Cypress Cove (microarchitecture) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sunny Cove is a codename for a CPU
 * On average 18% increase in
* On average 18% increase in
microarchitecture
In computer engineering, microarchitecture, also called computer organization and sometimes abbreviated as µarch or uarch, is the way a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented in a particular processor. A given ISA may be impl ...
developed by Intel, first released in September 2019. It succeeds the Palm Cove microarchitecture and is fabricated using Intel's 10 nm
The following are examples of orders of magnitude for different lengths.
__TOC__
Overview
Detailed list
To help compare different orders of magnitude, the following list describes various lengths between 1.6 \times 10^ metres and 10^ ...
process node. The microarchitecture is implemented in 10th-generation Intel Core processors for mobile (codenamed '' Ice Lake'') and third generation Xeon scalable server processors (codenamed ''Ice Lake-SP''). 10th-generation Intel Core mobile processors were released in September 2019, while the Xeon server processors were released in April 6, 2021.
There are no desktop products featuring Sunny Cove. However, a variant named Cypress Cove is used for the 11th-generation Intel Core desktop processors (codenamed '' Rocket Lake''). Cypress Cove is a version of the Sunny Cove microarchitecture backported to Intel's 14 nm process node.
The direct successor to the Sunny Cove microarchitecture is the Willow Cove
Willow Cove is a codename for a CPU microarchitecture developed by Intel and released in September 2020. Willow Cove is the successor to the Sunny Cove microarchitecture, and is fabricated using Intel's enhanced 10 nm process node called 10 ...
microarchitecture, which powers the 11th-generation Intel Core mobile processors.
Features
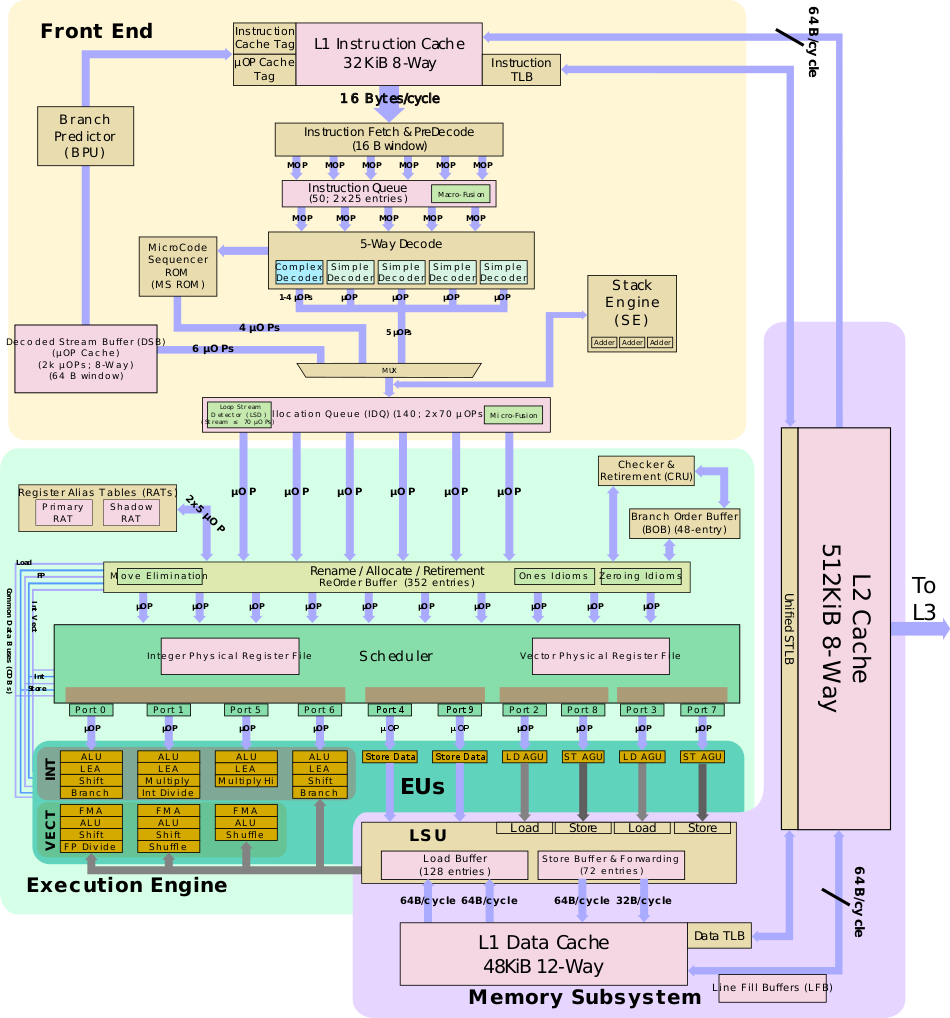
Sunny Cove was designed by Intel Israel's processor design team in Haifa, Israel. Intel released details of Ice Lake and its microarchitecture, Sunny Cove, during Intel Architecture Day in December 2018, stating that the Sunny Cove cores would be focusing on single-thread performance, new instructions, and scalability improvements. Intel stated that the performance improvements would be achieved by making the core "deeper, wider, and smarter". Sunny Cove features a 50% increase in the size of L1 data cache, a larger L2 cache dependent on product size, larger μOP cache, and larger second-level TLB. The core has also increased in width, by increasing execution ports from eight to ten and by doubling the L1 store bandwidth. Allocation width has also increased from four to five. The5-level paging
Intel 5-level paging, referred to simply as ''5-level paging'' in Intel documents, is a processor extension for the x86-64 line of processors. It extends the size of virtual addresses from 48 bits to 57 bits, increasing the addressabl ...
scheme supports a linear address space up to 57 bits and a physical address space up to 52 bits, increasing the virtual memory space to 128 petabytes, up from 256 terabytes, and the addressable physical memory to 4 petabytes, up from 64 terabytes.
Improvements
: * On average 18% increase in
* On average 18% increase in IPC
IPC may refer to:
Computing
* Infrastructure protection centre or information security operations center
* Instructions per cycle or instructions per clock, an aspect of central-processing performance
* Inter-process communication, the sharin ...
in comparison to 2015 Skylake Skylake or Sky Lake may refer to:
* Skylake (microarchitecture), the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the successor to Broadwell
* Skylake (Mysia), a town of ancient Mysia, now in Turkey
* Sky Lake, Florida
Sky La ...
running at the same frequency and memory configuration
* Increase L1 data cache: 48 kiB (from 32 kiB)
* L2 cache: 512 kiB
* Larger micro-instruction cache (2304 entries, up from 1536)
* Larger re-order buffer
A re-order buffer (ROB) is a hardware unit used in an extension to the Tomasulo algorithm to support out-of-order and speculative instruction execution. The extension forces instructions to be committed in-order.
The buffer is a circular buffer ...
(352, up from 224 entries)
* Dynamic Tuning 2.0 which allows the CPU to stay at turbo frequencies for longer
* Hardware acceleration for SHA operations (Secure Hash Algorithms
The Secure Hash Algorithms are a family of cryptographic hash functions published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS), including:
* SHA-0: A retronym applied t ...
)
* New AVX-512 instruction subsets:
** VPOPCNTDQ
** VBMI2
** BITALG
** VPCLMULQDQ
** GFNI
** VAES
** VNNI
* Wider decoder (from skylake’s 3 simple + 1 complex 4 way decoding to Sunny cove’s 4 simple + 1 complex 5 wide decoder)
* 1.6x larger ROB (352, up from 224 entries)
** Scheduler
*** 1.65x larger scheduler (160-entry, up from 97 entries)
*** Larger dispatch (10-way, up from 8-way)
** 1.55x larger integer register file (280-entry, up from 180)
** 1.33x larger vector register file (224-entry, up from 168)
** Distributed scheduling queues (4 scheduling queues, up from 2)
* Intel Deep Learning Boost
Intel's Deep Learning Boost (DL Boost) is a marketing name for instruction set architecture features on the x86-64 designed to improve performance on deep learning tasks such as training and inference. DL Boost consists of two sets of features:
...
, used for machine learning/ artificial intelligence inference
Inferences are steps in reasoning, moving from premises to logical consequences; etymologically, the word '' infer'' means to "carry forward". Inference is theoretically traditionally divided into deduction and induction, a distinction that in ...
acceleration
Cypress Cove
Cypress Cove is a CPU microarchitecture based on the Sunny Cove microarchitecture designed for 10 nm, backported to 14 nm. It succeeds theSkylake Skylake or Sky Lake may refer to:
* Skylake (microarchitecture), the codename for a processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the successor to Broadwell
* Skylake (Mysia), a town of ancient Mysia, now in Turkey
* Sky Lake, Florida
Sky La ...
microarchitecture, and is manufactured using Intel's 14 nm process node. Cypress Cove is identical to Sunny Cove, aside from a number of improvements and other changes. Notably the L1 data cache latency has been reduced from five cycles that is on Sunny Cove to just three cycles on Cypress Cove. Intel claims an increase of 19% in IPC in Cypress Cove-based Rocket Lake processors compared to Comet Lake.
Cypress Cove is implemented on 11th Gen Intel Core desktop processors (codenamed '' Rocket Lake''). Rocket Lake and its underlying microarchitecture were first described in November 2020, and was later released on March 30, 2021.
SGX is removed from Rocket Lake.
Products
Sunny Cove powers the 10th generation of Intel Core mobile processors (codenamed ''Ice Lake'') and the third generation of Xeon Scalable server processors (codenamed ''Ice Lake-SP''). Cypress Cove is implemented on 11th-generation Intel Core desktop processors (codenamed ''Rocket Lake'').References
{{Intel processor roadmap X86 microarchitectures Intel Intel microarchitectures