Egg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized
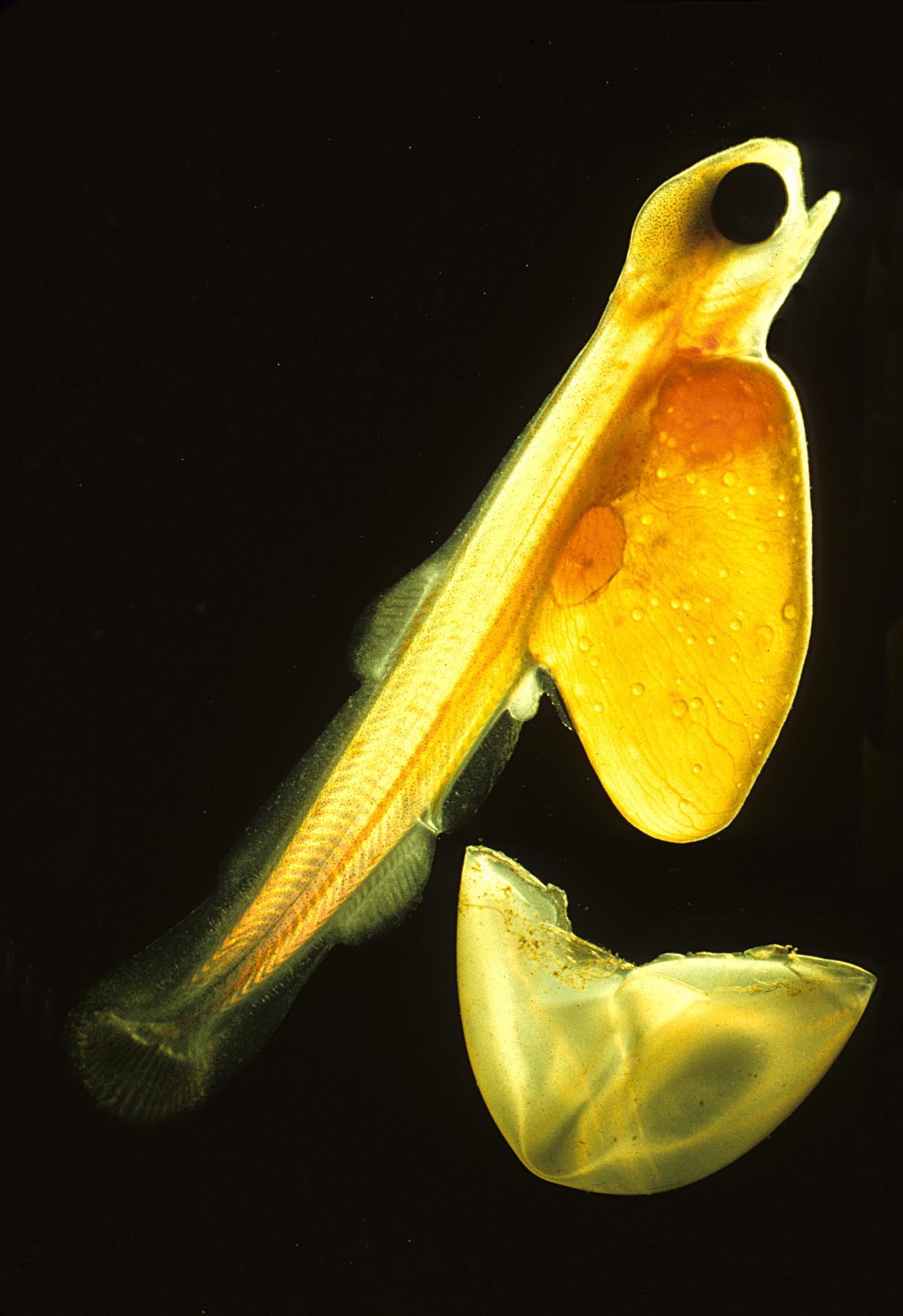 The most common reproductive strategy for
The most common reproductive strategy for  The eggs of fish and
The eggs of fish and
 The default colour of vertebrate eggs is the white of the
The default colour of vertebrate eggs is the white of the
 Most bird eggs have an oval shape, with one end rounded and the other more pointed. This shape results from the egg being forced through the
Most bird eggs have an oval shape, with one end rounded and the other more pointed. This shape results from the egg being forced through the
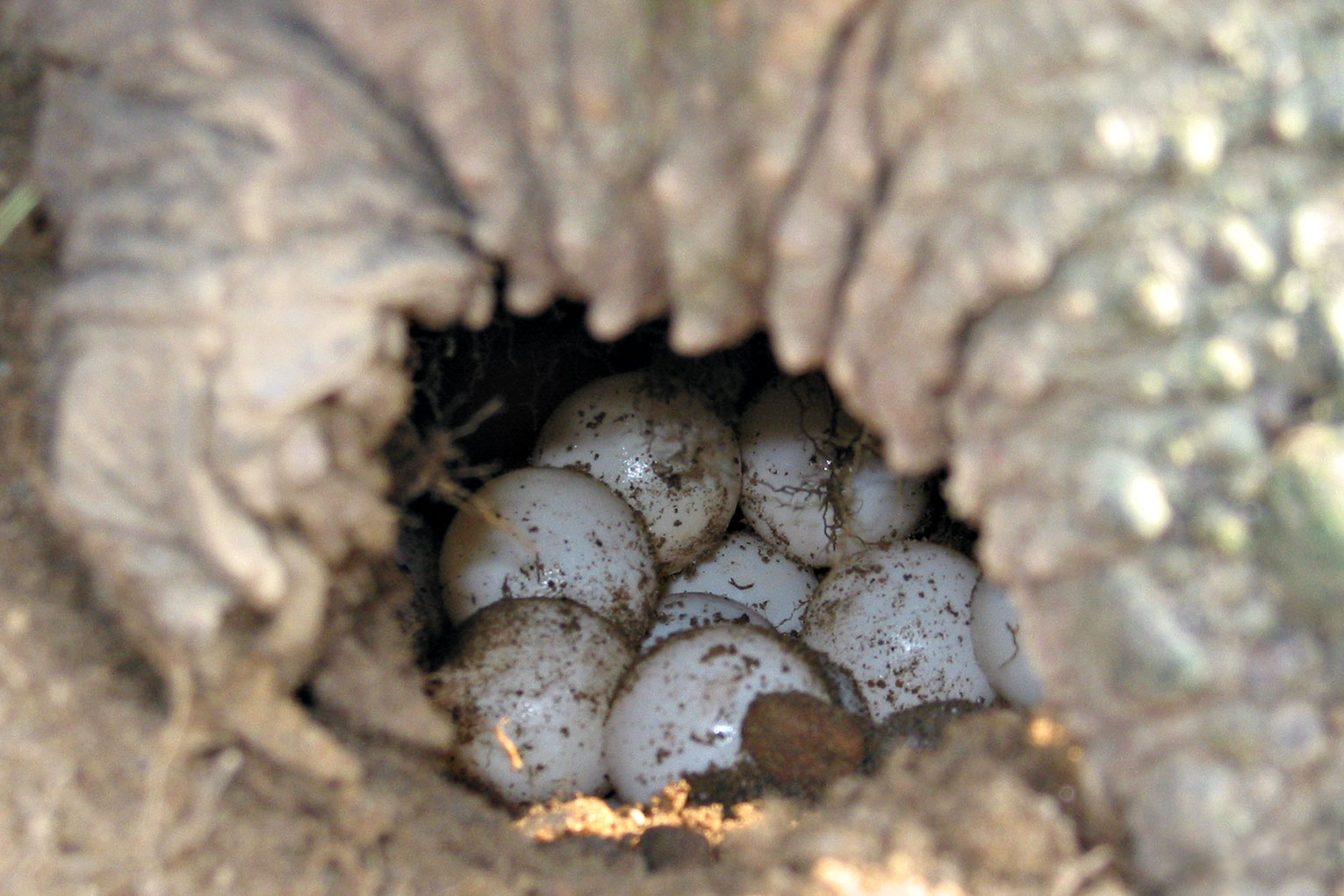 Like amphibians,
Like amphibians,
 Eggs are common among
Eggs are common among

 Small eggs with little yolk are called microlecithal. The yolk is evenly distributed, so the cleavage of the egg cell cuts through and divides the egg into cells of fairly similar sizes. In
Small eggs with little yolk are called microlecithal. The yolk is evenly distributed, so the cleavage of the egg cell cuts through and divides the egg into cells of fairly similar sizes. In
 Mesolecithal eggs have comparatively more yolk than the microlecithal eggs. The yolk is concentrated in one part of the egg (the ''vegetal pole''), with the
Mesolecithal eggs have comparatively more yolk than the microlecithal eggs. The yolk is concentrated in one part of the egg (the ''vegetal pole''), with the
 Eggs with a large yolk are called macrolecithal. The eggs are usually few in number, and the embryos have enough food to go through full fetal development in most groups. Macrolecithal eggs are only found in selected representatives of two groups:
Eggs with a large yolk are called macrolecithal. The eggs are usually few in number, and the embryos have enough food to go through full fetal development in most groups. Macrolecithal eggs are only found in selected representatives of two groups:
egg cell
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female Reproduction, reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female game ...
(a zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
) and to incubate from it an embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches.
Most arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s, vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
(excluding live-bearing mammals), and mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpion
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the Order (biology), order Scorpiones. They have eight legs and are easily recognized by a pair of Chela (organ), grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward cur ...
s, do not.
Reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
eggs, bird egg
Bird eggs are laid by the females and range in quantity from one (as in condors) to up to seventeen (the grey partridge). Avian clutch size, Clutch size may vary latitudinally within a species. Some birds lay eggs even when the eggs have not been ...
s, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard outer layer of a marine ani ...
, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering.
The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark
The whale shark (''Rhincodon typus'') is a slow-moving, filter feeder, filter-feeding carpet shark and the largest known Extant taxon, extant fish species. The largest confirmed individual had a length of . The whale shark holds many records for ...
and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the mother
A mother is the female parent of a child. A woman may be considered a mother by virtue of having given birth, by raising a child who may or may not be her biological offspring, or by supplying her ovum for fertilisation in the case of ges ...
. At and up to , the ostrich egg is the largest egg of any living bird, though the extinct elephant bird and some non-avian dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is ...
s laid larger eggs. The bee hummingbird
The bee hummingbird, zunzuncito or Helena hummingbird (''Mellisuga helenae'') is a species of hummingbird, native to the island of Cuba in the Caribbean. It is the smallest known bird. The bee hummingbird feeds on nectar of flowers and bugs foun ...
produces the smallest known bird egg, which measures between long and weighs half of a gram (around 0.02 oz). Some eggs laid by reptiles and most fish, amphibians, insects, and other invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s can be even smaller.
Reproductive structures similar to the egg in other kingdoms are termed "spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual reproduction, sexual (in fungi) or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for biological dispersal, dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores fo ...
s", or in spermatophyte
A seed plant or spermatophyte (; New Latin ''spermat-'' and Greek ' (phytón), plant), also known as a phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or a phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte (i.e. la ...
s "seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s", or in gametophyte
A gametophyte () is one of the two alternating multicellular phases in the life cycles of plants and algae. It is a haploid multicellular organism that develops from a haploid spore that has one set of chromosomes. The gametophyte is the se ...
s "egg cells".
Eggs of different animal groups
Several major groups of animals typically have readily distinguishable eggs.Fish and amphibian eggs
 The most common reproductive strategy for
The most common reproductive strategy for fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
is known as oviparity
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
, in which the female lays undeveloped eggs that are externally fertilized by a male. Typically large numbers of eggs are laid at one time (an adult female cod
Cod (: cod) is the common name for the demersal fish genus ''Gadus'', belonging to the family (biology), family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gad ...
can produce 4–6 million eggs in one spawning) and the eggs are then left to develop without parental care. When the larvae hatch from the egg, they often carry the remains of the yolk in a yolk sac which continues to nourish the larvae for a few days as they learn how to swim. Once the yolk is consumed, there is a critical point after which they must learn how to hunt and feed or they will die.
A few fish, notably the rays and most shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the ...
s use ovoviviparity
Ovoviviparity, ovovivipary, ovivipary, or aplacental viviparity is a "bridging" form of reproduction between egg-laying oviparous and live-bearing viviparous reproduction. Ovoviviparous animals possess embryos that develop inside eggs that r ...
in which the eggs are fertilized and develop internally. However, the larvae still grow inside the egg consuming the egg's yolk and without any direct nourishment from the mother. The mother then gives birth to relatively mature young. In certain instances, the physically most developed offspring will devour its smaller siblings for further nutrition while still within the mother's body. This is known as intrauterine cannibalism.
In certain scenarios, some fish such as the hammerhead shark and reef shark are viviparous, with the egg being fertilized and developed internally, but with the mother also providing direct nourishment.
 The eggs of fish and
The eggs of fish and amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s are jellylike. Cartilaginous fish (sharks, skates, rays, chimaeras) eggs are fertilized internally and exhibit a wide variety of both internal and external embryonic development. Most fish species spawn eggs that are fertilized externally, typically with the male inseminating the eggs after the female lays them. These eggs do not have a shell and would dry out in the air. Even air-breathing amphibians lay their eggs in water, or in protective foam as with the Coast foam-nest treefrog, '' Chiromantis xerampelina''.
Bird eggs
Bird eggs are laid by females and incubated for a time that varies according to the species; a single young hatches from each egg. Average clutch sizes range from one (as incondor
Condor is the common name for two species of New World vultures, each in a monotypic genus. The name derives from the Quechua language, Quechua ''kuntur''. They are the largest flying land birds in the Western Hemisphere.
One species, the And ...
s) to about 17 (the grey partridge). Some birds lay eggs even when not fertilized (e.g. hens); it is not uncommon for pet owners to find their lone bird nesting on a clutch of unfertilized eggs, which are sometimes called wind-eggs.
Colours
 The default colour of vertebrate eggs is the white of the
The default colour of vertebrate eggs is the white of the calcium carbonate
Calcium carbonate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a common substance found in Rock (geology), rocks as the minerals calcite and aragonite, most notably in chalk and limestone, eggshells, gastropod shells, shellfish skel ...
from which the shells are made, but some birds, mainly passerine
A passerine () is any bird of the order Passeriformes (; from Latin 'sparrow' and '-shaped') which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines generally have an anisodactyl arrangement of their ...
s, produce coloured eggs. The colour comes from pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored sub ...
s deposited on top of the calcium carbonate base; biliverdin
Biliverdin (from the Latin for green bile) is a green tetrapyrrolic bile pigment, and is a product of heme catabolism.Boron W, Boulpaep E. Medical Physiology: a cellular and molecular approach, 2005. 984–986. Elsevier Saunders, United States. ...
and its zinc chelate, and bilirubin
Bilirubin (BR) (adopted from German, originally bili—bile—plus ruber—red—from Latin) is a red-orange compound that occurs in the normcomponent of the straw-yellow color in urine. Another breakdown product, stercobilin, causes the brown ...
, give a green or blue ground colour, while protoporphyrin IX produces reds and browns as a ground colour or as spotting.
Non-passerines typically have white eggs, except in some ground-nesting groups such as the Charadriiformes
Charadriiformes (, from '' Charadrius'', the type genus of family Charadriidae) is a diverse order of small to medium-large birds. It includes about 390 species and has members in all parts of the world. Most charadriiform birds live near water ...
, sandgrouse
Sandgrouse is the common name for Pteroclidae (), a family (biology), family of sixteen species of bird, members of the order Pterocliformes (). They are traditionally placed in two Genus, genera. The two central Asian species are classified as ...
and nightjar
Nightjars are medium-sized nocturnal or crepuscular birds in the family Caprimulgidae and order Caprimulgiformes, characterised by long wings, short legs, and very short bills. They are sometimes called bugeaters, their primary source of food ...
s, where camouflage is necessary, and some parasitic cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae ( ) family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes ( ). The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals, and anis. The coucals and anis are somet ...
s which have to match the passerine host's egg. Most passerines, in contrast, lay coloured eggs, even if there is no need of cryptic colors. However, some have suggested that the protoporphyrin markings on passerine eggs actually act to reduce brittleness by acting as a solid-state lubricant. If there is insufficient calcium available in the local soil, the egg shell may be thin, especially in a circle around the broad end. Protoporphyrin speckling compensates for this, and increases inversely to the amount of calcium in the soil.
For the same reason, later eggs in a clutch are more spotted than early ones as the female's store of calcium is depleted.
The color of individual eggs is also genetically influenced, and appears to be inherited through the mother only, suggesting that the gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
responsible for pigmentation is on the sex-determining W chromosome (female birds are WZ, males ZZ).
It used to be thought that color was applied to the shell immediately before laying, but subsequent research shows that coloration is an integral part of the development of the shell, with the same protein responsible for depositing calcium carbonate, or protoporphyrins when there is a lack of that mineral.
In species such as the common guillemot, which nest in large groups, each female's eggs have very different markings, making it easier for females to identify their own eggs on the crowded cliff ledges on which they breed.
Yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
s of birds' eggs are yellow from carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
s, it is affected by their living conditions and diet.
Shell
Bird eggshells are diverse. For example: * cormorant eggs are rough and chalky * tinamou eggs are shiny *duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family (biology), family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and goose, geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfam ...
eggs are oily and waterproof
* cassowary eggs are heavily pitted
Tiny pores in bird eggshells allow the embryo to breathe. The domestic hen's egg has around 7000 pores.
Some bird eggshells have a coating of vaterite
Vaterite is a mineral, a polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (calcium, Cacarbon, Coxygen, O3). It was named after the German mineralogist Heinrich Vater. It is also known as mu-calcium carbonate (μ-CaCO3). Vaterite b ...
spherules, which is a rare polymorph of calcium carbonate. In Greater Ani ''Crotophaga major'' this vaterite coating is thought to act as a shock absorber, protecting the calcite shell from fracture during incubation, such as colliding with other eggs in the nest.
Shape
oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
. Muscles contract the oviduct behind the egg, pushing it forward. The egg's wall is still shapeable, and the pointed end develops at the back. One hypothesis is that long, pointy eggs are an incidental consequence of having a streamlined body typical of birds with strong flying abilities; flight narrows the oviduct, which changes the type of egg a bird can lay.
Cliff-nesting birds often have highly conical eggs. They are less likely to roll off, tending instead to roll around in a tight circle; this trait is likely to have arisen due to evolution via natural selection. In contrast, many hole-nesting birds have nearly spherical eggs.
Predation
Many animals feed on eggs. For example, principal predators of the black oystercatcher's eggs includeraccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
s, skunks, mink, river and sea otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among ...
s, gull
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the subfamily Larinae. They are most closely related to terns and skimmers, distantly related to auks, and even more distantly related to waders. Until the 21st century, most gulls were placed ...
s, crow
A crow is a bird of the genus ''Corvus'', or more broadly, a synonym for all of ''Corvus''. The word "crow" is used as part of the common name of many species. The related term "raven" is not linked scientifically to any certain trait but is rathe ...
s and foxes. The stoat (''Mustela erminea'') and long-tailed weasel
The long-tailed weasel (''Neogale frenata''), also known as the bridled weasel, masked ermine, or big stoat, is a species of weasel found in North America, North, Central America, Central, and South America. It is distinct from the Stoat, short-t ...
(''M. frenata'') steal ducks' eggs. Snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s of the genera '' Dasypeltis'' and '' Elachistodon'' specialize in eating eggs.
Brood parasitism occurs in birds when one species lays its eggs in the nest of another. In some cases, the host's eggs are removed or eaten by the female, or expelled by her chick. Brood parasites include the cowbirds and many Old World cuckoo
Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae ( ) family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes ( ). The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals, and anis. The coucals and anis are somet ...
s.
Amniote eggs and embryos
 Like amphibians,
Like amphibians, amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
s are air-breathing vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s, but they have complex eggs or embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
s, including an amniotic membrane
The amnion (: amnions or amnia) is a membrane that closely covers human and various other embryos when they first form. It fills with amniotic fluid, which causes the amnion to expand and become the amniotic sac that provides a protective en ...
. Amniotes include reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s (including dinosaurs and their descendants, birds) and mammals.
Reptile eggs are often rubbery and are always initially white. They are able to survive in the air. Often the sex of the developing embryo is determined by the temperature of the surroundings, with cooler temperatures favouring males. Not all reptiles lay eggs; some are viviparous ("live birth").
Dinosaurs laid eggs, some of which have been preserved as petrified fossils.
Among mammals, early extinct species laid eggs, as do platypuses and echidnas (spiny anteaters). Platypuses and two genera of echidna are Australian monotremes. Marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
and placental
Placental mammals (infraclass Placentalia ) are one of the three extant subdivisions of the class Mammalia, the other two being Monotremata and Marsupialia. Placentalia contains the vast majority of extant mammals, which are partly distinguished ...
mammals do not lay eggs, but their unborn young do have the complex tissues that identify amniotes.
Mammalian eggs
The eggs of the egg-laying mammals (the platypus and the echidnas) are macrolecithal eggs very much like those ofreptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s. The eggs of marsupial
Marsupials are a diverse group of mammals belonging to the infraclass Marsupialia. They are natively found in Australasia, Wallacea, and the Americas. One of marsupials' unique features is their reproductive strategy: the young are born in a r ...
s are likewise macrolecithal, but rather small, and develop inside the body of the female, but do not form a placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
. The young are born at a very early stage, and can be classified as a "larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
" in the biological sense.
In placental mammals, the egg itself is void of yolk, but develops an umbilical cord
In Placentalia, placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or ''funiculus umbilicalis'') is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord i ...
from structures that in reptiles would form the yolk sac. Receiving nutrients from the mother, the fetus completes the development while inside the uterus.
Invertebrate eggs
 Eggs are common among
Eggs are common among invertebrate
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordata, chordate s ...
s, including insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s, spider
Spiders (order (biology), order Araneae) are air-breathing arthropods that have eight limbs, chelicerae with fangs generally able to inject venom, and spinnerets that extrude spider silk, silk. They are the largest order of arachnids and ran ...
s, mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The ...
s, and crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s.
Evolution and structure
All sexually reproducing life, including both plants and animals, producesgametes
A gamete ( ) is a haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as sex cells. The name gamete was introduced by the Ge ...
. The male gamete cell, sperm
Sperm (: sperm or sperms) is the male reproductive Cell (biology), cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm ...
, is usually motile whereas the female gamete cell, the ovum, is generally larger and sessile. The male and female gametes combine to produce the zygote
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes.
The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individ ...
cell. In multicellular
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell (biology), cell, unlike unicellular organisms. All species of animals, Embryophyte, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organism ...
organisms, the zygote subsequently divides in an organised manner into smaller more specialised cells, so that this new individual develops into an embryo
An embryo ( ) is the initial stage of development for a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sp ...
. In most animals, the embryo is the sessile initial stage of the individual life cycle, and is followed by the emergence (that is, the hatching) of a motile stage. The zygote or the ovum itself or the sessile organic vessel containing the developing embryo may be called the egg.
A recent proposal suggests that the phylotypic animal body plan
A body plan, (), or ground plan is a set of morphology (biology), morphological phenotypic trait, features common to many members of a phylum of animals. The vertebrates share one body plan, while invertebrates have many.
This term, usually app ...
s originated in cell aggregates before the existence of an egg stage of development. Eggs, in this view, were later evolutionary innovations, selected for their role in ensuring genetic uniformity among the cells of incipient multicellular organisms.
Formation
The cycle of the egg's formation is started by thegamete
A gamete ( ) is a Ploidy#Haploid and monoploid, haploid cell that fuses with another haploid cell during fertilization in organisms that Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually. Gametes are an organism's reproductive cells, also referred to as s ...
ovum being released ( ovulated) and egg formation being started. The finished egg is then oviposition
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
ed and eventual egg incubation can start.
Scientific classifications
Scientists often classify animal reproduction according to the degree of development that occurs before the new individuals are expelled from the adult body, and by the yolk which the egg provides to nourish the embryo.Egg size and yolk
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
eggs can be classified by the relative amount of yolk
Among animals which produce eggs, the yolk (; also known as the vitellus) is the nutrient-bearing portion of the egg whose primary function is to supply food for the development of the embryo. Some types of egg contain no yolk, for example bec ...
. Simple eggs with little yolk are called ''microlecithal'', medium-sized eggs with some yolk are called ''mesolecithal'', and large eggs with a large concentrated yolk are called ''macrolecithal''. Romer, A. S. & Parsons, T. S. (1985): ''The Vertebrate Body.'' (6th ed.) Saunders, Philadelphia. This classification of eggs is based on the eggs of chordates
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics ( synapomorphies) that distinguish them from ot ...
, though the basic principle extends to the whole animal kingdom.
Microlecithal

 Small eggs with little yolk are called microlecithal. The yolk is evenly distributed, so the cleavage of the egg cell cuts through and divides the egg into cells of fairly similar sizes. In
Small eggs with little yolk are called microlecithal. The yolk is evenly distributed, so the cleavage of the egg cell cuts through and divides the egg into cells of fairly similar sizes. In sponges
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and ar ...
and cnidaria
Cnidaria ( ) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic invertebrates found both in fresh water, freshwater and marine environments (predominantly the latter), including jellyfish, hydroid (zoology), hydroids, ...
ns, the dividing eggs develop directly into a simple larva, rather like a morula with cilia
The cilium (: cilia; ; in Medieval Latin and in anatomy, ''cilium'') is a short hair-like membrane protrusion from many types of eukaryotic cell. (Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea.) The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike proj ...
. In cnidarians, this stage is called the planula, and either develops directly into the adult animals or forms new adult individuals through a process of budding
Budding or blastogenesis is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site. For example, the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is kno ...
.
Microlecithal eggs require minimal yolk mass. Such eggs are found in flatworm
Platyhelminthes (from the Greek language, Greek πλατύ, ''platy'', meaning "flat" and ἕλμινς (root: ἑλμινθ-), ''helminth-'', meaning "worm") is a Phylum (biology), phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, Segmentation (biology), ...
s, roundworms, annelid
The annelids (), also known as the segmented worms, are animals that comprise the phylum Annelida (; ). The phylum contains over 22,000 extant species, including ragworms, earthworms, and leeches. The species exist in and have adapted to vario ...
s, bivalve
Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally compressed soft bodies enclosed b ...
s, echinoderms
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as larv ...
, the lancelet and in most marine arthropod
Arthropods ( ) are invertebrates in the phylum Arthropoda. They possess an arthropod exoskeleton, exoskeleton with a cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate, a body with differentiated (Metam ...
s.Barns, R.D. (1968): Invertebrate Zoology. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia. 743 pages In anatomically simple animals, such as cnidarians and flatworms, the fetal development can be quite short, and even microlecithal eggs can undergo direct development. These small eggs can be produced in large numbers. In animals with high egg mortality, microlecithal eggs are the norm, as in bivalves and marine arthropods. However, the latter are more complex anatomically than e.g. flatworms, and the small microlecithal eggs do not allow full development. Instead, the eggs hatch into larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
e, which may be markedly different from the adult animal.
In placental mammals, where the embryo is nourished by the mother throughout the whole fetal period, the egg is reduced in size to essentially a naked egg cell.
Mesolecithal
 Mesolecithal eggs have comparatively more yolk than the microlecithal eggs. The yolk is concentrated in one part of the egg (the ''vegetal pole''), with the
Mesolecithal eggs have comparatively more yolk than the microlecithal eggs. The yolk is concentrated in one part of the egg (the ''vegetal pole''), with the cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (; : nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryote, eukaryotic cell (biology), cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have #Anucleated_cells, ...
and most of the cytoplasm
The cytoplasm describes all the material within a eukaryotic or prokaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, including the organelles and excluding the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. The material inside the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell a ...
in the other (the ''animal pole''). The cell cleavage is uneven, and mainly concentrated in the cytoplasma-rich animal pole.Hildebrand, M. & Gonslow, G. (2001): Analysis of Vertebrate Structure. 5th edition. ''John Wiley & Sons, Inc''. New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
The larger yolk content of the mesolecithal eggs allows for a longer fetal development. Comparatively anatomically simple animals will be able to go through the full development and leave the egg in a form reminiscent of the adult animal. This is the situation found in hagfish
Hagfish, of the Class (biology), class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and Order (biology), order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped Agnatha, jawless fish (occasionally called slime eels). Hagfish are the only known living Animal, animals that h ...
and some snail
A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gas ...
s. Animals with smaller size eggs or more advanced anatomy will still have a distinct larval stage, though the larva will be basically similar to the adult animal, as in lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are a group of Agnatha, jawless fish comprising the order (biology), order Petromyzontiformes , sole order in the Class (biology), class Petromyzontida. The adult lamprey is characterize ...
s, coelacanth and the salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s.
Macrolecithal
 Eggs with a large yolk are called macrolecithal. The eggs are usually few in number, and the embryos have enough food to go through full fetal development in most groups. Macrolecithal eggs are only found in selected representatives of two groups:
Eggs with a large yolk are called macrolecithal. The eggs are usually few in number, and the embryos have enough food to go through full fetal development in most groups. Macrolecithal eggs are only found in selected representatives of two groups: Cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
s and vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s.
Macrolecithal eggs go through a different type of development than other eggs. Due to the large size of the yolk, the cell division can not split up the yolk mass. The fetus instead develops as a plate-like structure on top of the yolk mass, and only envelopes it at a later stage. A portion of the yolk mass is still present as an external or semi-external yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous wikt:sac, sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac' ...
at hatching in many groups. This form of fetal development is common in bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, even though their eggs can be quite small. Despite their macrolecithal structure, the small size of the eggs does not allow for direct development, and the eggs hatch to a larval stage ("fry"). In terrestrial animals with macrolecithal eggs, the large volume to surface ratio necessitates structures to aid in transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide, and for storage of waste products so that the embryo does not suffocate or get poisoned from its own waste while inside the egg, see amniote
Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial animal, terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolution, evolved from amphibious Stem tet ...
.Stewart J. R. (1997): ''Morphology and evolution of the egg of oviparous amniotes''. In: S. Sumida and K. Martin (ed.) Amniote Origins-Completing the Transition to Land (1): 291–326. London: Academic Press.
In addition to bony fish and cephalopods, macrolecithal eggs are found in cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
, reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s, bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
s and monotreme mammals. The eggs of the coelacanths can reach a size of in diameter, and the young go through full development while in the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
, living on the copious yolk.
Egg-laying reproduction
Animals are commonly classified by their manner of reproduction, at the most general level distinguishing egg-laying (Latin. ''oviparous'') from live-bearing (Latin. ''viviparous''). These classifications are divided into more detail according to the development that occurs before the offspring are expelled from the adult's body. Traditionally: *Ovuliparity means the female spawns unfertilized eggs (ova), which must then be externally fertilised. Ovuliparity is typical ofbony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, anurans, echinoderms, bivalves and cnidarians. Most aquatic organisms are ovuliparous. The term is derived from the diminutive meaning "little egg".
*Oviparity is where fertilisation occurs internally and so the eggs laid by the female are zygotes (or newly developing embryos), often with important outer tissues added (for example, in a chicken egg, no part outside of the yolk originates with the zygote). Oviparity is typical of birds, reptiles, some cartilaginous fish and most arthropods. Terrestrial organisms are typically oviparous, with egg-casings that resist evaporation of moisture.
*Ovo-viviparity is where the zygote is retained in the adult's body but there are no ''trophic'' (feeding) interactions. That is, the embryo still obtains all of its nutrients from inside the egg. Most live-bearing fish, amphibians or reptiles are actually ovoviviparous. Examples include the reptile '' Anguis fragilis'', the sea horse (where zygotes are retained in the male's ventral "marsupium"), and the frogs ''Rhinoderma darwinii'' (where the eggs develop in the vocal sac) and ''Rheobatrachus'' (where the eggs develop in the stomach).
*Histotrophic viviparity means embryos develop in the female's oviduct
The oviduct in vertebrates is the passageway from an ovary. In human females, this is more usually known as the fallopian tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, or will dege ...
s but obtain nutrients by consuming other ova, zygotes or sibling embryos ( oophagy or adelphophagy
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecology, ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is also well ...
). This intra-uterine cannibalism occurs in some sharks and in the black salamander ''Salamandra atra''. Marsupials excrete a "uterine milk" supplementing the nourishment from the yolk sac.
*Hemotrophic viviparity is where nutrients are provided from the female's blood through a designated organ. This most commonly occurs through a placenta
The placenta (: placentas or placentae) is a temporary embryonic and later fetal organ that begins developing from the blastocyst shortly after implantation. It plays critical roles in facilitating nutrient, gas, and waste exchange between ...
, found in most mammals. Similar structures are found in some sharks and in the lizard ''Pseudomoia pagenstecheri''. In some hylid frogs, the embryo is fed by the mother through specialized gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s.
The term hemotrophic derives from the Latin for blood-feeding, contrasted with histotrophic for tissue-feeding.
Human use
Food
Eggs laid by many different species, including birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish, have probably been eaten by people for millennia. Popular choices for egg consumption are chicken, duck, roe, and caviar, but by a wide margin the egg most often humanly consumed is the chicken egg, typically unfertilized.Eggs and Kashrut
According to theKashrut
(also or , ) is a set of Food and drink prohibitions, dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to halakha, Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed ko ...
, that is the set of Jewish dietary laws, kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, ), from the Ashke ...
food may be consumed according to ''halakha
''Halakha'' ( ; , ), also Romanization of Hebrew, transliterated as ''halacha'', ''halakhah'', and ''halocho'' ( ), is the collective body of Judaism, Jewish religious laws that are derived from the Torah, Written and Oral Torah. ''Halakha'' is ...
'' (Jewish law). Eggs are considered ''pareve'' (neither meat nor dairy) despite being an animal product and can be mixed with either milk or kosher meat.
Vaccine manufacture
Many vaccines for infectious diseases are produced in fertile chicken eggs. The basis of this technology was the discovery in 1931 by Alice Miles Woodruff and Ernest William Goodpasture atVanderbilt University
Vanderbilt University (informally Vandy or VU) is a private university, private research university in Nashville, Tennessee, United States. Founded in 1873, it was named in honor of shipping and railroad magnate Cornelius Vanderbilt, who provide ...
that the rickettsia and virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are ...
es that cause a variety of diseases will grow in chicken embryos. This enabled the development of vaccines against influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
, chicken pox, smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (W ...
, yellow fever, typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposu ...
, Rocky mountain spotted fever
Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a bacterial disease spread by ticks. It typically begins with a fever and headache, which is followed a few days later with the development of a rash. The rash is generally Petechial rash, made up of small s ...
and other diseases.
Culture
Eggs are an important symbol in folklore and mythology, often representing life and rebirth, healing and protection, and sometimes featuring in creation myths. Egg decoration is a common practice in many cultures worldwide. Christians viewEaster egg
Easter eggs, also called Paschal eggs, are eggs that are decorated for the Christian holiday of Easter, which celebrates the resurrection of Jesus. As such, Easter eggs are commonly used during the season of Eastertide (Easter season). The ...
s as symbolic of the resurrection of Jesus Christ. A popular Easter tradition in some parts of the world is the decoration of hard-boiled eggs (usually by dyeing, but often by hand-painting or spray-painting). Adults often hide the eggs for children to find, an activity known as an Easter egg hunt. A similar tradition of egg painting exists in areas of the world influenced by the culture of Persia. Before the spring equinox in the Persian New Year tradition (called Norouz), each family member decorates a hard-boiled egg and sets them together in a bowl. The tradition of a dancing egg is held during the feast of Corpus Christi in Catalan cities since the 16th century. It consists of an emptied egg, positioned over the water jet from a fountain, which starts turning without falling.
Although a food item, raw eggs are sometimes thrown at houses, cars, or people. This act, known commonly as " egging" in the various English-speaking countries, is a minor form of vandalism and, therefore, usually a criminal offense and is capable of damaging property (egg whites can degrade certain types of vehicle paint) as well as potentially causing serious eye injury. On Halloween, for example, trick or treaters have been known to throw eggs (and sometimes flour) at property or people from whom they received nothing. Eggs are also often thrown in protests, as they are inexpensive and nonlethal, yet very messy when broken.
Collecting
Egg collecting was a popular hobby in some cultures, includingEuropean Australians
European Australians are citizens or residents of Australia whose ancestry originates from the peoples of Europe. They form the largest panethnicity, panethnic group in the country. At the 2021 census, the number of ancestry responses categor ...
. Traditionally, the embryo would be removed before a collector stored the egg shell.
Collecting eggs of wild birds is now banned by many jurisdictions, as the practice can threaten rare species. In the United Kingdom, the practice is prohibited by the Protection of Birds Act 1954 and Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981. However, illegal collection and trading persists.
Since the protection of wild bird eggs was regulated, early collections have come to the museums as curiosities. For example, the Australian Museum hosts a collection of about 20,000 registered clutches of eggs, and the collection in Western Australia Museum has been archived in a gallery. Scientists regard egg collections as a good natural-history data, as the details recorded in the collectors' notes have helped them to understand birds' nesting behaviors.
See also
* List of egg topics * Animal shell * Butterfly eggs *Egg white
Egg white is the clear liquid (also called the albumen or the glair/glaire) contained within an egg. In chickens, it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms a ...
* Fossil egg
* Haugh unit
* Oology
*Oviparous
Oviparous animals are animals that reproduce by depositing fertilized zygotes outside the body (i.e., by laying or spawning) in metabolically independent incubation organs known as eggs, which nurture the embryo into moving offsprings kno ...
*Trophic egg A trophic egg is an egg (biology), egg whose function is not reproduction but nutrition; in essence, the trophic egg serves as food for offspring hatched from viable eggs. In most species that produce them, a trophic egg is usually an Fertilization, ...
* Organic egg production
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Egg (Biology) Animal reproductive system Aviculture Bird breeding Oology