Dipnoi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lungfish are freshwater
 The
The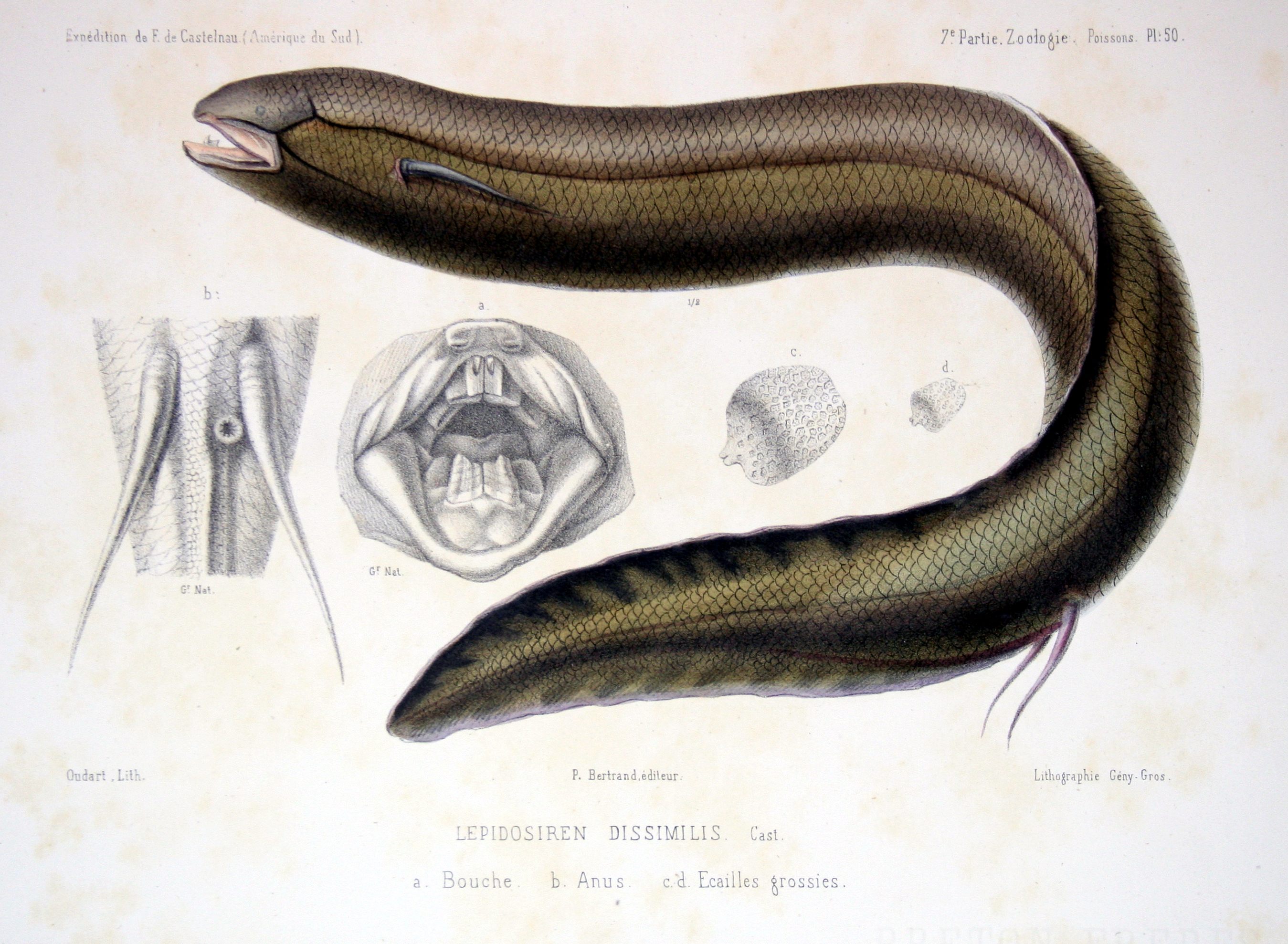  The
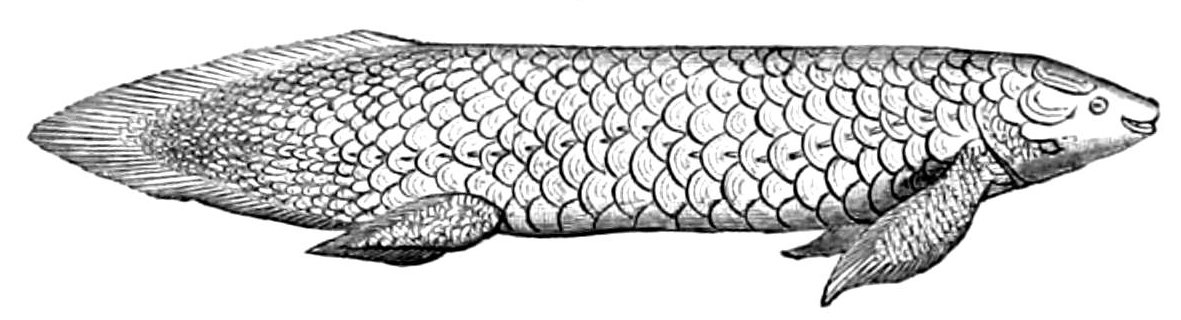
The  The marbled lungfish, ''Protopterus aethiopicus'', is found in Africa. The marbled lungfish is smooth and elongated with deeply embedded
The marbled lungfish, ''Protopterus aethiopicus'', is found in Africa. The marbled lungfish is smooth and elongated with deeply embedded
/ref> The pectoral and pelvic fins are also very long and thin, almost spaghetti-like. The newly hatched young have branched external gills much like those of newts. After 2 to 3 months the young transform (called The gilled lungfish, ''Protopterus amphibius'' is a species of lungfish found in
The gilled lungfish, ''Protopterus amphibius'' is a species of lungfish found in  The west African lungfish, ''Protopterus annectens'', is a species of lungfish found in West Africa. It has a prominent
The west African lungfish, ''Protopterus annectens'', is a species of lungfish found in West Africa. It has a prominent  The spotted lungfish, ''Protopterus dolloi'', is a species of lungfish found in Africa. Specifically, it is found in the Kouilou-Niari Basin of the
The spotted lungfish, ''Protopterus dolloi'', is a species of lungfish found in Africa. Specifically, it is found in the Kouilou-Niari Basin of the
/ref> ''Protopterus dolloi'' can aestivate on land by surrounding itself in a layer of dried
 The relationship of lungfishes to the rest of the
The relationship of lungfishes to the rest of the
vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
belonging to the class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class (biology), class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. The ...
, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s (which includes living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals). The mouths of lungfish typically bear tooth plates, which are used to crush hard shelled organisms.
Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country comprising mainland Australia, the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and list of islands of Australia, numerous smaller isl ...
, though they were formerly globally distributed. The fossil record of the group extends into the Early Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, over 410 million years ago. The earliest known members of the group were marine, while almost all post-Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
representatives inhabit freshwater environments.
Etymology
Dipnoi is Modern Latin derived from the Greek δίπνοος (dipnoos) with two breathing structures, from δι- twice and πνοή breathing, breath.Anatomy and morphology
All lungfish demonstrate an uninterrupted cartilaginousnotochord
The notochord is an elastic, rod-like structure found in chordates. In vertebrates the notochord is an embryonic structure that disintegrates, as the vertebrae develop, to become the nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral discs of the verteb ...
and an extensively developed palatal dentition. Basal (" primitive") lungfish groups may retain marginal teeth and an ossified braincase, but derived lungfish groups, including all modern species, show a significant reduction in the marginal bones and a cartilaginous braincase. The bones of the skull roof
The skull roof or the roofing bones of the skull are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes, including land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In com ...
in primitive lungfish are covered in a mineralized tissue
Mineralized tissues are biological tissues that incorporate minerals into soft matrices. Typically these tissues form a protective shield or structural support. Bone, mollusc shells, deep sea sponge ''Euplectella'' species, radiolarians, diatoms ...
called cosmine
Cosmine is a spongy, bony material that makes up the dentine-like layers in the scales of the lobe-finned fishes of the class Sarcopterygii. Fish scales that include layers of cosmine are known as cosmoid scales.
Description
As traditionally d ...
, but in post-Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
lungfishes, the skull roof lies beneath the skin and the cosmine covering is lost. All modern lungfish show significant reductions and fusions of the bones of the skull roof, and the specific bones of the skull roof show no homology to the skull roof bones of ray-finned fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ...
es or tetrapods
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four- limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetrapoda (). Tetrapods include all extant and extinct amphibians and amniotes, with the lat ...
. During the breeding season, the South American lungfish
The South American lungfish (''Lepidosiren paradoxa''), also known as the American mud-fish and scaly salamanderfish, is the single species of lungfish found in swamps and slow-moving waters of the Amazon Basin, Amazon, Paraguay River, Paraguay, ...
develops a pair of feathery appendages that are actually highly modified pelvic fins. These fins are thought to improve gas exchange around the fish's eggs in its nest.
Through convergent evolution
Convergent evolution is the independent evolution of similar features in species of different periods or epochs in time. Convergent evolution creates analogous structures that have similar form or function but were not present in the last comm ...
, lungfishes have evolved internal nostrils similar to the tetrapods' choana
The choanae (: choana), posterior nasal apertures or internal nostrils are two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the pharynx, in humans and other mammals (as well as crocodilians and most skinks). They ...
, and a brain with certain similarities to Lissamphibia
The Lissamphibia (from Greek λισσός (lissós, "smooth") + ἀμφίβια (amphíbia), meaning "smooth amphibians") is a group of tetrapods that includes all modern amphibians. Lissamphibians consist of three living groups: the Salientia ( ...
n brain (except for the Queensland lungfish, which branched off in its own direction about 277 million years ago and has a brain resembling that of the ''Latimeria
''Latimeria'' is a rare genus of fish which contains the two only living species of coelacanth. It includes two Extant taxon, extant species: the West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') and the Indonesian coelacanth (''Latimeria me ...
'').
The dentition of lungfish is different from that of any other vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
group. " Odontodes" on the palate and lower jaws develop in a series of rows to form a fan-shaped occlusion surface. These odontodes then wear to form a uniform crushing surface. In several groups, including the modern lepidosireniformes, these ridges have been modified to form occluding blades.
The modern lungfishes have a number of larval features, which suggest paedomorphosis
Neoteny (), also called juvenilization,Montagu, A. (1989). Growing Young. Bergin & Garvey: CT. is the delaying or slowing of the Physiology, physiological, or Somatic (biology), somatic, development of an organism, typically an animal. Neoteny i ...
. They also demonstrate the largest genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
among the vertebrates.
Modern lungfish all have an elongate body with fleshy, paired pectoral
Pectoral may refer to:
* The chest region and anything relating to it.
* Pectoral cross, a cross worn on the chest
* a decorative, usually jeweled version of a gorget
* Pectoral (Ancient Egypt), a type of jewelry worn in ancient Egypt
* Pectora ...
and pelvic
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an anatomical trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis or pelvic skeleton).
...
fins and a single unpaired caudal fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported only ...
replacing the dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
, caudal and anal fins of most fishes.
Lungs
Lungfish have a highly specializedrespiratory system
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies grea ...
. They have a distinct feature in that their lungs are connected to the larynx and pharynx without a trachea. While other species of fish can breathe air using modified, vascularized gas bladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift via swimming, ...
s, these bladders are usually simple sacs, devoid of complex internal structure. In contrast, the lungs of lungfish are subdivided into numerous smaller air sacs, maximizing the surface area available for gas exchange
Gas exchange is the physical process by which gases move passively by diffusion across a surface. For example, this surface might be the air/water interface of a water body, the surface of a gas bubble in a liquid, a gas-permeable membrane, or a b ...
.
Most extant lungfish species have two lungs, with the exception of the Australian lungfish, which has only one. The lungs of lungfish are homologous to the lungs of tetrapods. As in tetrapods and bichir
Bichirs and the reedfish comprise Polypteridae , a family (biology), family of archaic Actinopterygii, ray-finned fishes and the only family in the order (biology), order Polypteriformes .Helfman GS, Collette BB, Facey DE, Bowen BW. 2009. The D ...
s, the lungs extend from the ventral surface of the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
and gut.
Perfusion of water
Of extant lungfish, only theAustralian lungfish
The Australian lungfish (''Neoceratodus forsteri''), also known as the Queensland lungfish, Burnett salmon and barramunda, is the only surviving member of the family Neoceratodontidae. It is one of only six extant lungfish species in the world. ...
can breathe through its gills without needing air from its lung. In other species, the gills are too atrophied to allow for adequate gas exchange. When a lungfish is obtaining oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), non ...
from its gills, its circulatory system is configured similarly to the common fish. The spiral valve of the conus arteriosus
The infundibulum (also known as ''conus arteriosus'') is a conical pouch formed from the upper and left angle of the right ventricle in the chordate heart, from which the pulmonary trunk arises. It develops from the bulbus cordis. Typically, the ...
is open, the bypass arterioles of the third and fourth gill arches (which do not actually have gills) are shut, the second, fifth and sixth gill arch arterioles are open, the ductus arteriosus
The ductus arteriosus, also called the ductus Botalli, named after the Italian physiologist Leonardo Botallo, is a blood vessel in the developing fetus connecting the trunk of the pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aorta. It allows mos ...
branching off the sixth arteriole is open, and the pulmonary arteries are closed. As the water passes through the gills, the lungfish uses a buccal pump. Flow through the mouth and gills is unidirectional. Blood flow through the secondary lamellae is countercurrent to the water, maintaining a more constant concentration gradient.
Perfusion of air
When breathing air, the spiral valve of the conus arteriosus closes (minimizing the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood), the third and fourth gill arches open, the second and fifth gill arches close (minimizing the possible loss of the oxygen obtained in the lungs through the gills), the sixth arteriole's ductus arteriosus is closed, and the pulmonary arteries open. Importantly, during air breathing, the sixth gill is still used in respiration; deoxygenated blood loses some of its carbon dioxide as it passes through the gill before reaching the lung. This is because carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. Air flow through the mouth is tidal, and through the lungs it is bidirectional and observes "uniform pool" diffusion of oxygen.Ecology and life history
Lungfish areomnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize ...
, feeding on fish, insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s, worm
Worms are many different distantly related bilateria, bilateral animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limb (anatomy), limbs, and usually no eyes.
Worms vary in size from microscopic to over in length for marine ...
s, mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s and plant matter. They have an intestinal spiral valve rather than a true stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
.
African and South American lungfish are capable of surviving seasonal drying out of their habitats by burrowing into mud and estivating throughout the dry season. Changes in physiology
Physiology (; ) is the science, scientific study of function (biology), functions and mechanism (biology), mechanisms in a life, living system. As a branches of science, subdiscipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ syst ...
allow it to slow its metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the co ...
to as little as one sixtieth of the normal metabolic rate, and protein waste is converted from ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
to less-toxic urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest am ...
(normally, lungfish excrete nitrogenous waste as ammonia directly into the water).
Burrowing is seen in at least one group of fossil lungfish, the Gnathorhizidae
The Gnathorhizidae are an extinct family of lungfish that lived from the late Carboniferous until the middle Triassic. Gnathorhizid fossils have been found in North America, Madagascar, Australia, and possibly Eastern Europe and South Africa. ...
.
Lungfish can be extremely long-lived. A Queensland lungfish
The Australian lungfish (''Neoceratodus forsteri''), also known as the Queensland lungfish, Burnett salmon and barramunda, is the only surviving member of the family Neoceratodontidae. It is one of only six extant lungfish species in the world. ...
called "Granddad" at the Shedd Aquarium
Shedd Aquarium (formally the John G. Shedd Aquarium) is an indoor public aquarium in Chicago. Opened on May 30, 1930, the aquarium holds about 32,000 animals. It is the third largest aquarium in the Western Hemisphere (after the Georgia Aquariu ...
in Chicago
Chicago is the List of municipalities in Illinois, most populous city in the U.S. state of Illinois and in the Midwestern United States. With a population of 2,746,388, as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, it is the List of Unite ...
was part of the permanent live collection from 1933 to 2017 after a previous residence at the Sydney Aquarium; at 109 years old, it was euthanized following a decline in health consistent with old age.
As of 2022, the oldest lungfish, and probably the oldest aquarium fish in the world is "Methuselah
Methuselah (; ''Məṯūšélaḥ'', in pausa ''Məṯūšālaḥ'', "His death shall send" or "Man of the javelin" or "Death of sword"; ''Mathousalas'') was a biblical patriarch and a figure in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. He is clai ...
", an Australian lungfish long and weighing around . Methuselah is believed to be female, unlike its namesake, and is estimated to be over 90 years old.
Evolution
About 420 million years ago, during theDevonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, the last common ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assu ...
of lungfish and tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s split into two separate evolutionary lineages, with the ancestor of the extant coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, bi ...
s diverging a little earlier from a sarcopterygian
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates ar ...
progenitor. '' Youngolepis'' and ''Diabolepis
''Diabolepis'' is an extinct genus of very primitive marine lungfish which lived during the Early Devonian period. It contains a single species, ''D. speratus'' of Yunnan, China, from the mid-late Lochkovian of the Xitun Formation. It is one of ...
'', dating to 419–417 million years ago, during Early Devonian (Lochkovian
The Lochkovian is one of three faunal stages in the Early Devonian Epoch. It lasted from 419.2 ± 3.2 million years ago to 410.8 ± 2.8 million years ago. It marked the beginning of the Devonian Period, and was followed by the Pragian Stage. It is ...
), are the currently oldest known lungfish, and show that the lungfishes had adapted to a diet including hard-shelled prey (durophagy
Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume Seashell, hard-shelled or exoskeleton-bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including ...
) very early in their evolution. The earliest lungfish were marine. Almost all post-Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
lungfish inhabit or inhabited freshwater environments. There were likely at least two transitions amongst lungfish from marine to freshwater habitats. The last common ancestor of all living lungfish likely lived sometime between the Late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
and the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
. Lungfish remained present in the northern Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
n landmasses into the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period.
Lungfish and Convergent Evolution
Lungfish (Dipnoi) are a group of lobe-finned fishes that have undergone significant evolutionary adaptations, particularly in their respiratory, locomotor, and neurological systems. Through convergent evolution, lungfish have developed traits similar to those of early tetrapods, including air-breathing lungs, internal nostrils functionally analogous to choanae, and tetrapod-like locomotion. Additionally, certain brain structures and jaw-opening muscles in lungfish resemble those found in amphibians, suggesting functional convergence despite phylogenetic distance.
Evolution of Air-Breathing Lungs
The development of lungs in lungfish mirrors the pulmonary structures of early tetrapods. Lungfish lungs, which are derived from the swim bladder (an organ typically used for buoyancy in most bony fishes), are directly connected to the alimentary tract and lined with a dense network of blood vessels within honeycomb-like cavities. This anatomical specialization enables efficient gas exchange, a crucial adaptation for survival in freshwater environments prone to hypoxia (low oxygen levels).
Internal Nostrils and Convergent Traits with Tetrapods
Lungfish have evolved internal nostrils, enabling them to breathe air through nasal passages. These structures are functionally analogous to the choanae in tetrapods and are believed to have evolved independently in both groups, an example of convergent evolution.
Tetrapod-Like Locomotion and Skeletal Adaptations
Some species, such as the West African lungfish (Protopterus annectens), exhibit movement patterns that resemble those of early terrestrial vertebrates. Lungfish can propel themselves along a substrate using fin-supported, elongated bodies, sometimes lifting themselves in a quadrupedal fashion. This behavior suggests that certain locomotor features may have predated the full evolution of tetrapod limbs.
Furthermore, the synchronized rotation of the pectoral girdle and cranial rib, along with muscle shortening during buccal expansion, indicates that lungfish had preadaptations for air breathing requiring minimal morphological changes.
Neurological and Sensory Convergence
Neurological studies of the African lungfish (Protopterus) reveal structural and functional similarities to amphibians, especially in regions associated with cognitive and sensory processing. Despite their phylogenetic separation, these parallels may reflect convergent evolution in neural architecture.
Jaw-Opening Muscles and Functional Convergence
The South American (Lepidosiren) and African lungfish species possess a jaw-opening muscle that is topographically and functionally similar to the depressor mandibulae of salamanders. Although this suggests potential homology, the absence of this muscle in the Australian lungfish (Neoceratodus forsteri) and its absence in fossil records of primitive lungfishes support the idea that the muscle evolved independently in lepidosirenids. Differences in embryonic development between this muscle in lungfish and salamanders further support this conclusion.
Evolutionary History of Lungfish
The lineage of lungfish dates back to the Devonian period (~382–359 million years ago), with fossil genera such as Scaumenacia and Phaneropleuron displaying early morphological adaptations. These include a reduced first dorsal fin and a second dorsal fin that shifted toward the tail. By the Permian, lungfish evolved a more continuous fin structure along the dorsal, caudal, and anal regions, a feature that persists in modern species.
Locomotor behavior observed in fossil and living lungfish suggests that walking and bounding behaviors may have originated in sarcopterygian fishes before the evolution of true tetrapods. Protopterus annectens can lift its body using its fins, propelling itself across surfaces in a quadrupedal, and occasionally bipedal, manner.
Molecular and Genomic Insights into Lungfish Evolution
Molecular and genomic studies reveal that lungfish diverged from other lobe-finned fishes over 400 million years ago. The Australian lungfish (Neoceratodus forsteri) retains many primitive traits, making it especially valuable for evolutionary research.
The genome of the African lungfish (Protopterus annectens) is one of the largest known among vertebrates, approximately 40 billion base pairs, largely due to the accumulation of transposable elements. Despite its size, the lungfish genome maintains efficient transcription mechanisms that ensure proper gene expression.
Extant lungfish
 The
The Queensland lungfish
The Australian lungfish (''Neoceratodus forsteri''), also known as the Queensland lungfish, Burnett salmon and barramunda, is the only surviving member of the family Neoceratodontidae. It is one of only six extant lungfish species in the world. ...
, ''Neoceratodus forsteri'', is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
to Australia. Fossil records of this group date back 380 million years, around the time when the higher vertebrate classes were beginning to evolve. Fossils of lungfish belonging to the genus ''Neoceratodus'' have been uncovered in northern New South Wales
New South Wales (commonly abbreviated as NSW) is a States and territories of Australia, state on the Eastern states of Australia, east coast of :Australia. It borders Queensland to the north, Victoria (state), Victoria to the south, and South ...
, indicating that the Queensland lungfish has existed in Australia for at least 100 million years, making it a living fossil
A living fossil is a Deprecation, deprecated term for an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of or ...
and one of the oldest living vertebrate genera on the planet. It is the most primitive surviving member of the ancient air-breathing lungfish (Dipnoi) lineages. The five other freshwater lungfish species, four in Africa and one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sp ...
in South America, are very different morphologically to ''N. forsteri''. The Queensland lungfish can live for several days out of the water if it is kept moist, but will not survive total water depletion, unlike its African counterparts.
 The
The South American lungfish
The South American lungfish (''Lepidosiren paradoxa''), also known as the American mud-fish and scaly salamanderfish, is the single species of lungfish found in swamps and slow-moving waters of the Amazon Basin, Amazon, Paraguay River, Paraguay, ...
, ''Lepidosiren paradoxa'', is the single species of lungfish found in swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
s and slow-moving waters of the Amazon
Amazon most often refers to:
* Amazon River, in South America
* Amazon rainforest, a rainforest covering most of the Amazon basin
* Amazon (company), an American multinational technology company
* Amazons, a tribe of female warriors in Greek myth ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay, officially the Republic of Paraguay, is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the Argentina–Paraguay border, south and southwest, Brazil to the Brazil–Paraguay border, east and northeast, and Boli ...
, and lower Paraná River
The Paraná River ( ; ; ) is a river in south-central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some ."Parana River". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Online.
Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2012. Web. ...
basins
Basin may refer to:
Geography and geology
* Depression (geology)
** Back-arc basin, a submarine feature associated with island arcs and subduction zones
** Debris basin, designed to prevent damage from debris flow
** Drainage basin (hydrology), ...
in South America. Notable as an obligate
{{wiktionary, obligate
As an adjective, obligate means "by necessity" (antonym '' facultative'') and is used mainly in biology in phrases such as:
* Obligate aerobe, an organism that cannot survive without oxygen
* Obligate anaerobe, an organism ...
air-breather, it is the sole member of its family native to the Americas. Relatively little is known about the South American lungfish. When immature it is spotted with gold on a black background. In the adult this fades to a brown or gray color. Its tooth-bearing premaxillary and maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxil ...
ry bones are fused like other lungfish. South American lungfishes also share an autostylic jaw suspension (where the palatoquadrate is fused to the cranium
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
) and powerful adductor jaw muscles with the extant lungfish (Dipnoi). Like the African lungfishes, this species has an elongate, almost eel-like body. It may reach a length of . The pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s are thin and threadlike, while the pelvic fins are somewhat larger, and set far back. The fins are connected to the shoulder by a single bone, which is a marked difference from most fish, whose fins usually have at least four bones at their base; and a marked similarity with nearly all land-dwelling vertebrates. They have the lowest aquatic respiration of all extant lungfish species, and their gills are greatly reduced and essentially non-functional in the adults.
 The marbled lungfish, ''Protopterus aethiopicus'', is found in Africa. The marbled lungfish is smooth and elongated with deeply embedded
The marbled lungfish, ''Protopterus aethiopicus'', is found in Africa. The marbled lungfish is smooth and elongated with deeply embedded scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number ...
, and (starting from the head end) is cylindrical for much of its length. The tail is very long and tapers at the end. They are the largest of the African lungfish species as they can reach a length of up to 200 cm.Fishbase.org/ref> The pectoral and pelvic fins are also very long and thin, almost spaghetti-like. The newly hatched young have branched external gills much like those of newts. After 2 to 3 months the young transform (called
metamorphosis
Metamorphosis is a biological process by which an animal physically develops including birth transformation or hatching, involving a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and different ...
) into the adult form, losing the external gills for gill openings. These fish have a yellowish gray or pinkish toned ground color with dark slate-gray splotches, creating a marbling or leopard effect over the body and fins. The color pattern is darker along the top and lighter below. The marbled lungfish's genome
A genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as ...
contains 133 billion base pairs
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
, making it the largest known genome of any vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
. The only organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s known to have more base pairs are the protist
A protist ( ) or protoctist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, land plant, or fungus. Protists do not form a natural group, or clade, but are a paraphyletic grouping of all descendants of the last eukaryotic common ancest ...
''Polychaos dubium
''Polychaos dubium'' is a freshwater amoeboid and one of the larger species of single-celled eukaryote. Like other amoebozoans, ''P. dubium'' moves by means of temporary projections called pseudopods. ''P. dubium'' reportedly has one of the larg ...
'' and the flowering plant '' Paris japonica'' at 670 billion and 150 billion, respectively.
 The gilled lungfish, ''Protopterus amphibius'' is a species of lungfish found in
The gilled lungfish, ''Protopterus amphibius'' is a species of lungfish found in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
. It generally reaches only long, making it the smallest extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
lungfish in the world. This lungfish is uniform blue, or slate grey in colour. It has small or inconspicuous black spots, and a pale grey belly.
 The west African lungfish, ''Protopterus annectens'', is a species of lungfish found in West Africa. It has a prominent
The west African lungfish, ''Protopterus annectens'', is a species of lungfish found in West Africa. It has a prominent snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, Rostrum (anatomy), rostrum, beak or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the n ...
and small eye
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
s. Its body is long and eel-like, some 9–15 times the length of the head. It has two pairs of long, filamentous fins
A fin is a thin component or appendage attached to a larger body or structure. Fins typically function as foil (fluid mechanics), foils that produce lift (force), lift or thrust, or provide the ability to steer or stabilize motion while travelin ...
. The pectoral fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish aquatic locomotion, swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the vertebral column ...
s have a basal fringe and are about three times the head length, while its pelvic fin
Pelvic fins or ventral fins are paired fins located on the ventral (belly) surface of fish, and are the lower of the only two sets of paired fins (the other being the laterally positioned pectoral fins). The pelvic fins are homologous to the hi ...
s are about twice the head length. In general, three external gills
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
are inserted posterior to the gill slit
Gill slits are individual openings to gills, i.e., multiple gill arches, which lack a single outer cover. Such gills are characteristic of cartilaginous fish such as sharks and rays, as well as deep-branching vertebrates such as lampreys. In c ...
s and above the pectoral fins. It has cycloid scales embedded in the skin. There are 40–50 scales between the operculum and the anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
and 36–40 around the body before the origin of the dorsal fin
A dorsal fin is a fin on the back of most marine and freshwater vertebrates. Dorsal fins have evolved independently several times through convergent evolution adapting to marine environments, so the fins are not all homologous. They are found ...
. It has 34–37 pairs of rib
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs () are the long curved bones which form the rib cage, part of the axial skeleton. In most tetrapods, ribs surround the thoracic cavity, enabling the lungs to expand and thus facilitate breathing by expanding the ...
s. The dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
The fus ...
side is olive or brown in color and the ventral
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
side is lighter, with great blackish or brownish spots on the body and fins except on its belly. They reach a length of about 100 cm in the wild.
 The spotted lungfish, ''Protopterus dolloi'', is a species of lungfish found in Africa. Specifically, it is found in the Kouilou-Niari Basin of the
The spotted lungfish, ''Protopterus dolloi'', is a species of lungfish found in Africa. Specifically, it is found in the Kouilou-Niari Basin of the Republic of the Congo
The Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Democratic Republic of the Congo), is a country located on the western coast of Central ...
and Ogowe River basin in Gabon
Gabon ( ; ), officially the Gabonese Republic (), is a country on the Atlantic coast of Central Africa, on the equator, bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and ...
. It is also found in the lower and Middle Congo River Basins.Fishbase.org/ref> ''Protopterus dolloi'' can aestivate on land by surrounding itself in a layer of dried
mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
. It can reach a length of up to 130 cm.
Taxonomy
 The relationship of lungfishes to the rest of the
The relationship of lungfishes to the rest of the bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
is well understood:
* Lungfishes are most closely related to '' Powichthys'', and then to the Porolepiformes.
* Together, these taxa form the Dipnomorpha
Rhipidistia, also known as Dipnotetrapodomorpha, is a clade of lobe-finned fishes which includes the tetrapods and lungfishes. Rhipidistia formerly referred to a subgroup of Sarcopterygii consisting of the Porolepiformes and Osteolepiformes, a ...
, the sister group to the Tetrapodomorpha
Tetrapodomorpha (also known as Choanata) is a clade of vertebrates consisting of tetrapods (four-limbed vertebrates) and their closest sarcopterygian relatives that are more closely related to living tetrapods than to living lungfish. Advanced f ...
.
* Together, these form the Rhipidistia
Rhipidistia, also known as Dipnotetrapodomorpha, is a clade of lobe-finned fishes which includes the tetrapods and lungfishes. Rhipidistia formerly referred to a subgroup of Sarcopterygii consisting of the Porolepiformes and Osteolepiformes, a de ...
, the sister group to the coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, bi ...
s.
Recent molecular genetic analyses strongly support a sister relationship of lungfishes and tetrapods (Rhipidistia
Rhipidistia, also known as Dipnotetrapodomorpha, is a clade of lobe-finned fishes which includes the tetrapods and lungfishes. Rhipidistia formerly referred to a subgroup of Sarcopterygii consisting of the Porolepiformes and Osteolepiformes, a de ...
), with coelacanths branching slightly earlier.
The relationships among lungfishes are significantly more difficult to resolve. While Devonian lungfish had enough bone in the skull to determine relationships, post-Devonian lungfish are represented entirely by skull roofs and teeth, as the rest of the skull is cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. Semi-transparent and non-porous, it is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints ...
. Additionally, many of the taxa already identified may not be monophyletic
In biological cladistics for the classification of organisms, monophyly is the condition of a taxonomic grouping being a clade – that is, a grouping of organisms which meets these criteria:
# the grouping contains its own most recent co ...
.
Phylogeny after Kemp, Cavin & Guinot, 2017
Cladogram after Brownstein et al. 2023
See also
* '' Ceratodus'' * ''Lepidogalaxias salamandroides
''Lepidogalaxias salamandroides'' is a species of small freshwater fish of Western Australia. It is the monotypic, only member of the family Lepidogalaxiidae and genus ''Lepidogalaxias''. Common names for this fish include salamanderfish and Sha ...
''
* '' Polypteridae''
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
* * * * * {{Authority control Articles which contain graphical timelines Extant Early Devonian first appearances