Endothermic Gas on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Endothermic
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. p. ...
gas is a gas that inhibits or reverses oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a ...
on the surfaces it is in contact with. This gas is the product of incomplete combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
in a controlled environment. An example mixture is hydrogen gas
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, a ...
(H2), nitrogen gas
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at sevent ...
(N2), and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
(CO). The hydrogen and carbon monoxide are reducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are commonly reducing agents include the Earth m ...
s, so they work together to shield surfaces from oxidation.
Endothermic gas is often used as a carrier gas for gas carburizing
Carburising, carburizing (chiefly American English), or carburisation is a heat treatment process in which iron or steel absorbs carbon while the metal is heated in the presence of a carbon-bearing material, such as charcoal or carbon monoxid ...
and carbonitriding. An endothermic gas generator could be used to supply heat to form an endothermic reaction
In thermochemistry, an endothermic process () is any thermodynamic process with an increase in the enthalpy (or internal energy ) of the system.Oxtoby, D. W; Gillis, H.P., Butler, L. J. (2015).''Principle of Modern Chemistry'', Brooks Cole. ...
.
Synthesised in the catalytic retort(s) of endothermic generators, the gas in the endothermic atmosphere is combined with an additive gas including natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon ...
, propane
Propane () is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula . It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as ...
(C3H8) or air and is then used to improve the surface chemistry work positioned in the furnace.

Purposes
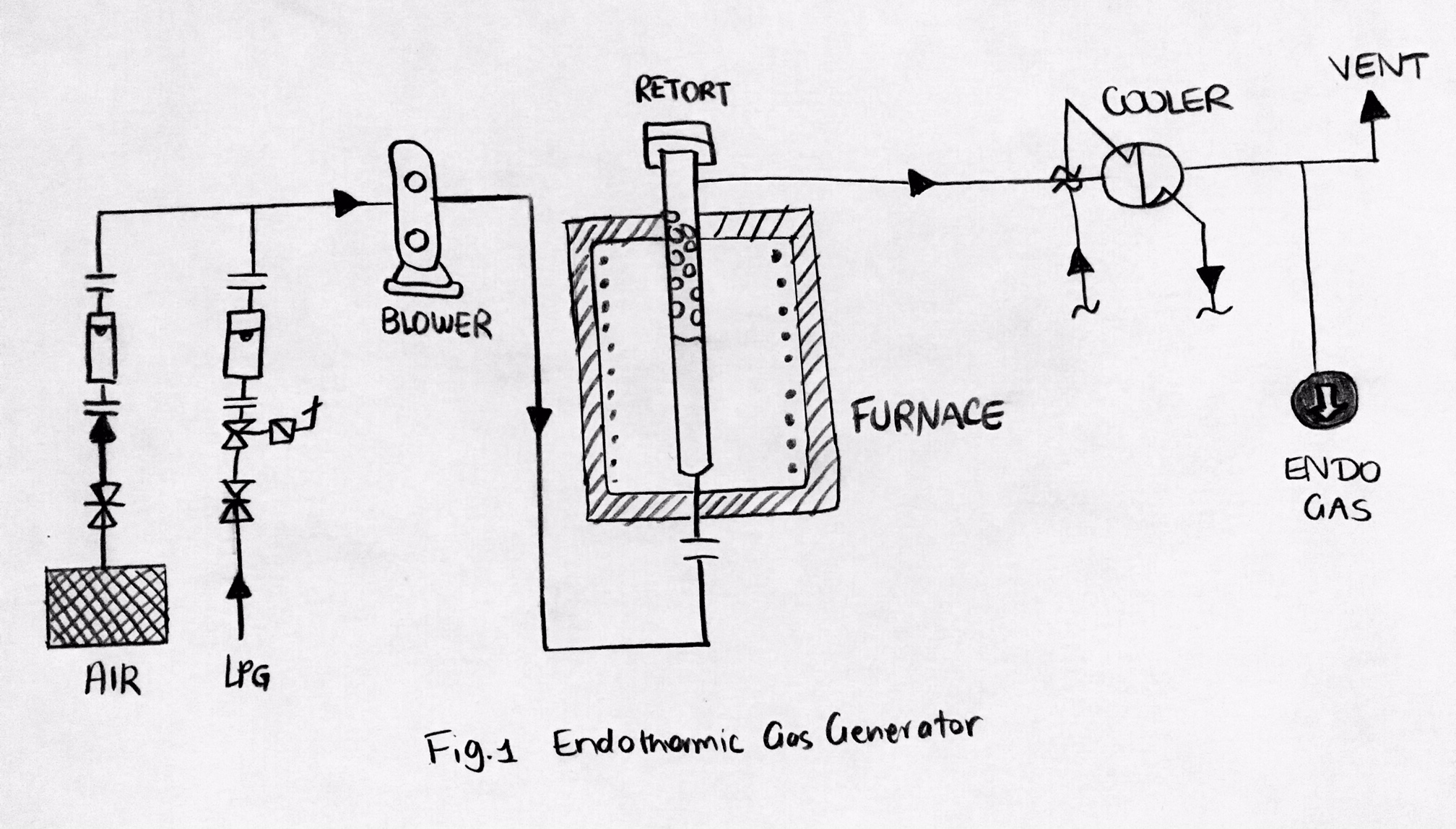
There are two common purposes of the atmospheres in the heat treating industry: # Protect the processed material from surface reactions (chemically inert) # Allow surface of processed material to change (chemically reactive)Principal components of a endothermic gas generator
Principal components of endothermic gas generators: # ''Heating chamber'' for supplying heat by electric heating elements ofcombustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combust ...
,
# Vertical ''cylindrical retorts'',
# Tiny, porous ''ceramic'' pieces that are saturated with nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow ...
, which acts as a catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
for the reaction,
# ''Cooling heat exchanger'' in order to cool the products of the reaction as quickly as possible so that it reaches a particular temperature which stops any further reaction,
# ''Control system'' which will help maintain the consistency of the temperature of the reaction which will help adjust the gas ratio, providing the wanted dew point.
Chemical composition
Chemistry of endothermic gas generators: * N2 (nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seve ...
) → 45.1% (volume)
* CO (carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide ( chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the si ...
) → 19.6% (volume)
* CO2 (carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
) → 0.4% (volume)
* H2 (hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
) → 34.6% (volume)
* CH4 (methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ear ...
) → 0.3% (volume)
* Dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will c ...
→ +20/+50
* Gas ratio → 2.6:1
Applications
Applications of endothermic gas generators: # Annealing: iron and steel #Brazing
Brazing is a metal-joining process in which two or more metal items are joined together by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, with the filler metal having a lower melting point than the adjoining metal.
Brazing differs from w ...
: copper and silver
# Carbon restoration: carburizing, carbonitriding, nitrocarburizing
# Neutral hardening: low, medium and high alloy carbon steels
# Normalizing: iron and steel
# Sintering
Clinker nodules produced by sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing ...
: powder metals
It is relatively simple to operate and maintain endothermic gas generators, however, maintenance such as the burnout process is often overlooked.{{cite web, last1=Pye, first1=David, title=Heat Treating Process, url=https://www.asminternational.org/documents/10192/1914052/htp00207p037.pdf/d711c8f7-b88a-4dd2-965a-24ed4b9b474a/HTP00207P037, accessdate=19 June 2018
See also
*Forming gas
Forming gas is a mixture of hydrogen (mole fraction varies) and nitrogen. It is sometimes called a "dissociated ammonia atmosphere" due to the reaction which generates it:
:2 NH3 → 3 H2 + N2
It can also be manufactured by thermal cra ...
References