|
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. Lower urinary tract infections may involve the bladder (cystitis) or urethra (urethritis) while upper urinary tract infections affect the kidney (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include suprapubic pain, painful urination (dysuria), frequency and urgency of urination despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection, on the other hand, are more systemic and include fever or Abdominal pain, flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely, the urine may appear Hematuria, bloody. Symptoms may be vague or non-specific at the extremities of age (i.e. in patients who are very young or old). The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes mellitus, diabetes, obesity, catheterisation, and famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Cell
White blood cells (scientific name leukocytes), also called immune cells or immunocytes, are cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign entities. White blood cells are generally larger than red blood cells. They include three main subtypes: granulocytes, lymphocytes and monocytes. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage ( myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. It consists of one part trimethoprim to five parts sulfamethoxazole. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) skin infections, travelers' diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, and cholera, among others. It is used both to treat and prevent pneumocystis pneumonia and toxoplasmosis in people with HIV/AIDS and other causes of immunosuppression. It can be given orally (swallowed by mouth) or intravenous infusion (slowly injected into a vein with an IV). Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 143rd most commonly prescribed medication in the Unit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit the air, soil, water, Hot spring, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria play a vital role in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients and the nitrogen fixation, fixation of nitrogen from the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of cadaver, dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
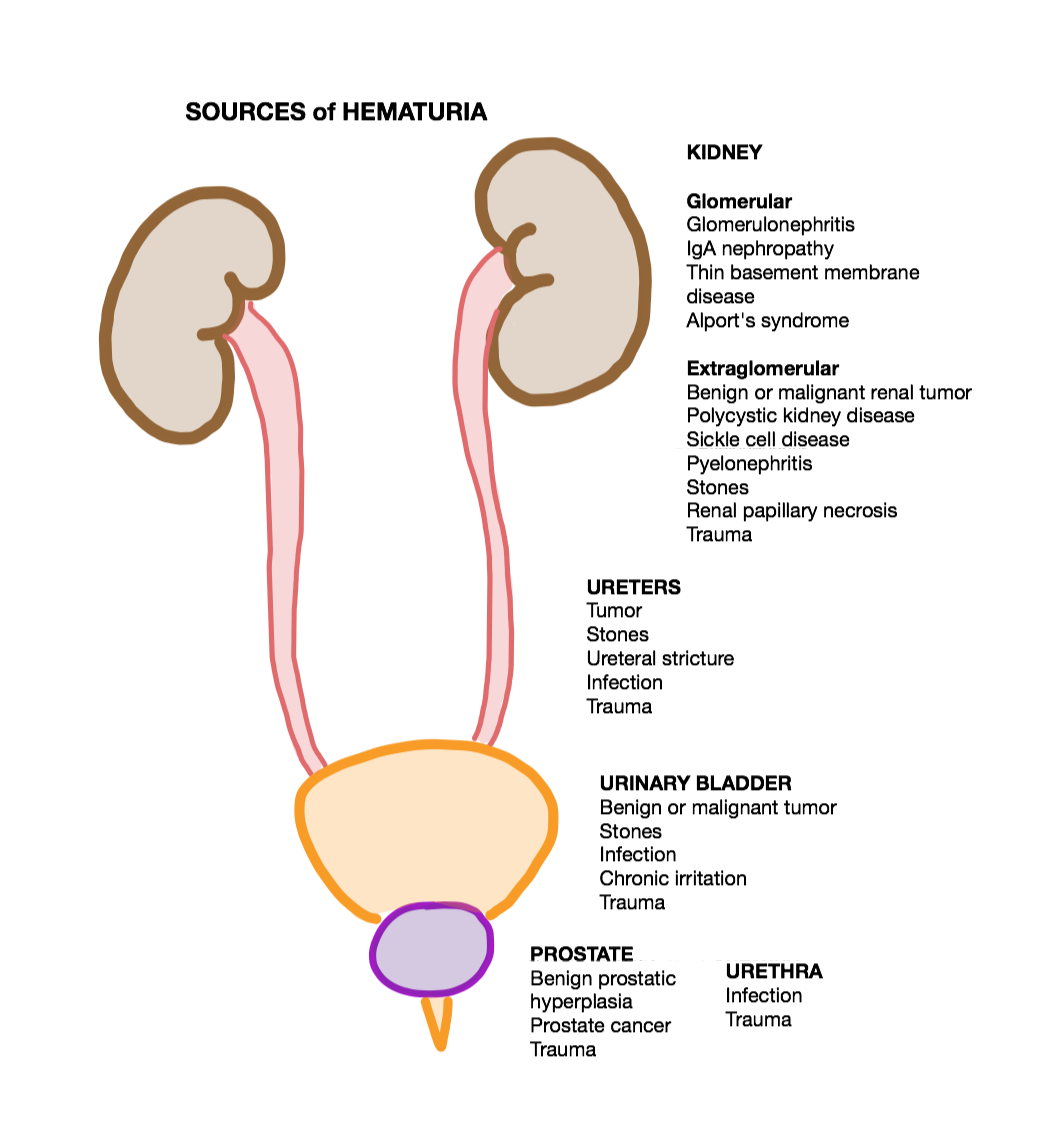
Hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with a microscope or laboratory test. Blood that enters and mixes with the urine can come from any location within the urinary system, including the kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra, and in men, the prostate. Common causes of hematuria include urinary tract infection (UTI), kidney stones, viral illness, trauma, bladder cancer, and exercise. These causes are grouped into glomerular and non-glomerular causes, depending on the involvement of the glomerulus of the kidney. But not all red urine is hematuria. Other substances such as certain medications and some foods (e.g. blackberries, beets, food dyes) can cause urine to appear red. Menstruation in women may also cause the appearance of hematuria and may result in a positive urine dips ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdominal Pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given that, approaching the examination of a person and planning of a differential diagnosis is extremely important. Common causes of pain in the abdomen include gastroenteritis and irritable bowel syndrome. About 15% of people have a more serious underlying condition such as appendicitis, leaking or ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm, diverticulitis, or ectopic pregnancy. In a third of cases, the exact cause is unclear. Signs and symptoms The onset of abdominal pain can be abrupt, quick, or gradual. Sudden onset pain happens in a split second. Rapidly onset pain starts mild and gets worse over the next few minutes. Pain that gradually intensifies only after several hours or even days has passed is referred to as gradual onset pain. One can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, set point in the hypothalamus. There is no single agreed-upon upper limit for normal temperature: sources use values ranging between in humans. The increase in set point triggers increased muscle tone, muscle contractions and causes a feeling of cold or chills. This results in greater heat production and efforts to conserve heat. When the set point temperature returns to normal, a person feels hot, becomes Flushing (physiology), flushed, and may begin to Perspiration, sweat. Rarely a fever may trigger a febrile seizure, with this being more common in young children. Fevers do not typically go higher than . A fever can be caused by many medical conditions ranging from non-serious to life-threatening. This includes viral infection, viral, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysuria
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination. It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency. Diagnosis The clinician should also look for physical findings of fever, rash, direct tenderness over the bladder area, and joint pain. Physical findings of increased temperature, increased pulse, low blood pressure in the presence of dysuria can indicate systemic infection. Urological obstruction due to stone or tumor can result in findings of hematuria, decreased urination, and bladder spasms. All these physical findings should be looked for carefully while obtaining history. History regarding recent sexual activity is crucial. Urinalysis is the most useful test to start the work up in a patient of dysuria. Urinalysis positive for nitrite carries a high predictive value of a positive urine culture. Also, urine dipstick showing leukocytes as equal predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprapubic
The hypogastrium (also called the hypogastric region or suprapubic region) is a region of the abdomen located below the umbilical region. Etymology The roots of the word ''hypogastrium'' mean "below the stomach The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ..."; the roots of ''suprapubic'' mean "above the pubic bone". Boundaries The upper limit is the umbilicus while the pubis bone constitutes its lower limit. The lateral boundaries are formed are drawing straight lines through the midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and symphisis pubis. References External links * Abdomen {{Anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
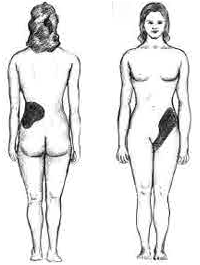
Pyelonephritis
Pyelonephritis is inflammation of the kidney, typically due to a bacterial infection. Symptoms most often include fever and flank tenderness. Other symptoms may include nausea, burning with urination, and frequent urination. Complications may include pus around the kidney, sepsis, or kidney failure. It is typically due to a bacterial infection, most commonly ''Escherichia coli''. Risk factors include sexual intercourse, prior urinary tract infections, diabetes, structural problems of the urinary tract, and spermicide use. The mechanism of infection is usually spread up the urinary tract. Less often infection occurs through the bloodstream. Diagnosis is typically based on symptoms and supported by urinalysis. If there is no improvement with treatment, medical imaging may be recommended. Pyelonephritis may be preventable by urination after sex and drinking sufficient fluids. Once present it is generally treated with antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin or ceftriaxone. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
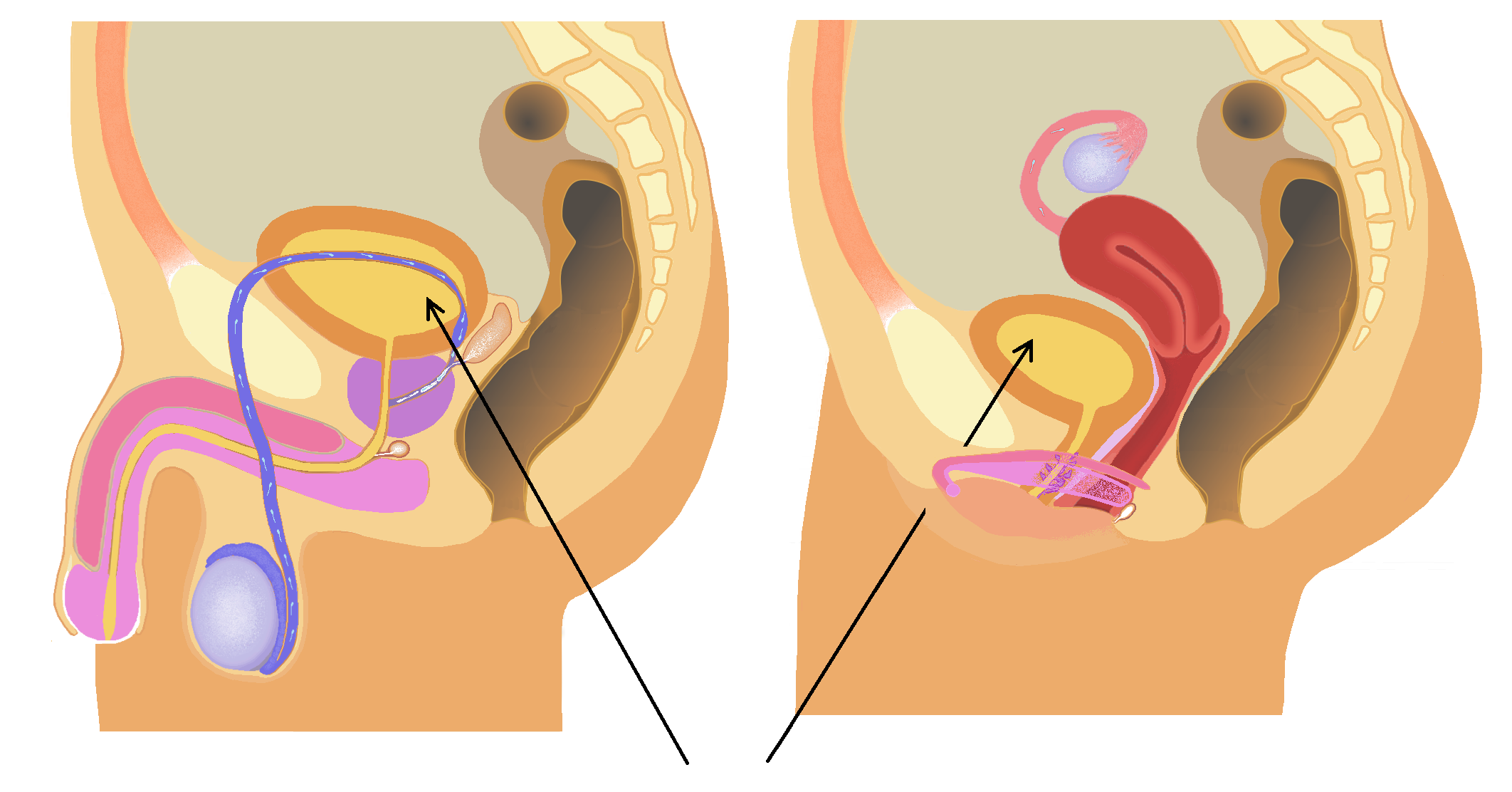
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (: urethras or urethrae) is the tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus, through which Placentalia, placental mammals Urination, urinate and Ejaculation, ejaculate. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The Internal urethral sphincter, internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, because it passes through the penis in males. Male In the human male, the urethra is on average long and opens at the end of the external urethral meatus. The urethra is divided into four parts in men, named after the lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward toward th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |