|
Tarsometatarsus
The tarsometatarsus is a bone that is only found in the lower leg of birds and some non-avian dinosaurs. It is formed from the fusion of several bird bones found in other types of animals, and homologous to the mammalian tarsus (ankle bones) and metatarsal bones (foot). Despite this, the tarsometatarsus of flying types is often referred to as just the shank, tarsus or metatarsus. Tarsometatarsal fusion occurred in several ways and extents throughout bird evolution. Paticularly, in Neornithes (modern birds), although the bones are joined along their entire length, the fusion is most thorough at the distal (metatarsal) end. In the Enantiornithes, a group of Mesozoic avialans, the fusion was complete at the proximal (tarsal) end, but the distal metatarsi were still partially distinct. While these fused bones are best known from birds and their relatives, avians are neither the only group nor the first to possess tarsometatarsi. In a remarkable case of parallel evolution, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiornithes
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct Avialae, avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over seventy species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs. Discovery and naming The first Enantiornithes to be discovered were incorrectly referred to modern bird groups. For example, the first known species of Enantiornithes, ''Gobipteryx minuta'', was originally considered a paleognath related to ostriches and tinamou. The Enantiornithes were first recognized as a distinct lineage, or "subclass" of birds, by Cyril A. Walker in 1981. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Anatomy
Bird anatomy, or the physiological structure of birds' bodies, shows many unique adaptations, mostly aiding flight. Birds have a light skeletal system and light but powerful musculature which, along with circulatory and respiratory systems capable of very high metabolic rates and oxygen supply, permit the bird to fly. The development of a beak has led to evolution of a specially adapted digestive system. Skeletal system Birds have many bones that are hollow ( pneumatized) with criss-crossing struts or trusses for structural strength. The number of hollow bones varies among species, though large gliding and soaring birds tend to have the most. Respiratory air sacs often form air pockets within the semi-hollow bones of the bird's skeleton. The bones of diving birds are often less hollow than those of non-diving species. Penguins, loons, puffins, and kiwis are without pneumatized bones entirely. Flightless birds, such as ostriches and emus, have pneumatized femurs and, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
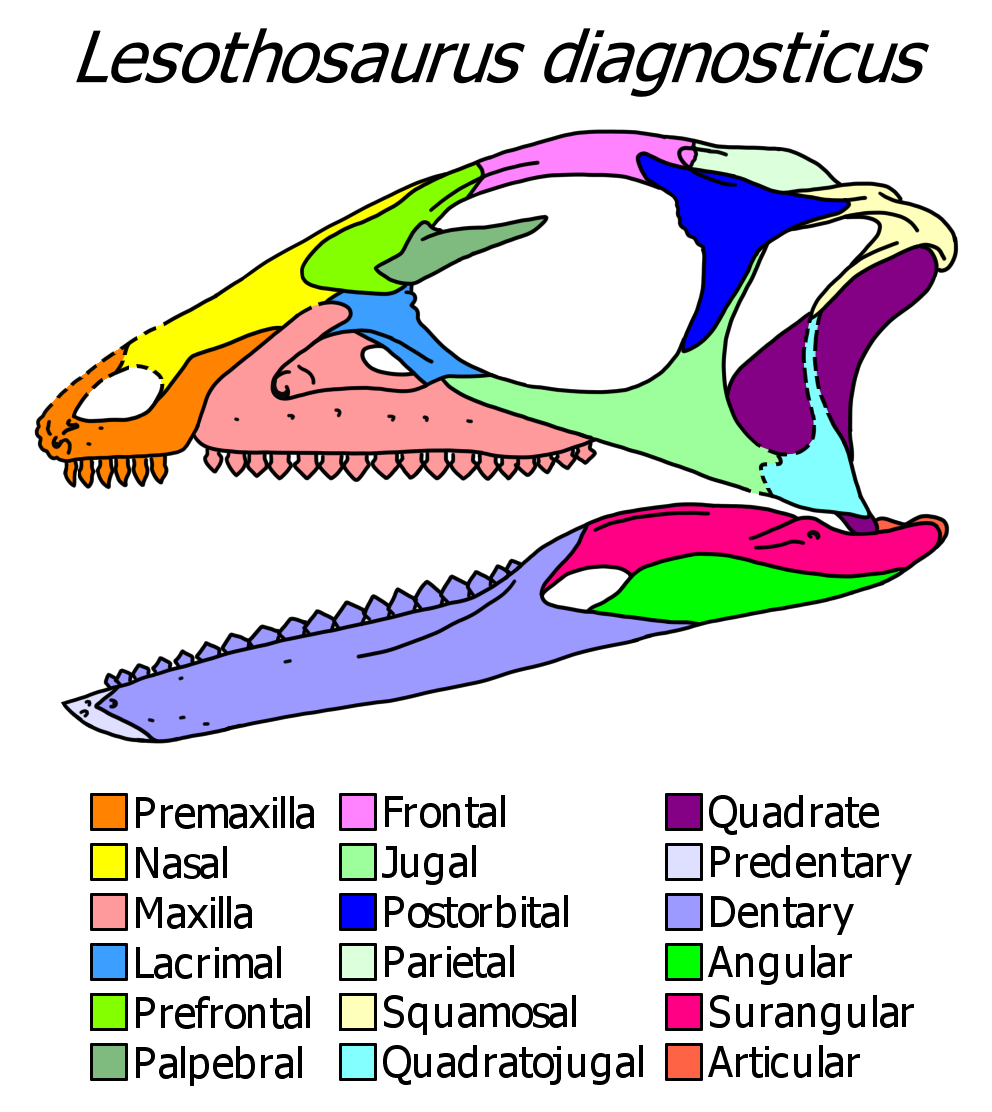
Heterodontosauridae
Heterodontosauridae is a family (biology), family of ornithischian dinosaurs that were likely among the most Basal (phylogenetics), basal (primitive) members of the group. Their phylogenetic placement is uncertain but they are most commonly found outside of the group Genasauria. Although their fossils are relatively rare and their group small in numbers, they have been found on all continents except Australia (continent), Australia and Antarctica, with a range spanning the Early Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. Heterodontosaurids were fox-sized dinosaurs less than in length, including a long tail. They are known mainly for their characteristic teeth, including enlarged canine (tooth), canine-like tusks and cheek teeth adapted for chewing, Analogy (biology), analogous to those of Cretaceous hadrosaurids. Their diet was herbivore, herbivorous or possibly omnivore, omnivorous. Description Among heterodontosaurids, only ''Heterodontosaurus'' itself is known from a complete ske ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodontosaurus Skeleton
''Heterodontosaurus'' is a genus of heterodontosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Early Jurassic, 200–190 million years ago. Its only known member species, ''Heterodontosaurus tucki'', was named in 1962 based on a skull discovered in South Africa. The genus name means "different toothed lizard", in reference to its unusual, heterodont dentition; the specific name honours G. C. Tuck, who supported the discoverers. Further specimens have since been found, including an almost complete skeleton in 1966. Though it was a small dinosaur, ''Heterodontosaurus'' was one of the largest members of its family, reaching between and possibly in length, and weighing between . The skull was elongated, narrow, and triangular when viewed from the side. The front of the jaws were covered in a horny beak. It had three types of teeth; in the upper jaw, small, incisor-like teeth were followed by long, canine-like tusks. A gap divided the tusks from the chisel-like cheek-teeth. The body was sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsus (skeleton)
In the human body, the tarsus (: tarsi) is a cluster of seven articulating bones in each foot situated between the lower end of the tibia and the fibula of the lower leg and the metatarsus. It is made up of the midfoot (Cuboid bone, cuboid, medial, intermediate, and lateral cuneiform bone, cuneiform, and navicular) and hindfoot (Talus bone, talus and calcaneus). The tarsus articulates with the bones of the metatarsus, which in turn articulate with the proximal phalanges of the toes. The joint between the tibia and fibula above and the tarsus below is referred to as the ankle, ankle joint proper. In humans the largest bone in the tarsus is the calcaneus, which is the weight-bearing bone within the heel of the foot. Human anatomy Bones The talus bone or ankle bone is connected superiorly to the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and fibula, to form the ankle, ankle joint or talocrural joint; inferiorly, at the subtalar joint, to the calcaneus or heel bone. Together, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatarsal Bones
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel and the ankle) and the phalanges ( toes). Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the medial side (the side of the great toe): the first, second, third, fourth, and fifth metatarsal (often depicted with Roman numerals). The metatarsals are analogous to the metacarpal bones of the hand. The lengths of the metatarsal bones in humans are, in descending order, second, third, fourth, fifth, and first. A bovine hind leg has two metatarsals. Structure The five metatarsals are dorsal convex long bones consisting of a shaft or body, a base ( proximally), and a head ( distally).Platzer 2004, p. 220 The body is prismoid in form, tapers gradually from the tarsal to the phalangeal extremity, and is curved longitudinally, so as to be concave below, slightly convex above. The base or posterior extremity is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Years Ago
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch and followed by the Early Jurassic Epoch. The corresponding series (stratigraphy), series of rock beds is known as the Upper Triassic. The Late Triassic is divided into the Carnian, Norian and Rhaetian Geologic time scale, ages. Many of the first dinosaurs evolved during the Late Triassic, including ''Plateosaurus'', ''Coelophysis'', ''Herrerasaurus'', and ''Eoraptor''. The Triassic–Jurassic extinction event began during this epoch and is one of the five major mass extinction events of the Earth. Etymology The Triassic was named in 1834 by Friedrich August von Namoh, Friedrich von Alberti, after a succession of three distinct rock layers (Greek meaning 'triad') that are widespread in southern Germany: the lower Buntsandstein (colourful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct clade of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek stem ' (), meaning "bird", and ' (), meaning "hip". However, as theropod dinosaurs, birds are only distantly related to this group. Ornithischians with well known anatomical adaptations include the ceratopsians or "horn-faced" dinosaurs (e.g. ''Triceratops''), the pachycephalosaurs or "thick-headed" dinosaurs, the armored dinosaurs ( Thyreophora) such as stegosaurs and ankylosaurs, and the ornithopods. There is strong evidence that certain groups of ornithischians lived in herds, often segregated by age group, with juveniles forming their own flocks separate from adults. Some were at least partially covered in filamentous (hair- or feather- like) pelts, and there is much debate over whether these filaments found in specimens of '' Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel Evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and parallel evolution at the amino acid sequence level. ''Mol. Biol. Evol.'' 14, 527-36. Parallel vs. convergent evolution Given a trait that occurs in each of two lineages descended from a specified ancestor, it is possible in theory to define parallel and convergent evolutionary trends strictly, and distinguish them clearly from one another. However, the criteria for defining convergent as opposed to parallel evolution are unclear in practice, so that arbitrary diagnosis is common. When two species share a trait, evolution is defined as parallel if the ancestors are known to have shared that similarity; if not, it is defined as convergent. However, the stated conditions are a matter of degree; all organisms share common ancestors. Scientis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles such as the dinosaurs, and of Gymnosperm, gymnosperms such as cycads, ginkgoaceae and Araucariaceae, araucarian conifers; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of significant tectonic, climatic, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |