Early 2000s recession on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The
The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The
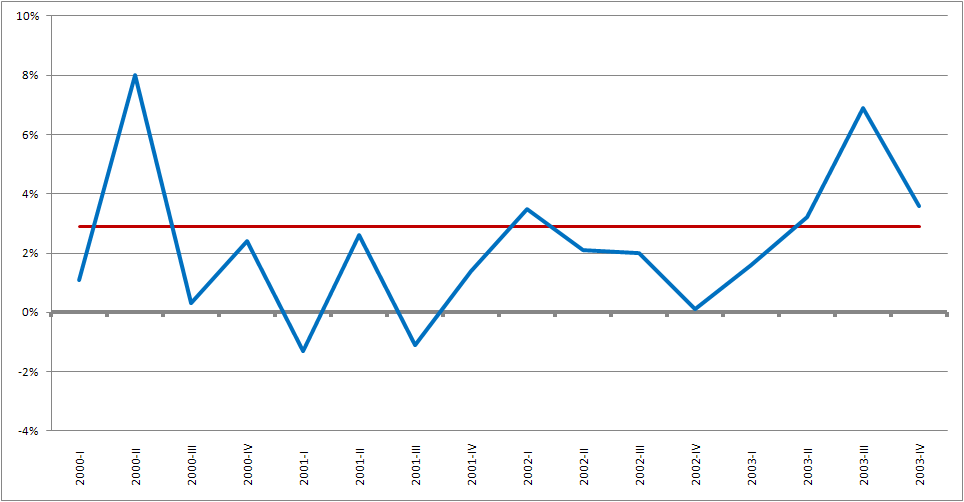 After the relatively mild 1990 recession ended in early 1991, the country hit a belated unemployment rate peak of 7.8% in mid-1992. Job growth was initially muted by large layoffs among defense related industries. However, payrolls accelerated in 1992 and experienced robust growth through 2000.
Predictions that the bubble would burst emerged during the
After the relatively mild 1990 recession ended in early 1991, the country hit a belated unemployment rate peak of 7.8% in mid-1992. Job growth was initially muted by large layoffs among defense related industries. However, payrolls accelerated in 1992 and experienced robust growth through 2000.
Predictions that the bubble would burst emerged during the
Economists Say Recession Started in 2000
''The Washington Post.'' In early 2004, NBER President Martin Feldstein said: However, in 2008, the NBER confirmed that the recession started in March 2001. From mid-1999 to 2001, the

 The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The
The early 2000s recession was a major decline in economic activity which mainly occurred in developed countries. The recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction that occurs when there is a period of broad decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be tr ...
affected the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
during 2000 and 2001 and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
from March to November 2001. The United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
avoided the recession, while Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, a nation that did not experience prosperity during the 1990s, began to recover from it. Japan's 1990s recession continued. A combination of the Dot Com Bubble collapse and the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
lengthed and worsened the recession.
This recession was predicted by economists because the boom of the 1990s, accompanied by both low inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
and low unemployment
Unemployment, according to the OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development), is the proportion of people above a specified age (usually 15) not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work du ...
, slowed in some parts of East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
during the 1997 Asian financial crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide eco ...
. The recession in industrialized countries was not as significant as either of the two previous worldwide recessions. Some economists in the United States object to characterizing it as a recession since there were no two consecutive quarters of negative growth.
United States
dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble (or dot-com boom) was a stock market bubble that ballooned during the late-1990s and peaked on Friday, March 10, 2000. This period of market growth coincided with the widespread adoption of the World Wide Web and the Interne ...
in the late 1990s. Predictions about a future burst increased following the October 27, 1997 mini-crash, in the wake of the 1997 Asian financial crisis
The 1997 Asian financial crisis gripped much of East Asia, East and Southeast Asia during the late 1990s. The crisis began in Thailand in July 1997 before spreading to several other countries with a ripple effect, raising fears of a worldwide eco ...
. This caused an uncertain economic climate during the first few months of 1998. However conditions improved, and the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
raised interest rates six times between June 1999 and May 2000 in an effort to cool the economy to achieve a soft landing. The burst of the stock market bubble occurred in the form of the NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list ...
crash in March 2000. Growth in gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the total market value of all the final goods and services produced and rendered in a specific time period by a country or countries. GDP is often used to measure the economic performanc ...
slowed considerably in the third quarter of 2000 to the lowest rate since a contraction in the first quarter of 1992.
According to the National Bureau of Economic Research
The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is an American private nonprofit research organization "committed to undertaking and disseminating unbiased economic research among public policymakers, business professionals, and the academic co ...
(NBER), which is the private, nonprofit, nonpartisan organization charged with determining economic recessions, the U.S. economy was in recession from March 2001 to November 2001, a period of eight months at the beginning of President George W. Bush's term of office. The NBER's Business Cycle Dating Committee determined that a peak in business activity occurred in the U.S. economy in March 2001. A peak marks the end of an expansion and the beginning of a recession. The determination of a peak date in March is thus a determination that the expansion that began in March 1991 ended in March 2001 and a recession began. The expansion lasted exactly 10 years, the longest in the NBER's chronology.
However, economic conditions did not satisfy the common shorthand definition of recession, which is "a fall of a country's real gross domestic product in two or more successive quarters", and has led to some confusion about the procedure for determining the starting and ending dates of a recession.
The NBER's Business Cycle Dating Committee (BCDC) uses monthly, rather than quarterly, indicators to determine peaks and troughs in business activity, as can be seen by noting that starting and ending dates are given by month and year, not quarters. However, controversy over the precise dates of the recession led to the characterization of the recession as the "Clinton Recession" by Republicans, if it could be traced to the final term of President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician and lawyer who was the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. A member of the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party, ...
. BCDC members suggested they would be open to revisiting the dates of the recession as newer and more definitive data became available.Henderson, Nell (January 22, 2004)Economists Say Recession Started in 2000
''The Washington Post.'' In early 2004, NBER President Martin Feldstein said: However, in 2008, the NBER confirmed that the recession started in March 2001. From mid-1999 to 2001, the
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of ...
, in a move to protect the economy from the overvalued stock market, made successive interest rate increases. Using the stock market as an unofficial benchmark, a recession would have begun in March 2000 when the NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market (; National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the U.S. by volume, and ranked second on the list ...
crashed following the collapse of the dot-com bubble. The Dow Jones Industrial Average
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), Dow Jones, or simply the Dow (), is a stock market index of 30 prominent companies listed on stock exchanges in the United States.
The DJIA is one of the oldest and most commonly followed equity indice ...
was relatively unscathed by the NASDAQ's crash until the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, after which the Dow Jones suffered its worst one-day loss and largest one-week losses in history up to that point. The market rebounded, only to crash once more in the final two quarters of 2002. In the final three quarters of 2003, the market finally rebounded permanently, agreeing with the unemployment statistics that a recession defined in this way would have lasted from 2001 through 2003.
The Labor Department estimates that a net 1.735 million jobs were shed in 2001, with an additional net 508,000 lost during 2002. 2003 saw a small gain of a mere 105,000 jobs. Unemployment rose from 4.2% in February 2001 to 5.5% in November 2001, but did not peak until June 2003 at 6.3%, after which it declined to 5% by mid-2005.
Canada
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
's economy is closely linked to that of the United States, and economic conditions south of the border tend to quickly make their way north. Canada's stock markets were especially hard hit by the collapse in high-tech stocks. For much of the 1990s the rapid rise of the TSX
The Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX; ) is a stock exchange located in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is the List of stock exchanges, 10th largest exchange in the world and the third largest in North America based on market capitalization. Based in th ...
had almost wholly been attributed to two stocks: Nortel
Nortel Networks Corporation (Nortel), formerly Northern Telecom Limited, was a Canadian Multinational corporation, multinational telecommunications and data networking equipment manufacturer headquartered in Ottawa, Ontario. It was founded in ...
and BCE. Both companies were hard hit by the downturn, especially Nortel, which was forced to lay off much of its workforce. The September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
also hurt the Canadian stock markets and were especially devastating to the already troubled airline sector.
However, in the wider economy, Canada was surprisingly unhurt by these events. While growth slowed, the economy never actually entered a recession. This was the first time that Canada had avoided following the United States into an economic downturn. The rate of job creation in Canada continued at the rapid pace of the 1990s. A number of explanations have been advanced to explain this. Canada was not as directly affected by 9/11 and the subsequent wars, and the downward pressure of these events was more muted. Canada's fiscal management during the period has been praised as the federal government continued to bring in large surpluses throughout this period, in sharp contrast to the United States. Unlike the United States no major tax cuts or major new expenditures were introduced. However, during this time, Canada did pursue an expansionary monetary policy in an effort to reduce the effects of a possible recession. Many provincial governments suffered greater problems with a number of them returning to deficits, which was blamed on the fiscal imbalance. 2003 saw elections in six Canadian provinces and in only one did the governing party not lose seats.
Russia
The Soviet Union's last year of economic growth was 1989, and throughout the 1990s, recession ensued in the Former Soviet Republics. In May 1998, following the 1997 crash of the East Asian economy, things began to get even worse in Russia. In August 1998, the value of the ruble fell 34% and people clamored to get their money out of banks (see1998 Russian financial crisis
The Russian financial crisis (also called the ruble crisis or the Russian flu) began in Russia on 17 August 1998. It resulted in the Russian government and the Russian Central Bank devaluing the Russian rouble, ruble and sovereign default, defau ...
). The government acted by dragging its feet on privatization programs. Russians responded to this situation with approval by electing the more pro- dirigist and less liberal Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who has served as President of Russia since 2012, having previously served from 2000 to 2008. Putin also served as Prime Minister of Ru ...
as President in 2000. Putin proceeded to reassert the role of the federal government, and gave it power it had not seen since the Soviet era. State-run businesses were used to out-compete some of the more wealthy rivals of Putin. Putin's policies were popular with the Russian people, gaining him re-election in 2004. At the same time, the export-oriented Russian economy enjoyed considerable influx of foreign currency thanks to rising worldwide oil prices (from $15 per barrel in early 1999 to an average of $30 per barrel during Putin's first term). The early 2000s recession was avoided in Russia due to rebound in exports and, to some degree, a return to dirigisme
Dirigisme or dirigism () is an economic doctrine in which the state plays a strong directive (policies) role, contrary to a merely regulatory or non-interventionist role, over a market economy. As an economic doctrine, dirigisme is the opposite ...
.
Japan
Japan's recession, which started in the early 1990s, continued into the 2000s, withdeflation
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% and becomes negative. While inflation reduces the value of currency over time, deflation increases i ...
being the main problem. Deflation began plaguing Japan in the fiscal year ending 1999, and by 2005 the yen had 103% of its 2000 buying power. The Bank of Japan attempted to cultivate inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the average price of goods and services in terms of money. This increase is measured using a price index, typically a consumer price index (CPI). When the general price level rises, each unit of curre ...
with high liquidity
Liquidity is a concept in economics involving the convertibility of assets and obligations. It can include:
* Market liquidity
In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is a market's feature whereby an individual or firm can quic ...
and a nominal 0% interest rate
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, ...
on loans. Other aspects of the Japanese economy were good during the early 2000s; unemployment remained relatively low, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
became somewhat dependent on the Japanese exports. The bear market
A market trend is a perceived tendency of the financial markets to move in a particular direction over time. Analysts classify these trends as ''secular'' for long time-frames, ''primary'' for medium time-frames, and ''secondary'' for short time ...
, however, continued in Japan, despite the best efforts of the Bank.
European Union
Transition left the economy of the European Union in a cautiously optimistic state during the early 2000s. The most difficult years were 2000–2001, precipitating the worst years of the American recession. The European Union introduced a new currency on January 1, 1999. Theeuro
The euro (currency symbol, symbol: euro sign, €; ISO 4217, currency code: EUR) is the official currency of 20 of the Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union. This group of states is officially known as the ...
, which was met with much anticipation, had its value immediately plummet, and it continued to be a weak currency throughout 2000 and 2001. Inflation struck the Eurozone
The euro area, commonly called the eurozone (EZ), is a Monetary union, currency union of 20 Member state of the European Union, member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (Euro sign, €) as their primary currency ...
for a few months in summer 2001 but the economy deflated within months. In 2002, the value of the euro began to rapidly rise (reaching parity with the US dollar on July 15, 2002). This hurt business for companies based in Europe, as the profits made abroad (especially in the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
) had an unfavorable exchange rate.
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
both entered recession towards the end of 2001, but in May 2002 both countries declared that their recessions had ended after a mere six months each. Both economies suffered from global tech crash with the ruling German party introducing the then unpopular austerity, tax cuts and labor reforms nicknamed Hartz concept
The Hartz concept (), also known as Hartz reforms or the Hartz plan, is a set of recommendations submitted by a committee on reforms to the Germany, German labour market in 2002. Named after the head of the committee, Peter Hartz, these recommenda ...
to boost the German economy in wake of an economic slump that would persist until the mid-2000s with unemployment peaking in early 2005 of 12.7%. However, some European Union countries – including the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
– managed to delay sliding into recession until the late 2000s.
References
Further reading
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Early 2000s Recession 20th century in economic history 21st century in economic history 2000 in economic history 2001 in economic history Recessions in the United States Presidency of George W. Bush 2001 in the United States