Dimorphic Sexual Behavior on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Sexual dimorphism is the condition where
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where

 Sexual dimorphism is the condition where
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sex
Sex is the biological trait that determines whether a sexually reproducing organism produces male or female gametes. During sexual reproduction, a male and a female gamete fuse to form a zygote, which develops into an offspring that inheri ...
es of the same species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
exhibit different morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual ...
. The condition occurs in most dioecious
Dioecy ( ; ; adj. dioecious, ) is a characteristic of certain species that have distinct unisexual individuals, each producing either male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproduction is ...
species, which consist of most animals and some plants. Differences may include secondary sex characteristic
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during pubert ...
s, size, weight, color, markings, or behavioral or cognitive traits. Male-male reproductive competition has evolved a diverse array of sexually dimorphic traits. Aggressive utility traits such as "battle" teeth and blunt heads reinforced as battering rams are used as weapons in aggressive interactions between rivals. Passive displays such as ornamental feathering or song-calling have also evolved mainly through sexual selection. These differences may be subtle or exaggerated and may be subjected to sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
and natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
. The opposite of dimorphism is ''monomorphism'', when both biological sexes are phenotypically
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology (physical form and structure), its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties ...
indistinguishable from each other.
Overview


Ornamentation and coloration
Common and easily identified types of dimorphism consist ofornamentation
An ornament is something used for decoration.
Ornament may also refer to:
Decoration
* Ornament (art), any purely decorative element in architecture and the decorative arts
* Ornamental turning
* Biological ornament, a characteristic of animals ...
and coloration, though not always apparent. A difference in the coloration of sexes within a given species is called sexual dichromatism, commonly seen in many species of birds and reptiles. Sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
leads to exaggerated dimorphic traits that are used predominantly in competition over mates. The increased fitness resulting from ornamentation offsets its cost to produce or maintain, suggesting complex evolutionary implications, but the costs and evolutionary implications vary from species to species.
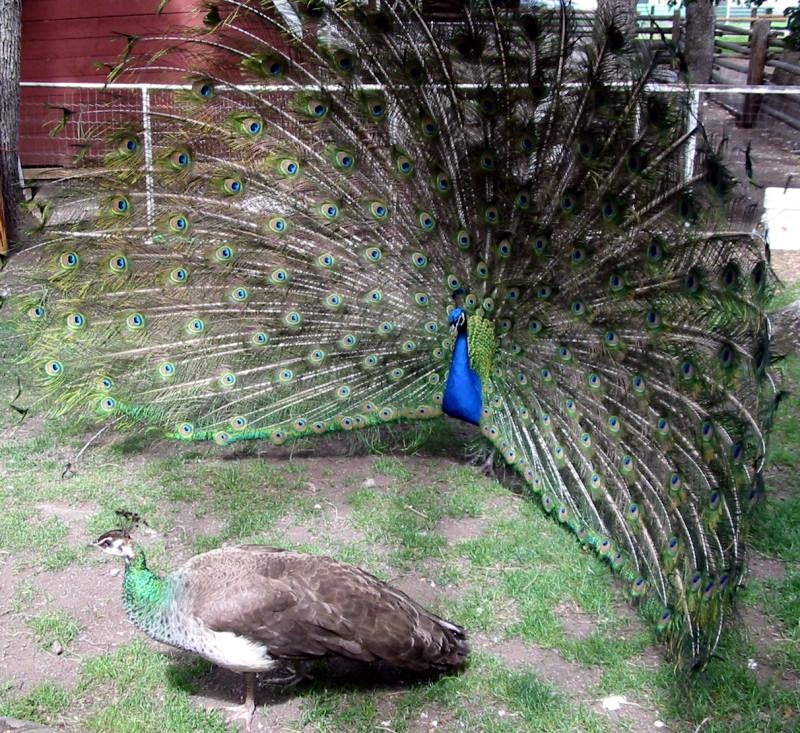
The peafowl
Peafowl is a common name for two bird species of the genus '' Pavo'' and one species of the closely related genus '' Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae (the pheasants and their allies). Male peafowl are referred t ...
constitute conspicuous illustrations of the principle. The ornate plumage
Plumage () is a layer of feathers that covers a bird and the pattern, colour, and arrangement of those feathers. The pattern and colours of plumage differ between species and subspecies and may vary with age classes. Within species, there can b ...
of peacocks, as used in the courting display, attracts peahen
Peafowl is a common name for two bird species of the genus '' Pavo'' and one species of the closely related genus ''Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae (the pheasants and their allies). Male peafowl are referred to ...
s. At first sight, one might mistake peacocks and peahens for completely different species because of the vibrant colours and the sheer size of the male's plumage; the peahen is of a subdued brown coloration. The plumage of the peacock increases its vulnerability to predators because it is a hindrance in flight, and it renders the bird conspicuous in general. Similar examples are manifold, such as in birds of paradise
The birds-of-paradise are members of the family Paradisaeidae of the order Passeriformes. The majority of species are found in eastern Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and eastern Australia. The family has 45 species in 17 genera. The members of this ...
and argus pheasants.
Another example of sexual dichromatism is that of nestling blue tit
The Eurasian blue tit (''Cyanistes caeruleus'') is a small passerine bird in the tit (bird), tit family, Paridae. It is easily recognizable by its blue and yellow plumage and small size.
Eurasian blue tits, usually resident bird, resident a ...
s. Males are chromatically more yellow than females. It is believed that this is obtained by the ingestion of green Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) or lepidopterans is an order (biology), order of winged insects which includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera have been described, representing 10% of the total described species of living organ ...
n larvae, which contain large amounts of the carotenoid
Carotenoids () are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, cana ...
s lutein
Lutein (;"Lutein"
 Insects display a wide variety of sexual dimorphism between taxa including size, ornamentation and coloration. The female-biased sexual size dimorphism observed in many taxa evolved despite intense male-male competition for mates. In ''
Insects display a wide variety of sexual dimorphism between taxa including size, ornamentation and coloration. The female-biased sexual size dimorphism observed in many taxa evolved despite intense male-male competition for mates. In ''
zeaxanthin
Zeaxanthin is one of the most common carotenoids in nature, and is used in the xanthophyll cycle. Synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms, it is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, goji ( wolfberries) ...
. This diet also affects the sexually dimorphic colours in the human-invisible ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
spectrum. Hence, the male birds, although appearing yellow to humans, actually have a violet-tinted plumage that is seen by females. This plumage is thought to be an indicator of male parental abilities. Perhaps this is a good indicator for females because it shows that they are good at obtaining a food supply from which the carotenoid is obtained. There is a positive correlation between the chromas of the tail and breast feathers and body condition. Carotenoids play an important role in immune function
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as cancer cells, parasitic worms, and also objects such as ...
for many animals, so carotenoid dependent signals might indicate health.
Frogs constitute another conspicuous illustration of the principle. There are two types of dichromatism for frog species: ontogenetic and dynamic. Ontogenetic frogs are more common and have permanent color changes in males or females. ''Ranoidea lesueuri'' is an example of a dynamic frog with temporary color changes in males during the breeding season. ''Hyperolius ocellatus
''Hyperolius ocellatus'' is a species of tropical West African frog in the family Hyperoliidae, that is split into the subspecies ''H. o. ocellatus'' and ''H. o. purpurescens''. It is found in Angola, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic ...
'' is an ontogenetic frog with dramatic differences in both color and pattern between the sexes. At sexual maturity, the males display a bright green with white dorsolateral lines. In contrast, the females are rusty red to silver with small spots. The bright coloration in the male population attracts females and is an aposematic
Aposematism is the Advertising in biology, advertising by an animal, whether terrestrial or marine, to potential predation, predators that it is not worth attacking or eating. This unprofitability may consist of any defenses which make the pr ...
sign to potential predators.
Females often show a preference for exaggerated male secondary sexual characteristics
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during puberty ...
in mate selection. The sexy son hypothesis
The sexy son hypothesis in evolutionary biology and sexual selection, proposed by Patrick J. Weatherhead and Raleigh J. Robertson of Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario in 1979, states that a female's ideal mate choice among potential mates ...
explains that females prefer more elaborate males and select against males that are dull in color, independent of the species' vision.
Similar sexual dimorphism and mating choice are also observed in many fish species. For example, male guppies
The Greater Underwater Propulsion Power Program (GUPPY) was initiated by the United States Navy after World War II to improve the submerged speed, maneuverability, and endurance of its submarines. (The "Y" in the acronym was added for pronouncea ...
have colorful spots and ornamentations, while females are generally grey. Female guppies prefer brightly colored males to duller males.
In redlip blennies, only the male fish develops an organ at the anal-urogenital region that produces antimicrobial substances. During parental care, males rub their anal-urogenital regions over their nests' internal surfaces, thereby protecting their eggs from microbial infections, one of the most common causes for mortality in young fish.
Plants
Mostflowering plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed with ...
s are hermaphroditic
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
but approximately 6% of species have separate males and females (dioecy
Dioecy ( ; ; adj. dioecious, ) is a characteristic of certain species that have distinct unisexual individuals, each producing either male or female gametes, either directly (in animals) or indirectly (in seed plants). Dioecious reproduction is ...
). Sexual dimorphism is common in dioecious plants and dioicous
Dioicy () is a sexual system in non-vascular plants where archegonia (female organs) and antheridia (male organs) are produced on separate plants in the gametophyte phase. It is one of the two main sexual systems in bryophytes, the other being ...
species.
Males and females in insect-pollinated
Entomophily or insect pollination is a form of pollination whereby pollen of plants, especially but not only of flowering plants, is distributed by insects. Flowers pollinated by insects typically advertise themselves with bright colours, somet ...
species generally look similar to one another because plants provide rewards (e.g. nectar
Nectar is a viscous, sugar-rich liquid produced by Plant, plants in glands called nectaries, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollination, pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to an ...
) that encourage pollinators
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are the ma ...
to visit another similar flower
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, m ...
, completing pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or bu ...
. ''Catasetum
''Catasetum'', abbreviated as Ctsm. in horticultural trade, is a genus of showy epiphytic Orchids, family Orchidaceae, subfamily Epidendroideae, tribe Cymbidieae, subtribe Catasetinae, with currently 200 accepted species, many of which are highl ...
'' orchids are one interesting exception to this rule. Male ''Catasetum
''Catasetum'', abbreviated as Ctsm. in horticultural trade, is a genus of showy epiphytic Orchids, family Orchidaceae, subfamily Epidendroideae, tribe Cymbidieae, subtribe Catasetinae, with currently 200 accepted species, many of which are highl ...
'' orchids
Orchids are plants that belong to the family Orchidaceae (), a diverse and widespread group of flowering plants with blooms that are often colourful and fragrant. Orchids are cosmopolitan plants that are found in almost every habitat on Earth ...
violently attach pollinia
A pollinium (: pollinia) is a coherent mass of pollen grains in a plant that are the product of only one anther, but are transferred, during pollination, as a single unit. This is regularly seen in plants such as orchids and many species of milkwee ...
to euglossine
The tribe Euglossini, in the subfamily Apinae, commonly known as orchid bees or euglossine bees, are the only group of corbiculate bees whose non-parasitic members do not all possess eusocial behavior.
Description, distribution, and behavior
...
bee pollinators. The bees will then avoid other male flowers but may visit the female, which looks different from the males.
Various other dioecious exceptions, such as ''Loxostylis alata
''Loxostylis'' is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Anacardiaceae.
The genus contains a single species called ''Loxostylis alata''. In English, this species goes by the common name tar wood. It has self supporting growth and i ...
'', have visibly different sexes, with the effect of eliciting the most efficient behavior from pollinators, who then use the most efficient strategy in visiting each gender of flower instead of searching, say, for pollen in a nectar-bearing female flower.
Some plants, such as some species of ''Geranium
''Geranium'' is a genus of 422 species of annual, biennial, and perennial plants that are commonly known as geraniums or cranesbills. They are found throughout the temperate regions of the world and the mountains of the tropics, with the gre ...
'', have what amounts to serial sexual dimorphism. The flowers of such species might, for example, present their anthers
The stamen (: stamina or stamens) is a part consisting of the male reproductive organs of a flower. Collectively, the stamens form the androecium., p. 10
Morphology and terminology
A stamen typically consists of a stalk called the filamen ...
on opening, then shed the exhausted anthers after a day or two and perhaps change their colours as well while the pistil
Gynoecium (; ; : gynoecia) is most commonly used as a collective term for the parts of a flower that produce ovules and ultimately develop into the fruit and seeds. The gynoecium is the innermost whorl (botany), whorl of a flower; it consists ...
matures; specialist pollinators are very much inclined to concentrate on the exact appearance of the flowers they serve, which saves their time and effort and serves the interests of the plant accordingly. Some such plants go even further and change their appearance once fertilized, thereby discouraging further visits from pollinators. This is advantageous to both parties because it avoids damaging the developing fruit and wasting the pollinator's effort on unrewarding visits. In effect, the strategy ensures that pollinators can expect a reward every time they visit an appropriately advertising flower.
Females of the aquatic plant ''Vallisneria americana
''Vallisneria americana'', commonly called wild celery, water-celery, tape grass, or eelgrass, is a plant in the family Hydrocharitaceae, the "tape-grasses". ''V. americana'' is a fresh water species that can tolerate salt, living in salinitie ...
'' have floating flowers attached by a long flower stalk that are fertilized if they contact one of the thousands of free-floating flowers released by a male. Sexual dimorphism is most often associated with wind-pollination in plants due to selection for efficient pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
dispersal in males vs pollen capture in females, e.g. ''Leucadendron rubrum''.
Sexual dimorphism in plants can also be dependent on reproductive development. This can be seen in ''Cannabis sativa
''Cannabis sativa'' is an annual Herbaceous plant, herbaceous flowering plant. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The specific epithet ''Sativum, sativa'' means 'cultivated'. Indigenous to East Asia, Eastern Asia, the pla ...
'', a type of hemp, which have higher photosynthesis rates in males while growing but higher rates in females once the plants become sexually mature. p. 206
Every sexually reproducing extant species of the vascular plant has an alternation of generations; the plants we see about us generally are diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, ...
sporophyte
A sporophyte () is one of the two alternation of generations, alternating multicellular organism, multicellular phases in the biological life cycle, life cycles of plants and algae. It is a diploid multicellular organism which produces asexual Spo ...
s, but their offspring are not the seeds that people commonly recognize as the new generation. The seed actually is the offspring of the haploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell (biology), cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for Autosome, autosomal and Pseudoautosomal region, pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the num ...
generation of microgametophytes (pollen
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains (highly reduced Gametophyte#Heterospory, microgametophytes), which produce male gametes (sperm ...
) and megagametophytes (the embryo sac
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the fe ...
s in the ovules
In seed plants, the ovule is the structure that gives rise to and contains the female reproductive cells. It consists of three parts: the ''integument'', forming its outer layer, the ''nucellus'' (or remnant of the megasporangium), and the fe ...
). Each pollen grain accordingly may be seen as a male plant in its own right; it produces a sperm cell and is dramatically different from the female plant, the megagametophyte that produces the female gamete.
Insects
 Insects display a wide variety of sexual dimorphism between taxa including size, ornamentation and coloration. The female-biased sexual size dimorphism observed in many taxa evolved despite intense male-male competition for mates. In ''
Insects display a wide variety of sexual dimorphism between taxa including size, ornamentation and coloration. The female-biased sexual size dimorphism observed in many taxa evolved despite intense male-male competition for mates. In ''Osmia rufa
''Osmia bicornis'' (synonym ''Osmia rufa'') is a species of mason bee, and is known as the red mason bee due to its covering of dense gingery hair.hackberry emperor females are similarly larger than males. The reason for the sexual dimorphism is due to provision size mass, in which females consume more pollen than males.
In some species, there is evidence of male dimorphism, but it appears to be for distinctions of roles. This is seen in the bee species ''
Macrotera portalis
''Macrotera portalis'' is a species of communal, ground nesting, partially bivoltine bees found in arid grasslands and desert regions of North America. An oligolectic bee, ''M. portalis'' gathers pollen only from plants in the genus ''Sphaeralcea ...
'' in which there is a small-headed morph, capable of flight, and large-headed morph, incapable of flight, for males. ''Anthidium manicatum
''Anthidium manicatum'', commonly called the European wool carder bee, is a species of bee in the family Megachilidae, the leaf-cutter bees or mason bees.
They get the name "carding, carder" from their behaviour of scraping hair from leaves such ...
'' also displays male-biased sexual dimorphism. The selection for larger size in males rather than females in this species may have resulted due to their aggressive territorial behavior and subsequent differential mating success. Another example is ''Lasioglossum hemichalceum
''Lasioglossum hemichalceum'', which has sometimes been confused with '' L. erythrurum,'' is a sweat bee endemic to Australia. Large numbers of unrelated females will typically share a single nest, a behavior referred to as "communal". Nests are ...
'', which is a species of sweat bee that shows drastic physical dimorphisms between male offspring. Not all dimorphism has to have a drastic difference between the sexes. ''Andrena agilissima
''Andrena agilissima'' is a species of mining bee. They are present in most of Europe, the Near East and North Africa and can be found from April through July. ''Andrena agilissima'' is an ''Oligolecty, oligolectic'' species, feeding only on the ...
'' is a mining bee where the females only have a slightly larger head than the males.
Weaponry leads to increased fitness by increasing success in male–male competition in many insect species. The beetle horns in '' Onthophagus taurus'' are enlarged growths of the head or thorax expressed only in the males. ''Copris ochus'' also has distinct sexual and male dimorphism in head horns. Another beetle with a distinct horn-related sexual dimorphism is ''Allomyrina dichotoma,'' also known as the Japanese rhinoceros beetle. These structures are impressive because of the exaggerated sizes. There is a direct correlation between male horn lengths and body size and higher access to mates and fitness. In other beetle species, both males and females may have ornamentation such as horns.
Generally, insect sexual size dimorphism (SSD) within species increases with body size.
Sexual dimorphism within insects is also displayed by dichromatism. In butterfly genera ''Bicyclus
''Bicyclus'' is a butterfly genus from the subfamily Satyrinae in the family Nymphalidae. The species are found in the Afrotropical realm.
Species
*''Bicyclus abnormis'' (Dudgeon, 1909)
*''Bicyclus albocincta'' (Rebel, 1914)
*''Bicyclus alboplag ...
'' and ''Junonia
''Junonia'' is a genus of nymphalid butterflies, described by Jacob Hübner in 1819. They are commonly known as buckeyes, pansies or commodores. This genus flies on every continent except Antarctica and Europe. The genus contains roughly 30 to 3 ...
'', dimorphic wing patterns evolved due to sex-limited expression, which mediates the intralocus sexual conflict Intralocus sexual conflict is a type of sexual conflict that occurs when a genetic locus harbours alleles which have opposing effects on the fitness of each sex, such that one allele improves the fitness of males (at the expense of females), whil ...
and leads to increased fitness in males. The sexual dichromatic nature of ''Bicyclus anynana
''Bicyclus anynana'' (squinting bush brown) is a small brown butterfly in the family Nymphalidae, the most globally diverse family of butterflies. It is primarily found in eastern Africa from southern Sudan to Swaziland, Eswatini.common brimstone also displays sexual dichromatism; males have yellow and iridescent wings, while female wings are white and non-iridescent. Naturally selected deviation in protective female coloration is displayed in mimetic butterflies.
 Many
Many
 Possible mechanisms have been proposed to explain macroevolution of sexual size dimorphism in birds. These include sexual selection, selection for fecundity in females, niche divergence between the sexes, and allometry, but their relative importance is still not fully understood . Sexual dimorphism in birds can be manifested in size or plumage differences between the sexes. Sexual size dimorphism varies among taxa, with males typically being larger, though this is not always the case, e.g.
Possible mechanisms have been proposed to explain macroevolution of sexual size dimorphism in birds. These include sexual selection, selection for fecundity in females, niche divergence between the sexes, and allometry, but their relative importance is still not fully understood . Sexual dimorphism in birds can be manifested in size or plumage differences between the sexes. Sexual size dimorphism varies among taxa, with males typically being larger, though this is not always the case, e.g.  Migratory patterns and behaviors also influence sexual dimorphisms. This aspect also stems back to size dimorphism in species. It has been shown that the larger males are better at coping with the difficulties of migration and thus are more successful in reproducing when reaching the breeding destination. When viewing this from an evolutionary standpoint, many theories and explanations come into consideration. If these are the result for every migration and breeding season, the expected results should be a shift towards a larger male population through sexual selection. Sexual selection is strong when the factor of environmental selection is also introduced. Environmental selection may support a smaller chick size if those chicks were born in an area that allowed them to grow to a larger size, even though under normal conditions they would not be able to reach this optimal size for migration. When the environment gives advantages and disadvantages of this sort, the strength of selection is weakened and the environmental forces are given greater morphological weight. The sexual dimorphism could also produce a change in timing of migration leading to differences in mating success within the bird population. When the dimorphism produces that large of a variation between the sexes and between the members of the sexes, multiple evolutionary effects can take place. This timing could even lead to a speciation phenomenon if the variation becomes strongly drastic and favorable towards two different outcomes. Sexual dimorphism is maintained by the counteracting pressures of natural selection and sexual selection. For example, sexual dimorphism in coloration increases the vulnerability of bird species to predation by European sparrowhawks in Denmark. Presumably, increased sexual dimorphism means males are brighter and more conspicuous, leading to increased predation. Moreover, the production of more exaggerated ornaments in males may come at the cost of suppressed immune function. So long as the reproductive benefits of the trait due to sexual selection are greater than the costs imposed by natural selection, then the trait will propagate throughout the population. Reproductive benefits arise in the form of a larger number of offspring, while natural selection imposes costs in the form of reduced survival. This means that even if the trait causes males to die earlier, the trait is still beneficial so long as males with the trait produce more offspring than males lacking the trait. This balance keeps dimorphism alive in these species and ensures that the next generation of successful males will also display these traits that are attractive to females.
Such differences in form and reproductive roles often cause differences in behavior. As previously stated, males and females often have different roles in reproduction. The courtship and mating behavior of males and females are regulated largely by hormones throughout a bird's lifetime. Activational hormones occur during puberty and adulthood and serve to 'activate' certain behaviors when appropriate, such as territoriality during breeding season. Organizational hormones occur only during a critical period early in development, either just before or just after hatching in most birds, and determine patterns of behavior for the rest of the bird's life. Such behavioral differences can cause disproportionate sensitivities to anthropogenic pressures. Females of the whinchat in Switzerland breed in intensely managed grasslands. Earlier harvesting of the grasses during the breeding season lead to more female deaths. Populations of many birds are often male-skewed and when sexual differences in behavior increase this ratio, populations decline at a more rapid rate. Also not all male dimorphic traits are due to hormones like testosterone, instead they are a naturally occurring part of development, for example plumage. In addition, the strong hormonal influence on phenotypic differences suggests that the genetic mechanism and genetic basis of these sexually dimorphic traits may involve transcription factors or cofactors rather than regulatory sequences.
Migratory patterns and behaviors also influence sexual dimorphisms. This aspect also stems back to size dimorphism in species. It has been shown that the larger males are better at coping with the difficulties of migration and thus are more successful in reproducing when reaching the breeding destination. When viewing this from an evolutionary standpoint, many theories and explanations come into consideration. If these are the result for every migration and breeding season, the expected results should be a shift towards a larger male population through sexual selection. Sexual selection is strong when the factor of environmental selection is also introduced. Environmental selection may support a smaller chick size if those chicks were born in an area that allowed them to grow to a larger size, even though under normal conditions they would not be able to reach this optimal size for migration. When the environment gives advantages and disadvantages of this sort, the strength of selection is weakened and the environmental forces are given greater morphological weight. The sexual dimorphism could also produce a change in timing of migration leading to differences in mating success within the bird population. When the dimorphism produces that large of a variation between the sexes and between the members of the sexes, multiple evolutionary effects can take place. This timing could even lead to a speciation phenomenon if the variation becomes strongly drastic and favorable towards two different outcomes. Sexual dimorphism is maintained by the counteracting pressures of natural selection and sexual selection. For example, sexual dimorphism in coloration increases the vulnerability of bird species to predation by European sparrowhawks in Denmark. Presumably, increased sexual dimorphism means males are brighter and more conspicuous, leading to increased predation. Moreover, the production of more exaggerated ornaments in males may come at the cost of suppressed immune function. So long as the reproductive benefits of the trait due to sexual selection are greater than the costs imposed by natural selection, then the trait will propagate throughout the population. Reproductive benefits arise in the form of a larger number of offspring, while natural selection imposes costs in the form of reduced survival. This means that even if the trait causes males to die earlier, the trait is still beneficial so long as males with the trait produce more offspring than males lacking the trait. This balance keeps dimorphism alive in these species and ensures that the next generation of successful males will also display these traits that are attractive to females.
Such differences in form and reproductive roles often cause differences in behavior. As previously stated, males and females often have different roles in reproduction. The courtship and mating behavior of males and females are regulated largely by hormones throughout a bird's lifetime. Activational hormones occur during puberty and adulthood and serve to 'activate' certain behaviors when appropriate, such as territoriality during breeding season. Organizational hormones occur only during a critical period early in development, either just before or just after hatching in most birds, and determine patterns of behavior for the rest of the bird's life. Such behavioral differences can cause disproportionate sensitivities to anthropogenic pressures. Females of the whinchat in Switzerland breed in intensely managed grasslands. Earlier harvesting of the grasses during the breeding season lead to more female deaths. Populations of many birds are often male-skewed and when sexual differences in behavior increase this ratio, populations decline at a more rapid rate. Also not all male dimorphic traits are due to hormones like testosterone, instead they are a naturally occurring part of development, for example plumage. In addition, the strong hormonal influence on phenotypic differences suggests that the genetic mechanism and genetic basis of these sexually dimorphic traits may involve transcription factors or cofactors rather than regulatory sequences.
 Sexual dimorphism may also influence differences in parental investment during times of food scarcity. For example, in the
Sexual dimorphism may also influence differences in parental investment during times of food scarcity. For example, in the
 Marine mammals show some of the greatest sexual size differences of mammals, because of sexual selection and environmental factors like breeding location. The mating system of pinnipeds varies from polygamy to serial monogamy. Pinnipeds are known for early differential growth and maternal investment since the only nutrients for newborn pups is the milk provided by the mother. For example, the males are significantly larger (about 10% heavier and 2% longer) than the females at birth in sea lion pups. The pattern of differential investment can be varied principally prenatally and post-natally. ''Mirounga leonina'', the southern elephant seal, is one of the most dimorphic mammals.
Marine mammals show some of the greatest sexual size differences of mammals, because of sexual selection and environmental factors like breeding location. The mating system of pinnipeds varies from polygamy to serial monogamy. Pinnipeds are known for early differential growth and maternal investment since the only nutrients for newborn pups is the milk provided by the mother. For example, the males are significantly larger (about 10% heavier and 2% longer) than the females at birth in sea lion pups. The pattern of differential investment can be varied principally prenatally and post-natally. ''Mirounga leonina'', the southern elephant seal, is one of the most dimorphic mammals.
 These traits could be ones that allow him to fight off other males for control of territory or a Harem (zoology), harem, such as large size or weapons; or they could be traits that females, for whatever reason, prefer in mates. Male–male competition poses no deep theoretical questions but mate choice does.
Females may choose males that appear strong and healthy, thus likely to possess "good alleles" and give rise to healthy offspring. In some species, however, females seem to choose males with traits that do not improve offspring survival rates, and even traits that reduce it (potentially leading to traits like the peacock's tail). Two hypotheses for explaining this fact are the
These traits could be ones that allow him to fight off other males for control of territory or a Harem (zoology), harem, such as large size or weapons; or they could be traits that females, for whatever reason, prefer in mates. Male–male competition poses no deep theoretical questions but mate choice does.
Females may choose males that appear strong and healthy, thus likely to possess "good alleles" and give rise to healthy offspring. In some species, however, females seem to choose males with traits that do not improve offspring survival rates, and even traits that reduce it (potentially leading to traits like the peacock's tail). Two hypotheses for explaining this fact are the
Spiders and sexual cannibalism
 Many
Many arachnid
Arachnids are arthropods in the Class (biology), class Arachnida () of the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, opiliones, harvestmen, Solifugae, camel spiders, Amblypygi, wh ...
groups exhibit sexual dimorphism, but it is most widely studied in the spiders. In the orb-weaving spider ''Zygiella x-notata
''Zygiella x-notata'', sometimes known as the missing sector orb weaver or the silver-sided sector spider,Factsheet 6: Missing-sector Orbweaver (Zygiella x-notata)', British Arachnological Society, 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2016 is a spider sp ...
'', for example, adult females have a larger body size than adult males. Size dimorphism shows a correlation with sexual cannibalism
Sexual cannibalism is when an animal, usually the female, Cannibalism, cannibalizes its mate prior to, during, or after Copulation (zoology), copulation. This trait is observed in many arachnid orders, several insect and crustacean clades, Gastro ...
, which is prominent in spiders (it is also found in insects such as praying mantis
Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate ...
es). In the size dimorphic wolf spider
Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae (), named for their robust and agile hunting skills and excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude, hunt alone, and usually do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters, pouncing upon ...
'' Tigrosa helluo'', food-limited females cannibalize more frequently. Therefore, there is a high risk of low fitness for males due to pre-copulatory cannibalism, which led to male selection of larger females for two reasons: higher fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the capability to produc ...
and lower rates of cannibalism. In addition, female fecundity is positively correlated with female body size and large female body size is selected for, which is seen in the family Araneidae
Orb-weaver spiders are members of the spider family Araneidae. They are the most common group of builders of spiral wheel-shaped webs often found in gardens, fields, and forests. The English word "orb" can mean "circular", hence the English name ...
. All ''Argiope'' species, including ''Argiope bruennichi
''Argiope bruennichi'', commonly known as the wasp spider, is a species of orb-weaver spider found across Central and Northern Europe, several regions of Asia and Africa and the Azores. Like many other members of the same genus '' Argiope'', th ...
'', use this method. Some males evolved ornamentation including binding the female with silk, having proportionally longer legs, modifying the female's web, mating while the female is feeding, or providing a nuptial gift in response to sexual cannibalism. Male body size is not under selection due to cannibalism in all spider species such as ''Nephila pilipes
''Nephila pilipes'' (northern golden orb weaver or giant golden orb weaver''Nephila pilipes''
Ar ...
'', but is more prominently selected for in less dimorphic species of spiders, which often selects for larger male size. In the species ''Ar ...
Maratus volans
''Maratus volans'' is a species in the jumping spider family (Salticidae), belonging to the genus ''Maratus'' (peacock spiders). These spiders are native to certain areas in Australia and occupy a wide distribution of habitats. They have a specia ...
'', the males are known for their characteristic colorful fan which attracts the females during mating.
Fish
Ray-finned fish are an ancient and diverse class, with the widest degree of sexual dimorphism of any animal class. Fairbairn notes that "females are generally larger than males but males are often larger in species with male–male combat or male paternal care ... izes rangefrom dwarf males to males more than 12 times heavier than females." There are cases where males are substantially larger than females. An example is '' Lamprologus callipterus'', a type of cichlid fish. In this fish, the males are characterized as being up to 60 times larger than the females. The male's increased size is believed to be advantageous because males collect and defend empty snail shells in each of which a female breeds. Males must be larger and more powerful in order to collect the largest shells. The female's body size must remain small because in order for her to breed, she must lay her eggs inside the empty shells. If she grows too large, she will not fit in the shells and will be unable to breed. The female's small body size is also likely beneficial to her chances of finding an unoccupied shell. Larger shells, although preferred by females, are often limited in availability. Hence, the female is limited to the growth of the size of the shell and may actually change her growth rate according to shell size availability. In other words, the male's ability to collect large shells depends on his size. The larger the male, the larger the shells he is able to collect. This then allows for females to be larger in his brooding nest which makes the difference between the sizes of the sexes less substantial. Male–male competition in this fish species also selects for large size in males. There is aggressive competition by males over territory and access to larger shells. Large males win fights and steal shells from competitors. Another example is thedragonet
Dragonets are small Percomorpha, percomorph marine fish of the diverse family Callionymidae (from the Greek language, Greek ''kallis'', "beautiful" and ', "name") found mainly in the tropical waters of the western Indo-Pacific. They are Benthos, ...
, in which males are considerably larger than females and possess longer fins.
Sexual dimorphism also occurs in hermaphroditic fish. These species are known as sequential hermaphrodites
Sequential hermaphroditism (called dichogamy in botany) is one of the two types of hermaphroditism, the other type being simultaneous hermaphroditism. It occurs when the organism's sex changes at some point in its life. A sequential hermaphrodite ...
. In fish, reproductive histories often include the sex-change from female to male where there is a strong connection between growth, the sex of an individual, and the mating system within which it operates. In protogynous mating systems where males dominate mating with many females, size plays a significant role in male reproductive success. Males have a propensity to be larger than females of a comparable age but it is unclear whether the size increase is due to a growth spurt at the time of the sexual transition or due to the history of faster growth in sex changing individuals. Larger males are able to stifle the growth of females and control environmental resources.
Social organization plays a large role in the changing of sex by the fish. It is often seen that a fish will change its sex when there is a lack of a dominant male within the social hierarchy. The females that change sex are often those who attain and preserve an initial size advantage early in life. In either case, females which change sex to males are larger and often prove to be a good example of dimorphism.
In other cases with fish, males will go through noticeable changes in body size, and females will go through morphological changes that can only be seen inside of the body. For example, in sockeye salmon
The sockeye salmon (''Oncorhynchus nerka''), also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, blueback salmon, or simply sockeye, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a ...
, males develop larger body size at maturity, including an increase in body depth, hump height, and snout length. Females experience minor changes in snout length, but the most noticeable difference is the huge increase in gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a Heterocrine gland, mixed gland and sex organ that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gon ...
size, which accounts for about 25% of body mass.
Sexual selection was observed for female ornamentation in ''Gobiusculus flavescens
The two-spotted goby (''Pomatoschistus flavescens'') is a species of goby native to marine and brackish waters of the eastern Atlantic Ocean where it can be found from the Faeroes and Norway to the northwestern coast of Spain. It has also been ...
'', known as two-spotted gobies. Traditional hypotheses suggest that male–male competition drives selection. However, selection for ornamentation within this species suggests that showy female traits can be selected through either female–female competition or male mate choice. Since carotenoid-based ornamentation suggests mate quality, female two-spotted guppies that develop colorful orange bellies during breeding season are considered favorable to males. The males invest heavily in offspring during incubation, which leads to the sexual preference in colorful females due to higher egg quality.
Amphibians and non-avian reptiles
In amphibians and reptiles, the degree of sexual dimorphism varies widely among taxonomic groups. The sexual dimorphism in amphibians and reptiles may be reflected in any of the following: anatomy; relative length of tail; relative size of head; overall size as in many species ofvipers
Vipers are snakes in the family Viperidae, found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, New Zealand, Ireland, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-viper ...
and lizards
Lizard is the common name used for all squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The ...
; coloration as in many amphibians
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
, snakes
Snakes are elongated Limbless vertebrate, limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales much like other members of ...
, and lizards, as well as in some turtles
Turtles are reptiles of the order Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked turtle ...
; an ornament as in many newts
A newt is a salamander in the subfamily Pleurodelinae. The terrestrial juvenile phase is called an eft. Unlike other members of the family Salamandridae, newts are semiaquatic, alternating between aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Not all aqua ...
and lizards; the presence of specific sex-related behaviour is common to many lizards; and vocal qualities which are frequently observed in frogs
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely semiaquatic group of short-bodied, tailless amphibian vertebrates composing the order Anura (coming from the Ancient Greek , literally 'without tail'). Frog species with rough skin texture due to ...
.
Anole
Dactyloidae are a family of lizards commonly known as anoles (singular anole ) and native to warmer parts of the Americas, ranging from southeastern United States to Paraguay. Instead of treating it as a family, some authorities prefer to treat ...
lizards show prominent size dimorphism with males typically being significantly larger than females. For instance, the average male ''Anolis sagrei
The brown anole (''Anolis sagrei''), also known commonly as the Cuban brown anole, Bahaman anole, or De la Sagra's anole, is a species of lizard in the family Dactyloidae. The species is native to Cuba, the Bahamas, Little Cayman, Cayman Brac, J ...
'' was 53.4 mm vs. 40 mm in females. Different sizes of the heads in anoles have been explained by differences in the estrogen pathway. The sexual dimorphism in lizards is generally attributed to the effects of sexual selection, but other mechanisms including ecological divergence and fecundity selection provide alternative explanations.Pinto, A., Wiederhecker, H., & Colli, G. (2005). Sexual dimorphism in the Neotropical lizard, Tropidurus torquatus (Squamata, Tropiduridae). Amphibia-Reptilia. The development of color dimorphism in lizards is induced by hormonal changes at the onset of sexual maturity, as seen in ''Psamodromus algirus'', ''Sceloporus gadoviae'', and ''S. undulates erythrocheilus''. Sexual dimorphism in size is also seen in frog species like '' P. bibroniaging
Ageing (or aging in American English) is the process of becoming Old age, older until death. The term refers mainly to humans, many other animals, and fungi; whereas for example, bacteria, perennial plants and some simple animals are potentiall ...
. Male coloration appears to reflect innate anti-oxidation capacity that protects against oxidative DNA damage. Male breeding coloration is likely an indicator to females of the underlying level of oxidative DNA damage (a significant component of aging) in potential mates.
Birds
 Possible mechanisms have been proposed to explain macroevolution of sexual size dimorphism in birds. These include sexual selection, selection for fecundity in females, niche divergence between the sexes, and allometry, but their relative importance is still not fully understood . Sexual dimorphism in birds can be manifested in size or plumage differences between the sexes. Sexual size dimorphism varies among taxa, with males typically being larger, though this is not always the case, e.g.
Possible mechanisms have been proposed to explain macroevolution of sexual size dimorphism in birds. These include sexual selection, selection for fecundity in females, niche divergence between the sexes, and allometry, but their relative importance is still not fully understood . Sexual dimorphism in birds can be manifested in size or plumage differences between the sexes. Sexual size dimorphism varies among taxa, with males typically being larger, though this is not always the case, e.g. birds of prey
Birds of prey or predatory birds, also known as (although not the same as) raptors, are hypercarnivorous bird species that actively predation, hunt and feed on other vertebrates (mainly mammals, reptiles and smaller birds). In addition to speed ...
, hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Cen ...
s, and some species of flightless birds. Plumage dimorphism, in the form of ornamentation or coloration, also varies, though males are typically the more ornamented or brightly colored sex. Such differences have been attributed to the unequal reproductive contributions of the sexes. This difference produces a stronger female choice since they have more risk in producing offspring. In some species, the male's contribution to reproduction ends at copulation, while in other species the male becomes the main (or only) caregiver. Plumage polymorphisms have evolved to reflect these differences and other measures of reproductive fitness, such as body condition or survival. The male phenotype sends signals to females who then choose the 'fittest' available male.
Sexual dimorphism is a product of both genetics and environmental factors. An example of sexual polymorphism determined by environmental conditions exists in the red-backed fairywren
The red-backed fairywren (''Malurus melanocephalus'') is a species of passerine bird in the Australasian wren family, Maluridae. It is Endemism, endemic to Australia and can be found near rivers and coastal areas along the northern and eastern ...
. Red-backed fairywren males can be classified into three categories during breeding season
Seasonal breeders are animal species that successfully mate only during certain times of the year. These times of year allow for the optimization of survival of young due to factors such as ambient temperature, food and water availability, and ch ...
: black breeders, brown breeders, and brown auxiliaries. These differences arise in response to the bird's body condition: if they are healthy they will produce more androgens thus becoming black breeders, while less healthy birds produce less androgens and become brown auxiliaries. The reproductive success
Reproductive success is an individual's production of offspring per breeding event or lifetime. This is not limited by the number of offspring produced by one individual, but also the reproductive success of these offspring themselves.
Reproduct ...
of the male is thus determined by his success during each year's non-breeding season, causing reproductive success to vary with each year's environmental conditions.
 Migratory patterns and behaviors also influence sexual dimorphisms. This aspect also stems back to size dimorphism in species. It has been shown that the larger males are better at coping with the difficulties of migration and thus are more successful in reproducing when reaching the breeding destination. When viewing this from an evolutionary standpoint, many theories and explanations come into consideration. If these are the result for every migration and breeding season, the expected results should be a shift towards a larger male population through sexual selection. Sexual selection is strong when the factor of environmental selection is also introduced. Environmental selection may support a smaller chick size if those chicks were born in an area that allowed them to grow to a larger size, even though under normal conditions they would not be able to reach this optimal size for migration. When the environment gives advantages and disadvantages of this sort, the strength of selection is weakened and the environmental forces are given greater morphological weight. The sexual dimorphism could also produce a change in timing of migration leading to differences in mating success within the bird population. When the dimorphism produces that large of a variation between the sexes and between the members of the sexes, multiple evolutionary effects can take place. This timing could even lead to a speciation phenomenon if the variation becomes strongly drastic and favorable towards two different outcomes. Sexual dimorphism is maintained by the counteracting pressures of natural selection and sexual selection. For example, sexual dimorphism in coloration increases the vulnerability of bird species to predation by European sparrowhawks in Denmark. Presumably, increased sexual dimorphism means males are brighter and more conspicuous, leading to increased predation. Moreover, the production of more exaggerated ornaments in males may come at the cost of suppressed immune function. So long as the reproductive benefits of the trait due to sexual selection are greater than the costs imposed by natural selection, then the trait will propagate throughout the population. Reproductive benefits arise in the form of a larger number of offspring, while natural selection imposes costs in the form of reduced survival. This means that even if the trait causes males to die earlier, the trait is still beneficial so long as males with the trait produce more offspring than males lacking the trait. This balance keeps dimorphism alive in these species and ensures that the next generation of successful males will also display these traits that are attractive to females.
Such differences in form and reproductive roles often cause differences in behavior. As previously stated, males and females often have different roles in reproduction. The courtship and mating behavior of males and females are regulated largely by hormones throughout a bird's lifetime. Activational hormones occur during puberty and adulthood and serve to 'activate' certain behaviors when appropriate, such as territoriality during breeding season. Organizational hormones occur only during a critical period early in development, either just before or just after hatching in most birds, and determine patterns of behavior for the rest of the bird's life. Such behavioral differences can cause disproportionate sensitivities to anthropogenic pressures. Females of the whinchat in Switzerland breed in intensely managed grasslands. Earlier harvesting of the grasses during the breeding season lead to more female deaths. Populations of many birds are often male-skewed and when sexual differences in behavior increase this ratio, populations decline at a more rapid rate. Also not all male dimorphic traits are due to hormones like testosterone, instead they are a naturally occurring part of development, for example plumage. In addition, the strong hormonal influence on phenotypic differences suggests that the genetic mechanism and genetic basis of these sexually dimorphic traits may involve transcription factors or cofactors rather than regulatory sequences.
Migratory patterns and behaviors also influence sexual dimorphisms. This aspect also stems back to size dimorphism in species. It has been shown that the larger males are better at coping with the difficulties of migration and thus are more successful in reproducing when reaching the breeding destination. When viewing this from an evolutionary standpoint, many theories and explanations come into consideration. If these are the result for every migration and breeding season, the expected results should be a shift towards a larger male population through sexual selection. Sexual selection is strong when the factor of environmental selection is also introduced. Environmental selection may support a smaller chick size if those chicks were born in an area that allowed them to grow to a larger size, even though under normal conditions they would not be able to reach this optimal size for migration. When the environment gives advantages and disadvantages of this sort, the strength of selection is weakened and the environmental forces are given greater morphological weight. The sexual dimorphism could also produce a change in timing of migration leading to differences in mating success within the bird population. When the dimorphism produces that large of a variation between the sexes and between the members of the sexes, multiple evolutionary effects can take place. This timing could even lead to a speciation phenomenon if the variation becomes strongly drastic and favorable towards two different outcomes. Sexual dimorphism is maintained by the counteracting pressures of natural selection and sexual selection. For example, sexual dimorphism in coloration increases the vulnerability of bird species to predation by European sparrowhawks in Denmark. Presumably, increased sexual dimorphism means males are brighter and more conspicuous, leading to increased predation. Moreover, the production of more exaggerated ornaments in males may come at the cost of suppressed immune function. So long as the reproductive benefits of the trait due to sexual selection are greater than the costs imposed by natural selection, then the trait will propagate throughout the population. Reproductive benefits arise in the form of a larger number of offspring, while natural selection imposes costs in the form of reduced survival. This means that even if the trait causes males to die earlier, the trait is still beneficial so long as males with the trait produce more offspring than males lacking the trait. This balance keeps dimorphism alive in these species and ensures that the next generation of successful males will also display these traits that are attractive to females.
Such differences in form and reproductive roles often cause differences in behavior. As previously stated, males and females often have different roles in reproduction. The courtship and mating behavior of males and females are regulated largely by hormones throughout a bird's lifetime. Activational hormones occur during puberty and adulthood and serve to 'activate' certain behaviors when appropriate, such as territoriality during breeding season. Organizational hormones occur only during a critical period early in development, either just before or just after hatching in most birds, and determine patterns of behavior for the rest of the bird's life. Such behavioral differences can cause disproportionate sensitivities to anthropogenic pressures. Females of the whinchat in Switzerland breed in intensely managed grasslands. Earlier harvesting of the grasses during the breeding season lead to more female deaths. Populations of many birds are often male-skewed and when sexual differences in behavior increase this ratio, populations decline at a more rapid rate. Also not all male dimorphic traits are due to hormones like testosterone, instead they are a naturally occurring part of development, for example plumage. In addition, the strong hormonal influence on phenotypic differences suggests that the genetic mechanism and genetic basis of these sexually dimorphic traits may involve transcription factors or cofactors rather than regulatory sequences.
 Sexual dimorphism may also influence differences in parental investment during times of food scarcity. For example, in the
Sexual dimorphism may also influence differences in parental investment during times of food scarcity. For example, in the blue-footed booby
The blue-footed booby (''Sula nebouxii'') is a marine bird native to subtropical and tropical regions of the eastern Pacific Ocean. It is one of six species of the genus ''booby, Sula'' – known as boobies. It is easily recognizable by its dis ...
, the female chicks grow faster than the males, resulting in booby parents producing the smaller sex, the males, during times of food shortage. This then results in the maximization of parental lifetime reproductive success. In Black-tailed Godwits ''Limosa limosa limosa'' females are also the larger sex, and the growth rates of female chicks are more susceptible to limited environmental conditions.
Sexual dimorphism may also only appear during mating season; some species of birds only show dimorphic traits in seasonal variation. The males of these species will molt into a less bright or less exaggerated color during the off-breeding season. This occurs because the species is more focused on survival than on reproduction, causing a shift into a less ornate state.
Consequently, sexual dimorphism has important ramifications for conservation. However, sexual dimorphism is not only found in birds and is thus important to the conservation of many animals. Such differences in form and behavior can lead to sexual segregation, defined as sex differences in space and resource use. Most sexual segregation research has been done on ungulates, but such research extends to bat
Bats are flying mammals of the order Chiroptera (). With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most birds, flying with their very long spread-out ...
s, kangaroo
Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use, the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern gre ...
s, and birds. Sex-specific conservation plans have even been suggested for species with pronounced sexual segregation.
The term sesquimorphism (the Latin numeral prefix
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
*triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon, hexagon, octagon ...
''sesqui''- means one-and-one-half, so halfway between ''mono''- (one) and ''di''- (two)) has been proposed for bird species in which "both sexes have basically the same plumage pattern, though the female is clearly distinguishable by reason of her paler or washed-out Examples include Cape sparrow
The Cape sparrow (''Passer melanurus''), or mossie, is a bird of the Old World sparrow, sparrow family (biology), family Passeridae found in southern Africa. A medium-sized sparrow at , it has distinctive plumage, including large pale head stri ...
(''Passer melanurus''), rufous sparrow (subspecies ''P. motinensis motinensis''), and saxaul sparrow
The saxaul sparrow (''Passer ammodendri'') is a passerine bird of the Old World sparrow, sparrow family (biology), family Passeridae, found in parts of Central Asia. At and , it is among the larger sparrows. Both sexes have plumage ranging from ...
(''P. ammodendri'').
Non-avian dinosaurs
Examining fossils of non-avian dinosaurs in search of sexually dimorphic characteristics requires the supply of complete and articulated skeletal and tissue remains. As terrestrial organisms, dinosaur carcasses are subject to ecological and geographical influence that inevitably constitutes the degree of preservation. The availability of well-preserved remains is not a probable outcome as a consequence ofdecomposition
Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is ess ...
and fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
ization. Some paleontologists
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
have looked for sexual dimorphism among dinosaurs using statistics and comparison to ecologically or phylogenetically
In biology, phylogenetics () is the study of the evolutionary history of life using observable characteristics of organisms (or genes), which is known as phylogenetic inference. It infers the relationship among organisms based on empirical data ...
related modern animals.
Apatosaurus and Diplodocus
Female ''Apatosaurus
''Apatosaurus'' (; meaning "deceptive lizard") is a genus of herbivorous sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. Othniel Charles Marsh described and named the first-known species, ''A. ajax'', in 1877, a ...
'' and ''Diplodocus
''Diplodocus'' (, , or ) is an extinct genus of diplodocid sauropod dinosaurs known from the Late Jurassic of North America. The first fossils of ''Diplodocus'' were discovered in 1877 by S. W. Williston. The generic name, coined by Othnie ...
'' had interconnected caudal vertebrae
Caudal vertebrae are the vertebrae of the tail in many vertebrates. In birds, the last few caudal vertebrae fuse into the pygostyle, and in apes, including humans, the caudal vertebrae are fused into the coccyx.
In many reptiles, some of the caud ...
that allowed them to keep their tails elevated to aid in copulation. Discovering that this fusion occurred in only 50% of ''Apatosaurus'' and ''Diplodocus'' skeletons and 25% of ''Camarasaurus
''Camarasaurus'' ( ) is a genus of sauropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Jurassic period. Its fossil remains have been found in the Morrison Formation, dating to the Kimmeridgian and Tithonian ages of the Jurassic, betwe ...
'' skeletons indicated that this is a sexually dimorphic trait.
Theropoda
It has been hypothesized that male theropods
Theropoda (; from ancient Greek , (''therion'') "wild beast"; , (''pous, podos'') "foot"">wiktionary:ποδός"> (''pous, podos'') "foot" is one of the three major groups (clades) of dinosaurs, alongside Ornithischia and Sauropodom ...
possessed a retractable penis, a feature similar to modern day crocodilia
Crocodilia () is an order of semiaquatic, predatory reptiles that are known as crocodilians. They first appeared during the Late Cretaceous and are the closest living relatives of birds. Crocodilians are a type of crocodylomorph pseudosuchia ...
ns. Crocodilian skeletons were examined to determine whether there is a skeletal component that is distinctive between both sexes, to help provide an insight on the physical disparities between male and female theropods. Findings revealed the caudal chevrons
Chevron (often relating to V-shaped patterns) may refer to:
Science and technology
* Chevron (aerospace), sawtooth patterns on some jet engines
* Chevron (anatomy), a bone
* '' Eulithis testata'', a moth
* Chevron (geology), a fold in rock la ...
of male crocodiles, used to anchor the penis muscles, were significantly larger than those of females. There have been criticisms of these findings, but it remains a subject of debate among advocates and adversaries.
Ornithopoda
Studies of sexual dimorphism in hadrosaurs
Hadrosaurids (), also hadrosaurs or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod fami ...
have generally centered on the distinctive cranial crests, which likely provided a function in sexual display. A biometric study of 36 skulls found sexual dimorphism was exhibited in the crest of 3 species of hadrosaurids. The crests could be categorized as full (male) or narrow (female) and may have given some advantage in intrasexual mating-competition.
Ceratopsians
According to Scott D. Sampson, if ceratopsids were to exhibit sexual dimorphism, modern ecological analogues suggest it would be found in display structures, such as horns and frills. No convincing evidence for sexual dimorphism in body size or mating signals is known in ceratopsids, although there is evidence that the more primitive ceratopsian ''Protoceratops andrewsi
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. helleni ...
'' possessed sexes that were distinguishable based on frill and nasal prominence size. This is consistent with other known tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
groups where midsized animals tend to exhibit markedly more sexual dimorphism than larger ones. However, it has been proposed that these differences can be better explained by intraspecific and ontogenic variation rather than sexual dimorphism. In addition, many sexually dimorphic traits that may have existed in ceratopsians include soft tissue variations such as coloration or dewlaps
A dewlap is a longitudinal flap of skin or similar flesh that hangs beneath the lower jaw or neck of many vertebrates. More loosely, it can be various similar structures in the neck area, such as those caused by a double chin or the submandibul ...
, which would be unlikely to have been preserved in the fossil record.
Stegosaurians
A 2015 study on specimens of Hesperosaurus, ''Hesperosaurus'' ''mjosi'' found evidence of sexual dimorphism in the shape of the dermal plates. Two plate morphs were described: one was short, wide, and oval-shaped, the other taller and narrower.
Mammals
In 45% of mammal species, males are larger than females, in 39%, males and females are the same size and in 16% of mammals, females are larger than males. Both genes and hormones affect the formation of many animal brains before "birth" (or egg (biology), hatching), and also behaviour of adult individuals. Hormones significantly affect human brain formation, and also brain development at puberty. A 2004 review in ''Nature Reviews Neuroscience'' observed that "because it is easier to manipulate hormone levels than the expression of sex chromosome genes, the effects of hormones have been studied much more extensively, and are much better understood, than the direct actions in the brain of sex chromosome genes." It concluded that while "the differentiating effects of gonadal secretions seem to be dominant," the existing body of research "support the idea that sex differences in neural expression of X and Y genes significantly contribute to sex differences in brain functions and disease."Pinnipeds
 Marine mammals show some of the greatest sexual size differences of mammals, because of sexual selection and environmental factors like breeding location. The mating system of pinnipeds varies from polygamy to serial monogamy. Pinnipeds are known for early differential growth and maternal investment since the only nutrients for newborn pups is the milk provided by the mother. For example, the males are significantly larger (about 10% heavier and 2% longer) than the females at birth in sea lion pups. The pattern of differential investment can be varied principally prenatally and post-natally. ''Mirounga leonina'', the southern elephant seal, is one of the most dimorphic mammals.
Marine mammals show some of the greatest sexual size differences of mammals, because of sexual selection and environmental factors like breeding location. The mating system of pinnipeds varies from polygamy to serial monogamy. Pinnipeds are known for early differential growth and maternal investment since the only nutrients for newborn pups is the milk provided by the mother. For example, the males are significantly larger (about 10% heavier and 2% longer) than the females at birth in sea lion pups. The pattern of differential investment can be varied principally prenatally and post-natally. ''Mirounga leonina'', the southern elephant seal, is one of the most dimorphic mammals.
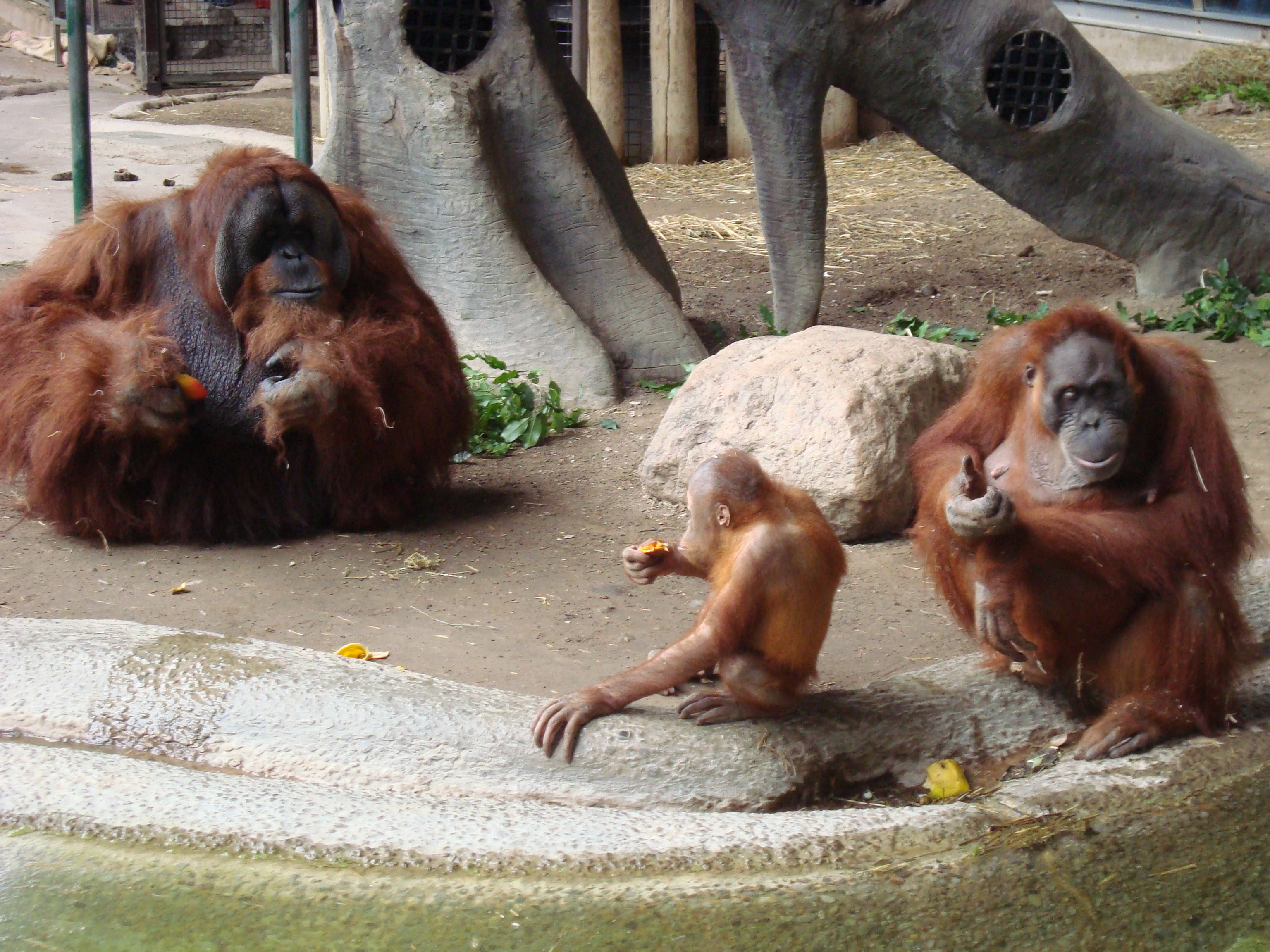
Primates
Most Simian, anthropoid primates are sexually dimorphic for different biological characteristics, such as body size, canine tooth size, craniofacial structure, skeletal dimensions, pelage color and markings, and vocalization. But strepsirrhine primates and tarsiers are mostly monomorphic.Humans
According to Clark Spencer Larsen, modern day ''Homo sapiens'' show a range of sexual dimorphism, with average body mass between the sexes differing by roughly 15%. Substantial discussion in academic literature considers potential evolutionary advantages associated with sexual competition (both intrasexual and intersexual), as well as short- and long-term sexual strategies. According to Daly and Wilson, "The sexes differ more in human beings than in monogamous mammals, but much less than in extremely polygamous mammals." Pubertal changes in males lead to a ten times increase in testosterone compared to females. It is because of the effects of testosterone that males develop stronger and denser bones, as well as increased muscle mass and strength during puberty. On average, adult males have 10-20 times more testosterone than adult females, with male testosterone levels ranging from 300 to 1,000 nanograms per deciliter (ng/dL), while adult females have testosterone levels between 15 and 70 ng/dL. Studies show that men have a higher Bone density, Bone Mineral Density (BMD) than women. It shows BMD values of approximately 3.88 g/cm² for men and 2.90 g/cm² for women, showing that male bones are about 30% denser than female bones. The average basal metabolic rate is about 6 percent higher in adolescent males than females and increases to about 10 percent higher after puberty. Females tend to convert more food into fat, while males convert more into muscle and expendable circulating energy reserves. According to Tim Hewett, director of research in the department of sports medicine at Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, women have 60% of the upper body strength of men and 80-90% of the lower body strength of men. The difference in strength relative to body mass is less pronounced in trained individuals. In Olympic weightlifting, male records vary from 5.5× body mass in the lowest weight category to 4.2× in the highest weight category, while female records vary from 4.4× to 3.8×, a weight-adjusted difference of only 10–20%, and an absolute difference of about 30% (i.e., 492 kg vs 348 kg for unlimited weight classes; see List of world records in Olympic weightlifting, Olympic weightlifting records). A study, carried out by analyzing annual world rankings from 1980 to 1996, found that males' running times were, on average, 10% faster than females', due to wider hips in females being a biomechanical disadvantage for running. This is because wider hips lead to a larger Q-angle (the angle between the hip and knee), which alters the alignment of the lower limbs in females. This would affect the efficiency of force transmission through the legs during running, and also less efficient running biomechanics compared to males with narrower hips and longer femurs. However, females have higher endurance than males. In early adolescence, females are on average taller than males (as females tend to Puberty#Differences between male and female puberty, go through puberty earlier), but males, on average, surpass them in height in later adolescence and adulthood. In the United States, adult males are on average 9% taller and 16.5% heavier than adult females. Males typically have larger Vertebrate trachea, tracheae and branching Bronchus, bronchi, with about 30 percent greater Lung volumes, lung volume per body mass. On average, males have larger hearts, slower heart rates, 10 percent higher red blood cell count, higher hemoglobin, hence greater oxygen-carrying capacity. They also have higher circulating Coagulation, clotting factors (vitamin K, prothrombin and platelets). These differences lead to faster healing of wounds and lower sensitivity to nerve pain after injury. In males, pain-causing injury to the Peripheral nervous system, peripheral nerve occurs through the microglia, while in females it occurs through the T cells (except in pregnant women, who follow a male pattern). Females typically have more white blood cells (stored and circulating), as well as more granulocytes and B and T lymphocytes. Additionally, they produce more Antibody, antibodies at a faster rate than males, hence they develop fewer Infection, infectious diseases and succumb for shorter periods. Ethology, Ethologists argue that females, interacting with other females and multiple offspring in social groups, have experienced such traits as a Natural selection, selective advantage. Females have a higher sensitivity to pain due to aforementioned nerve differences that increase the sensation, and females thus require higher levels of pain medication after injury. Hormonal changes in females affect pain sensitivity, and pregnant women have the same sensitivity as males. Acute pain tolerance is also more consistent over a lifetime in females than males, despite these hormonal changes. Despite differences in physical feeling, both sexes have similar psychological tolerance to (or ability to Coping, cope with and ignore) pain. In the human brain, a difference between sexes was observed in the gene transcription, transcription of the PCDH11X/Y gene pair unique to ''Homo sapiens''. Sexual differentiation in the human brain from the undifferentiated state is triggered by testosterone from the fetal testis. Testosterone is converted to estrogen in the brain through the action of the enzyme aromatase. Testosterone acts on many brain areas, including the INAH 3, SDN-POA, to create the masculinized brain pattern. The brains of pregnant females carrying male fetuses may be shielded from the masculinizing effects of androgen through the action of sex hormone-binding globulin. The relationship between sex differences in the brain and human behavior is a subject of controversy in psychology and society at large. Many females tend to have a higher ratio of gray matter in the left hemisphere of the brain in comparison to males. Males on average have larger brains than females; however, when adjusted for total brain volume, the gray matter differences between sexes are almost nonexistent. Thus, the percentage of gray matter appears to be more related to brain size than it is to sex. Differences in brain physiology between sexes do not necessarily relate to differences in intellect. Haier ''et al.'' found in a 2004 study that "men and women apparently achieve similar IQ results with different brain regions, suggesting that there is no singular underlying neuroanatomical structure to general intelligence and that different types of brain designs may manifest equivalent intellectual performance". (See the sex and intelligence article for more on this subject.) Strict graph-theoretical analysis of the human brain connections revealed that in numerous graph-theoretical parameters (e.g., minimum bipartition width, edge number, the expander graph property, minimum vertex cover), the structural connectome of women are significantly "better" connected than the connectome of men. It was shown that the graph-theoretical differences are due to the sex and not to the differences in the cerebral volume, by analyzing the data of 36 females and 36 males, where the brain volume of each man in the group was smaller than the brain volume of each woman in the group. Sexual dimorphism was also described in the gene level and shown to extend from the sex chromosomes. Overall, about 6500 genes have been found to have sex-differential expression in at least one tissue. Many of these genes are not directly associated with reproduction, but rather linked to more general biological features. In addition, it has been shown that genes with sex-specific expression undergo reduced selection efficiency, which leads to higher population frequencies of deleterious mutations and contributes to the prevalence of several human diseases.Immune function
Sexual dimorphism in immune function is a common pattern in vertebrates and also in a number of invertebrates. Most often, females are more 'immunocompetent' than males. This trait is not consistent among all animals, but differs depending on taxonomy, with the most female-biased immune systems being found in insects. In mammals this results in more frequent and severe infections in males and higher rates of autoimmune disorders in females. One potential cause may be differences in gene expression of immune cells between the sexes. Another explanation is that endocrinological differences between the sexes impact the immune system – for example, testosterone acts as an immunosuppressive agent.Cells
Phenotypic differences between sexes are evident even in cell culture, cultured cells from tissues. For example, female muscle-derived stem cells have a better muscle regeneration efficiency than male ones. There are reports of several metabolic differences between male and female cells and they also respond to stress (biology), stress differently. These differences align with concepts of cell autonomous sex identity, where cells maintain intrinsic sex-based traits regardless of systemic influences.Reproductively advantageous
In theory, larger females are favored by competition for mates, especially in polygamous species. Larger females offer an advantage in fertility, since the physiological demands of reproduction are limiting in females. Hence there is a theoretical expectation that females tend to be larger in species that are monogamous. Females are larger in many species of insects, many spiders, many fish, many reptiles, owls, birds of prey and certain mammals such as the spotted hyena, and baleen whales such as blue whale. As an example, in some species, females are sedentary, and so males must search for them. Fritz Vollrath and Geoff Parker argue that this difference in behaviour leads to radically different selection pressures on the two sexes, evidently favouring smaller males. Cases where the male is larger than the female have been studied as well, and require alternative explanations. One example of this type of sexual size dimorphism is the bat ''Myotis nigricans'', (black myotis bat) where females are substantially larger than males in terms of body weight, skull measurement, and forearm length. The interaction between the sexes and the energy needed to produce viable offspring makes it favorable for females to be larger in this species. Females bear the energetic cost of producing eggs, which is much greater than the cost of making sperm by the males. The fecundity advantage hypothesis states that a larger female is able to produce more offspring and give them more favorable conditions to ensure their survival; this is true for most ectotherms. A larger female can provide parental care for a longer time while the offspring matures. The gestation and lactation periods are fairly long in ''M. nigricans'', the females suckling their offspring until they reach nearly adult size. They would not be able to fly and catch prey if they did not compensate for the additional mass of the offspring during this time. Smaller male size may be an adaptation to increase maneuverability and agility, allowing males to compete better with females for food and other resources. Some species of anglerfish also display extreme sexual dimorphism. Females are more typical in appearance to other fish, whereas males are tiny rudimentary creatures with stunted digestive systems. A male must find a female and fuse with her: he then lives parasitically, becoming little more than a sperm-producing body in what amounts to an effectively hermaphrodite composite organism. A similar situation is found in the Zeus water bug ''Phoreticovelia disparata'' where the female has a glandular area on her back that can serve to feed a male, which clings to her (although males can survive away from females, they generally are not free-living). This is taken to the logical extreme in the Rhizocephala crustaceans, like the Sacculina, where the male injects itself into the female's body and becomes nothing more than sperm producing cells, to the point that the superorder used to be mistaken for hermaphroditic. Some plant species also exhibit dimorphism in which the females are significantly larger than the males, such as in the moss ''Dicranum'' and the liverwort ''Sphaerocarpos''. There is some evidence that, in these genera, the dimorphism may be tied to a sex chromosome, or to chemical signalling from females. Another complicated example of sexual dimorphism is in ''Vespula squamosa'', the southern yellowjacket. In this wasp species, the female workers are the smallest, the male workers are slightly larger, and the female queens are significantly larger than her female workers and male counterparts.Evolution
In 1871, Charles Darwin advanced the theory of sexual selection, which related sexual dimorphism tosexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
.
The first step towards sexual dimorphism is the size differentiation of sperm and eggs (anisogamy). Anisogamy and the usually large number of small male gametes relative to the larger female gametes usually lies in the development of strong sperm competition, because small sperm enable organisms to produce a large number of sperm, and make males (or male function of hermaphrodites) more redundant.
Volvocine algae have been useful in understanding the evolution of sexual dimorphism and species like the beetle ''Callosobruchus maculatus, C. maculatus'', where the females are larger than the males, are used to study its underlying genetic mechanisms.
In many non-monogamous species, the benefit to a male's reproductive fitness of mating with multiple females is large, whereas the benefit to a female's reproductive fitness of mating with multiple males is small or nonexistent. In these species, there is a selection pressure for whatever traits enable a male to have more matings. The male may therefore come to have different traits from the female.
sexy son hypothesis
The sexy son hypothesis in evolutionary biology and sexual selection, proposed by Patrick J. Weatherhead and Raleigh J. Robertson of Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario in 1979, states that a female's ideal mate choice among potential mates ...
and the handicap principle.
The sexy son hypothesis states that females may initially choose a trait because it improves the survival of their young, but once this preference has become widespread, females must continue to choose the trait, even if it becomes harmful. Those that do not will have sons that are unattractive to most females (since the preference is widespread) and so receive few matings.
The handicap principle states that a male who survives despite possessing some sort of handicap thus proves that the rest of his genes are "good alleles". If males with "bad alleles" could not survive the handicap, females may evolve to choose males with this sort of handicap; the trait is acting as a hard-to-fake signal of fitness.
See also
* Bateman's principle * List of homologues of the human reproductive system * Sex differences in humans * Sex differences in human psychology * Sexual differentiation * Sexual dimorphism measures * Sexually dimorphic nucleus * GynandromorphismReferences
Sources
* * *Further reading
* * *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Sexual Dimorphism Sexual dimorphism, Animal anatomy Sexual selection Polymorphism (biology) Asymmetry