|
Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other Taxon, taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a neural tube, hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anus, anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three phylum, subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateria
Bilateria () is a large clade of animals characterised by bilateral symmetry during embryonic development. This means their body plans are laid around a longitudinal axis with a front (or "head") and a rear (or "tail") end, as well as a left–right–symmetrical belly ( ventral) and back ( dorsal) surface. Nearly all bilaterians maintain a bilaterally symmetrical body as adults; the most notable exception is the echinoderms, which have pentaradial symmetry as adults, but bilateral symmetry as embryos. With few exceptions, bilaterian embryos are triploblastic, having three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm, and have complete digestive tracts with a separate mouth and anus. Some bilaterians lack body cavities, while others have a primary body cavity derived from the blastocoel, or a secondary cavity, the coelom. Cephalization is a characteristic feature among most bilaterians, where the sense organs and central nerve ganglia become concentrated at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
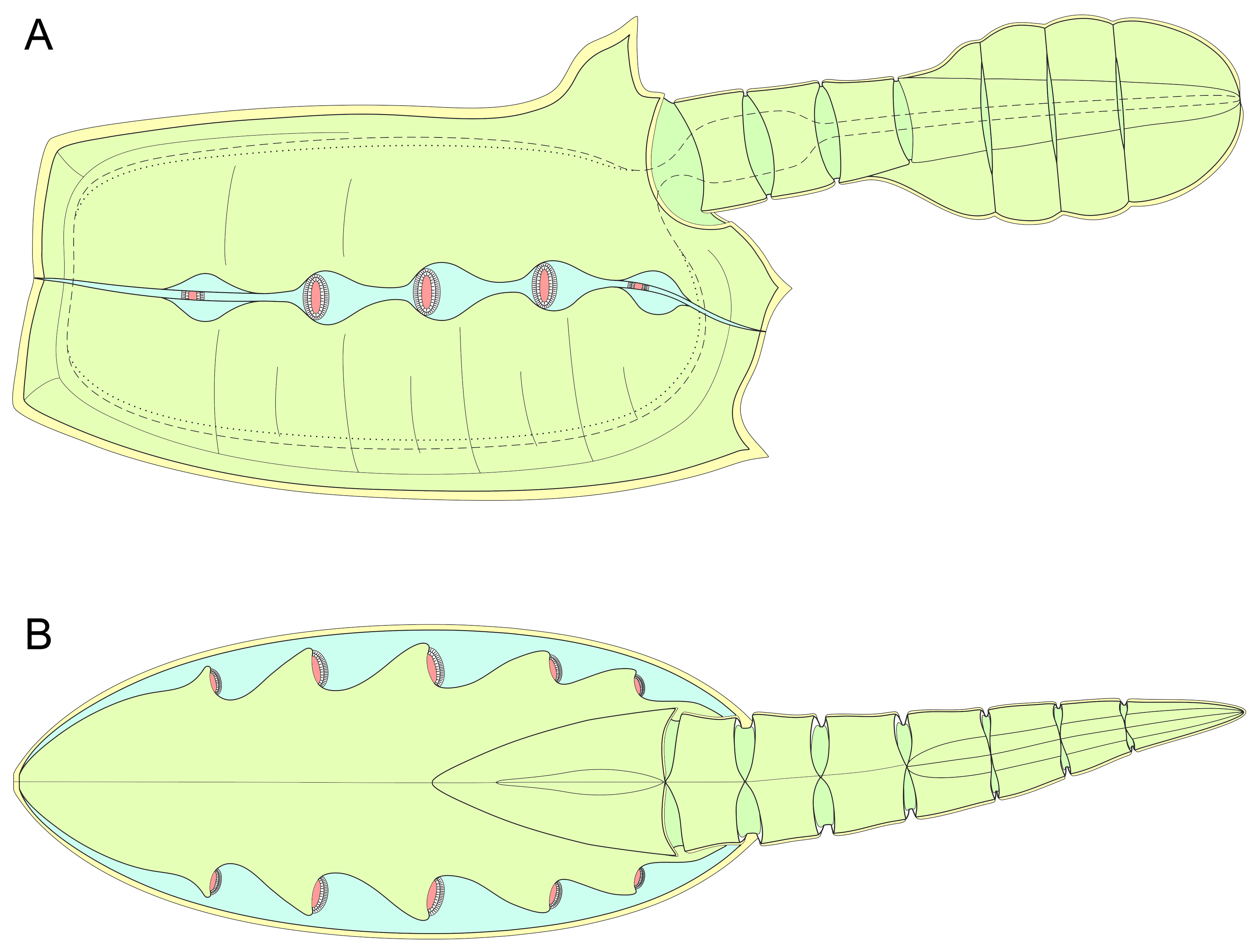
Vetulicolia
Vetulicolia is a group of bilaterian marine animals encompassing several extinct species from the Cambrian, and possibly Ediacaran, periods. As of 2023, the majority of workers favor placing Vetulicolians in the stem group of the Chordata, but some continue to favor a more crownward placement as a sister group to the Tunicata. It was initially erected as a monophyletic clade with the rank of phylum in 2001, with subsequent work supporting its monophyly. However, more recent research suggests that vetulicolians may be paraphyletic and form a basal evolutionary grade of stem chordates. Etymology The taxon name, Vetulicolia, is derived from the type genus, '' Vetulicola'', which is a compound Latin word composed of ''vetuli'' "old" and ''cola'' "inhabitant". It was named after '' Vetulicola cuneata'', the first species of the group described in 1987. Description The vetulicolian body plan comprises two parts: a voluminous rostral (anterior) forebody, tipped with an anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, have myocytes and are motility, able to move, can reproduce sexually, and grow from a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Animals form a clade, meaning that they arose from a single common ancestor. Over 1.5 million extant taxon, living animal species have been species description, described, of which around 1.05 million are insects, over 85,000 are molluscs, and around 65,000 are vertebrates. It has been estimated there are as many as 7.77 million animal species on Earth. Animal body lengths range from to . They have complex ecologies and biological interaction, interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactores
Olfactores is a clade within the Chordata that comprises the Tunicata ( Urochordata) and the Vertebrata (sometimes referred to as Craniata). Olfactores represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, as the Cephalochordata are the only chordates not included in the clade. This clade is defined by a more advanced olfactory system which, in the immediate vertebrate generation, gave rise to nostrils. Etymology The name Olfactores comes from Latin *''olfactores'' ("smellers," from purposive supine ''olfactum'' of ''olfacio'', "to smell," with plural masculine agentive nominalizing suffix ''-tores''), due to the development of pharyngeal respiratory and sensory functions, in contrast with cephalochordates such as the lancelet which lack a respiratory system and specialized sense organs. Olfactores hypothesis The long-standing Euchordata hypothesis that Cephalochordata is a sister taxon to Craniata was once widely accepted, likely influenced by significant tunicate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnanozoon
''Yunnanozoon lividum'' (Yunnan + Greek ζῷον ''zôion'' (animal), with species name Latin ''lividum''; (lead-coloured), referring to preserved colour of specimens) is an extinct species of bilaterian animal from the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang biota of Yunnan province, China. Its affinities have been long the subject of controversy. Description The body of ''Yunnanozoon'' was fusiform, with specimens ranging from in length. The body was strongly laterally compressed, meaning that it was taller than it was wide. A segmented dorsal unit was present on the top of the body. The first segment of which was triangular, while the other segments were approximately rectangular. Axial stripes also ran down the body in the region immediately below the dorsal unit. Towards the front of the animal were 7 pairs of filamentous arches. These arches were covered by sac-like structures which had openings between them. Towards the back of the body a tube-like structure was present, possibly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tunicate
Tunicates are marine invertebrates belonging to the subphylum Tunicata ( ). This grouping is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time called Urochordata, and the term urochordates is still sometimes used for these animals. Despite their simple appearance and very different adult form, their close relationship to the vertebrates is certain. Both groups are chordates, as evidenced by the fact that during their mobile larval stage, tunicates possess a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, post-anal tail, and an endostyle. They resemble a tadpole. Tunicates are the only chordates that have lost their Myomere, myomeric segmentation, with the possible exception of the seriation of the gill slits. However, Doliolida, doliolids still display segmentation of the muscle bands. Some tunicates live as solitary individuals, but others replicate by budding and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caudata
The Caudata are a group of amphibians containing the extant salamanders (the order Urodela) and all extinct species of amphibians more closely related to salamanders than to frogs. They are typically characterized by a superficially lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. Disagreement exists between different authorities as to the definition of the terms "Caudata" and "Urodela". Some maintain that Urodela should be restricted to the crown group, with Caudata being used for the total group. Others restrict the name Caudata to the crown group and use Urodela for the total group. The former approach seems to be most widely adopted and is used in this article. Evolution The origins and evolutionary relationships between the three main groups of amphibians ( apodans, urodeles and anurans) is a matter of debate. A 2005 molecular phylogeny, based on rDNA a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conodont
Conodonts, are an extinct group of marine jawless vertebrates belonging to the class Conodonta (from Ancient Greek κῶνος (''kōnos''), meaning " cone", and ὀδούς (''odoús''), meaning "tooth"). They are primarily known from their hard, mineralised tooth-like structures called "conodont elements" that in life were present in the oral cavity and used to process food. Rare soft tissue remains suggest that they had elongate eel-like bodies with large eyes. Conodonts were a long-lasting group with over 300 million years of existence from the Cambrian (over 500 million years ago) to the beginning of the Jurassic (around 200 million years ago). Conodont elements are highly distinctive to particular species and are widely used in biostratigraphy as indicative of particular periods of geological time. Discovery and understanding of conodonts The teeth-like fossils of the conodont were first discovered by Heinz Christian Pander and the results published in Saint Petersburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaspriggina
''Metaspriggina'' is a genus of chordate initially known from two specimens in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and 44 specimens found in 2012 at the Marble Canyon bed in Kootenay National Park. Whilst named after the Ediacaran organism ''Spriggina'', later work has shown the two to be unrelated. ''Metaspriggina'' is considered to represent a primitive chordate, possibly transitional between cephalochordates and the earliest vertebrates, albeit this has been questioned because it seems to possess most of the characteristics attributed to craniates. It lacked fin A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. F ...s and had a weakly developed Skull, cranium, but it did possess two well-developed, upward-facing eyes with nostrils behind them. ''Metaspriggina'' also possess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarnemia
''Yarnemia ascidiformis'' is a fossil tentatively classified as a tunicate. While ''Y. ascidiformis'' looks similar to tunicates, the oldest unequivocal tunicate, ''Shankouclava'' dates to the Cambrian period, while ''Y. ascidiformis'' is Ediacaran in age. Discovery and name The holotype A holotype (Latin: ''holotypus'') is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of s ... fossil of ''Yarnemia'' was found from the Ustʹ Pinega Formation between 1976 and 1978, and described in 1984. The generic name ''Yarnemia'' comes from the village of Yarnema near which the first specimens were found. The specific epithet, ''ascidiformis'', refers to the likeness to ascidians. Description ''Yarnemia ascidiformis'' is a possible tunicate, growing up to in length, with the standard oblong body and two openings, or siphons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrichthyes
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. Chondrichthyes are aquatic vertebrates with paired fins, paired nares, placoid scales, conus arteriosus in the heart, and a lack of opercula and swim bladders. Within the infraphylum Gnathostomata, cartilaginous fishes are distinct from all other jawed vertebrates. The class is divided into two subclasses: Elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, skates and sawfish) and Holocephali ( chimaeras, sometimes called ghost sharks, which are sometimes separated into their own class). Extant chondrichthyans range in size from the finless sleeper ray to the over whale shark. Anatomy Skeleton The skeleton is cartilaginous. The notochord is gradually replaced by a vertebral column during development, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |