Eiffel Tower on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Eiffel Tower ( ; ) is a wrought-iron
 The new version gained Eiffel's support: he bought the rights to the patent on the design which Koechlin, Nouguier, and Sauvestre had taken out, and the design was put on display at the Exhibition of Decorative Arts in the autumn of 1884 under the company name. On 30 March 1885, Eiffel presented his plans to the ; after discussing the technical problems and emphasising the practical uses of the tower, he finished his talk by saying the tower would symbolise
Little progress was made until 1886, when Jules Grévy was re-elected as president of France and
The new version gained Eiffel's support: he bought the rights to the patent on the design which Koechlin, Nouguier, and Sauvestre had taken out, and the design was put on display at the Exhibition of Decorative Arts in the autumn of 1884 under the company name. On 30 March 1885, Eiffel presented his plans to the ; after discussing the technical problems and emphasising the practical uses of the tower, he finished his talk by saying the tower would symbolise
Little progress was made until 1886, when Jules Grévy was re-elected as president of France and
 The proposed tower had been a subject of controversy, drawing criticism from those who did not believe it was feasible and those who objected on artistic grounds. Prior to the Eiffel Tower's construction, no structure had ever been constructed to a height of 300 m, or even 200 m for that matter, and many people believed it was impossible. These objections were an expression of a long-standing debate in France about the relationship between architecture and engineering. It came to a head as work began at the Champ de Mars: a "Committee of Three Hundred" (one member for each metre of the tower's height) was formed, led by the prominent architect Charles Garnier and including some of the most important figures of the arts, such as
The proposed tower had been a subject of controversy, drawing criticism from those who did not believe it was feasible and those who objected on artistic grounds. Prior to the Eiffel Tower's construction, no structure had ever been constructed to a height of 300 m, or even 200 m for that matter, and many people believed it was impossible. These objections were an expression of a long-standing debate in France about the relationship between architecture and engineering. It came to a head as work began at the Champ de Mars: a "Committee of Three Hundred" (one member for each metre of the tower's height) was formed, led by the prominent architect Charles Garnier and including some of the most important figures of the arts, such as  Gustave Eiffel responded to these criticisms by comparing his tower to the
Gustave Eiffel responded to these criticisms by comparing his tower to the
File:Construction tour eiffel.JPG, 18 July 1887:
The start of the erection of the metalwork File:Construction tour eiffel2.JPG, 7 December 1887:
Construction of the legs with scaffolding File:Construction tour eiffel3.JPG, 20 March 1888:
Completion of the first level File:Construction tour eiffel4.JPG, 15 May 1888:
Start of construction on the second stage File:Construction tour eiffel5.JPG,
Completion of the second level File:Construction tour eiffel6.JPG, 26 December 1888:
Construction of the upper stage File:Construction tour eiffel7.JPG,
Construction of the
 On the second level, the French newspaper ''Le Figaro'' had an office and a printing press, where a special souvenir edition, ''Le Figaro de la Tour'', was made.
At the top, there was a post office where visitors could send letters and postcards as a memento of their visit.
On the second level, the French newspaper ''Le Figaro'' had an office and a printing press, where a special souvenir edition, ''Le Figaro de la Tour'', was made.
At the top, there was a post office where visitors could send letters and postcards as a memento of their visit.
 On 19 October 1901,
On 19 October 1901,  On two separate but related occasions in 1925, the con artist Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal. A year later, in February 1926, pilot Leon Collet was killed trying to fly under the tower. His aircraft became entangled in an aerial belonging to a wireless station. A bust of Gustave Eiffel by
On two separate but related occasions in 1925, the con artist Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal. A year later, in February 1926, pilot Leon Collet was killed trying to fly under the tower. His aircraft became entangled in an aerial belonging to a wireless station. A bust of Gustave Eiffel by  For its "Countdown to the Year 2000" celebration on 31 December 1999, flashing lights and high-powered
For its "Countdown to the Year 2000" celebration on 31 December 1999, flashing lights and high-powered
 The puddle iron (wrought iron) of the Eiffel Tower weighs 7,300
The puddle iron (wrought iron) of the Eiffel Tower weighs 7,300
 When it was built, Eiffel was accused of trying to create something artistic with no regard to the principles of engineering. However, Eiffel and his team were experienced bridge builders. In an interview with the newspaper ''
When it was built, Eiffel was accused of trying to create something artistic with no regard to the principles of engineering. However, Eiffel and his team were experienced bridge builders. In an interview with the newspaper ''
 The four columns of the tower each house access stairs and lifts to the first two floors, while at the south column only the lift to the second floor restaurant is publicly accessible.
The four columns of the tower each house access stairs and lifts to the first two floors, while at the south column only the lift to the second floor restaurant is publicly accessible.
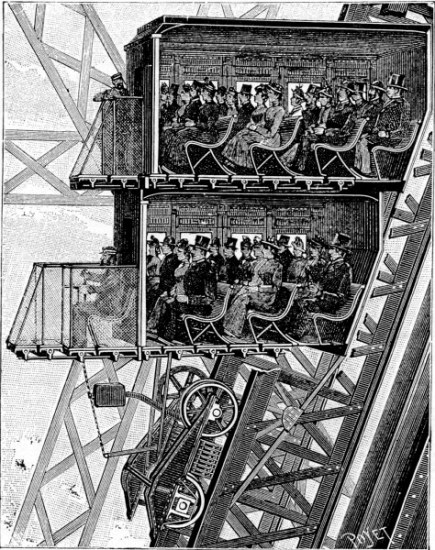 Installing lifts to the second level was more of a challenge because a straight track was impossible. No French company wanted to undertake the work. The European branch of Otis Brothers & Company submitted a proposal, but this was rejected: the fair's charter ruled out the use of any foreign material in the construction of the tower. The deadline for bids was extended, but still no French companies put themselves forward, and eventually the contract was given to Otis in July 1887.Vogel, pp. 23–24. Otis were confident they would eventually be given the contract and had already started creating designs.
The car was divided into two superimposed compartments, each holding 25 passengers, with the lift operator occupying an exterior platform on the first level. Motive power was provided by an inclined hydraulic ram long and in diameter in the tower leg with a stroke of : this moved a carriage carrying six sheaves. Five fixed sheaves were mounted higher up the leg, producing an arrangement similar to a
Installing lifts to the second level was more of a challenge because a straight track was impossible. No French company wanted to undertake the work. The European branch of Otis Brothers & Company submitted a proposal, but this was rejected: the fair's charter ruled out the use of any foreign material in the construction of the tower. The deadline for bids was extended, but still no French companies put themselves forward, and eventually the contract was given to Otis in July 1887.Vogel, pp. 23–24. Otis were confident they would eventually be given the contract and had already started creating designs.
The car was divided into two superimposed compartments, each holding 25 passengers, with the lift operator occupying an exterior platform on the first level. Motive power was provided by an inclined hydraulic ram long and in diameter in the tower leg with a stroke of : this moved a carriage carrying six sheaves. Five fixed sheaves were mounted higher up the leg, producing an arrangement similar to a
 Gustave Eiffel engraved on the building of the tower the names of 72 French scientists, engineers and mathematicians as a recognition of their contributions. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protest. At the beginning of the 20th century, the engravings were painted over, but they were restored in 1986–87 by the , a company operating the tower.
Gustave Eiffel engraved on the building of the tower the names of 72 French scientists, engineers and mathematicians as a recognition of their contributions. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protest. At the beginning of the 20th century, the engravings were painted over, but they were restored in 1986–87 by the , a company operating the tower.
 The tower is painted in three shades: lighter at the top, getting progressively darker towards the bottom to complement the Parisian sky. It was originally reddish brown; this changed in 1968 to a bronze colour known as "Eiffel Tower Brown". In what is expected to be a temporary change, the tower was painted
The tower is painted in three shades: lighter at the top, getting progressively darker towards the bottom to complement the Parisian sky. It was originally reddish brown; this changed in 1968 to a bronze colour known as "Eiffel Tower Brown". In what is expected to be a temporary change, the tower was painted

 More than 300 million people have visited the tower since it was completed in 1889. In 2015, there were 6.91 million visitors. The tower is the most-visited paid monument in the world. An average of 25,000 people ascend the tower every day (which can result in long queues).
More than 300 million people have visited the tower since it was completed in 1889. In 2015, there were 6.91 million visitors. The tower is the most-visited paid monument in the world. An average of 25,000 people ascend the tower every day (which can result in long queues).
 The tower and its image have been in the
The tower and its image have been in the
lattice tower
A lattice tower or truss tower is a freestanding vertical latticework, framework tower. This construction is widely used in transmission towers carrying high-voltage electric power lines, in radio masts and towers (a self-radiating tower or as a ...
on the Champ de Mars
Champ, CHAMP or The Champ may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional characters
* Champ (cartoon character), an animated dog introduced in 1960
* The Champ, played on radio and created by Jake Edwards (radio personality), Jake Edwards
* Champ ...
in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel
Alexandre Gustave Eiffel ( , ; Bonickhausen dit Eiffel; 15 December 1832 – 27 December 1923) was a French civil engineer. A graduate of École Centrale des Arts et Manufactures, he made his name with various bridges for the French railway net ...
, whose company designed and built the tower from 1887 to 1889.
Locally nicknamed "''La dame de fer''" (French for "Iron Lady"), it was constructed as the centrepiece of the 1889 World's Fair, and to crown the centennial anniversary of the French Revolution. Although initially criticised by some of France's leading artists and intellectuals for its design, it has since become a global cultural icon
A cultural icon is a person or an cultural artifact, artifact that is identified by members of a culture as representative of that culture. The process of identification is subjective, and "icons" are judged by the extent to which they can be seen ...
of France and one of the most recognisable structures in the world. The tower received 5,889,000 visitors in 2022. The Eiffel Tower is the most visited monument with an entrance fee in the world: 6.91 million people ascended it in 2015. It was designated a in 1964, and was named part of a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
("Paris, Banks of the Seine") in 1991.
The tower is tall, about the same height as an 81- building, and the tallest structure in Paris. Its base is square, measuring on each side. During its construction, the Eiffel Tower surpassed the Washington Monument
The Washington Monument is an obelisk on the National Mall in Washington, D.C., built to commemorate George Washington, a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father of the United States, victorious commander-in-chief of the Continen ...
to become the tallest human-made structure in the world, a title it held for 41 years until the Chrysler Building
The Chrysler Building is a , Art Deco skyscraper in the East Midtown neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, United States. Located at the intersection of 42nd Street and Lexington Avenue, it is the tallest brick building in the world wit ...
in New York City was finished in 1930. It was the first structure in the world to surpass both the 200 meters and 300 meters mark in height. Due to the addition of a broadcasting aerial at the top of the tower in 1957, it is now taller than the Chrysler Building by . Excluding transmitters, the Eiffel Tower is the second tallest free-standing structure in France after the Millau Viaduct
The Millau Viaduct (, ) is a multispan cable-stayed bridge completed in 2004 across the Canyon, gorge valley of the Tarn (river), Tarn near (west of) Millau in the Aveyron department in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Region, i ...
.
The tower has three levels for visitors, with restaurants on the first and second levels. The top level's upper platform is above the ground—the highest public observation deck in the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
. Tickets can be purchased to ascend by stairs or lift to the first and second levels. The climb from ground level to the first level is over 300 steps, as is the climb from the first level to the second, making the entire ascent a 600-step climb. Although there is a staircase to the top level, it is usually accessible only by lift. On this top, third level, is a private apartment built for Gustave Eiffel, who decorated it with furniture made by Jean Lachaise and invited friends such as Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, ...
.
History
Origin
The design of the Eiffel Tower is attributed to Maurice Koechlin and Émile Nouguier, two senior engineers working for the Compagnie des Établissements Eiffel. It was envisaged after discussion about a suitable centrepiece for the proposed 1889 Exposition Universelle, aworld's fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition, is a large global exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specific site for a perio ...
to celebrate the centennial of the French Revolution. In May 1884, working at home, Koechlin made a sketch of their idea, described by him as "a great pylon, consisting of four lattice girders standing apart at the base and coming together at the top, joined together by metal truss
A truss is an assembly of ''members'' such as Beam (structure), beams, connected by ''nodes'', that creates a rigid structure.
In engineering, a truss is a structure that "consists of two-force members only, where the members are organized so ...
es at regular intervals". Eiffel initially showed little enthusiasm, but he did approve further study, and the two engineers then asked Stephen Sauvestre, the head of the company's architectural department, to contribute to the design. Sauvestre added decorative arches to the base of the tower, a glass pavilion to the first level, and other embellishments.
 The new version gained Eiffel's support: he bought the rights to the patent on the design which Koechlin, Nouguier, and Sauvestre had taken out, and the design was put on display at the Exhibition of Decorative Arts in the autumn of 1884 under the company name. On 30 March 1885, Eiffel presented his plans to the ; after discussing the technical problems and emphasising the practical uses of the tower, he finished his talk by saying the tower would symbolise
Little progress was made until 1886, when Jules Grévy was re-elected as president of France and
The new version gained Eiffel's support: he bought the rights to the patent on the design which Koechlin, Nouguier, and Sauvestre had taken out, and the design was put on display at the Exhibition of Decorative Arts in the autumn of 1884 under the company name. On 30 March 1885, Eiffel presented his plans to the ; after discussing the technical problems and emphasising the practical uses of the tower, he finished his talk by saying the tower would symbolise
Little progress was made until 1886, when Jules Grévy was re-elected as president of France and Édouard Lockroy
Édouard Lockroy (18 July 183822 November 1913) was a French politician born in Paris, the son of Joseph Philippe Simon (1803–1891), an actor and dramatist who took the name of Lockroy, and of Antoinette Stéphanie Lockroy who wrote two books ...
was appointed as minister for trade. A budget for the exposition was passed and, on 1 May, Lockroy announced an alteration to the terms of the open competition being held for a centrepiece to the exposition, which effectively made the selection of Eiffel's design a foregone conclusion, as entries had to include a study for a four-sided metal tower on the Champ de Mars. (A 300-metre tower was then considered a herculean engineering effort.) On 12 May, a commission was set up to examine Eiffel's scheme and its rivals, which, a month later, decided that all the proposals except Eiffel's were either impractical or lacking in details.
After some debate about the exact location of the tower, a contract was signed on 8 January 1887. Eiffel signed it acting in his own capacity rather than as the representative of his company, the contract granting him 1.5 million francs
The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription ''francorum rex'' ( King of the Franks) used on early French coins and until the 18th centur ...
toward the construction costs: less than a quarter of the estimated 6.5 million francs. Eiffel was to receive all income from the commercial exploitation of the tower during the exhibition and for the next 20 years. He later established a separate company to manage the tower, putting up half the necessary capital himself.
A French bank, the '' Crédit Industriel et Commercial'' (CIC), helped finance the construction of the Eiffel Tower. During the period of the tower's construction, the CIC was acquiring funds from predatory loans to the National Bank of Haiti, some of which went towards the financing of the tower. These loans were connected to an indemnity controversy that saw France force Haiti's government to financially compensate French slaveowners for lost income as a result of the Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution ( or ; ) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolution was the only known Slave rebellion, slave up ...
, and required Haiti to pay the CIC and its partner nearly half of all taxes collected on exports, "effectively choking off the nation's primary source of income". According to ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''NYT'') is an American daily newspaper based in New York City. ''The New York Times'' covers domestic, national, and international news, and publishes opinion pieces, investigative reports, and reviews. As one of ...
'', " ta time when the ICwas helping finance one of the world's best-known landmarks, the Eiffel Tower, as a monument to French liberty, it was choking Haiti's economy, taking much of the young nation's income back to Paris and impairing its ability to start schools, hospitals and the other building blocks of an independent country."
Artists' protest
 The proposed tower had been a subject of controversy, drawing criticism from those who did not believe it was feasible and those who objected on artistic grounds. Prior to the Eiffel Tower's construction, no structure had ever been constructed to a height of 300 m, or even 200 m for that matter, and many people believed it was impossible. These objections were an expression of a long-standing debate in France about the relationship between architecture and engineering. It came to a head as work began at the Champ de Mars: a "Committee of Three Hundred" (one member for each metre of the tower's height) was formed, led by the prominent architect Charles Garnier and including some of the most important figures of the arts, such as
The proposed tower had been a subject of controversy, drawing criticism from those who did not believe it was feasible and those who objected on artistic grounds. Prior to the Eiffel Tower's construction, no structure had ever been constructed to a height of 300 m, or even 200 m for that matter, and many people believed it was impossible. These objections were an expression of a long-standing debate in France about the relationship between architecture and engineering. It came to a head as work began at the Champ de Mars: a "Committee of Three Hundred" (one member for each metre of the tower's height) was formed, led by the prominent architect Charles Garnier and including some of the most important figures of the arts, such as William-Adolphe Bouguereau
William-Adolphe Bouguereau (; 30 November 1825 – 19 August 1905) was a French Academic art, academic painter. In his realistic genre paintings, he used mythological themes, making modern interpretations of Classicism, classical subjects, with a ...
, Guy de Maupassant, Charles Gounod
Charles-François Gounod (; ; 17 June 181818 October 1893), usually known as Charles Gounod, was a French composer. He wrote twelve operas, of which the most popular has always been ''Faust (opera), Faust'' (1859); his ''Roméo et Juliette'' (18 ...
and Jules Massenet
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet (; 12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic music, Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are ''Manon'' (1884 ...
. A petition called "Artists against the Eiffel Tower" was sent to the Minister of Works and Commissioner for the Exposition, Adolphe Alphand, and it was published by ''Le Temps
' (, ) is a Swiss French-language daily newspaper published in Berliner format in Geneva by Le Temps SA. The paper was launched in 1998, formed out of the merger of two other newspapers, and (the former being a merger of two other papers), ...
'' on 14 February 1887:
Egyptian pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Most were built as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old and Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom periods. At least 138 identi ...
: "My tower will be the tallest edifice ever erected by man. Will it not also be grandiose in its way? And why would something admirable in Egypt become hideous and ridiculous in Paris?" These criticisms were also dealt with by Édouard Lockroy in a letter of support written to Alphand, sardonically saying, "Judging by the stately swell of the rhythms, the beauty of the metaphors, the elegance of its delicate and precise style, one can tell this protest is the result of collaboration of the most famous writers and poets of our time", and he explained that the protest was irrelevant since the project had been decided upon months before, and construction on the tower was already under way.
Garnier was a member of the Tower Commission that had examined the various proposals, and had raised no objection. Eiffel pointed out to a journalist that it was premature to judge the effect of the tower solely on the basis of the drawings, that the Champ de Mars was distant enough from the monuments mentioned in the protest for there to be little risk of the tower overwhelming them, and putting the aesthetic argument for the tower: "Do not the laws of natural forces always conform to the secret laws of harmony?"
Some of the protesters changed their minds when the tower was built; others remained unconvinced. Guy de Maupassant supposedly ate lunch in the tower's restaurant every day because it was the one place in Paris where the tower was not visible.
By 1918, it had become a symbol of Paris and of France after Guillaume Apollinaire wrote a nationalist poem in the shape of the tower (a calligram
A calligram is a set of words arranged in such a way that it forms a thematically related image. It can be a poem, a phrase, a portion of scripture, or a single word; the visual arrangement can rely on certain use of the typeface, calligraphy o ...
) to express his feelings about the war against Germany. Today, it is widely considered to be a remarkable piece of structural art
Certain works of structural engineering design are also works of structural art. Such works can be classified as structural art when they attain excellence in the three areas of efficiency, economy, and elegance, as defined by Prof. David P. Bil ...
, and is often featured in films and literature.
Construction
Work on the foundations started on 28 January 1887. Those for the east and south legs were straightforward, with each leg resting on four concrete slabs, one for each of the principal girders of each leg. The west and north legs, being closer to the riverSeine
The Seine ( , ) is a river in northern France. Its drainage basin is in the Paris Basin (a geological relative lowland) covering most of northern France. It rises at Source-Seine, northwest of Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plat ...
, were more complicated: each slab needed two piles installed by using compressed-air caissons long and in diameter driven to a depth of to support the concrete slabs, which were thick. Each of these slabs supported a block of limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
with an inclined top to bear a supporting shoe for the ironwork.
Each shoe was anchored to the stonework by a pair of bolts in diameter and long. The foundations were completed on 30 June, and the erection of the ironwork began. The visible work on-site was complemented by the enormous amount of exacting preparatory work that took place behind the scenes: the drawing office produced 1,700 general drawings and 3,629 detailed drawings of the 18,038 different parts needed. The task of drawing the components was complicated by the complex angles involved in the design and the degree of precision required: the position of rivet holes was specified to within and angles worked out to one second of arc
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a tu ...
. The finished components, some already riveted together into sub-assemblies, arrived on horse-drawn carts from a factory in the nearby Parisian suburb of Levallois-Perret
Levallois-Perret () is a Communes of France, commune in the Hauts-de-Seine Departments of France, department and Île-de-France Regions of France, region of north-central France. It lies on the right bank of the Seine, some from the Kilometre z ...
and were first bolted together, with the bolts being replaced with rivets as construction progressed. No drilling or shaping was done on site: if any part did not fit, it was sent back to the factory for alteration. In all, 18,038 pieces were joined using 2.5 million rivets.
At first, the legs were constructed as cantilever
A cantilever is a rigid structural element that extends horizontally and is unsupported at one end. Typically it extends from a flat vertical surface such as a wall, to which it must be firmly attached. Like other structural elements, a cantilev ...
s, but about halfway to the first level construction was paused to create a substantial timber scaffold. This renewed concerns about the structural integrity of the tower, and sensational headlines such as "Eiffel Suicide!" and "Gustave Eiffel Has Gone Mad: He Has Been Confined in an Asylum" appeared in the tabloid press. Multiple famous artists of that time, Charles Garnier and Alexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (born Alexandre Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie, 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas , was a French novelist and playwright.
His works have been translated into many languages and he is one of the mos ...
, thought poorly of the newly made tower. Charles Garnier thought it was a "truly tragic street lamp". Alexandre Dumas said that it was like "Odius shadow of the odious column built of rivets and iron plates extending like a black blot". There were multiple protests over the style and the reasoning of placing it in the middle of Paris. At this stage, a small "creeper" crane designed to move up the tower was installed in each leg. They made use of the guides for the lifts which were to be fitted in the four legs. The critical stage of joining the legs at the first level was completed by the end of March 1888. Although the metalwork had been prepared with the utmost attention to detail, provision had been made to carry out small adjustments to precisely align the legs; hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
jacks were fitted to the shoes at the base of each leg, capable of exerting a force of 800 tonnes, and the legs were intentionally constructed at a slightly steeper angle than necessary, being supported by sandboxes on the scaffold. Although construction involved 300 on-site employees, due to Eiffel's safety precautions and the use of movable gangways, guardrails and screens, only one person died.
The start of the erection of the metalwork File:Construction tour eiffel2.JPG, 7 December 1887:
Construction of the legs with scaffolding File:Construction tour eiffel3.JPG, 20 March 1888:
Completion of the first level File:Construction tour eiffel4.JPG, 15 May 1888:
Start of construction on the second stage File:Construction tour eiffel5.JPG,
Completion of the second level File:Construction tour eiffel6.JPG, 26 December 1888:
Construction of the upper stage File:Construction tour eiffel7.JPG,
Construction of the
cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout.
The word derives, via Ital ...
Inauguration and the 1889 exposition
The main structural work was completed at the end of March 1889 and, on 31 March, Eiffel celebrated by leading a group of government officials, accompanied by representatives of the press, to the top of the tower. Because the lifts were not yet in operation, the ascent was made by foot, and took over an hour, with Eiffel stopping frequently to explain various features. Most of the party chose to stop at the lower levels, but a few, including the structural engineer, Émile Nouguier, the head of construction, Jean Compagnon, the President of the City Council, and reporters from ''Le Figaro
() is a French daily morning newspaper founded in 1826. It was named after Figaro, a character in several plays by polymath Pierre Beaumarchais, Beaumarchais (1732–1799): ''Le Barbier de Séville'', ''The Guilty Mother, La Mère coupable'', ...
'' and '' Le Monde Illustré'', completed the ascent. At 2:35 pm, Eiffel hoisted a large Tricolour to the accompaniment of a 25-gun salute fired at the first level.
There was still work to be done, particularly on the lifts and facilities, and the tower was not opened to the public until nine days after the opening of the exposition on 6 May; even then, the lifts had not been completed. The tower was an instant success with the public, and nearly 30,000 visitors made the 1,710-step climb to the top before the lifts entered service on 26 May. Tickets cost 2 francs for the first level, 3 for the second, and 5 for the top, with half-price admission on Sundays, and by the end of the exhibition there had been 1,896,987 visitors.
After dark, the tower was lit by hundreds of gas lamps, and a beacon sent out three beams of red, white and blue light. Two searchlights mounted on a circular rail were used to illuminate various buildings of the exposition. The daily opening and closing of the exposition were announced by a cannon at the top.
 On the second level, the French newspaper ''Le Figaro'' had an office and a printing press, where a special souvenir edition, ''Le Figaro de la Tour'', was made.
At the top, there was a post office where visitors could send letters and postcards as a memento of their visit.
On the second level, the French newspaper ''Le Figaro'' had an office and a printing press, where a special souvenir edition, ''Le Figaro de la Tour'', was made.
At the top, there was a post office where visitors could send letters and postcards as a memento of their visit. Graffiti
Graffiti (singular ''graffiti'', or ''graffito'' only in graffiti archeology) is writing or drawings made on a wall or other surface, usually without permission and within public view. Graffiti ranges from simple written "monikers" to elabor ...
sts were also catered for: sheets of paper were mounted on the walls each day for visitors to record their impressions of the tower. Gustave Eiffel described the collection of responses as "truly curious".
Famous visitors to the tower included the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
, Sarah Bernhardt
Sarah Bernhardt (; born Henriette-Rosine Bernard; 22 October 1844 – 26 March 1923) was a French stage actress who starred in some of the most popular French plays of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, including by Alexandre Dumas fils, ...
, "Buffalo Bill" Cody (his Wild West show was an attraction at the exposition) and Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison (February11, 1847October18, 1931) was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, ...
. Eiffel invited Edison to his private apartment at the top of the tower, where Edison presented him with one of his phonograph
A phonograph, later called a gramophone, and since the 1940s a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogue reproduction of sound. The sound vibration Waveform, waveforms are recorded as correspond ...
s, a new invention and one of the many highlights of the exposition. Edison signed the guestbook with this message on September 10, 1889:
Eiffel made use of his apartment at the top of the tower to carry out meteorological observations, and also used the tower to perform experiments on the action of air resistance on falling bodies.
Subsequent events
Eiffel had a permit for the tower to stand for 20 years. It was to be dismantled in 1909, when its ownership would revert to the City of Paris. The city had planned to tear it down (part of the original contest rules for designing a tower was that it should be easy to dismantle) but as the tower proved to be valuable for many innovations in the early 20th century, particularlyradio telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is the transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies fo ...
, it was allowed to remain after the expiry of the permit, and from 1910 it also became part of the International Time Service.
For the 1900 ''Exposition Universelle'', the lifts in the east and west legs were replaced by lifts running as far as the second level constructed by the French firm Fives-Lille. These had a compensating mechanism to keep the floor level as the angle of ascent changed at the first level, and were driven by a similar hydraulic mechanism as the Otis lifts, although this was situated at the base of the tower. Hydraulic pressure was provided by pressurised accumulators located near this mechanism. At the same time the lift in the north pillar was removed and replaced by a staircase to the first level. The layout of both first and second levels was modified, with the space available for visitors on the second level. The original lift in the south pillar was removed 13 years later.
 On 19 October 1901,
On 19 October 1901, Alberto Santos-Dumont
Alberto Santos-Dumont (self-stylised as Alberto Santos=Dumont; 20 July 1873 – 23 July 1932) was a Brazilian aeronaut, sportsman, inventor, and one of the few people to have contributed significantly to the early development of both lighter-t ...
, flying his No.6 airship
An airship, dirigible balloon or dirigible is a type of aerostat (lighter-than-air) aircraft that can navigate through the air flying powered aircraft, under its own power. Aerostats use buoyancy from a lifting gas that is less dense than the ...
, won a 100,000-franc prize offered by Henri Deutsch de la Meurthe for the first person to make a flight from St. Cloud to the Eiffel Tower and back in less than half an hour.
From 1910, the astronomical clocks
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanism (technology), mechanisms and dial (measurement), dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, a ...
of the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (, ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centres in the world. Its historic building is on the Left Ban ...
sent the time to sea daily through the Eiffel Tower within a radius of 5 000 km. The development of wireless telegraphy
Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is the transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using electrical cable, cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimenta ...
allowed unifying Universal Time
Universal Time (UT or UT1) is a time standard based on Earth's rotation. While originally it was mean solar time at 0° longitude, precise measurements of the Sun are difficult. Therefore, UT1 is computed from a measure of the Earth's angle wi ...
. On 9 March 1911, France adopted Greenwich Mean Time
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the local mean time at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being ...
by law. However, the law did not refer to Greenwich Prime Meridian, but to the local mean time
Local mean time (LMT) is a form of solar time that corrects the variations of local apparent time, forming a uniform time scale at a specific longitude. This measurement of time was used for everyday use during the 19th century before time zones ...
of Paris delayed by 9 minutes
Minutes, also known as minutes of meeting, protocols or, informally, notes, are the instant written record of a meeting or hearing. They typically describe the events of the meeting and may include a list of attendees, a statement of the activit ...
and 21 seconds
The second (symbol: s) is a unit of time derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes, and finally to 60 seconds each (24 × 60 × 60 = 86400). The current and formal definition in the International System of ...
. In 1912, following a report by Gustave Ferrié, the Bureau des Longitudes
__NOTOC__
The ''Bureau des Longitudes'' () is a French scientific institution, founded by decree of 25 June 1795 and charged with the improvement of nautical navigation, standardisation of time-keeping, geodesy and astronomical observation. Durin ...
organized at the Paris Observatory a ''Conférence internationale de l'heure radiotélégraphique'' (International Radiotelegraph Time Conference). The International Time Bureau
The International Time Bureau (, abbreviated BIH), seated at the Paris Observatory, was the international bureau responsible for combining different measurements of Universal Time.
The bureau also played an important role in the research of tim ...
was created and installed in the premises of the Paris Observatory. However, due to World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the International Convention was never ratified. In 1919, the existence of the International Time Bureau was formalized under the authority of an International Time Commission, under the aegis of the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; , UAI) is an international non-governmental organization (INGO) with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach, education, and developmen ...
, created by Benjamin Baillaud
Édouard Benjamin Baillaud (; 14 February 1848 – 8 July 1934) was a French astronomer.
Biography
Born in Chalon-sur-Saône, Baillaud studied at the École Normale Supérieure (1866-1869) and the University of Paris. He worked as an assi ...
.
In 1910, Father
A father is the male parent of a child. Besides the paternal bonds of a father to his children, the father may have a parental, legal, and social relationship with the child that carries with it certain rights and obligations. A biological fat ...
Theodor Wulf measured radiant energy
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calcul ...
at the top and bottom of the tower. He found more at the top than expected, incidentally discovering what are known today as cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s.Theodor Wulf. ''Physikalische Zeitschrift''. Contains results of the four-day-long observation done by Theodor Wulf at the top of the Eiffel Tower in 1910. Two years later, on 4 February 1912, Austrian tailor Franz Reichelt died after jumping from the first level of the tower (a height of 57 m) to demonstrate his parachute
A parachute is a device designed to slow an object's descent through an atmosphere by creating Drag (physics), drag or aerodynamic Lift (force), lift. It is primarily used to safely support people exiting aircraft at height, but also serves va ...
design. In 1914, at the outbreak of World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, a radio transmitter located in the tower jammed German radio communications, seriously hindering their advance on Paris and contributing to the Allied victory at the First Battle of the Marne
The First Battle of the Marne or known in France as the Miracle on the Marne () was a battle of the First World War fought from the 5th to the 12th September 1914. The German army invaded France with a plan for winning the war in 40 days by oc ...
.
During World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, the Eiffel Tower's wireless station played a crucial role in intercepting enemy communications from Berlin. In 1914, French forces successfully launched a counter-attack during the Battle of the Marne after gaining critical intelligence on the German Army's movements. In 1917, the station intercepted a coded message between Germany and Spain that referenced 'Operative H-21.' This information contributed to the arrest, conviction, and execution of Mata Hari
Margaretha Geertruida MacLeod (, ; 7 August 187615 October 1917), better known by the stage name Mata Hari ( , ; , ), was a Dutch Stripper, exotic dancer and courtesan who was convicted of being a spy for German Empire, Germany during World War ...
, the famous spy accused of working for Germany.
From 1925 to 1934, illuminated signs for Citroën
Citroën ()The double-dot diacritic over the 'e' is a diaeresis () indicating the two vowels are sounded separately, and not as a diphthong. is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded on 4 June 19 ...
adorned three of the tower's sides, making it the tallest advertising space in the world at the time. In April 1935, the tower was used to make experimental low-resolution television transmissions, using a shortwave
Shortwave radio is radio transmission using radio frequencies in the shortwave bands (SW). There is no official definition of the band range, but it always includes all of the high frequency band (HF), which extends from 3 to 30 MHz (app ...
transmitter of 200 watts power. On 17 November, an improved 180-line transmitter was installed.
 On two separate but related occasions in 1925, the con artist Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal. A year later, in February 1926, pilot Leon Collet was killed trying to fly under the tower. His aircraft became entangled in an aerial belonging to a wireless station. A bust of Gustave Eiffel by
On two separate but related occasions in 1925, the con artist Victor Lustig "sold" the tower for scrap metal. A year later, in February 1926, pilot Leon Collet was killed trying to fly under the tower. His aircraft became entangled in an aerial belonging to a wireless station. A bust of Gustave Eiffel by Antoine Bourdelle
Antoine Bourdelle (; 30 October 1861 – 1 October 1929), born Émile Antoine Bordelles, was an influential and prolific French sculptor and teacher. He was a student of Auguste Rodin, a teacher of Giacometti and Henri Matisse, and an important ...
was unveiled at the base of the north leg on 2 May 1929. In 1930, the tower lost the title of the world's tallest structure when the Chrysler Building
The Chrysler Building is a , Art Deco skyscraper in the East Midtown neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, United States. Located at the intersection of 42nd Street and Lexington Avenue, it is the tallest brick building in the world wit ...
in New York City was completed. In 1938, the decorative arcade around the first level was removed.
Upon the German occupation of Paris in 1940, the lift cables were cut by the French. The tower was restricted to German visitors during the occupation and the lifts were not repaired until 1946.Harriss, 1976 pp. 180–84. In 1940, German soldiers had to climb the tower to hoist a swastika-centred Reichskriegsflagge, but the flag was so large it blew away just a few hours later, and was replaced by a smaller one. When visiting Paris, Hitler chose to stay on the ground. When the Allies were nearing Paris in August 1944, Hitler ordered General Dietrich von Choltitz
Dietrich Hugo Hermann von Choltitz (; 9 November 1894 – 5 November 1966) was a German general. Sometimes referred to as the Saviour of Paris, he served in the Wehrmacht (armed forces) of Nazi Germany during World War II, as well as serving i ...
, the military governor of Paris, to demolish the tower along with the rest of the city. Von Choltitz disobeyed the order. On 25 August, before the Germans had been driven out of Paris, the German flag was replaced with a Tricolour by two men from the French Naval Museum, who narrowly beat three men led by Lucien Sarniguet, who had lowered the Tricolour on 13 June 1940 when Paris fell to the Germans.
A fire started in the television transmitter on 3 January 1956, damaging the top of the tower. Repairs took a year, and in 1957, the present radio aerial was added to the top. In 1964, the Eiffel Tower was officially declared to be a historical monument by the Minister of Cultural Affairs, André Malraux
Georges André Malraux ( ; ; 3 November 1901 – 23 November 1976) was a French novelist, art theorist, and minister of cultural affairs. Malraux's novel ''La Condition Humaine'' (''Man's Fate'') (1933) won the Prix Goncourt. He was appointed ...
. A year later, an additional lift system was installed in the north pillar.
According to interviews, in 1967, Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
Mayor Jean Drapeau
Jean Drapeau (; 18 February 1916 – 12 August 1999) was a Canadian politician who served as mayor of Montreal for 2 non-consecutive terms from 1954 to 1957 and from 1960 to 1986.
Major accomplishments of the Drapeau Administration include ...
negotiated a secret agreement with Charles de Gaulle
Charles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle (22 November 18909 November 1970) was a French general and statesman who led the Free France, Free French Forces against Nazi Germany in World War II and chaired the Provisional Government of the French Re ...
for the tower to be dismantled and temporarily relocated to Montreal to serve as a landmark and tourist attraction during Expo 67
The 1967 International and Universal Exposition, commonly known as Expo 67, was a general exhibition from April 28 to October 29, 1967. It was a category one world's fair held in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. It is considered to be one of the most s ...
. The plan was allegedly vetoed by the company operating the tower out of fear that the French government could refuse permission for the tower to be restored in its original location.
In 1982, the original lifts between the second and third levels were replaced after 97 years in service. These had been closed to the public between November and March because the water in the hydraulic drive tended to freeze. The new cars operate in pairs, with one counterbalancing the other, and perform the journey in one stage, reducing the journey time from eight minutes to less than two minutes. At the same time, two new emergency staircases were installed, replacing the original spiral staircases. In 1983, the south pillar was fitted with an electrically driven Otis lift to serve the Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet and playwright.
His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraor ...
restaurant. The Fives-Lille lifts in the east and west legs, fitted in 1899, were extensively refurbished in 1986. The cars were replaced, and a computer system was installed to completely automate the lifts. The motive power was moved from the water hydraulic system to a new electrically driven oil-filled hydraulic system, and the original water hydraulics were retained solely as a counterbalance system. A service lift was added to the south pillar for moving small loads and maintenance personnel three years later.
Robert Moriarty flew a Beechcraft Bonanza
The Beechcraft Bonanza is an American general aviation aircraft introduced in 1947 by Beech Aircraft Corporation of Wichita, Kansas. The six-seater, single-engined aircraft is still produced by Beechcraft and has been in continuous productio ...
under the tower on 31 March 1984. In 1987, A. J. Hackett made one of his first bungee jumps from the top of the Eiffel Tower, using a special cord he had helped develop. Hackett was arrested by the police. On 27 October 1991, Thierry Devaux, along with mountain guide Hervé Calvayrac, performed a series of acrobatic figures while bungee jumping from the second floor of the tower. Facing the Champ de Mars, Devaux used an electric winch between figures to go back up to the second floor. When firemen arrived, he stopped after the sixth jump.
 For its "Countdown to the Year 2000" celebration on 31 December 1999, flashing lights and high-powered
For its "Countdown to the Year 2000" celebration on 31 December 1999, flashing lights and high-powered searchlight
A searchlight (or spotlight) is an apparatus that combines an extremely luminosity, bright source (traditionally a carbon arc lamp) with a mirrored parabolic reflector to project a powerful beam of light of approximately parallel rays in a part ...
s were installed on the tower. During the last three minutes of the year, the lights were turned on starting from the base of the tower and continuing to the top to welcome 2000 with a huge fireworks show. An exhibition above a cafeteria on the first floor commemorates this event. The searchlights on top of the tower made it a beacon in Paris's night sky, and 20,000 flashing bulbs gave the tower a sparkly appearance for five minutes every hour on the hour.
The lights sparkled blue for several nights to herald the new millennium on 31 December 2000. The sparkly lighting continued for 18 months until July 2001. The sparkling lights were turned on again on 21 June 2003, and the display was planned to last for 10 years before they needed replacing.
The tower received its th guest on 28 November 2002. The tower has operated at its maximum capacity of about 7 million visitors per year since 2003. In 2004, the Eiffel Tower began hosting a seasonal ice rink on the first level. A glass floor
Glass floors are made with transparent glass when it is useful to view something from above or below; whereas translucent glass is used when there is no need to view through. In either case, toughened glass is usually chosen, for its durabili ...
was installed on the first level during the 2014 refurbishment.
Design
Material
 The puddle iron (wrought iron) of the Eiffel Tower weighs 7,300
The puddle iron (wrought iron) of the Eiffel Tower weighs 7,300 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s, and the addition of lifts, shops and antennae have brought the total weight to approximately 10,100 tonnes. As a demonstration of the economy of design, if the 7,300 tonnes of metal in the structure were melted down, it would fill the square base, on each side, to a depth of only assuming the density of the metal to be 7.8 tonnes per cubic metre. Additionally, a cubic box surrounding the tower (324 m × 125 m × 125 m) would contain tonnes of air, weighing almost as much as the iron itself. Depending on the ambient temperature, the top of the tower may shift away from the sun by up to due to thermal expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
of the metal on the side facing the sun.
Wind and weather considerations
 When it was built, Eiffel was accused of trying to create something artistic with no regard to the principles of engineering. However, Eiffel and his team were experienced bridge builders. In an interview with the newspaper ''
When it was built, Eiffel was accused of trying to create something artistic with no regard to the principles of engineering. However, Eiffel and his team were experienced bridge builders. In an interview with the newspaper ''Le Temps
' (, ) is a Swiss French-language daily newspaper published in Berliner format in Geneva by Le Temps SA. The paper was launched in 1998, formed out of the merger of two other newspapers, and (the former being a merger of two other papers), ...
'' published on 14 February 1887, Eiffel said:
He used graphical methods to determine the strength of the tower and empirical evidence
Empirical evidence is evidence obtained through sense experience or experimental procedure. It is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law.
There is no general agreement on how the ...
to account for the effects of wind, rather than a mathematical formula. Close examination of the tower reveals a basically exponential
Exponential may refer to any of several mathematical topics related to exponentiation, including:
* Exponential function, also:
**Matrix exponential, the matrix analogue to the above
*Exponential decay, decrease at a rate proportional to value
* Ex ...
shape. All parts of the tower were overdesigned to ensure maximum resistance to wind forces. The top half was assumed to have no gaps in the latticework. After it was completed, some have put forward various mathematical hypotheses in an attempt to explain the success of the design. A one devised in 2004 after letters sent by Eiffel to the French Society of Civil Engineers in 1885 were translated into English described it as a non-linear integral equation based on counteracting the wind pressure on any point of the tower with the tension between the construction elements at that point.
The Eiffel Tower sways by up to in the wind.
Floors
Ground floor
1st floor
The first floor is publicly accessible by lift or stairs. When originally built, the first level contained three restaurants—one French, one Russian and one Flemish—and an "Anglo-American Bar". After the exposition closed, the Flemish restaurant was converted to a 250-seat theatre. Today there is the restaurant and other facilities.2nd floor
The second floor is publicly accessible by lift or stairs and has a restaurant called , agourmet
Gourmet (, ) is a cultural idea associated with the culinary arts of fine food and drink, or haute cuisine, which is characterized by their high level of refined and elaborate food preparation techniques and displays of balanced meals that have ...
restaurant with its own lift going up from the south column to the second level. This restaurant has one star in the Michelin Red Guide. It was run by the multi-Michelin star
The ''Michelin Guides'' ( ; ) are a series of guide books that have been published by the French tyre company Michelin since 1900. The ''Guide'' awards up to three Michelin stars for excellence to a select few restaurants in certain geographic ...
chef Alain Ducasse
Alain Ducasse (; born 13 September 1956) is a French-born Monégasque chef. He operates a number of restaurants, including Alain Ducasse at The Dorchester, which holds three stars (the top rating) in the Michelin Guide.
Early life and career
D ...
from 2007 to 2017. As of May 2019, it is managed by three-star chef Frédéric Anton. It owes its name to the famous science-fiction writer Jules Verne
Jules Gabriel Verne (;''Longman Pronunciation Dictionary''. ; 8 February 1828 – 24 March 1905) was a French novelist, poet and playwright.
His collaboration with the publisher Pierre-Jules Hetzel led to the creation of the ''Voyages extraor ...
.
3rd floor
The third floor is the top floor, publicly accessible by lift. Originally there were laboratories for various experiments, and a small apartment reserved for Gustave Eiffel to entertain guests, which is now open to the public, complete with period decorations and lifelikemannequin
A mannequin (sometimes spelled as manikin and also called a dummy, lay figure, or dress form) is a doll, often articulated, used by artists, tailors, dressmakers, window dressers and others, especially to display or fit clothing and show off dif ...
s of Eiffel and some of his notable guests.
From 1937 until 1981, there was a restaurant near the top of the tower. It was removed due to structural considerations; engineers had determined it was too heavy and was causing the tower to sag. This restaurant was sold to an American restaurateur and transported to New York and then New Orleans. It was rebuilt on the edge of New Orleans' Garden District as a restaurant and later event hall. Today there is a champagne bar.
Lifts
The arrangement of the lifts has been changed several times during the tower's history. Given the elasticity of the cables and the time taken to align the cars with the landings, each lift, in normal service, takes an average of 8 minutes and 50 seconds to do the round trip, spending an average of 1 minute and 15 seconds at each level. The average journey time between levels is 1 minute. The original hydraulic mechanism is on public display in a small museum at the base of the east and west legs. Because the mechanism requires frequent lubrication and maintenance, public access is often restricted. The rope mechanism of the north tower can be seen as visitors exit the lift. Equipping the tower with adequate and safe passenger lifts was a major concern of the government commission overseeing the Exposition. Although some visitors could be expected to climb to the first level, or even the second, lifts had to be the main means of ascent.Vogel, pp. 20–21. Constructing lifts to reach the first level was done by making the legs wide enough at the bottom and so nearly straight that they could contain a straight track. A contract was given to the French company Roux, Combaluzier & Lepape for two lifts to be fitted in the east and west legs.Vogel, p. 28. Roux, Combaluzier & Lepape used a pair of endless chains with rigid, articulated links to which the car was attached. Lead weights on some links of the upper or return sections of the chains counterbalanced most of the car's weight. The car was pushed up from below, not pulled up from above: to prevent the chain buckling, it was enclosed in a conduit. At the bottom of the run, the chains passed around diametersprocket
A sprocket, sprocket-wheel or chainwheel is a profiled wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the whe ...
s. Smaller sprockets at the top guided the chains.
 Installing lifts to the second level was more of a challenge because a straight track was impossible. No French company wanted to undertake the work. The European branch of Otis Brothers & Company submitted a proposal, but this was rejected: the fair's charter ruled out the use of any foreign material in the construction of the tower. The deadline for bids was extended, but still no French companies put themselves forward, and eventually the contract was given to Otis in July 1887.Vogel, pp. 23–24. Otis were confident they would eventually be given the contract and had already started creating designs.
The car was divided into two superimposed compartments, each holding 25 passengers, with the lift operator occupying an exterior platform on the first level. Motive power was provided by an inclined hydraulic ram long and in diameter in the tower leg with a stroke of : this moved a carriage carrying six sheaves. Five fixed sheaves were mounted higher up the leg, producing an arrangement similar to a
Installing lifts to the second level was more of a challenge because a straight track was impossible. No French company wanted to undertake the work. The European branch of Otis Brothers & Company submitted a proposal, but this was rejected: the fair's charter ruled out the use of any foreign material in the construction of the tower. The deadline for bids was extended, but still no French companies put themselves forward, and eventually the contract was given to Otis in July 1887.Vogel, pp. 23–24. Otis were confident they would eventually be given the contract and had already started creating designs.
The car was divided into two superimposed compartments, each holding 25 passengers, with the lift operator occupying an exterior platform on the first level. Motive power was provided by an inclined hydraulic ram long and in diameter in the tower leg with a stroke of : this moved a carriage carrying six sheaves. Five fixed sheaves were mounted higher up the leg, producing an arrangement similar to a block and tackle
A block and tackle or only tackle is a system of two or more pulleys with a rope or cable threaded between them, used to provide tension and lift heavy loads.
The pulleys are assembled to form blocks and then blocks are paired so that one is ...
but acting in reverse, multiplying the stroke of the piston rather than the force generated. The hydraulic pressure in the driving cylinder was produced by a large open reservoir on the second level. After being exhausted from the cylinder, the water was pumped back up to the reservoir by two pumps in the machinery room at the base of the south leg. This reservoir also provided power to the lifts to the first level.
The original lifts for the journey between the second and third levels were supplied by Léon Edoux. A pair of hydraulic rams were mounted on the second level, reaching nearly halfway up to the third level. One lift car was mounted on top of these rams: cables ran from the top of this car up to sheaves on the third level and back down to a second car. Each car travelled only half the distance between the second and third levels and passengers were required to change lifts halfway by means of a short gangway. The 10-ton cars each held 65 passengers.
Engraved names
 Gustave Eiffel engraved on the building of the tower the names of 72 French scientists, engineers and mathematicians as a recognition of their contributions. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protest. At the beginning of the 20th century, the engravings were painted over, but they were restored in 1986–87 by the , a company operating the tower.
Gustave Eiffel engraved on the building of the tower the names of 72 French scientists, engineers and mathematicians as a recognition of their contributions. Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the artists' protest. At the beginning of the 20th century, the engravings were painted over, but they were restored in 1986–87 by the , a company operating the tower.
Aesthetics
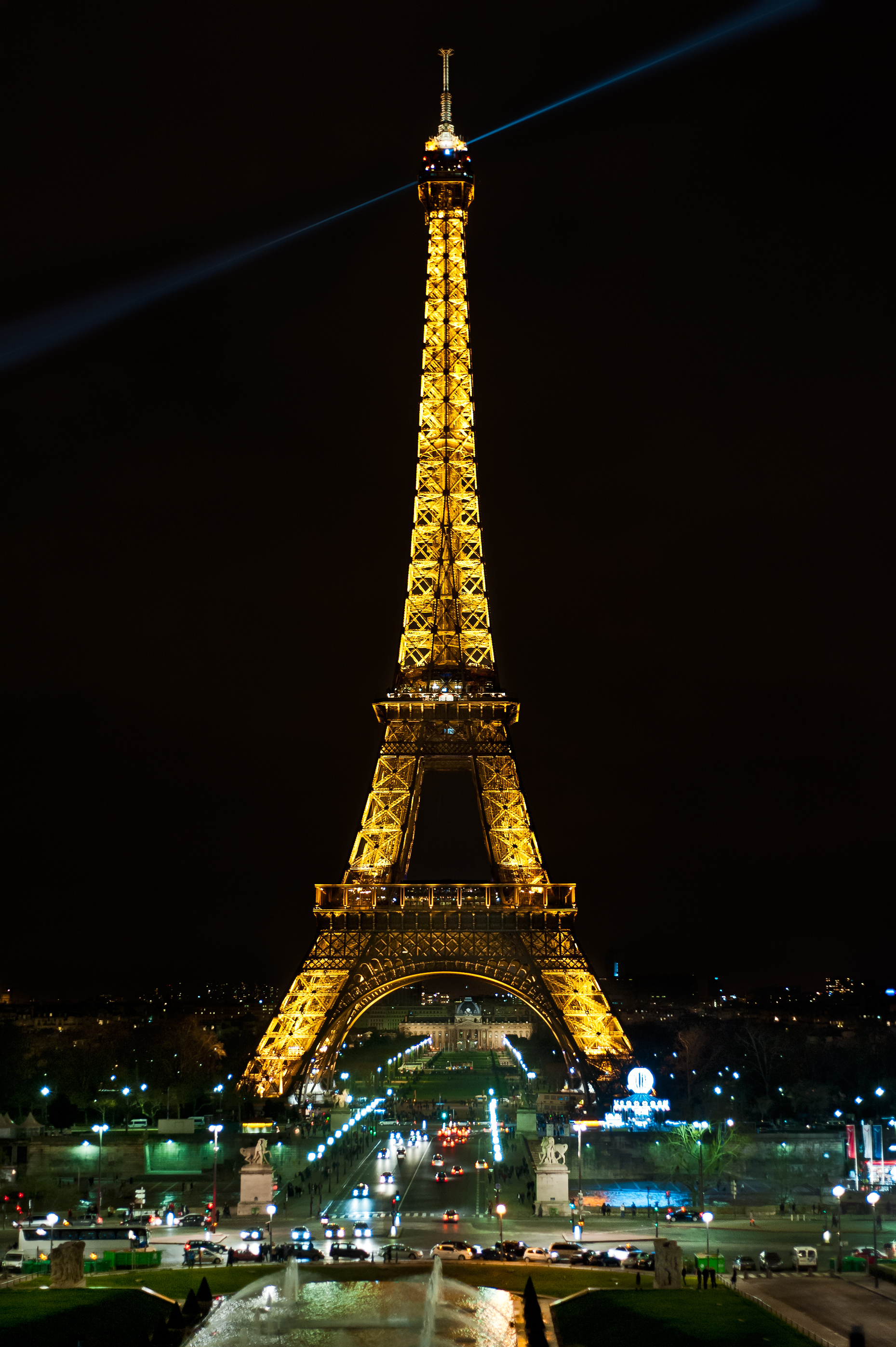
 The tower is painted in three shades: lighter at the top, getting progressively darker towards the bottom to complement the Parisian sky. It was originally reddish brown; this changed in 1968 to a bronze colour known as "Eiffel Tower Brown". In what is expected to be a temporary change, the tower was painted
The tower is painted in three shades: lighter at the top, getting progressively darker towards the bottom to complement the Parisian sky. It was originally reddish brown; this changed in 1968 to a bronze colour known as "Eiffel Tower Brown". In what is expected to be a temporary change, the tower was painted gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
in commemoration of the 2024 Summer Olympics
The 2024 Summer Olympics (), officially the Games of the XXXIII Olympiad () and branded as Paris 2024, were an international multi-sport event held in France from 26 July to 11 August 2024, with several events started from 24 July. P ...
in Paris.
Following the 2024 Summer Olympics held in Paris, Mayor Anne Hidalgo
Ana María "Anne" Hidalgo Aleu (, ; born 19 June 1959) is a Spanish-French politician who has served as Mayor of Paris since 2014, the first woman to hold the office. She is a member of the Socialist Party (France), Socialist Party (PS).
Hidalg ...
proposed keeping the Olympic rings
The International Olympic Committee (IOC) uses icons, flags, and symbols to represent and enhance the Olympic Games. These symbols include those commonly used during Olympic competitions such as the flame, fanfare, and theme as well as those u ...
on the tower permanently. The rings, which measure wide and high, were initially installed for the Games and were scheduled for removal after the Paralympics. Hidalgo's decision faced criticism from the Eiffel family and some residents concerned about altering the protected monument. The original 30-ton rings would be replaced with lighter versions for long-term display.
The only non-structural elements are the four decorative grill-work arches, added in Sauvestre's sketches, which served to make the tower look more substantial and to make a more impressive entrance to the exposition.
A pop-culture movie cliché is that the view from a Parisian window always includes the tower. In reality, since zoning restrictions limit the height of most buildings in Paris to seven storeys, only a small number of tall buildings have a clear view of the tower.
Maintenance
Maintenance of the tower includes applying 60 tons of paint every 7 years to prevent it fromrust
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually reddish-brown oxide formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the catalytic presence of water or air moisture. Rust consists of hydrous iron(III) oxides (Fe2O3·nH2O) and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH) ...
ing. The tower has been completely repainted at least 19 times since it was built, with the most recent being in 2010. Lead paint
Lead paint or lead-based paint is paint containing lead. As pigment, lead(II) chromate (, "chrome yellow"), lead(II,IV) oxide, (, "red lead"), and lead(II) carbonate (, "white lead") are the most common forms.. Lead is added to paint to acceler ...
was still being used as recently as 2001 when the practice was stopped out of concern for the environment.
Communications
The tower has been used for making radio transmissions since the beginning of the 20th century. Until the 1950s, sets of aerial wires ran from thecupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout.
The word derives, via Ital ...
to anchors on the Avenue de Suffren and Champ de Mars. These were connected to longwave
In radio, longwave (also spelled long wave or long-wave and commonly abbreviated LW) is the part of the radio spectrum with wavelengths longer than what was originally called the medium-wave (MW) broadcasting band. The term is historic, dati ...
transmitters in small bunkers. In 1909, a permanent underground radio centre was built near the south pillar, which still exists today. On 20 November 1913, the Paris Observatory
The Paris Observatory (, ), a research institution of the Paris Sciences et Lettres University, is the foremost astronomical observatory of France, and one of the largest astronomical centres in the world. Its historic building is on the Left Ban ...
, using the Eiffel Tower as an aerial, exchanged wireless signals with the United States Naval Observatory
The United States Naval Observatory (USNO) is a scientific and military facility that produces geopositioning, navigation and timekeeping data for the United States Navy and the United States Department of Defense. Established in 1830 as the ...
, which used an aerial in Arlington County, Virginia
Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati ...
. The object of the transmissions was to measure the difference in longitude between Paris and Washington, D.C. Today, radio and digital television signals are transmitted from the Eiffel Tower.
FM radio
Digital television
A television antenna was first installed on the tower in 1957, increasing its height by . Work carried out in 2000 added a further , giving a total height of . Analogue television signals from the Eiffel Tower ceased on 8 March 2011.Dimensions
Height changes
The pinnacle height of the Eiffel Tower has changed multiple times over the years as described in the chart below.Taller structures
The Eiffel Tower was the world's tallest structure when completed in 1889, a distinction it retained until 1929 when theChrysler Building
The Chrysler Building is a , Art Deco skyscraper in the East Midtown neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, United States. Located at the intersection of 42nd Street and Lexington Avenue, it is the tallest brick building in the world wit ...
in New York City was topped out. The tower also lost its standing as the world's tallest tower to the Tokyo Tower
, also known as the Japan Radio Tower (, ) is a Radio masts and towers, communications and observation tower in the district of Shiba-koen in Minato, Tokyo, Japan, completed in 1958. At , it was the List of tallest structures in Japan, tallest ...
in 1958 but retains its status as the tallest freestanding (non-guyed) structure in France.
Lattice towers taller than the Eiffel Tower
Structures in France taller than the Eiffel Tower
Tourism
Transport
The nearestParis Métro
The Paris Métro (, , or , ), short for Métropolitain (), is a rapid transit system serving the Paris metropolitan area in France. A symbol of the city, it is known for its density within the capital's territorial limits, uniform architectur ...
station is Bir-Hakeim and the nearest RER station is Champ de Mars-Tour Eiffel. The tower itself is located at the intersection of the quai Branly and the Pont d'Iéna.
Popularity
Illumination copyright
 The tower and its image have been in the
The tower and its image have been in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
since 1993, 70 years after Eiffel's death. In June 1990, a French court ruled that a special lighting display on the tower in 1989 to mark the tower's 100th anniversary was an "original visual creation" protected by copyright. The Court of Cassation
A court of cassation is a high-instance court that exists in some judicial systems. Courts of cassation do not re-examine the facts of a case; they only interpret the relevant law. In this, they are appellate courts of the highest instance. In ...
, France's judicial court of last resort, upheld the ruling in March 1992. The (SETE) now considers any illumination of the tower to be a separate work of art that falls under copyright. As a result, the SNTE alleges that it is illegal to publish contemporary photographs of the lit tower at night without permission in France and some other countries for commercial use. For this reason, it is often rare to find images or videos of the lit tower at night on stock image sites, and media outlets rarely broadcast images or videos of it.
The imposition of copyright has been controversial. The Director of Documentation for what was then called the (SNTE), Stéphane Dieu, commented in 2005: "It is really just a way to manage commercial use of the image, so that it isn't used in ways f whichwe don't approve". SNTE made over €1 million from copyright fees in 2002. However, it could also be used to restrict the publication of tourist photographs of the tower at night, as well as hindering non-profit and semi-commercial publication of images of the illuminated tower.
The copyright claim itself has never been tested in courts to date, according to a 2014 article in the ''Art Law Journal'', and there has never been an attempt to track down millions of people who have posted and shared their images of the illuminated tower on the Internet worldwide. However, the article adds that commercial uses of such images, like in a magazine, on a film poster, or on product packaging, may require prior permission.
French doctrine and jurisprudence allows pictures incorporating a copyrighted work as long as their presence is incidental or accessory to the subject being represented, a reasoning akin to the ''de minimis
''De minimis'' is a legal doctrine by which a court refuses to consider trifling matters. The name of the doctrine is a Latin expression meaning "pertaining to minimal things" or "with trifles", normally in the terms ("The praetor does not conce ...
'' rule. Therefore, SETE may be unable to claim copyright on photographs of Paris which happen to include the lit tower.
The author of the 1989 lighting display, lighting director Pierre Bideau, died in 2021; this makes the said display under artistic copyright until 2091, 70 years after the director's death.
Replicas
As one of the most famous landmarks in the world, the Eiffel Tower has been the inspiration for the creation of many replicas and similar towers. An early example isBlackpool Tower
Blackpool Tower is a tourist attraction in Blackpool, Lancashire, England, which was opened to the public on 14 May 1894. When it opened, Blackpool Tower was the tallest man-made structure in the British Empire. Inspired by the Eiffel Tower in P ...
in England. The mayor of Blackpool, Sir John Bickerstaffe, was so impressed on seeing the Eiffel Tower at the 1889 exposition that he commissioned a similar tower to be built in his town. It opened in 1894 and is tall. Tokyo Tower
, also known as the Japan Radio Tower (, ) is a Radio masts and towers, communications and observation tower in the district of Shiba-koen in Minato, Tokyo, Japan, completed in 1958. At , it was the List of tallest structures in Japan, tallest ...
in Japan, built as a communications tower in 1958, was also inspired by the Eiffel Tower. Well known is the Petřín Lookout Tower
The Petřín Lookout Tower () is a steel-framework tower tall on Petřín Hill in Prague, built in 1891. It resembles the Eiffel Tower and was used as an observation tower as well as a transmission tower. Today the tower is a major tourist attr ...
in Prague
Prague ( ; ) is the capital and List of cities and towns in the Czech Republic, largest city of the Czech Republic and the historical capital of Bohemia. Prague, located on the Vltava River, has a population of about 1.4 million, while its P ...
too.
There are various scale models of the tower in the United States, including a half-scale version at the Paris Las Vegas
Paris Las Vegas is a casino hotel on the Las Vegas Strip in Paradise, Nevada. It is owned and operated by Caesars Entertainment. Property features include a casino, 3,672 hotel rooms, a 1,400-seat performance theater, and various restaurants. ...
, Nevada, one in Paris, Texas built in 1993, and two 1:3 scale models at Kings Island, located in Mason, Ohio
Mason is a city in southwestern Warren County, Ohio, United States, approximately north of downtown Cincinnati. As of the United States Census 2020, 2020 census, Mason's population was 34,792. It is home to Kings Island amusement park and one of ...
, and Kings Dominion
Kings Dominion is an amusement park in Doswell, Virginia, United States, north of Richmond, Virginia, Richmond and south of Washington, D.C. Owned and operated by Six Flags, the park opened to the public on May 3, 1975, featuring over 60 rid ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, amusement parks opened in 1972 and 1975 respectively. Two 1:3 scale models can be found in China, one in Durango, Mexico that was donated by the local French community, and several across Europe.
In 2011, the TV show ''Pricing the Priceless'' on the National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by the National Geographic Global Networks unit of Disney Enter ...
speculated that a full-size replica of the tower would cost approximately US$480 million to build. This would be more than ten times the cost of the original (nearly 8 million in 1890 francs; around US$40 million in 2018 dollars).
See also
* List of tallest buildings and structures in the Paris region *List of tallest buildings and structures
This is the History of the world's tallest structures.
Overall
Below is a list of the tallest structures supported by land. For most of the period from around 2650 BC to 1240 AD, the Egyptian pyramids (culminating in the Great Pyramid of Giz ...
* List of tourist attractions in Paris
Paris, the capital of France, has an annual 30 million foreign visitors, and so is one of the most visited cities in the world. Paris's sights include monuments and architecture, such as its Arc de Triomphe, Eiffel Tower and neo-classic Baron H ...
* List of tallest towers
The tallest structure in the world is the Burj Khalifa skyscraper at . Listed are guyed masts (such as telecommunication masts), self-supporting towers (such as the CN Tower), skyscrapers (such as the Willis Tower), oil platforms, electricity ...
* List of tallest freestanding structures
The tallest structure in the world is the Burj Khalifa skyscraper at . Listed are guyed masts (such as telecommunication masts), self-supporting towers (such as the CN Tower), skyscrapers (such as the Willis Tower), oil platforms, electricity t ...
* List of tallest freestanding steel structures
* List of tallest structures built before the 20th century
List of pre-twentieth century structures by height
See also
*History of the world's tallest buildings
*List of tallest buildings and structures
References
{{Tallest buildings and structures
Lists of tallest structures, Ancient structur ...
* List of transmission sites
* List of the 72 names on the Eiffel Tower
On the Eiffel Tower, 72 names of France, French men (scientists, engineers, and mathematicians) are engraved in recognition of their contributions. Gustave Eiffel chose this "invocation of science" because of his concern over the Eiffel Tower#Art ...
* Lattice tower
A lattice tower or truss tower is a freestanding vertical latticework, framework tower. This construction is widely used in transmission towers carrying high-voltage electric power lines, in radio masts and towers (a self-radiating tower or as a ...
* ''Eiffel Tower
The Eiffel Tower ( ; ) is a wrought-iron lattice tower on the Champ de Mars in Paris, France. It is named after the engineer Gustave Eiffel, whose company designed and built the tower from 1887 to 1889.
Locally nicknamed "''La dame de fe ...
'', 1909–1928 painting series by Robert Delaunay
Robert Delaunay (; 12 April 1885 – 25 October 1941) was a French artist of the School of Paris movement; who, with his wife Sonia Delaunay and others, co-founded the Orphism (art), Orphism art movement, noted for its use of strong colours and g ...
* '' Panorama of the Paris Exhibition No. 3'' (1900), silent film depicting Paris and the Eiffel Tower
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * {{Authority control Articles containing video clips Buildings and structures in the 7th arrondissement of Paris Former world's tallest buildings Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks Landmarks in France Michelin-starred restaurants in France Observation towers in France Restaurant towers Tourist attractions in Paris Towers in Paris Towers completed in 1889 Venues of the 2024 Summer Olympics Olympic volleyball venues Lattice towers Architectural controversies 1889 establishments in France Exposition Universelle (1889) World's fair architecture in Paris Monuments historiques of Paris