|
Metaspriggina
''Metaspriggina'' is a genus of chordate initially known from two specimens in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and 44 specimens found in 2012 at the Marble Canyon bed in Kootenay National Park. Whilst named after the Ediacaran organism ''Spriggina'', later work has shown the two to be unrelated. ''Metaspriggina'' is considered to represent a primitive chordate, possibly transitional between cephalochordates and the earliest vertebrates, albeit this has been questioned because it seems to possess most of the characteristics attributed to craniates. It lacked fin A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foils that produce lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while traveling in water, air, or other fluids. F ...s and had a weakly developed Skull, cranium, but it did possess two well-developed, upward-facing eyes with nostrils behind them. ''Metaspriggina'' also possess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaspriggina NT Small
''Metaspriggina'' is a genus of chordate initially known from two specimens in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and 44 specimens found in 2012 at the Marble Canyon bed in Kootenay National Park. Whilst named after the Ediacaran organism ''Spriggina'', later work has shown the two to be unrelated. ''Metaspriggina'' is considered to represent a primitive chordate, possibly transitional between cephalochordates and the earliest vertebrates, albeit this has been questioned because it seems to possess most of the characteristics attributed to craniates. It lacked fins and had a weakly developed cranium, but it did possess two well-developed, upward-facing eyes with nostrils behind them. ''Metaspriggina'' also possessed a notochord, along with seven pairs of pharyngeal bars, possibly made of cartilage. Surprisingly, they were not formed from a singular bone, but they were formed of multiple separate pairs of bones, along with first two of them that were enlarged compared to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambrian Chordate
The Cambrian chordates are an extinct group of animals belonging to the phylum Chordata that lived during the Cambrian, between 538 and 485 million years ago. The first Cambrian chordate known is '' Pikaia gracilens'', a lancelet-like animal from the Burgess Shale in British Columbia, Canada. The discoverer, Charles Doolittle Walcott, described it as a kind of worm (annelid) in 1911, but it was later identified as a chordate. Subsequent discoveries of other Cambrian fossils from the Burgess Shale in 1991, and from the Chengjiang biota of China in 1991, which were later found to be of chordates, several Cambrian chordates are known, with some fossils considered as putative chordates. The Cambrian chordates are characterised by the presence of segmented muscle blocks called myomeres and notochord, the two defining features of chordates. Before the full understanding of Cambrian fossils, chordates as members the most advanced phylum were believed to appear on Earth much later than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble Canyon (Canadian Rockies)
Marble Canyon surrounds Tokumm Creek just above its confluence with the Vermilion River, at the north end of Kootenay National Park in the Canadian Rockies of British Columbia. South of the canyon on Highway 93 is Numa Falls on the Vermilion River. As described by '' Canadian Alpine Journal'' in 1913, " okumm Creekjoins Vermilion River through a magnificent gorge, or box canyon, so narrow that at several places the fissure, for it seems little more than a crack in the rock strata, is bridged by great boulders that have become wedged across it. It was a feature well worth seeing." Cambrian Lagerstatte A major new find was announced in early 2014 of fossilized Cambrian soft-bodied organisms in or near Marble Canyon that rival or even surpass the nearby Burgess Shale fossil site in size and preservation. The report said that 22% of the observed species found in the initial excavation were new to science. Additionally, several species previously known only from Chinese Lagerstätt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordata
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (Apomorphy and synapomorphy, synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other Taxon, taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a neural tube, hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anus, anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three phylum, subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pikaia
''Pikaia gracilens'' is an extinct, primitive chordate marine animal known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. Described in 1911 by Charles Doolittle Walcott as an annelid, and in 1979 by Harry B. Whittington and Simon Conway Morris as a chordate, it became "the most famous early chordate fossil", or "famously known as the earliest described Cambrian chordate". It is estimated to have lived during the latter period of the Cambrian explosion. Since its initial discovery, more than a hundred specimens have been recovered. The body structure resembles that of the lancelet and it swam perhaps much like an eel. A notochord and myomeres (segmented blocks of skeletal muscles) span the entire length of the body, and are considered the defining signatures of chordate characters. Its primitive nature is indicated by the body covering, a cuticle, which is characteristic of invertebrates and some protochordates. A reinterpretation in 2024 found evidence of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
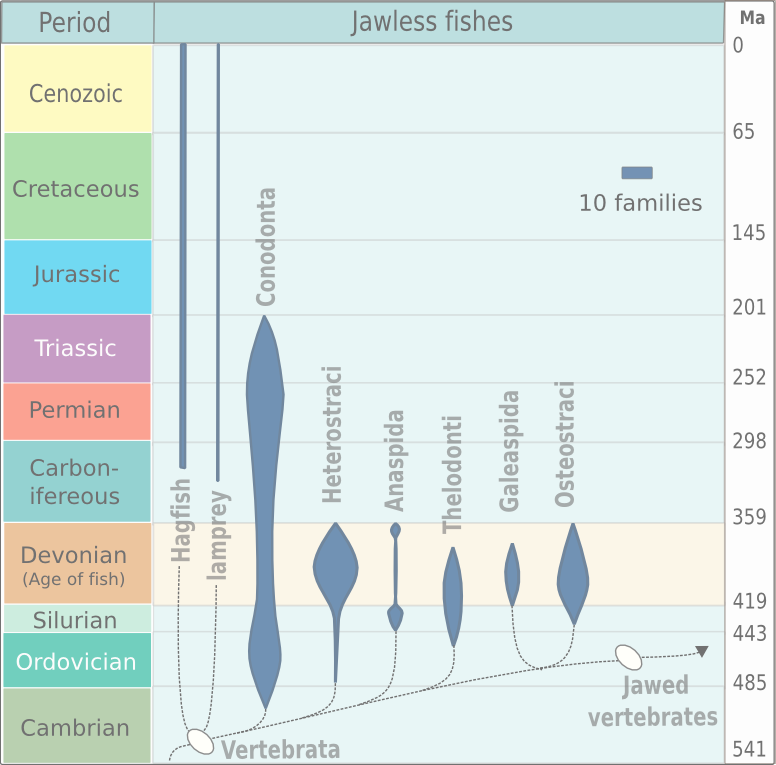
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nostril
A nostril (or naris , : nares ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbinates, whose function is to warm air on inhalation and remove moisture on exhalation. Fish do not breathe through noses, but they do have two small holes used for smelling, which can also be referred to as nostrils (with the exception of Cyclostomi, which have just one nostril). In humans, the nasal cycle is the normal ultradian cycle of each nostril's blood vessels becoming engorged in swelling, then shrinking. The nostrils are separated by the septum. The septum can sometimes be deviated, causing one nostril to appear larger than the other. With extreme damage to the septum and columella, the two nostrils are no longer separated and form a single larger external opening. Like other tetrapod A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wikti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the vertebral column. In non-vertebrate chordates a notochord persists. The notochord is derived from the embryonic mesoderm and consists of an inner core of vacuolated cells filled with glycoproteins, covered by two helical collagen-elastin sheaths. It lies longitudinally along the rostral-caudal (head to tail) axis of the body, dorsal to the gut tube, and ventral to the dorsal nerve cord. Some chordate invertebrates, such as tunicates, develop a notochord during the larval stage but lose it through subsequent stages into adulthood. The notochord is important for signaling the dorso-ventral patterning of cells coming from the mesodermal progenitors. This helps form the precursors needed for certain organs and the embryo to develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans and cyclostomes, it constitutes a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. It usually grows quicker than bone. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seabed
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as seabeds. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, Continental slope, slope, and Continental shelf, shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the "depth below seafloor". The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the "benthos". Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |