Doric columns on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Doric order is one of the three orders of

Antike Polychromie 1.jpg, Original Doric polychromy
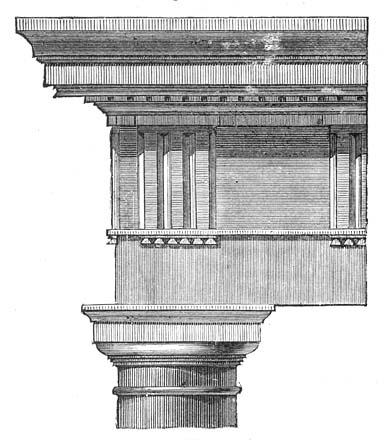
File:Doric-order-labeled.jpg, Upper parts, labelled
File:Schema Saeulenordnungen (cropped).jpg, Three Greek Doric columns
File:Fotothek df tg 0003893 Architektur ^ Säule ^ Ordnung.jpg, The Five Orders, originally illustrated by Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola, 1640
File:ARCHITECTURE ORDERS Greeks Etruscan Roman (Doric Ionic Corinthian Tuscan Composite) by Paolo Villa ENG edition.pdf, Compared of the Doric, Tuscan, Ionic, Corinthian and Composite orders
 Before
Before
File:Hatshepsut temple12.JPG, Possible inspiration for the Doric order:
Alexander Tzonis website
google books
* Watkin, David, ''A History of Western Architecture'', 1986, Barrie & Jenkins, * Yarwood, Doreen, ''The Architecture of Europe'', 1987 (first edn. 1974), Spring Books,
Classical orders and elements
{{DEFAULTSORT:Doric Order Orders of columns Ancient Greek architecture Order
ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of the columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above.
The Greek Doric column was fluted, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Doric temples. In stone they are purely ornamental.
The relatively uncommon Roman and Renaissance Doric retained these, and often introduced thin layers of moulding or further ornament, as well as often using plain columns. More often they used versions of the Tuscan order, elaborated for nationalistic reasons by Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( ) was a period in History of Italy, Italian history between the 14th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Western Europe and marked t ...
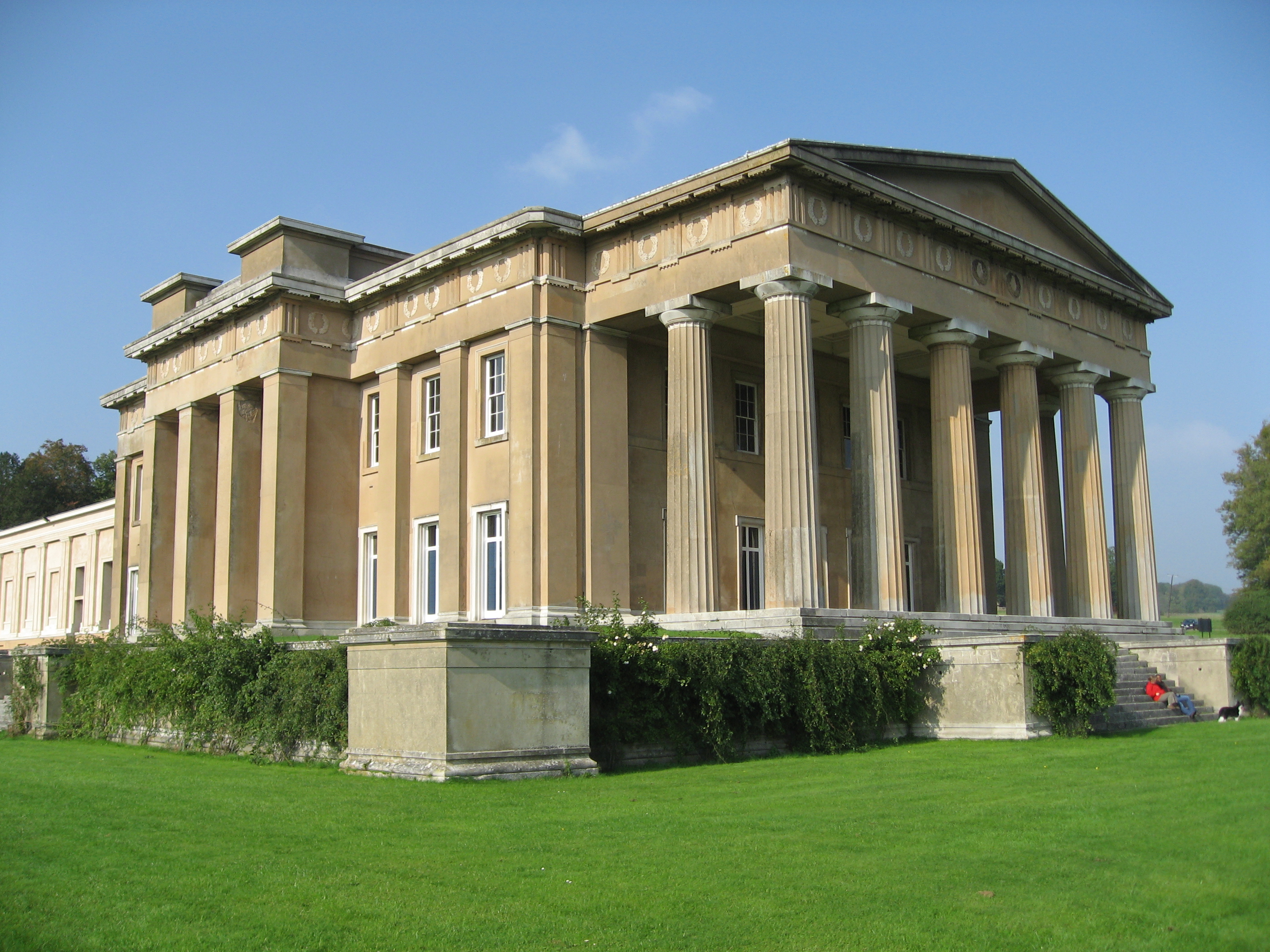
writers, which is in effect a simplified Doric, with un-fluted columns and a simpler entablature with no triglyphs or guttae. The Doric order was much used in Greek Revival architecture
Greek Revival architecture is a architectural style, style that began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe, the United States, and Canada, ...
from the 18th century onwards; often earlier Greek versions were used, with wider columns and no bases to them.
The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
associates the Doric with masculine proportions (the Ionic representing the feminine). It is also normally the cheapest of the orders to use. When the three orders are superposed, it is usual for the Doric to be at the bottom, with the Ionic and then the Corinthian above, and the Doric, as "strongest", is often used on the ground floor below another order in the storey above.
History
Greek
In their original Greek version, Doric columns stood directly on the flat pavement (the ''stylobate'') of a temple without a base. With a height only four to eight times their diameter, the columns were the most squat of all the classical orders; their vertical shafts were fluted with 20 parallel concave grooves, each rising to a sharp edge called an arris. They were topped by a smooth capital that flared from the column to meet a squareabacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
at the intersection with the horizontal beam ( architrave) that they carried.
The Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
is in the Doric order, and in antiquity and subsequently has been recognized as the most perfect example of the evolved order. It was most popular in the Archaic Period (750–480 BC) in mainland Greece, and also found in Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
(southern Italy), as in the three temples at Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
. These are in Archaic Doric, where the capitals spread wide from the column compared to later Classical forms, as exemplified in the Parthenon.
Pronounced features of both Greek and Roman versions of the Doric order are the alternating triglyphs and metopes. The triglyphs are decoratively grooved with two vertical grooves ("tri-glyph") and represent the original wooden end-beams, which rest on the plain architrave that occupies the lower half of the entablature. Under each triglyph are peglike "stagons" or "guttae" (literally: drops) that appear as if they were hammered in from below to stabilize the post-and-beam ( trabeated) construction. They also served to "organize" rainwater runoff from above. The spaces between the triglyphs are the "metopes". They may be left plain, or they may be carved in low relief.

Spacing the triglyphs
The spacing of the triglyphs caused problems which took some time to resolve. A triglyph is centered above every column, with another (or sometimes two) between columns, though the Greeks felt that the corner triglyph should form the corner of the entablature, creating an inharmonious mismatch with the supporting column. The architecture followed rules of harmony. Since the original design probably came from wooden temples and the triglyphs were real heads of wooden beams, every column had to bear a beam which lay across the centre of the column. Triglyphs were arranged regularly; the last triglyph was centred upon the last column (''illustration, right: I.''). This was regarded as the ideal solution which had to be reached. Changing to stone cubes instead of wooden beams required full support of the architrave load at the last column. At the first temples the final triglyph was moved (''illustration, right: II.''), still terminating the sequence, but leaving a gap disturbing the regular order. Even worse, the last triglyph was not centered with the corresponding column. That "archaic" manner was not regarded as a harmonious design. The resulting problem is called the doric corner conflict. Another approach was to apply a broader corner triglyph (''III.'') but was not really satisfying. Because the metopes are somewhat flexible in their proportions, the modular space between columns ("intercolumniation") can be adjusted by the architect. Often the last two columns were set slightly closer together (''corner contraction''), to give a subtle visual strengthening to the corners. That is called the "classic" solution of the corner conflict (''IV.''). Triglyphs could be arranged in a harmonic manner again, and the corner was terminated with a triglyph, though the final triglyph and column were often not centered. Roman aesthetics did not demand that a triglyph form the corner, and filled it with a half (''demi''-) metope, allowing triglyphs centered over columns (''illustration, right, V.'').Temples
There are many theories as to the origins of the Doric order in temples. The term Doric is believed to have originated from the Greek-speaking Dorian tribes. One belief is that the Doric order is the result of early wood prototypes of previous temples. With no hard proof and the sudden appearance of stone temples from one period after the other, this becomes mostly speculation. Another belief is that the Doric was inspired by the architecture ofEgypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
. With the Greeks being present in Ancient Egypt as soon the 7th-century BC, it is possible that Greek traders were inspired by the structures they saw in what they would consider foreign land. Finally, another theory states that the inspiration for the Doric came from Mycenae. At the ruins of this civilization lies architecture very similar to the Doric order. It is also in Greece, which would make it very accessible.
Some of the earliest examples of the Doric order come from the 7th-century BC. These examples include the Temple of Apollo at Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
and the Temple of Zeus at Nemea. Other examples of the Doric order include the three 6th-century BC temples at Paestum in southern Italy, a region called Magna Graecia, which was settled by Greek colonists. Compared to later versions, the columns are much more massive, with a strong entasis or swelling, and wider capitals.
The Temple of the Delians is a " peripteral" Doric order temple, the largest of three dedicated to Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
on the island of Delos. It was begun in 478 BC and never completely finished. During their period of independence from Athens, the Delians reassigned the temple to the island of Poros. It is "hexastyle", with six columns across the pedimented end and thirteen along each long face. All the columns are centered under a triglyph in the frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
, except for the corner columns. The plain, unfluted shafts on the columns stand directly on the platform (the ''stylobate''), without bases. The recessed "necking" in the nature of fluting at the top of the shafts and the wide cushionlike echinus may be interpreted as slightly self-conscious archaising features, for Delos is Apollo's ancient birthplace. However, the similar fluting at the base of the shafts might indicate an intention for the plain shafts to be capable of wrapping in drapery.
A classic statement of the Greek Doric order is the Temple of Hephaestus in Athens, built about 447 BC. The contemporary Parthenon, the largest temple in classical Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, is also in the Doric order, although the sculptural enrichment is more familiar in the Ionic order: the Greeks were never as doctrinaire in the use of the Classical vocabulary as Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
theorists or Neoclassical architects. The detail, part of the basic vocabulary of trained architects from the later 18th century onwards, shows how the width of the metopes was flexible: here they bear the famous sculptures including the battle of Lapiths and Centaurs.

Roman
In the Roman Doric version, the height of the entablature has been reduced. The endmost triglyph is centered over the column rather than occupying the corner of the architrave. The columns are slightly less robust in their proportions. Below their caps, an astragal molding encircles the column like a ring. Crown moldings soften transitions between frieze and cornice and emphasize the upper edge of theabacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
, which is the upper part of the capital.
Roman Doric columns also have moldings at their bases and stand on low square pads or are even raised on plinths. In the Roman Doric mode, columns are not usually fluted; indeed, fluting is rare. Since the Romans did not insist on a triglyph covered corner, now both columns and triglyphs could be arranged equidistantly again and centered together. The architrave corner needed to be left "blank", which is sometimes referred to as a half, or ''demi-'', metope (''illustration, V., in Spacing the Columns above'').
The Roman architect Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
, following contemporary practice, outlined in his treatise the procedure for laying out constructions based on a module, which he took to be one half a column's diameter, taken at the base. An illustration of Andrea Palladio's Doric order, as it was laid out, with modules identified, by Isaac Ware, in ''The Four Books of Palladio's Architecture'' (London, 1738) is illustrated at Vitruvian module.
According to Vitruvius, the height of Doric columns is six or seven times the diameter at the base. This gives the Doric columns a shorter, thicker look than Ionic columns, which have 8:1 proportions. It is suggested that these proportions give the Doric columns a masculine appearance, whereas the more slender Ionic columns appear to represent a more feminine look. This sense of masculinity and femininity was often used to determine which type of column would be used for a particular structure.
Later periods reviving classical architecture
Classical architecture typically refers to architecture consciously derived from the principles of Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or more specifically, from ''De archit ...
used the Roman Doric until Neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of t ...
arrived in the later 18th century. This followed the first good illustrations and measured descriptions of Greek Doric buildings. The most influential, and perhaps the earliest, use of the Doric in Renaissance architecture
Renaissance architecture is the European architecture of the period between the early 15th and early 16th centuries in different regions, demonstrating a conscious revival and development of certain elements of Ancient Greece, ancient Greek and ...
was in the circular ''Tempietto'' by Donato Bramante (1502 or later), in the courtyard of San Pietro in Montorio
San Pietro in Montorio (English: "Saint Peter on the Golden Mountain") is a church in Rome, Italy, which includes in its courtyard the ''Tempietto'', a small commemorative ''martyrium'' ('martyry') built by Donato Bramante.
History
The Church o ...
, Rome.
Graphics of ancient forms
Modern
 Before
Before Greek Revival architecture
Greek Revival architecture is a architectural style, style that began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe, the United States, and Canada, ...
grew, initially in England, in the 18th century, the Greek or elaborated Roman Doric order had not been very widely used, though "Tuscan" types of round capitals were always popular, especially in less formal buildings. It was sometimes used in military contexts, for example the Royal Hospital Chelsea
The Royal Hospital Chelsea is an Old soldiers' home, Old Soldiers' retirement home and nursing home for some 300 veterans of the British Army. Founded as an almshouse — the ancient sense of the word "hospital" — by King Charles II of Eng ...
(1682 onwards, by Christopher Wren
Sir Christopher Wren FRS (; – ) was an English architect, astronomer, mathematician and physicist who was one of the most highly acclaimed architects in the history of England. Known for his work in the English Baroque style, he was ac ...
). The first engraved illustrations of the Greek Doric order dated to the mid-18th century. Its appearance in the new phase of Classicism
Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. In its purest form, classicism is an aesthe ...
brought with it new connotations of high-minded primitive simplicity, seriousness of purpose, noble sobriety.
In Germany it suggested a contrast with the French, and in the United States republican virtues. In a customs house, Greek Doric suggested incorruptibility; in a Protestant church a Greek Doric porch promised a return to an untainted early church; it was equally appropriate for a library, a bank or a trustworthy public utility. The revived Doric did not return to Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
until 1789, when a French architect researching the ancient Greek temples designed an entrance to the Botanical Gardens in Palermo
Palermo ( ; ; , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan province. The ...
.
Examples
;Ancient Greek, Archaic * Temple of Artemis, Corfu, the earliest known stone Doric temple * Temple of Hera, Olympia * Delphi, temple of Apollo *The three temples atPaestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
, Italy
* Valle dei Templi, Agrigento, Temple of Juno, Agrigento and others
* Temple of Aphaea
;Ancient Greek, Classical
* Temple of Zeus, Olympia
* Temple of Hephaestus
* Bassae, Temple of Apollo
*Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
, Athens
* Sounion, Temple of Poseidon
;Renaissance and Baroque
*The ''Tempietto'' by Donato Bramante, in the courtyard of San Pietro in Montorio
San Pietro in Montorio (English: "Saint Peter on the Golden Mountain") is a church in Rome, Italy, which includes in its courtyard the ''Tempietto'', a small commemorative ''martyrium'' ('martyry') built by Donato Bramante.
History
The Church o ...
, Rome
* Palace of Charles V, Granada
Granada ( ; ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada (Spain), Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence ...
, 1527, circular arcade in the courtyard, under Ionic in the upper storey
* Basilica Palladiana, in Vicenza, Andrea Palladio, 1546 on, arcade under Ionic above
* Valladolid Cathedral, Juan de Herrera, begun 1589
;Neoclassical and Greek Revival
*Brandenburg Gate
The Brandenburg Gate ( ) is an 18th-century Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical monument in Berlin. One of the best-known landmarks of Germany, it was erected on the site of a former city gate that marked the start of the road from Berlin t ...
, Berlin, 1788
* The Grange, Northington, 1804
* Lord Hill's Column, Shrewsbury, England, 1814, high
* Neue Wache, Berlin, 1816
* Royal High School, Edinburgh, completed 1829
* Walhalla, Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
, Bavaria, 1842
* Propylaea, Munich, 1854
;United States
*Second Bank of the United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Second Report on Public Credit, Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January ...
, Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, 1824
* Naval Medical Center Portsmouth, 1827, pedimented temple front with ten columns
* Perry's Victory and International Peace Memorial in Put-in-Bay, Ohio, is the world's tallest and most massive Doric column at .
* Harding Tomb in Marion, Ohio, is a circular Greek temple design with Doric columns.
Gallery
Ancient Egyptian
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
columns of the shrine of Anubis at the Temple of Hatshepsut, Deir el-Bahari, Egypt, 1470 BC
Jacques Ignace Hittorff - Temple T at Selinunte (Sicily), reconstructed elevation of the main facade - Google Art Project.jpg, 19th century illustration of the main façade of the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
Temple T at Selinunte, Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, Italy, showing how all the ancient Doric buildings were polychromatic
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery, or sculpture in multiple colors.
When looking at artworks and a ...
, by Jacques Ignace Hittorff, before 1859
Illustration of the peristyle from the home of a rich Athenian woman, from Wonders - Images of the Ancient World, 1907.jpg, Illustration of a peristyle with Doric columns the home of a rich Athenian woman, showing the polychromy Doric columns had in antiquity, from ''Wonders - Images of the Ancient World'', 1907
Korinth BW 2017-10-10 10-55-47.jpg, Ancient Greek columns of the Temple of Apollo, Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
, Greece, 540 BC
File:"Als Mittelpunkt der Welt" galt Delphi für die Menschen der Antike. 08.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns and entablature of the Athenian Treasury, Delphi
Delphi (; ), in legend previously called Pytho (Πυθώ), was an ancient sacred precinct and the seat of Pythia, the major oracle who was consulted about important decisions throughout the ancient Classical antiquity, classical world. The A ...
, Greece, 525 BC
File:Order of the columns of the portico Fig 1 Profile of the necking of the columns Fig 2 Plan of the shaf below the capital - Wilkins William - 1807.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric capital of the Temple of Hera I, Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
, Italy, with a band of compressed leafs just under the echine, 425 BC
File:Paestum, Italy (15036271487).jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns of the Temple of Hera I, with their usually large entasis on the shafts
File:The plan and elevation of two Doric columns of the Temple of Apollo at Delos - Stuart James & Revett Nicholas - 1794.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns of the Temple of the Delians, Delos, Greece, fluted only at the top and bottom of the shaft, 5th century BC
File:20190507 169 bassae.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric capitals in the Temple of Apollo at Bassae, Bassae, Greece, 429-400 BC
File:Allard Pierson Museum Cult statue in temple amphora 7770.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric temple depicted stylized on an amphora shard, 400-385 BC, ceramic, Allard Pierson Museum, Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , ; ; ) is the capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, largest city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. It has a population of 933,680 in June 2024 within the city proper, 1,457,018 in the City Re ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
File:Φθινοπωρινή ιστορια.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns of the Tholos of Delphi, Greece, 375 BC
File:Temple of Nemean Zeus, 330 BC, 201757.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns of the Temple of Zeus, Nemea
Nemea (; ; ) is an ancient site in the northeastern part of the Peloponnese, in Greece. Formerly part of the territory of Cleonae (Argolis), Cleonae in ancient Argolis, it is today situated in the regional units of Greece, regional unit of Corin ...
, Greece, 330 BC
File:Agios Athanasios, Ancient Macedonian Tomb - I (37120832445).jpg, Ancient Greek Doric pilasters and entablature of the Tomb III, Agios Athanasios, Greece, 325-300 BC
Krisseos (Judgement) Makedonian Tomb.jpg, Ancient Greek Doric columns of the Great Tomb of Lefkadia, Mieza, Greece, 300 BC
File:Sarcofago di scipione barbato, a forma di altare con volute ioniche, in marmo peperino, 280 ac., dal sepolcro degli scipioni sull'appia antica.jpg, Roman Doric frieze on the Sarcophagus of Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus, Vatican Museums, Rome, 270 BC
file:Piranesi-4038.jpg, Roman Doric order of the Theatre of Marcellus, Rome, 1st century BC
Tempietto del Bramante Vorderseite.jpg, Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
Doric columns and entablature of The Tempietto, San Pietro in Montorio
San Pietro in Montorio (English: "Saint Peter on the Golden Mountain") is a church in Rome, Italy, which includes in its courtyard the ''Tempietto'', a small commemorative ''martyrium'' ('martyry') built by Donato Bramante.
History
The Church o ...
, Rome, by Donato Bramante, 1502
Altar enframement MET DP271811.jpg, Renaissance Doric altar enframement, probably from Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence.
Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its in ...
, Italy, 1530–1550, marble, Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of larg ...
, New York City
Chateau d'anet 004.jpg, Renaissance Doric columns and entablature of the entrance gateway of the Château d'Anet, near Dreux, France, by Philibert de l'Orme, 1547–1552
Dorique_2_-_Serlio_-_en.jpg, Renaissance Doric capital at Hôtel d'Assézat designed according to a model published by Sebastiano Serlio, France, 1555–1556
Château du Pailly -3 (cropped corbels).jpg, Renaissance combination of Doric pilaster
In architecture, a pilaster is both a load-bearing section of thickened wall or column integrated into a wall, and a purely decorative element in classical architecture which gives the appearance of a supporting column and articulates an ext ...
s and corbels of the Château du Pailly, Le Pailly, France, 1563–1573
File:Maisons-Laffitte Chateau de Maisons 2011 19.jpg, Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
columns and entablature of the Château de Maisons
The Château de Maisons (now Château de Maisons-Laffitte ), designed by François Mansart from 1630 to 1651, is a prime example of French Baroque architecture and a reference point in the history of French architecture. The château is located in ...
, France, by François Mansart, 1630–1651
Hôtel de Castries (Montpeller) - Porta.jpg, Baroque Doric pilasters and entablature on the facade of the Hôtel de Castries (Rue Saint-Guilhem no. 31), Montpellier
Montpellier (; ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of France, department of ...
, France, by Simon Levesville, 1647
File:ASC - sala lettura camino O3250026.JPG, Chinoiserie reinterpretation of the Doric frieze on a fireplace in the oval room inside the Oratorio dei Filippini, Rome, by Francesco Borromini
Francesco Borromini (, ), byname of Francesco Castelli (; 25 September 1599 – 2 August 1667), was an Italian architect born in the modern Switzerland, Swiss canton of Ticino
, 1637–1650
Basílica, Ottobeuren, Alemania, 2019-06-21, DD 103.jpg, Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
Doric columns and pilasters on the facade of the abbey church of Ottobeuren
Ottobeuren ( Swabian: ''Ottobeire'', Medieval Latin: ''Ottobura'') is a market town and municipality in Bavaria, Germany, located 11 km southeast of Memmingen near the A7. It is famous for Ottobeuren Abbey, situated next to the Basilica. Th ...
, Germany, by Johann Michael Fischer, 1748–1754
The Casino at Marino - panoramio.jpg, Neoclassical columns and entablature of the Casino
A casino is a facility for gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shops, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos also host live entertainment, such as stand-up comedy, conce ...
at the Marino House, near Dublin
Dublin is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. Situated on Dublin Bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, and is bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, pa ...
, Ireland, by William Chambers, 1758–1776
File:Saloon dome frieze, 1 of 4 - Stowe House - Buckinghamshire, England - DSC07187.jpg, Neoclassical Doric frieze with circular motifs in the metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze
, a decorative band above an architrave.
In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and ...
s that alternate with mascarons, in the Marble Saloon of the Stowe House, Stowe, Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire (, abbreviated ''Bucks'') is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-east, Hertfordshir ...
, UK, probably by Vincenzo Valdrè, 1775–1788
File:Kepler Denkmal (Regensburg).JPG, Greek Revival columns of the Johannes Kepler Monuments, Regensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
, Germany, inspired by those of the Temple of the Delians in Delos, designed by Emanuel Herigoyen and sculpted by Philipp Jakob Scheffauer and Johann Heinrich Dannecker, 1808
150214 Neue Wache Berlin.jpg, Greek Revival columns of the Neue Wache, Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
, where the triglyphs were replaced by Nike figures, by Karl Friedrich Schinkel and Salomo Sachs, 1816
Paris Bibliothèque Sainte-Geneviève 20161111 16h31.jpg, Neoclassical Doric pilasters with arch
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but stru ...
es on the entrance front façade of the Sainte-Geneviève Library, Paris, designed by Henri Labrouste in 1838–1839, built in 1834–1850
Casimir Perier’s grave, Pere Lachaise, Paris.JPG, Neoclassical Doric pilasters on the Grave of Casimir Pierre Perier, Père-Lachaise Cemetery, Paris, designed by Achille Leclère, and sculpted by François-Joseph Bosio and Jean-Pierre Cortot, 1837
Pair of doric pilasters in the avant-foyer of the Opéra Garnier.jpg, Beaux Arts Doric pilasters in the avant-foyer of the Palais Garnier
The (, Garnier Palace), also known as (, Garnier Opera), is a historic 1,979-seatBeauvert 1996, p. 102. opera house at the Place de l'Opéra in the 9th arrondissement of Paris, France. It was built for the Paris Opera from 1861 to 1875 at the ...
, Paris, by Charles Garnier, 1861–1874
File:Façaden und Details moderner Bauten (1886) - T008.jpg, Renaissance Revival Doric pilasters with bossages on them, of the Deutsche Bank ( Mauerstraße no. 29), Berlin, by W. Martens, 1882
92 rue du Ranelagh, Paris 16e 3.jpg, Eclectic façade with triglyphs and metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze
, a decorative band above an architrave.
In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and ...
s of the Suriname Embassy ( Rue du Ranelagh no. 94), Paris, unknown architect, 1885
STUCK, FRANZ-VON - SüNDE - CC-BY-SA BSTGS 7925.jpg, Vienna Secession Doric columns on the frame of ''Die Sünde'', painted by Franz Stuck, 1893, gilt wood and oil on canvas
File:W 44 St Sep 2021 159.jpg, Greek Revival columns at the entrance of the House of the New York City Bar Association, New York City, inspired by the one from the Temple of Hera I at Paestum, but decorated with meanders on the abacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
es and bands of compressed leafs that are a little more complex and bases you would never see on Ancient Greek Doric columns (not visible in this photo), by Cyrus Eidlitz, 1895
File:Musee d'Orsay, North view 140402 1.jpg, Beaux Arts Doric pilasters on the façade of the Gare d'Orsay, Paris, designed by Victor Laloux in 1896–1897, and built in 1898–1900
File:Leopold bauer per jw. müller, vienna 1900-02, credenza.jpg, Vienna Secession Doric columns on a dresser, by Leopold Bauer, 1900–1902, various types of wood, in a temporary exhibition called Il Liberty e la rivoluzione europea delle arti at the Museum of Decorative Arts in Prague
Park Güell - panoramio (11).jpg, Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
Doric columns and entablature of The Greek Theatre in the Park Güell, Barcelona
Barcelona ( ; ; ) is a city on the northeastern coast of Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second-most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Spain, by Antoni Gaudí
Antoni Gaudí i Cornet ( , ; ; 25 June 1852 – 10 June 1926) was a Catalans, Catalan architect and designer from Spain, widely known as the greatest exponent of Catalan ''Modernisme''. Gaudí's works have a style, with most located in Barc ...
, 1900–1914
Pont Bir Hakeim Paris 21.jpg, Beaux Arts Doric pilasters of the Pont de Bir-Hakeim, Paris, by Jean Camille Formigé and Louis Biette, 1903–1905
File:Avenue du Président-Wilson 18.jpg, Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
reinterpretation of the Doric pilasters on the facade of Avenue du Président-Wilson no. 18, Paris, by Henri Tauzin, 1913
File:Westmorland House (4870178224).jpg, Art Deco reinterpretation of the Doric columns, with no flutings and with little or no entasis, on the Westmorland House ( Regent Street no. 117–131), London, by Burnet & Tait, 1920-1925
Gustave Simon caveau.jpg, Art Deco reinterpretation of the Doric columns, with no capitals or bases, on the Gustave Simon Grave, Préville Cemetery, Nancy, France, unknown architect, after 1926
Grave of the Vasile I. Prodanof Family in the Bellu Cemetery in Bucharest, Romania (01).jpg, Neoclassical and Art Deco Doric columns of the Vasile I. Prodanof family tomb, Bellu Cemetery, Bucharest, unknown architect,
File:Stuttgart - Neue Staatsgalerie (35736940202) (cropped columns).jpg, Postmodern Doric columns of the Neue Staatsgalerie, Stuttgart
Stuttgart (; ; Swabian German, Swabian: ; Alemannic German, Alemannic: ; Italian language, Italian: ; ) is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Baden-Württemberg by population, largest city of the States of Germany, German state of ...
, Germany, by James Stirling, 1984
File:Chicago, Illinois, U.S. (2023) - 166.jpg, Postmodern reinterpretation of the Doric columns in the Harold Washington Library, Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
, by Hammond, Beeby & Babka, 1991
File:Cmglee Judge Business School rear.jpg, Postmodern Doric columns of the Judge Business School, University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209, the University of Cambridge is the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, wo ...
, England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, by John Outram, 1995
File:Duncanhall.JPG, Postmodern Doric pilasters and columns of the Duncan Hall, Rice University
William Marsh Rice University, commonly referred to as Rice University, is a Private university, private research university in Houston, Houston, Texas, United States. Established in 1912, the university spans 300 acres.
Rice University comp ...
, US, by John Outram, 1996
Entrance of Queen's Gallery, Buckingham Palace (cropped).jpg, New Classical Doric columns of the Queen's Gallery, Buckingham Palace
Buckingham Palace () is a royal official residence, residence in London, and the administrative headquarters of the monarch of the United Kingdom. Located in the City of Westminster, the palace is often at the centre of state occasions and r ...
, London, inspired by the one from the Temple of Hera I at Paestum, by John Simpson, 2000-2002
File:US Federal Building and Courthouse in Tuscaloosa, Alabama..jpg, New Classical Doric columns of the Federal Building and Courthouse, Tuscaloosa, Alabama
Alabama ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South, Deep Southern regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gu ...
, US, inspired by those of the Temple of Zeus in Nemea, by the Chicago architectural firm Hammond Beeby Rupert Ainge, 2011
See also
* GeisonNotes
References
* Summerson, John, '' The Classical Language of Architecture'', 1980 edition, Thames and Hudson ''World of Art'' series, *James Stevens Curl, ''Classical Architecture: An Introduction to Its Vocabulary and Essentials, with a Select Glossary of Terms'' *Georges Gromort, ''The Elements of Classical Architecture'' * * Lawrence, A. W., ''Greek Architecture'', 1957, Penguin, Pelican history of art *Alexander Tzonis, ''Classical Architecture: The Poetics of Order''Alexander Tzonis website
google books
* Watkin, David, ''A History of Western Architecture'', 1986, Barrie & Jenkins, * Yarwood, Doreen, ''The Architecture of Europe'', 1987 (first edn. 1974), Spring Books,
External links
Classical orders and elements
{{DEFAULTSORT:Doric Order Orders of columns Ancient Greek architecture Order