|
Latimeria
''Latimeria'' is a rare genus of fish which contains the two only living species of coelacanth. It includes two Extant taxon, extant species: the West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') and the Indonesian coelacanth (''Latimeria menadoensis''). They follow the oldest known living Lineage (evolution), lineage of Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish and tetrapods), which means they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (amphibians, reptiles and mammals) than to the common ray-finned fishes and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fishes. They are found along the coastlines of the Indian Ocean and Indonesia. Since there are only two known species of coelacanth and both are threatened, it is one of the most endangered genera of animals in the world. The West Indian Ocean coelacanth is a critically endangered species. Biological characteristics Based on growth rings in the creatures' ear bones (otoliths), scientists infer that individual coelacanths may live as long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelacanth Off Pumula On The KwaZulu-Natal South Coast, South Africa, On 22 November 2019
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the Class (biology), class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus ''Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine Geological formation, deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was Species description, described from specimens Fishing, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
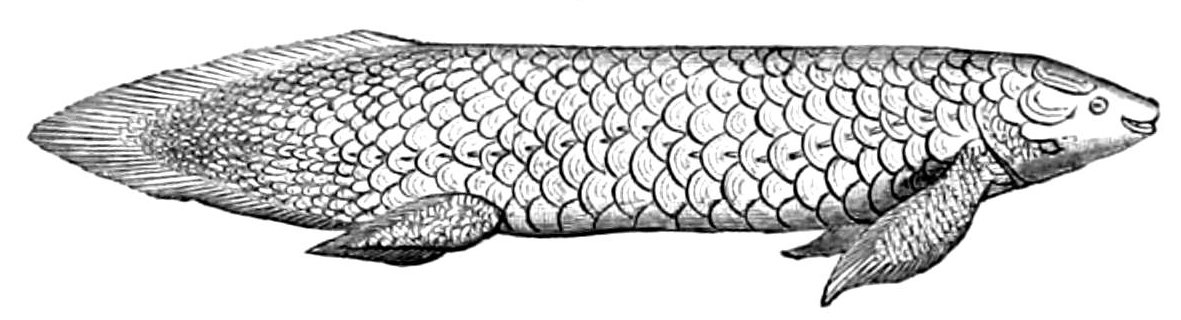
Coelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals) than to ray-finned fish. The name coelacanth originates from the Permian genus '' Coelacanthus'', which was the first scientifically named genus of coelacanths (in 1839), becoming the type genus of Coelacanthiformes as other species were discovered and named. Well-represented in freshwater and marine deposits from as early as the Devonian period (more than 410million years ago), they were thought to have become extinct in the Late Cretaceous, around 66million years ago. The first living species, ''Latimeria chalumnae'', the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, was described from specimens fished off the coast of South Africa from 1938 onward; they are now also known to inhabit the seas around the Comoro Islands off the eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Indian Ocean Coelacanth
The West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') (sometimes known as gombessa, African coelacanth, or simply coelacanth) is a crossopterygian, one of two extant species of coelacanth, a rare order of vertebrates more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods than to the common ray-finned fishes. The other extant species is the Indonesian coelacanth (''L. menadoensis''). The West Indian Ocean coelacanth was historically known by fishermen around the Comoro Islands (where it is known as ''gombessa''), Madagascar, and Mozambique in the western Indian Ocean, but first scientifically recognised from a specimen collected in South Africa in 1938. This coelacanth was once thought to be evolutionarily conservative, but discoveries have shown initial morphological diversity. It has a vivid blue pigment, and is the better known of the two extant species. The species has been assessed as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. Anatomy and physiology The average weight of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latimeria Chalumnae
The West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') (sometimes known as gombessa, African coelacanth, or simply coelacanth) is a Sarcopterygii, crossopterygian, one of two extant species of coelacanth, a rare order of vertebrates more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods than to the common ray-finned fishes. The other extant species is the Indonesian coelacanth (''L. menadoensis''). The West Indian Ocean coelacanth was historically known by fishermen around the Comoro Islands (where it is known as ''gombessa''), Madagascar, and Mozambique in the western Indian Ocean, but first scientifically recognised from a specimen collected in South Africa in 1938. This coelacanth was once thought to be evolutionarily conservative, but discoveries have shown initial morphological diversity. It has a vivid blue pigment, and is the better known of the two extant species. The species has been assessed as Critically endangered species, critically endangered on the IUCN Red List. Ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latimeria Menadoensis
The Indonesian coelacanth (''Latimeria menadoensis'', Indonesian: ''raja laut''), also called Sulawesi coelacanth, is one of two living species of coelacanth, identifiable by its brown color. ''Latimeria menadoensis'' is a lobe-finned fish belonging to the class Actinistia and order Coelacanthiformes, classified under the family Latimeriidae and genus ''Latimeria''. As a deep-sea predator, this species plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. It is listed as vulnerable by the IUCN, and it was quickly given protected status under Indonesian National Law Number 7/1999 after its discovery. The other species of coelacanth, the West Indian Ocean coelacanth, is listed as critically endangered. Separate populations of the Indonesian coelacanth are found in the waters of north Sulawesi, Papua, Southwest Papua, and North Maluku. This species offers insights into the early existence of fish and the first tetrapods. Discovery On September 18, 1997, Arnaz and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latimeria
''Latimeria'' is a rare genus of fish which contains the two only living species of coelacanth. It includes two Extant taxon, extant species: the West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae'') and the Indonesian coelacanth (''Latimeria menadoensis''). They follow the oldest known living Lineage (evolution), lineage of Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish and tetrapods), which means they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (amphibians, reptiles and mammals) than to the common ray-finned fishes and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fishes. They are found along the coastlines of the Indian Ocean and Indonesia. Since there are only two known species of coelacanth and both are threatened, it is one of the most endangered genera of animals in the world. The West Indian Ocean coelacanth is a critically endangered species. Biological characteristics Based on growth rings in the creatures' ear bones (otoliths), scientists infer that individual coelacanths may live as long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; )—sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii ()—is a clade (traditionally a class (biology), class or subclass) of vertebrate animals which includes a group of bony fish commonly referred to as lobe-finned fish. These vertebrates are characterised by prominent muscular limb buds (lobes) within their fish fin, fins, which are supported by articulated appendicular skeletons. This is in contrast to the other clade of bony fish, the Actinopterygii, which have only skin-covered lepidotrichia, bony spines supporting the fins. The tetrapods, a mostly terrestrial animal, terrestrial clade of vertebrates, are now recognized as having evolved from sarcopterygian ancestors and are most closely related to lungfishes. Their paired pectoral fins, pectoral and pelvic fins evolved into limb (anatomy), limbs, and their lung bud, foregut diverticulum eventually evolved into air-breathing lungs. Cladistics, Cladistically, this would make the tetrapods a subgroup within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by a ribless endoskeleton, dermal denticles, five to seven gill slits on each side, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the Division (taxonomy), division Selachii and are the sister group to the Batoidea, Batomorphi (Batoidea, rays and skate (fish), skates). Some sources extend the term "shark" as an informal category including Extinction, extinct members of Chondrichthyes (cartilaginous fish) with a shark-like morphology, such as hybodonts. Shark-like chondrichthyans such as ''Cladoselache'' and ''Doliodus'' first appeared in the Devonian Period (419–359 million years), though some fossilized chondrichthyan-like scales are as old as the Ordovician, Late Ordovician (458–444 million years ago). The earliest confirmed modern sharks (Selachii) are known from the Early Jurassic around , with the oldest known member being ''Agaleus'', though records of true shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
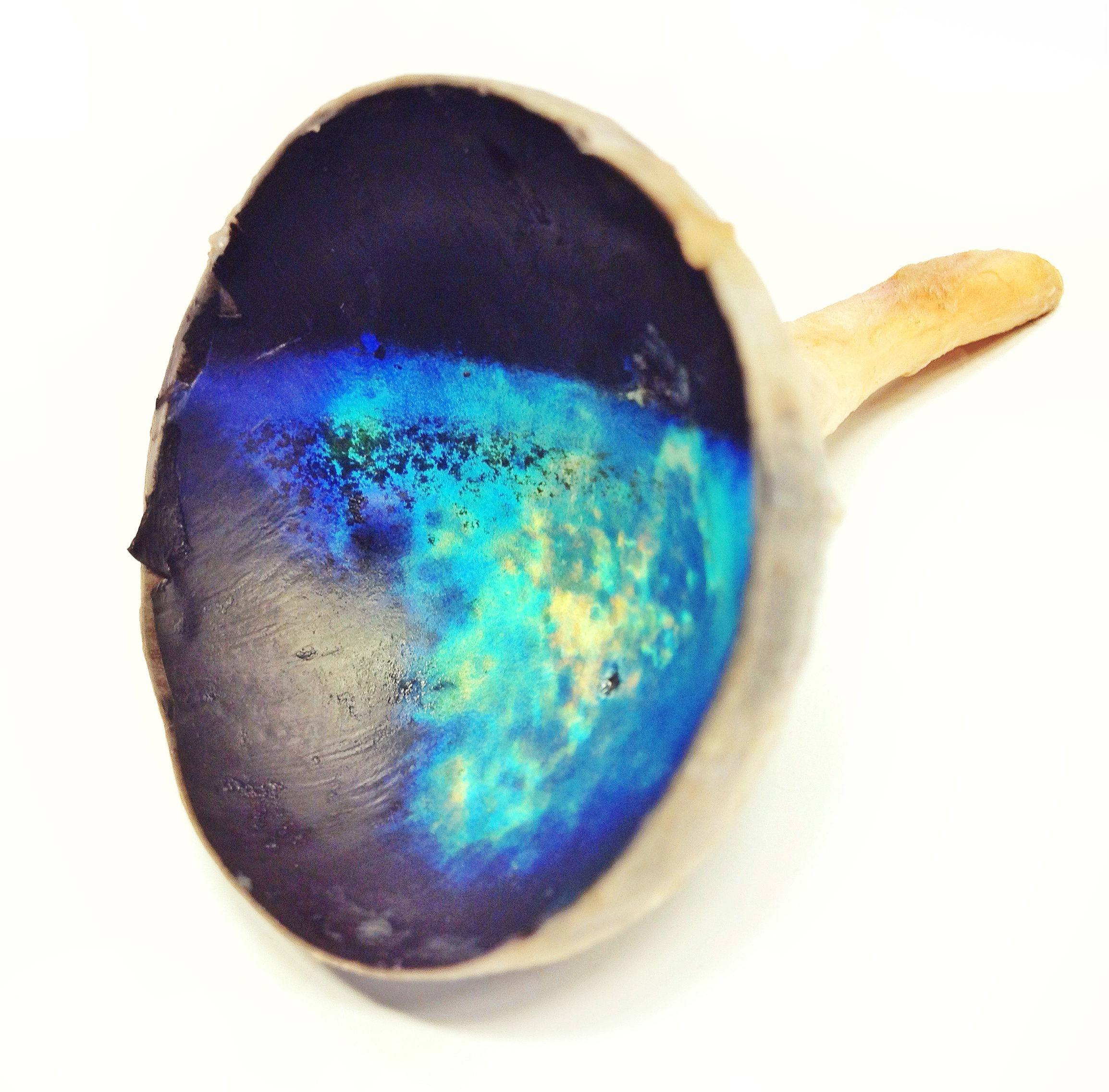
Tapetum Lucidum
The ; ; : tapeta lucida) is a layer of tissue in the eye of many vertebrates and some other animals. Lying immediately behind the retina, it is a retroreflector. It Reflection (physics), reflects visible light back through the retina, increasing the light available to the Photoreceptor cell, photoreceptors (although slightly blurring the image). The tapetum lucidum contributes to the superior night vision of some animals. Many of these animals are nocturnality, nocturnal, especially carnivores, while others are Deep-sea community, deep-sea animals. Similar adaptations occur in some species of spiders. Haplorhini, Haplorhine primates, including humans, are Diurnality, diurnal and lack a tapetum lucidum. Function and mechanism The presence of a tapetum lucidum enables animals to see in dimmer light than would otherwise be possible. The tapetum lucidum, which is iridescent, reflects light roughly on the Interference (wave propagation), interference principles of thin-film opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods (which includes living amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals). The mouths of lungfish typically bear tooth plates, which are used to crush hard shelled organisms. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia, though they were formerly globally distributed. The fossil record of the group extends into the Early Devonian, over 410 million years ago. The earliest known members of the group were marine, while almost all post-Carboniferous representatives inhabit freshwater environments. Etymology Dipnoi is Modern Latin derived from the Greek δίπν ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rostral Organ
The rostral organ of the coelacanth or other fish is a large gel-filled cavity in the snout, with three pairs of canals to the outside. It is surrounded by an insulating layer of adipose tissue and innervated by the superficial ophthalmic nerve The ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) is a sensory nerve of the head. It is one of three divisions of the trigeminal nerve (CN V), a cranial nerve. It has three major branches which provide sensory innervation to the eye, and the skin of the upper face .... Its anatomy and innervation suggest it is an electroreceptive organ used for finding prey in the dark. This is supported by experiments which showed that coelacanths react to electrical fields produced by a submersible. References Sensory organs in animals Fish anatomy {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |