally, cysts, tumours, and stones may be found on ultrasound. Post-void residual volume of more than 100 ml may indicate significant obstruction. Prostate size of 30 cc or more indicates enlargement of the prostate.
Prostatic calcification can be detected through transrectal ultrasound (TRUS). Calcification is due to solidification of prostatic secretions or calcified corpora amylacea (hyaline
A hyaline substance is one with a glassy appearance. The word is derived from , and .
Histopathology
Hyaline cartilage is named after its glassy appearance on fresh gross pathology. On light microscopy of H&E stained slides, the extracellula ...
masses on the prostate gland). Calcification is also found in a variety of other conditions such as prostatitis, chronic pelvic pain syndrome, and prostate cancer. For those with elevated levels of PSA, TRUS guided biopsy is performed to take a sample of the prostate for investigation. Although MRI is more accurate than TRUS in determining prostate volume, TRUS is less expensive and almost as accurate as MRI. Therefore, TRUS is still preferred to measure prostate volume.
Differential diagnosis
Medical conditions
The differential diagnosis for LUTS is broad and includes various medical conditions, neurologic disorders, and other diseases of the bladder, urethra, and prostate such asbladder cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in thei ...
, urinary tract infection, urethral stricture, urethral calculi (stones), chronic prostatitis, and prostate cancer. Neurogenic bladder can cause urinary retention and cause symptoms similar to those of BPH. This may occur as a result of uncoordinated contraction of the bladder muscle or impairment in the timing of bladder muscle contraction and urethral sphincter relaxation. Notable causes of neurogenic bladder include disorders of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
such as Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a neurodegenerative disease primarily of the central nervous system, affecting both motor system, motor and non-motor systems. Symptoms typically develop gradually and non-motor issues become ...
, multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune disease resulting in damage to myelinthe insulating covers of nerve cellsin the brain and spinal cord. As a demyelinating disease, MS disrupts the nervous system's ability to Action potential, transmit ...
, and spinal cord injuries as well as disorders of the peripheral nervous system such as diabetes mellitus
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of common endocrine diseases characterized by sustained hyperglycemia, high blood sugar levels. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough of the hormone insulin, or th ...
, vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency, also known as cobalamin deficiency, is the medical condition in which the blood and tissue have a lower than normal level of Vitamin B12, vitamin B12. Symptoms can vary from none to severe. Mild deficiency may have fe ...
, and alcohol-induced nerve damage. Individuals affected by heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to Cardiac cycle, fill with and pump blood.
Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF ...
often experience nighttime awakenings to urinate due to redistribution of fluid accumulated in swollen legs.
Medications
Certain medications can increase urination difficulties by increasing bladder outlet resistance due to increasedsmooth muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called bec ...
tone at the prostate or bladder neck and contribute to LUTS. Alpha-adrenergic agonist medications, such as decongestants with pseudoephedrine can increase bladder outlet resistance. In contrast, calcium channel blocker
Calcium channel blockers (CCB), calcium channel antagonists or calcium antagonists are a group of medications that disrupt the movement of calcium () through calcium channels. Calcium channel blockers are used as antihypertensive drugs, i.e., as ...
s and anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
medications can worsen urinary retention by promoting bladder muscle relaxation. Diuretic medications such as loop diuretic
Loop diuretics are pharmacological agents that primarily inhibit the Na-K-Cl cotransporter located on the luminal membrane of cells along the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. They are often used for the treatment of hypertension and e ...
s (e.g., furosemide) or thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The firs ...
s (e.g., chlorthalidone) can cause or worsen urinary frequency and nighttime awakenings to urinate.
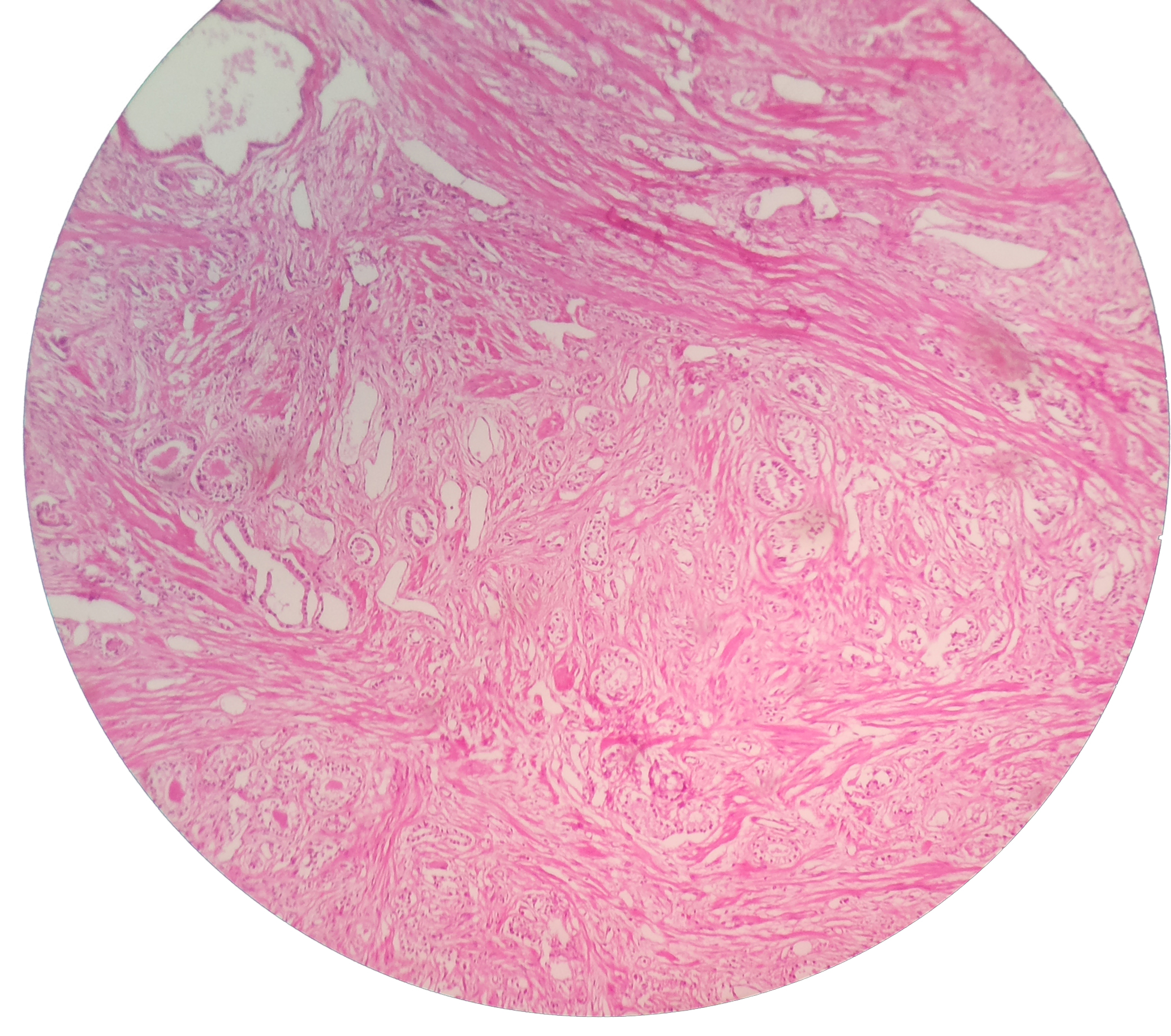
Micrograph
A micrograph is an image, captured photographically or digitally, taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnify, magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken ...
showing nodular hyperplasia (left off center) of the prostate from a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). H&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin–eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diag ...
.
File:Prostate histology.jpg, Microscopic examination of different types of prostate tissues (stained with immunohistochemical
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett ...
techniques): A. Normal (non-neoplastic) prostatic tissue (NNT). B. Benign prostatic hyperplasia. C. High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. D. Prostatic adenocarcinoma (PCA).
Management
When treating and managing benign prostatic hyperplasia, the aim is to prevent complications related to the disease and improve or relieve symptoms. Approaches used include lifestyle modifications, medications, catheterization, and surgery.Lifestyle
 Lifestyle alterations to address the symptoms of BPH include physical activity, decreasing fluid intake before bedtime, moderating the consumption of alcohol and caffeine-containing products, and following a timed voiding schedule.
Patients can also attempt to avoid products and medications with
Lifestyle alterations to address the symptoms of BPH include physical activity, decreasing fluid intake before bedtime, moderating the consumption of alcohol and caffeine-containing products, and following a timed voiding schedule.
Patients can also attempt to avoid products and medications with anticholinergic
Anticholinergics (anticholinergic agents) are substances that block the action of the acetylcholine (ACh) neurotransmitter at synapses in the central nervous system, central and peripheral nervous system.
These agents inhibit the parasympatheti ...
properties that may exacerbate urinary retention symptoms of BPH, including antihistamine
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides ...
s, decongestants, opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s, and tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and were marketed later in the decade. They are named after their chemical structure, which contains ...
s; however, changes in medications should be done with input from a medical professional.
Physical activity
Physical activity has been recommended as a treatment for urinary tract symptoms. A 2019 Cochrane review of six studies involving 652 men assessing the effects of physical activity alone, and physical activity as a part of a self-management program, among others. However, the quality of evidence was very low and therefore it remains uncertain whether physical activity is helpful in men experiencing urinary symptoms caused by benign prostatic hyperplasia.Voiding position
Voiding position when urinating may influence urodynamic parameters (urinary flow rate, voiding time, and post-void residual volume). Ameta-analysis
Meta-analysis is a method of synthesis of quantitative data from multiple independent studies addressing a common research question. An important part of this method involves computing a combined effect size across all of the studies. As such, th ...
found no differences between the standing and sitting positions for healthy males, but that, for elderly males with lower urinary tract symptoms, voiding in the sitting position--
* decreased the post-void residual volume;
* increased the maximum urinary flow, comparable with pharmacological intervention; and
* decreased the voiding time.
This urodynamic profile is associated with a lower risk of urologic complications, such as cystitis and bladder stones.
Medications
The two main medication classes for BPH management are alpha blockers and 5α-reductase inhibitors.Alpha-blockers
Selective α1-blockers are the most common choice for initial therapy. They include alfuzosin,doxazosin
Doxazosin, sold under the brand name Cardura among others, is a medication used to treat symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (enlarged prostate), hypertension (high blood pressure), and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). For high bloo ...
, silodosin, tamsulosin, terazosin, and naftopidil. They have a small to moderate benefit at improving symptoms. Selective alpha-1 blockers are similar in effectiveness but have slightly different side effect profiles. Alpha blockers relax smooth muscle in the prostate and the bladder neck, thus decreasing the blockage of urine flow. Common side effects of alpha-blockers include orthostatic hypotension
Orthostatic hypotension, also known as postural hypotension, is a medical condition wherein a person's blood pressure drops when they are standing up ( orthostasis) or sitting down. Primary orthostatic hypotension is also often referred to as ne ...
(a head rush or dizzy spell when standing up or stretching), ejaculation
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the penis through the urethra. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential component of natural conception. ...
changes, erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
, headaches, nasal congestion, and weakness. For men with LUTS due to an enlarged prostate, the effects of naftopidil, tamsulosin, and silodosin on urinary symptoms and quality of life may be similar. Naftopidil and tamsulosin may have similar levels of unwanted sexual side effects but fewer unwanted side effects than silodosin.
Tamsulosin and silodosin are selective α1 receptor blockers that preferentially bind to the α1A receptor in the prostate instead of the α1B receptor in the blood vessels. Less-selective α1 receptor blockers such as terazosin and doxazosin may lower blood pressure. The older, less selective α1-adrenergic blocker prazosin is not a first-line choice for either high blood pressure
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major ri ...
or prostatic hyperplasia; it is a choice for patients who present with both problems at the same time. The older, broadly non-selective alpha-blocker medications such as phenoxybenzamine are not recommended for control of BPH. Non-selective alpha-blockers such as terazosin and doxazosin may also require slow dose adjustments as they can lower blood pressure and cause syncope (fainting) if the response to the medication is too strong.
5α-reductase inhibitors
The 5α-reductase inhibitorsfinasteride
Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat hirsutism, excessive hair growth in women. It ...
and dutasteride
Dutasteride, sold under the brand name Avodart among others, is a medication primarily used to treat the symptoms of a benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), an enlarged prostate not associated with cancer. A few months may be required before bene ...
may also be used in people with BPH. These medications inhibit the 5α-reductase enzyme, which, in turn, inhibits the production of DHT, a hormone responsible for enlarging the prostate. Effects may take longer to appear than alpha blockers, but they persist for many years. When used together with alpha-blockers, no benefit was reported in short-term trials, but in a longer-term study (3–4 years) there was a greater reduction in BPH progression to acute urinary retention and surgery than with either agent alone, especially in people with more severe symptoms and larger prostates. Other trials have confirmed reductions in symptoms, within 6 months in one trial, an effect that was maintained after withdrawal of the alpha blocker. Side effects include decreased libido
In psychology, libido (; ) is psychic drive or energy, usually conceived of as sexual in nature, but sometimes conceived of as including other forms of desire. The term ''libido'' was originally developed by Sigmund Freud, the pioneering origin ...
and ejaculatory or erectile dysfunction. The 5α-reductase inhibitors are contraindicated in pregnant women because of their teratogenicity due to interference with fetal testosterone metabolism, and as a precaution, pregnant women should not handle crushed or broken tablets.

Phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE)
A 2018 Cochrane review of studies on men over 60 with moderate to severe lower urinary tract symptoms analyzed the impacts of phosphodiesterase inhibitors (PDE) in comparison to other drugs. These drugs may improve urinary symptoms slightly and reduce urinary bother but may also cause more side effects than placebo. The evidence in this review found that there is probably no difference between PDE and alpha blockers, however when used in combination they may provide a greater improvement in symptoms (with more side effects). PDE also likely improves symptoms when used with 5-alpha reductase inhibitors. Several phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors are also effective but may require multiple doses daily to maintain adequate urine flow. Tadalafil, a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, was considered then rejected by NICE in the UK for the treatment of symptoms associated with BPH. In 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved tadalafil to treat the signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia, and for the treatment of BPH and erectile dysfunction (ED), when the conditions occur simultaneously.Others
Antimuscarinic
A muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, also simply known as a muscarinic antagonist or as an antimuscarinic agent, is a type of anticholinergic drug that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs). The muscarin ...
s such as tolterodine may also be used, especially in combination with alpha-blockers. They act by decreasing acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Par ...
effects on the smooth muscle of the bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
, thus helping control symptoms of an overactive bladder
Overactive bladder (OAB) is a common condition where there is a frequent feeling of needing to urinate to a degree that it negatively affects a person's life. The frequent need to urinate may occur during the day, at night, or both. Loss of bl ...
.
Self-catheterization
Intermittent urinary catheterization is used to relieve the bladder in people withurinary retention
Urinary retention is an inability to completely empty the bladder. Onset can be sudden or gradual. When of sudden onset, symptoms include an inability to urinate and lower abdominal pain. When of gradual onset, symptoms may include urinary incont ...
. Self-catheterization is an option in BPH when it is difficult or impossible to empty the bladder. Urinary tract infection is the most common complication of intermittent catheterization. Several techniques and types of catheter are available, including sterile (single-use) and clean (multiple use) catheters, but, based on current information, none is superior to others in reducing the incidence of urinary tract infection.
Surgery
 If medical treatment is not effective, surgery may be performed. Surgical techniques used include the following:
* Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): the gold standard. TURP is thought to be the most effective approach for improving urinary symptoms and urinary flow, however, this surgical procedure may be associated with complications in up to 20% of men. Surgery carries some risk of complications, such as
If medical treatment is not effective, surgery may be performed. Surgical techniques used include the following:
* Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): the gold standard. TURP is thought to be the most effective approach for improving urinary symptoms and urinary flow, however, this surgical procedure may be associated with complications in up to 20% of men. Surgery carries some risk of complications, such as retrograde ejaculation
Retrograde ejaculation occurs when semen which would be ejaculated via the urethra is redirected to the urinary bladder. Normally, the sphincter of the bladder contracts before ejaculation, inhibiting urination and preventing a reflux of semen ...
(most commonly), erectile dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also referred to as impotence, is a form of sexual dysfunction in males characterized by the persistent or recurring inability to achieve or maintain a Human penis, penile erection with sufficient rigidity and durat ...
, urinary incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a significant effect on quality of life. Urinary incontinence is common in older women ...
, urethral strictures.
* Transurethral incision of the prostate
Transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP or TIP) is a surgical procedure for treating prostate gland enlargement (benign prostatic hyperplasia).
See also
*
*
*
*
References
External links
Mayo Clinic description
male genital su ...
(TUIP): rarely performed; the technique is similar to TURP but less definitive.
* Open male genital su ...
prostatectomy
Prostatectomy (from the Ancient Greek language, Greek , "prostate" and , "excision") is the surgical removal of all or part of the prostate gland. This operation is done for benignity, benign conditions that cause urinary retention, as well as ...
: not usually performed nowadays due to its high morbidity, even if the results are excellent.
Other less invasive surgical approaches (requiring spinal anesthesia
Spinal anaesthesia (or spinal anesthesia), also called spinal block, subarachnoid block, intradural block and intrathecal block, is a form of neuraxial regional anaesthesia involving the injection of a local anaesthetic with or without an opioi ...
) include:
* Holmium laser ablation of the prostate (HoLAP)
* Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate (HoLeP)
* Thulium laser transurethral vaporesection of the prostate (ThuVARP)
* Photoselective vaporization of the prostate (PVP)
* Aquablation therapy: a type of surgery using a water jet to remove prostatic tissue.
Minimally invasive procedures
Some less invasive procedures are available according to patients' preferences and co-morbidities. These are performed asoutpatient procedure
A patient is any recipient of health care services that are performed by healthcare professionals. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, nurse, optometrist, dentist, veterinarian, or other heal ...
s with local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is any technique to induce the absence of sense, sensation in a specific part of the body, generally for the aim of inducing local analgesia, i.e. local insensitivity to pain, although other local senses may be affected as well. ...
.
* Prostatic artery embolization: an endovascular procedure performed in interventional radiology
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as Fluoroscopy, x-ray fluoroscopy, CT scan, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultraso ...
. Through catheter
In medicine, a catheter ( ) is a thin tubing (material), tube made from medical grade materials serving a broad range of functions. Catheters are medical devices that can be inserted in the body to treat diseases or perform a surgical procedure. ...
s, embolic agents are released in the main branches of the prostatic artery, in order to induce a decrease in the size of the prostate gland, thus reducing the urinary symptoms.
* Water vapor thermal therapy (marketed as Rezum): This is a newer office procedure for removing prostate tissue using steam aimed at preserving sexual function.
* Prostatic urethral lift (marketed as UroLift): This intervention consists of a system of a device and an implant designed to pull the prostatic lobe away from the urethra.
* Transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT) is an outpatient procedure that is less invasive compared to surgery and involves using microwaves (heat) to shrink prostate tissue that is enlarged.
* Temporary implantable nitinol device (TIND and ): is a device that is placed in the urethra that, when released, is expanded, reshaping the urethra and the bladder neck.

Alternative medicine
While herbal remedies are commonly used, a 2016 review found the herbs studied to be no better thanplacebo
A placebo ( ) can be roughly defined as a sham medical treatment. Common placebos include inert tablets (like sugar pills), inert injections (like saline), sham surgery, and other procedures.
Placebos are used in randomized clinical trials ...
s. Particularly, several reviews found that saw palmetto extract, while one of the most commonly used, is no better than a placebo both in symptom relief and in decreasing prostate size.
Epidemiology
prevalence
In epidemiology, prevalence is the proportion of a particular population found to be affected by a medical condition (typically a disease or a risk factor such as smoking or seatbelt use) at a specific time. It is derived by comparing the number o ...
rate is 2.7% for men aged 45–49, it increases to 24% by the age of 80 years.
References
External links
Extrinsic Compression by Prostate
{{Authority control Andrology Men's health Neoplastic and hyperplastic prostate disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate