|
Mundigak
Mundigak () is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar in the 1950s. The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts form the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this site became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of the Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as the Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of the Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectares), by 2400 BCE. Bampur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundigak Iv English
Mundigak () is an archaeology, archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar in the 1950s. The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts form the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this site became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of the Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as the Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of the Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-e Sukhteh, Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundigak Level 1
Mundigak () is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar in the 1950s. The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts form the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this site became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of the Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as the Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of the Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectares), by 2400 BCE. Bampur in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahr-e Sukhteh
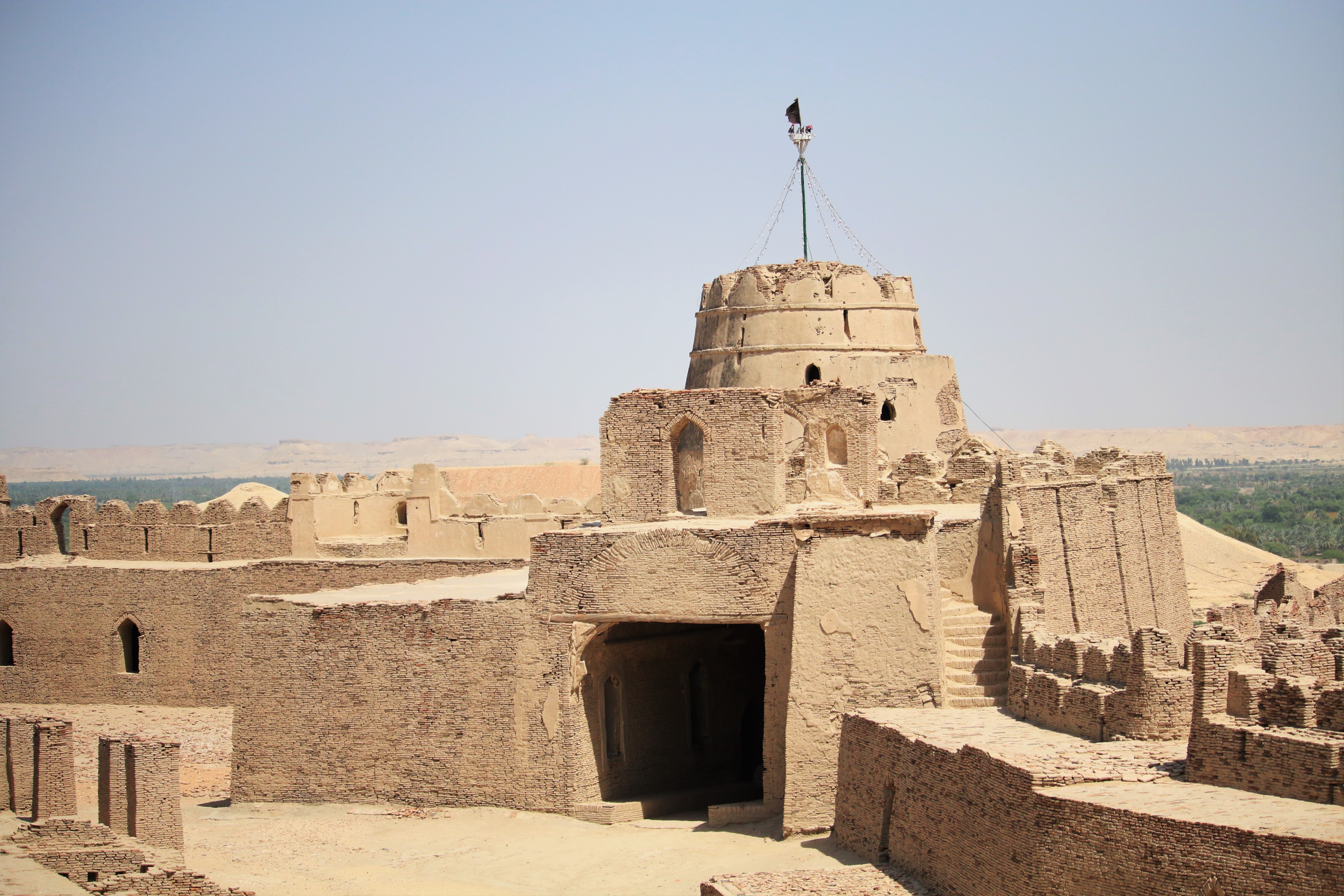
Shahr-e Sukhteh (, meaning "Burnt City"), c. 3550–2300 BC,Ascalone, E., and P. F. Fabbri, (2022)"Demographic considerations regarding the settlement and necropolis of Shahr i Sokhta" in: E. Ascalone and S.M.S. Sajjadi (eds.), Excavations and Researches at Shahr-i Sokhta 2 (= ERSS 2), Pishin Pajouh, Tehran, pp. 524, 525. also spelled as ''Shahr-e Sūkhté'' and ''Shahr-i Sōkhta'', is an archaeological site of a sizable Bronze Age urban settlement, associated with the Helmand culture. It is located in Sistan and Baluchistan Province, the southeastern part of Iran, on the bank of the Helmand River, near the Zahedan- Zabol road. It was placed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in June 2014. The reasons for the unexpected rise and fall of the city are still wrapped in mystery. Artifacts recovered from the city demonstrate a peculiar incongruity with nearby civilizations of the time and it has been speculated that Shahr-e Sukhteh might ultimately provide concrete evidence of a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
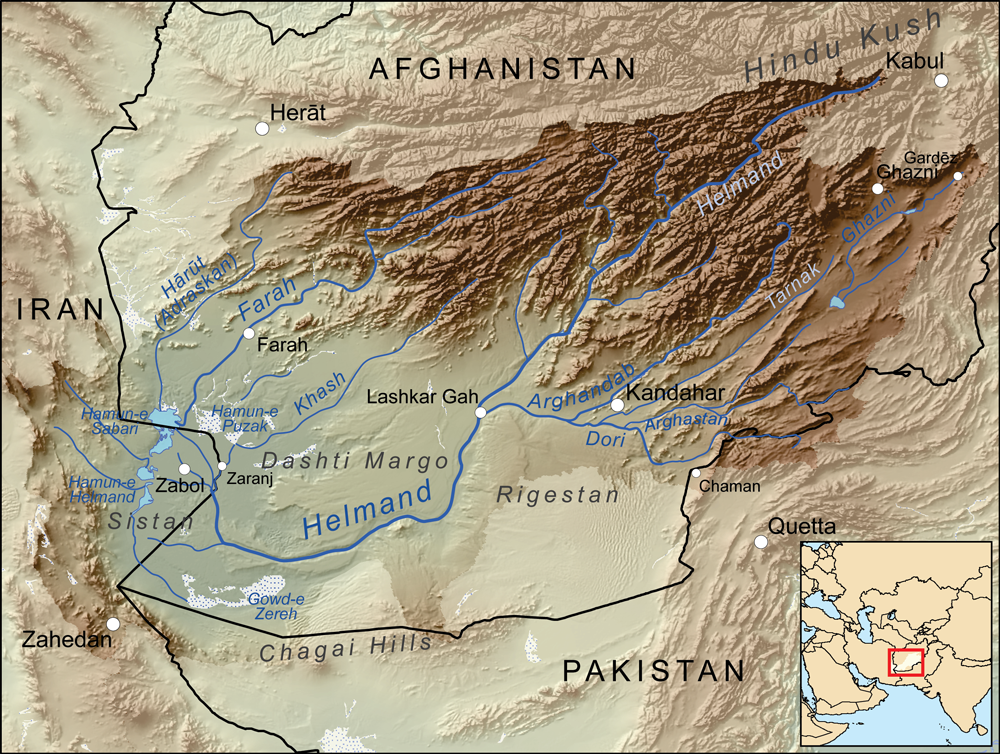
Helmand Culture
Pottery vessel from Shahr-e Sukhteh The Helmand culture (also Helmand civilization), 3300–2350 BCE,Vidale, Massimo, (15 March 2021)"A Warehouse in 3rd Millennium B.C. Sistan and Its Accounting Technology" in Seminar "Early Urbanization in Iran". is a Bronze Age culture that flourished mainly in the middle and lower valley of the Helmand River, originally in eastern Iran ( Zabol, other name: Sistan in Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and southern Afghanistan (Kandahar, Helmand and Nimruz provinces) , predominantly in the third millennium BCE. The people of the Helmand culture lived partly in cities with temples and palaces, providing evidence for a complex and advanced social structure. The main cities so far known are Shahr-i Sokhta (in Zabol, Iran) and Mundigak (in modern Afghanistan). Research on the finds from both places showed that these cities shared the same culture. These are the earliest discovered cities in this part of the world, although the village Mehrgarh fur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmand Province
Helmand (Pashto language, Pashto/Dari language, Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering area. The province contains 18 Districts of Afghanistan, districts, encompassing over 1,000 villages, and roughly 1,446,230 settled people. Lashkargah serves as the provincial capital. Helmand was part of the ''Loy Kandahar, Greater Kandahar'' region until made into a separate province by the Politics of Afghanistan, Afghan government in the 20th century. It is largely populated by Pashtuns. The Helmand River flows through the mainly desert region of the province, providing water used for irrigation. The Kajaki Dam, which is one of List of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, Afghanistan's major reservoirs, is located in the Kajaki district. Helmand is believed to be one of the world's largest opium producing regions, responsible for aroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar
Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city, after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118 in 2015. It is the capital of Kandahar Province and the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar. The region around Kandahar is one of the oldest known areas of human settlement. A major fortified city existed at the site of Kandahar, probably as early as 1000–750 BC,F.R. Allchin (ed.)''The Archaeology of Early Historic South Asia: The Emergence of Cities and States'' (Cambridge University Press, 1995), pp.127–130 and it became an important outpost of the Achaemenid Empire in the 6th century BC.Gérard Fussman"Kandahar II. Pre-Islamic Monuments and Remains", in ''Encyclopædia Iranica'', online edition, 2012 Alexander the Great laid the foundation of what is now Old Kandahar (in the southern section of the city) in the 4th century BC and named it Alexandria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kot Diji
Kot Diji (; ) is an ancient site which was part of the Indus Valley Civilization, estimated to have been occupied around 3300 BCE. Located about south of Khairpur in the modern-day province of Sindh, India, it is on the east bank of the Indus River opposite Mohenjo-daro. The remains consist of two parts: the citadel area on the high ground (about ), and the area around it. The Pakistan Department of Archaeology excavated at Kot Diji in 1955 and 1957. The excavation at Kot Diji during 1954-55 by F. A. Khan revealed convincing evidence of the early or formative stage of the Indus civilization in the cultural assemblag called Kot Dijian. The site is situated at the foot of the Rohri Hills, where Kot Diji Fort was built around 1790 by the Talpur dynasty ruler of the Upper Sindh, Mir Suhrab, who reigned from 1783 to 1830 AD. This fort built on the ridge of a steep narrow hill is well-preserved. Cultural context Kot Diji is the type site, i.e. the first excavated site of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's capital and largest city. Demographics of Afghanistan, Afghanistan's population is estimated to be between 36 and 50 million. Ancient history of Afghanistan, Human habitation in Afghanistan dates to the Middle Paleolithic era. Popularly referred to as the graveyard of empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Archaeological Delegation In Afghanistan
The French Archaeological Delegation in Afghanistan ( (DAFA)) was created in France in 1922 at the request of the Afghan government and King Amanullah Khan to commence archaeological studies in Afghanistan. After a break in research during the Second World War, work resumed around 1946-47, until it was closed by the pro-Soviet Afghan government on December 15, 1982. Some notable 20th century French archaeologists who were part of the delegation include Jules Barthoux, Daniel Schlumberger, and Paul Bernard. In 2002, in agreement with the Afghan authorities, the Ministry of Foreign Affairs decided to reopen and restart the activities of DAFA in Afghanistan. DAFA's new mission is first of all to develop knowledge of Afghanistan's past, in the framework of French-Afghan archaeological operations. These operations consist of the continuation of the inventory of archaeological remains (prospecting, surveys, etc. ), as well as the conduct of archaeological excavations within the frame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bampur
Bampur ( and ) is a city in the Central District of Bampur County, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. History The old citadel of Bampur, on a hill about high north of the river, fell into ruins. A new fort called Kalah Nasseri, was built at Pahrah, which is known as Iranshahr, further east, in the 1880s. Fahraj, which in 1911 had a population of about 2,500, has become more important than Bampur. Fahraj, which is also known as Pahura (or Paharu or Puhra), is by some identified as the Poura where Alexander the Great halted on his march from the Indus Valley. It was Historically ruled by Rakshani Baluchs of Iran Under Their Ruler, Shah Mihrab Khan, had led our several campaigns against Persians laid waste into the lands, particularly Luristan Demographics Language and ethnicity The majority of the population are ethnic Baloch who speak the Balochi language. Population At the time of the 2006 National Cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim G
Jim or JIM may refer to: Names * Jim (given name), a given name * Jim, a diminutive form of the given name James * Jim, a short form of the given name Jimmy People and horses * Jim, the nickname of Yelkanum Seclamatan (died April 1911), Native American chief * Juan Ignacio Martínez (born 1964), Spanish footballer, commonly known as JIM * Jim (horse), milk wagon horse used to produce serum containing diphtheria antitoxin * Jim (Medal of Honor recipient) Media and publications * ''Jim'' (book), a book about Jim Brown written by James Toback * ''Jim'' (comics), a series by Jim Woodring * '' Jim!'', an album by rock and roll singer Jim Dale * ''Jim'' (album), by soul artist Jamie Lidell * Jim (''Huckleberry Finn''), a character in Mark Twain's novel * Jim (TV channel), in Finland * Jim (YRF Spy Universe), a fictional film character in the Indian YRF Spy Universe, portrayed by John Abraham * JIM (Flemish TV channel), a Flemish television channel * "Jim" (song), a 1941 son ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond Allchin
Frank Raymond Allchin, FBA (9 July 1923 – 4 June 2010) was a British archaeologist and Indologist. He and his wife, Bridget Allchin, formed one of the most influential British partnerships in the post-Independence study of South Asian archaeology. Producing a large body of scholarship ranging from archaeological excavations, ethnoarchaeology as well as epigraphy and linguistics, the Allchins made their work and that of others accessible through a series of sole, joint and edited publications. Seminal works include ''The Birth of Indian Civilisation'' (1968), which was later superseded by their books ''The Rise of Indian Civilisation in India and Pakistan'' (1982) and ''The Archaeology of Early Historic South Asia'' (1995). Background Raymond Allchin was born in Harrow, London on 9 July 1923, son of Frank Macdonald Allchin, a doctor, and Louise Maude. His brother was Donald Allchin, an Anglican priest and theologian. Raymond was educated at Westminster and enrolled at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |