Early Dynastic III on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Early Dynastic Period (abbreviated ED Period or ED) is an
 The ED was divided into the sub-periods ED I, II, and III. This was primarily based on complete changes over time in the plan of the Abu Temple of Tell Asmar, which had been rebuilt multiple times on exactly the same spot. During the 20th century, many archaeologists also tried to impose the scheme of ED I–III upon archaeological remains excavated elsewhere in both Iraq and Syria, dated to 3000–2000 BC. However, evidence from sites elsewhere in Iraq has shown that the ED I–III periodization, as reconstructed for the Diyala river valley region, could not be directly applied to other regions.
Research in Syria has shown that developments there were quite different from those in the Diyala river valley region or southern Iraq, rendering the traditional Lower Mesopotamian chronology useless. During the 1990s and 2000s, attempts were made by various scholars to arrive at a local Upper Mesopotamian chronology, resulting in the Early Jezirah (EJ) 0–V chronology that encompasses everything from 3000 to 2000 BC. The use of the ED I–III chronology is now generally limited to Lower Mesopotamia, with the ED II sometimes being further restricted to the Diyala river valley region or discredited altogether.
The ED was divided into the sub-periods ED I, II, and III. This was primarily based on complete changes over time in the plan of the Abu Temple of Tell Asmar, which had been rebuilt multiple times on exactly the same spot. During the 20th century, many archaeologists also tried to impose the scheme of ED I–III upon archaeological remains excavated elsewhere in both Iraq and Syria, dated to 3000–2000 BC. However, evidence from sites elsewhere in Iraq has shown that the ED I–III periodization, as reconstructed for the Diyala river valley region, could not be directly applied to other regions.
Research in Syria has shown that developments there were quite different from those in the Diyala river valley region or southern Iraq, rendering the traditional Lower Mesopotamian chronology useless. During the 1990s and 2000s, attempts were made by various scholars to arrive at a local Upper Mesopotamian chronology, resulting in the Early Jezirah (EJ) 0–V chronology that encompasses everything from 3000 to 2000 BC. The use of the ED I–III chronology is now generally limited to Lower Mesopotamia, with the ED II sometimes being further restricted to the Diyala river valley region or discredited altogether.
 There may have been a common or shared cultural identity among the Early Dynastic Sumerian city-states, despite their political fragmentation. This notion was expressed by the terms ''kalam'' or ''ki-engir''. Numerous texts and cylinder seals seem to indicate the existence of a league or amphictyony of Sumerian city-states. For example, clay tablets from Ur bear
There may have been a common or shared cultural identity among the Early Dynastic Sumerian city-states, despite their political fragmentation. This notion was expressed by the terms ''kalam'' or ''ki-engir''. Numerous texts and cylinder seals seem to indicate the existence of a league or amphictyony of Sumerian city-states. For example, clay tablets from Ur bear  The texts from
The texts from
 Somewhat reliable information on then-contemporary political events in Mesopotamia is available only for the ED IIIb period. These texts come mainly from Lagash and detail the recurring conflict with Umma over control of irrigated land. The kings of Lagash are absent from the Sumerian King List, as are their rivals, the kings of Umma. This suggests that these states, while powerful in their own time, were later forgotten.
The royal inscriptions from Lagash also mention wars against other Lower Mesopotamian city-states, as well as against kingdoms farther away. Examples of the latter include Mari,
Somewhat reliable information on then-contemporary political events in Mesopotamia is available only for the ED IIIb period. These texts come mainly from Lagash and detail the recurring conflict with Umma over control of irrigated land. The kings of Lagash are absent from the Sumerian King List, as are their rivals, the kings of Umma. This suggests that these states, while powerful in their own time, were later forgotten.
The royal inscriptions from Lagash also mention wars against other Lower Mesopotamian city-states, as well as against kingdoms farther away. Examples of the latter include Mari,
 The preceding Uruk period in Lower Mesopotamia saw the appearance of the first cities, early state structures, administrative practices, and writing. Evidence for these practices was attested to during the Early Dynastic Period.
The ED Period is the first for which it is possible to say something about the ethnic composition of the population of Lower Mesopotamia. This is due to the fact that texts from this period contained sufficient phonetic signs to distinguish separate languages. They also contained personal names, which can potentially be linked to an ethnic identity. The textual evidence suggested that Lower Mesopotamia during the ED Period was largely dominated by
The preceding Uruk period in Lower Mesopotamia saw the appearance of the first cities, early state structures, administrative practices, and writing. Evidence for these practices was attested to during the Early Dynastic Period.
The ED Period is the first for which it is possible to say something about the ethnic composition of the population of Lower Mesopotamia. This is due to the fact that texts from this period contained sufficient phonetic signs to distinguish separate languages. They also contained personal names, which can potentially be linked to an ethnic identity. The textual evidence suggested that Lower Mesopotamia during the ED Period was largely dominated by  Textual evidence indicated the existence of a Semitic population in the upper reaches of Lower Mesopotamia. The texts in question contained personal names and words from a
Textual evidence indicated the existence of a Semitic population in the upper reaches of Lower Mesopotamia. The texts in question contained personal names and words from a  The dominant political structure was the
The dominant political structure was the

 Urbanization also increased in western Syria, notably in the second half of the third millennium BC. Sites like Tell Banat, Tell Hadidi,
Urbanization also increased in western Syria, notably in the second half of the third millennium BC. Sites like Tell Banat, Tell Hadidi,
 The maritime trade in the Gulf extended as far east as the
The maritime trade in the Gulf extended as far east as the
 Thorkild Jacobsen defined a "primitive democracy" with reference to Sumerian epics, myths, and historical records. He described a form of government determined by a majority of men who were free citizens. There was little specialisation and only a loose power structure. Kings such as
Thorkild Jacobsen defined a "primitive democracy" with reference to Sumerian epics, myths, and historical records. He described a form of government determined by a majority of men who were free citizens. There was little specialisation and only a loose power structure. Kings such as
 The following extracts are taken from the "Reform Document":
# "From the border territory of Ningirsu to the sea, no person shall serve as officers."
# "For a corpse being brought to the grave, his beer shall be 3 jugs and his bread 80 loaves. 1 bed and 1 lead goat shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the person(s) take away."
# "When to the reeds of Enki a person has been brought, his beer will be 4 jugs, and his bread 420 loaves. 1 barig of barley shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the persons of ... take away. 1 woman’s headband, and 1 sila of princely fragrance shall the eresh-dingir priestess take away. 420 loaves of bread that have sat are the bread duty, 40 loaves of hot bread are for eating, and 10 loaves of hot bread are the bread of the table. 5 loaves of bread are for the persons of the levy, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Girsu. 490 loaves of bread, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Lagash. 406 of bread, 2 mud vessels, and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the other lamentation singers. 250 loaves of bread and 1 mud vessel of beer are for the old wailing women. 180 loaves of bread and one mud vessel of beer are for the men of Nigin."
# "The blind one who stands in ..., his bread for eating is 1 loaf, 5 loaves of bread are his at midnight, 1 loaf is his bread at midday, and 6 loaves are his bread in the evening."
# "60 loaves of bread, 1 mud vessel of beer, and 3 ban of barley are for the person who is to perform as the sagbur priest."
The following extracts are taken from the "Reform Document":
# "From the border territory of Ningirsu to the sea, no person shall serve as officers."
# "For a corpse being brought to the grave, his beer shall be 3 jugs and his bread 80 loaves. 1 bed and 1 lead goat shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the person(s) take away."
# "When to the reeds of Enki a person has been brought, his beer will be 4 jugs, and his bread 420 loaves. 1 barig of barley shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the persons of ... take away. 1 woman’s headband, and 1 sila of princely fragrance shall the eresh-dingir priestess take away. 420 loaves of bread that have sat are the bread duty, 40 loaves of hot bread are for eating, and 10 loaves of hot bread are the bread of the table. 5 loaves of bread are for the persons of the levy, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Girsu. 490 loaves of bread, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Lagash. 406 of bread, 2 mud vessels, and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the other lamentation singers. 250 loaves of bread and 1 mud vessel of beer are for the old wailing women. 180 loaves of bread and one mud vessel of beer are for the men of Nigin."
# "The blind one who stands in ..., his bread for eating is 1 loaf, 5 loaves of bread are his at midnight, 1 loaf is his bread at midday, and 6 loaves are his bread in the evening."
# "60 loaves of bread, 1 mud vessel of beer, and 3 ban of barley are for the person who is to perform as the sagbur priest."
 Imports to Ur came from the
Imports to Ur came from the
File:Mesopotamia male worshiper 2750-2600 B.C.jpg, Statue of a male figure, recovered from Tell Asmar
File:Female worshipper with tufted dress and wrapped headdress, Khafajah, Nintu Temple VII, Early Dynastic period, 2600-2500 BC, gypsum - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC07453.JPG, Statue of a female figure, recovered from
Bas-reliefs created from perforated stone slabs are another hallmark of Early Dynastic sculpture. They also served a votive purpose, but their exact function is unknown. Examples include the votive relief of king
File:P1150886 Louvre bas-relief scènes banquet AO31015 rwk.jpg, Bas-relief of a banquet and boating scene, 3000-2334 BCE,
File:Bull statuette Louvre AO2151.jpg, Statue of a bull (ED III)
File:Vessel stand with ibex support - MET - ED III.jpg, Vessel stand in the shape of an ibex. Copper-based alloy with


 Examples of
Examples of
Golden Lyre of Ur
, Bill Taylor They are over 4,500 years oldQueen's Lyre - From Ur, southern Iraq, about 2600-2400 BC
Iraq’s Ancient Past
nbsp;—
Sumerian Language Page
perhaps the oldest Sumerian website on the web (it dates back to 1996), features compiled lexicon, detailed FAQ, extensive links, and so on.
ETCSL: The Electronic Text Corpus of Sumerian Literature
has complete translations of more than 400 Sumerian literary texts.
PSD: The Pennsylvania Sumerian Dictionary
while still in its initial stages, can be searched on-line, from August 2004.
CDLI: Cuneiform Digital Library Initiative
a large corpus of Sumerian texts in transliteration, largely from the Early Dynastic and Ur III periods, accessible with images. {{coord, 32.0, 45.5, dim:250km, display=title Ancient Mesopotamia Archaeology of Iraq
archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
(modern-day Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
) that is generally dated to and was preceded by the Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
and Jemdet Nasr
Jemdet Nasr () (also Jamdat Nasr and Jemdat Nasr) is a Tell (archaeology), tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate, Iraq that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period (c. 3100–2900 BC), under an alternate period ...
periods. It saw the development of writing and the formation of the first cities
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agree ...
and states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
. The ED itself was characterized by the existence of multiple city-states
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
: small states with a relatively simple structure that developed and solidified over time. This development ultimately led, directly after this period, to broad Mesopotamian unification under the rule of Sargon, the first monarch of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
. Despite their political fragmentation, the ED city-states shared a relatively homogeneous material culture. Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian cities such as Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, Ur, Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
, Umma
Umma () in modern Dhi Qar Province in Iraq, was an ancient city in Sumer. There is some scholarly debate about the Sumerian and Akkadian names for this site. Traditionally, Umma was identified with Tell Jokha. More recently it has been sugges ...
, and Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Ca ...
located in Lower Mesopotamia were very powerful and influential. To the north and west stretched states centered on cities such as Kish
Kish may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* KISH, a radio station in Guam
* Kish Air, an Iranian airline
* Korean International School in Hanoi, Vietnam
People
* Kish (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Kish, a former ...
, Mari, Nagar, and Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
.
The study of Central and Lower Mesopotamia has long been given priority over neighboring regions. Archaeological sites
An archaeological site is a place (or group of physical sites) in which evidence of past activity is preserved (either prehistoric or historic or contemporary), and which has been, or may be, investigated using the discipline of archaeology an ...
in Central and Lower Mesopotamia—notably Girsu but also Eshnunna
Eshnunna (also Esnunak) (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Althou ...
, Khafajah
Khafajah or Khafaje (), ancient Tutub, is an archaeological site in Diyala Governorate, Iraq east of Baghdad. Khafajah lies on the Diyala River, a tributary of the Tigris. Occupied from the Uruk period, Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods through the e ...
, Ur, and many others—have been excavated since the 19th century. These excavations have yielded cuneiform texts and many other important artifacts. As a result, this area was better known than neighboring regions, but the excavation and publication of the archives of Ebla
Ebla (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', , modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a Tell (archaeology), tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was ...
have changed this perspective by shedding more light on surrounding areas, such as Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia constitutes the Upland and lowland, uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the regio ...
, western Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, and southwestern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
. These new findings revealed that Lower Mesopotamia shared many socio-cultural developments with neighboring areas and that the entirety of the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
participated in an exchange network in which material goods and ideas were being circulated.
History of research
Dutch archaeologistHenri Frankfort
Henri "Hans" Frankfort (24 February 1897 – 16 July 1954) was a Dutch Egyptology, Egyptologist, archaeologist and orientalism, orientalist.
Early life and education
Born in Amsterdam, into a "Reform Judaism, liberal Jewish" family, Frankfort stud ...
coined the term Early Dynastic (ED) period for Mesopotamia, the naming convention having been borrowed from the similarly named Early Dynastic (ED) period for Egypt. The periodization
In historiography, periodization is the process or study of categorizing the past into discrete, quantified, and named blocks of time for the purpose of study or analysis.Adam Rabinowitz.It's about time: historical periodization and Linked Ancie ...
was developed in the 1930s during excavations that were conducted by Henri Frankfort on behalf of the University of Chicago Oriental Institute
The Institute for the Study of Ancient Cultures, West Asia & North Africa (ISAC), formerly known as the Oriental Institute, is the University of Chicago's interdisciplinary research center for ancient Near Eastern studies and archaeology museum. ...
at the archaeological sites of Tell Khafajah, Tell Agrab, and Tell Asmar in the Diyala Region of Iraq.
 The ED was divided into the sub-periods ED I, II, and III. This was primarily based on complete changes over time in the plan of the Abu Temple of Tell Asmar, which had been rebuilt multiple times on exactly the same spot. During the 20th century, many archaeologists also tried to impose the scheme of ED I–III upon archaeological remains excavated elsewhere in both Iraq and Syria, dated to 3000–2000 BC. However, evidence from sites elsewhere in Iraq has shown that the ED I–III periodization, as reconstructed for the Diyala river valley region, could not be directly applied to other regions.
Research in Syria has shown that developments there were quite different from those in the Diyala river valley region or southern Iraq, rendering the traditional Lower Mesopotamian chronology useless. During the 1990s and 2000s, attempts were made by various scholars to arrive at a local Upper Mesopotamian chronology, resulting in the Early Jezirah (EJ) 0–V chronology that encompasses everything from 3000 to 2000 BC. The use of the ED I–III chronology is now generally limited to Lower Mesopotamia, with the ED II sometimes being further restricted to the Diyala river valley region or discredited altogether.
The ED was divided into the sub-periods ED I, II, and III. This was primarily based on complete changes over time in the plan of the Abu Temple of Tell Asmar, which had been rebuilt multiple times on exactly the same spot. During the 20th century, many archaeologists also tried to impose the scheme of ED I–III upon archaeological remains excavated elsewhere in both Iraq and Syria, dated to 3000–2000 BC. However, evidence from sites elsewhere in Iraq has shown that the ED I–III periodization, as reconstructed for the Diyala river valley region, could not be directly applied to other regions.
Research in Syria has shown that developments there were quite different from those in the Diyala river valley region or southern Iraq, rendering the traditional Lower Mesopotamian chronology useless. During the 1990s and 2000s, attempts were made by various scholars to arrive at a local Upper Mesopotamian chronology, resulting in the Early Jezirah (EJ) 0–V chronology that encompasses everything from 3000 to 2000 BC. The use of the ED I–III chronology is now generally limited to Lower Mesopotamia, with the ED II sometimes being further restricted to the Diyala river valley region or discredited altogether.
Periodization
The ED was preceded by theJemdet Nasr
Jemdet Nasr () (also Jamdat Nasr and Jemdat Nasr) is a Tell (archaeology), tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate, Iraq that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period (c. 3100–2900 BC), under an alternate period ...
and then succeeded by the Akkadian period, during which, for the first time in history, large parts of Mesopotamia were united under a single ruler. The entirety of the ED is now generally dated to approximately 2900–2350 BC according to the widely accepted middle chronology
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
or 2800–2230 BC according to the short chronology
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
, which is increasingly less accepted by scholars. The ED was divided into the ED I, ED II, ED IIIa, and ED IIIb sub-periods. ED I–III were more or less contemporary with the Early Jezirah (EJ) I–III in Upper Mesopotamia. The exact dating of the ED sub-periods varies between scholars—with some abandoning ED II and using only Early ED and Late ED instead and others extending ED I while allowing ED III begin earlier so that ED III was to begin immediately after ED I with no gap between the two.
Many historical periods in the Near East are named after the dominant political force at that time, such as the Akkadian or Ur III periods. This is not the case for the ED Period. It is an archaeological division that does not reflect political developments, and it is based upon perceived changes in the archaeological record, e.g. pottery and glyptics. This is because the political history of the ED is unknown for most of its duration. As with the archaeological subdivision, the reconstruction of political events is hotly debated among researchers.
The ED I (2900–2750/2700 BC) is poorly known, relative to the sub-periods that followed it. In Lower Mesopotamia, it shared characteristics with the final stretches of the Uruk (–3100 BC) and Jemdet Nasr (–2900 BC) periods. ED I is contemporary with the culture of the Scarlet Ware pottery typical of sites along the Diyala in Lower Mesopotamia, the Ninevite V culture in Upper Mesopotamia, and the Proto-Elamite culture in southwestern Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.
New artistic traditions developed in Lower Mesopotamia during the ED II (2750/2700–2600 BC). These traditions influenced the surrounding regions. According to later Mesopotamian historical tradition, this was the time when legendary mythical kings such as Lugalbanda
Lugalbanda was a deified Sumerian king of Uruk who, according to various sources of Mesopotamian literature, was the father of Gilgamesh. Early sources mention his consort Ninsun and his heroic deeds in an expedition to Aratta by King Enmerkar ...
, Enmerkar
Enmerkar () was an ancient Sumerian ruler to whom the construction of the city of Uruk and a 420-year reign was attributed. According to literary sources, he led various campaigns against the land of Aratta.
He is credited in Sumerian legend as ...
, Gilgamesh
Gilgamesh (, ; ; originally ) was a hero in ancient Mesopotamian mythology and the protagonist of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', an epic poem written in Akkadian during the late 2nd millennium BC. He was possibly a historical king of the Sumer ...
, and Aga ruled over Mesopotamia. Archaeologically, this sub-period has not been well-attested to in excavations of Lower Mesopotamia, leading some researchers to abandon it altogether.
The ED III (2600–2350 BC) saw an expansion in the use of writing and increasing social inequality. Larger political entities developed in Upper Mesopotamia and southwestern Iran. ED III is usually further subdivided into the ED IIIa (2600–2500/2450 BC) and ED IIIb (2500/2450–2350 BC). The Royal Cemetery at Ur
The Royal Cemetery at Ur is an archaeological site in modern-day Dhi Qar Governorate in southern Iraq. The initial excavations at Ur took place between 1922 and 1934 under the direction of Leonard Woolley in association with the British Museum and ...
and the archives of Fara and Abu Salabikh date back to ED IIIa. The ED IIIb is especially well known through the archives of Girsu (part of Lagash) in Iraq and Ebla in Syria.
The end of the ED is not defined archaeologically but rather politically. The conquests of Sargon and his successors upset the political equilibrium throughout Iraq, Syria, and Iran. The conquests lasted many years into the reign of Naram-Sin of Akkad
Naram-Sin, also transcribed Narām-Sîn or Naram-Suen (: '' DNa-ra-am D Sîn'', meaning "Beloved of the Moon God Sîn", the "𒀭" a determinative marking the name of a god; died 2218 BC), was a ruler of the Akkadian Empire, who reigned –22 ...
and built on ongoing conquests during the ED. The transition is much harder to pinpoint within an archaeological context. It is virtually impossible to date a particular site as being that of either ED III or Akkadian period using ceramic or architectural evidence alone.
History
The contemporary sources from the Early Dynastic Period do not allow the reconstruction of a political history. Royal inscriptions only offer a glimpse of the military conflicts and relations among the different city-states. Instead, rulers were more interested in glorifying their pious acts, such as the construction and restoration of temples and offerings to the gods. For the ED I and ED II periods, there are no contemporary documents shedding any light on warfare or diplomacy. Only for the end of the ED III period are contemporary texts available from which a political history can be reconstructed. The largest archives come from Lagash and Ebla. Smaller collections ofclay tablet
In the Ancient Near East, clay tablets (Akkadian language, Akkadian ) were used as a writing medium, especially for writing in cuneiform, throughout the Bronze Age and well into the Iron Age.
Cuneiform characters were imprinted on a wet clay t ...
s have been found at Ur, Tell Beydar, Tell Fara, Abu Salabikh, and Mari. They show that the Mesopotamian states were constantly involved in diplomatic contacts, leading to political and perhaps even religious alliances. Sometimes one state would gain hegemony over another, which foreshadows the rise of the Akkadian Empire.
The well-known Sumerian King List
The ''Sumerian King List'' (abbreviated ''SKL'') or ''Chronicle of the One Monarchy'' is an ancient Composition (language), literary composition written in Sumerian language, Sumerian that was likely created and redacted to legitimize the claims ...
dates to the early second millennium BC. It consists of a succession of royal dynasties from different Sumerian cities, ranging back into the Early Dynastic Period. Each dynasty rises to prominence and dominates the region, only to be replaced by the next. The document was used by later Mesopotamian kings to legitimize their rule. While some of the information in the list can be checked against other texts such as economic documents, much of it is probably fictional, and its use as a historical document for the Early Dynastic Period is limited to none.
Diplomacy
 There may have been a common or shared cultural identity among the Early Dynastic Sumerian city-states, despite their political fragmentation. This notion was expressed by the terms ''kalam'' or ''ki-engir''. Numerous texts and cylinder seals seem to indicate the existence of a league or amphictyony of Sumerian city-states. For example, clay tablets from Ur bear
There may have been a common or shared cultural identity among the Early Dynastic Sumerian city-states, despite their political fragmentation. This notion was expressed by the terms ''kalam'' or ''ki-engir''. Numerous texts and cylinder seals seem to indicate the existence of a league or amphictyony of Sumerian city-states. For example, clay tablets from Ur bear cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
impressions with signs representing other cities. Similar impressions have also been found at Jemdet Nasr
Jemdet Nasr () (also Jamdat Nasr and Jemdat Nasr) is a Tell (archaeology), tell or settlement mound in Babil Governorate, Iraq that is best known as the eponymous type site for the Jemdet Nasr period (c. 3100–2900 BC), under an alternate period ...
, Uruk, and Susa. Some impressions show exactly the same list of cities. It has been suggested that this represented a system in which specific cities were associated with delivering offerings to the major Sumerian temples, similar to the ''bala'' system of the Ur III period
The Third Dynasty of Ur or Ur III was a Sumerian dynasty based in the city of Ur in the 22nd and 21st centuries BC (middle chronology). For a short period they were the preeminent power in Mesopotamia and their realm is sometimes referred to by ...
.
 The texts from
The texts from Shuruppak
Shuruppak ( , SU.KUR.RUki, "the healing place"), modern Tell Fara, was an ancient Sumerian city situated about 55 kilometres (35 mi) south of Nippur and 30 kilometers north of ancient Uruk on the banks of the Euphrates in Iraq's Al-Qādisiy ...
, dating to ED IIIa, also seem to confirm the existence of a ''ki-engir'' league. Member cities of the alliance included Umma, Lagash, Uruk, Nippur, and Adab. Kish may have had a leading position, whereas Shuruppak may have been the administrative center. The members may have assembled in Nippur, but this is uncertain. This alliance seems to have focused on economic and military collaboration, as each city would dispatch soldiers to the league. The primacy of Kish is illustrated by the fact that its ruler Mesilim (c. 2500 BC) acted as arbitrator in a conflict between Lagash and Umma. However, it is not certain whether Kish held this elevated position during the entire period, as the situation seems to have been different during later conflicts between Lagash and Umma. Later, rulers from other cities would use the title 'King of Kish' to strengthen their hegemonic ambitions and possibly also because of the symbolic value of the city.
The texts of this period also reveal the first traces of a wide-ranging diplomatic network. For example, the peace treaty between Entemena of Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
and Lugal-kinishe-dudu of Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, recorded on a clay nail, represents the oldest known agreement of this kind. Tablets from Girsu record reciprocal gifts between the royal court and foreign states. Thus, Baranamtarra, wife of king Lugalanda of Lagash, exchanged gifts with her peers from Adab and even Dilmun.
War
The first recorded war in history took place in Mesopotamia in around 2700 B.C. during the ED Period, between the forces ofSumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
and Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
. The Sumerians, under the command of Enmebaragesi, the King of Kish, defeated the Elamites and is recorded ''"carried away as spoils the weapons of Elam"''.
It is only for the later parts of the ED Period that information on political events becomes available, either as echoes in later writings or from contemporary sources. Writings from the end of the third millennium, including several Sumerian heroic narratives and the Sumerian King List, seem to echo events and military conflicts that may have occurred during the ED II period. For example, the reigns of legendary figures like king Gilgamesh
Gilgamesh (, ; ; originally ) was a hero in ancient Mesopotamian mythology and the protagonist of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', an epic poem written in Akkadian during the late 2nd millennium BC. He was possibly a historical king of the Sumer ...
of Uruk and his adversaries Enmebaragesi and Aga of Kish possibly date to ED II. These semi-legendary narratives seem to indicate an age dominated by two major powers: Uruk in Sumer and Kish in the Semitic country. However, the existence of the kings of this "heroic age" remains controversial.
 Somewhat reliable information on then-contemporary political events in Mesopotamia is available only for the ED IIIb period. These texts come mainly from Lagash and detail the recurring conflict with Umma over control of irrigated land. The kings of Lagash are absent from the Sumerian King List, as are their rivals, the kings of Umma. This suggests that these states, while powerful in their own time, were later forgotten.
The royal inscriptions from Lagash also mention wars against other Lower Mesopotamian city-states, as well as against kingdoms farther away. Examples of the latter include Mari,
Somewhat reliable information on then-contemporary political events in Mesopotamia is available only for the ED IIIb period. These texts come mainly from Lagash and detail the recurring conflict with Umma over control of irrigated land. The kings of Lagash are absent from the Sumerian King List, as are their rivals, the kings of Umma. This suggests that these states, while powerful in their own time, were later forgotten.
The royal inscriptions from Lagash also mention wars against other Lower Mesopotamian city-states, as well as against kingdoms farther away. Examples of the latter include Mari, Subartu
The land of Subartu (, Assyrian: '' mât Šubarri'') or Subar (, ) is mentioned in Bronze Age literature. The name also appears as ''Subari'' in the Amarna letters, and, in the form ''Šbr'', in Ugarit.
Subartu was apparently a kingdom in Uppe ...
, and Elam. These conflicts show that already in this stage in history there was a trend toward stronger states dominating larger territories. For example, king Eannatum
Eannatum ( ; ) was a Sumerian ''Ensi (Sumerian), Ensi'' (ruler or king) of Lagash. He established one of the first verifiable empires in history, subduing Elam and destroying the city of Susa, and extending his domain over the rest of Sumer and Akk ...
of Lagash was able to defeat Mari and Elam around 2450 B.C. Enshakushanna of Uruk seized Kish and imprisoned its king Embi-Ishtar around 2350 B.C. Lugal-zage-si, king of Uruk and Umma, was able to seize most of Lower Mesopotamia around 2358 B.C. This phase of warring city-states came to an end with the emergence of the Akkadian Empire under the rule of Sargon of Akkad
Sargon of Akkad (; ; died 2279 BC), also known as Sargon the Great, was the first ruler of the Akkadian Empire, known for his conquests of the Sumerian city-states in the 24th to 23rd centuries BC.The date of the reign of Sargon is highly unc ...
in 2334 B.C. ( middle).
Neighboring areas
The political history of Upper Mesopotamia and Syria is well known from the royal archives recovered at Ebla. Ebla, Mari, and Nagar were the dominant states for this period. The earliest texts indicate that Ebla paid tribute to Mari but was able to reduce it after it won a military victory. Cities likeEmar
Emar (, ), is an archaeological site at Tell Meskene in the Aleppo Governorate of northern Syria. It sits in the great bend of the mid-Euphrates, now on the shoreline of the man-made Lake Assad near the town of Maskanah.
It has been the sourc ...
on the Upper Euphrates and Abarsal (location unknown) were vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain ...
s of Ebla. Ebla exchanged gifts with Nagar, and a royal marriage was concluded between the daughter of a king of Ebla and the son of his counterpart at Nagar. The archives also contain letters from more distant kingdoms, such as Kish and possibly Hamazi, although it is also possible that there were cities with the same names closer to Ebla. In many ways, the diplomatic interactions in the wider Ancient Near East during this period resemble those from the second millennium BC, which are particularly well known from the Amarna letters.
Recent discoveries
In March 2020, archaeologists announced the discovery of a 5,000-year-old cultic area filled with more than 300 broken ceremonial ceramic cups, bowls, jars, animal bones and ritual processions dedicated toNingirsu
Ninĝirsu was a Mesopotamia, Mesopotamian god regarded as the tutelary deity of the city of Girsu, Ĝirsu, and as the chief god of the local pantheon of the state of Lagash. He shares many aspects with the god Ninurta. Ninĝirsu was identified as ...
at the site of Girsu. One of the remains was a duck-shaped bronze figurine with eyes made from bark which is thought to be dedicated to Nanshe.
Early Dynastic kingdoms and rulers
The Early Dynastic Period is preceded by theUruk period
The Uruk period (; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistory, protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after the S ...
() and the Jemdet Nasr period
The Jemdet Nasr Period (also Jemdat Nasr period) is an archaeological culture in southern Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq). It is generally dated from 3100 to 2900 BC. It is named after the type site Tell Jemdet Nasr, where the assemblage typical fo ...
(). The Early Dynastic Period () is followed by the rise of the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first known empire, succeeding the long-lived city-states of Sumer. Centered on the city of Akkad (city), Akkad ( or ) and its surrounding region, the empire united Akkadian language, Akkadian and Sumerian languag ...
().
Geographical context
Lower Mesopotamia
 The preceding Uruk period in Lower Mesopotamia saw the appearance of the first cities, early state structures, administrative practices, and writing. Evidence for these practices was attested to during the Early Dynastic Period.
The ED Period is the first for which it is possible to say something about the ethnic composition of the population of Lower Mesopotamia. This is due to the fact that texts from this period contained sufficient phonetic signs to distinguish separate languages. They also contained personal names, which can potentially be linked to an ethnic identity. The textual evidence suggested that Lower Mesopotamia during the ED Period was largely dominated by
The preceding Uruk period in Lower Mesopotamia saw the appearance of the first cities, early state structures, administrative practices, and writing. Evidence for these practices was attested to during the Early Dynastic Period.
The ED Period is the first for which it is possible to say something about the ethnic composition of the population of Lower Mesopotamia. This is due to the fact that texts from this period contained sufficient phonetic signs to distinguish separate languages. They also contained personal names, which can potentially be linked to an ethnic identity. The textual evidence suggested that Lower Mesopotamia during the ED Period was largely dominated by Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
and primarily occupied by the Sumerian people, who spoke a non-Semitic language isolate
A language isolate is a language that has no demonstrable genetic relationship with any other languages. Basque in Europe, Ainu and Burushaski in Asia, Sandawe in Africa, Haida and Zuni in North America, Kanoê in South America, and Tiwi ...
( Sumerian). It is debated whether Sumerian was already in use during the Uruk period.
 Textual evidence indicated the existence of a Semitic population in the upper reaches of Lower Mesopotamia. The texts in question contained personal names and words from a
Textual evidence indicated the existence of a Semitic population in the upper reaches of Lower Mesopotamia. The texts in question contained personal names and words from a Semitic language
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic,
Amharic, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by mo ...
, identified as Old Akkadian. However, the use of the term ''Akkadian'' before the emergence of the Akkadian Empire is problematic, and it has been proposed to refer to this Old Akkadian phase as being of the "Kish civilization
According to a theory proposed by Ignace Gelb, the Kish civilization encompassed the sites of Ebla and Mari in the Levant, Nagar in the north, and the proto- Akkadian sites of Abu Salabikh and Kish in central Mesopotamia in to the early East Se ...
" named after Kish
Kish may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* KISH, a radio station in Guam
* Kish Air, an Iranian airline
* Korean International School in Hanoi, Vietnam
People
* Kish (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Kish, a former ...
(the seemingly most powerful city during the ED Period) instead. Political and socioeconomic structures in these two regions also differed, although Sumerian influence is unparalleled during the Early Dynastic Period.
Agriculture in Lower Mesopotamia relied on intensive irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
. Cultivars included barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
and date palm
''Phoenix dactylifera'', commonly known as the date palm, is a flowering-plant species in the palm family Arecaceae, cultivated for its edible sweet #Fruits, fruit called dates. The species is widely cultivated across North Africa, northern A ...
s in combination with gardens and orchards. Animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, animal fiber, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, management, production, nutrition, selective breeding, and the raising ...
was also practiced, focusing on sheep and goats. This agricultural system was probably the most productive in the entire ancient Near East. It allowed the development of a highly urbanized society. It has been suggested that, in some areas of Sumer, the population of the urban centers during ED III represented three-quarters of the entire population.
 The dominant political structure was the
The dominant political structure was the city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world throughout history, including cities such as Rome, ...
in which a large urban center dominated the surrounding rural settlements. The territories of these city-states were in turn delimited by other city-states that were organized along the same principles. The most important centers were Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, Ur, Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
, Adab, and Umma-Gisha. Available texts from this period point to recurring conflicts between neighboring kingdoms, notably between Umma and Lagash.
The situation may have been different further north, where Semitic people seem to have been dominant. In this area, Kish was possibly the center of a large territorial state, competing with other powerful political entities such as Mari and Akshak.
The Diyala River
The Diyala (Arabic: ; ; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of the Sirwan and Tanjaro rivers in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of .
...
valley is another region for which the ED Period is relatively well-known. Along with neighboring areas, this region was home to Scarlet Ware—a type of painted pottery characterized by geometric motifs representing natural and anthropomorphic figures. In the Jebel Hamrin
Hamrin is a town in northern Iraq which sits on the western shore of a man-made lake of the same name, both of which are at the southern extreme of the Hamrin Mountains. Hamrin is home to approximately 25,000 people. Most revenue comes from fishi ...
, fortresses such as Tell Gubba and Tell Maddhur were constructed. It has been suggested that these sites were established to protect the main trade route from the Mesopotamian lowlands to the Iranian plateau. The main Early Dynastic sites in this region are Tell Asmar and Khafajah. Their political structure is unknown, but these sites were culturally influenced by the larger cities in the Mesopotamian lowland.
Neighboring regions
Upper Mesopotamia and Central Syria
At the beginning of the third millennium BC, the Ninevite V culture flourished in Upper Mesopotamia and the Middle Euphrates River region. It extended from Yorghan Tepe in the east to the Khabur Triangle in the west. Ninevite V was contemporary with ED I and marked an important step in theurbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from Rural area, rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. ...
of the region. The period seems to have experienced a phase of decentralization, as reflected by the absence of large monumental buildings and complex administrative systems similar to what had existed at the end of the fourth millennium BC.
Starting in 2700 BC and accelerating after 2500, the main urban sites grew considerably in size and were surrounded by towns and villages that fell inside their political sphere of influence. This indicated that the area was home to many political entities. Many sites in Upper Mesopotamia, including Tell Chuera
Tell Chuera (also Tell Ḫuera and Tall Ḥuwaira and Tall Chuera and Tell Khuera) is an ancient Near Eastern Tell (archaeology), tell site in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. It lies between the Balikh River, Balikh and Khabur (Euphrates), Khab ...
and Tell Beydar
Tell Beydar is a village and ancient site along the Khabur river in the modern Al-Hasakah Governorate, Syria about 30 kilometers north of the modern city of Hasake. It was the Ancient Near Eastern city of Nabada. It is connected by road to Al-Darb ...
, shared a similar layout: a main tell surrounded by a circular lower town. German archaeologist Max von Oppenheim
Baron Max von Oppenheim (15 July 1860 – 17 November 1946) was a German people, German lawyer, diplomat, ancient historian, Panislamism, pan-Islamist and archaeologist. He was a member of the Oppenheim family, Oppenheim banking dynasty. Aban ...
called them ''Kranzhügel'', or "cup-and-saucer-hills". Among the important sites of this period are Tell Brak
Tell Brak (Nagar, Nawar) was an ancient city in Syria; it is one the earliest known cities in the world. Its remains constitute a tell located in the Upper Khabur region, near the modern village of Tell Brak, 50 kilometers north-east of ...
(Nagar), Tell Mozan, Tell Leilan
Tell Leilan is an archaeological site situated near the Wadi Jarrah in the Khabur River basin in Al-Hasakah Governorate, northeastern Syria. The site has been occupied since the 5th millennium BC. During the late third millennium, the site was ...
, and Chagar Bazar in the Jezirah and Mari on the middle Euphrates.

 Urbanization also increased in western Syria, notably in the second half of the third millennium BC. Sites like Tell Banat, Tell Hadidi,
Urbanization also increased in western Syria, notably in the second half of the third millennium BC. Sites like Tell Banat, Tell Hadidi, Umm el-Marra
Umm el-Marra, (), east of modern Aleppo in the Jabbul Plain of northern Syria, was one of the ancient Near East's oldest cities, located on a crossroads of two trade routes northwest of Ebla, in a landscape that was much more fertile than it is t ...
, Qatna
Qatna (modern: , Tell al-Mishrifeh; also Tell Misrife or Tell Mishrifeh) was an ancient city located in Homs Governorate, Syria. Its remains constitute a tell situated about northeast of Homs near the village of al-Mishrifeh. The city was an ...
, Ebla, and Al-Rawda developed early state structures, as evidenced by the written documentation of Ebla. Substantial monumental architecture such as palaces, temples, and monumental tombs appeared in this period. There is also evidence for the existence of a rich and powerful local elite.
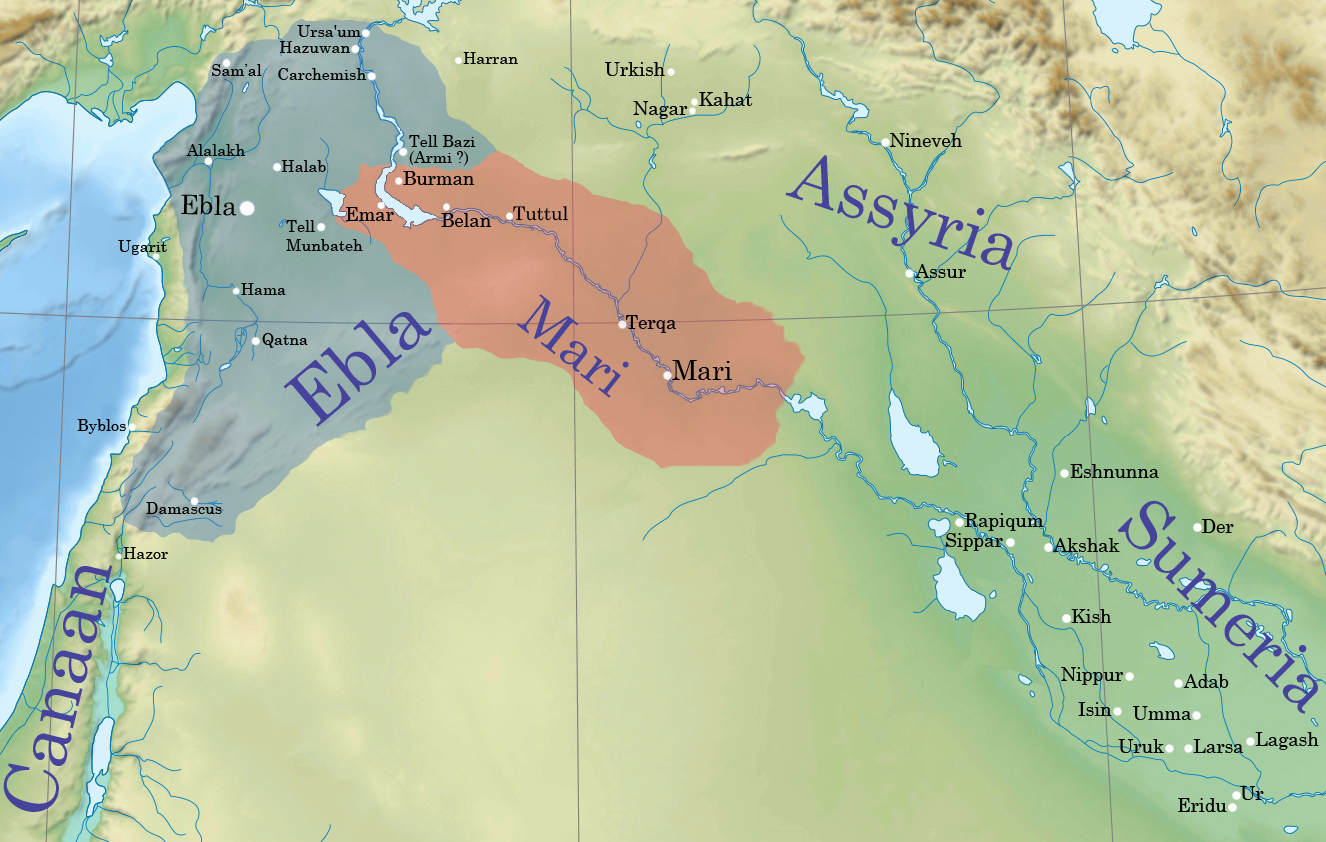
The two cities of Mari and Ebla dominate the historical record for this region. According to the excavator of Mari, the circular city on the middle Euphrates was founded ''ex nihilo
(Latin, 'creation out of nothing') is the doctrine that matter is not eternal but had to be created by some divine creative act. It is a theistic answer to the question of how the universe came to exist. It is in contrast to ''creatio ex mate ...
'' at the time of the Early Dynastic I period in Lower Mesopotamia. Mari was one of the main cities of the Middle East during this period, and it fought many wars against Ebla during the 24th century BC. The archives of Ebla, capital city of a powerful kingdom during the ED IIIb period, indicated that writing and the state were well-developed, contrary to what had been believed about this area before its discovery. However, few buildings from this period have been excavated at the site of Ebla itself.
The territories of these kingdoms were much larger than in Lower Mesopotamia. Population density
Population density (in agriculture: Standing stock (disambiguation), standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geog ...
, however, was much lower than in the south where subsistence agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow crops on smallholdings to meet the needs of themselves and their families. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements. Planting decisions occu ...
and pastoralism
Pastoralism is a form of animal husbandry where domesticated animals (known as "livestock") are released onto large vegetated outdoor lands (pastures) for grazing, historically by nomadic people who moved around with their herds. The anim ...
were more intensive. Towards the west, agriculture takes on more "Mediterranean" aspects: the cultivation of olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
and grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
was very important in Ebla. Sumerian influence was notable in Mari and Ebla. At the same time, these regions with a Semitic population shared characteristics with the Kish civilization
According to a theory proposed by Ignace Gelb, the Kish civilization encompassed the sites of Ebla and Mari in the Levant, Nagar in the north, and the proto- Akkadian sites of Abu Salabikh and Kish in central Mesopotamia in to the early East Se ...
while also maintaining their own unique cultural traits.
Iranian Plateau
In southwestern Iran, the first half of the Early Dynastic Period corresponded with theProto-Elamite
The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from . In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the o ...
period. This period was characterized by indigenous art, a script that has not yet been deciphered, and an elaborate metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
in the Lorestan region. This culture disappeared toward the middle of the third millennium, to be replaced by a less sedentary way of life. Due to the absence of written evidence and a lack of archaeological excavations targeting this period, the socio-political situation of Proto-Elamite Iran is not well understood. Mesopotamian texts indicated that the Sumerian kings dealt with political entities in this area. For example, legends relating to the kings of Uruk referred to conflicts against Aratta
Aratta is a land that appears in Sumerian myths surrounding Enmerkar and Lugalbanda, two early and possibly mythical kings of Uruk also mentioned on the Sumerian king list.
Role in Sumerian literature
Aratta is described as follows in Sumer ...
. Aratta had not been identified, but it is believed to have been located somewhere in southwestern Iran.
In the middle third millennium BC, Elam
Elam () was an ancient civilization centered in the far west and southwest of Iran, stretching from the lowlands of what is now Khuzestan and Ilam Province as well as a small part of modern-day southern Iraq. The modern name ''Elam'' stems fr ...
emerged as a powerful political entity in the area of southern Lorestan and northern Khuzestan
Khuzestan province () is one of the 31 Provinces of Iran. Located in the southwest of the country, the province borders Iraq and the Persian Gulf, covering an area of . Its capital is the city of Ahvaz. Since 2014, it has been part of Iran's ...
. Susa
Susa ( ) was an ancient city in the lower Zagros Mountains about east of the Tigris, between the Karkheh River, Karkheh and Dez River, Dez Rivers in Iran. One of the most important cities of the Ancient Near East, Susa served as the capital o ...
(level IV) was a central place in Elam and an important gateway between southwestern Iran and southern Mesopotamia. Hamazi
Hamazi or Khamazi ( Sumerian: , ''ha-ma-zi''ki, or ''Ḫa-ma-zi2''ki) was an ancient kingdom or city-state which became prominent during the Early Dynastic period. Its exact location is unknown.
History
In the early days of archaeology two pot ...
was located in the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
to the north or east of Elam, possibly between the Great Zab
The Great Zab or Upper Zab (; or ; ; ) is an approximately long river flowing through Turkey and Iraq. It rises in Turkey near Lake Van and joins the Tigris in Iraq south of Mosul. During its course, the river collects water from many tributar ...
and the Diyala River
The Diyala (Arabic: ; ; Farsi: , ) is a river and tributary of the Tigris. It is formed by the confluence of the Sirwan and Tanjaro rivers in Darbandikhan Dam in the Sulaymaniyah Governorate of Northern Iraq. It covers a total distance of .
...
, near Halabja
Halabja (, ) is a city in the Kurdistan Region of Iraq and the capital of Halabja Governorate, located about northeast of Baghdad and from the Iranian border.
The city lies at the base of what is often referred to as the greater Hewraman re ...
.
This is also the area where the still largely unknown Jiroft culture
The Jiroft culture,Oscar White MuscarellaJiroft(2008), in: Encyclopedia Iranica. "For archeological accuracy the terms "Jiroft" or "Jiroft culture" employed to define a specific ancient Iranian culture and its artifacts should only be cited withi ...
emerged in the third millennium BC, as evidenced by excavation and looting of archaeological sites. The areas further north and to the east were important participants in the international trade of this period due to the presence of tin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
(central Iran and the Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central Asia, Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and eastern Afghanistan into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the wester ...
) and lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
(Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
and northern Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
). Settlements such as Tepe Sialk
Tepe Sialk () is a large ancient archeological site (a ''tepe'', "hill, tell") in a suburb of the city of Kashan, Isfahan Province, in central Iran, close to Fin Garden. The culture that inhabited this area has been linked to the Zayandeh Rive ...
, Tureng Tepe
Tureng Tepe (, "Hill of the Pheasants"; alternatively spelled in English as Turang Tappe/Tape/Tappa/Tappeh) is a Neolithic and Chalcolithic archaeological site in northeastern Iran, in the Gorgan plain, approximately 17 kilometers northeast of the ...
, Tepe Hissar, Namazga-Tepe, Altyndepe, Shahr-e Sukhteh
Shahr-e Sukhteh (, meaning "Burnt City"), c. 3550–2300 BC,Ascalone, E., and P. F. Fabbri, (2022)"Demographic considerations regarding the settlement and necropolis of Shahr i Sokhta" in: E. Ascalone and S.M.S. Sajjadi (eds.), Excavations and R ...
, and Mundigak served as local exchange and production centres but do not seem to have been capitals of larger political entities.
Persian Gulf
The further development of maritime trade in thePersian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
led to increased contacts between Lower Mesopotamia and other regions. Starting in the previous period, the area of modern-day Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
—known in ancient texts as Magan
Magan may refer to:
Places
* Magan (civilization)
* Magan, Russia
* Magan Airport
* Magán, Spain
*Magan, alternative name of Mahin, a village in Iran
* Aman Magan, a village in Iran
People
* Magan (name)
Film and television
*'' Azhagiya Tamil ...
—had seen the development of the oasis
In ecology, an oasis (; : oases ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environmentcopper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
deposits. These deposits were located in the mountains, notably near Hili, where copper workshops and monumental tombs testifying to the area's affluence has been excavated.
Further to the west was an area called Dilmun
Dilmun, or Telmun, ( Sumerian: ,Transliteration: Similar text: later 𒉌𒌇(𒆠), NI.TUKki = dilmunki; ) was an ancient East Semitic–speaking civilization in Eastern Arabia mentioned from the 3rd millennium BC onwards. Based on contextual ...
, which in later periods corresponds to what is today known as Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
. However, while Dilmun was mentioned in contemporary ED texts, no sites from this period have been excavated in this area. This may indicate that Dilmun may have referred to the coastal areas that served as a place of transit for the maritime trade network.
Indus valley
 The maritime trade in the Gulf extended as far east as the
The maritime trade in the Gulf extended as far east as the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
, where the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the Northwestern South Asia, northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 Common Era, BCE to 1300 BCE, and in i ...
flourished. This trade intensified during the third millennium and reached its peak during the Akkadian and Ur III periods.
The artifacts found in the royal tombs of the First Dynasty of Ur indicate that foreign trade was particularly active during this period, with many materials coming from foreign lands, such as Carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semiprecious stone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker; the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used int ...
likely coming from the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
or Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
, Lapis Lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
from Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, silver from Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, copper from Oman
Oman, officially the Sultanate of Oman, is a country located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in West Asia and the Middle East. It shares land borders with Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, and Yemen. Oman’s coastline ...
, and gold from several locations such as Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Nubia
Nubia (, Nobiin language, Nobiin: , ) is a region along the Nile river encompassing the area between the confluence of the Blue Nile, Blue and White Nile, White Niles (in Khartoum in central Sudan), and the Cataracts of the Nile, first cataract ...
, Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
or Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
.British Museum notice " Grave goods from Ur" Carnelian beads from the Indus were found in Ur tombs dating to 2600–2450, in an example of Indus-Mesopotamia relations. In particular, carnelian beads with an etched design in white were probably imported from the Indus Valley, and made according to a technique developed by the Harappa
Harappa () is an archaeological site in Punjab, Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal, that takes its name from a modern village near the former course of the Ravi River, which now runs to the north. Harappa is the type site of the Bronze Age Indus ...
ns.British Museum notice: "Gold and carnelians beads. The two beads etched with patterns in white were probably imported from the Indus Valley. They were made by a technique developed by the Harappan civilization" Photograph of the necklace in question These materials were used in the manufacture of ornamental and ceremonial objects in the workshops of Ur.
The First Dynasty of Ur had enormous wealth as shown by the lavishness of its tombs. This was probably due to the fact that Ur acted as the main harbour for trade with India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, which put her in a strategic position to import and trade vast quantities of gold, carnelian or lapis lazuli. In comparison, the burials of the kings of Kish
Kish may refer to:
Businesses and organisations
* KISH, a radio station in Guam
* Kish Air, an Iranian airline
* Korean International School in Hanoi, Vietnam
People
* Kish (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Kish, a former ...
were much less lavish. High-prowed Sumerian ships may have traveled as far as Meluhha, thought to be the Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans- Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northwest through the dis ...
region, for trade.
Government and economy
Administration
Each city was centered around a temple that was dedicated to a particular patron deity. A city was governed by both/either a " lugal" (king) and/or an " ensi" (priest). It was understood that rulers were determined by the deity of the city and rule could be transferred from one city to another.Hegemony
Hegemony (, , ) is the political, economic, and military predominance of one State (polity), state over other states, either regional or global.
In Ancient Greece (ca. 8th BC – AD 6th c.), hegemony denoted the politico-military dominance of ...
from the Nippur
Nippur (Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Nibru'', often logogram, logographically recorded as , EN.LÍLKI, "Enlil City;"I. E. S. Edwards, C. J. Gadd, N. G. L. Hammond, ''The Cambridge Ancient History: Prolegomena & Prehistory'': Vol. 1, Part 1, Ca ...
priesthood moved between competing dynasties of the Sumerian cities. Traditionally, these included Eridu
Eridu (; Sumerian: eridugki; Akkadian: ''irîtu'') was a Sumerian city located at Tell Abu Shahrain (), also Abu Shahrein or Tell Abu Shahrayn, an archaeological site in Lower Mesopotamia. It is located in Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq, near the ...
, Bad-tibira
Bad-tibira (also Patibira) ( Sumerian: , bad3-tibiraki) was an ancient Sumerian city on the Iturungal canal dating back to the
Early Dynastic period, which appears among antediluvian cities in the Sumerian King List. In the earliest days of Akkadi ...
, Larsa
Larsa (, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossus, Berossos and connected with the biblical Arioch, Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the Cult (religious pra ...
, Sippar
Sippar (Sumerian language, Sumerian: , Zimbir) (also Sippir or Sippara) was an ancient Near Eastern Sumerian and later Babylonian city on the east bank of the Euphrates river. Its ''Tell (archaeology), tell'' is located at the site of modern Tell ...
, Shuruppak
Shuruppak ( , SU.KUR.RUki, "the healing place"), modern Tell Fara, was an ancient Sumerian city situated about 55 kilometres (35 mi) south of Nippur and 30 kilometers north of ancient Uruk on the banks of the Euphrates in Iraq's Al-Qādisiy ...
, Kish, Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, Ur, Adab, and Akshak. Other relevant cities from outside the Tigris–Euphrates river system
The Tigris–Euphrates river system is a large river system in West Asia that flows into the Persian Gulf. Its primary rivers are the Tigris and Euphrates, along with smaller tributary, tributaries.
From their sources and upper courses in the Ar ...
included Hamazi
Hamazi or Khamazi ( Sumerian: , ''ha-ma-zi''ki, or ''Ḫa-ma-zi2''ki) was an ancient kingdom or city-state which became prominent during the Early Dynastic period. Its exact location is unknown.
History
In the early days of archaeology two pot ...
, Awan (in present-day Iran), and Mari (in present-day Syria but which is credited on the ''SKL'' as having "exercised kingship" during the ED II period).
 Thorkild Jacobsen defined a "primitive democracy" with reference to Sumerian epics, myths, and historical records. He described a form of government determined by a majority of men who were free citizens. There was little specialisation and only a loose power structure. Kings such as
Thorkild Jacobsen defined a "primitive democracy" with reference to Sumerian epics, myths, and historical records. He described a form of government determined by a majority of men who were free citizens. There was little specialisation and only a loose power structure. Kings such as Gilgamesh
Gilgamesh (, ; ; originally ) was a hero in ancient Mesopotamian mythology and the protagonist of the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', an epic poem written in Akkadian during the late 2nd millennium BC. He was possibly a historical king of the Sumer ...
of the first dynasty of Uruk did not yet hold an autocracy
Autocracy is a form of government in which absolute power is held by the head of state and Head of government, government, known as an autocrat. It includes some forms of monarchy and all forms of dictatorship, while it is contrasted with demo ...
. Rather, they governed together with councils of elders and councils of younger men, who were likely free men bearing arms. Kings would consult the councils on all major decisions, including whether to go to war. Jacobsen's definition of a democracy as a relationship between primitive monarchs and men of the noble classes has been questioned. Jacobsen conceded that the available evidence could not distinguish a "Mesopotamian democracy" from a "primitive oligarchy".
" Lugal" ( Sumerian: 𒈗, a Sumerogram
A Sumerogram is the use of a Sumerian cuneiform character or group of characters as an ideogram or logogram rather than a syllabogram in the graphic representation of a language other than Sumerian, such as Akkadian, Eblaite, or Hittite. Th ...
ligature Ligature may refer to:
Language
* Ligature (writing), a combination of two or more letters into a single symbol (typography and calligraphy)
* Ligature (grammar), a morpheme that links two words
Medicine
* Ligature (medicine), a piece of suture us ...
of two signs: " 𒃲" meaning "big" or "great" and "𒇽" meaning "man") (a Sumerian language
Sumerian ) was the language of ancient Sumer. It is one of the List of languages by first written account, oldest attested languages, dating back to at least 2900 BC. It is a local language isolate that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia, in the a ...
title translated into English as either "king" or "ruler") was one of three possible titles affixed to a ruler of a Sumerian city-state. The others were "EN" and "ensi".
The sign for "lugal" became the understood logograph
In a written language, a logogram (from Ancient Greek 'word', and 'that which is drawn or written'), also logograph or lexigraph, is a written character that represents a semantic component of a language, such as a word or morpheme. Chines ...
for "king" in general. In the Sumerian language, "lugal" meant either an "owner" of property such as a boat or a field, or alternatively, the "head" of an entity or a family. The cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
sign for "lugal" serves as a determinative
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they ...
in cuneiform texts, indicating that the following word would be the name of a king.
The definition of "lugal" during the ED Period of Mesopotamia is uncertain. The ruler of a city-state was usually referred to as "ensi". However, the ruler of a confederacy may have been referred to as "lugal". A lugal may have been "a young man of outstanding qualities from a rich landowning family".
Jacobsen made a distinction between a "lugal" as an elected war leader and "EN" as an elected governor concerned with internal issues. The functions of a lugal might include military defense, arbitration in border disputes, and ceremonial and ritualistic activities. At the death of the lugal, he was succeeded by his eldest son.Plamen Rusev, Mesalim, Lugal Na Kish: Politicheska Istoriia Na Ranen Shumer (XXVIII-XXVI V. Pr. N. E.), Faber, 2001 (in Bulgarian) Mesalim, Lugal of Kish. Political History of Early Sumer (XXVIII–XXVI century BC). The earliest rulers with the title "lugal" include Enmebaragesi and Mesilim of Kish and Meskalamdug, Mesannepada, and several of Mesannepada's successors at Ur.
" Ensi" (Sumerian: 𒑐𒋼𒋛, meaning "Lord of the Plowland") was a title associated with the ruler or prince of a city. The people understood that the ensi was a direct representative of the city's patron deity. Initially, the term "ensi" may have been specifically associated with rulers of Lagash
Lagash (; cuneiform: LAGAŠKI; Sumerian language, Sumerian: ''Lagaš'') was an ancient city-state located northwest of the junction of the Euphrates and Tigris rivers and east of Uruk, about east of the modern town of Al-Shatrah, Iraq. Lagash ( ...
and Umma
Umma () in modern Dhi Qar Province in Iraq, was an ancient city in Sumer. There is some scholarly debate about the Sumerian and Akkadian names for this site. Traditionally, Umma was identified with Tell Jokha. More recently it has been sugges ...
. However, in Lagesh, "lugal" sometimes referred to the city's patron deity, "Ningirsu
Ninĝirsu was a Mesopotamia, Mesopotamian god regarded as the tutelary deity of the city of Girsu, Ĝirsu, and as the chief god of the local pantheon of the state of Lagash. He shares many aspects with the god Ninurta. Ninĝirsu was identified as ...
". In later periods, the title "ensi" presupposed subordinance to a "lugal".
" EN" (Sumerian: 𒂗; Sumerian cuneiform for "lord
Lord is an appellation for a person or deity who has authority, control, or power (social and political), power over others, acting as a master, chief, or ruler. The appellation can also denote certain persons who hold a title of the Peerage o ...
" or "priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in parti ...
") referred to a high priest or priestess of the city's patron deity. It may also have been part of the title of the ruler of Uruk. "Ensi", "EN", and "Lugal" may have been local terms for the ruler of Lagash, Uruk, and Ur, respectively.
Temples
The centers ofEridu
Eridu (; Sumerian: eridugki; Akkadian: ''irîtu'') was a Sumerian city located at Tell Abu Shahrain (), also Abu Shahrein or Tell Abu Shahrayn, an archaeological site in Lower Mesopotamia. It is located in Dhi Qar Governorate, Iraq, near the ...
and Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
, two of the earliest cities, developed large temple complexes built of mud-brick. Developed as small shrines in the earliest settlements, by the ED the temples became the most imposing structures in their cities, each dedicated to its own deity.
Each city had at least one major deity. Sumer was divided into about thirteen independent cities which were divided by canals
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow u ...
and boundary stones during the ED.
Population
Uruk, which was one of Sumer's largest cities, has been estimated to have had a population of 50,000 – 80,000 at its peak. Given the other cities in Sumer and its large agricultural population, a rough estimate for Sumer's population might have been somewhere between 800,000 and 1,500,000. The global human population at this time has been estimated to have been about 27,000,000.Law
Code of Urukagina
The énsi Urukagina, of the city-state of Lagash, is best known for his reforms to combat corruption, and the Code of Urukagina is sometimes cited as the earliest known example of alegal code
A code of law, also called a law code or legal code, is a systematic collection of statutes. It is a type of legislation that purports to exhaustively cover a complete system of laws or a particular area of law as it existed at the time the co ...
in recorded history
Recorded history or written history describes the historical events that have been recorded in a written form or other documented communication which are subsequently evaluated by historians using the historical method. For broader world h ...
. The Code of Urukagina has also been widely hailed as the first recorded example of government reform, as it sought to achieve a higher level of freedom
Freedom is the power or right to speak, act, and change as one wants without hindrance or restraint. Freedom is often associated with liberty and autonomy in the sense of "giving oneself one's own laws".
In one definition, something is "free" i ...
and equality
Equality generally refers to the fact of being equal, of having the same value.
In specific contexts, equality may refer to:
Society
* Egalitarianism, a trend of thought that favors equality for all people
** Political egalitarianism, in which ...
. Although the actual Code of Urukagina text has yet to be discovered, much of its content may be surmised from other references to it that have been found. In the Code of Urukagina, Urukagina exempted widows and orphans from taxes, compelled the city to pay funeral expenses (including the ritual food and drink libations for the journey of the dead into the lower world), and decreed that the rich had to use silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
when purchasing from the poor. If the poor did not wish to sell, the powerful man (the rich man or the priest) could not force him to do so. The Code of Urukagina limited the power of both the priesthood and large property owners and established measures against usury, burdensome controls, hunger, theft, murder, and seizure of people's property and persons—as Urukagina stated: "The widow and the orphan were no longer at the mercy of the powerful man."
Despite these attempts to curb the excesses of the elite class, elite or royal women may have had even greater influence and prestige in Urukagina's reign than previously. Urukagina greatly expanded the royal "Household of Women" from about 50 persons to about 1,500 persons and renamed it to "Household of Goddess Bau". He gave it ownership of vast amounts of land confiscated from the former priesthood and placed it under the supervision of Urukagina's wife Shasha, or Shagshag. During the second year of Urukagina's reign, his wife presided over the lavish funeral of his predecessor's queen Baranamtarra, who had been an important personage in her own right.
In addition to such changes, two of Urukagina's other surviving decrees, first published and translated by Samuel Kramer in 1964, have attracted controversy in recent decades:
# Urukagina seems to had abolished the former custom of polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives ...
in his country, on pain of the woman taking multiple husbands being stoned with rocks upon which her crime was written.
# A statute that stated: "If a woman says ext illegible...to a man, her mouth is crushed with burnt bricks."
No comparable laws
Law is a set of rules that are created and are law enforcement, enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a Socia ...
from Urukagina addressing penalties for adultery by men have survived. The discovery of these fragments has led some modern critics to assert that they provide "the first written evidence of the degradation of women."
Reform Document
 The following extracts are taken from the "Reform Document":
# "From the border territory of Ningirsu to the sea, no person shall serve as officers."
# "For a corpse being brought to the grave, his beer shall be 3 jugs and his bread 80 loaves. 1 bed and 1 lead goat shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the person(s) take away."
# "When to the reeds of Enki a person has been brought, his beer will be 4 jugs, and his bread 420 loaves. 1 barig of barley shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the persons of ... take away. 1 woman’s headband, and 1 sila of princely fragrance shall the eresh-dingir priestess take away. 420 loaves of bread that have sat are the bread duty, 40 loaves of hot bread are for eating, and 10 loaves of hot bread are the bread of the table. 5 loaves of bread are for the persons of the levy, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Girsu. 490 loaves of bread, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Lagash. 406 of bread, 2 mud vessels, and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the other lamentation singers. 250 loaves of bread and 1 mud vessel of beer are for the old wailing women. 180 loaves of bread and one mud vessel of beer are for the men of Nigin."
# "The blind one who stands in ..., his bread for eating is 1 loaf, 5 loaves of bread are his at midnight, 1 loaf is his bread at midday, and 6 loaves are his bread in the evening."
# "60 loaves of bread, 1 mud vessel of beer, and 3 ban of barley are for the person who is to perform as the sagbur priest."
The following extracts are taken from the "Reform Document":
# "From the border territory of Ningirsu to the sea, no person shall serve as officers."
# "For a corpse being brought to the grave, his beer shall be 3 jugs and his bread 80 loaves. 1 bed and 1 lead goat shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the person(s) take away."
# "When to the reeds of Enki a person has been brought, his beer will be 4 jugs, and his bread 420 loaves. 1 barig of barley shall the undertaker take away, and 3 ban of barley shall the persons of ... take away. 1 woman’s headband, and 1 sila of princely fragrance shall the eresh-dingir priestess take away. 420 loaves of bread that have sat are the bread duty, 40 loaves of hot bread are for eating, and 10 loaves of hot bread are the bread of the table. 5 loaves of bread are for the persons of the levy, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Girsu. 490 loaves of bread, 2 mud vessels and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the lamentation singers of Lagash. 406 of bread, 2 mud vessels, and 1 sadug vessel of beer are for the other lamentation singers. 250 loaves of bread and 1 mud vessel of beer are for the old wailing women. 180 loaves of bread and one mud vessel of beer are for the men of Nigin."
# "The blind one who stands in ..., his bread for eating is 1 loaf, 5 loaves of bread are his at midnight, 1 loaf is his bread at midday, and 6 loaves are his bread in the evening."
# "60 loaves of bread, 1 mud vessel of beer, and 3 ban of barley are for the person who is to perform as the sagbur priest."
Trade
 Imports to Ur came from the
Imports to Ur came from the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
and the Old World
The "Old World" () is a term for Afro-Eurasia coined by Europeans after 1493, when they became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia in the Eastern Hemisphere, previously ...
. Goods such as obsidian
Obsidian ( ) is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock. Produced from felsic lava, obsidian is rich in the lighter element ...
from Turkey, lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
from Badakhshan
Badakhshan is a historical region comprising the Wakhan Corridor in northeast Afghanistan, eastern Tajikistan, and Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County in China. Badakhshan Province is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan. Much of historic ...
in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, beads from Bahrain
Bahrain, officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, is an island country in West Asia. Situated on the Persian Gulf, it comprises a small archipelago of 50 natural islands and an additional 33 artificial islands, centered on Bahrain Island, which mak ...
, and seals inscribed with the Indus Valley script from India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
have been found in Ur. Metals were imported. Sumerian stonemasons
Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar ...
and jewelers used gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
, lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
, chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite (oxyanion), halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as s ...
, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and Tooth, teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mamm ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, and carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semiprecious stone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker; the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used int ...
. Resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
from Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
was found in the tomb of Queen Puabi at Ur.
The cultural and trade connections of Ur are reflected by archaeological finds of imported items. In the ED III period, items from geographically distant places were found. These included gold, silver, lapis lazuli and carnelian. These types of items were not found in Mesopotamia.
Gold items were located in graves at the Royal Cemetery of Ur, royal treasuries and temples, indicating prestigious and religious functions. Gold items discovered included personal ornaments, weapons, tools, sheet-metal cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s, fluted bowls, goblets, imitation cockle shells, and sculptures.
Silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
was found as items such as belts, vessels, hair ornaments, pins, weapons, cockle shells, and sculptures. There are very few literary references or physical clues as to the sources of the silver.
Lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
has been found in items such as jewelry, plaques, gaming boards, lyres, ostrich-egg vessels, and also in parts of a larger sculpture known as ''Ram in a Thicket''. Some of the larger objects included a spouted cup, a dagger-hilt, and a whetstone. It indicates high status.
Chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite (oxyanion), halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as s ...
stone artifacts from the ED are commonly found. they include disc beads, ornaments, and stone vases. The vases rarely exceed 25 cm in height. They often have human and animal motifs and semiprecious stone inlays. They may have carried precious oils.
Culture
Sculpting
Early Dynastic stone sculptures have mainly been recovered from excavated temples. They can be separated into two groups: three-dimensional prayer statues and perforatedbas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s. The so-called Tell Asmar Hoard is a well-known example of Early Dynastic sculpture. It was recovered in a temple and consists of standing figures with their hands folded in prayer or holding a goblet for a libation
A libation is a ritual pouring of a liquid as an Sacrifice, offering to a deity or spirit, or in Veneration of the dead, memory of the dead. It was common in many religions of Ancient history, antiquity and continues to be offered in cultures t ...
ritual. Other statues feature seated figures also in devotional postures. Male figures wear a plain or fringed dress, or kaunakes. The statues usually represent notables or rulers. They served as ex-voto
An ex-voto is a votive offering to a saint or a divinity, given in fulfillment of a vow (hence the Latin term, short for ''ex voto suscepto'', "from the vow made") or in gratitude or devotion. The term is usually restricted to Christian example ...
s and were placed in temples to pray on behalf of the spender. The Sumerian style clearly influenced neighbouring regions, as similar statues have been recovered from sites in Upper Mesopotamia, including Assur, Tell Chuera, and Mari. However, some statues showed greater originality and had less stylistic characteristics in common with Sumerian sculpture.
Khafajah
Khafajah or Khafaje (), ancient Tutub, is an archaeological site in Diyala Governorate, Iraq east of Baghdad. Khafajah lies on the Diyala River, a tributary of the Tigris. Occupied from the Uruk period, Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods through the e ...
File:Kneeling Nude Male Holding Vase on Head, Tell Agrab, Shara Temple, Early Dynastic period, 2900-2700 BC, calcite - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC07462.JPG, Statue of a kneeling male figure holding a vase, recovered from Tell Agrab
File:Ebih-Il Louvre AO17551 n01.jpg, Statue of Ebih-Il, recovered from Mari (ED IIIb)
File:Stone statue of Kurlil Early Dynastic III 2500 BC Tell Al-'Ubaid, Iraq.jpg, Stone statue of Kurlil, Early Dynastic III, 2500 BC Tell Al-'Ubaid.
Ur-Nanshe
Ur-Nanshe (, ; ) also Ur-Nina, was the first king of the First Dynasty of Lagash in the Sumerian Early Dynastic Period III. He is known through inscriptions to have commissioned many building projects, including canals and temples, in the state of ...
of Lagash and his family found at Girsu and that of Dudu, a priest of Ningirsu
Ninĝirsu was a Mesopotamia, Mesopotamian god regarded as the tutelary deity of the city of Girsu, Ĝirsu, and as the chief god of the local pantheon of the state of Lagash. He shares many aspects with the god Ninurta. Ninĝirsu was identified as ...
. The latter showed mythological creatures such as a lion-headed eagle. The Stele of the Vultures
The Stele of the Vultures is a monument from the Early Dynastic Period (Mesopotamia), Early Dynastic IIIb period (2600–2350 BC) in Mesopotamia celebrating a victory of the city-state of Lagash over its neighbour Umma. It shows various battle and ...
, created by Eannatum
Eannatum ( ; ) was a Sumerian ''Ensi (Sumerian), Ensi'' (ruler or king) of Lagash. He established one of the first verifiable empires in history, subduing Elam and destroying the city of Susa, and extending his domain over the rest of Sumer and Akk ...
of Lagash, is remarkable in that it represents different scenes that together tell the narrative of the victory of Lagash over its rival Umma. Reliefs like these have been found in Lower Mesopotamia and the Diyala region but not in Upper Mesopotamia or Syria.
Kish (Sumer)
Kish (Sumerian language, Sumerian: Kiš; transliteration: :wikt:𒆧, KišKi (earth), ki; cuneiform: ; , near modern Tell al-Uhaymir) is an important archaeological site in Babil Governorate (Iraq), located south of Baghdad and east of the anc ...
.
File:Banquet plaque, Tell Agrab, Main Shara Temple, Early Dynastic period, 2700-2600 BC, limestone - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC07369.JPG, Bas-relief of a banquet scene, recovered from Tell Agrab
File:Mesopotamia, Periodo proto-dinastico, placca con scena di banchetto, da khafajah, 2650-2550 ac ca.jpg, Banquet scene, Khafajah
Khafajah or Khafaje (), ancient Tutub, is an archaeological site in Diyala Governorate, Iraq east of Baghdad. Khafajah lies on the Diyala River, a tributary of the Tigris. Occupied from the Uruk period, Uruk and Jemdet Nasr periods through the e ...
, 2650-2550 BCE
File:Relief Dudu Louvre AO2394.jpg, Votive relief of the priest Dudu, of the time of Entemena, recovered from Girsu. Circa 2400 BCE
Metalworking and goldsmithing
Sumerianmetallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
and goldsmith
A goldsmith is a Metalworking, metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Modern goldsmiths mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, they have also made cutlery, silverware, platter (dishware), plat ...
ing were highly developed. This is all the more remarkable for a region where metals had to be imported. Known metals included gold, silver, copper, bronze, lead, electrum, and tin. The use of binary, tertiary, and quaternary alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s was already present during the Uruk period. Sumerians used bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
, although the scarcity of tin meant that they used arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
instead. Metalworking techniques included lost-wax casting
Lost-wax castingalso called investment casting, precision casting, or ''cire perdue'' (; borrowed from French)is the process by which a duplicate sculpture (often a metal, such as silver, gold, brass, or bronze) is cast from an original scul ...
, plating
Plating is a finishing process in which a metal is deposited on a surface. Plating has been done for hundreds of years; it is also critical for modern technology. Plating is used to decorate objects, for corrosion inhibition, to improve solderab ...
, filigree
Filigree (also less commonly spelled ''filagree'', and formerly written ''filigrann'' or ''filigrene'') is a form of intricate metalwork used in jewellery and other small forms of metalwork.
In jewellery, it is usually of gold and silver, m ...
, and granulation.
Numerous metal objects have been excavated from temples and graves, including dishes, weapons, jewelry, statuettes, foundation nails, and various other objects of worship. The most remarkable gold objects come from the Royal Cemetery at Ur
The Royal Cemetery at Ur is an archaeological site in modern-day Dhi Qar Governorate in southern Iraq. The initial excavations at Ur took place between 1922 and 1934 under the direction of Leonard Woolley in association with the British Museum and ...
, including musical instruments
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
and the complete inventory of Puabi
Puabi ( Akkadian: 𒅤𒀜 pu3-AD ), also called Shubad or Shudi-Ad due to a misinterpretation by Sir Charles Woolley, was an important queen in the Sumerian city of Ur, during the First Dynasty of Ur. Commonly labeled as a "queen", her stat ...
’s tomb. Metal vases have also been excavated at other sites in Lower Mesopotamia, including the Vase of Entemena at Lagash.
nacre
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother-of-pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer. It is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent.
Nacre is ...
and lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
inlays, created with the lost-wax method (ED III)
File:Reconstructed sumerian headgear necklaces british museum.JPG, Reconstructed headgear of Puabi
Puabi ( Akkadian: 𒅤𒀜 pu3-AD ), also called Shubad or Shudi-Ad due to a misinterpretation by Sir Charles Woolley, was an important queen in the Sumerian city of Ur, during the First Dynasty of Ur. Commonly labeled as a "queen", her stat ...
, found in the Royal Cemetery at Ur
The Royal Cemetery at Ur is an archaeological site in modern-day Dhi Qar Governorate in southern Iraq. The initial excavations at Ur took place between 1922 and 1934 under the direction of Leonard Woolley in association with the British Museum and ...
(ED III)
File:Perfume dropper, bracelet, earrings, and headdress leaves, Ur, early Dynastic III, mid 3rd millennium BCE - Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art - DSC08127.jpg, Gold objects from the Royal Cemetery at Ur
The Royal Cemetery at Ur is an archaeological site in modern-day Dhi Qar Governorate in southern Iraq. The initial excavations at Ur took place between 1922 and 1934 under the direction of Leonard Woolley in association with the British Museum and ...
File:Pendants, Tell Asmar, North Palace, room E 16 in hoard 11, Early Dynastic period, 2900-2350 BC, lapis lazuli, silver, carnelian - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC07316.JPG, Animal-shaped pendants of gold, lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
and carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semiprecious stone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker; the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used int ...
from Eshnunna
Eshnunna (also Esnunak) (modern Tell Asmar in Diyala Governorate, Iraq) was an ancient Sumerian (and later Akkadian) city and city-state in central Mesopotamia 12.6 miles northwest of Tell Agrab and 15 miles northwest of Tell Ishchali. Althou ...
File:Beads, modern restringing, Tell Agrab, Earlier Shara Temple, Early Dynastic period, 2900-2800 BC, lapis lazuli, carnelian, silver - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC07362.JPG, Pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle (mollusc), mantle) of a living Exoskeleton, shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pear ...
, lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color. Originating from the Persian word for the gem, ''lāžward'', lapis lazuli is ...
, carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semiprecious stone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker; the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used int ...
and silver beads from Tell Agrab (ED I)
Cylinder seals

Cylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in width, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s were used to authenticate documents like sales and to control access by sealing a lump of clay on doors of storage rooms. The use of cylinder seals increased significantly during the ED Period, suggesting an expansion and increased the complexity of administrative activities.
During the preceding Uruk period, a wide variety of scenes were engraved on cylinder seals. This variety disappeared at the start of the third millennium, to be replaced by an almost exclusive focus on mythological and cultural scenes in Lower Mesopotamia and the Diyala region. During the ED I period, seal designs included geometric motifs and stylized pictograms. Later on, combat scenes between real and mythological animals became the dominant theme, together with scenes of heroes fighting animals. Their exact meaning is unclear. Common mythological creatures include anthropomorphic bulls and scorpion-men. Real creatures include lions and eagles. Some anthropomorphic creatures are probably deities, as they wear a horned tiara, which was a symbol of divinity.
Scenes with cultic themes, including banquet scenes, became common during ED II. Another common ED III theme was the so-called god-boat, but its meaning is unclear. During the ED III period, ownership of seals was started to be registered. Glyptic development in Upper Mesopotamia and Syria was strongly influenced by Sumerian art.
Inlays

 Examples of
Examples of inlay
Inlay covers a range of techniques in sculpture and the decorative arts for inserting pieces of contrasting, often colored materials into depressions in a base object to form Ornament (art), ornament or pictures that normally are flush with the ...
have been found at several sites and used materials such as nacre
Nacre ( , ), also known as mother-of-pearl, is an organicinorganic composite material produced by some molluscs as an inner shell layer. It is also the material of which pearls are composed. It is strong, resilient, and iridescent.
Nacre is ...
(mother of pearl), white and coloured limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science) ...
, lapis lazuli, and marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
. Bitumen
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscosity, viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American Engl ...
was used to attach the inlay in wooden frames, but these have not survived in the archaeological record. The inlay-panels usually showed mythological or historical scenes. Like bas-reliefs
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
, these panels allow the reconstruction of early forms of narrative art. However, this type of work seems to have been abandoned in subsequent periods.
The best preserved inlaid object is the Standard of Ur
The Standard of Ur is a Sumerian Artifact (archaeology), artifact of the 3rd millennium BCE that is now in the collection of the British Museum. It comprises a hollow wooden box measuring wide by long, inlaid with a mosaic of shell, red limesto ...
found in one of the royal tombs of this city. It represents two principal scenes on its two sides: a battle and a banquet that probably follows a military victory. The "dairy frieze" found at Tell al-'Ubaid represents, as its name suggests, dairy activities (milking cows, cowsheds, preparing dairy products). It is our source of the most information on this practice in ancient Mesopotamia
Similar mosaic elements were discovered at Mari, where a mother-of-pearl engraver's workshop was identified, and at Ebla where marble fragments were found from a 3-meter-high panel decorating a room of the royal palace. The scenes of the two sites have strong similarities in their style and themes. In Mari the scenes are military (a parade of prisoners) or religious (a ram's sacrifice). In Ebla, they show a military triumph and mythological animals.
Music
TheLyres of Ur
Yoke lutes, commonly called lyres, are a class of string instruments, subfamily of lutes, indicated with the codes List of musical instruments by Hornbostel–Sachs number: 321.21, 321.21 and List of musical instruments by Hornbostel–Sachs number ...
(or Harps of Ur) are considered to be the world's oldest surviving stringed instrument
In musical instrument classification, string instruments, or chordophones, are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer strums, plucks, strikes or sounds the strings in varying manners.
Musicians play so ...
s. In 1929, archaeologists led by Leonard Woolley
Sir Charles Leonard Woolley (17 April 1880 – 20 February 1960) was a British archaeologist best known for his Excavation (archaeology), excavations at Ur in Mesopotamia. He is recognized as one of the first "modern" archaeologists who excavat ...
discovered the instruments when excavating the Royal Cemetery of Ur between from 1922 and 1934. They discovered pieces of three lyre
The lyre () (from Greek λύρα and Latin ''lyra)'' is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute family of instruments. In organology, a ...
s and one harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or ...
in Ur located in what was Ancient Mesopotamia
The Civilization of Mesopotamia ranges from the earliest human occupation in the Paleolithic period up to Late antiquity. This history is pieced together from evidence retrieved from archaeological excavations and, after the introduction of writ ...
and now is Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
., Bill Taylor
British Museum
The British Museum is a Museum, public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is the largest in the world. It documents the story of human cu ...
from ancient Mesopotamia during the ED III. The decorations on the lyres are fine examples of the court Art of Mesopotamia
The art of Mesopotamia has survived in the record from early hunter-gatherer societies (8th millennium BC) on to the Bronze Age cultures of the Sumerian, Akkadian Empire, Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires. These empires were later replace ...
of the period.
References
Further reading
* Ascalone, Enrico. 2007. ''Mesopotamia: Assyrians, Sumerians, Babylonians (Dictionaries of Civilizations; 1)''. Berkeley: University of California Press. (paperback). * Bottéro, Jean, André Finet, Bertrand Lafont, and George Roux. 2001. ''Everyday Life in Ancient Mesopotamia''. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. * Crawford, Harriet E. W. 2004. ''Sumer and the Sumerians''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. * Frayne, Douglas. 2008. ''Pre-Sargonic Period: Early Periods, Volume 1 (2700–2350 BC)'', University of Toronto Press. * Leick, Gwendolyn. 2002. ''Mesopotamia: Invention of the City''. London and New York: Penguin. * Lloyd, Seton. 1978. ''The Archaeology of Mesopotamia: From the Old Stone Age to the Persian Conquest''. London: Thames and Hudson. * Nemet-Nejat, Karen Rhea. 1998. ''Daily Life in Ancient Mesopotamia''. London and Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. * * Kramer, Samuel Noah. ''Sumerian Mythology: A Study of Spiritual and Literary Achievement in the Third Millennium BC''. * Roux, Georges. 1992. ''Ancient Iraq'', 560 pages. London: Penguin (earlier printings may have different pagination: 1966, 480 pages, Pelican; 1964, 431 pages, London: Allen and Urwin). * Schomp, Virginia. ''Ancient Mesopotamia: The Sumerians, Babylonians, And Assyrians''. * ''Sumer: Cities of Eden (Timelife Lost Civilizations)''. Alexandria, VA:Time-Life Books
Time Life, Inc. (also habitually represented with a hyphen as Time-Life, Inc., even by the company itself) was an American multi-media conglomerate company formerly known as a prolific production/publishing company and direct marketeer seller ...
, 1993 (hardcover, ).
*
* Woolley, C. Leonard. 1929. ''The Sumerians''. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
External links
Iraq’s Ancient Past
nbsp;—
Penn Museum
The Penn Museum is an archaeology and anthropology museum at the University of Pennsylvania. It is located on Penn's campus in the University City, Philadelphia, University City neighborhood of Philadelphia, at the intersection of 33rd and Sout ...
Language
Sumerian Language Page
perhaps the oldest Sumerian website on the web (it dates back to 1996), features compiled lexicon, detailed FAQ, extensive links, and so on.
ETCSL: The Electronic Text Corpus of Sumerian Literature
has complete translations of more than 400 Sumerian literary texts.
PSD: The Pennsylvania Sumerian Dictionary
while still in its initial stages, can be searched on-line, from August 2004.
CDLI: Cuneiform Digital Library Initiative
a large corpus of Sumerian texts in transliteration, largely from the Early Dynastic and Ur III periods, accessible with images. {{coord, 32.0, 45.5, dim:250km, display=title Ancient Mesopotamia Archaeology of Iraq