Deccan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Deccan is a
 Several dynasties such as the Pandyas of
Several dynasties such as the Pandyas of

 The Deccan Plateau is one of the oldest and most stable land formations in the
The Deccan Plateau is one of the oldest and most stable land formations in the
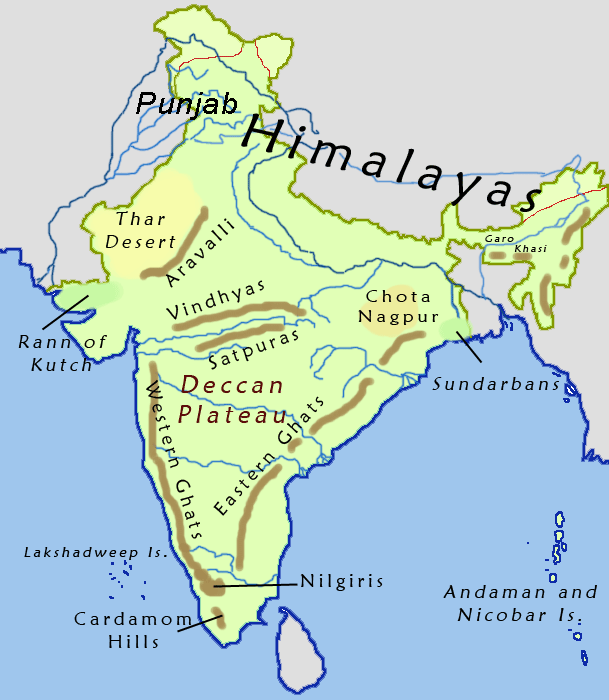 Historians have used the term Deccan differently across various time periods. Firishta (16th century), R. G. Bhandarkar (1920), and Richard Eaton (2005) demarcate the region based on linguistic lines. K. M. Panikkar (1969) defines it as the entire Indian peninsula south of the Vindhyas. Stewart Gordon (1998) notes that Deccan is a "relational term" and historically the border of Deccan has varied from Tapti River to the
Historians have used the term Deccan differently across various time periods. Firishta (16th century), R. G. Bhandarkar (1920), and Richard Eaton (2005) demarcate the region based on linguistic lines. K. M. Panikkar (1969) defines it as the entire Indian peninsula south of the Vindhyas. Stewart Gordon (1998) notes that Deccan is a "relational term" and historically the border of Deccan has varied from Tapti River to the
 The Deccan forms one of the major watersheds of India, feeding many perennial rivers. The major river systems originating in the Western Ghats are the
The Deccan forms one of the major watersheds of India, feeding many perennial rivers. The major river systems originating in the Western Ghats are the
 The largest linguistic group in the region is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The
The largest linguistic group in the region is the Dravidian family of languages, of approximately 73 languages. The
 There is an extensive road network composed of
There is an extensive road network composed of
plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
in the south. It is bound by the mountain ranges of the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches along the East Coast of India, eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of , it traverses the states and union territories of India, states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Prade ...
on the sides, which separate the region from the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Coastal Plains
The Eastern Coastal Plains is a stretch of landmass lying between the eastern part of the Deccan plateau and the Bay of Bengal in India. The plains stretch from the Mahanadi delta to Kaniyakumari at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula with ...
respectively. It covers most of the Indian State
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respe ...
s of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
and Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
excluding the coastal regions, and minor portions of Tamil Nadu and Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
.
The plateau is marked by rocky terrain with an average elevation of about . It is subdivided into Maharashtra Plateau, Karnataka Plateau, and Rayalaseema & Telangana Plateau. The Deccan Traps in the north west were formed by multiple layers of igneous
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.
The magma can be derived from partial ...
rocks laid down by basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% ...
lava flow
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a Natural satellite, moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a Fissure vent, fractu ...
s following a massive volcanic eruption
A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior h ...
that occurred during the end of the Cretaceous period (66 mya). The underlying bed consists of granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
and sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedim ...
formed during the Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
era and the formation of Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
.
The region forms one of the major watersheds of India, with many perennial river systems such as Godavari
The Godavari (, �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga River and drains the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharash ...
, Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
, and Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery) is a Rivers of India, major river flowing across Southern India. It is the third largest river in the region after Godavari River, Godavari and Krishna River, Krishna.
The catchment area of the Kaveri basin i ...
flowing through the region. The plateau slopes gently from the west to east, resulting in most of the principal rivers flowing eastwards towards the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
. As the Western Ghats blocks the rain bearing winds, the plateau region is drier than the coastal region and has a semi-arid climate.
The Deccan plateau region was ruled by several kingdoms in Indian history such as Pallavas, Cholas, Pandyas, Satavahanas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas
The Rashtrakuta Empire was a royal Indian polity ruling large parts of the Indian subcontinent between the 6th and 10th centuries. The earliest known Rashtrakuta Indian inscriptions, inscription is a 7th-century copper plate grant detailing th ...
, Hoysalas, Kadambas, Kakatiyas, and Western Gangas. In the later medieval era
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and t ...
, the lower plateau was ruled by the Vijayanagara empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
, and the upper portion by the Bahmani kingdom, and its successors, the Deccan sultanates
The Deccan sultanates is a historiographical term referring to five late medieval to early modern Persianate Indian Muslim kingdoms on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range. They were created from the disintegrati ...
. It later housed the Kingdom of Mysore
The Kingdom of Mysore was a geopolitical realm in southern India founded in around 1399 in the vicinity of the modern-day city of Mysore and prevailed until 1950. The territorial boundaries and the form of government transmuted substantially ...
, Maratha confederacy
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent Maratha states under the nominal leadership of the former.
...
, and Nizam's dominions. It was under the control of British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
for nearly two centuries before Indian Independence in 1947. The Reorganisation of Indian states in the 1950s resulted in the creation of states on linguistic lines.
Etymology
The word ''Deccan'' is an anglicised version of thePrakrit
Prakrit ( ) is a group of vernacular classical Middle Indo-Aryan languages that were used in the Indian subcontinent from around the 5th century BCE to the 12th century CE. The term Prakrit is usually applied to the middle period of Middle Ind ...
word ', which evolved from the Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; stem form ; nominal singular , ,) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in northwest South Asia after its predecessor languages had Trans-cultural ...
word ''dakṣiṇa'', meaning "south".
History
Carbon dating
Radiocarbon dating (also referred to as carbon dating or carbon-14 dating) is a method for determining the age of an object containing organic material by using the properties of radiocarbon, a radioactive isotope of carbon.
The method was ...
shows that ash mounds associated with Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
cultures in region date back to 8000 BCE. Towards the beginning of 1000 BCE, iron technology spread through the region though geological evidence does not point to a fully developed Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
in existence prior to the Iron Age. Since at least the 1st century BCE, the region was connected to the Silk Road
The Silk Road was a network of Asian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over , it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and religious interactions between the ...
and was involved in trade with the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and East Asia
East Asia is a geocultural region of Asia. It includes China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan, plus two special administrative regions of China, Hong Kong and Macau. The economies of Economy of China, China, Economy of Ja ...
.
 Several dynasties such as the Pandyas of
Several dynasties such as the Pandyas of Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is ...
, the Cholas of Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
, the Zamorin
The Samoothiri (Anglicised as Zamorin; Malayalam: , , Arabic: ''Sāmuri'', Portuguese: ''Samorim'', Dutch: ''Samorijn'', Chinese: ''Shamitihsi''Ma Huan's Ying-yai Sheng-lan: 'The Overall Survey of the Ocean's Shores' 433 Translated and Edi ...
s of Kozhikode
Kozhikode (), also known as Calicut, is a city along the Malabar Coast in the state of Kerala in India. Known as the City of Spices, Kozhikode is listed among the City of Literature, UNESCO's Cities of Literature.
It is the nineteenth large ...
, the Satavahanas of Amaravati
Amaravati ( , Telugu language, Telugu: ) is the capital city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located in Guntur district on the right bank of the Krishna River, southwest of Vijayawada. The city derives its name from the nearby his ...
, the Pallavas of Kanchi, the Kadambas of Banavasi, the Western Gangas of Kolar
Kolar may refer to:
Places India
* Kolar, Karnataka, a city in India
**Kolar Assembly constituency
*Kolar district, in Karnataka, India
*Kolar Gold Fields, former gold mines in Karnataka, India
**KGF (disambiguation)
**Kolar Gold Field Assembly co ...
, the Rashtrakutas of Manyakheta, the Chalukyas of Badami, the Hoysalas of Belur, and the Kakatiyas of Orugallu ruled over the region from the 6th century BCE to the 14th century CE. In the Late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, Vijayanagara empire
The Vijayanagara Empire, also known as the Karnata Kingdom, was a late medieval Hinduism, Hindu empire that ruled much of southern India. It was established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara I and Bukka Raya I of the Sangama dynasty, belongi ...
conquered most of the southern part of the pleateu region. The upper portion was ruled by the Bahmani kingdom, and later by its successors, the Deccan sultanates
The Deccan sultanates is a historiographical term referring to five late medieval to early modern Persianate Indian Muslim kingdoms on the Deccan Plateau between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range. They were created from the disintegrati ...
.
The Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
arrived in the 15th century CE and by the middle of the 18th century, the French and the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
were involved in a protracted struggle for military control over the region. The Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern India, early modern polity in the Indian subcontinent. It comprised the realms of the Peshwa and four major independent List of Maratha dynasties and states, Ma ...
founded by Chatrapati Shivaji, briefly captured the region in the early 18th century CE. After the defeat of Mysore Kingdom in the late 18th century CE and the Vellore Mutiny in 1806 CE, the British East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
consolidated their power over much of the region. The British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
took control of the region from the British East India Company in 1857.
During the British colonial rule, the region was divided between the Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency or Madras Province, officially called the Presidency of Fort St. George until 1937, was an administrative subdivision (province) of British India and later the Dominion of India. At its greatest extent, the presidency i ...
, Bombay Presidency, Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state in the Deccan region of south-central India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and the ...
, and Mysore
Mysore ( ), officially Mysuru (), is a city in the southern Indian state of Karnataka. It is the headquarters of Mysore district and Mysore division. As the traditional seat of the Wadiyar dynasty, the city functioned as the capital of the ...
. The region played a major role in the Indian independence movement
The Indian independence movement was a series of historic events in South Asia with the ultimate aim of ending British Raj, British colonial rule. It lasted until 1947, when the Indian Independence Act 1947 was passed.
The first nationalistic ...
. After Indian Independence in 1947, majority of the region was organised into four states Bombay State
Bombay State was a large Indian state created in 1950 from the erstwhile Bombay Province, with other regions being added to it in the succeeding years. Bombay Province (in British India roughly equating to the present-day Indian state of Mah ...
, Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state in the Deccan region of south-central India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and the ...
, Madras State
Madras State was a state in the Indian Republic, which was in existence during the mid-20th century as a successor to the Madras Presidency of British India. The state came into existence on 26 January 1950 when the Constitution of India was ad ...
, and Mysore State. The Reorganisation of Indian states on linguistic lines in the 1950s resulted in the creation of the states of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
, Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
, Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, and Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
. Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
was created in 2014 by bifurcating Andhra Pradesh.
Geology

 The Deccan Plateau is one of the oldest and most stable land formations in the
The Deccan Plateau is one of the oldest and most stable land formations in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. The plateau is marked by rocky terrain with an average of about 600 m (2,000 ft). The Deccan Traps consist of multiple layers of igneous rocks
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main Rock (geology)#Classification, rock types, the others being sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidifi ...
, which are more than in thickness. These rocks were laid down by basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron ( mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% ...
lava flows which emerged from deep inside the Earth's crust
Earth's crust is its thick outer shell of rock, referring to less than one percent of the planet's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a solidified division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper ...
following a massive volcanic eruption
A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior h ...
.
The eruption event occurred during the end of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period (66 mya) and is the second largest volcanic eruption ever recorded on land. Scientists state that the volcanic event would have released large amounts of ash, dust and carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
into the atmosphere. The release would have blocked sunlight
Sunlight is the portion of the electromagnetic radiation which is emitted by the Sun (i.e. solar radiation) and received by the Earth, in particular the visible spectrum, visible light perceptible to the human eye as well as invisible infrare ...
resulting in lower temperatures and caused major climatic changes on Earth. The eruption would have resulted in high levels of sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms ...
, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
and other toxic gases in the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
. Researchers argue that the volcanic event would have contributed to the extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
of various species including some of the dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
.
The volcanic deposits stretch more than encompassing neighbouring central highlands. The deposits consist of three subgroups based on the time and level of deposition. Underlying the lava deposits are granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
and sedimentary rocks
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedim ...
formed during the Precambrian
The Precambrian ( ; or pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pC, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of t ...
era and the formation of Gondwanaland. The Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
rests on hard crystalline rocks which connect the Himalayan region with the plateau region. Apart from granite, parts of the region consists of metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
such as gneiss
Gneiss (pronounced ) is a common and widely distributed type of metamorphic rock. It is formed by high-temperature and high-pressure metamorphic processes acting on formations composed of igneous or sedimentary rocks. This rock is formed under p ...
, and schist
Schist ( ) is a medium-grained metamorphic rock generally derived from fine-grained sedimentary rock, like shale. It shows pronounced ''schistosity'' (named for the rock). This means that the rock is composed of mineral grains easily seen with a l ...
.
The Deccan Plateau region is rich in mineral deposits like iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the f ...
, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, and mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into fragile elastic plates. This characteristic is described as ''perfect basal cleavage''. Mica is co ...
. Precious and semi precious stones have also been mined from the region. Large uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Ura ...
deposits have been discovered in the region in the 21st century. There are two major soil types, forming distinct sub-regions of the plateau. Most of the region with igneous basaltic rock consists of black soil. These soils have a high clay content, retain moisture and are resistant to erosion, but develop cracks during the dry season. The gneiss peneplain region in the low rainfall areas in the eastern vicinity of the Western Ghats consist of infertile red soil.
Geography
 Historians have used the term Deccan differently across various time periods. Firishta (16th century), R. G. Bhandarkar (1920), and Richard Eaton (2005) demarcate the region based on linguistic lines. K. M. Panikkar (1969) defines it as the entire Indian peninsula south of the Vindhyas. Stewart Gordon (1998) notes that Deccan is a "relational term" and historically the border of Deccan has varied from Tapti River to the
Historians have used the term Deccan differently across various time periods. Firishta (16th century), R. G. Bhandarkar (1920), and Richard Eaton (2005) demarcate the region based on linguistic lines. K. M. Panikkar (1969) defines it as the entire Indian peninsula south of the Vindhyas. Stewart Gordon (1998) notes that Deccan is a "relational term" and historically the border of Deccan has varied from Tapti River to the Godavari River
The Godavari (, Help:IPA/Sanskrit, �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganges River, Ganga River and drains the third largest Drainage basin, basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. It ...
, depending on the southern boundary of the northern empires and is used to denote "the area beyond the southern border of a northern-based kingdom" of India.
Geographers have defined the extent of Deccan region using various physical features and indices such as rainfall, vegetation, or soil type. As per a broader geographical definition, the region consists of the peninsular tableland lying to the south of the Tropic of Cancer
The Tropic of Cancer, also known as the Northern Tropic, is the Earth's northernmost circle of latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. This occurs on the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun ...
, marked by the Vindhya- Satpura ranges in the north. The Deccan is a plateau region extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It is shaped like an inverted triangle with its upper boundary at the Narmada River
The Narmada River, previously also known as ''Narbada'' or anglicised as ''Nerbudda'', is the 5th longest river in India and overall the longest west-flowing river in the country. It is also the largest flowing river in the state of Madhya Prade ...
basin near the Vindhya-Satpura ranges and the lower boundary at the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is the southernmost States and union territories of India, state of India. The List of states and union territories of India by area, tenth largest Indian state by area and the List of states and union territories of Indi ...
in the south.
The region is bound by the mountain ranges of the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats
The Eastern Ghats is a mountain range that stretches along the East Coast of India, eastern coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of , it traverses the states and union territories of India, states of Odisha, Telangana, Andhra Prade ...
on the sides, which separate the region from the Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
and Eastern Coastal Plains
The Eastern Coastal Plains is a stretch of landmass lying between the eastern part of the Deccan plateau and the Bay of Bengal in India. The plains stretch from the Mahanadi delta to Kaniyakumari at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula with ...
respectively. It covers most of the Indian state
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, for a total of 36 subnational entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into 800 districts and smaller administrative divisions by the respe ...
s of Maharashtra
Maharashtra () is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to th ...
, Telangana
Telangana is a States and union territories of India, state in India situated in the Southern India, south-central part of the Indian subcontinent on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, ele ...
, Karnataka
Karnataka ( ) is a States and union territories of India, state in the southwestern region of India. It was Unification of Karnataka, formed as Mysore State on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Re ...
and Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (ISO 15919, ISO: , , AP) is a States and union territories of India, state on the East Coast of India, east coast of southern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by area, seventh-largest state and th ...
excluding the coastal regions, and minor portions of Tamil Nadu and Kerala
Kerala ( , ) is a States and union territories of India, state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile ...
. The western side of the plateau is elevated gently slopes towards the east. It is subdivided into Maharashtra Plateau, Karnataka Plateau, and Telangana Plateau.
Hydrography and climate
Godavari
The Godavari (, �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga River and drains the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharash ...
, Kaveri
The Kaveri (also known as Cauvery) is a Rivers of India, major river flowing across Southern India. It is the third largest river in the region after Godavari River, Godavari and Krishna River, Krishna.
The catchment area of the Kaveri basin i ...
, and Krishna
Krishna (; Sanskrit language, Sanskrit: कृष्ण, ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme God (Hinduism), Supreme God in his own right. He is the god of protection, c ...
. Most rivers flow eastwards towards the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
owing to the steeper gradient moving from east to west, with only smaller streams flowing in the opposite direction. The streams and rivers give rise to numerous waterfalls in the region. The rivers have been dammed for hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering of plants) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has bee ...
purposes, with major reservoirs spread across the region.
The region has largely semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a aridity, dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below Evapotranspiration#Potential evapotranspiration, potential evapotranspiration, but not as l ...
climate in the northern parts and tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of or higher in the coolest month, featuring hot te ...
in most of the other areas. The summer months of AprilMay are dry and hot with maximum temperatures often rising more than . During the dry summer months of AprilMay, heat builds up on the interior of the Deccan Plaeau, which draws air from the sea. The air, which picks up moisture along the way and flows eastward from the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
, is blocked by the Western Ghats. The rising air cools and brings about orographic precipitation along the western coast, which signifies the onset of the monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annu ...
season in June.
By the time the air rises above the mountains, it becomes dry, resulting in a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from body of water, bodies of water (such as oceans and larg ...
region with very little rainfall on the leeward
In geography and seamanship, windward () and leeward () are directions relative to the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e., towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point o ...
side towards the interior of the Deccan plateau. The monsoon winds rounding up the peninsula and moving from the east from the Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. Geographically it is positioned between the Indian subcontinent and the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese peninsula, located below the Bengal region.
Many South Asian and Southe ...
pass over the Eastern Ghats and bring some rainfall to the eastern region of the plateau. The region receives most of the rainfall during the months of July to September and the rains feed the rivers that flow into basins and then into the Bay of Bengal.
Flora and fauna
There is a wide diversity of plants and animals in the region, resulting from its varied climates and geography. scrub lands are common in the low rainfall regions with dry deciduous forests found in the southern part of the plateau. The woodlands of the region are older than theHimalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
. The central part of the plateau is covered by woodlands formed by trees such as hardwickia, teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panic ...
, siris, axlewood, boswellia
''Boswellia'' is a genus of trees in the order (biology), order Sapindales, known for its fragrant resin. The biblical incense frankincense is an extract from the resin of the tree ''Boswellia sacra'', and is now produced also from ''Boswellia fre ...
, and acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as wattles or acacias, is a genus of about of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa, South America, and Austral ...
trees. The region hosts significant populations of endangered Bengal tigers and Indian elephants Other mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
found in the region include gaur, blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is a medium-sized antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the sh ...
, chinkara, four-horned antelope, wild buffalo, and Indian wild dog.
Demographics
Telugus
Telugu people (), also called Āndhras, are an ethno-linguistic group who speak the Telugu language and are native to the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Telangana and Yanam district of Puducherry. They are the most populous of the four ...
and Kannadigas
The Kannadigas or Kannadigaru (), often referred to as Kannada people, are a Dravidian ethno-linguistic group who natively speak Kannada, primarily in the south Indian state of Karnataka and its surrounding regions. The Kannada language belongs ...
who speak Telugu and Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of the population in all neighbouring states. It has 44 million native speakers, and is additionally a ...
form the major demographic groups in the central region. Tamils
The Tamils ( ), also known by their endonym Tamilar, are a Dravidian peoples, Dravidian ethnic group who natively speak the Tamil language and trace their ancestry mainly to the southern part of the Indian subcontinent. The Tamil language is o ...
and Malayalis
The Malayali people (; also spelt Malayalee and sometimes known by the demonym Keralite) are a Dravidian languages, Dravidian ethnolinguistic group originating from the present-day state of Kerala and Union Territory of Lakshadweep in India, ...
form a part of the southern end of the plateau. Marathi people
The Marathi people (; Marathi language, Marathi: , ''Marāṭhī lōk'') or Marathis (Marathi: मराठी, ''Marāṭhī'') are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are native to Maharashtra in western India. They ...
, who speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language, form the majority in the north-western part of the plateau. English is also widely spoken in urban areas of the region. Deccani Urdu a regional dialect of Urdu
Urdu (; , , ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken chiefly in South Asia. It is the Languages of Pakistan, national language and ''lingua franca'' of Pakistan. In India, it is an Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of Indi ...
is spoken by the Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
. Evidence of prehistoric religion in the region comes from scattered Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Ancient Greek language, Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic i ...
rock paintings depicting dances and rituals, such as the Kupgal petroglyphs of eastern Karnataka, at Stone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistory, prehistoric period during which Rock (geology), stone was widely used to make stone tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years and ended b ...
sites. Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is the major religion today in the region.
The total fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
in the region was less than the population replacement level and as a result, the proportion of the population of the region to India's total population has declined in the last four decades. The economies of the states in the region registered a growth higher than the national average over the past three decades. While the states have improved in some of the socio-economic
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analys ...
metrics, there is wide disparity within the region.
Economy
Agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
is often difficult in low rainfall areas, which require additional irrigation facilities while it is more feasible in the river valleys. Agriculture is still the primary occupation in the region. Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
is the staple food and major crop in the region. Others crops cultivated include sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
, banana
A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large treelike herbaceous flowering plants in the genus '' Musa''. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing the ...
, cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
, turmeric
Turmeric (), or ''Curcuma longa'' (), is a flowering plant in the ginger family Zingiberaceae. It is a perennial, rhizomatous, herbaceous plant native to the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia that requires temperatures between and high ...
, millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most millets belong to the tribe Paniceae.
Millets are important crops in the Semi-arid climate, ...
s, pulses, and spices
In the culinary arts, a spice is any seed, fruit, root, Bark (botany), bark, or other plant substance in a form primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of pl ...
. The urban centres are significant contributors to the Indian and global Information Technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
economy. The presence of these hubs has spurred economic growth and attracted foreign investments and job seekers from other parts of the country. Manufacturing and textiles are other major industries in the region.
Culture
As defined byMinistry of Culture Ministry of Culture may refer to:
* Ministry of Tourism, Cultural Affairs, Youth and Sports (Albania)
* Ministry of Culture (Algeria)
* Ministry of Culture (Argentina)
* Minister for the Arts (Australia)
* Ministry of Culture (Azerbaijan)Ministry o ...
of the Government of India to promote and preserve the cultural heritage
Cultural heritage is the heritage of tangible and intangible heritage assets of a group or society that is inherited from past generations. Not all heritages of past generations are "heritage"; rather, heritage is a product of selection by socie ...
, the region falls under the purview of West and South Zone Cultural Centers. The women traditionally wear a '' sari'', a garment that consists of a drape varying from to in length and to in breadth that is typically wrapped around the waist, with one end draped over the shoulder, baring the midriff, as according to Indian philosophy, the navel is considered as the source of life and creativity. The men wear a '' dhoti'', a long, white rectangular piece of non-stitched cloth often bordered in brightly coloured stripes. It is usually wrapped around the waist and the legs and knotted at the waist. A colourful '' lungi'' with typical batik
Batik is a dyeing technique using wax Resist dyeing, resist. The term is also used to describe patterned textiles created with that technique. Batik is made by drawing or stamping wax on a cloth to prevent colour absorption during the dyein ...
patterns is the most common form of male attire in the countryside. People in urban areas generally wear tailored clothing, and western dress is popular. Western-style school uniforms are worn by both boys and girls in schools, even in rural areas.
The region has a rich cuisine involving both traditional non-vegetarian and vegetarian dishes. The traditional way of eating a meal involves eating food served on a banana leaf using the right hand. Rice
Rice is a cereal grain and in its Domestication, domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much l ...
is the staple food in meals of the region. Bhakri made of millets and roti
Roti is a round flatbread originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is commonly consumed in many South Asian, Southeast Asian, Caribbean, East African, and Southeast African countries.
It is made from stoneground whole-wheat flour, kno ...
or chapathi made of wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
served with dal
Dal is a term in the Indian subcontinent for dried, split pulses.
Dal or DAL may also refer to:
Places
Cambodia
*Dal, Ke Chong
Finland
* Laakso, a neighbourhood of Helsinki
India
* Dal Lake, in Srinagar, Jammu and Kashmir, India
* Dal ...
are popular in the north and western parts of the region. '' Idli'' and '' dosa'' served with sambar and chutney
A chutney () is a spread typically associated with cuisines of the Indian subcontinent. Chutneys are made in a wide variety of forms, such as a tomato relish, a ground peanut garnish, yogurt, or curd, cucumber, spicy coconut, spicy onion ...
for breakfast and rice served with ''sambar'' and '' rasam'' for lunch are popular in the eastern and southern parts of the region. Hyderabadi cuisine is popular for its '' biryani''.
The region is home to various music and dance forms such as Kuchipudi, Lavani
Lavani is a genre of music popular in Maharashtra, India. Lavani is a combination of traditional song and dance, which particularly performed to the beats of ''Dholki'', a percussion instrument. Lavani is noted for its powerful rhythm. Lavani h ...
, Yakshagana
Yakshagana is a traditional theatre, found in Dakshina Kannada, Udupi, Kasaragod district and Uttara Kannada, Shimoga and western parts of Chikmagalur district, Chikmagalur districts, in the state of Karnataka and in Kasaragod district in Keral ...
, and Bharatanatyam
''Bharatanatyam'' is a Indian classical dance form that came from Tamil Nadu, India. It is a classical dance form recognized by the Sangeet Natak Akademi, and expresses South Indian religious themes and spiritual ideas of Hinduism and Jainism.< ...
. There are three distinct styles of rock architecture, the '' Dravidian'' style of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, the '' Vesara'' style of Karnataka, Telangana, and the '' Nagara'' style of Maharashtra. In Dravidian architecture, the temples considered of large gate-pyramids or ''Gopuram
A ''gopuram'' or ''gopura'' ( Tamil: கோபுரம், Telugu: గోపురం, Kannada
Kannada () is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly in the state of Karnataka in southwestern India, and spoken by a minority of th ...
s'' in quadrangular enclosures that surround the temple with large pillared halls. '' Vimanam'' are similar structures built over the ''garbhagriha
A ''garbhagriha'' () is the innermost sanctuary of Hindu and Jain temples, often referred to as the "holy of holies" or " sanctum sanctorum".
The term ''garbhagriha'' (literally, "womb chamber") comes from the Sanskrit words ''garbha'' for ...
'' or inner sanctum of the temple but are usually smaller than the gopurams in the Dravidian architecture. In the Nagara style, the temples had one or more ''shikhara
''Shikhara'' (IAST: '), a Sanskrit word translating literally to "mountain peak", refers to the rising tower in the Hindu temple architecture of North India, and also often used in Jain temples. A ''shikhara'' over the ''garbhagriha'' chamber ...
s'', which are towers similar to the vimanas. The Vesara style is a hybrid of both these architectural styles.
Transport
National Highways
National Highways (NH), formerly Highways England and before that the Highways Agency, is a State-owned enterprise, government-owned company charged with operating, maintaining and improving Roads in England, motorways and major A roads in Eng ...
, State Highways
A state highway, state road, or state route (and the equivalent provincial highway, provincial road, or provincial route) is usually a road that is either Route number, numbered or maintained by a sub-national state or province. A road numbered ...
and other roads in the region. The Golden Quadrilateral
The Golden Quadrilateral (; abbreviated GQ) is a network of National Highway (India), national highways connecting major cities of India. It roughly forms a quadrilateral with major cities – Delhi (north), Kolkata (east), Mumbai (west) and ...
connecting the major cities in the country traverses across the region. Public bus services are mostly provided by state-run transport corporations.
The Madras Railway was established in 1845 and the Great Indian Peninsular Railway was incorporated in 1849. The construction on the first main line in the South between Royapuram in Madras and Arcot started in 1853, which became operational on 1 July 1856. In 1879, the Nizam's Guaranteed State Railway was established which built railway lines across the then Hyderabad State
Hyderabad State () was a princely state in the Deccan region of south-central India with its capital at the city of Hyderabad. It is now divided into the present-day state of Telangana, the Kalyana-Karnataka region of Karnataka, and the ...
and the Mysore State Railway was established to build an extension of Madras Railway in Mysore State. In 1880, the Great Indian Peninsula Railway built a railway network radiating from Madras. The Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway was founded on 1 January 1908 by merging the Madras Railway and the Southern Mahratta Railway
Southern Mahratta Railway (SMR) was a railway company in British India founded in 1882.
History
Captain Charles Cooper Johnson, officiating as constructing engineer of railways in 1858, forwarded the proposal for a railway to be constructed an ...
. In 1950, there were about 42 different railway companies across the countrym which were amalgamated in steps to form a single entity named as Indian Railways
Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise that is organised as a departmental undertaking of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of the Government of India and operates India's national railway system. , it manages the fou ...
. On 14 April 1951, the Madras and Southern Mahratta Railway, the South Indian Railway, and the Mysore State Railway were merged to form the Southern Railway, the first zone of Indian Railways
Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise that is organised as a departmental undertaking of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of the Government of India and operates India's national railway system. , it manages the fou ...
. The Western
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
was established on 5 November 1951, the South Central zone on 2 October 1966, and the South Western zone on 1 April 2003. Most of the region is covered by these four zones, with small portions of the coasts covered by East Coast Railway and Konkan Railway
The Konkan Railway (abbreviated KR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India with its headquarters at CBD Belapur in Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. The Konkan Railway line from Roha to Thokur is operated and maintained by Konkan Railway co ...
. Metro and suburban systems are operational in major cities.
Air transport in the region started in the late 1910s with commercial services beginning in the 1930s. The region has multiple international and domestic airports. Chennai International Airport serves as the Southern Regional Headquarters of the Airports Authority of India, the Southern Region comprising the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, and Mumbai International Airport serves the state of Maharashtra. The southern region comes under the purview of the Southern Air Command of the Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflicts. It was officially established on 8 Octob ...
and the north western region comes under the South Western Air Command.
See also
* Central Highlands *Eastern Coastal Plains
The Eastern Coastal Plains is a stretch of landmass lying between the eastern part of the Deccan plateau and the Bay of Bengal in India. The plains stretch from the Mahanadi delta to Kaniyakumari at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula with ...
* Indo-Gangetic Plain
The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the Northern Plain or North Indian River Plain, is a fertile plain spanning across the northern and north-eastern part of the Indian subcontinent. It encompasses North India, northern and East India, easte ...
* Western Coastal Plains
References
External links
* {{Authority controlDeccan Plateau
The Deccan is a plateau extending over an area of and occupies the majority of the Indian peninsula. It stretches from the Satpura Range, Satpura and Vindhya Ranges in the north to the northern fringes of Tamil Nadu in the south. It is bound ...
Natural regions of India