Diffuse Alopecia Areata on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alopecia areata (AA), also known as spot baldness, is a condition in which hair is lost from some or all areas of the body. It often results in a few bald spots on the scalp, each about the size of a coin.
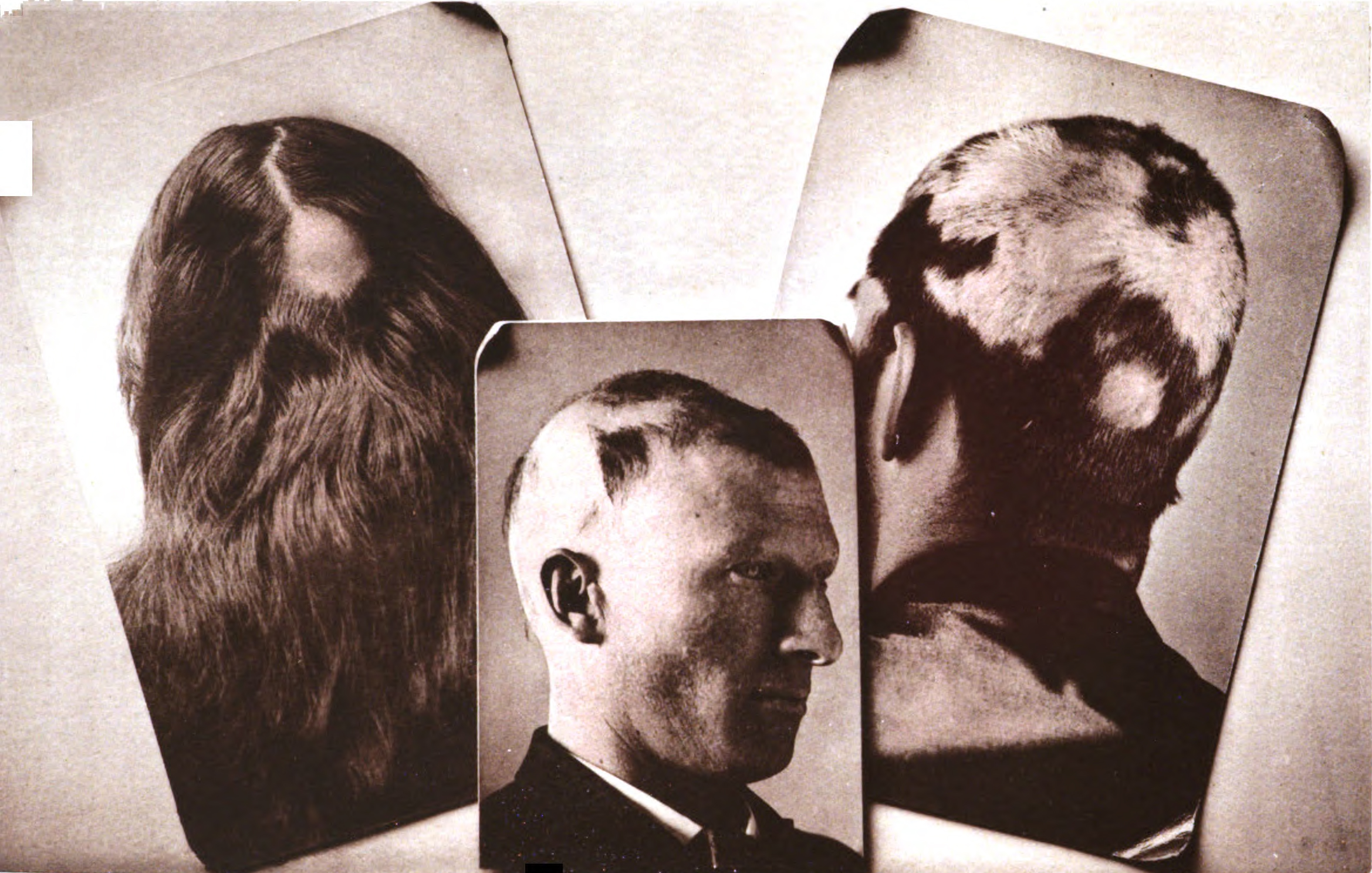 Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful. Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other.
Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present. These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches.
When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy.
Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia. Onychoptosis defluvium, also known as alopecia unguium, is casting off the nail seen in association with alopecia areata.>
Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful. Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other.
Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present. These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches.
When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy.
Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia. Onychoptosis defluvium, also known as alopecia unguium, is casting off the nail seen in association with alopecia areata.>
 Alopecia areata is thought to be a systemic autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own anagen
Alopecia areata is thought to be a systemic autoimmune disorder in which the body attacks its own anagen
 Commonly, alopecia areata involves hair loss in one or more round spots on the scalp..
* Hair may also be lost more diffusely over the whole scalp, in which case the condition is called diffuse alopecia areata.
* Alopecia areata monolocularis describes baldness in only one spot. It may occur anywhere on the head.
* Alopecia areata multilocularis refers to multiple areas of hair loss.
* Ophiasis refers to hair loss in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head.
* The disease may be limited only to the beard, in which case it is called alopecia areata barbae.
* If the person loses all the hair on the scalp, the disease is then called alopecia areata totalis.
* If all body hair, including
Commonly, alopecia areata involves hair loss in one or more round spots on the scalp..
* Hair may also be lost more diffusely over the whole scalp, in which case the condition is called diffuse alopecia areata.
* Alopecia areata monolocularis describes baldness in only one spot. It may occur anywhere on the head.
* Alopecia areata multilocularis refers to multiple areas of hair loss.
* Ophiasis refers to hair loss in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head.
* The disease may be limited only to the beard, in which case it is called alopecia areata barbae.
* If the person loses all the hair on the scalp, the disease is then called alopecia areata totalis.
* If all body hair, including
Psychological stress
In psychology, stress is a feeling of emotional strain and pressure. Stress is a form of psychological and mental discomfort. Small amounts of stress may be beneficial, as it can improve athletic performance, motivation and reaction to the envi ...
and illness are possible factors in bringing on alopecia areata in individuals at risk, but in most cases there is no obvious trigger. People are generally otherwise healthy. In a few cases, all the hair on the scalp is lost (''alopecia totalis
Alopecia totalis is the loss of all hair on the head and face. Its causes are unclear, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disorder. Research suggests there may be a genetic link: the presence of DRB1*0401 and DQB1*0301, both of which are hu ...
''), or all body hair is lost (''alopecia universalis
__NOTOC__
Alopecia universalis (AU), also known as alopecia areata universalis, is a medical condition involving the loss of all body hair, including eyebrows, eyelashes, chest hair, armpit hair, and pubic hair. It is the most severe form of alop ...
''). Hair loss can be permanent or temporary.
Alopecia areata is believed to be an autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
resulting from a breach in the immune privilege
Certain sites of the mammalian body have immune privilege (no immune response), meaning they are able to tolerate the introduction of antigens without eliciting an inflammatory immune response. Tissue grafts are normally recognised as foreign an ...
of the hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
s. Risk factors include a family history of the condition. Among identical twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of Twin Last Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two e ...
, if one is affected, the other has about a 50% chance of also being affected. The underlying mechanism involves failure by the body to recognize its own cells, with subsequent immune-mediated destruction of the hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
.
No cure for the condition is known. Some treatments, particularly triamcinolone
Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid used to treat certain skin diseases, allergies, and rheumatic disorders among others. It is also used to prevent worsening of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can be taken in variou ...
injections and 5% minoxidil
Minoxidil is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive and a vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in oral administration, oral tablet (pharmacy), ...
topical creams, are effective in speeding hair regrowth. Sunscreen
Sunscreen, also known as sunblock, sun lotion or sun cream, is a photoprotection, photoprotective topical product for the Human skin, skin that helps protect against sunburn and prevent skin cancer. Sunscreens come as lotions, sprays, gels, fo ...
, head coverings to protect from cold and sun, and glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are vision eyewear with clear or tinted lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically u ...
, if the eyelashes
An eyelash (also called lash) (Neo-Latin: ''cilium'', plural ''cilia'') is one of the hairs that grows at the edges of the top and bottom eyelids, spanning outwards and away from the eyes. The lashes grow in up to six layers on each of the upper ...
are missing, are also recommended. In more than 50% of cases of sudden-onset localized "patchy" disease, hair regrows within a year. In patients with only one or two patches, this one-year recovery will occur in up to 80%. However, many people will have more than one episode over the course of a lifetime. In many patients, hair loss and regrowth occurs simultaneously over the course of several years. Among those in whom all body hair is lost, fewer than 10% recover.
About 0.15% of people are affected at any one time, and 2% of people are affected at some point in time. Onset is usually in childhood. Females are affected at higher rates than males.
Signs and symptoms
 Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful. Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other.
Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present. These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches.
When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy.
Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia. Onychoptosis defluvium, also known as alopecia unguium, is casting off the nail seen in association with alopecia areata.>
Typical first symptoms of alopecia areata are small bald patches. The underlying skin is unscarred and looks superficially normal. Although these patches can take many shapes, they are usually round or oval. Alopecia areata most often affects the scalp and beard, but may occur on any part of the body with hair. Different areas of the skin may exhibit hair loss and regrowth at the same time. The disease may also go into remission for a time, or may be permanent. It is common in children.
The area of hair loss may tingle or be mildly painful. Dermatologic Disease Database. Aocd.org. Retrieved on 3 December 2007. The hair tends to fall out over a short period of time, with the loss commonly occurring more on one side of the scalp than the other.
Exclamation point hairs, narrower along the length of the strand closer to the base, producing a characteristic "exclamation point" appearance, are often present. These hairs are very short (3–4 mm), and can be seen surrounding the bald patches.
When healthy hair is pulled out, at most a few should come out, and ripped hair should not be distributed evenly across the tugged portion of the scalp. In cases of alopecia areata, hair tends to pull out more easily along the edge of the patch where the follicles are already being attacked by the body's immune system than away from the patch where they are still healthy.
Nails may have pitting or trachyonychia. Onychoptosis defluvium, also known as alopecia unguium, is casting off the nail seen in association with alopecia areata.>
Causes
hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction betwee ...
s and suppresses or stops hair growth. For example, T cell
T cells (also known as T lymphocytes) are an important part of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell ...
lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
cluster around affected follicles, causing inflammation and subsequent hair loss. Hair follicles in a normal state are thought to be kept secure from the immune system, a phenomenon called immune privilege. A breach in this immune privilege state is considered as the cause of alopecia areata. A few cases of babies being born with congenital
A birth defect is an abnormal condition that is present at childbirth, birth, regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disability, disabilities that may be physical disability, physical, intellectual disability, intellectual, or dev ...
alopecia areata have been reported. It is recognized as a type 1 inflammatory disease.
Alopecia areata is not contagious. It occurs more frequently in people who have affected family members, suggesting heredity
Heredity, also called inheritance or biological inheritance, is the passing on of traits from parents to their offspring; either through asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction, the offspring cells or organisms acquire the genetic infor ...
may be a factor. Strong evidence of genetic association with increased risk for alopecia areata was found by studying families with two or more affected members. This study identified at least four regions in the genome that are likely to contain these genes. In addition, alopecia areata shares genetic risk factors with other autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and h ...
, type 1 diabetes
Type 1 diabetes (T1D), formerly known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease that occurs when the body's immune system destroys pancreatic cells (beta cells). In healthy persons, beta cells produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone require ...
, and celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
. It may be the only manifestation of celiac disease.
Lifestyle factors such as smoking, sleep quality, and obesity may also contribute to the onset and progression of alopecia areata. Studies indicate that smokers have a higher risk of developing the condition, potentially due to tobacco-induced Th17-mediated inflammation in hair follicles. While some research suggests a link between sleep disorder
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sle ...
s and alopecia areata, findings remain inconclusive. However, since sleep disturbances impact immune function, they may play a role in disease pathogenesis. Additionally, obesity is associated with an increased risk of alopecia areata, likely due to adipokine
The adipokines, or adipocytokines (Greek ', fat; ', cell; and ', movement) are cytokines (cell signaling proteins) secreted by adipose tissue. Some contribute to an obesity-related low-grade state of inflammation or to the development of metabolic ...
dysregulation, which promotes chronic low-grade inflammation and alters immune response, as seen in other inflammatory skin conditions.
Endogenous retinoid
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are utilized in cosmetic formulations, clinical dermatology, and the treatment of some forms of cancer ...
s metabolic defect is a key part of the pathogenesis of the alopecia areata.
In 2010, a genome-wide association study was completed that identified 129 single nucleotide polymorphisms that were associated with alopecia areata. The genes that were identified include those involved in
controlling the activation and proliferation of regulatory T cells, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4, interleukin-2, interleukin-2 receptor A, and Eos (also known as Ikaros family zinc finger 4), as well as the human leukocyte antigen. The study also identified two genes, ''PRDX5'' and ''STX17'', that are expressed in the hair follicle.
There is emerging evidence suggesting a possible link between AA and vaccinations, including influenza, zoster, and human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccines. One possible explanation is that vaccinations could trigger immune system activation, which has been observed to exacerbate preexisting autoimmune or autoinflammatory conditions in at-risk populations. A small study observed hair loss exacerbation in three patients following COVID-19 mRNA vaccinations ( Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna Moderna, Inc. ( ) is an American pharmaceutical and biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, that focuses on RNA therapeutics, primarily mRNA vaccines. These vaccines use a copy of a molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA) to carry inst ...
). These patients, who were younger on average (30.6 years) compared to unaffected individuals (37.2 years), experienced worsening hair loss within two weeks post-vaccination. Similar cases have been reported with the AstraZeneca
AstraZeneca plc () (AZ) is a British-Swedish multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with its headquarters at the Cambridge Biomedical Campus in Cambridge, UK. It has a portfolio of products for major diseases in areas includi ...
and Johnson & Johnson
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical technologies corporation headquartered in New Brunswick, New Jersey, and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange. Its common stock is a c ...
COVID-19 vaccines. However, AA flares have also been linked to SARS-CoV-2 infection, either as an exacerbation of preexisting disease or a new diagnosis. In the study's non-vaccinated AA cohort, the only observed case of hair loss worsening occurred after a COVID-19 infection. While causality remains unclear, these findings emphasize the need for further research into the relationship between vaccinations and AA progression.
A psychodermatological connection is noted with impairment in psychiatric comorbidities including mental well-being, self esteem and mental disorders acting as pathogenic triggers for alopecia areata.
Diagnosis
Alopecia areata is usually diagnosed based on clinical features.Trichoscopy
Trichoscopy is a method of hair and scalp evaluation and is used for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases. The method is based on dermoscopy. In trichoscopy hair and scalp structures may be visualized at many-fold magnification. Currently magnificat ...
may aid in establishing the diagnosis. In alopecia areata, trichoscopy shows regularly distributed "yellow dots" (hyperkeratotic
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the Epidermis (skin), epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins ...
plugs), small exclamation-mark hairs, and "black dots" (destroyed hairs in the hair follicle opening).
Oftentimes, however, discrete areas of hair loss surrounded by exclamation mark hairs is sufficient for clinical diagnosis of alopecia areata. Sometimes, reddening of the skin, erythema
Erythema (, ) is redness of the skin or mucous membranes, caused by hyperemia (increased blood flow) in superficial capillaries. It occurs with any skin injury, infection, or inflammation. Examples of erythema not associated with pathology inc ...
, may also be present in the balding area.
A biopsy is rarely needed to make the diagnosis or aid in the management of alopecia areata. Histologic
Histology,
also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visi ...
findings may include peribulbar lymphocytic
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and inn ...
infiltration resembling a "swarm of bees", a shift in the anagen
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between ho ...
-to-telogen ratio towards telogen, and dilated follicular infundibulae. Other helpful findings can include pigment incontinence in the hair bulb and follicular stelae. Occasionally, in inactive alopecia areata, no inflammatory infiltrates are found.
Classification
 Commonly, alopecia areata involves hair loss in one or more round spots on the scalp..
* Hair may also be lost more diffusely over the whole scalp, in which case the condition is called diffuse alopecia areata.
* Alopecia areata monolocularis describes baldness in only one spot. It may occur anywhere on the head.
* Alopecia areata multilocularis refers to multiple areas of hair loss.
* Ophiasis refers to hair loss in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head.
* The disease may be limited only to the beard, in which case it is called alopecia areata barbae.
* If the person loses all the hair on the scalp, the disease is then called alopecia areata totalis.
* If all body hair, including
Commonly, alopecia areata involves hair loss in one or more round spots on the scalp..
* Hair may also be lost more diffusely over the whole scalp, in which case the condition is called diffuse alopecia areata.
* Alopecia areata monolocularis describes baldness in only one spot. It may occur anywhere on the head.
* Alopecia areata multilocularis refers to multiple areas of hair loss.
* Ophiasis refers to hair loss in the shape of a wave at the circumference of the head.
* The disease may be limited only to the beard, in which case it is called alopecia areata barbae.
* If the person loses all the hair on the scalp, the disease is then called alopecia areata totalis.
* If all body hair, including pubic hair
Pubic hair (or pubes , ) is terminal hair, terminal body hair that is found in the sex organ, genital area and pubic region of adolescent and adult humans. The hair is located on and around the sex organs, and sometimes at the top of the inside ...
, is lost, the diagnosis then becomes alopecia areata universalis.
Alopecia areata totalis and universalis are rare.
Treatment
The objective assessment of treatment efficacy is very difficult and spontaneous remission is unpredictable, but if the affected area is patchy, the hair may regrow spontaneously in many cases. None of the existing therapeutic options are curative or preventive. A 2020 systematic review showed greater than 50% hair regrowth in 80.9% of patients treated with 5 mg/mLtriamcinolone
Triamcinolone is a glucocorticoid used to treat certain skin diseases, allergies, and rheumatic disorders among others. It is also used to prevent worsening of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It can be taken in variou ...
injections. A Cochrane-style systematic review published in 2019 showed 5% topical minoxidil
Minoxidil is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive and a vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in oral administration, oral tablet (pharmacy), ...
was more than eight times more associated with >50% hair regrowth at 6 months compared to placebo. In cases of severe hair loss, limited success has been achieved by using the corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
medications clobetasol or fluocinonide
Fluocinonide is a potent glucocorticoid used topically as an anti-inflammatory agent for the treatment of skin disorders such as eczema and seborrhoeic dermatitis. It relieves itching, redness, dryness, crusting, scaling, inflammation
...
as an injection or cream. Application of corticosteroid creams to the affected skin is less effective and takes longer to produce results. Steroid injections are commonly used in sites where the areas of hair loss on the head are small or especially where eyebrow hair has been lost. Whether they are effective is uncertain. Some other medications that have been used are minoxidil
Minoxidil is a medication used for the treatment of high blood pressure and pattern hair loss. It is an antihypertensive and a vasodilator. It is available as a generic medication by prescription in oral administration, oral tablet (pharmacy), ...
, Elocon (mometasone) ointment (steroid cream), irritants ( anthralin or topical coal tar
Coal tar is a thick dark liquid which is a by-product of the production of coke and coal gas from coal. It is a type of creosote. It has both medical and industrial uses. Medicinally it is a topical medication applied to skin to treat psoria ...
), and topical immunotherapy ciclosporin
Ciclosporin, also spelled cyclosporine and cyclosporin, is a calcineurin inhibitor, used as an immunosuppressant medication. It is taken Oral administration, orally or intravenously for rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, Crohn's disease, nephr ...
, sometimes in different combinations. Topical corticosteroids frequently fail to enter the skin deeply enough to affect the hair bulbs, which are the treatment target, and small lesions typically also regrow spontaneously. Oral corticosteroids may decrease the hair loss, but only for the period during which they are taken, and these medications can cause serious side effects
In medicine, a side effect is an effect of the use of a medicinal drug or other treatment, usually adverse but sometimes beneficial, that is unintended. Herbal and traditional medicines also have side effects.
A drug or procedure usually used ...
. No one treatment is effective in all cases, and some individuals may show no response to any treatment.
For more severe cases, studies have shown promising results with the individual use of the immunosuppressant methotrexate or adjunct use with corticosteroids.
When alopecia areata is associated with celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine. Patients develop intolerance to gluten, which is present in foods such as wheat, rye, spel ...
, treatment with a gluten-free diet
A gluten-free diet (GFD) is a nutritional plan that strictly excludes gluten, which is a mixture of prolamin proteins found in wheat (and all of its species and hybrids, such as spelt, kamut, and triticale), as well as barley, rye, and oats ...
allows for complete and permanent regrowth of scalp and other body hair in many people, but in others, remissions and recurrences are seen. This improvement is probably due to the normalization of the immune response
An immune response is a physiological reaction which occurs within an organism in the context of inflammation for the purpose of defending against exogenous factors. These include a wide variety of different toxins, viruses, intra- and extracellula ...
as a result of gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain Cereal, cereal grains. The term ''gluten'' usually refers to the elastic network of a wheat grain's proteins, gliadin and glutenin primarily, that forms readily with the addition of water ...
withdrawal from the diet.
In June 2022, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) authorized baricitinib
Baricitinib, sold under the brand name Olumiant among others, is an immunomodulatory medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia areata, and COVID-19. It acts as an inhibitor of janus kinase (JAK), blocking the subty ...
, a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor, for the treatment of severe alopecia areata.
Ritlecitinib (Litfulo) was approved for medical use in the United States in June 2023.
Fecal matter transplants (FMT) have been shown to reverse AA and support hair growth, with long lasting results, even going as far as growing additional hair on arms and face while grey hairs even regained colour. This supports the idea of a connection between gut microbiota having a part in hair loss.
Hair transplantation may be an alternative for patients with chronic local alopecia areata. The fact that the disease is autoimmune and progresses with relapses is one of the biggest question marks before surgery. There have been case reports in the literature since the early 2000s. However, in an article published long-term follow-up; It is reported that the hair transplanted to the eyebrow area falls out again due to the recurrence of the disease. A similar situation was not mentioned in previous studies on this subject. Perhaps the long-term follow-ups of other studies were not sufficient.
Deuruxolitinib (Leqselvi) was approved for medical use in the United States in July 2024.
Prognosis
In most cases that begin with a small number of patches of hair loss, hair grows back after a few months to a year. In cases with a greater number of patches, hair can either grow back or progress to alopecia areata totalis or, in rare cases, alopecia areata universalis. No loss of body function occurs, and the effects of alopecia areata are psychological (loss of self-image due to hair loss), although these can be severe. Loss of hair also means the scalp burns more easily in the sun. Patients may also have aberrant nail formation becausekeratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, feathers, horn (anatomy), horns, claws, Hoof, hoove ...
forms both hair and nails.
Hair may grow back and then fall out again later. This may not indicate a recurrence of the condition, but rather a natural cycle of growth-and-shedding from a relatively synchronised start; such a pattern will fade over time. Episodes of alopecia areata before puberty predispose to chronic recurrence of the condition.
Alopecia can be the cause of psychological stress. Because hair loss can lead to significant changes in appearance, individuals with it may experience social phobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impairing ability to function in at least some as ...
, anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, and depression.
Epidemiology
The condition affects 0.1%–0.2% of the population, with a lifetime risk of 1%-2%, and is more common in females. Alopecia areata occurs in people who are otherwise healthy and have no other skin disorders. Initial presentation most commonly occurs in the early childhood, lateteenage
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human physical and psychological development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with ...
years, or young adulthood, but can happen at any ages. Patients also tend to have a slightly higher incidence of conditions related to the immune system, such as asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, allergies, atopic
Atopy is the tendency to produce an exaggerated immunoglobulin E (IgE) immune response to otherwise harmless substances in the environment. Allergic diseases are clinical manifestations of such inappropriate, atopic responses.
Atopy may have a ...
dermatitis, and hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, co ...
.
Ethnic and socioeconomic disparities
The prevalence and impact of AA vary across different ethnic groups and socioeconomic backgrounds. Studies indicate that people of Asian descent have the highest risk, with nearly 6 cases per 100 people, compared to fewer than 2 cases per 100 people among White individuals. People living in urban or economically disadvantaged areas face a higher likelihood of developing AA. The effects of the condition also differ by ethnicity: individuals of Black descent with AA are more likely to experienceanxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
and require medical leave from work. These findings suggest that genetic, environmental, and social factors may influence both the likelihood of developing AA and its broader personal and professional impact.
Society and culture
The term "alopecia", used by physicians dating back toHippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referr ...
, originates from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
word for fox, "alopex", and was so-named due to fur loss seen in fox mange. "Areata" is derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
word, "area", meaning a vacant space or patch.
Alopecia areata and alopecia barbae have been identified by some as the biblical condition that is part of the greater family of skin disorders; the said disorders are purported to being discussed in the Book of Leviticus
The Book of Leviticus (, from , ; , , 'And He called'; ) is the third book of the Torah (the Pentateuch) and of the Old Testament, also known as the Third Book of Moses. Many hypotheses presented by scholars as to its origins agree that it de ...
, chapter 13.
Notable people
NASCAR driverJoey Logano
Joseph Thomas Logano (born May 24, 1990) is an American professional stock car racing driver. He competes full-time in the NASCAR Cup Series, driving the No.22 Ford Mustang (seventh generation), Ford Mustang Dark Horse for NASCAR operations of Tea ...
, obstacle athlete Kevin Bull, politicians Peter Dutton
Peter Craig Dutton (born 18 November 1970) is an Australian former politician who served as the Leader of the Opposition (Australia), Leader of the Opposition and the Leader of the Liberal Party of Australia, leader of the Liberal Party from 2 ...
and Ayanna Pressley
Ayanna Soyini Pressley (born February 3, 1974) is an American politician who has served as the United States House of Representatives, U.S. representative for Massachusetts's 7th congressional district since 2019. This district, which was once re ...
, K-pop
K-pop (; an abbreviation of "Korean popular music") is a form of popular music originating in South Korea. It emerged in the 1990s as a form of youth subculture, with Korean musicians taking influence from Western Electronic dance music, danc ...
singer Peniel Shin of BtoB
B2B, B to B, or B-to-B may refer to: Sports
* B2B, a controversial and short lived class in the 1979 Sidecar World Championship
* Bay to Breakers, an annual footrace in San Francisco, California on the third Sunday of May
* Budapest-Bamako, now t ...
, actors Christopher Reeve
Christopher D'Olier Reeve (September 25, 1952 – October 10, 2004) was an American actor, activist, director, and author. He amassed Christopher Reeve on stage and screen, several stage and screen credits in his 34-year career, including playin ...
, Anthony Carrigan, Greg Grunberg
Gregory Phillip Grunberg (born July 11, 1966) is an American film and television actor known for starring as Eric Weiss in the ABC series '' Alias'', Matt Parkman in the NBC series '' Heroes'', Temmin "Snap" Wexley in '' Star Wars: The Force ...
and Alan Fletcher, and actresses Jada Pinkett Smith
Jada Koren Pinkett Smith (née Pinkett; born September 18, 1971) is an American actress, businesswoman, and talk show host. She is co-host of the Facebook Watch talk show ''Red Table Talk'', for which she has won a Daytime Emmy Awards, Daytim ...
, May Calamawy, and Lili Reinhart all have some form of alopecia areata.
Research
Many medications are being studied. In 2014, preliminary findings showing that oralruxolitinib
Ruxolitinib (sold under the brand names Jakafi and Jakavi among others, and as Opzelura in cream form) is a medication used for the treatment of intermediate or high-risk myelofibrosis, a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm that affects the b ...
, a drug approved by the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) for bone marrow disorder myelofibrosis
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a rare bone marrow blood cancer. It is classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a type of myeloproliferative neoplasm, a group of cancers in which there is activation and growth of mutated cells in ...
, restored hair growth in three individuals with long-standing and severe disease.
In March 2020, the US FDA granted breakthrough therapy
Breakthrough therapy is a United States Food and Drug Administration designation that expedites drug development that was created by Congress under Section 902 of the 9 July 2012 Food and Drug Administration Safety and Innovation Act. The FDA's "b ...
designation to baricitinib
Baricitinib, sold under the brand name Olumiant among others, is an immunomodulatory medication used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, alopecia areata, and COVID-19. It acts as an inhibitor of janus kinase (JAK), blocking the subty ...
for the systematic treatment of alopecia areata and granted approval in June 2022, with a 32% efficacy rate for people with 50% hair loss reaching 80% scalp coverage in 36 weeks. It acts as an inhibitor of janus kinase (JAK), blocking the subtypes JAK1 and JAK2
Janus kinase 2 (commonly called JAK2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a member of the Janus kinase family and has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family (e.g. interferon receptors), the GM-CSF ...
.
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Alopecia Areata Autoimmune diseases Conditions of the skin appendages Human hair Hair diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate