Eastern Wild Turkey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an
 An adult male (tom or gobbler) normally weighs from and measures in length. The adult female (hen) is typically much smaller at and is long. Per two large studies, the average weight of adult males is and the average weight of adult females is . The record-sized adult male wild turkey, according to the
An adult male (tom or gobbler) normally weighs from and measures in length. The adult female (hen) is typically much smaller at and is long. Per two large studies, the average weight of adult males is and the average weight of adult females is . The record-sized adult male wild turkey, according to the  The turkey has the second-highest maximum average weight of any North American bird, after the
The turkey has the second-highest maximum average weight of any North American bird, after the
 Wild turkeys prefer
Wild turkeys prefer
 Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400'' ''m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys do not migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400'' ''m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys do not migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
 Wild turkeys are
Wild turkeys are  Turkey populations can reach large numbers in small areas because of their ability to forage for different types of food. Early morning and late afternoon are the desired times for eating.
Turkey populations can reach large numbers in small areas because of their ability to forage for different types of food. Early morning and late afternoon are the desired times for eating.

 Males are
Males are
 In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by great horned owls (''Bubo virginianus''), American goshawk (''Accipiter atricapillus''), dog, domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris''), cat, domestic cats (''Felis catus''), and
In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by great horned owls (''Bubo virginianus''), American goshawk (''Accipiter atricapillus''), dog, domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris''), cat, domestic cats (''Felis catus''), and  Occasionally, if cornered, adult turkeys may try to fight off predators and large male toms can be especially aggressive in self-defense. When fighting off predators, turkeys may kick with their legs, using the spurs on their back of the legs as a weapon, bite with their beak, and ram with their relatively large bodies and may be able to deter predators up to the size of mid-sized mammals. Hens have been observed chasing off at least two species of hawks in flight when their poults are threatened.
Wild turkeys are not usually aggressive towards humans, but can be frightened or provoked to behave with aggression. They are most likely to attack if startled, cornered, harassed, or if approached too closely. Attacks and potential injuries can usually be avoided by giving wild turkeys a respectful amount of space and keeping outdoor spaces clean and undisturbed. Also, turkeys that are habituated to seeing people, at places like parks or campgrounds, can be tame and will even feed from the hands of people. Male toms occasionally will attack parked cars and reflective surfaces, thinking they see another turkey and must defend their territory.
Occasionally, if cornered, adult turkeys may try to fight off predators and large male toms can be especially aggressive in self-defense. When fighting off predators, turkeys may kick with their legs, using the spurs on their back of the legs as a weapon, bite with their beak, and ram with their relatively large bodies and may be able to deter predators up to the size of mid-sized mammals. Hens have been observed chasing off at least two species of hawks in flight when their poults are threatened.
Wild turkeys are not usually aggressive towards humans, but can be frightened or provoked to behave with aggression. They are most likely to attack if startled, cornered, harassed, or if approached too closely. Attacks and potential injuries can usually be avoided by giving wild turkeys a respectful amount of space and keeping outdoor spaces clean and undisturbed. Also, turkeys that are habituated to seeing people, at places like parks or campgrounds, can be tame and will even feed from the hands of people. Male toms occasionally will attack parked cars and reflective surfaces, thinking they see another turkey and must defend their territory.


 Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of Mexico and the southernmost parts of Arizona and New Mexico. Gould's wild turkeys are heavily protected and regulated. The subspecies was first described in 1856. They exist in small numbers in the U.S. but are abundant in northwestern portions of Mexico. A small population has been established in southern Arizona. Gould's are the largest of the six subspecies. They have longer legs, larger feet, and longer tail feathers. The main colors of the body feathers are copper and greenish-gold. This subspecies is heavily protected owing to its skittish nature and threatened status.
Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of Mexico and the southernmost parts of Arizona and New Mexico. Gould's wild turkeys are heavily protected and regulated. The subspecies was first described in 1856. They exist in small numbers in the U.S. but are abundant in northwestern portions of Mexico. A small population has been established in southern Arizona. Gould's are the largest of the six subspecies. They have longer legs, larger feet, and longer tail feathers. The main colors of the body feathers are copper and greenish-gold. This subspecies is heavily protected owing to its skittish nature and threatened status.
 The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many Native American tribes all over North America. It is a favorite meal in eastern tribes. Eastern Native American tribes consumed both the eggs and meat, sometimes turning the latter into a type of jerky to preserve it and make it last through cold weather. They provided habitat by burning down portions of forests to create meadows which would attract mating birds, and thus give a clear shot to hunters. The feathers of turkeys also often made their way into the rituals and headgear of many tribes. Many leaders, such as Catawba (tribe), Catawba chiefs, traditionally wore turkey feather headdresses.
Significant peoples of several tribes, including Muscogee Creek and Wampanoag people, Wampanoag, wore turkey feather cloaks. The turkey clan is one of the three Lenape clans. Movements of wild turkeys inspired the Caddo tribe's turkey dance. The Navajo people of Northeastern Arizona, New Mexico and Utah call the turkey and relate the bird to the corn and seeds which The Turkey in Navajo folklore brought from the Third Navajo World. It is one of the Navajos' sacred birds, with the Navajo people using the feathers and parts in multiple traditional ceremonies.
The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many Native American tribes all over North America. It is a favorite meal in eastern tribes. Eastern Native American tribes consumed both the eggs and meat, sometimes turning the latter into a type of jerky to preserve it and make it last through cold weather. They provided habitat by burning down portions of forests to create meadows which would attract mating birds, and thus give a clear shot to hunters. The feathers of turkeys also often made their way into the rituals and headgear of many tribes. Many leaders, such as Catawba (tribe), Catawba chiefs, traditionally wore turkey feather headdresses.
Significant peoples of several tribes, including Muscogee Creek and Wampanoag people, Wampanoag, wore turkey feather cloaks. The turkey clan is one of the three Lenape clans. Movements of wild turkeys inspired the Caddo tribe's turkey dance. The Navajo people of Northeastern Arizona, New Mexico and Utah call the turkey and relate the bird to the corn and seeds which The Turkey in Navajo folklore brought from the Third Navajo World. It is one of the Navajos' sacred birds, with the Navajo people using the feathers and parts in multiple traditional ceremonies.
Turkey as U.S. national bird
*View the [http://www.ensembl.org/Meleagris_gallopavo/Info/Index/ turkey genome] in Ensembl * * {{Authority control Meleagris Birds described in 1758 Birds of Canada Game birds Native American cuisine Hunting in the United States Birds of the United States Birds of Mexico Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Symbols of Alabama New England cuisine category:Cuisine of the Southwestern United States category:Thanksgiving food
upland game bird
Upland game bird is an American term which refers to non-waterfowl game birds in groundcover-rich terrestrial ecosystems above wetlands and riparian zones (i.e. "uplands"), which are commonly hunted with gun dogs (pointing breeds, flushing spaniel ...
native to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
, one of two extant species of turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes
Galliformes is an order (biology), order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkey (bird), turkeys, chickens, Old World quail, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems ...
. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey
The domestic turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo domesticus'') is a large fowl, one of the two species in the genus ''Meleagris'' and the same species as the wild turkey. Although turkey domestication was thought to have occurred in central Mesoamerica ...
(''M. g. domesticus''), which was originally derived from a southern Mexican subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
of wild turkey (not the related ocellated turkey
The ocellated turkey (''Meleagris ocellata'') is a species of turkey residing primarily in the Yucatán Peninsula, Mexico, as well as in parts of Belize and Guatemala. A relative of the North American wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo''), it wa ...
).
Taxonomy
The wild turkey wasformally described
A species description is a formal scientific description of a newly encountered species, typically articulated through a scientific publication. Its purpose is to provide a clear description of a new species of organism and explain how it differ ...
in 1758 by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae
' (originally in Latin written ' with the Orthographic ligature, ligature æ) is one of the major works of the Sweden, Swedish botanist, zoologist and physician Carl Linnaeus (1707–1778) and introduced the Linnaean taxonomy. Although the syste ...
'' under its current binomial name
In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammatical forms, altho ...
''Meleagris gallopavo''. The type locality is Mexico. The genus name ''Meleagris'' is from Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
μελεαγρις/''meleagris'' meaning "guineafowl". The specific epithet ''gallopavo'' is a late Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Church, Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Western Roman Empire, Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidi ...
word for a wild turkey: it combines Latin ''gallus'' meaning "fowl" and ''pavo'' meaning "peacock". The word was used in 1555 by the Swiss naturalist Conrad Gessner
Conrad Gessner (; ; 26 March 1516 – 13 December 1565) was a Swiss physician, naturalist, bibliographer, and philologist. Born into a poor family in Zürich, Switzerland, his father and teachers quickly realised his talents and supported him t ...
in his ''Historiae animalium
("History of the Animals"), published in Zurich in 1551–1558 and 1587, is an encyclopedic "inventory of renaissance zoology" by Conrad Gessner (1516–1565). Gessner was a medical doctor and professor at the Carolinum in Zürich, the precurso ...
''.
Six subspecies
In Taxonomy (biology), biological classification, subspecies (: subspecies) is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (Morphology (biology), morpholog ...
are recognised:
* ''Meleagris gallopavo silvestris'' Vieillot
Louis Pierre Vieillot (10 May 1748, Yvetot – 24 August 1830, Sotteville-lès-Rouen) was a French ornithologist.
Vieillot is the author of the first scientific descriptions and Linnaean names of a number of birds, including species he collecte ...
, 1817 – south Canada and central, east USA
* ''Meleagris gallopavo osceola'' Scott
Scott may refer to:
Places
Canada
* Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec
* Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380
* Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Sas ...
, 1890 – Florida (USA)
* ''Meleagris gallopavo intermedia'' Sennett, 1879 – north Texas to central east Mexico
* ''Meleagris gallopavo mexicana'' Gould
Gould may refer to:
People
* Gould (name), a surname
Places United States
* Gould, Arkansas, a city
* Gould, Colorado, an unincorporated community
* Gould, Ohio, an unincorporated community
* Gould, Oklahoma, a town
* Gould, West Virginia, an ...
, 1856 – northwest, central north Mexico (includes ''onusta'')
* ''Meleagris gallopavo merriami'' Nelson
Nelson may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Nelson'' (1918 film), a historical film directed by Maurice Elvey
* ''Nelson'' (1926 film), a historical film directed by Walter Summers
* ''Nelson'' (opera), an opera by Lennox Berkeley to a lib ...
, 1900 – west USA
* ''Meleagris gallopavo gallopavo'' Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming o ...
, 1758 – south Mexico
Description
 An adult male (tom or gobbler) normally weighs from and measures in length. The adult female (hen) is typically much smaller at and is long. Per two large studies, the average weight of adult males is and the average weight of adult females is . The record-sized adult male wild turkey, according to the
An adult male (tom or gobbler) normally weighs from and measures in length. The adult female (hen) is typically much smaller at and is long. Per two large studies, the average weight of adult males is and the average weight of adult females is . The record-sized adult male wild turkey, according to the National Wild Turkey Federation
The National Wild Turkey Federation is an international non-profit organization whose mission is 'the conservation of the wild turkey and the preservation of our hunting heritage.' It currently has more than 250,000 members in the United States ...
, weighed , with records of tom turkeys weighing over uncommon but not rare. Considering its maximum and average weight, it is among the heaviest flying birds in the world.
The wings are relatively small, as is typical of the galliform order, and the wingspan ranges from . The wing chord is only . The bill
Bill(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Banknote, paper cash (especially in the United States)
* Bill (law), a proposed law put before a legislature
* Invoice, commercial document issued by a seller to a buyer
* Bill, a bird or animal's beak
Pl ...
is also relatively small, as adults measure in culmen length. The tarsus of the wild turkey is quite long and sturdy, measuring from . The tail is also relatively long, ranging from .
Fully-grown wild turkeys have long, reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. Each foot has three front toes, with a shorter, rear-facing toe; males have a spur behind each of their lower legs, used to spar with other males.
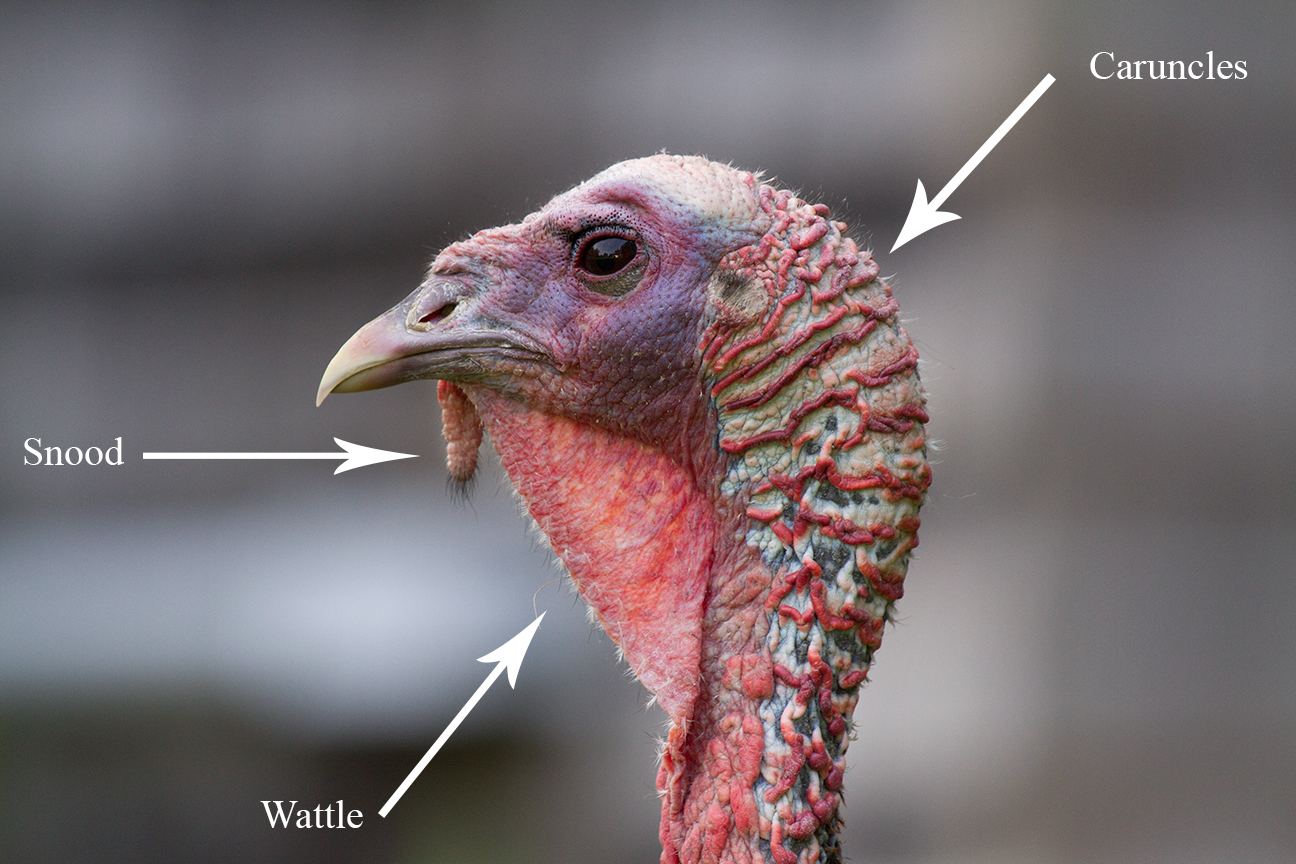
The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes gray-brown, overall, with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in older males. Mature males have a large, featherless, reddish head and red throat, with red wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy, unique growths called caruncles, which may be used to identify certain birds from one another. When toms are excited, a fleshy flap on the bill (called a snood) expands, and this, the wattles and the bare skin of the head and neck all become red with enhanced flow of blood to the head. Tail feathers are of the same length in adults but of different lengths in juveniles.
Males have a long, dark, fan-shaped tail and glossy, bronze wings. As with many other species of Galliformes
Galliformes is an order (biology), order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkey (bird), turkeys, chickens, Old World quail, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems ...
, turkeys exhibit strong sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
. The male is substantially larger than the female, and his feathers have areas of red, purple, green, copper, bronze, and gold iridescence
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear gradually to change colour as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Iridescence is caused by wave interference of light in microstru ...
. The preen gland (uropygial gland
The uropygial gland, informally known as the preen gland or the oil gland, is a bilobed sebaceous gland possessed by the majority of birds used to distribute the gland's oil through the plumage by means of Preening (bird), preening. It is locate ...
) is also larger in males compared to females. In contrast to the majority of other birds, they are colonized by bacteria of unknown function (''Corynebacterium uropygiale
''Corynebacterium'' () is a genus of Gram-positive bacteria and most are aerobic. They are bacilli (rod-shaped), and in some phases of life they are, more specifically, club-shaped, which inspired the genus name (''coryneform'' means "club-sha ...
''). Males typically have at least one "beard", a tuft of coarse hair-like filaments (mesofiloplumes), growing from the center of the breast. Beards grow continuously during the turkey's lifespan and a one-year-old male has a beard up to long. Approximately 10% of females have a beard, usually shorter and thinner than that of the male.
Females have feathers that are duller overall, in shades of brown and gray. Parasites can dull the coloration of both sexes; in males, vivid coloration may serve as a signal of health. The primary wing feathers have white bars. Turkeys have approximately 5,000 to 6,000 feathers. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between jakes and toms is that jakes have very short "beards" and tail fans with longer feathers in the middle. The tom's tail fan feathers are uniform in length.
 The turkey has the second-highest maximum average weight of any North American bird, after the
The turkey has the second-highest maximum average weight of any North American bird, after the trumpeter swan
The trumpeter swan (''Cygnus buccinator'') is a species of swan found in North America. The heaviest living bird native to North America, it is also the largest extant species of waterfowl, with a wingspan of 185 to 304.8 cm (6 ft 2 in ...
(''Cygnus buccinator''). By average mass, however, several other American birds surpass the mean weight of the turkey, including the American white pelican
The American white pelican (''Pelecanus erythrorhynchos'') is a large aquatic soaring bird from the order Pelecaniformes. It breeds in interior North America, moving south and to the coasts, as far as Costa Rica, in winter.
Taxonomy
The Americ ...
(''Pelecanus erythrorhynchos''), the tundra swan
The tundra swan (''Cygnus columbianus'') is a small swan of the Holarctic. The two taxa within it are usually regarded as conspecific, but are also sometimes split into two species: Bewick's swan (''Cygnus bewickii'') of the Palaearctic and the w ...
(''Cygnus columbianus columbianus''), the endangered California condor
The California condor (''Gymnogyps californianus'') is a New World vulture and the largest North American land bird. It became extinct in the wild in 1987 when all remaining wild individuals were captured, but has since been reintroduced to n ...
(''Gymnogyps californianus''), and whooping crane
The whooping crane (''Grus americana'') is an endangered Crane (bird), crane species, native to North America, named for its "whooping" calls. Along with the sandhill crane (''Antigone canadensis''), it is one of only two crane species native to ...
(''Grus americana'').
Habitat
hardwood
Hardwood is wood from Flowering plant, angiosperm trees. These are usually found in broad-leaved temperate and tropical forests. In temperate and boreal ecosystem, boreal latitudes they are mostly deciduous, but in tropics and subtropics mostl ...
and mixed conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
-hardwood forests with scattered openings such as pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing.
Types of pasture
Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, c ...
s, field
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
s, orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit tree, fruit- or nut (fruit), nut-producing trees that are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also so ...
s and seasonal marsh
In ecology, a marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous plants rather than by woody plants.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p More in genera ...
es. They seemingly can adapt to virtually any dense native plant community as long as coverage and openings are widely available. Open, mature forest with a variety of interspersion of tree species appear to be preferred. In the Northeast of North America, turkeys are most profuse in hardwood timber of oak
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
-hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
(''Quercus
An oak is a hardwood tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' of the beech family. They have spirally arranged leaves, often with lobed edges, and a nut called an acorn, borne within a cup. The genus is widely distributed in the Northern Hemisp ...
''-''Carya
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
'') and forests of red oak (''Quercus rubra
''Quercus rubra'', the northern red oak, is an oak tree in the red oak group (''Quercus'' section ''Lobatae''). It is a native of North America, in the eastern and central United States and southeast and south-central Canada. It has been intro ...
''), beech (''Fagus grandifolia
Beech (genus ''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to subtropical (accessory forest element) and temperate (as dominant element of mesophytic forests) Eurasia and North America. There are 14 accepted species i ...
''), cherry (''Prunus serotina
''Prunus serotina'', commonly called black cherry,World Economic Plants: A Standard Reference, Second Edition'. CRC Press; 19 April 2016. . p. 833–. wild black cherry, rum cherry, or mountain black cherry, is a deciduous tree or shrub in the r ...
'') and white ash (''Fraxinus americana
''Fraxinus americana'', the white ash or American ash, is a fast-growing species of ash tree native to eastern and central North America.
White ash trees are threatened by the invasive emerald ash borer. The tree is highly valued as lumber.
...
''). Best ranges for turkeys in the Coastal Plain
A coastal plain (also coastal plains, coastal lowland, coastal lowlands) is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a sea coast. A fall line commonly marks the border between a coastal plain and an upland area.
Formation
Coastal plains can f ...
and Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
sections have an interspersion of clearings, farms, and plantations with preferred habitat along principal rivers and in cypress (''Taxodium distichum
''Taxodium distichum'' (baldcypress, bald-cypress, bald cypress, swamp cypress; ;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a ...
'') and tupelo (''Nyssa sylvatica
''Nyssa sylvatica'', commonly known as tupelo, black tupelo, black gum or sour gum, is a medium-sized deciduous tree native to eastern North America from the coastal Northeastern United States and southern Ontario south to central Florida and ea ...
'') swamps.
In the Appalachian Plateau
The Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a range that run from Nova Scotia in Canada to Alabama in the United States.
The Appalachi ...
and Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms " Al ...
birds occupy mixed forest of oaks and pines on southern and western slopes, also hickory with diverse understories. Bald cypress and sweet gum (''Liquidambar styraciflua
''Liquidambar styraciflua'', commonly known as the American sweetgum among other names, is a deciduous tree in the genus ''Liquidambar'' native to warm temperate areas of eastern North America and tropical montane regions of Mexico and Central A ...
'') swamps of south Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
; also hardwood of ''Cliftonia
''Cliftonia monophylla'', the buck-wheat tree, buckwheat tree or black titi, is a tree native to the southeastern United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily l ...
'' (a heath) and oak in north-central Florida. Lykes Fisheating Creek
Fisheating Creek is a stream that flows into Lake Okeechobee in Florida. It is the only remaining free-flowing water course feeding into the lake, and the second-largest natural source for the lake. Most of the land surrounding the stream is eithe ...
area of south Florida has up to 51% cypress, 12% hardwood hammocks, 17% glades of short grasses with isolated live oak (''Quercus virginiana
''Quercus virginiana'', also known as the southern live oak, is an evergreen oak tree endemic to the Southeastern United States. Though many other species are loosely called live oak, the southern live oak is particularly iconic of the Old South. ...
''); nesting in neighboring prairies. Original habitat here was mainly longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris
The longleaf pine (''Pinus palustris'') is a pine species native to the Southeastern United States, found along the coastal plain from East Texas to southern Virginia, extending into northern and central Florida. In this area it is also known as ...
'') with turkey oak (''Quercus laevis
''Quercus laevis'', the turkey oak, is a member of the red oak group of oaks. It is native to the southeastern United States. The name turkey oak derives from the resemblance of the leaves to a turkey's foot. A Turkish and southern European spe ...
'') and slash pine (''Pinus elliottii
''Pinus elliottii'', commonly known as slash pine,Family, P. P. (1990). Pinus elliottii Engelm. slash pine. ''Silvics of North America: Conifers'', (654), 338. is a conifer tree native to the Southeastern United States. Slash pine is named after ...
'') "flatwoods", now mainly replaced by slash pine plantations.
In California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, turkeys live in a wide range of habitats; acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s are a favorite food, in addition to wild oats (''Avena barbata
''Avena barbata'' is a species of Avena, wild oat known by the common name slender wild oat. It has edible seeds. It is a diploidized autotetraploid grass (2n=4x=28). Its diploid ancestors are ''A. hirtula'' Lag. and ''A. wiestii'' Steud (2n=2x=1 ...
''), drawing turkeys to areas of open oak forest and oak savanna across the central areas of the state. They frequent the lower-elevation oak woodlands of the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
foothills and Coast Ranges, and the central coast north through Mendocino County
Mendocino County (; ''Mendocino'', Spanish language, Spanish for "of Antonio de Mendoza, Mendoza") is a County (United States), county located on the North Coast (California), North Coast of the U.S. state of California. As of the 2020 United S ...
, which is primarily open conifer forest with various species of ferns
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
growing in the understory. They can also be found in the conifer foothills and fern-heavy forested areas of the Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains are a rugged and lightly populated mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the western United States. As a mountain system within both the greater Pacific Coast Ranges and the California Coast R ...
and Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington (state), Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as m ...
in the northern areas of the state. In San Diego County
San Diego County (), officially the County of San Diego, is a county in the southwest corner of the U.S. state of California, north to its border with Mexico. As of the 2020 census, the population was 3,298,634; it is the second-most populous ...
, turkeys tend to be found farther from the coast, usually a minimum of 30–50 miles inland, at reasonably higher elevation; there is a healthy turkey population inhabiting the montane conifer woods and open oak forest habitats of the Cleveland National Forest
Cleveland National Forest is a National forest (United States), U.S. national forest in Southern California that encompasses 460,000 acres/ of inland Montane ecosystems, montane regions. It is approximately 60 miles from the Pacific Ocean, withi ...
, a region which borders on high desert and generally receives very minimal annual precipitation. Turkeys in these areas can be found in dense thickets of manzanita (''Arctostaphylos
''Arctostaphylos'' (; from "bear" and "bunch of grapes") is a genus of plants comprising the manzanitas () and bearberries. There are about 60 species of ''Arctostaphylos'', ranging from ground-hugging arctic, coastal, and mountain shrub t ...
''), often growing on arid hillsides, for shelter and nesting sites, as well as rocky and boulder-strewn chaparral
Chaparral ( ) is a shrubland plant plant community, community found primarily in California, southern Oregon, and northern Baja California. It is shaped by a Mediterranean climate (mild wet winters and hot dry summers) and infrequent, high-intens ...
foothills.
Behavior
Flight
 Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400'' ''m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys do not migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
Despite their weight, wild turkeys, unlike their domesticated counterparts, are agile, fast fliers. In ideal habitat of open woodland or wooded grasslands, they may fly beneath the canopy top and find perches. They usually fly close to the ground for no more than 400'' ''m (a quarter mile).
Wild turkeys have very good eyesight, but their vision is very poor at night. They will generally not see a predator until it is too late. At twilight most turkeys will head for the trees and roost well off the ground: it is safer to sleep there in numbers than to risk being victim to predators who hunt by night. Because wild turkeys do not migrate, in snowier parts of the species's habitat like the Northeast, Rockies, much of Canada, and the Midwest, it is very important for this bird to learn to select large conifer trees where they can fly onto the branches and shelter from blizzards.
Vocalizations
Wild turkeys have many calls: assemblycall
Call or Calls may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Games
* Call (poker), a bet matching an opponent's
* Call, in the game of contract bridge, a bid, pass, double, or redouble in the bidding stage
Music and dance
* Call (band), from L ...
, gobble, plain yelp, purr, cluck and purr, cluck, cutt, excited yelp, fly-down cackle, tree call, kee kee run, and putt. In early spring, males older than a year old and, occasionally to a lesser extent, males younger than a year old gobble to announce their presence to females and competing males. The gobble of a wild turkey can be heard up to a mile away. Males also emit a low-pitched "drumming" sound, produced by the movement of air in the air sac
Air sacs are spaces within an organism where there is the constant presence of air. Among modern animals, birds possess the most air sacs (9–11), with their extinct dinosaurian relatives showing a great increase in the pneumatization (presence ...
in the chest, similar to the booming of a prairie chicken
''Tympanuchus'' is a small genus of birds in the grouse family. They are commonly referred to as prairie-chickens.
Taxonomy
The genus ''Tympanuchus'' was introduced in 1841 by the German zoologist Constantin Wilhelm Lambert Gloger for the gre ...
. In addition they produce a sound known as the "spit", which is a sharp expulsion of air from this air sac.
Foraging
 Wild turkeys are
Wild turkeys are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize ...
, foraging on the ground or climbing shrubs and small trees to feed. They prefer eating acorn
The acorn is the nut (fruit), nut of the oaks and their close relatives (genera ''Quercus'', ''Notholithocarpus'' and ''Lithocarpus'', in the family Fagaceae). It usually contains a seedling surrounded by two cotyledons (seedling leaves), en ...
s, nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed
* Nut (food), a dry and edible fruit or seed, including but not limited to true nuts
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut, NUT or Nuts may also refer to:
A ...
, and other hard mast
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio mas ...
of various trees, including hazel
Hazels are plants of the genus ''Corylus'' of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family, Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K ...
, chestnut
The chestnuts are the deciduous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Castanea'', in the beech family Fagaceae. The name also refers to the edible nuts they produce. They are native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Description
...
, hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes 19 species accepted by ''Plants of the World Online''.
Seven species are native to southeast Asia in China, Indochina, and northeastern India (Assam), and twelve ...
, and pinyon pine
The pinyon or piñon pine group grows in southwestern North America, especially in New Mexico, Colorado, Arizona, and Utah, with the single-leaf pinyon pine just reaching into southern Idaho. The trees yield edible Pine nut, nuts, which are a sta ...
, as well as various seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds ...
s, berries
A berry is a small, pulpy, and often edible fruit. Typically, berries are juicy, rounded, brightly colored, sweet, sour or tart, and do not have a stone fruit, stone or pit (fruit), pit although many wikt:pip#Etymology 2, pips or seeds may be p ...
such as juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' ( ) of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere as far south ...
and bearberry
Bearberries are three species of dwarf shrubs in the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. Unlike the other species of ''Arctostaphylos'' (see manzanita), they are adapted to Arctic and subarctic climates, and have a circumpolar distribution in northern N ...
, bud
In botany, a bud is an undeveloped or Plant embryogenesis, embryonic Shoot (botany), shoot and normally occurs in the axil of a leaf or at the tip of a Plant stem, stem. Once formed, a bud may remain for some time in a dormancy, dormant conditi ...
s, leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, ...
, fern fronds, roots, and insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s. Turkeys also occasionally consume amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s such as salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s and small reptile
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocepha ...
s such as lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
s and small snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
s. Poults have been observed eating insects, berries, and seeds. Wild turkeys often feed in cow pasture
Pasture (from the Latin ''pastus'', past participle of ''pascere'', "to feed") is land used for grazing.
Types of pasture
Pasture lands in the narrow sense are enclosed tracts of farmland, grazed by domesticated livestock, such as horses, c ...
s, sometimes visit backyard bird feeders, and favor croplands after harvest to scavenge seeds on the ground. Turkeys are also known to eat a wide variety of grass
Poaceae ( ), also called Gramineae ( ), is a large and nearly ubiquitous family (biology), family of monocotyledonous flowering plants commonly known as grasses. It includes the cereal grasses, bamboos, the grasses of natural grassland and spe ...
es.
 Turkey populations can reach large numbers in small areas because of their ability to forage for different types of food. Early morning and late afternoon are the desired times for eating.
Turkey populations can reach large numbers in small areas because of their ability to forage for different types of food. Early morning and late afternoon are the desired times for eating.
Social structure and mating

 Males are
Males are polygamous
Polygamy (from Late Greek , "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, it is called polygyny. When a woman is married to more than one h ...
, mating with as many hens as they can. Male wild turkeys display
Display may refer to:
Technology
* Display device, output device for presenting information, including:
** Electronic visual display, output device to present information for visual or tactile reception
*** Cathode-ray tube (CRT), that uses an el ...
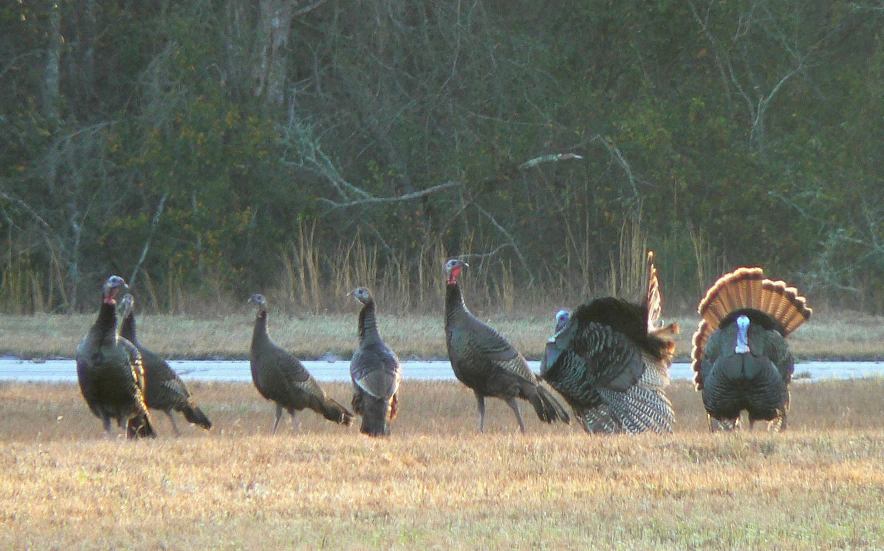
for females by puffing out their feathers, spreading out their tails, and dragging their wings. This behavior is most commonly referred to as strutting. Their heads and necks are colored with red, white, and blue. The color can change with the turkey's mood, with a solid white head and neck being the most excited. They use gobbling, drumming/booming, and spitting as signs of social dominance, and to attract females. Courtship begins during the months of March and April, which is when turkeys are still flocked together in winter areas.
Males may be seen courting in groups, often with the dominant male gobbling, spreading his tail feathers (strutting), drumming/booming, and spitting. In a study, the average dominant male that courted as part of a pair of males fathered six more eggs than males that courted alone. Genetic analysis of pairs of males courting together shows that they are close relatives, with half of their genetic material being identical. The theory behind team-courtship is that the less-dominant male has a greater chance of passing along shared genetic material than if he were courting alone.
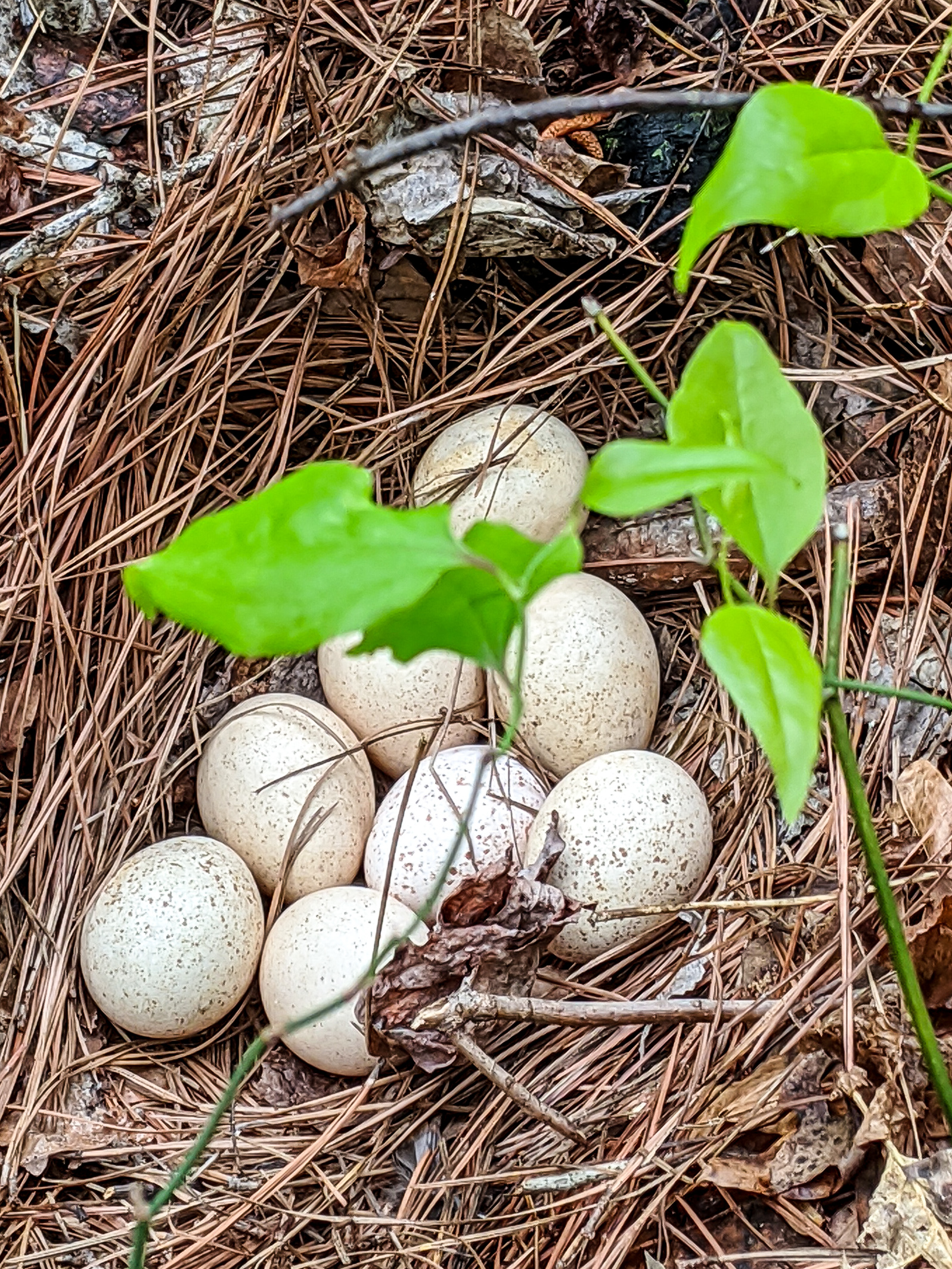
When mating is finished, females search for nest sites. Nests are shallow dirt depressions engulfed with woody vegetation. Hens lay a clutch of 10–14 eggs, usually one per day. The eggs are incubated for at least 28 days. The poults are precocial
Precocial species in birds and mammals are those in which the young are relatively mature and mobile from the moment of birth or hatching. They are normally nidifugous, meaning that they leave the nest shortly after birth or hatching. Altricial ...
and nidifugous
In biology, nidifugous ( , ) organisms are those that leave the nest shortly after hatching or birth. The term is derived from Latin ''nidus'' for "nest" and ''fugere'', meaning "to flee". The terminology is most often used to describe birds and w ...
, leaving the nest in about 12–24 hours. Turkeys are a ground nesting bird, and because of this they are heavily predated on; reproductively-active wild turkeys have a lower annual survival rate due to predation of nests.
Positive relationships with other wild species
Turkeys will occasionally forage withdeer
A deer (: deer) or true deer is a hoofed ruminant ungulate of the family Cervidae (informally the deer family). Cervidae is divided into subfamilies Cervinae (which includes, among others, muntjac, elk (wapiti), red deer, and fallow deer) ...
and squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae (), a family that includes small or medium-sized rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrel ...
s, and may even play with them. By foraging together, each can help the other watch for predators with their different senses: the deer with their improved olfactory sense, the turkey with its superior sight, and squirrels providing an additional set of eyes from the air.
Predators
Predators of eggs and nestlings includeraccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the North American, northern or common raccoon (also spelled racoon) to distinguish it from Procyonina, other species of raccoon, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest ...
s (''Procyon lotor''), Virginia opossum
The Virginia opossum (''Didelphis virginiana''), also known as the North American opossum, is a member of the opossum family found from southern Canada to northern Costa Rica, making it the northernmost marsupial in the world and the only marsup ...
s (''Didelphis virginiana''), striped skunk
The striped skunk (''Mephitis mephitis'') is a skunk of the genus ''Mephitis (genus), Mephitis'' that occurs across much of North America, including southern Canada, the United States, and northern Mexico. It is currently listed as least concern ...
s (''Mephitis mephitis''), spotted skunk
The genus ''Spilogale'' includes all skunks commonly known as spotted skunks. Currently, there are four accepted extant species: ''S. gracilis'', ''S. putorius'', ''S. pygmaea'', and ''S. angustifrons''. New research, however, proposes that ther ...
s (''Spilogale'' ssp.), red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
es (''Vulpes vulpes''), gray fox
The gray fox (''Urocyon cinereoargenteus''), or grey fox, is an omnivorous mammal of the family Canidae, widespread throughout North America and Central America. This species and its only congener (biology), congener, the diminutive island fox ...
es (''Urocyon citnereoargenteus''), groundhog
The groundhog (''Marmota monax''), also known as the woodchuck, is a rodent of the family Sciuridae, belonging to the group of large ground squirrels known as marmots.
A lowland creature of North America, it is found through much of the Easte ...
s (''Marmota monax''), among other rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal specie ...
s. Predators of poults in addition to nestlings and eggs also include several species of snake, namely rat snake
Rat snakes are members – along with kingsnakes, milk snakes, Oxybelis, vine snakes and indigo snakes – of the subfamily Colubrinae of the family Colubridae. They are medium to large Constriction, constrictors and are found throughout much o ...
s (''Elaphe'' ssp.), gopher snakes (''Pituophis catenifer''), and pinesnakes (''Pituophis'' ssp.).
Avian predators of poults include Bird of prey, raptors such as bald eagles (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus''), barred owl (''Strix varia''), red-shouldered hawk, red-shouldered (''Buteo lineatus''), red-tailed hawk, red-tailed (''Buteo jamaicensis''), white-tailed hawk, white-tailed (''Geranoaetus albicaudatus''), Harris's hawk, Harris's hawks (''Parabuteo unicinctus''), Cooper's hawk (''Accipiter cooperii''), and broad-winged hawk (''Buteo platypterus'') (both likely of very small poults). Mortality of poults is greatest in the first 14 days of life, especially of those roosting on the ground, decreasing most notably after half a year, when they attain near adult sizes.
 In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by great horned owls (''Bubo virginianus''), American goshawk (''Accipiter atricapillus''), dog, domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris''), cat, domestic cats (''Felis catus''), and
In addition to poults, hens and adult-sized fledglings (but not, as far as is known, adult male toms) are vulnerable to predation by great horned owls (''Bubo virginianus''), American goshawk (''Accipiter atricapillus''), dog, domestic dogs (''Canis familiaris''), cat, domestic cats (''Felis catus''), and red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
es (''Vulpes vulpes''). Predators of both adults and poults include coyotes (''Canis latrans''), gray wolf, gray wolves (''Canis lupus''), bobcats (''Lynx rufus''), cougars (''Puma concolor''), Canada lynx (''Lynx canadensis'')'','' golden eagles (''Aquila chrysaetos''), and possibly American black bears (''Ursus americanus''), which also will eat the eggs if they find them. The American alligator (''Alligator mississippiensis'') is a predator to all turkeys of all ages in the Southeast and will eat them if they get too close to water. Humans are now the leading predator of adult turkeys. When approached by potential predators, turkeys and their poults usually run rather than fly away, though they may also fly short distances if pressed. Another alternative behaviour, common in Galliformes
Galliformes is an order (biology), order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkey (bird), turkeys, chickens, Old World quail, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems ...
, is that when surprised with no time to flee, the poulets hide under the wings and body of the hen while she sits tight and still. Presumably, the hen has vocal and behavioural signals that trigger the poults to instinctively run to the hen for cover. Occasionally, if cornered, adult turkeys may try to fight off predators and large male toms can be especially aggressive in self-defense. When fighting off predators, turkeys may kick with their legs, using the spurs on their back of the legs as a weapon, bite with their beak, and ram with their relatively large bodies and may be able to deter predators up to the size of mid-sized mammals. Hens have been observed chasing off at least two species of hawks in flight when their poults are threatened.
Wild turkeys are not usually aggressive towards humans, but can be frightened or provoked to behave with aggression. They are most likely to attack if startled, cornered, harassed, or if approached too closely. Attacks and potential injuries can usually be avoided by giving wild turkeys a respectful amount of space and keeping outdoor spaces clean and undisturbed. Also, turkeys that are habituated to seeing people, at places like parks or campgrounds, can be tame and will even feed from the hands of people. Male toms occasionally will attack parked cars and reflective surfaces, thinking they see another turkey and must defend their territory.
Occasionally, if cornered, adult turkeys may try to fight off predators and large male toms can be especially aggressive in self-defense. When fighting off predators, turkeys may kick with their legs, using the spurs on their back of the legs as a weapon, bite with their beak, and ram with their relatively large bodies and may be able to deter predators up to the size of mid-sized mammals. Hens have been observed chasing off at least two species of hawks in flight when their poults are threatened.
Wild turkeys are not usually aggressive towards humans, but can be frightened or provoked to behave with aggression. They are most likely to attack if startled, cornered, harassed, or if approached too closely. Attacks and potential injuries can usually be avoided by giving wild turkeys a respectful amount of space and keeping outdoor spaces clean and undisturbed. Also, turkeys that are habituated to seeing people, at places like parks or campgrounds, can be tame and will even feed from the hands of people. Male toms occasionally will attack parked cars and reflective surfaces, thinking they see another turkey and must defend their territory.
Range and population
The Californian turkey (''Meleagris californica'') is an extinct species of turkey (bird), turkey indigenous to the Pleistocene and early Holocene ofCalifornia
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
. It became extinct about 10,000 years ago. The present Californian wild turkey population derives from wild turkeys introduced to the region during the 1960s and 1970s from other areas by game officials. They proliferated after 2000 to become an everyday sight in the East Bay by 2015.
At the beginning of the 20th century the range and numbers of wild turkeys had plummeted due to overhunting and habitat loss. When Europeans arrived in the New World, they were found from the southeastern US to Mexico. Turkeys were first domesticated by native peoples in Mexico and brought back to Europe during colonization. European settlers brought domesticated turkeys to the northern portions of North America during the 17th century. Habitat loss and market hunting were major factors in the decline of wild populations for the next two centuries.
Game managers estimate that the entire population of wild turkeys in the United States was as low as 30,000 by the late 1930s. By the 1940s, it was almost totally extirpated from Canada and had become localized in pockets in the United States, in the north-east effectively restricted to the Appalachians, only as far north as central Pennsylvania. Early attempts used hand-reared birds, a practice that failed miserably as the birds were unable to survive in the wild at all and many had imprinted far too much on humans to effectively survive. Game officials later made efforts to protect and encourage the breeding of the surviving wild population. They would wait for numbers to grow, catch the surplus birds with a device that would have a projectile net that would ensnare the creature, move it to another unoccupied territory, and repeat the cycle. Over time this included some in the western states where it was not native. There is evidence that the bird does well when near farmland, which provides grain and also berry-bearing shrubs at its edges. As wild turkey numbers rebounded, hunting became legal in 49 U.S. states (excluding Alaska). In 1973, the total U.S. population was estimated to be 1.3 million, and current estimates place the entire wild turkey population at 7 million individuals. Since the 1980s, "trap and transfer" projects have reintroduced wild turkeys to several provinces of Canada as well, sometimes from across the border in the United States. They appear to be very successful as of 2018 as wild turkeys have multiplied rapidly and flourished in places where they were not expected to survive by Canadian scientists, often quite far north of their original expected range.
Attempts to introduce the wild turkey to Great Britain, Britain as a game bird in the 18th century were unsuccessful. George II of Great Britain, George II is said to have kept a flock of a few thousand in Richmond Park near London, but they were too easy for local poaching, poachers to steal, and the fights with poachers became too dangerous for the gamekeepers. They were hunted with dogs and then shot out of trees where they took refuge. Several other populations, introduced or escaped, have survived for periods elsewhere in Britain and Ireland, but seem to have died out, perhaps from a combination of lack of winter feed and poaching. Small populations, probably descended from farm as well as wild stock, in the Czech Republic and Germany have been more successful, and there are wild populations of some size following introductions in Hawaii and New Zealand.
Subspecies
There are subtle differences in the coloration, habitat, and behavior of the different subspecies of wild turkeys. The six subspecies are:Eastern wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo silvestris'')
This was the turkey subspecies Europeans first encountered in the wild: by the Puritans, the founders of Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown, the Dutch who lived in New York, and by the Acadians. Its range is one of the largest of all subspecies, covering the entire eastern half of the United States from Maine in the north to northern Florida and extending as far west as Minnesota, Illinois, and into Missouri. In Canada, its range extends into Southeastern Manitoba, Ontario, Southwestern Quebec (including Pontiac, Quebec and the lower half of the Western Quebec Seismic Zone), and the Maritimes, Maritime Provinces. They number from 5.1 to 5.3 million birds. They were first named 'forest turkey' in 1817, and can grow up to tall. The upper tail coverts are tipped with chestnut brown. Males can reach in weight. The eastern wild turkey is heavily hunted in the Eastern USA and is the most hunted wild turkey subspecies.Osceola wild turkey or Florida wild turkey (''MMeleagris gallopavo osceola'')
Most common in the Florida peninsula, they number from 80,000 to 100,000 birds. This bird is named for the famous Seminole leader Osceola, and was first described in 1890. It is smaller and darker than the eastern wild turkey. The wing feathers are very dark with smaller amounts of the white barring seen on other subspecies. Their overall body feathers are an Iridescence, iridescent green-purple color. They are often found in scrub patches of palmetto and occasionally near swamps, where amphibian prey is abundant. Osceola turkeys are the smallest subspecies weighing .
Rio Grande wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo intermedia'')
The Rio Grande wild turkey ranges through Texas to Oklahoma, Kansas, New Mexico, Colorado, Oregon, Utah, and was introduced to central and westernCalifornia
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, as well as parts of a few northeastern states. It was also introduced to Hawaii, Hawaii in the late 1950s. Population estimates for this subspecies are around 1,000,000. This subspecies, native to the central plain states, was first described in 1879, and has relatively long legs, better adapted to a prairie habitat. Its body feathers often have a green-coppery sheen. The tips of the tail and lower back feathers are a buff-to-very light tan color. Its habitats are brush areas next to streams, rivers or mesquite, pine and scrub oak forests. The Rio Grande turkey is gregarious.
Merriam's wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo merriami'')
The Merriam's wild turkey ranges through the Rocky Mountains and the neighboring prairies of Wyoming, Montana and South Dakota, as well as much of the high mesa country of New Mexico, Arizona, southern Utah and the Navajo Nation, with number from 334,460 to 344,460 birds. The subspecies has also been introduced into Oregon. The initial releases of Merriam's turkeys in 1961 resulted in establishing a remnant population of Merriam's turkeys along the east-slope of Mt. Hood and natural immigration of turkeys from Idaho has established Merriam's flocks along the eastern border of Oregon. Merriam's wild turkeys live in ponderosa pine and mountainous regions. The subspecies was named in 1900 in honor of Clinton Hart Merriam, the first chief of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, U.S. Biological Survey. The tail and lower back feathers have white tips and purple and bronze reflections.Gould's wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo mexicana'')
 Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of Mexico and the southernmost parts of Arizona and New Mexico. Gould's wild turkeys are heavily protected and regulated. The subspecies was first described in 1856. They exist in small numbers in the U.S. but are abundant in northwestern portions of Mexico. A small population has been established in southern Arizona. Gould's are the largest of the six subspecies. They have longer legs, larger feet, and longer tail feathers. The main colors of the body feathers are copper and greenish-gold. This subspecies is heavily protected owing to its skittish nature and threatened status.
Native from the central valleys to the northern mountains of Mexico and the southernmost parts of Arizona and New Mexico. Gould's wild turkeys are heavily protected and regulated. The subspecies was first described in 1856. They exist in small numbers in the U.S. but are abundant in northwestern portions of Mexico. A small population has been established in southern Arizona. Gould's are the largest of the six subspecies. They have longer legs, larger feet, and longer tail feathers. The main colors of the body feathers are copper and greenish-gold. This subspecies is heavily protected owing to its skittish nature and threatened status.
South Mexican wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo gallopavo'')
The south Mexican wild turkey is considered the nominate subspecies, and the only one that is not found in the United States or Canada. In central Mexico, archaeological ''M. gallopavo'' bones have been identified at sites dating to 800–100'' ''BC. It is unclear whether these early specimens represent wild or domestic individuals, but domestic turkeys were likely established in central Mexico by the first half of the Classic Period (c. AD'' ''200–1000). Late Preclassic (300'' ''BC–AD'' ''100) turkey remains identified at the archaeological site of El Mirador (Petén, Guatemala) represent the earliest evidence of the export of the south Mexican wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo gallopavo'') to the ancient Maya world. The south Mexico, Mexican wild subspecies, ''M. g. gallopavo'', was Agriculture in Mesoamerica, domesticated either in Mexico or by Preclassic peoples in Mesoamerica, giving rise to thedomestic turkey
The domestic turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo domesticus'') is a large fowl, one of the two species in the genus ''Meleagris'' and the same species as the wild turkey. Although turkey domestication was thought to have occurred in central Mesoamerica ...
(''M. g. domesticus''). The Spaniards brought this tamed subspecies back to Europe with them in the mid-16th century; from Spain it spread to France and later Britain as a farmyard animal, usually becoming the centerpiece of a feast for the well-to-do. By 1620 it was common enough so that Pilgrim settlers of Massachusetts could bring turkeys with them from England, unaware that it had a larger close relative already occupying the forests of Massachusetts. It is one of the smallest subspecies and is best known in Spanish from its Aztec-derived name, . This wild turkey subspecies is thought to be critically endangered, as of 2010.

Benjamin Franklin and the myth of U.S. national bird suggestion
The idea that Benjamin Franklin preferred the turkey as the national bird of the United States comes from a letter he wrote to his daughter Sarah Bache on 26 January 1784. The main subject of the letter is a criticism of the Society of the Cincinnati, which he likened to a chivalric order, which contradicted the ideals of the newly founded American republic. In one section of the letter, Franklin remarked on the appearance of the bald eagle on the Society's crest: Franklin never publicly voiced opposition to the bald eagle as a national symbol, nor did he ever publicly suggest the turkey as a national symbol.Significance to Native Americans
 The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many Native American tribes all over North America. It is a favorite meal in eastern tribes. Eastern Native American tribes consumed both the eggs and meat, sometimes turning the latter into a type of jerky to preserve it and make it last through cold weather. They provided habitat by burning down portions of forests to create meadows which would attract mating birds, and thus give a clear shot to hunters. The feathers of turkeys also often made their way into the rituals and headgear of many tribes. Many leaders, such as Catawba (tribe), Catawba chiefs, traditionally wore turkey feather headdresses.
Significant peoples of several tribes, including Muscogee Creek and Wampanoag people, Wampanoag, wore turkey feather cloaks. The turkey clan is one of the three Lenape clans. Movements of wild turkeys inspired the Caddo tribe's turkey dance. The Navajo people of Northeastern Arizona, New Mexico and Utah call the turkey and relate the bird to the corn and seeds which The Turkey in Navajo folklore brought from the Third Navajo World. It is one of the Navajos' sacred birds, with the Navajo people using the feathers and parts in multiple traditional ceremonies.
The wild turkey, throughout its range, plays a significant role in the cultures of many Native American tribes all over North America. It is a favorite meal in eastern tribes. Eastern Native American tribes consumed both the eggs and meat, sometimes turning the latter into a type of jerky to preserve it and make it last through cold weather. They provided habitat by burning down portions of forests to create meadows which would attract mating birds, and thus give a clear shot to hunters. The feathers of turkeys also often made their way into the rituals and headgear of many tribes. Many leaders, such as Catawba (tribe), Catawba chiefs, traditionally wore turkey feather headdresses.
Significant peoples of several tribes, including Muscogee Creek and Wampanoag people, Wampanoag, wore turkey feather cloaks. The turkey clan is one of the three Lenape clans. Movements of wild turkeys inspired the Caddo tribe's turkey dance. The Navajo people of Northeastern Arizona, New Mexico and Utah call the turkey and relate the bird to the corn and seeds which The Turkey in Navajo folklore brought from the Third Navajo World. It is one of the Navajos' sacred birds, with the Navajo people using the feathers and parts in multiple traditional ceremonies.
See also
* Heritage turkey * Turkeypox virusNotes
References
External links
Turkey as U.S. national bird
*View the [http://www.ensembl.org/Meleagris_gallopavo/Info/Index/ turkey genome] in Ensembl * * {{Authority control Meleagris Birds described in 1758 Birds of Canada Game birds Native American cuisine Hunting in the United States Birds of the United States Birds of Mexico Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus Symbols of Alabama New England cuisine category:Cuisine of the Southwestern United States category:Thanksgiving food