Crack lung on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant
Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant
 Crack vaporizes near temperature 90 °C (194 °F), much lower than the cocaine hydrochloride melting point of 190 °C (374 °F). Whereas cocaine hydrochloride cannot be smoked (burns with no effect),
Crack cocaine can also be injected intravenously with the same effect as powder cocaine. However, whereas powder cocaine dissolves in water, crack must be dissolved in an acidic solution such as lemon juice (containing
Crack vaporizes near temperature 90 °C (194 °F), much lower than the cocaine hydrochloride melting point of 190 °C (374 °F). Whereas cocaine hydrochloride cannot be smoked (burns with no effect),
Crack cocaine can also be injected intravenously with the same effect as powder cocaine. However, whereas powder cocaine dissolves in water, crack must be dissolved in an acidic solution such as lemon juice (containing
DEA-cocaine
. "Life or Meth – CRACK OF THE 90'S", Salt Lake City Police Department, Utah, 2008, PDF file:
Methlife-PDF
. Its initial effect is to release a large amount of
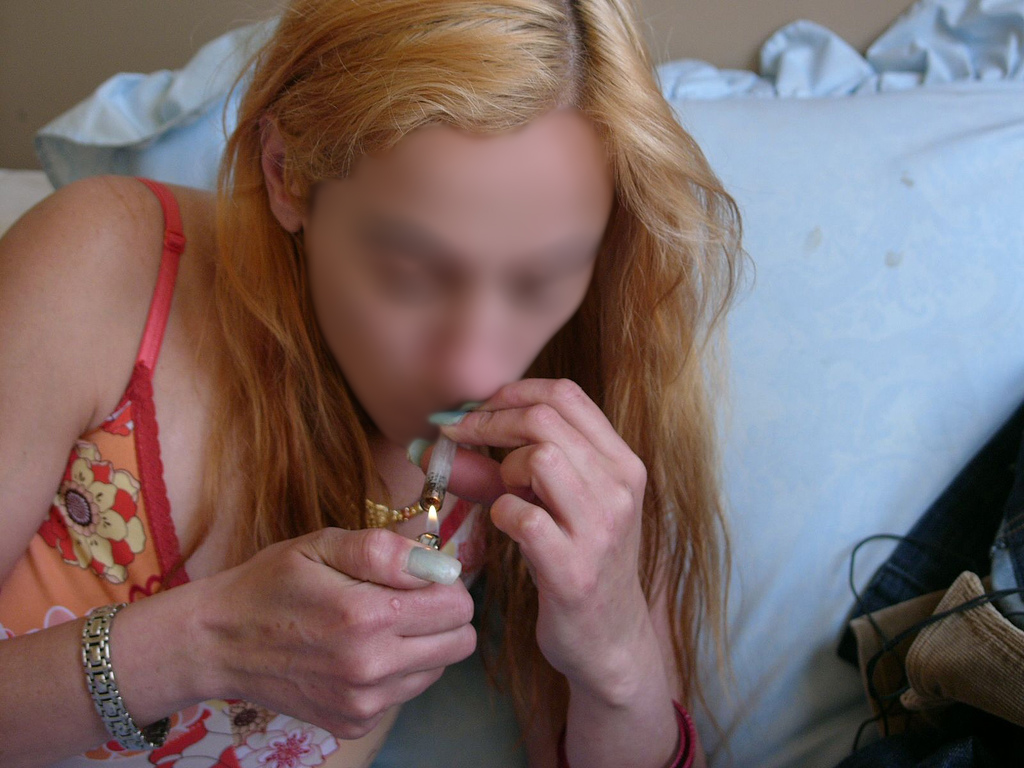 Crack cocaine is usually heated in a drug pipe until sublimation occurs at a relatively low temperature (about 90°C) and the
Crack cocaine is usually heated in a drug pipe until sublimation occurs at a relatively low temperature (about 90°C) and the
 People often freebase crack with a pipe made from a small glass tube, often taken from " love roses", small glass tubes with a paper rose that are promoted as romantic gifts. These are sometimes called "stems", "horns", "blasters" and "straight shooters". A small piece of clean heavy copper or occasionally stainless steel scouring padoften called a "brillo" (actual
People often freebase crack with a pipe made from a small glass tube, often taken from " love roses", small glass tubes with a paper rose that are promoted as romantic gifts. These are sometimes called "stems", "horns", "blasters" and "straight shooters". A small piece of clean heavy copper or occasionally stainless steel scouring padoften called a "brillo" (actual
 Incidental exposure of the eye to sublimated cocaine while smoking crack cocaine can cause serious injury to the
Incidental exposure of the eye to sublimated cocaine while smoking crack cocaine can cause serious injury to the
UCDavis-delusional
People experiencing these hallucinations might scratch themselves to the extent of serious skin damage and bleeding, especially when they are delirious. Paranoia and anxiety are among the most common psychological symptoms of crack cocaine use. Psychosis is more closely associated with smoking crack cocaine than intranasal and intravenous use.
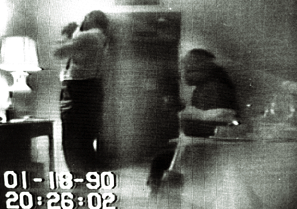 In the United Kingdom, crack is a List of controlled drugs in the United Kingdom, Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. In the Netherlands it is a List 1 drug of the Opium Law.
In the United Kingdom, crack is a List of controlled drugs in the United Kingdom, Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. In the Netherlands it is a List 1 drug of the Opium Law.
 Many major American urban areas contain Drug house, crack houses. In some cases, enraged citizens have burned crack houses to the ground, in hopes that by destroying the sites for drug operations they would also drive the illegal industries from their neighborhoods.
Many major American urban areas contain Drug house, crack houses. In some cases, enraged citizens have burned crack houses to the ground, in hopes that by destroying the sites for drug operations they would also drive the illegal industries from their neighborhoods.
 Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant
Crack cocaine, commonly known simply as crack, and also known as rock, is a free base form of the stimulant cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
that can be smoked. Crack offers a short, intense high to smokers. The ''Manual of Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment'' calls it the most addictive form of cocaine.
Crack cocaine first saw widespread use as a recreational drug
Recreational drug use is the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness, either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime. When a psychoactive drug enters the user's body, it induces an Sub ...
in primarily impoverished neighborhoods in New York City, Philadelphia, Baltimore, Washington, D.C., Los Angeles, San Francisco and Miami in late 1984 and 1985. This rapid increase in use and availability was named the "crack epidemic
The crack epidemic was a surge of crack cocaine use in major cities across the United States throughout the entirety of the 1980s and the early 1990s. This resulted in several social consequences, such as increasing crime and violence in Americ ...
", which began to wane in the 1990s. The use of another highly addictive stimulant drug, crystal meth, became popular between 1994 and 2004.
Terminology
The origin of the name "crack" comes from the "crackling" sound (and hence theonomatopoeic
Onomatopoeia (or rarely echoism) is a type of word, or the process of creating a word, that phonetically imitates, resembles, or suggests the sound that it describes. Common onomatopoeias in English include animal noises such as ''oink'', '' ...
moniker "crack") that is produced when the cocaine and its impurities (i.e. water, sodium bicarbonate) are heated past the point of vaporization.
It is also commonly called "rock" on the street, a name that comes from its physical appearance after processing. When bulk quantities of powdered cocaine are mixed with baking soda or ammonia and water, then heated, it forms small, hard, solid crystals or pellets that resemble rocks.
Contraindications
Pregnancy
''Crack baby'' is a term for a child born to a mother who used crack cocaine during her pregnancy. The threat that cocaine use duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
poses to the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
is now considered exaggerated. Studies show that prenatal cocaine exposure (independent of other effects such as, for example, alcohol, tobacco, or physical environment) has no appreciable effect on childhood growth and development.
In 2007, the National Institute on Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is a United States federal government research institute whose mission is to "advance science on the causes and consequences of drug use and addiction and to apply that knowledge to improve individual ...
of the United States warned about health risks while cautioning against stereotyping:
Chemistry
As the name implies, "freebase" is the base form of cocaine, as opposed to thesalt
In common usage, salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl). When used in food, especially in granulated form, it is more formally called table salt. In the form of a natural crystalline mineral, salt is also known as r ...
form. It is practically insoluble in water whereas hydrochloride salt is water-soluble.
Smoking freebase cocaine has the additional effect of releasing methylecgonidine into the user's system due to the pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
of the substance (a side effect which insufflating or injecting powder cocaine does not create). Some research suggests that smoking freebase cocaine can be even more cardiotoxic than other routes of administration
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance ...
because of methylecgonidine's effects on lung tissue and liver tissue.
Pure cocaine is prepared by neutralizing its compounding salt with an alkaline solution, which will precipitate
In an aqueous solution, precipitation is the "sedimentation of a solid material (a precipitate) from a liquid solution". The solid formed is called the precipitate. In case of an inorganic chemical reaction leading to precipitation, the chemic ...
non-polar basic cocaine. It is further refined through aqueous-solvent liquid–liquid extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction, also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds or metal complexes, based on their relative solubility, solubilities in two different Miscibility, immiscible liquids, usually wate ...
.
Purer forms of crack resemble off-white, jagged-edged "rocks" of a hard, brittle plastic, with a slightly higher density than candle wax. Like cocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
in other forms, crack rock acts as a local anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensati ...
, numbing the tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper s ...
or mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
only where directly placed. Purer forms of crack will sink in water and melt at the edges when near a flame (crack vaporizes at 90 °C, 194 °F).
Crack cocaine sold on the streets may be adulterated (or "cut") with other substances mimicking the appearance of crack to increase bulk. Use of toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
adulterants such as levamisole
Levamisole, sold under the brand name Ergamisol among others, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infections, specifically ascariasis and hookworm infections. It is taken by mouth.
Side effects may include abdominal pain, vomiting, ...
, a drug used to treat parasitic worm
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other par ...
infections, has been documented.
Synthesis
Sodium bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate ( IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cat ...
(NaHCO3, common baking soda) is a base used in the preparation of crack, although other weak base
A weak base is a base that, upon dissolution in water, does not dissociate completely, so that the resulting aqueous solution contains only a small proportion of hydroxide ions and the concerned basic radical, and a large proportion of undissocia ...
s may substitute for it.
The net reaction when using sodium bicarbonate is
:Coc-H+Cl− + NaHCO3 → Coc + H2O + CO2 + NaCl
With ammonium bicarbonate
Ammonium bicarbonate is an inorganic compound with formula (NH4)HCO3. The compound has many names, reflecting its long history. Chemically speaking, it is the bicarbonate salt of the ammonium ion. It is a colourless solid that degrades readily to ...
:
:Coc-H+Cl− + NH4HCO3 → Coc + NH4Cl + CO2 + H2O
With ammonium carbonate:
:2(Coc-H+Cl−) + (NH4)2CO3 → 2 Coc + 2 NH4Cl + CO2 + H2O
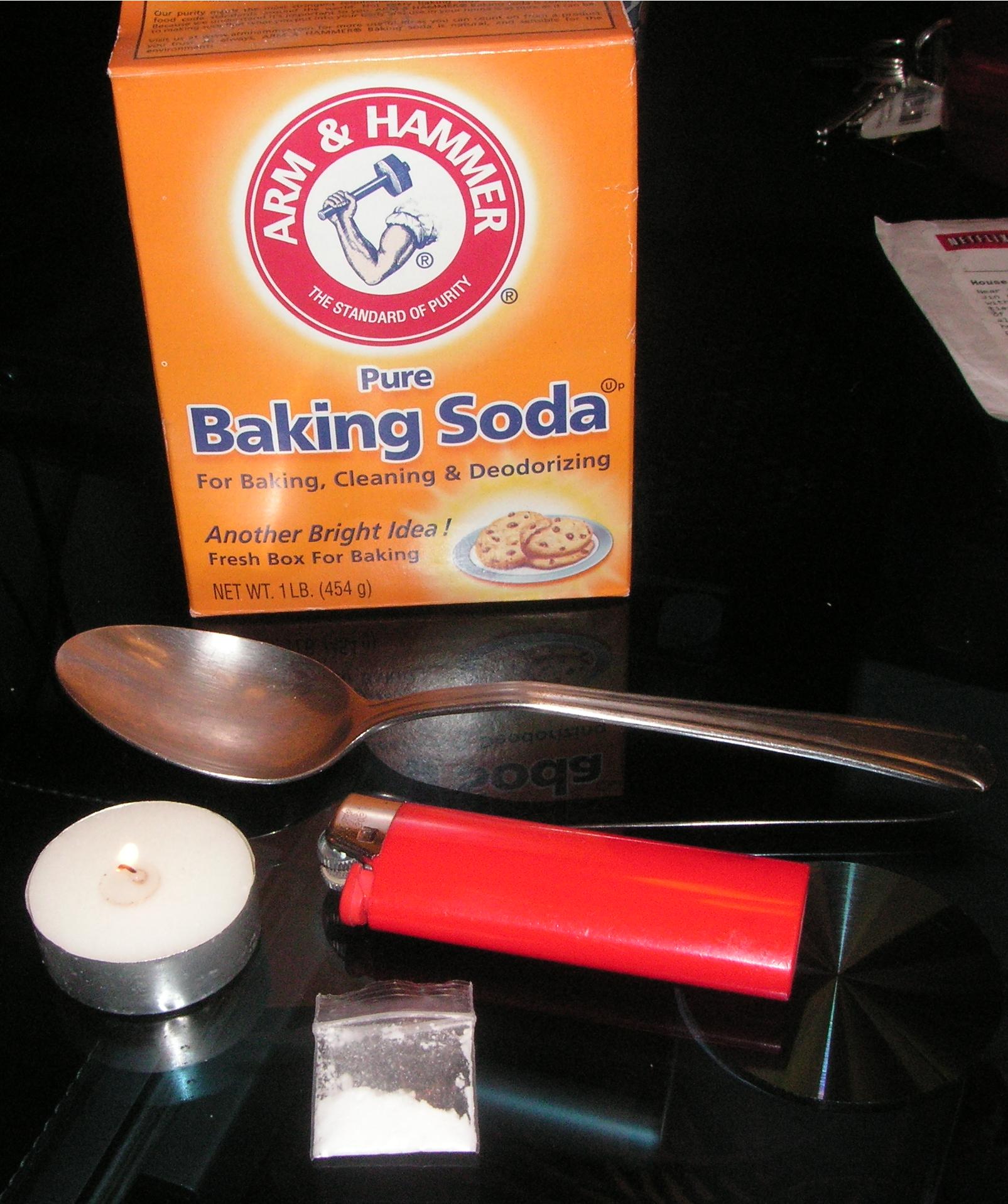
Crack cocaine is frequently purchased already in rock form, although it is not uncommon for some users to "wash up" or "cook" powder cocaine into crack themselves. This process is frequently done with baking soda
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda (or simply “bicarb” especially in the UK) is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt (chemistry), salt compose ...
(sodium bicarbonate), water, and a spoon. Once mixed and heated, the bicarbonate reacts with the hydrochloride of the powder cocaine, forming free base cocaine and carbonic acid
Carbonic acid is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . The molecule rapidly converts to water and carbon dioxide in the presence of water. However, in the absence of water, it is quite stable at room temperature. The interconversion ...
(H2CO3) in a reversible acid-base reaction. The heating accelerates the degradation of carbonic acid into carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
(CO2) and water. Loss of CO2 prevents the reaction from reversing back to cocaine hydrochloride. Free base cocaine separates as an oily layer, floating on the top of the now leftover aqueous phase. It is at this point that the oil is picked up rapidly, usually with a pin or long thin object. This pulls the oil up and spins it, allowing air to set and dry the oil, and allows the maker to roll the oil into the rock-like shape.
citric acid
Citric acid is an organic compound with the formula . It is a Transparency and translucency, colorless Weak acid, weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in Citrus, citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, ...
) or white vinegar (containing acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main compone ...
), a process that effectively reverses the original conversion of powder cocaine to crack. Harm reduction
Harm reduction, or harm minimization, refers to a range of intentional practices and public health policies designed to lessen the negative social and/or physical consequences associated with various human behaviors, both legal and illegal. H ...
and public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the de ...
agencies may distribute packets of citric acid or ascorbic acid
Ascorbic acid is an organic compound with formula , originally called hexuronic acid. It is a white solid, but impure samples can appear yellowish. It dissolves freely in water to give mildly acidic solutions. It is a mild reducing agent.
Asco ...
(vitamin C) for this purpose.
Recreational use
Effects of crack cocaine includeeuphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
, supreme confidence, loss of appetite, insomnia
Insomnia, also known as sleeplessness, is a sleep disorder where people have difficulty sleeping. They may have difficulty falling asleep, or staying asleep for as long as desired. Insomnia is typically followed by daytime sleepiness, low ene ...
, alertness
Alertness is a state of active attention characterized by high sensory awareness. Someone who is alert is vigilant and promptly meets danger or emergency, or is quick to perceive and act. Alertness is a psychological and physiological state.
Lac ...
, increased energy, a craving for more cocaine,
and paranoia (ending after use)."DEA, Drug Information, Cocaine",
United States DOJ Drug Enforcement Administration, 2008, webpage:
DEA-cocaine
. "Life or Meth – CRACK OF THE 90'S", Salt Lake City Police Department, Utah, 2008, PDF file:
Methlife-PDF
. Its initial effect is to release a large amount of
dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
, a brain chemical inducing feelings of euphoria. The high usually lasts from five to ten minutes, after which time dopamine levels in the brain plummet, leaving the user feeling depressed and low. When (powder) cocaine is dissolved and injected, the absorption into the bloodstream is at least as rapid as the absorption of the drug which occurs when crack cocaine is smoked, and similar euphoria may be experienced.
In a 2000 Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratories, United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, New York, a hamlet of the Brookhaven, New York, Town of Brookhaven. It w ...
medical department study, based on self-reports of 32 people who used cocaine who participated in the study, "peak high" was found at a mean of 1.4 ± 0.5 minutes.
The onset of cocaine's euphoric effects is fastest with inhalation, beginning after 3–5 seconds. The drug is then quickly transported to the brain, where it acts on the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
, producing an almost immediate "high" that can be very powerful – this initial crescendo of stimulation known as a rush. This is followed by an equally intense low, leaving the user craving more of the drug. Addiction to crack usually occurs within four to six weeks - much more rapidly than regular cocaine.
Route of administration
 Crack cocaine is usually heated in a drug pipe until sublimation occurs at a relatively low temperature (about 90°C) and the
Crack cocaine is usually heated in a drug pipe until sublimation occurs at a relatively low temperature (about 90°C) and the vapor
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-our, -or, see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R ...
is inhaled. This process is commonly referred to as "freebasing." Although commonly called "smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
," this method actually involves vaporizing the drug rather than burning it. If crack cocaine is burned directly, such as in a regular tobacco pipe
A tobacco pipe, often called simply a pipe, is a device specifically made to smoke tobacco. It comprises a chamber (the bowl (smoking), bowl) for the tobacco from which a thin hollow stem (shank) emerges, ending in a mouthpiece. Pipes can range ...
or roll-your-own cigarette, higher temperatures may lead to decomposition of the active compound, reducing its effectiveness. This is why vaporization at lower temperatures, rather than combustion
Combustion, or burning, is a high-temperature exothermic redox chemical reaction between a fuel (the reductant) and an oxidant, usually atmospheric oxygen, that produces oxidized, often gaseous products, in a mixture termed as smoke. Combustion ...
, is the preferred method for administration. While no formal studies have specifically quantified the extent of drug loss during combustion, users commonly choose to vaporize crack cocaine in order to maximize its effects and potentially avoid wasting money. Additionally, vaporizing is generally considered less harsh on the throat and lungs compared to smoking crack through a tobacco pipe, as combustion can produce more irritating and toxic by-products.
Pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
products of cocaine that occur only when heated/smoked have been shown to change the effect profile, ''i.e.'' anhydroecgonine methyl ester, when co-administered with cocaine, increases the dopamine in CPu and NAc brain regions, and has M1 — and M3 — receptor affinity
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (''K''D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a Complex ...
.
The effects felt almost immediately after inhaled, are very intense and do not last long — usually 2 to 10 minutes. When smoked, cocaine is sometimes combined with other drugs, such as cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae that is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from the continent of Asia. However, the number of species is disputed, with as many as three species be ...
, often rolled into a joint or blunt
Blunt may refer to:
* Blunt (surname), a surname (and list of people with the name)
* Blunt (cigar), a term used in the cigar industry to designate blunt-tipped, usually factory-rolled cigars
* Blunt (cannabis), a slang term used in cannabis cult ...
.
= Love rose
= People often freebase crack with a pipe made from a small glass tube, often taken from " love roses", small glass tubes with a paper rose that are promoted as romantic gifts. These are sometimes called "stems", "horns", "blasters" and "straight shooters". A small piece of clean heavy copper or occasionally stainless steel scouring padoften called a "brillo" (actual
People often freebase crack with a pipe made from a small glass tube, often taken from " love roses", small glass tubes with a paper rose that are promoted as romantic gifts. These are sometimes called "stems", "horns", "blasters" and "straight shooters". A small piece of clean heavy copper or occasionally stainless steel scouring padoften called a "brillo" (actual Brillo Pad
Brillo is a trade name for a scouring pad, used for cleaning dishes, and made from steel wool filled with soap. The concept was patented in 1913, at a time when aluminium pots and pans were replacing cast iron in the kitchen; the new cookware ...
s contain soap, and are not used) or "chore" (named for Chore Boy
Chore Boy is a brand name of cleaning product, which includes copper and stainless steel scouring pads, and abrasive impregnated scouring cloths.
During the first half of the 20th century, the product was marketed under the name Chore Girl.
Copp ...
brand copper scouring pads)serves as a reduction base and flow modulator in which the "rock" can be melted and boiled to vapor. Crack is smoked by placing it at the end of the pipe; a flame held close to it produces vapor, which is then inhaled by the smoker.
Adverse effects
Physiological
 Incidental exposure of the eye to sublimated cocaine while smoking crack cocaine can cause serious injury to the
Incidental exposure of the eye to sublimated cocaine while smoking crack cocaine can cause serious injury to the cornea
The cornea is the transparency (optics), transparent front part of the eyeball which covers the Iris (anatomy), iris, pupil, and Anterior chamber of eyeball, anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and Lens (anatomy), lens, the cornea ...
and long-term loss of visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye ...
.
The short-term physiological effects of cocaine include constricted blood vessels, dilated pupils, and increased temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Some users of cocaine report feelings of restlessness, irritability, and anxiety. In rare instances, sudden death can occur on the first use of cocaine or unexpectedly thereafter. Cocaine-related deaths are often a result of cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (also known as sudden cardiac arrest CA is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. When the heart stops beating, blood cannot properly Circulatory system, circulate around the body and the blood flow to the ...
or seizures followed by respiratory arrest.
Like other forms of cocaine, smoking crack can increase heart rate and blood pressure, leading to long-term cardiovascular problems. Some research suggests that smoking crack or free base cocaine has additional health risks compared to other methods of taking cocaine. Many of these issues relate specifically to the release of methylecgonidine and its effect on the heart, lungs, and liver.
*Toxic adulterant
An adulterant is a substance secretly added to another that may compromise the safety or effectiveness. Typical substances that are adulterated include food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals or fuels.
Definition
Adulteration is the practice of secre ...
s: Many substances may have been added to expand the weight and volume of a batch, while still appearing to be pure crack. Occasionally, highly toxic substances are used, with a range of corresponding short and long-term health risks. Adulterants used with crack and cocaine include milk powder, sugars such as glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
, starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diet ...
, caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness pr ...
, lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anae ...
, benzocaine
Benzocaine, sold under the brand name Orajel amongst others, is a local anesthetic, belonging to the amino ester drug class, commonly used as a topical painkiller or in cough drops. It is the active ingredient in many over-the-counter ...
, paracetamol
Paracetamol, or acetaminophen, is a non-opioid analgesic and antipyretic agent used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. It is a widely available over-the-counter drug sold under various brand names, including Tylenol and Panadol.
Parac ...
, amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
, scopolamine
Scopolamine, also known as hyoscine, or Devil's Breath, is a medication used to treat motion sickness and postoperative nausea and vomiting. It is also sometimes used before surgery to decrease saliva. When used by injection, effects begin a ...
and strychnine
Strychnine (, , American English, US chiefly ) is a highly toxicity, toxic, colorless, bitter, crystalline alkaloid used as a pesticide, particularly for killing small vertebrates such as birds and rodents. Strychnine, when inhaled, swallowed, ...
.
*Smoking problems: Any route of administration
In pharmacology and toxicology, a route of administration is the way by which a medication, drug, fluid, poison, or other substance is taken into the body.
Routes of administration are generally classified by the location at which the substance ...
poses its own set of health risks; in the case of crack cocaine, smoking tends to be more harmful than other routes. Crack users tend to smoke the drug because that has a higher bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is the fraction (%) of an administered drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
By definition, when a medication is administered intravenously, its bioavailability is 100%. H ...
than other routes typically used for drugs of abuse, such as insufflation. Crack has a melting point of around , and the smoke does not remain potent for long. Therefore, crack pipes are generally very short, to minimize the time between evaporating and ingestion (thereby minimizing loss of potency). Having a very hot pipe pressed against the lips often causes cracked and blistered lips, colloquially known as "crack lip". The use of "convenience store crack pipes"—glass tubes which originally contained small artificial roses—may contribute to this condition. These 4-inch (10-cm) pipes are not durable and will quickly develop breaks; users may continue to use the pipe even though it has been broken to a shorter length. The hot pipe might burn the lips, tongue, or fingers, especially when passed between people who take hits in rapid succession, causing the short pipe to reach higher temperatures than if used by one person alone.
*Pure or large doses: Because the quality of crack can vary greatly, some people might smoke larger amounts of diluted crack, unaware that a similar amount of a new batch of purer crack could cause an overdose. This can trigger heart problems or cause unconsciousness.
*Pathogens on pipes: When pipes are shared, bacteria or viruses can be transferred from person to person.
Crack cocaine causes DNA damage
DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. A weakened capacity for DNA repair is a risk factor for the development of cancer. DNA is constantly modified ...
in multiple organs of rats and mice.
Crack lung
In crack users, acute respiratory symptoms have been reported, sometimes termed "crack lung". Symptoms include fever, coughing up blood and difficulty breathing. In the 48-hour period after use, people with these symptoms have also had associated radiographic findings on chest X-ray of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary edema),interstitial pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns Pulmonar ...
, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, and eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
infiltration.
Physical side effects from chronic smoking of cocaine include coughing up blood, bronchospasm
Bronchospasm or a bronchial spasm is a sudden bronchoconstriction, constriction of the muscles in the walls of the bronchioles. It is caused by the release (degranulation) of substances from mast cells or basophils under the influence of anaphylat ...
, itching
An itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes a strong desire or reflex to scratch. Itches have resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itches have many similarities to pain, and while both ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, diffuse alveolar infiltrates without effusions, pulmonary and systemic eosinophilia
Eosinophilia is a condition in which the eosinophil count in the peripheral blood exceeds . Hypereosinophilia is an elevation in an individual's circulating blood eosinophil count above 1.5 billion/ L (1,500/ μL). The hypereosinophilic syndrome ...
, chest pain, lung trauma, sore throat, asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
, hoarse voice, dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
(shortness of breath), and an aching, flu-like syndrome.
Crack cocaine users sometimes smoke "fry," which refers to cigarettes or marijuana sticks that have been dipped in embalming fluid and laced with PCP. Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as ...
and methyl alcohol are the main ingredients found in fry, and their use has been linked to a range of physical health problems, including bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
, destruction of body tissues, brain and lung damage, impaired coordination, and inflammation or sores in the throat, nose, and esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
.
Psychological
Intranasal cocaine and crack use are both associated with pharmacological violence. Crack-related violence is also systemic, relating to disputes between crack dealers and users. Stimulant drug abuse (particularlyamphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
and cocaine) can lead to delusional parasitosis
Delusional parasitosis (DP), also called delusional infestation, is a mental health condition where a person falsely believes that their body is infested with living or nonliving agents. Common examples of such agents include parasites, insects, o ...
(aka Ekbom's Syndrome: a mistaken belief they are infested with parasites). For example, excessive cocaine use can lead to formication
Formication is the sensation resembling that of small insects crawling on (or delusional parasitosis, under) the skin, in the absence of actual insects. It is one specific form of a set of sensations known as paresthesias, which also include the ...
, nicknamed "cocaine bugs" or "coke bugs", where the affected people believe they have, or feel, parasites crawling under their skin (similar delusions may also be associated with high fever or in connection with alcohol withdrawal
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) is a set of symptoms that can occur following a reduction in or cessation of alcohol use after a period of excessive use. Symptoms typically include anxiety, shakiness, sweating, vomiting, fast heart rate, a ...
, sometimes accompanied by visual hallucinations of insects—see ''delirium tremens
Delirium tremens (DTs; ) is a rapid onset of confusion usually caused by withdrawal from alcohol. When it occurs, it is often three days into the withdrawal symptoms and lasts for two to three days. Physical effects may include shaking, sh ...
'').
"Delusional Parasitosis", The Bohart Museum of Entomology
Entomology (from Ancient Greek ἔντομον (''éntomon''), meaning "insect", and -logy from λόγος (''lógos''), meaning "study") is the branch of zoology that focuses on insects. Those who study entomology are known as entomologists. In ...
,
2005, webpage:
UCDavis-delusional
People experiencing these hallucinations might scratch themselves to the extent of serious skin damage and bleeding, especially when they are delirious. Paranoia and anxiety are among the most common psychological symptoms of crack cocaine use. Psychosis is more closely associated with smoking crack cocaine than intranasal and intravenous use.
Pregnancy and nursing
''Crack baby'' is a term for a child born to a mother who used crack cocaine during her pregnancy. The threat that cocaine use duringpregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
poses to the fetus
A fetus or foetus (; : fetuses, foetuses, rarely feti or foeti) is the unborn offspring of a viviparous animal that develops from an embryo. Following the embryonic development, embryonic stage, the fetal stage of development takes place. Pren ...
is now considered exaggerated. Studies show that prenatal cocaine exposure (independent of other effects such as, for example, alcohol, tobacco, or physical environment) has no appreciable effect on childhood growth and development. However, the official opinion of the National Institute on Drug Abuse
The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) is a United States federal government research institute whose mission is to "advance science on the causes and consequences of drug use and addiction and to apply that knowledge to improve individual ...
of the United States warns about health risks while cautioning against stereotyping:
There are also warnings about the threat of breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Orga ...
: The March of Dimes
March of Dimes is a United States nonprofit organization that works to improve the health of mothers and babies. The organization was founded by US President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1938, as the National Foundation for Infantile Paralysis, to co ...
said "it is likely that cocaine will reach the baby through breast milk," and advises the following regarding cocaine use during pregnancy:
Reinforcement disorders
Tolerance
An appreciable tolerance to cocaine's high may develop, with many addicts reporting that they seek but fail to achieve as much pleasure as they did from their first experience. Some users will frequently increase their doses to intensify and prolong the euphoric effects. While tolerance to the high can occur, users might also become more sensitive ( drug sensitization) to cocaine's local anesthetic (painkilling) and convulsant (seizure-inducing) effects, without increasing the dose taken; this increased sensitivity ''may'' explain some deaths occurring after apparent low doses of cocaine.Addiction
Crack cocaine is popularly thought to be the most addictive form of cocaine. However, this claim has been contested: Morgan and Zimmer wrote that available data indicated that "smoking cocaine by itself does not increase markedly the likelihood of dependence ... The claim that cocaine is much more addictive when smoked must be reexamined." They argued that cocaine users who are already prone to abuse are most likely to "move toward a more efficient mode of ingestion" (that is, smoking). The intense desire to recapture the initial high is what is so addictive for many users. On the other hand, Reinarman et al. wrote that the nature of crack addiction depends on the social context in which it is used and the psychological characteristics of users, pointing out that many heavy crack users can go for days or weeks without using the drug.Overdose
A typical response among users is to have another hit of the drug; however, the levels ofdopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. It is an amine synthesized ...
in the brain take a long time to replenish themselves, and each hit taken in rapid succession leads to progressively less intense highs. Nonetheless, a person might binge for 3 or more days without sleep, while inhaling hits from a pipe.
Use of cocaine in a binge, during which the drug is taken repeatedly and at increasingly high doses, leads to a state of increasing irritability, restlessness, and paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety, suspicion, or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of co ...
. This may result in total paranoid psychosis, in which the individual loses touch with reality and experiences auditory hallucinations.
Large amounts of crack cocaine (several hundred milligrams or more) intensify the user's high, but may also lead to bizarre, erratic, and violent behavior. Large amounts can induce tremors, vertigo
Vertigo is a condition in which a person has the sensation that they are moving, or that objects around them are moving, when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. It may be associated with nausea, vomiting, perspira ...
, muscle twitches, paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety, suspicion, or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of co ...
, or, with repeated doses, a toxic reaction closely resembling amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
poisoning.
Society and culture
Synonyms
Synonyms used to refer to crack cocaine include ''atari''; ''base''; ''bazooka''; ''beamers''; ''beemers''; ''bebe''; ''bee-bee''; ''berry''; ''bing''; ''bolo''; ''bomb''; ''boulder''; ''boulders''; ''butter''; ''caine''; ''cane''; ''Casper''; ''Casper the ghost''; ''cavvy''; ''chemical''; ''chewies''; ''cloud''; ''cloud nine''; ''crills''; ''crunch and munch''; ''dip''; ''famous dimes''; ''fan''; ''fish scale''; ''fries''; ''fry''; ''glo''; ''golfball''; ''gravel''; ''grit''; ''hail''; ''hamburger helper''; ''hard''; ''hubba''; ''ice cube''; ''kangaroo''; ''kibbles and bits''; ''kibbles''; ''krills''; ''lightem''; ''paste''; ''patico''; ''pebbles''; ''pee wee''; ''pony''; ''raw''; ''ready''; ''ready rocks''; ''redi rocks''; ''roca''; ''rock''; ''rooster''; ''rox''; ''Roxanne''; ''scud''; ''Scotty''; ''scramble''; ''scruples''; ''seven-up''; ''sleet''; ''snowballs''; ''stones''; ''teeth''; ''tension''; ''top gun''; ''tweak''; ''ultimate''; ''wash''; ''white cloud''; ''work''; ''yahoo''; ''yale''; ''yay''; ''yayoo''; ''yeah-O''; ''yeyo''; ''yeo''; and ''yuck''.Drug combinations
Crack cocaine may be combined withamphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from Alpha and beta carbon, alpha-methylphenethylamine, methylphenethylamine) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, an ...
("croak"); tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
("coolie"); marijuana
Cannabis (), commonly known as marijuana (), weed, pot, and ganja, List of slang names for cannabis, among other names, is a non-chemically uniform psychoactive drug from the ''Cannabis'' plant. Native to Central or South Asia, cannabis has ...
("buddha"; "caviar"; "chronic"; "cocoa puffs"; "fry daddy"; "gimmie"; "gremmie"; "juice"; "primo"; "torpedo"; "turbo"; "woolie"; "woola"); heroin ("moon rock"); and phencyclidine ("clicker"; "p-funk"; "spacebase").
Consumption
Crack smoking ("hitting the pipe"; "puffing"; "beaming up (to Scotty)") is commonly performed with utensils such as pipes ("bowl"; "devil's dick"; "glass dick"; "horn"; "Uzi"); improvised pipes made from a plastic bottle ("Masarati"); water pipes ("bong"; "hubbly-bubbly"); and laboratory pipettes ("demo").Legal status
Cocaine is listed as a Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs#Schedules of drugs, Schedule I drug in the United Nations 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, making it illegal for non-state-sanctioned production, manufacture, export, import, distribution, trade, use and possession. In most states (except in the United States) crack falls under the same category ascocaine
Cocaine is a tropane alkaloid and central nervous system stimulant, derived primarily from the leaves of two South American coca plants, ''Erythroxylum coca'' and ''Erythroxylum novogranatense, E. novogranatense'', which are cultivated a ...
.
Australia
In Australia, crack falls under the same category as cocaine, which is listed as a Standard for the Uniform Scheduling of Medicines and Poisons, Schedule 8 controlled drug, indicating that any substances and preparations for therapeutic use under this category have a high potential for abuse and addiction. It is permitted for some medical use but is otherwise outlawed.Canada
As a Controlled Drugs and Substances Act#Schedule I, Schedule I substance under the Controlled Drugs and Substances Act, crack is not differentiated from cocaine and other coca products. However, the court may weigh the socio-economic factors of crack usage in sentencing. As a guideline, Schedule I drugs carry a maximum seven-year prison sentence for possession for an indictable offense and up to life imprisonment for trafficking and production. A summary conviction on possession carries a $1000–2000 fine and/or six months to a year imprisonment.United States
In the United States, cocaine is a Controlled Substances Act#Schedule II controlled substances, Schedule II drug under the Controlled Substances Act, indicating that it has a high abuse potential but also carries a medicinal purpose. Under the Controlled Substances Act, crack and cocaine are considered the same drug. The Anti-Drug Abuse Act of 1986 increased penalties for crack cocaine possession and usage. It mandated a mandatory minimum sentence of five years without parole for possession of five grams of crack; to receive the same sentence with powder cocaine one had to have 500 grams. This sentencing disparity was reduced from to by the Fair Sentencing Act of 2010.Europe
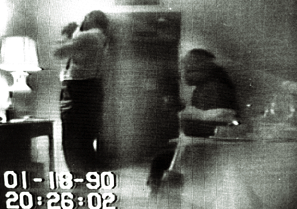 In the United Kingdom, crack is a List of controlled drugs in the United Kingdom, Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. In the Netherlands it is a List 1 drug of the Opium Law.
In the United Kingdom, crack is a List of controlled drugs in the United Kingdom, Class A drug under the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971. In the Netherlands it is a List 1 drug of the Opium Law.
Political scandals
Marion Barry, Mayor of Washington, D.C., Washington D.C., was filmed smoking crack in 1990 in a sting operation. Rob Ford, Mayor of Toronto, Ontario was Timeline of Rob Ford video scandal, filmed smoking crack in 2013 by gang members while holding office.Impact
See also
* Calixcoca, an experimental vaccine against the effect of crack cocaine being developed by UFMG * CIA involvement in Contra cocaine trafficking * Cocaine paste ("paco")References
Further reading
* *External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Crack Cocaine American inventions Cocaine Drug culture